|
Army Nuclear Power Program
The Army Nuclear Power Program (ANPP) was a program of the United States Army to develop small pressurized water and boiling water nuclear power reactors to generate electrical and space-heating energy primarily at remote, relatively inaccessible sites. The ANPP had several accomplishments, but ultimately it was considered to be "a solution in search of a problem." The U.S. Army Engineer Reactors Group managed this program and it was headquartered at Fort Belvoir, Virginia. The program began in 1954 and had effectively terminated by about 1977, with the last class of NPP operators graduating in 1977. Work continued for some time thereafter either for decommissioning of the plants or placing them into SAFSTOR, SAFSTOR (long term storage and monitoring before decommissioning). The current development of small modular reactors has led to a renewed interest in military applications. Background There was interest in the possible application of nuclear power to land-based military ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Army Corps Of Engineers Chiefs Of Engineers
The Chief of Engineers is a principal United States Army staff officer at The Pentagon. The Chief advises the Army on engineering matters, and serves as the Army's topographer and proponent for real estate and other related engineering programs. The Chief of Engineers is the senior service engineer for the Department of Defense, responsible for integrating all aspects of combat, general and geospatial engineering across the Joint Force. The Chief of Engineers also commands the United States Army Corps of Engineers. As commander of the US Army Corps of Engineers, the Chief of Engineers leads a major Army command that is the world's largest public engineering, design and construction management agency. This office defines policy and guidance, and it plans direction for the organizations within the Corps. The Chief of Engineers is currently a lieutenant general billet but in the past has been held by field grade officers as low as major. Civilian oversight of the Chief of Engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idaho Reactor Testing Station
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. While the laboratory does other research, historically it has been involved with nuclear research. Much of current knowledge about how nuclear reactors behave and misbehave was discovered at what is now Idaho National Laboratory. John Grossenbacher, former INL director, said, "The history of nuclear energy for peaceful application has principally been written in Idaho". Various organizations have built more than 50 reactors at what is commonly called "the Site", including the ones that gave the world its first usable amount of electricity from nuclear power and the power plant for the world's first nuclear submarine. Although many are now decommissioned, these facilities are the largest concentration of reactors in the world. It is on a complex in the high desert of eastern Idaho, between Arco to the west and Idaho F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
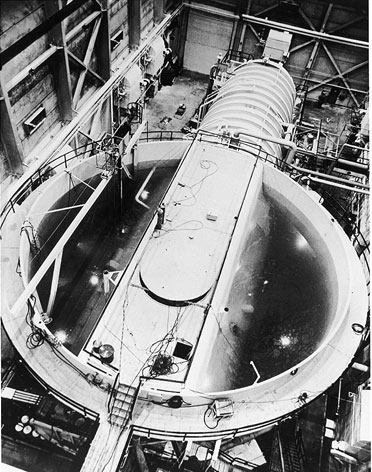
SL-1
Stationary Low-Power Reactor Number One, also known as SL-1 or the Argonne Low Power Reactor (ALPR), was a United States Army experimental nuclear reactor in the western United States at the National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS), later the Idaho National Laboratory, west of Idaho Falls, Idaho. It experienced a steam explosion on the night of January 3, 1961, killing all three of its young military operators, and pinning one of them to the ceiling of the facility with a reactor vessel plug. The event is the only reactor accident in U.S. history that resulted in immediate fatalities. The direct cause was the over-withdrawal of the central control rod, responsible for absorbing neutrons in the reactor's core. The accident released about of iodine-131, which was not considered significant due to its location in the remote high desert of eastern Idaho. About of fission products were released into the atmosphere. The facility housing SL-1, located approximately west of Idah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of hydrogen-2 (''deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiating lithium metal or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radioluminescent lights for watches, gun sights, numerous instruments and tools, and even novelty items such as self-illuminating key chains. It is used in a medical and scientific setting as a rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Nuclear Power Program
The Army Nuclear Power Program (ANPP) was a program of the United States Army to develop small pressurized water and boiling water nuclear power reactors to generate electrical and space-heating energy primarily at remote, relatively inaccessible sites. The ANPP had several accomplishments, but ultimately it was considered to be "a solution in search of a problem." The U.S. Army Engineer Reactors Group managed this program and it was headquartered at Fort Belvoir, Virginia. The program began in 1954 and had effectively terminated by about 1977, with the last class of NPP operators graduating in 1977. Work continued for some time thereafter either for decommissioning of the plants or placing them into SAFSTOR, SAFSTOR (long term storage and monitoring before decommissioning). The current development of small modular reactors has led to a renewed interest in military applications. Background There was interest in the possible application of nuclear power to land-based military ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer of locomotives, diesel generators, steel, and tanks that operated from 1901 to 1969. The company was formed by the merger of seven smaller locomotive manufacturers and Schenectady Locomotive Engine Manufactory of Schenectady, New York. A subsidiary, American Locomotive Automobile Company, designed and manufactured automobiles under the Alco brand from 1905 to 1913. ALCO also produced nuclear reactors from 1954 to 1962. The company changed its name to Alco Products, Incorporated in 1955. In 1964, the Worthington Corporation acquired the company. The company went out of business in 1969. The ALCO name is currently being used by Fairbanks Morse Engine for their FM, ALCO line. Foundation and early history The company was created in 1901 from the merger of seven smaller locomotive manufacturers with Schenectady Locomotive Engine Manufactory of Schenectady, New York: *Brooks Locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grid Connection
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power Transmission: Background and Policy Issues. The Capital.Net, Government Series. Pp. 1-42. * power stations: often located near energy and away from heavily populated areas * electrical substations to step voltage up or down * electric power transmission to carry power long distances * electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same time). This allows transmission of AC power throughout the area, connecting a large number of electricity generators and consumers and potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shippingport Reactor
The Shippingport Atomic Power Station was (according to the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission) the world's first full-scale atomic electric power plant devoted exclusively to peacetime uses.Though Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant was connected to the Moscow Grid in 1954 and was the first nuclear reactor that produced commercial electricity, it can still be considered a small scale station designed principally to carry out nuclear experiments. The first British Magnox reactor at Calder Hall was connected to the grid on 27 August 1956, its primary purpose was to produce plutonium for military uses.The Vallecitos Nuclear Center started producing electric power in October 1957, but it served as a test or pilot plant. It was located near the present-day Beaver Valley Nuclear Generating Station on the Ohio River in Beaver County, Pennsylvania, United States, about 25 miles (40 km) from Pittsburgh. The reactor reached criticality on December 2, 1957, and aside from stoppages for thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM-1
SM-1 (Stationary, Medium-size reactor, prototype #1) was a 2-megawatt nuclear reactor developed by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) and the United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) as part of the US Army Nuclear Power Program (ANPP) in the mid-1950s. The compact "package" reactor was designed to produce electricity and generate heat for remote military facilities. The first, the SM-1, served as the Army's primary training facility to train reactor operations personnel from all three services (Army, Navy and Air Force). In 1954, the Department of Defense placed the US Army in charge of all military nuclear power plants except those used for propulsion by the US Navy. The Army's Chief of Engineers established the US Army Engineer Reactors Group in April 1954, and decided to construct the SM-1 facility at the Corps of Engineers headquarters at Fort Belvoir, Virginia, about 18 miles south of Washington, D.C. About 800 personnel were trained on the SM-1 during its operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |