|
Halstead Complexity Measures
Halstead complexity measures are software metrics introduced by Maurice Howard Halstead in 1977 as part of his treatise on establishing an empirical science of software development. Halstead made the observation that metrics of the software should reflect the implementation or expression of algorithms in different languages, but be independent of their execution on a specific platform. These metrics are therefore computed statically from the code. Halstead's goal was to identify measurable properties of software, and the relations between them. This is similar to the identification of measurable properties of matter (like the volume, mass, and pressure of a gas) and the relationships between them (analogous to the gas equation). Thus his metrics are actually not just complexity metrics. Calculation For a given problem, let: * \,\eta_1 = the number of distinct operators * \,\eta_2 = the number of distinct operands * \,N_1 = the total number of operators * \,N_2 = the total numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Metric
In software engineering and development, a software metric is a standard of measure of a degree to which a software system or process possesses some property. Even if a metric is not a measurement (metrics are functions, while measurements are the numbers obtained by the application of metrics), often the two terms are used as synonyms. Since quantitative measurements are essential in all sciences, there is a continuous effort by computer science practitioners and theoreticians to bring similar approaches to software development. The goal is obtaining objective, reproducible and quantifiable measurements, which may have numerous valuable applications in schedule and budget planning, cost estimation, quality assurance, testing, software debugging, software performance optimization, and optimal personnel task assignments. Common software measurements Common software measurements include: * ABC Software Metric * Balanced scorecard * Bugs per line of code * Code coverage * Coh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maurice Halstead
Maurice may refer to: *Maurice (name), a given name and surname, including a list of people with the name Places * or Mauritius, an island country in the Indian Ocean *Maurice, Iowa, a city *Maurice, Louisiana, a village *Maurice River, a tributary of the Delaware River in New Jersey Other uses *Maurice (2015 film), ''Maurice'' (2015 film), a Canadian short drama film *Maurice (horse), a Thoroughbred racehorse *Maurice (novel), ''Maurice'' (novel), a 1913 novel by E. M. Forster, published in 1971 **Maurice (1987 film), ''Maurice'' (1987 film), a British film based on the novel *Maurice (Shelley), ''Maurice'' (Shelley), a children's story by Mary Shelley *Maurice, a List of Madagascar (franchise) characters#Maurice, character from the Madagascar ''franchise'' *Maurices, an American retail clothing chain *Maurice or Maryse, a type of cooking spatula See also *Church of Saint Maurice (other) * *Maurice Debate, a 1918 debate in the British House of Commons *Maurice L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
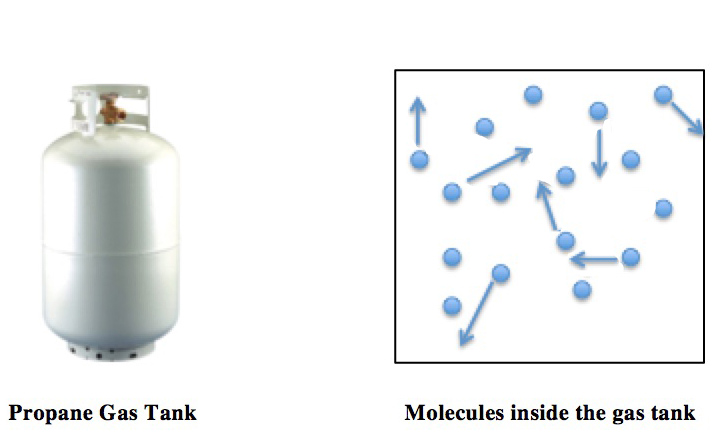
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Code Review
Code review (sometimes referred to as peer review) is a software quality assurance activity in which one or more people examine the source code of a computer program, either after implementation or during the development process. The persons performing the checking, excluding the author, are called "reviewers". At least one reviewer must not be the code's author. Code review differs from related software quality assurance techniques like static code analysis, self-checks, testing, and pair programming. Static analysis relies primarily on automated tools, self-checks involve only the author, testing requires code execution, and pair programming is performed continuously during development rather than as a separate step. Goal Although direct discovery of quality problems is often the main goal, code reviews are usually performed to reach a combination of goals: * ''Improving code quality'' Improve internal code quality and maintainability through better readability, uniformit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Function Point
The function point is a "unit of measurement" to express the amount of business functionality an information system (as a product) provides to a user. Function points are used to compute a functional size measurement (FSM) of software. The cost (in dollars or hours) of a single unit is calculated from past projects. Standards There are several recognized standards and/or public specifications for sizing software based on Function Point. 1. ISO Standards * FiSMA: ISO/IEC 29881:2010 Information technology – Systems and software engineering – FiSMA 1.1 functional size measurement method. * IFPUG: ISO/IEC 20926:2009 Software and systems engineering – Software measurement – IFPUG functional size measurement method. * Mark-II: ISO/IEC 20968:2002 Software engineering – Ml II Function Point Analysis – Counting Practices Manual * Nesma: ISO/IEC 24570:2018 Software engineering – Nesma functional size measurement method version 2.3 – Definitions and counting guidelines for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyclomatic Complexity
Cyclomatic complexity is a software metric used to indicate the complexity of a program. It is a quantitative measure of the number of linearly independent paths through a program's source code. It was developed by Thomas J. McCabe, Sr. in 1976. Cyclomatic complexity is computed using the control-flow graph of the program. The nodes of the graph correspond to indivisible groups of commands of a program, and a directed edge connects two nodes if the second command might be executed immediately after the first command. Cyclomatic complexity may also be applied to individual functions, modules, methods, or classes within a program. One testing strategy, called basis path testing by McCabe who first proposed it, is to test each linearly independent path through the program. In this case, the number of test cases will equal the cyclomatic complexity of the program. Description Definition There are multiple ways to define cyclomatic complexity of a section of source code. One com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |