Cooling System (nuclear Reactor) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission
 Just as conventional thermal power stations generate electricity by harnessing the thermal energy released from burning
Just as conventional thermal power stations generate electricity by harnessing the thermal energy released from burning
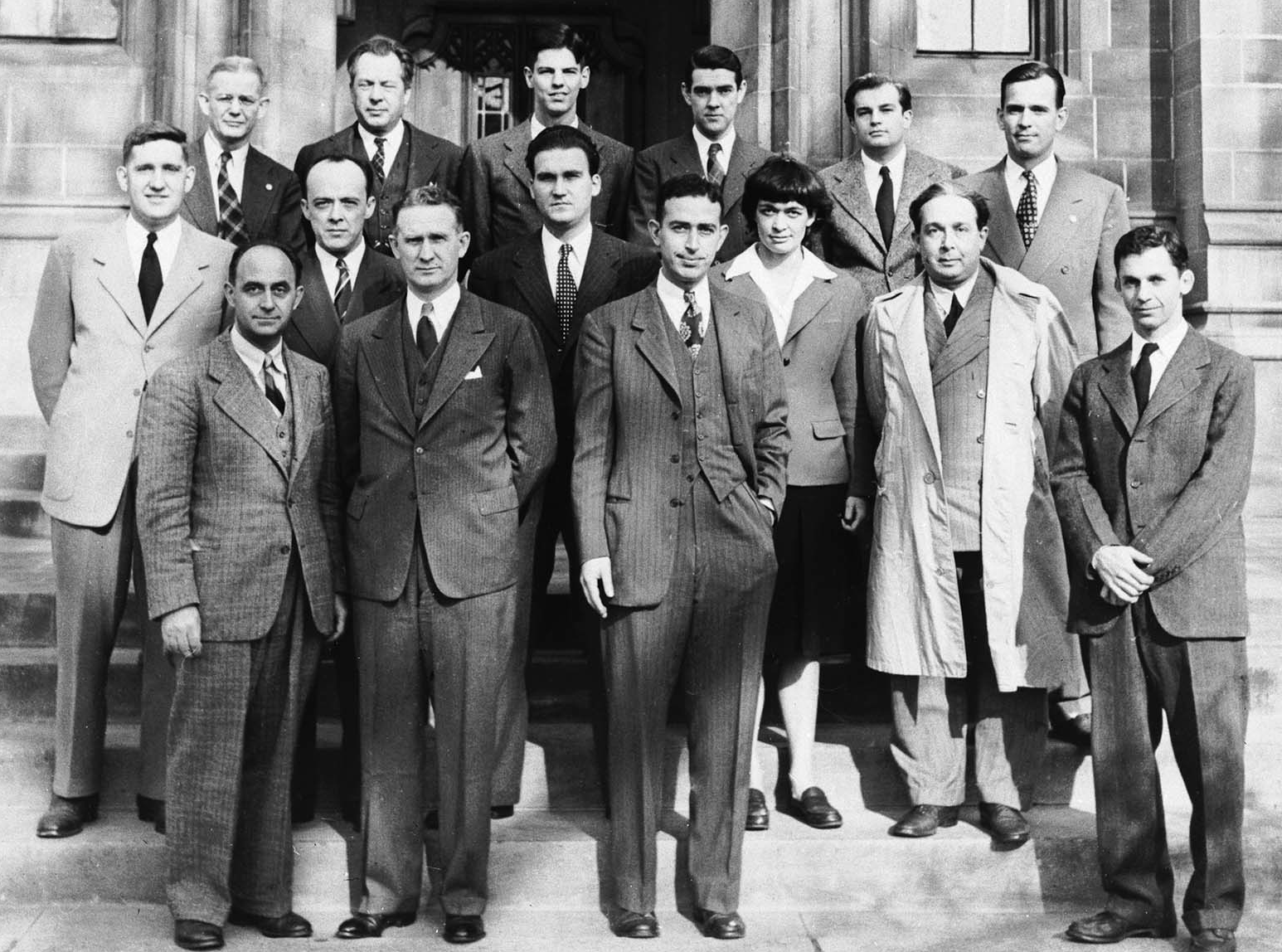
 The neutron was discovered in 1932 by British physicist James Chadwick. The concept of a nuclear chain reaction brought about by nuclear reactions mediated by neutrons was first realized shortly thereafter, by Hungarian scientist Leó Szilárd, in 1933. He filed a patent for his idea of a simple reactor the following year while working at the Admiralty in London. However, Szilárd's idea did not incorporate the idea of nuclear fission as a neutron source, since that process was not yet discovered. Szilárd's ideas for nuclear reactors using neutron-mediated nuclear chain reactions in light elements proved unworkable.
Inspiration for a new type of reactor using uranium came from the discovery by Otto Hahn,
The neutron was discovered in 1932 by British physicist James Chadwick. The concept of a nuclear chain reaction brought about by nuclear reactions mediated by neutrons was first realized shortly thereafter, by Hungarian scientist Leó Szilárd, in 1933. He filed a patent for his idea of a simple reactor the following year while working at the Admiralty in London. However, Szilárd's idea did not incorporate the idea of nuclear fission as a neutron source, since that process was not yet discovered. Szilárd's ideas for nuclear reactors using neutron-mediated nuclear chain reactions in light elements proved unworkable.
Inspiration for a new type of reactor using uranium came from the discovery by Otto Hahn, 

 * Water cooled reactor. These constitute the great majority of operational nuclear reactors: as of 2014, 93% of the world's nuclear reactors are water cooled, providing about 95% of the world's total nuclear generation capacity.
** Pressurized water reactor (PWR) Pressurized water reactors constitute the large majority of all Western nuclear power plants.
*** A primary characteristic of PWRs is a pressurizer, a specialized
* Water cooled reactor. These constitute the great majority of operational nuclear reactors: as of 2014, 93% of the world's nuclear reactors are water cooled, providing about 95% of the world's total nuclear generation capacity.
** Pressurized water reactor (PWR) Pressurized water reactors constitute the large majority of all Western nuclear power plants.
*** A primary characteristic of PWRs is a pressurizer, a specialized
 * Pressurized water reactors (PWR) oderator: high-pressure water; coolant: high-pressure water
:: These reactors use a pressure vessel to contain the nuclear fuel, control rods, moderator, and coolant. The hot radioactive water that leaves the pressure vessel is looped through a steam generator, which in turn heats a secondary (nonradioactive) loop of water to steam that can run turbines. They represent the majority (around 80%) of current reactors. This is a thermal neutron reactor design, the newest of which are the Russian VVER-1200, Japanese Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor, American AP1000, Chinese Hualong Pressurized Reactor and the Franco-German
* Pressurized water reactors (PWR) oderator: high-pressure water; coolant: high-pressure water
:: These reactors use a pressure vessel to contain the nuclear fuel, control rods, moderator, and coolant. The hot radioactive water that leaves the pressure vessel is looped through a steam generator, which in turn heats a secondary (nonradioactive) loop of water to steam that can run turbines. They represent the majority (around 80%) of current reactors. This is a thermal neutron reactor design, the newest of which are the Russian VVER-1200, Japanese Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor, American AP1000, Chinese Hualong Pressurized Reactor and the Franco-German  * Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) oderator: high-pressure heavy water; coolant: high-pressure heavy water
:: A Canadian design (known as
* Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) oderator: high-pressure heavy water; coolant: high-pressure heavy water
:: A Canadian design (known as  * Reaktor Bolshoy Moschnosti Kanalniy (High Power Channel Reactor) ( RBMK) oderator: graphite; coolant: high-pressure water
:: A Soviet design, RBMKs are in some respects similar to CANDU in that they are refuelable during power operation and employ a pressure tube design instead of a PWR-style pressure vessel. However, unlike CANDU they are very unstable and large, making containment buildings for them expensive. A series of critical safety flaws have also been identified with the RBMK design, though some of these were corrected following the
* Reaktor Bolshoy Moschnosti Kanalniy (High Power Channel Reactor) ( RBMK) oderator: graphite; coolant: high-pressure water
:: A Soviet design, RBMKs are in some respects similar to CANDU in that they are refuelable during power operation and employ a pressure tube design instead of a PWR-style pressure vessel. However, unlike CANDU they are very unstable and large, making containment buildings for them expensive. A series of critical safety flaws have also been identified with the RBMK design, though some of these were corrected following the 
 * Gas-cooled reactor (GCR) and advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) oderator: graphite; coolant: carbon dioxide
:: These designs an have a high thermal efficiency compared with PWRs due to higher operating temperatures. There are a number of operating reactors of this design, mostly in the United Kingdom, where the concept was developed. Older designs (i.e. Magnox stations) are either shut down or will be in the near future. However, the AGRs have an anticipated life of a further 10 to 20 years. This is a thermal-neutron reactor design. Decommissioning costs can be high due to large volume of reactor core.
* Liquid metal fast-breeder reactor (LMFBR) oderator: none; coolant: liquid metal
* Gas-cooled reactor (GCR) and advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) oderator: graphite; coolant: carbon dioxide
:: These designs an have a high thermal efficiency compared with PWRs due to higher operating temperatures. There are a number of operating reactors of this design, mostly in the United Kingdom, where the concept was developed. Older designs (i.e. Magnox stations) are either shut down or will be in the near future. However, the AGRs have an anticipated life of a further 10 to 20 years. This is a thermal-neutron reactor design. Decommissioning costs can be high due to large volume of reactor core.
* Liquid metal fast-breeder reactor (LMFBR) oderator: none; coolant: liquid metal :: This totally unmoderated reactor design produces more fuel than it consumes. They are said to "breed" fuel, because they produce fissionable fuel during operation because of neutron capture. These reactors can function much like a PWR in terms of efficiency, and do not require much high-pressure containment, as the liquid metal does not need to be kept at high pressure, even at very high temperatures. These reactors are fast neutron, not thermal neutron designs. These reactors come in two types:
:: This totally unmoderated reactor design produces more fuel than it consumes. They are said to "breed" fuel, because they produce fissionable fuel during operation because of neutron capture. These reactors can function much like a PWR in terms of efficiency, and do not require much high-pressure containment, as the liquid metal does not need to be kept at high pressure, even at very high temperatures. These reactors are fast neutron, not thermal neutron designs. These reactors come in two types:
 ::: Lead-cooled
:::: Using lead as the liquid metal provides excellent radiation shielding, and allows for operation at very high temperatures. Also, lead is (mostly) transparent to neutrons, so fewer neutrons are lost in the coolant, and the coolant does not become radioactive. Unlike sodium, lead is mostly inert, so there is less risk of explosion or accident, but such large quantities of lead may be problematic from toxicology and disposal points of view. Often a reactor of this type would use a lead-bismuth eutectic mixture. In this case, the bismuth would present some minor radiation problems, as it is not quite as transparent to neutrons, and can be transmuted to a radioactive isotope more readily than lead. The Russian Alfa class submarine uses a lead-bismuth-cooled fast reactor as its main power plant.
::: Sodium-cooled
:::: Most LMFBRs are of this type. The
::: Lead-cooled
:::: Using lead as the liquid metal provides excellent radiation shielding, and allows for operation at very high temperatures. Also, lead is (mostly) transparent to neutrons, so fewer neutrons are lost in the coolant, and the coolant does not become radioactive. Unlike sodium, lead is mostly inert, so there is less risk of explosion or accident, but such large quantities of lead may be problematic from toxicology and disposal points of view. Often a reactor of this type would use a lead-bismuth eutectic mixture. In this case, the bismuth would present some minor radiation problems, as it is not quite as transparent to neutrons, and can be transmuted to a radioactive isotope more readily than lead. The Russian Alfa class submarine uses a lead-bismuth-cooled fast reactor as its main power plant.
::: Sodium-cooled
:::: Most LMFBRs are of this type. The
 Serious, though rare, nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred. These include the Windscale fire (October 1957), the SL-1 accident (1961), the Three Mile Island accident (1979),
Serious, though rare, nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred. These include the Windscale fire (October 1957), the SL-1 accident (1961), the Three Mile Island accident (1979),
p. 14. the K-27 reactor accident (1968), and the K-431 reactor accident (1985).The Worst Nuclear Disasters
''Time''. Nuclear reactors have been launched into Earth orbit at least 34 times. A number of incidents connected with the unmanned nuclear-reactor-powered Soviet RORSAT especially
The Database on Nuclear Power Reactors – IAEA
Uranium Conference adds discussion of Japan accident
A Debate: Is Nuclear Power The Solution to Global Warming?
Union of Concerned Scientists, Concerns re: US nuclear reactor program
Freeview Video 'Nuclear Power Plants — What's the Problem' A Royal Institution Lecture by John Collier by the Vega Science Trust.
Nuclear Energy Institute — How it Works: Electric Power Generation
Annotated bibliography of nuclear reactor technology from the Alsos Digital Library
*
ソヴィエト連邦における宇宙用原子炉の開発とその実用
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nuclear Reactor Technology Energy conversion Nuclear technology Power station technology Pressure vessels Nuclear research reactors
 A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
is passed to a working fluid (water or gas), which in turn runs through steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
s. These either drive a ship's propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
s or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. , the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.
In the early era of nuclear reactors (1940s), a reactor was known as a nuclear pile or atomic pile (so-called because the graphite moderator blocks of the first reactor were placed into a tall pile).
Operation
fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ...
, nuclear reactors convert the energy released by controlled nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
into thermal energy for further conversion to mechanical or electrical forms.
Fission
When a large fissile atomic nucleus such as uranium-235, Uranium-233 or plutonium-239 absorbs a neutron, it may undergo nuclear fission. The heavy nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei, (thefission products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
), releasing kinetic energy, gamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically s ...
, and free neutrons. A portion of these neutrons may be absorbed by other fissile atoms and trigger further fission events, which release more neutrons, and so on. This is known as a nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
.
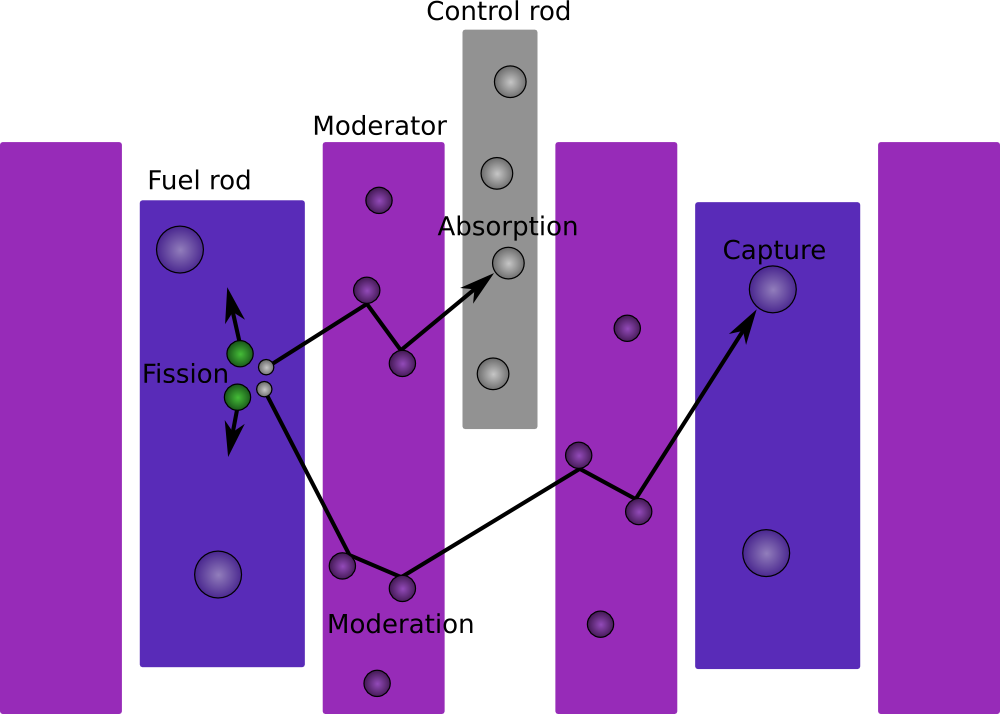
To control such a nuclear chain reaction, control rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
s containing neutron poisons and neutron moderators can change the portion of neutrons that will go on to cause more fission.
Nuclear reactors generally have automatic and manual systems to shut the fission reaction down if monitoring or instrumentation detects unsafe conditions.
Heat generation
The reactor core generates heat in a number of ways: * The kinetic energy of fission products is converted to thermal energy when these nuclei collide with nearby atoms. * The reactor absorbs some of the gamma rays produced during fission and converts their energy into heat. * Heat is produced by theradioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
of fission products and materials that have been activated by neutron absorption. This decay heat source will remain for some time even after the reactor is shut down.
A kilogram of uranium-235 (U-235) converted via nuclear processes releases approximately three million times more energy than a kilogram of coal burned conventionally (7.2 × 1013 joules per kilogram of uranium-235 versus 2.4 × 107 joules per kilogram of coal).
The fission of one kilogram of uranium-235 releases about 19 billion kilocalories
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of on ...
, so the energy released by 1 kg of uranium-235 corresponds to that released by burning 2.7 million kg of coal.
Cooling
A nuclear reactor coolant – usually water but sometimes a gas or a liquid metal (like liquid sodium or lead) or molten salt – is circulated past the reactor core to absorb the heat that it generates. The heat is carried away from the reactor and is then used to generate steam. Most reactor systems employ a cooling system that is physically separated from the water that will be boiled to produce pressurized steam for the turbines, like the pressurized water reactor. However, in some reactors the water for the steam turbines is boiled directly by the reactor core; for example the boiling water reactor.Reactivity control
The rate of fission reactions within a reactor core can be adjusted by controlling the quantity of neutrons that are able to induce further fission events. Nuclear reactors typically employ several methods of neutron control to adjust the reactor's power output. Some of these methods arise naturally from the physics of radioactive decay and are simply accounted for during the reactor's operation, while others are mechanisms engineered into the reactor design for a distinct purpose. The fastest method for adjusting levels of fission-inducing neutrons in a reactor is via movement of thecontrol rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
s. Control rods are made of neutron poisons and therefore absorb neutrons. When a control rod is inserted deeper into the reactor, it absorbs more neutrons than the material it displaces – often the moderator. This action results in fewer neutrons available to cause fission and reduces the reactor's power output. Conversely, extracting the control rod will result in an increase in the rate of fission events and an increase in power.
