Code Maintenance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Software maintenance is the modification of software after delivery.
Software maintenance is often considered lower skilled and less rewarding than new development. As such, it is a common target for outsourcing or
 Despite testing and
Despite testing and
 Frequently, software is delivered in an incomplete state. Developers will test a product until running out of time or funding, because they face fewer consequences for an imperfect product than going over time or budget. The transition from the development to the maintenance team is often inefficient, without lists of known issues or validation tests, which the maintenance team will likely recreate. After release, members of the development team are likely to be reassigned or otherwise become unavailable. The maintenance team will require additional resources for the first year after release, both for
Frequently, software is delivered in an incomplete state. Developers will test a product until running out of time or funding, because they face fewer consequences for an imperfect product than going over time or budget. The transition from the development to the maintenance team is often inefficient, without lists of known issues or validation tests, which the maintenance team will likely recreate. After release, members of the development team are likely to be reassigned or otherwise become unavailable. The maintenance team will require additional resources for the first year after release, both for
offshoring
Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another—typically an operational process, such as manufacturing, or supporting processes, such as accounting. Usually this refers to a company business, although state gover ...
. Usually, the team developing the software is different from those who will be maintaining it. The developers lack an incentive to write the code to be easily maintained. Software is often delivered incomplete and almost always contains some bugs that the maintenance team must fix. Software maintenance often initially includes the development of new functionality, but as the product nears the end of its lifespan, maintenance is reduced to the bare minimum and then cut off entirely before the product is withdrawn.
Each maintenance cycle begins with a change request typically originating from an end user. That request is evaluated and if it is decided to implement it, the programmer studies the existing code to understand how it works before implementing the change. Testing to make sure the existing functionality is retained and the desired new functionality is added often comprises the majority of the maintenance cost.
Software maintenance is not as well studied as other phases of the software life cycle, despite comprising the majority of costs. Understanding has not changed significantly since the 1980s. Software maintenance can be categorized into several types depending on whether it is preventative or reactive and whether it is seeking to add functionality or preserve existing functionality, the latter typically in the face of a changed environment.
History
In the early 1970s, companies began to separate out software maintenance with its own team of engineers to free upsoftware development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
teams from support tasks. In 1972, R. G. Canning published "The Maintenance 'Iceberg, in which he contended that software maintenance was an extension of software development with an additional input: the existing system. The discipline of software maintenance has changed little since then. One twenty-first century innovation has been companies deliberately releasing incomplete software and planning to finish it post-release. This type of change, and others that expand functionality, is often called software evolution
Software evolution is the continual development of a piece of software after its initial release to address changing stakeholder and/or market requirements. Software evolution is important because organizations invest large amounts of money in the ...
instead of maintenance.Software life cycle
 Despite testing and
Despite testing and quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to assure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
, virtually all software contains bugs where the system does not work as intended. Post-release maintenance is necessary to remediate these bugs when they are found. Most software is a combination of pre-existing commercial off-the-shelf
Commercial-off-the-shelf or commercially available off-the-shelf (COTS) products are packaged or canned (ready-made) hardware or software, which are adapted aftermarket to the needs of the purchasing organization, rather than the commissioning of ...
(COTS) and open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
components with custom-written code. COTS and open-source software is typically updated over time, which can reduce the maintenance burden, but the modifications to these software components will need to be adjusted for in the final product. Unlike software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
, which is focused on meeting specified requirements, software maintenance is driven by events—such as user requests or detection of a bug. Its main purpose is to preserve the usefulness of the software, usually in the face of changing requirements.
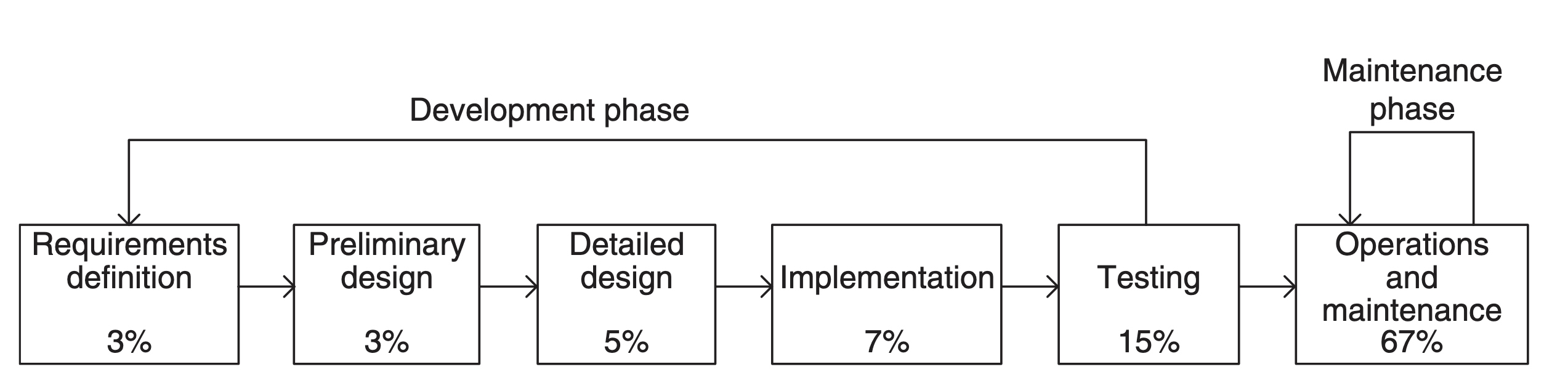
If conceived of as part of the software development life cycle
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or s ...
, maintenance is the last and typically the longest phase of the cycle, comprising 80 to 90 percent of the lifecycle cost. Other models consider maintenance separate from software development, instead as part of the software maintenance life cycle (SMLC). SMLC models typically include understanding the code, modifying it, and revalidating it. Transition from release to maintenance to end of the lifespan
 Frequently, software is delivered in an incomplete state. Developers will test a product until running out of time or funding, because they face fewer consequences for an imperfect product than going over time or budget. The transition from the development to the maintenance team is often inefficient, without lists of known issues or validation tests, which the maintenance team will likely recreate. After release, members of the development team are likely to be reassigned or otherwise become unavailable. The maintenance team will require additional resources for the first year after release, both for
Frequently, software is delivered in an incomplete state. Developers will test a product until running out of time or funding, because they face fewer consequences for an imperfect product than going over time or budget. The transition from the development to the maintenance team is often inefficient, without lists of known issues or validation tests, which the maintenance team will likely recreate. After release, members of the development team are likely to be reassigned or otherwise become unavailable. The maintenance team will require additional resources for the first year after release, both for technical support
Technical support, commonly shortened as tech support, is a customer service provided to customers to resolve issues, commonly with consumer electronics. This is commonly provided via call centers, online chat and email. Many companies provid ...
and fixing defects left over from development.
Initially, software may go through a period of enhancements after release. New features are added according to user feedback. At some point, the company may decide that it is no longer profitable to make functional improvements, and restrict support to bug fixing and emergency updates. Changes become increasingly difficult and expensive due to lack of expertise or decaying architecture due to software aging
In software engineering, software aging is the tendency for software to Software failure, fail or cause a system failure after running continuously for a certain time, or because of ongoing changes in systems surrounding the software. Software a ...
. After a product is no longer maintained, and does not receive even this limited level of updating, some vendors will seek to extract revenue from the software as long as possible, even though the product is likely to become increasingly avoided. Eventually, the software will be withdrawn from the market, although it may remain in use. During this process, the software becomes a legacy system
Legacy or Legacies may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Comics
* " Batman: Legacy", a 1996 Batman storyline
* '' DC Universe: Legacies'', a comic book series from DC Comics
* ''Legacy'', a 1999 quarterly series from Antarctic Press
* ''Legacy ...
.
Change cycle
The first step in the change cycle is receiving a change request from a customer and analyzing it to confirm the problem and decide whether to implement the change. This may require input from multiple departments; for example, the marketing team can help evaluate whether the change is expected to bring more business.Software development effort estimation
In software development, effort estimation is the process of predicting the most realistic amount of effort (expressed in terms of person-hours or money) required to develop or maintain software based on incomplete, uncertain and noisy input. Effor ...
is a difficult problem, including for maintenance change requests, but the request is likely to be declined if it is too expensive or infeasible. If it is decided to implement the request, it can be assigned to a scheduled release and implemented. Although agile methodology
Agile software development is an umbrella term for approaches to developing software that reflect the values and principles agreed upon by ''The Agile Alliance'', a group of 17 software practitioners, in 2001. As documented in their ''Manifesto ...
does not have a maintenance phase, the change cycle can be enacted as a scrum sprint.
Understanding existing code is an essential step before modifying it. The rate of understanding depends both on the code base as well as the skill of the programmer. Following coding conventions such as using clear function and variable names that correspond to their purpose makes understanding easier. Use of conditional loop statements only if the code could execute more than once, and eliminating code that will never execute can also increase understandability. Experienced programmers have an easier time understanding what the code does at a high level. Software visualization
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th cen ...
is sometimes used to speed up this process.
