Christendom Press on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which
Merriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"
/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwined with. Following the spread of Christianity from the
 Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
 "Christendom" has referred to the
"Christendom" has referred to the
''Europese democratieën: vrijheid, gelijkheid, solidariteit en soevereiniteit in praktijk''
/ref> or arguably, including the
 The European Miracle, the
The European Miracle, the

 An
An
 Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from
Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from


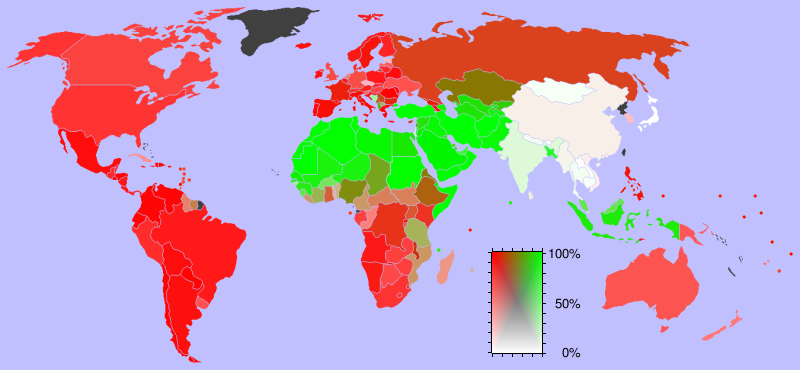 In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%, Latin America with 92%, North America with 81%, and Oceania with 79%. There are also large Christian communities in other parts of the world, such as China, India and Central Asia, where Christianity is the second-largest religion after Islam. The United States is home to the world's largest Christian population, followed by Brazil and Mexico.
Many Christians not only live under, but also have an official status in, a state religion of the following nations: Argentina (Roman Catholic Church), Armenia (Armenian Apostolic Church), Costa Rica (Roman Catholic Church), Denmark (Church of Denmark), El Salvador (Roman Catholic Church), England (Church of England), Georgia (country), Georgia (Georgian Orthodox Church), Greece (Church of Greece), Iceland (Church of Iceland), Liechtenstein (Roman Catholic Church), Malta (Roman Catholic Church), Monaco (Roman Catholic Church), Romania (Romanian Orthodox Church), Norway (Church of Norway), Vatican City (Roman Catholic Church), Switzerland (Roman Catholic Church, Swiss Reformed Church and Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland).
In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%, Latin America with 92%, North America with 81%, and Oceania with 79%. There are also large Christian communities in other parts of the world, such as China, India and Central Asia, where Christianity is the second-largest religion after Islam. The United States is home to the world's largest Christian population, followed by Brazil and Mexico.
Many Christians not only live under, but also have an official status in, a state religion of the following nations: Argentina (Roman Catholic Church), Armenia (Armenian Apostolic Church), Costa Rica (Roman Catholic Church), Denmark (Church of Denmark), El Salvador (Roman Catholic Church), England (Church of England), Georgia (country), Georgia (Georgian Orthodox Church), Greece (Church of Greece), Iceland (Church of Iceland), Liechtenstein (Roman Catholic Church), Malta (Roman Catholic Church), Monaco (Roman Catholic Church), Romania (Romanian Orthodox Church), Norway (Church of Norway), Vatican City (Roman Catholic Church), Switzerland (Roman Catholic Church, Swiss Reformed Church and Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland).
Encyclopedia of Biblical Spiritualism; Or, A Concordance to the Principal Passages of the Old and New Testament Scriptures Which Prove or Imply Spiritualism; Together with a Brief History of the Origin of Many of the Important Books of the Bible
Chicago: M. Hull, 1895. (ed.
reprint version
is available) * Bosanquet, Bernard
The Civilization of Christendom, And Other Studies
London: S. Sonnenschein, 1893. * * * * * * * * * * *
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"
/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwined with. Following the spread of Christianity from the
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
to Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
during the early Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, Christendom has been divided in the pre-existing Greek East and Latin West. Consequently, internal sects within Christian religion arose with their own beliefs and practices, centred around the cities of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
(Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity ( Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic ...
, whose community was called Western or Latin Christendom) and Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
(Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
, whose community was called Eastern Christendom). From the 11th to 13th centuries, Latin Christendom
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
rose to the central role of the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. The history of the Christian world spans about 1,700 years and includes a variety of socio-political developments, as well as advances in the arts, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, and technology.
The term usually refers to the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and to the Early Modern period during which the Christian world represented a geopolitical power that was juxtaposed with both the pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
and especially the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
.