The physics of radioactive decay also affects neutron populations in a reactor. One such process is delayed neutron emission by a number of neutron-rich fission isotopes. These delayed neutrons account for about 0.65% of the total neutrons produced in fission, with the remainder (termed " prompt neutrons") released immediately upon fission. The fission products which produce delayed neutrons have half-lives for their decay by neutron emission that range from milliseconds to as long as several minutes, and so considerable time is required to determine exactly when a reactor reaches the critical point. Keeping the reactor in the zone of chain reactivity where delayed neutrons are ''necessary'' to achieve a critical mass state allows mechanical devices or human operators to control a chain reaction in "real time"; otherwise the time between achievement of criticality and nuclear meltdown as a result of an exponential power surge from the normal nuclear chain reaction, would be too short to allow for intervention. This last stage, where delayed neutrons are no longer required to maintain criticality, is known as the prompt critical point. There is a scale for describing criticality in numerical form, in which bare criticality is known as ''zero dollars'' and the prompt critical point is ''one dollar'', and other points in the process interpolated in cents.
In some reactors, the coolant also acts as a neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely mo ...
. A moderator increases the power of the reactor by causing the fast neutrons that are released from fission to lose energy and become thermal neutrons. Thermal neutrons are more likely than fast neutrons to cause fission. If the coolant is a moderator, then temperature changes can affect the density of the coolant/moderator and therefore change power output. A higher temperature coolant would be less dense, and therefore a less effective moderator.
In other reactors the coolant acts as a poison by absorbing neutrons in the same way that the control rods do. In these reactors power output can be increased by heating the coolant, which makes it a less dense poison. Nuclear reactors generally have automatic and manual systems to scram the reactor in an emergency shut down. These systems insert large amounts of poison (often boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
in the form of boric acid) into the reactor to shut the fission reaction down if unsafe conditions are detected or anticipated.
Most types of reactors are sensitive to a process variously known as xenon poisoning, or the iodine pit. The common fission product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
Xenon-135 produced in the fission process acts as a neutron poison that absorbs neutrons and therefore tends to shut the reactor down. Xenon-135 accumulation can be controlled by keeping power levels high enough to destroy it by neutron absorption as fast as it is produced. Fission also produces iodine-135, which in turn decays (with a half-life of 6.57 hours) to new xenon-135. When the reactor is shut down, iodine-135 continues to decay to xenon-135, making restarting the reactor more difficult for a day or two, as the xenon-135 decays into cesium-135, which is not nearly as poisonous as xenon-135, with a half-life of 9.2 hours. This temporary state is the "iodine pit." If the reactor has sufficient extra reactivity capacity, it can be restarted. As the extra xenon-135 is transmuted to xenon-136, which is much less a neutron poison, within a few hours the reactor experiences a "xenon burnoff (power) transient". Control rods must be further inserted to replace the neutron absorption of the lost xenon-135. Failure to properly follow such a procedure was a key step in the Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
.
Reactors used in nuclear marine propulsion (especially nuclear submarines) often cannot be run at continuous power around the clock in the same way that land-based power reactors are normally run, and in addition often need to have a very long core life without refueling. For this reason many designs use highly enriched uranium but incorporate burnable neutron poison in the fuel rods. This allows the reactor to be constructed with an excess of fissionable material, which is nevertheless made relatively safe early in the reactor's fuel burn cycle by the presence of the neutron-absorbing material which is later replaced by normally produced long-lived neutron poisons (far longer-lived than xenon-135) which gradually accumulate over the fuel load's operating life.
Electrical power generation
The energy released in the fission process generates heat, some of which can be converted into usable energy. A common method of harnessing this thermal energy is to use it to boil water to produce pressurized steam which will then drive asteam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
that turns an alternator and generates electricity.
Early reactors

 The neutron was discovered in 1932 by British physicist James Chadwick. The concept of a nuclear chain reaction brought about by nuclear reactions mediated by neutrons was first realized shortly thereafter, by Hungarian scientist Leó Szilárd, in 1933. He filed a patent for his idea of a simple reactor the following year while working at the Admiralty in London. However, Szilárd's idea did not incorporate the idea of nuclear fission as a neutron source, since that process was not yet discovered. Szilárd's ideas for nuclear reactors using neutron-mediated nuclear chain reactions in light elements proved unworkable.
Inspiration for a new type of reactor using uranium came from the discovery by Otto Hahn,
The neutron was discovered in 1932 by British physicist James Chadwick. The concept of a nuclear chain reaction brought about by nuclear reactions mediated by neutrons was first realized shortly thereafter, by Hungarian scientist Leó Szilárd, in 1933. He filed a patent for his idea of a simple reactor the following year while working at the Admiralty in London. However, Szilárd's idea did not incorporate the idea of nuclear fission as a neutron source, since that process was not yet discovered. Szilárd's ideas for nuclear reactors using neutron-mediated nuclear chain reactions in light elements proved unworkable.
Inspiration for a new type of reactor using uranium came from the discovery by Otto Hahn, Lise Meitner
Elise Meitner ( , ; 7 November 1878 – 27 October 1968) was an Austrian-Swedish physicist who was one of those responsible for the discovery of the element protactinium and nuclear fission. While working at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute on rad ...
, Fritz Strassmann in 1938 that bombardment of uranium with neutrons (provided by an alpha-on-beryllium fusion reaction, a "neutron howitzer
A neutron howitzer is a neutron source that emits neutrons in a single direction. It was discovered in the 1930s that alpha radiation that strikes the beryllium nucleus would release neutrons. The high speed of the alpha is sufficient to overcome ...
") produced a barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
residue, which they reasoned was created by the fissioning of the uranium nuclei. Subsequent studies in early 1939 (one of them by Szilárd and Fermi) revealed that several neutrons were also released during the fissioning, making available the opportunity for the nuclear chain reaction that Szilárd had envisioned six years previously.
On 2 August 1939 Albert Einstein signed a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt (written by Szilárd) suggesting that the discovery of uranium's fission could lead to the development of "extremely powerful bombs of a new type", giving impetus to the study of reactors and fission. Szilárd and Einstein knew each other well and had worked together years previously, but Einstein had never thought about this possibility for nuclear energy until Szilard reported it to him, at the beginning of his quest to produce the Einstein-Szilárd letter to alert the U.S. government.
Shortly after, Hitler's Germany invaded Poland in 1939, starting World War II in Europe. The U.S. was not yet officially at war, but in October, when the Einstein-Szilárd letter was delivered to him, Roosevelt commented that the purpose of doing the research was to make sure "the Nazis don't blow us up." The U.S. nuclear project followed, although with some delay as there remained skepticism (some of it from Fermi) and also little action from the small number of officials in the government who were initially charged with moving the project forward.
The following year the U.S. Government received the Frisch–Peierls memorandum
The Frisch–Peierls memorandum was the first technical exposition of a practical nuclear weapon. It was written by expatriate German-Jewish physicists Otto Frisch and Rudolf Peierls in March 1940 while they were both working for Mark Oliphant a ...
from the UK, which stated that the amount of uranium needed for a chain reaction was far lower than had previously been thought. The memorandum was a product of the MAUD Committee, which was working on the UK atomic bomb project, known as Tube Alloys, later to be subsumed within the Manhattan Project.
Eventually, the first artificial nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1
Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1) was the world's first artificial nuclear reactor. On 2 December 1942, the first human-made self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction was initiated in CP-1, during an experiment led by Enrico Fermi. The secret development of t ...
, was constructed at the University of Chicago, by a team led by Italian physicist Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi (; 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian (later naturalized American) physicist and the creator of the world's first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and ...
, in late 1942. By this time, the program had been pressured for a year by U.S. entry into the war. The Chicago Pile achieved criticality on 2 December 1942 at 3:25 PM. The reactor support structure was made of wood, which supported a pile (hence the name) of graphite blocks, embedded in which was natural uranium oxide 'pseudospheres' or 'briquettes'.
Soon after the Chicago Pile, the U.S. military developed a number of nuclear reactors for the Manhattan Project starting in 1943. The primary purpose for the largest reactors (located at the Hanford Site in Washington), was the mass production of plutonium for nuclear weapons. Fermi and Szilard applied for a patent on reactors on 19 December 1944. Its issuance was delayed for 10 years because of wartime secrecy.
"World's first nuclear power plant" is the claim made by signs at the site of the EBR-I, which is now a museum near Arco, Idaho. Originally called "Chicago Pile-4", it was carried out under the direction of Walter Zinn
Walter Henry Zinn (December 10, 1906 – February 14, 2000) was an American nuclear physicist who was the first director of the Argonne National Laboratory from 1946 to 1956. He worked at the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory during W ...
for Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a science and engineering research United States Department of Energy National Labs, national laboratory operated by University of Chicago, UChicago Argonne LLC for the United States Department of Energy. The facil ...
. This experimental LMFBR operated by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President ...
produced 0.8 kW in a test on 20 December 1951 and 100 kW (electrical) the following day, having a design output of 200 kW (electrical).
Besides the military uses of nuclear reactors, there were political reasons to pursue civilian use of atomic energy. U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
made his famous Atoms for Peace speech to the UN General Assembly on 8 December 1953. This diplomacy led to the dissemination of reactor technology to U.S. institutions and worldwide.
The first nuclear power plant built for civil purposes was the AM-1 Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant, launched on 27 June 1954 in the Soviet Union. It produced around 5 MW (electrical). It was built after the F-1 (nuclear reactor)
The F-1 (from "First Physical Reactor") is a research reactor operated by the Kurchatov Institute in Moscow, Russia. When started on December 25, 1946, it became the first nuclear reactor in Europe to achieve a self-sustaining nuclear chain reac ...
which was the first reactor to go critical in Europe, and was also built by the Soviet Union.
After World War II, the U.S. military sought other uses for nuclear reactor technology. Research by the Army led to the power stations for Camp Century, Greenland and McMurdo Station, Antarctica Army Nuclear Power Program. The Air Force Nuclear Bomber project resulted in the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment. The U.S. Navy succeeded when they steamed the USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571) on nuclear power 17 January 1955.
The first commercial nuclear power station, Calder Hall in Sellafield
Sellafield is a large multi-function nuclear site close to Seascale on the coast of Cumbria, England. As of August 2022, primary activities are nuclear waste processing and storage and nuclear decommissioning. Former activities included nucle ...
, England was opened in 1956 with an initial capacity of 50 MW (later 200 MW).
The first portable nuclear reactor "Alco PM-2A" was used to generate electrical power (2 MW) for Camp Century from 1960 to 1963.

Reactor types
Classifications
By type of nuclear reaction
All commercial power reactors are based onnuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
. They generally use uranium and its product plutonium as nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.
Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergoing ...
, though a thorium fuel cycle is also possible. Fission reactors can be divided roughly into two classes, depending on the energy of the neutrons that sustain the fission chain reaction:
* Thermal-neutron reactors use slowed or thermal neutrons to keep up the fission of their fuel. Almost all current reactors are of this type. These contain neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely mo ...
materials that slow neutrons until their neutron temperature is ''thermalized'', that is, until their kinetic energy approaches the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles. Thermal neutrons have a far higher cross section (probability) of fissioning the fissile nuclei uranium-235, plutonium-239, and plutonium-241, and a relatively lower probability of neutron capture by uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it ...
(U-238) compared to the faster neutrons that originally result from fission, allowing use of low-enriched uranium or even natural uranium
Natural uranium (NU or Unat) refers to uranium with the same isotopic ratio as found in nature. It contains 0.711% uranium-235, 99.284% uranium-238, and a trace of uranium-234 by weight (0.0055%). Approximately 2.2% of its radioactivity comes fr ...
fuel. The moderator is often also the coolant, usually water under high pressure to increase the boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envir ...
. These are surrounded by a reactor vessel, instrumentation to monitor and control the reactor, radiation shielding, and a containment building.
* Fast-neutron reactors use fast neutrons to cause fission in their fuel. They do not have a neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely mo ...
, and use less-moderating coolants. Maintaining a chain reaction requires the fuel to be more highly enriched in fissile material (about 20% or more) due to the relatively lower probability of fission versus capture by U-238. Fast reactors have the potential to produce less transuranic waste because all actinides are fissionable with fast neutrons, but they are more difficult to build and more expensive to operate. Overall, fast reactors are less common than thermal reactors in most applications. Some early power stations were fast reactors, as are some Russian naval propulsion units. Construction of prototypes is continuing (see fast breeder or generation IV reactors).
In principle, fusion power could be produced by nuclear fusion of elements such as the deuterium isotope of hydrogen. While an ongoing rich research topic since at least the 1940s, no self-sustaining fusion reactor for any purpose has ever been built.
By moderator material
Used by thermal reactors: * Graphite-moderated reactors * Water moderated reactors **Heavy-water reactor
A pressurized heavy-water reactor (PHWR) is a nuclear reactor that uses heavy water ( deuterium oxide D2O) as its coolant and neutron moderator. PHWRs frequently use natural uranium as fuel, but sometimes also use very low enriched uranium. The ...
s (Used in Canada, India, Argentina, China, Pakistan, Romania and South Korea).
** Light-water-moderated reactors (LWRs). Light-water reactors (the most common type of thermal reactor) use ordinary water to moderate and cool the reactors. Because the light hydrogen isotope is a slight neutron poison these reactors need artificially enriched fuels. When at operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
, if the temperature of the water increases, its density drops, and fewer neutrons passing through it are slowed enough to trigger further reactions. That negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by ...
stabilizes the reaction rate. Graphite and heavy-water reactors tend to be more thoroughly thermalized than light water reactors. Due to the extra thermalization, and the absence of the light hydrogen poisoning effects these types can use natural uranium
Natural uranium (NU or Unat) refers to uranium with the same isotopic ratio as found in nature. It contains 0.711% uranium-235, 99.284% uranium-238, and a trace of uranium-234 by weight (0.0055%). Approximately 2.2% of its radioactivity comes fr ...
/unenriched fuel.
* Light-element-moderated reactors.
** Molten-salt reactors (MSRs) are moderated by light elements such as lithium or beryllium, which are constituents of the coolant/fuel matrix salts "LiF" and "BeF2", "LiCl" and "BeCl2" and other light element containing salts can all cause a moderating effect.
** Liquid metal cooled reactors, such as those whose coolant is a mixture of lead and bismuth, may use BeO as a moderator.
* Organically moderated reactors (OMR) use biphenyl
Biphenyl (also known as diphenyl, phenylbenzene, 1,1′-biphenyl, lemonene or BP) is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one ...
and terphenyl as moderator and coolant.
By coolant

 * Water cooled reactor. These constitute the great majority of operational nuclear reactors: as of 2014, 93% of the world's nuclear reactors are water cooled, providing about 95% of the world's total nuclear generation capacity.
** Pressurized water reactor (PWR) Pressurized water reactors constitute the large majority of all Western nuclear power plants.
*** A primary characteristic of PWRs is a pressurizer, a specialized
* Water cooled reactor. These constitute the great majority of operational nuclear reactors: as of 2014, 93% of the world's nuclear reactors are water cooled, providing about 95% of the world's total nuclear generation capacity.
** Pressurized water reactor (PWR) Pressurized water reactors constitute the large majority of all Western nuclear power plants.
*** A primary characteristic of PWRs is a pressurizer, a specialized pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
. Most commercial PWRs and naval reactors use pressurizers. During normal operation, a pressurizer is partially filled with water, and a steam bubble is maintained above it by heating the water with submerged heaters. During normal operation, the pressurizer is connected to the primary reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and the pressurizer "bubble" provides an expansion space for changes in water volume in the reactor. This arrangement also provides a means of pressure control for the reactor by increasing or decreasing the steam pressure in the pressurizer using the pressurizer heaters.
*** Pressurized heavy water reactors are a subset of pressurized water reactors, sharing the use of a pressurized, isolated heat transport loop, but using heavy water as coolant and moderator for the greater neutron economies it offers.
** Boiling water reactor (BWR)
*** BWRs are characterized by boiling water around the fuel rods in the lower portion of a primary reactor pressure vessel. A boiling water reactor uses 235U, enriched as uranium dioxide, as its fuel. The fuel is assembled into rods housed in a steel vessel that is submerged in water. The nuclear fission causes the water to boil, generating steam. This steam flows through pipes into turbines. The turbines are driven by the steam, and this process generates electricity. During normal operation, pressure is controlled by the amount of steam flowing from the reactor pressure vessel to the turbine.
** Supercritical water reactor
The supercritical water reactor (SCWR) is a concept Generation IV reactor, designed as a light water reactor (LWR) that operates at supercritical pressure (i.e. greater than 22.1 MPa). The term ''critical'' in this context refers to the c ...
(SCWR)
*** SCWRs are a Generation IV reactor concept where the reactor is operated at supercritical pressures and water is heated to a supercritical fluid, which never undergoes a transition to steam yet behaves like saturated steam, to power a steam generator.
** Reduced moderation water reactor MWR MWR may refer to:
* Michael Waltrip Racing, a NASCAR racing team
* ''Monthly Weather Review'', an American Meteorological Society journal
* Morale, Welfare and Recreation, an American military support network
* Museum of World Religions, a museum i ...
which use more highly enriched fuel with the fuel elements set closer together to allow a faster neutron spectrum sometimes called an Epithermal neutron Spectrum.