Modification to the code may take place in any way. On the one hand, it is common to haphazardly apply a quick fix without being granted enough time to update the code documentation. On the other hard structured iterative enhancement can begin by changing the top-level requirements document and propagating the change down to lower levels of the system. Modification often includes code refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing source code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, ...
(improving the structure without changing functionality) and restructuring (improving structure and functionality at the same time). Unlike commercial software, free and open source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a Software license, license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term ...
change cycles are largely restricted to coding and testing, with minimal documentation. Open-source software projects instead rely on mailing lists and a large number of contributors to understand the code base and fix bugs efficiently.
An additional problem with maintenance is that nearly every change to code will introduce new bugs or unexpected ripple effect
A ripple effect occurs when an initial disturbance to a system propagates outward to disturb an increasingly larger portion of the system, like ripples expanding across the water when an object is dropped into it.
The ripple effect is often use ...
s, which require another round of fixes. Testing can consume the majority of maintenance resource for safety-critical code, due to the need to revalidate the entire software if any changes are made. Revalidation may include code review
Code review (sometimes referred to as peer review) is a software quality assurance activity in which one or more people examine the source code of a computer program, either after implementation or during the development process. The persons perf ...
, regression test
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regr ...
ing with a subset of unit test
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the integration ...
s, integration test
Integration testing is a form of software testing in which multiple software components, modules, or services are tested together to verify they work as expected when combined. The focus is on testing the interactions and data exchange between i ...
s, and system test
System testing, a.k.a. end-to-end (E2E) testing, is testing conducted on a complete software system.
System testing describes testing at the system level to contrast to testing at the system integration, integration or unit level.
System tes ...
s. The goal of the testing is to verify that previous functionality is retained, and the new functionality has been added.
Categories of software maintenance
The key purpose of software maintenance is ensuring that the product continues to meet usability requirements. At times, this may mean extending the product's capabilities beyond what was initially envisioned. According to theISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
/IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of ...
14764 specification, software maintenance can be classified into four types:
* Corrective maintenance
Corrective maintenance is a maintenance task performed to identify, isolate, and rectify a fault so that the failed equipment, machine, or system can be restored to an operational condition within the tolerances or limits established for in-serv ...
: modification of software to fix a bug or other failure to meet requirements, typically reported by an end user.
* Preventive maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
: forward-looking modification of software after delivery to ensure it continues to meet requirements or fix problems that have not manifested yet. This type of maintenance is performed especially on systems that are required to be highly safe or available. Software rejuvenation is one form of preventative maintenance to clean up state and prevent future problems.
* Adaptive maintenance: modification of software performed after delivery to ensure its continuing usability in a changed or changing environment.
* Perfective maintenance: enhancement of software after delivery to improve qualities such as user experience
User experience (UX) is how a user interacts with and experiences a product, system or service. It includes a person's perceptions of utility, ease of use, and efficiency. Improving user experience is important to most companies, designers, a ...
, processing efficiency, and maintainability
Maintainability is the ease of maintaining or providing maintenance for a functioning product or service. Depending on the field, it can have slightly different meanings.
Usage in different fields Engineering
In engineering, maintainability ...
. Perfective maintenance is necessary if other types of maintenance are carried out, because modification of an existing code base will otherwise increase complexity and cause the existing structure to deteriorate. Perfective maintenance may include rewriting documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge managem ...
, code refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing source code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, ...
, and performance tuning.
According to some estimates, enhancement (the latter two categories) comprises some 80 percent of software maintenance.Maintainability
Maintainability is the quality of software enabling it to be easily modified without breaking existing functionality. According to the ISO/IEC 14764 specification, activity to ensure software maintainability prior to release counts as part of software maintenance. Many software development organizations neglect maintainability, even though doing so will increase long-term costs.Technical debt
In software development and other information technology fields, technical debt (also known as design debt or code debt) refers to the implied cost of additional work in the future resulting from choosing an expedient solution over a more robust o ...
is incurred when programmers, often out of laziness or urgency to meet a deadline, choose quick and dirty solutions rather than build maintainability into their code. A common cause is underestimates in software development effort estimation
In software development, effort estimation is the process of predicting the most realistic amount of effort (expressed in terms of person-hours or money) required to develop or maintain software based on incomplete, uncertain and noisy input. Effor ...
, leading to insufficient resources allocated to development. One important aspect is having a large amount of automated software test
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the quality of software and the risk of its failure to a user or sponsor.
Software testing ...
s that can detect if existing functionality is compromised by a change.
A maintainability index can be calculated with certain formulae from lines-of-code measures, McCabe measures and Halstead complexity measures
Halstead complexity measures are software metrics introduced by Maurice Howard Halstead in 1977 as part of his treatise on establishing an empirical science of software development.