Terminology
TheAnglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
term ''crīstendōm'' appears to have been invented in the 9th century by a scribe somewhere in southern England, possibly at the court of king Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
of Wessex. The scribe was translating Paulus Orosius' book ''History Against the Pagans'' (c. 416) and in need for a term to express the concept of the universal culture focused on Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
. It had the sense now taken by ''Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
'' (as is still the case with the cognate Dutch ''christendom'', where it denotes mostly the religion itself, just like the German ''Christentum''.
The current sense of the word of "lands where Christianity is the dominant religion" emerged in Late Middle English (by c. 1400).
Canadian theology professor Douglas John Hall
Douglas John Hall (born 1928) is an emeritus professor of theology at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, and a minister of the United Church of Canada. Prior to joining the McGill Faculty of Religious Studies in 1975 he was MacDougald Professo ...
stated (1997) that "Christendom" ..means literally the dominion or sovereignty of the Christian religion." Thomas John Curry, Roman Catholic auxiliary bishop of Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, defined (2001) Christendom as "the system dating from the fourth century by which governments upheld and promoted Christianity." Curry states that the end of Christendom came about because modern governments refused to "uphold the teachings, customs, ethos, and practice of Christianity." British church historian Diarmaid MacCulloch
Diarmaid Ninian John MacCulloch (; born 31 October 1951) is an English academic and historian, specialising in ecclesiastical history and the history of Christianity. Since 1995, he has been a fellow of St Cross College, Oxford; he was former ...
described (2010) Christendom as "the union between Christianity and secular power."
There is a common and nonliteral sense of the word that is much like the terms ''Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
'', '' known world'' or '' Free World''. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christianity and Christendom"; many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity
Pan-European identity is the sense of personal identification with Europe, in a cultural or political sense. The concept is discussed in the context of European integration, historically in connection with hypothetical proposals, but since th ...
.
History
Rise of Christendom
 Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
sect, which historians refer to as Jewish Christianity. It may be divided into two distinct phases: the apostolic period, when the first apostles were alive and organizing the Church, and the post-apostolic period
Christianity in the ante-Nicene period was the time in Christian history up to the First Council of Nicaea. This article covers the period following the Apostolic Age of the first century, c. 100 AD, to Nicaea in 325 AD.
The second and third c ...
, when an early episcopal structure developed, whereby bishoprics were governed by bishops
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
(overseers).
The post-apostolic period concerns the time roughly after the death of the apostles when bishops emerged as overseers of urban Christian populations. The earliest recorded use of the terms ''Christianity'' (Greek ) and ''catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
'' (Greek ), dates to this period, the 2nd century
The 2nd century is the period from 101 ( CI) through 200 ( CC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.
Early in the century, the Roman Empire attained its greatest ex ...
, attributed to Ignatius of Antioch
Ignatius of Antioch (; Greek: Ἰγνάτιος Ἀντιοχείας, ''Ignátios Antiokheías''; died c. 108/140 AD), also known as Ignatius Theophorus (, ''Ignátios ho Theophóros'', lit. "the God-bearing"), was an early Christian writer ...
''c.'' 107. Early Christendom would close at the end of imperial persecution of Christians after the ascension of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
and the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan ( la, Edictum Mediolanense; el, Διάταγμα τῶν Μεδιολάνων, ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 AD agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. ( ...
in AD 313 and the First Council of Nicaea in 325.
According to Malcolm Muggeridge (1980), Christ founded Christianity, but Constantine founded Christendom. Canadian theology professor Douglas John Hall
Douglas John Hall (born 1928) is an emeritus professor of theology at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, and a minister of the United Church of Canada. Prior to joining the McGill Faculty of Religious Studies in 1975 he was MacDougald Professo ...
dates the 'inauguration of Christendom' to the 4th century, with Constantine playing the primary role (so much so that he equates Christendom with "Constantinianism") and Theodosius I ( Edict of Thessalonica, 380) and Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
secondary roles.Hall (2002), p. 1–9.
Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
and renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
notion of the ''Christian world'' as a polity
A polity is an identifiable Politics, political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relation, social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize ...
. In essence, the earliest vision of Christendom was a vision of a Christian theocracy
Theocracy is a form of government in which one or more deity, deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries who manage the government's daily affairs.
Etymology
The word theocracy origina ...
, a government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
founded upon and upholding Christian values, whose institutions are spread through and over with Christian doctrine. In this period, members of the Christian clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
wield political authority
In political philosophy and ethics, political authority describes any of the moral principles legitimizing differences between individuals' rights and duties by virtue of their relationship with the state. Political authority grants members of ...