** Pool-type reactor can refer to unpressurized water cooled open pool reactor
NC State's PULSTAR Reactor is a 1 MW pool-type research reactor with 4% enriched, pin-type fuel consisting of UO2 pellets in zircaloy cladding.image:Pulstar1.jpg, The control room of North Carolina State University, NC State's Pulstar Nuclear R ...
s, but not to be confused with pool type LMFBRs which are sodium cooled
** Some reactors have been cooled by heavy water which also served as a moderator. Examples include:
***Early CANDU
The CANDU (Canada Deuterium Uranium) is a Canadian pressurized heavy-water reactor design used to generate electric power. The acronym refers to its deuterium oxide ( heavy water) moderator and its use of (originally, natural) uranium fuel. C ...
reactors (later ones use heavy water moderator but light water coolant)
*** DIDO class research reactors
* Liquid metal cooled reactor. Since water is a moderator, it cannot be used as a coolant in a fast reactor. Liquid metal coolants have included sodium, NaK, lead, lead-bismuth eutectic, and in early reactors, mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
.
** Sodium-cooled fast reactor
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is a fast neutron reactor cooled by liquid sodium.
The initials SFR in particular refer to two Generation IV reactor proposals, one based on existing liquid metal cooled reactor (LMFR) technology using mixed oxide fue ...
** Lead-cooled fast reactor
* Gas cooled reactors are cooled by a circulating gas. In commercial nuclear power plants carbon dioxide has usually been used, for example in current British AGR nuclear power plants and formerly in a number of first generation British, French, Italian, & Japanese plants. Nitrogen and helium have also been used, helium being considered particularly suitable for high temperature designs. Utilization of the heat varies, depending on the reactor. Commercial nuclear power plants run the gas through a heat exchanger to make steam for a steam turbine. Some experimental designs run hot enough that the gas can directly power a gas turbine.
* Molten-salt reactors (MSRs) are cooled by circulating a molten salt, typically a eutectic mixture of fluoride salts, such as FLiBe. In a typical MSR, the coolant is also used as a matrix in which the fissile material is dissolved. Other eutectic salt combinations used include "ZrF4" with "NaF" and "LiCh" with "BeCh2".
* Organic nuclear reactor
An organic nuclear reactor, or organic cooled reactor (OCR), is a type of nuclear reactor that uses some form of organic fluid, typically a hydrocarbon substance like polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB), for cooling and sometimes as a neutron moderat ...
s use organic fluids such as biphenyl and terphenyl as coolant rather than water.
By generation
* Generation I reactor (early prototypes such as Shippingport Atomic Power Station, research reactors, non-commercial power producing reactors) * Generation II reactor (most currentnuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s, 1965–1996)
* Generation III reactor
Generation III reactors, or Gen III reactors, are a class of nuclear reactors designed to succeed Generation II reactors, incorporating evolutionary improvements in design. These include improved fuel technology, higher thermal efficiency, sign ...
(evolutionary improvements of existing designs, 1996–2016)
* Generation III+ reactor (evolutionary development of Gen III reactors, offering improvements in safety over Gen III reactor designs, 2017–2021)
* Generation IV reactor (technologies still under development; unknown start date, possibly 2030)
* Generation V reactor (designs which are theoretically possible, but which are not being actively considered or researched at present).
In 2003, the French Commissariat à l'Énergie Atomique (CEA) was the first to refer to "Gen II" types in ''Nucleonics Week''.
The first mention of "Gen III" was in 2000, in conjunction with the launch of the Generation IV International Forum
Generation IV reactors (Gen IV) are six nuclear reactor designs recognized by the Generation IV International Forum. The designs target improved safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost.
The most developed Gen IV reactor design is the sodium ...
(GIF) plans.
"Gen IV" was named in 2000, by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), for developing new plant types.
By phase of fuel
* Solid fueled * Fluid fueled ** Aqueous homogeneous reactor ** Molten-salt reactor * Gas fueled (theoretical)By shape of the core
* Cubical * Cylindrical * Octagonal * Spherical * Slab * AnnulusBy use
* Electricity **Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s including small modular reactors
* Propulsion, see nuclear propulsion
** Nuclear marine propulsion
** Various proposed forms of rocket propulsion
* Other uses of heat
** Desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
** Heat for domestic and industrial heating
** Hydrogen production for use in a hydrogen economy
* Production reactors for transmutation
Transmutation may refer to:
Pseudoscience and science Alchemy
*Chrysopoeia and argyropoeia, the turning of inexpensive metals, such as lead or copper, into gold and silver
* Magnum opus (alchemy), the creation of the philosopher's stone
* Menta ...
of elements
** Breeder reactors are capable of producing more fissile material
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be ty ...
than they consume during the fission chain reaction (by converting fertile
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertilit ...
U-238 to Pu-239, or Th-232 to U-233). Thus, a uranium breeder reactor, once running, can be refueled with natural or even depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU; also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy or D-38) is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope than natural uranium.: "Depleted uranium possesses only 60% of the radioactivity of natural uranium, hav ...
, and a thorium breeder reactor can be refueled with thorium; however, an initial stock of fissile material is required. ; see "Fuel Cycles and Sustainability"
** Creating various radioactive isotopes, such as americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was na ...
for use in smoke detectors, and cobalt-60, molybdenum-99 and others, used for imaging and medical treatment.
** Production of materials for nuclear weapons such as weapons-grade plutonium
* Providing a source of neutron radiation (for example with the pulsed Godiva device) and positron radiation
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (). Positron ...
(e.g. neutron activation analysis
Neutron activation analysis (NAA) is the nuclear process used for determining the concentrations of elements in many materials. NAA allows discrete sampling of elements as it disregards the chemical form of a sample, and focuses solely on atomic ...
and potassium-argon dating)
* Research reactor: Typically reactors used for research and training, materials testing, or the production of radioisotopes for medicine and industry. These are much smaller than power reactors or those propelling ships, and many are on university campuses. There are about 280 such reactors operating, in 56 countries. Some operate with high-enriched uranium fuel, and international efforts are underway to substitute low-enriched fuel.
Current technologies
 * Pressurized water reactors (PWR) oderator: high-pressure water; coolant: high-pressure water
:: These reactors use a pressure vessel to contain the nuclear fuel, control rods, moderator, and coolant. The hot radioactive water that leaves the pressure vessel is looped through a steam generator, which in turn heats a secondary (nonradioactive) loop of water to steam that can run turbines. They represent the majority (around 80%) of current reactors. This is a thermal neutron reactor design, the newest of which are the Russian VVER-1200, Japanese Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor, American AP1000, Chinese Hualong Pressurized Reactor and the Franco-German
* Pressurized water reactors (PWR) oderator: high-pressure water; coolant: high-pressure water
:: These reactors use a pressure vessel to contain the nuclear fuel, control rods, moderator, and coolant. The hot radioactive water that leaves the pressure vessel is looped through a steam generator, which in turn heats a secondary (nonradioactive) loop of water to steam that can run turbines. They represent the majority (around 80%) of current reactors. This is a thermal neutron reactor design, the newest of which are the Russian VVER-1200, Japanese Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor, American AP1000, Chinese Hualong Pressurized Reactor and the Franco-German European Pressurized Reactor
The EPR is a Generation III reactor, third generation pressurised water reactor design. It has been designed and developed mainly by Framatome (part of Areva between 2001 and 2017) and Électricité de France (EDF) in France, and Siemens in Germ ...
. All the United States Naval reactors are of this type.
* Boiling water reactors (BWR) oderator: low-pressure water; coolant: low-pressure water
:: A BWR is like a PWR without the steam generator. The lower pressure of its cooling water allows it to boil inside the pressure vessel, producing the steam that runs the turbines. Unlike a PWR, there is no primary and secondary loop. The thermal efficiency of these reactors can be higher, and they can be simpler, and even potentially more stable and safe. This is a thermal-neutron reactor design, the newest of which are the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor and the Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor
The Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR) is a passively safe generation III+ reactor design derived from its predecessor, the Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (SBWR) and from the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR). All are designs ...
.
 * Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) oderator: high-pressure heavy water; coolant: high-pressure heavy water
:: A Canadian design (known as
* Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) oderator: high-pressure heavy water; coolant: high-pressure heavy water
:: A Canadian design (known as CANDU
The CANDU (Canada Deuterium Uranium) is a Canadian pressurized heavy-water reactor design used to generate electric power. The acronym refers to its deuterium oxide ( heavy water) moderator and its use of (originally, natural) uranium fuel. C ...
), very similar to PWRs but using heavy water. While heavy water is significantly more expensive than ordinary water, it has greater neutron economy (creates a higher number of thermal neutrons), allowing the reactor to operate without fuel enrichment facilities. Instead of using a single large pressure vessel as in a PWR, the fuel is contained in hundreds of pressure tubes. These reactors are fueled with natural uranium and are thermal-neutron reactor designs. PHWRs can be refueled while at full power, ( online refueling) which makes them very efficient in their use of uranium (it allows for precise flux control in the core). CANDU PHWRs have been built in Canada, Argentina, China, India, Pakistan, Romania, and South Korea. India also operates a number of PHWRs, often termed 'CANDU derivatives', built after the Government of Canada halted nuclear dealings with India following the 1974 Smiling Buddha nuclear weapon test.