Halstead made the observation that metrics of the software should ...
.
The measurement and tracking of maintainability are intended to help reduce or reverse a system's tendency toward "code entropy" or degraded integrity, and to indicate when it becomes cheaper and/or less risky to rewrite the code than it is to change it.
A challenge with maintainability is that many software engineering courses do not emphasize it, and give out one-and-done assignments that have clear and unchanging specifications. Software engineering courses do not cover systems as complex as occur in the real world. Development engineers who know that they will not be responsible for maintaining the software do not have an incentive to build in maintainability.
Workforce
Maintenance is often considered an unrewarding job forsoftware engineer
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software applications. It involves applying engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop ...
s, who, if assigned to maintenance, were more likely to quit. It often pays less than a comparable job in software development. The task is often assigned to temporary workers or lesser-skilled staff, although maintenance engineers are also typically older than developers, partly because they must be familiar with outdated technologies. In 2008, around 900,000 of the 1.3 million software engineers and programmers working in the United States were doing maintenance.
Companies started separate teams for maintenance, which led to outsourcing
Outsourcing is a business practice in which companies use external providers to carry out business processes that would otherwise be handled internally. Outsourcing sometimes involves transferring employees and assets from one firm to another ...
this work to a different company, and by the turn of the twenty-first century, sometimes offshoring
Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another—typically an operational process, such as manufacturing, or supporting processes, such as accounting. Usually this refers to a company business, although state gover ...
the work to another country—whether as part of the original company or a separate entity. The typical sources of outsourcing are developed countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Australia, while destinations are usually lower-cost countries such as China, India, Russia, and Ireland. Reasons for offshoring include taking advantage of lower labor costs, enabling around-the-clock support, reducing time pressure on developers, and to move support closer to the market for the product. Downsides of offshoring include communication barriers in the form of such factors as time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
and organizational disjunction and cultural differences. Despite many employers considering maintenance lower-skilled work and the phase of software development most suited to offshoring, it requires close communication with the customer and rapid response, both of which are hampered by these communication difficulties.
Alternatives to maintenance
In software engineering, the termlegacy system
Legacy or Legacies may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Comics
* " Batman: Legacy", a 1996 Batman storyline
* '' DC Universe: Legacies'', a comic book series from DC Comics
* ''Legacy'', a 1999 quarterly series from Antarctic Press
* ''Legacy ...
does not have a fixed meaning, but often refers to older systems which are large, difficult to modify, and also necessary for current business needs. Often legacy systems are written in obsolete programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s, lack documentation, have a deteriorating structure after years of changes, and depend on experts to keep it operational. When dealing with these systems, at some point so much technical debt accumulates that maintenance is not practical or economical. Other choices include:
*Freezing—do no more work on the legacy system. This option may be chosen if the vendor wants to continue to extract revenue as long as possible while avoiding maintenance costs.
*Outsourcing
Outsourcing is a business practice in which companies use external providers to carry out business processes that would otherwise be handled internally. Outsourcing sometimes involves transferring employees and assets from one firm to another ...
functionality of the legacy system to a different company, especially if it is not considered a core business function.
*Discarding the existing legacy system and redeveloping a new application from scratch to fulfill the same purpose as the legacy system. However, this approach is inefficient due to discarding a working system, and with this approach there is a danger that the new system will not fulfill changing business requirements.
*Wrapping the legacy application in an abstraction layer
In computing, an abstraction layer or abstraction level is a way of hiding the working details of a subsystem. Examples of software models that use layers of abstraction include the OSI model for network protocols, OpenGL, and other graphics libra ...
to simplify outdated interfaces. The source code is not modified but the new interface allows a tried and tested component to be accessed by newer applications. This approach does not fix any of the issues with maintaining a legacy system. Databases, functions, and entire applications may be wrapped in this way.
*Migrating the legacy system to a new platform, which can reduce the expense of new software development by reusing the implementation, design, specification, and requirements of the legacy system. Migration can take 5 to 10 years, but results in greater flexibility and long-term savings in software maintenance. As much as 80 percent of the expense is in testing; that is, ensuring that the new system has the same output as the old system. After the new system is finished, there needs to be a transition from the old system to the new system with minimum disruption to business functions.
Research
Despite taking up the lion's share of software development resources, maintenance is the least studied phase of software development. Much of the literature has focused on how to develop maintainable code from the outset, with less focus on motivating engineers to make maintainability a priority. , automated solutions for code refactoring to reduce maintenance effort are an active area of research, as is machine-learning enhanced maintainability assessment.References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * {{ISO standards IEEE standards ISO/IEC standards