. The specific relationship between the political leader
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking, a ...
s and the clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
varied but, in theory, the national and political divisions were at times subsumed under the leadership of the church as an institution. This model of church-state relations was accepted by various Church leaders and political leaders in European history.
The Church gradually became a defining institution of the Roman Empire. Emperor Constantine
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea ...
issued the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan ( la, Edictum Mediolanense; el, Διάταγμα τῶν Μεδιολάνων, ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 AD agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. ( ...
in 313 proclaiming toleration for the Christian religion, and convoke
A convocation (from the Latin '' convocare'' meaning "to call/come together", a translation of the Greek ἐκκλησία ''ekklēsia'') is a group of people formally assembled for a special purpose, mostly ecclesiastical or academic.
In ac ...
d the First Council of Nicaea in 325 whose Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
included belief in "one holy catholic and apostolic Church". Emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
made Nicene
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
Christianity the state church of the Roman Empire
Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire when Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, which recognized the catholic orthodoxy of Nicene Christians in the Great Church as the Roman Empire's state religion. ...
with the Edict of Thessalonica of 380. In terms of prosperity and cultural life, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
was one of the peaks in Christian history and Christian civilization,. and Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
remained the leading city of the Christian world in size, wealth, and culture. There was a renewed interest in classical Greek philosophy, as well as an increase in literary output in vernacular Greek..
As the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
disintegrated into feudal kingdoms and principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
, the concept of Christendom changed as the western church became one of five patriarchates of the Pentarchy and the Christians of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
developed. The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
was the last bastion of Christendom. Christendom would take a turn with the rise of the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, a Germanic tribe who converted to the Christian faith and entered into communion with Rome
Full communion is a communion or relationship of full agreement among different Christian denominations that share certain essential principles of Christian theology. Views vary among denominations on exactly what constitutes full communion, bu ...
.
On Christmas Day 800 AD, Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlemagne's position b ...
crowned Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
, resulting in the creation of another Christian king beside the Christian emperor in the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
state. The Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
created a definition of ''Christendom'' in juxtaposition with the Byzantine Empire, that of a distributed versus centralized culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
respectively.
The classical heritage flourished throughout the Middle Ages in both the Byzantine Greek East and the Latin West. In the Greek philosopher Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
's ideal state there are three major classes, which was representative of the idea of the “tripartite soul”, which is expressive of three functions or capacities of the human soul: “reason”, “the spirited element”, and “appetites” (or “passions”). Will Durant made a convincing case that certain prominent features of Plato's ideal community where discernible in the organization, dogma and effectiveness of "the" Medieval Church in Europe:
... For a thousand years Europe was ruled by an order of guardians considerably like that which was visioned by our philosopher. During the Middle Ages it was customary to classify the population of Christendom into ''laboratores'' (workers), ''bellatores'' (soldiers), and ''oratores'' (clergy). The last group, though small in number, monopolized the instruments and opportunities of culture, and ruled with almost unlimited sway half of the most powerful continent on the globe. The clergy, like Plato's guardians, were placed in authority... by their talent as shown in ecclesiastical studies and administration, by their disposition to a life of meditation and simplicity, and ... by the influence of their relatives with the powers of state and church. In the latter half of the period in which they ruled 00 AD onwards the clergy were as free from family cares as even Plato could desireor such guardians Or or OR may refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television * "O.R.", a 1974 episode of M*A*S*H * Or (My Treasure), a 2004 movie from Israel (''Or'' means "light" in Hebrew) Music * ''Or'' (album), a 2002 album by Golden Boy with Miss ..... lericalCelibacy was part of the psychological structure of the power of the clergy; for on the one hand they were unimpeded by the narrowing egoism of the family, and on the other their apparent superiority to the call of the flesh added to the awe in which lay sinners held them....'' ''In the latter half of the period in which they ruled, the clergy were as free from family cares as even Plato could desire.
Later Middle Ages and Renaissance
After thecollapse of Charlemagne's empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
, the southern remnants of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
became a collection of states loosely connected to the Holy See of Rome
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rom ...
. Tensions between Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 J ...
and secular rulers ran high, as the pontiff
A pontiff (from Latin ''pontifex'') was, in Roman antiquity, a member of the most illustrious of the colleges of priests of the Roman religion, the College of Pontiffs."Pontifex". "Oxford English Dictionary", March 2007 The term "pontiff" was late ...
exerted control over their temporal counterparts in the west and vice versa. The pontificate
The pontificate is the form of government used in Vatican City. The word came to English from French and simply means ''papacy'', or "to perform the functions of the Pope or other high official in the Church". Since there is only one bishop of Ro ...
of Innocent III is considered the height of temporal power of the papacy. The ''Corpus Christianum
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwine ...