: * Reaktor Bolshoy Moschnosti Kanalniy (High Power Channel Reactor) ( RBMK) oderator: graphite; coolant: high-pressure water
:: A Soviet design, RBMKs are in some respects similar to CANDU in that they are refuelable during power operation and employ a pressure tube design instead of a PWR-style pressure vessel. However, unlike CANDU they are very unstable and large, making containment buildings for them expensive. A series of critical safety flaws have also been identified with the RBMK design, though some of these were corrected following the
* Reaktor Bolshoy Moschnosti Kanalniy (High Power Channel Reactor) ( RBMK) oderator: graphite; coolant: high-pressure water
:: A Soviet design, RBMKs are in some respects similar to CANDU in that they are refuelable during power operation and employ a pressure tube design instead of a PWR-style pressure vessel. However, unlike CANDU they are very unstable and large, making containment buildings for them expensive. A series of critical safety flaws have also been identified with the RBMK design, though some of these were corrected following the Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
. Their main attraction is their use of light water and unenriched uranium. As of 2022, 8 remain open, mostly due to safety improvements and help from international safety agencies such as the DOE. Despite these safety improvements, RBMK reactors are still considered one of the most dangerous reactor designs in use. RBMK reactors were deployed only in the former Soviet Union.

 :: This totally unmoderated reactor design produces more fuel than it consumes. They are said to "breed" fuel, because they produce fissionable fuel during operation because of neutron capture. These reactors can function much like a PWR in terms of efficiency, and do not require much high-pressure containment, as the liquid metal does not need to be kept at high pressure, even at very high temperatures. These reactors are fast neutron, not thermal neutron designs. These reactors come in two types:
:: This totally unmoderated reactor design produces more fuel than it consumes. They are said to "breed" fuel, because they produce fissionable fuel during operation because of neutron capture. These reactors can function much like a PWR in terms of efficiency, and do not require much high-pressure containment, as the liquid metal does not need to be kept at high pressure, even at very high temperatures. These reactors are fast neutron, not thermal neutron designs. These reactors come in two types:
 ::: Lead-cooled
:::: Using lead as the liquid metal provides excellent radiation shielding, and allows for operation at very high temperatures. Also, lead is (mostly) transparent to neutrons, so fewer neutrons are lost in the coolant, and the coolant does not become radioactive. Unlike sodium, lead is mostly inert, so there is less risk of explosion or accident, but such large quantities of lead may be problematic from toxicology and disposal points of view. Often a reactor of this type would use a lead-bismuth eutectic mixture. In this case, the bismuth would present some minor radiation problems, as it is not quite as transparent to neutrons, and can be transmuted to a radioactive isotope more readily than lead. The Russian Alfa class submarine uses a lead-bismuth-cooled fast reactor as its main power plant.
::: Sodium-cooled
:::: Most LMFBRs are of this type. The
::: Lead-cooled
:::: Using lead as the liquid metal provides excellent radiation shielding, and allows for operation at very high temperatures. Also, lead is (mostly) transparent to neutrons, so fewer neutrons are lost in the coolant, and the coolant does not become radioactive. Unlike sodium, lead is mostly inert, so there is less risk of explosion or accident, but such large quantities of lead may be problematic from toxicology and disposal points of view. Often a reactor of this type would use a lead-bismuth eutectic mixture. In this case, the bismuth would present some minor radiation problems, as it is not quite as transparent to neutrons, and can be transmuted to a radioactive isotope more readily than lead. The Russian Alfa class submarine uses a lead-bismuth-cooled fast reactor as its main power plant.
::: Sodium-cooled
:::: Most LMFBRs are of this type. The TOPAZ
Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al Si O( F, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can mak ...
, BN-350 and BN-600 in USSR; Superphénix
Superphénix ( en, Superphoenix) or SPX was a nuclear power station prototype on the Rhône river at Creys-Malville in France, close to the border with Switzerland. Superphénix was a 1,242 MWe fast breeder reactor with the twin goals of reproce ...
in France; and Fermi-I in the United States were reactors of this type. The sodium is relatively easy to obtain and work with, and it also manages to actually prevent corrosion on the various reactor parts immersed in it. However, sodium explodes violently when exposed to water, so care must be taken, but such explosions would not be more violent than (for example) a leak of superheated fluid from a pressurized-water reactor. The Monju reactor
was a Japanese sodium-cooled fast reactor, located near the Tsuruga Nuclear Power Plant, Fukui Prefecture. Its name is a reference to Manjusri. Construction started in 1986 and the reactor achieved criticality for the first time in April 1994. ...
in Japan suffered a sodium leak in 1995 and could not be restarted until May 2010. The EBR-I, the first reactor to have a core meltdown, in 1955, was also a sodium-cooled reactor.
* Pebble-bed reactors (PBR) oderator: graphite; coolant: helium:: These use fuel molded into ceramic balls, and then circulate gas through the balls. The result is an efficient, low-maintenance, very safe reactor with inexpensive, standardized fuel. The prototypes were the AVR and the THTR-300 in Germany, which produced up to 308MW of electricity between 1985 and 1989 until it was shut down after experiencing a series of incidents and technical difficulties. The HTR-10 is operating in China, where the HTR-PM is being developed. The HTR-PM is expected to be the first generation IV reactor to enter operation.
* Molten-salt reactors (MSR) oderator: graphite, or none for fast spectrum MSRs; coolant: molten salt mixture::These dissolve the fuels in fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typ ...
or chloride salts, or use such salts for coolant. MSRs potentially have many safety features, including the absence of high pressures or highly flammable components in the core. They were initially designed for aircraft propulsion due to their high efficiency and high power density. One prototype, the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment, was built to confirm the feasibility of the Liquid fluoride thorium reactor, a thermal spectrum reactor which would breed fissile uranium-233 fuel from thorium.
* Aqueous homogeneous reactor (AHR) oderator: high-pressure light or heavy water; coolant: high-pressure light or heavy water
:: These reactors use as fuel soluble nuclear salts (usually uranium sulfate
Uranium(IV) sulfate (U(SO4)2) is a water-soluble salt of uranium. It is a very toxic compound. Uranium sulfate minerals commonly are widespread around uranium bearing mine sites, where they usually form during the evaporation of acid sulfate-rich m ...
or uranium nitrate
Uranyl nitrate is a water-soluble yellow uranium salt with the formula . The hexa-, tri-, and dihydrates are known. The compound is mainly of interest because it is an intermediate in the preparation of nuclear fuels.
Uranyl nitrate can be prepa ...
) dissolved in water and mixed with the coolant and the moderator. As of April 2006, only five AHRs were in operation.
Future and developing technologies
Advanced reactors
More than a dozen advanced reactor designs are in various stages of development. Some are evolutionary from the PWR,BWR
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is a design different from a Soviet graphite-moderated RBMK. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuc ...
and PHWR designs above, some are more radical departures. The former include the advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR), two of which are now operating with others under construction, and the planned passively safe Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor
The Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR) is a passively safe generation III+ reactor design derived from its predecessor, the Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (SBWR) and from the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR). All are designs ...
(ESBWR) and AP1000 units (see Nuclear Power 2010 Program
The "Nuclear Power 2010 Program" was launched in 2002 by President George W. Bush in 2002, 13 months after the beginning of his presidency, in order to restart orders for nuclear power reactors in the U.S. by providing subsidies for a handful of ...
).
* The integral fast reactor (IFR) was built, tested and evaluated during the 1980s and then retired under the Clinton administration in the 1990s due to nuclear non-proliferation policies of the administration. Recycling spent fuel is the core of its design and it therefore produces only a fraction of the waste of current reactors.
* The pebble-bed reactor, a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGCR), is designed so high temperatures reduce power output by Doppler broadening of the fuel's neutron cross-section. It uses ceramic fuels so its safe operating temperatures exceed the power-reduction temperature range. Most designs are cooled by inert helium. Helium is not subject to steam explosions, resists neutron absorption leading to radioactivity, and does not dissolve contaminants that can become radioactive. Typical designs have more layers (up to 7) of passive containment than light water reactors (usually 3). A unique feature that may aid safety is that the fuel balls actually form the core's mechanism, and are replaced one by one as they age. The design of the fuel makes fuel reprocessing expensive.
* The small, sealed, transportable, autonomous reactor (SSTAR) is being primarily researched and developed in the US, intended as a fast breeder reactor that is passively safe and could be remotely shut down in case the suspicion arises that it is being tampered with.
* The Clean and Environmentally Safe Advanced Reactor (CAESAR) is a nuclear reactor concept that uses steam as a moderator – this design is still in development.
* The reduced moderation water reactor builds upon the Advanced boiling water reactor ABWR) that is presently in use, it is not a complete fast reactor instead using mostly epithermal neutrons, which are between thermal and fast neutrons in speed.
* The hydrogen-moderated self-regulating nuclear power module The hydrogen-moderated self-regulating nuclear power module (HPM), also referred to as the compact self-regulating transportable reactor (ComStar), is a type of nuclear power reactor using hydride as a neutron moderator. The design is inherently saf ...
(HPM) is a reactor design emanating from the Los Alamos National Laboratory that uses uranium hydride as fuel.
* Subcritical reactors are designed to be safer and more stable, but pose a number of engineering and economic difficulties. One example is the energy amplifier.
* Thorium-based reactors — It is possible to convert Thorium-232 into U-233 in reactors specially designed for the purpose. In this way, thorium, which is four times more abundant than uranium, can be used to breed U-233 nuclear fuel. U-233 is also believed to have favourable nuclear properties as compared to traditionally used U-235, including better neutron economy and lower production of long lived transuranic waste.
** Advanced heavy-water reactor
The advanced heavy-water reactor (AHWR) or AHWR-300 is the latest Indian design for a next-generation nuclear reactor that burns thorium in its fuel core. It is slated to form the third stage in India's three-stage fuel-cycle plan. This phase ...
(AHWR) — A proposed heavy water moderated nuclear power reactor that will be the next generation design of the PHWR type. Under development in the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), India.
** KAMINI – A unique reactor using Uranium-233 isotope for fuel. Built in India by BARC and Indira Gandhi Center for Atomic Research ( IGCAR).
** India is also planning to build fast breeder reactors using the thorium – Uranium-233 fuel cycle. The FBTR (Fast Breeder Test Reactor) in operation at Kalpakkam (India) uses Plutonium as a fuel and liquid sodium as a coolant.
** China, which has control of the Cerro Impacto Cerro Impacto is a large mineral deposit in the southern Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, cons ...
deposit, has a reactor and hopes to replace coal energy with nuclear energy.
Rolls-Royce aims to sell nuclear reactors for the production of synfuel
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming ...
for aircraft.
Generation IV reactors
Generation IV reactors are a set of theoretical nuclear reactor designs currently being researched. These designs are generally not expected to be available for commercial construction before 2030. Current reactors in operation around the world are generally considered second- or third-generation systems, with the first-generation systems having been retired some time ago. Research into these reactor types was officially started by the Generation IV International Forum (GIF) based on eight technology goals. The primary goals being to improve nuclear safety, improve proliferation resistance, minimize waste and natural resource utilization, and to decrease the cost to build and run such plants. * Gas-cooled fast reactor * Lead-cooled fast reactor * Molten-salt reactor *Sodium-cooled fast reactor
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is a fast neutron reactor cooled by liquid sodium.
The initials SFR in particular refer to two Generation IV reactor proposals, one based on existing liquid metal cooled reactor (LMFR) technology using mixed oxide fue ...
* Supercritical water reactor
The supercritical water reactor (SCWR) is a concept Generation IV reactor, designed as a light water reactor (LWR) that operates at supercritical pressure (i.e. greater than 22.1 MPa). The term ''critical'' in this context refers to the c ...
* Very-high-temperature reactor
Generation V+ reactors
Generation V reactors are designs which are theoretically possible, but which are not being actively considered or researched at present. Though some generation V reactors could potentially be built with current or near term technology, they trigger little interest for reasons of economics, practicality, or safety. * Liquid-core reactor. A closed loop liquid-core nuclear reactor, where the fissile material is molten uranium or uranium solution cooled by a working gas pumped in through holes in the base of the containment vessel. * Gas-core reactor. A closed loop version of the nuclear lightbulb rocket, where the fissile material is gaseous uranium hexafluoride contained in a fused silica vessel. A working gas (such as hydrogen) would flow around this vessel and absorb the UV light produced by the reaction. This reactor design could also function as a rocket engine, as featured in Harry Harrison's 1976 science-fiction novel ''Skyfall''. In theory, using UF6 as a working fuel directly (rather than as a stage to one, as is done now) would mean lower processing costs, and very small reactors. In practice, running a reactor at such high power densities would probably produce unmanageable neutron flux, weakening most reactor materials, and therefore as the flux would be similar to that expected in fusion reactors, it would require similar materials to those selected by theInternational Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility
The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility, also known as IFMIF, is a projected material testing facility in which candidate materials for the use in an energy producing fusion reactor can be fully qualified. IFMIF will be an acceler ...
.
** Gas core EM reactor. As in the gas core reactor, but with photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
arrays converting the UV light directly to electricity. This approach is similar to the experimentally proved photoelectric effect that would convert the X-rays generated from aneutronic fusion into electricity, by passing the high energy photons through an array of conducting foils to transfer some of their energy to electrons, the energy of the photon is captured electrostatically, similar to a capacitor. Since X-rays can go through far greater material thickness than electrons, many hundreds or thousands of layers are needed to absorb the X-rays.
* Fission fragment reactor. A fission fragment reactor is a nuclear reactor that generates electricity by decelerating an ion beam of fission byproducts instead of using nuclear reactions to generate heat. By doing so, it bypasses the Carnot cycle and can achieve efficiencies of up to 90% instead of 40–45% attainable by efficient turbine-driven thermal reactors. The fission fragment ion beam would be passed through a magnetohydrodynamic generator to produce electricity.
* Hybrid nuclear fusion. Would use the neutrons emitted by fusion to fission a blanket of fertile material, like U-238 or Th-232 and transmute other reactor's spent nuclear fuel/nuclear waste into relatively more benign isotopes.
Fusion reactors
Controlled nuclear fusion could in principle be used in fusion power plants to produce power without the complexities of handling actinides, but significant scientific and technical obstacles remain. Despite research having started in the 1950s, no commercial fusion reactor is expected before 2050. TheITER
ITER (initially the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, ''iter'' meaning "the way" or "the path" in Latin) is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy by replicating, on Earth ...
project is currently leading the effort to harness fusion power.
Nuclear fuel cycle
Thermal reactors generally depend on refined and enriched uranium. Some nuclear reactors can operate with a mixture of plutonium and uranium (see MOX). The process by which uranium ore is mined, processed, enriched, used, possibly reprocessed and disposed of is known as the nuclear fuel cycle. Under 1% of the uranium found in nature is the easily fissionable U-235 isotope and as a result most reactor designs require enriched fuel. Enrichment involves increasing the percentage of U-235 and is usually done by means of gaseous diffusion or gas centrifuge. The enriched result is then converted into uranium dioxide powder, which is pressed and fired into pellet form. These pellets are stacked into tubes which are then sealed and called fuel rods. Many of these fuel rods are used in each nuclear reactor. Most BWR and PWR commercial reactors use uranium enriched to about 4% U-235, and some commercial reactors with a high neutron economy do not require the fuel to be enriched at all (that is, they can use natural uranium). According to theInternational Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
there are at least 100 research reactors in the world fueled by highly enriched (weapons-grade/90% enrichment) uranium. Theft risk of this fuel (potentially used in the production of a nuclear weapon) has led to campaigns advocating conversion of this type of reactor to low-enrichment uranium (which poses less threat of proliferation).
Fissile U-235 and non-fissile but fissionable and fertile
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertilit ...
U-238 are both used in the fission process. U-235 is fissionable by thermal (i.e. slow-moving) neutrons. A thermal neutron is one which is moving about the same speed as the atoms around it. Since all atoms vibrate proportionally to their absolute temperature, a thermal neutron has the best opportunity to fission U-235 when it is moving at this same vibrational speed. On the other hand, U-238 is more likely to capture a neutron when the neutron is moving very fast. This U-239 atom will soon decay into plutonium-239, which is another fuel. Pu-239 is a viable fuel and must be accounted for even when a highly enriched uranium fuel is used. Plutonium fissions will dominate the U-235 fissions in some reactors, especially after the initial loading of U-235 is spent. Plutonium is fissionable with both fast and thermal neutrons, which make it ideal for either nuclear reactors or nuclear bombs.
Most reactor designs in existence are thermal reactors and typically use water as a neutron moderator (moderator means that it slows down the neutron to a thermal speed) and as a coolant. But in a fast breeder reactor, some other kind of coolant is used which will not moderate or slow the neutrons down much. This enables fast neutrons to dominate, which can effectively be used to constantly replenish the fuel supply. By merely placing cheap unenriched uranium into such a core, the non-fissionable U-238 will be turned into Pu-239, "breeding" fuel.
In thorium fuel cycle thorium-232 absorbs a neutron in either a fast or thermal reactor. The thorium-233 beta decays to protactinium-233 and then to uranium-233, which in turn is used as fuel. Hence, like uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it ...
, thorium-232 is a fertile material.
Fueling of nuclear reactors
The amount of energy in the reservoir ofnuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.
Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergoing ...
is frequently expressed in terms of "full-power days," which is the number of 24-hour periods (days) a reactor is scheduled for operation at full power output for the generation of heat energy. The number of full-power days in a reactor's operating cycle (between refueling outage times) is related to the amount of fissile uranium-235 (U-235) contained in the fuel assemblies at the beginning of the cycle. A higher percentage of U-235 in the core at the beginning of a cycle will permit the reactor to be run for a greater number of full-power days.