'' described the then-current notion of the community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, tow ...
of all Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
united under the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The community was to be guided by Christian values in its politics, economics and social life. Its legal basis was the '' corpus iuris canonica'' (body of canon law).
In the East, Christendom became more defined as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
's gradual loss of territory to an expanding Islam and the Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
Th ...
. This caused Christianity to become important to the Byzantine identity. Before the East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a ...
which divided the Church religiously, there had been the notion of a ''universal Christendom'' that included the East and the West. After the East–West Schism, hopes of regaining religious unity with the West were ended by the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, when Crusaders conquered the Byzantine capital of Constantinople and hastened the decline of the Byzantine Empire on the path to its destruction. With the breakup of the Byzantine Empire into individual nations with nationalist Orthodox Churches, the term Christendom described Western Europe, Catholicism, Orthodox Byzantines, and other Eastern rites of the Church.
The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
's peak of authority over all European Christians and their common endeavours of the Christian community — for example, the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, the fight against the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
and against the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
— helped to develop a sense of communal identity against the obstacle of Europe's deep political divisions. The popes, formally just the bishops of Rome, claimed to be the focus of all Christendom, which was largely recognised in Western Christendom from the 11th century until the Reformation, but not in Eastern Christendom. Moreover, this authority was also sometimes abused, and fostered the Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
and anti-Jewish pogroms
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
, to root out divergent elements and create a religiously uniform community. Ultimately, the Inquisition was done away with by order of Pope Innocent III.
Christendom ultimately was led into specific crisis in the late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
, when the kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
of France managed to establish a French national church during the 14th century and the papacy became ever more aligned with the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. Known as the Western Schism, western Christendom was a split between three men, who were driven by politics rather than any real theological disagreement for simultaneously claiming to be the true pope. The Avignon Papacy developed a reputation for corruption that estranged major parts of Western Christendom. The Avignon schism was ended by the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the res ...
.
Before the modern period, Christendom was in a general crisis at the time of the Renaissance Popes
The Renaissance Papacy was a period of papal history between the Western Schism and the Reformation. From the election of Pope Martin V of the Council of Constance in 1417 to the Reformation in the 16th century, Western Christianity was largely f ...
because of the moral laxity of these pontiffs and their willingness to seek and rely on temporal power as secular rulers did. Many in the Catholic Church's hierarchy in the Renaissance became increasingly entangled with insatiable greed for material wealth and temporal power, which led to many reform movements, some merely wanting a moral reformation of the Church's clergy, while others repudiated the Church and separated from it in order to form new sects. The Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
produced ideas or institutions by which men living in society could be held together in harmony. In the early 16th century, Baldassare Castiglione ('' The Book of the Courtier'') laid out his vision of the ideal gentleman and lady, while Machiavelli cast a jaundiced eye on "la verità effetuale delle cose" — the actual truth of things — in ''The Prince
''The Prince'' ( it, Il Principe ; la, De Principatibus) is a 16th-century political treatise written by Italian diplomat and political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli as an instruction guide for new princes and royals. The general theme of ''The ...
'', composed, humanist style, chiefly of parallel ancient and modern examples of Virtù
Virtù is a concept theorized by Niccolò Machiavelli, centered on the martial spirit and ability of a population or leader, but also encompassing a broader collection of traits necessary for maintenance of the State (polity), state and "the achi ...
. Some Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
or renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
( cf. Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' wa ...
). The Catholic Church fell partly into general neglect under the Renaissance Popes, whose inability to govern the Church by showing personal example of high moral standards set the climate for what would ultimately become the Protestant Reformation. During the Renaissance, the papacy was mainly run by the wealthy families and also had strong secular interests. To safeguard Rome and the connected Papal States the popes became necessarily involved in temporal matters, even leading armies, as the great patron of arts Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or th ...
did. It during these intermediate times popes strove to make Rome the capital of Christendom while projecting it, through art, architecture, and literature, as the center of a Golden Age of unity, order, and peace.