At the end of the operating cycle, the fuel in some of the assemblies is "spent", having spent four to six years in the reactor producing power. This spent fuel is discharged and replaced with new (fresh) fuel assemblies. Though considered "spent," these fuel assemblies contain a large quantity of fuel. In practice it is economics that determines the lifetime of nuclear fuel in a reactor. Long before all possible fission has taken place, the reactor is unable to maintain 100%, full output power, and therefore, income for the utility lowers as plant output power lowers. Most nuclear plants operate at a very low profit margin due to operating overhead, mainly regulatory costs, so operating below 100% power is not economically viable for very long. The fraction of the reactor's fuel core replaced during refueling is typically one-third, but depends on how long the plant operates between refueling. Plants typically operate on 18 month refueling cycles, or 24 month refueling cycles. This means that one refueling, replacing only one-third of the fuel, can keep a nuclear reactor at full power for nearly two years. The disposition and storage of this spent fuel is one of the most challenging aspects of the operation of a commercial nuclear power plant. This nuclear waste is highly radioactive and its toxicity presents a danger for thousands of years. After being discharged from the reactor, spent nuclear fuel is transferred to the on-site spent fuel pool. The spent fuel pool is a large pool of water that provides cooling and shielding of the spent nuclear fuel. Once the energy has decayed somewhat (approximately five years), the fuel can be transferred from the fuel pool to dry shielded casks, that can be safely stored for thousands of years. After loading into dry shielded casks, the casks are stored on-site in a specially guarded facility in impervious concrete bunkers. On-site fuel storage facilities are designed to withstand the impact of commercial airliners, with little to no damage to the spent fuel. An average on-site fuel storage facility can hold 30 years of spent fuel in a space smaller than a football field.
Not all reactors need to be shut down for refueling; for example, pebble bed reactors, RBMK reactors, molten-salt reactors, Magnox, AGR and CANDU
The CANDU (Canada Deuterium Uranium) is a Canadian pressurized heavy-water reactor design used to generate electric power. The acronym refers to its deuterium oxide ( heavy water) moderator and its use of (originally, natural) uranium fuel. C ...
reactors allow fuel to be shifted through the reactor while it is running. In a CANDU reactor, this also allows individual fuel elements to be situated within the reactor core that are best suited to the amount of U-235 in the fuel element.
The amount of energy extracted from nuclear fuel is called its burnup, which is expressed in terms of the heat energy produced per initial unit of fuel weight. Burnup is commonly expressed as megawatt days thermal per metric ton of initial heavy metal.
Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety covers the actions taken to prevent nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents or to limit their consequences. The nuclear power industry has improved the safety and performance of reactors, and has proposed new, safer (but generally untested) reactor designs but there is no guarantee that the reactors will be designed, built and operated correctly. Mistakes do occur and the designers of reactors atFukushima
may refer to:
Japan
* Fukushima Prefecture, Japanese prefecture
**Fukushima, Fukushima, capital city of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan
*** Fukushima University, national university in Japan
*** Fukushima Station (Fukushima) in Fukushima, Fukushim ...
in Japan did not anticipate that a tsunami generated by an earthquake would disable the backup systems that were supposed to stabilize the reactor after the earthquake, despite multiple warnings by the NRG and the Japanese nuclear safety administration. According to UBS
UBS Group AG is a multinational Investment banking, investment bank and financial services company founded and based in Switzerland. Co-headquartered in the cities of Zürich and Basel, it maintains a presence in all major financial centres ...
AG, the Fukushima I nuclear accidents have cast doubt on whether even an advanced economy like Japan can master nuclear safety. Catastrophic scenarios involving terrorist attacks are also conceivable. An interdisciplinary team from MIT has estimated that given the expected growth of nuclear power from 2005 to 2055, at least four serious nuclear accidents would be expected in that period.
Nuclear accidents
 Serious, though rare, nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred. These include the Windscale fire (October 1957), the SL-1 accident (1961), the Three Mile Island accident (1979),
Serious, though rare, nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred. These include the Windscale fire (October 1957), the SL-1 accident (1961), the Three Mile Island accident (1979), Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
(April 1986), and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
(March 2011). Nuclear-powered submarine mishaps include the K-19 reactor accident (1961),Strengthening the Safety of Radiation Sourcesp. 14. the K-27 reactor accident (1968), and the K-431 reactor accident (1985).The Worst Nuclear Disasters
''Time''. Nuclear reactors have been launched into Earth orbit at least 34 times. A number of incidents connected with the unmanned nuclear-reactor-powered Soviet RORSAT especially
Kosmos 954
Kosmos 954 (russian: Космос 954) was a reconnaissance satellite launched by the Soviet Union in 1977. A malfunction prevented safe separation of its onboard nuclear reactor; when the satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere the follow ...
radar satellite which resulted in nuclear fuel reentering the Earth's atmosphere from orbit and being dispersed in northern Canada (January 1978).
Natural nuclear reactors
Almost two billion years ago a series of self-sustaining nuclear fission "reactors" self-assembled in the area now known as Oklo in Gabon, West Africa. The conditions at that place and time allowed a natural nuclear fission to occur with circumstances that are similar to the conditions in a constructed nuclear reactor. Fifteen fossil natural fission reactors have so far been found in three separate ore deposits at the Oklo uranium mine in Gabon. First discovered in 1972 by French physicistFrancis Perrin Francis Perrin may refer to:
* Francis Perrin (actor) (born 1947), French actor, screenwriter and director
* Francis Perrin (physicist) (1901–1992), French physicist
See also
* Perrin (disambiguation)
{{hndis, Perrin, Francis ...
, they are collectively known as the Oklo Fossil Reactors
A natural nuclear fission reactor is a uranium deposit where self-sustaining nuclear chain reactions occur. The conditions under which a natural nuclear reactor could exist had been predicted in 1956 by Japanese American chemist Paul Kuroda. Th ...
. Self-sustaining nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
reactions took place in these reactors approximately 1.5 billion years ago, and ran for a few hundred thousand years, averaging 100 kW of power output during that time. The concept of a natural nuclear reactor was theorized as early as 1956 by Paul Kuroda at the University of Arkansas.
Such reactors can no longer form on Earth in its present geologic period. Radioactive decay of formerly more abundant uranium-235 over the time span of hundreds of millions of years has reduced the proportion of this naturally occurring fissile isotope to below the amount required to sustain a chain reaction with only plain water as a moderator.
The natural nuclear reactors formed when a uranium-rich mineral deposit became inundated with groundwater that acted as a neutron moderator, and a strong chain reaction took place. The water moderator would boil away as the reaction increased, slowing it back down again and preventing a meltdown. The fission reaction was sustained for hundreds of thousands of years, cycling on the order of hours to a few days.
These natural reactors are extensively studied by scientists interested in geologic radioactive waste disposal. They offer a case study of how radioactive isotopes migrate through the Earth's crust. This is a significant area of controversy as opponents of geologic waste disposal fear that isotopes from stored waste could end up in water supplies or be carried into the environment.
Emissions
Nuclear reactors produce tritium as part of normal operations, which is eventually released into the environment in trace quantities. As an isotope of hydrogen, tritium (T) frequently binds to oxygen and forms T2O. This molecule is chemically identical to H2O and so is both colorless and odorless, however the additional neutrons in the hydrogen nuclei cause the tritium to undergo beta decay with a half-life of 12.3 years. Despite being measurable, the tritium released by nuclear power plants is minimal. The United States NRC estimates that a person drinking water for one year out of a well contaminated by what they would consider to be a significant tritiated water spill would receive a radiation dose of 0.3 millirem. For comparison, this is an order of magnitude less than the 4 millirem a person receives on a round trip flight from Washington, D.C. to Los Angeles, a consequence of less atmospheric protection against highly energetic cosmic rays at high altitudes. The amounts of strontium-90 released from nuclear power plants under normal operations is so low as to be undetectable above natural background radiation. Detectable strontium-90 in ground water and the general environment can be traced to weapons testing that occurred during the mid-20th century (accounting for 99% of the Strontium-90 in the environment) and the Chernobyl accident (accounting for the remaining 1%).See also
* List of nuclear reactors * List of small modular reactor designs *List of United States Naval reactors
List of United States Naval reactors is a comprehensive annotated list of all naval reactors designed, built, or used by the United States Navy.
Reactor designations
Each nuclear reactor design is given a three-character designation consisti ...
* Neutron transport
* Nuclear decommissioning
Nuclear decommissioning is the process whereby a nuclear facility is dismantled to the point that it no longer requires measures for radiation protection.
The presence of radioactive material necessitates processes that are potentially occupat ...
* Nuclear power by country
* Nuclear power in space
* One Less Nuclear Power Plant
* Radioisotope thermoelectric generator
* Safety engineering
* Sayonara Nuclear Power Plants
is an anti-nuclear organization and campaign in Japan.Sayonara-nukes.org
Accessed: December 27, 2013. Tr ...
* Small modular reactor
* Thorium-based nuclear power
* Traveling-wave reactor (TWR)
* '' World Nuclear Industry Status Report''
Accessed: December 27, 2013. Tr ...
References
External links
The Database on Nuclear Power Reactors – IAEA
Uranium Conference adds discussion of Japan accident
A Debate: Is Nuclear Power The Solution to Global Warming?
Union of Concerned Scientists, Concerns re: US nuclear reactor program
Freeview Video 'Nuclear Power Plants — What's the Problem' A Royal Institution Lecture by John Collier by the Vega Science Trust.
Nuclear Energy Institute — How it Works: Electric Power Generation
Annotated bibliography of nuclear reactor technology from the Alsos Digital Library
*
ソヴィエト連邦における宇宙用原子炉の開発とその実用
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nuclear Reactor Technology Energy conversion Nuclear technology Power station technology Pressure vessels Nuclear research reactors
Nuclear power reactor types
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
Neutron sources