Professor Frederick J. McGinness described Rome as essential in understanding the legacy the Church and its representatives encapsulated best by The Eternal City: No other city in Europe matches Rome in its traditions, history, legacies, and influence in the Western world. Rome in the Renaissance under the papacy not only acted as guardian and transmitter of these elements stemming from the Roman Empire but also assumed the role as artificer and interpreter of its myths and meanings for the peoples of Europe from the Middle Ages to modern times... Under the patronage of the popes, whose wealth and income were exceeded only by their ambitions, the city became a cultural center for master architects, sculptors, musicians, painters, and artisans of every kind...In its myth and message, Rome had become the sacred city of the popes, the prime symbol of a triumphant Catholicism, the center of orthodox Christianity, a new Jerusalem.It is clearly noticeable that the popes of the Italian Renaissance have been subjected by many writers with an overly harsh tone. Pope Julius II, for example, was not only an effective secular leader in military affairs, a deviously effective politician but foremost one of the greatest patron of the Renaissance period and person who also encouraged open criticism from noted humanists. The blossoming of renaissance humanism was made very much possible due to the universality of the institutions of Catholic Church and represented by personalities such as
Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II ( la, Pius PP. II, it, Pio II), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini ( la, Aeneas Silvius Bartholomeus, links=no; 18 October 1405 – 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 August ...
, Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic Church, Catholic cano ...
, Leon Battista Alberti, Desiderius Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' wa ...
, sir Thomas More, Bartolomé de Las Casas, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
and Teresa of Ávila. George Santayana in his work ''The Life of Reason
''The Life of Reason: The Phases of Human Progress'' is a book published in five volumes from 1905 to 1906, by Spanish-born American philosopher George Santayana. It consists of ''Reason in Common Sense'', ''Reason in Society'', ''Reason in Religi ...
'' postulated the tenets of the all encompassing order the Church had brought and as the repository of the legacy of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
:
The enterprise of individuals or of small aristocratic bodies has meantime sown the world which we call civilised with some seeds and nuclei of order. There are scattered about a variety of churches, industries, academies, and governments. But the universal order once dreamt of and nominally almost established, the empire of universal peace, all-permeating rational art, and philosophical worship, is mentioned no more. An unformulated conception, the prerational ethics of private privilege and national unity, fills the background of men's minds. It represents feudal traditions rather than the tendency really involved in contemporary industry, science, or philanthropy. Those dark ages, from which our political practice is derived, had a political theory which we should do well to study; for their theory about a universal empire and a Catholic church was in turn the echo of a former age of reason, when a few men conscious of ruling the world had for a moment sought to survey it as a whole and to rule it justly.
Reformation and Early Modern era
Developments inwestern philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ' ...
and European events brought change to the notion of the ''Corpus Christianum''. The Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
accelerated the process of transforming France from a feudal monarchy to a centralized state. The rise of strong, centralized monarchies denoted the European transition from feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
to capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
. By the end of the Hundred Years' War, both France and England were able to raise enough money through taxation to create independent standing armies. In the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
, Henry Tudor took the crown of England. His heir, the absolute Absolute may refer to:
Companies
* Absolute Entertainment, a video game publisher
* Absolute Radio, (formerly Virgin Radio), independent national radio station in the UK
* Absolute Software Corporation, specializes in security and data risk manage ...
king Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
establishing the English church
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
.
In modern history
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
, the Reformation and rise of modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular socio-cultural norm (social), norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the Renaissancein the " ...
in the early 16th century entailed a change in the ''Corpus Christianum''. In the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, the Peace of Augsburg of 1555 officially ended the idea among secular leaders that all Christians must be united under one church. The principle of ''cuius regio, eius religio
() is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective (if not individual ...
'' ("whose the region is, his religion") established the religious, political and geographic divisions of Christianity, and this was established with the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peac ...
in 1648, which legally ended the concept of a single Christian hegemony in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire, despite the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
's doctrine that it alone is the one true Church founded by Christ.
Subsequently, each government determined the religion of their own state. Christians living in states where their denomination was ''not'' the established one were guaranteed the right to practice their faith in public during allotted hours and in private at their will. At times there were mass expulsions of dissenting faiths as happened with the Salzburg Protestants. Some people passed as adhering to the official church, but instead lived as Nicodemite
A Nicodemite () is a person suspected of publicly misrepresenting their religious faith to conceal their true beliefs. The term is sometimes defined as referring to a Protestant Christian who lived in a Roman Catholic country and escaped persecuti ...
s or crypto-protestants.
The European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Chu ...
are usually taken to have ended with the Treaty of Westphalia (1648),''Europese democratieën: vrijheid, gelijkheid, solidariteit en soevereiniteit in praktijk''
/ref> or arguably, including the
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
and the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
in this period, with the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713. In the 18th century, the focus shifts away from religious conflicts, either between Christian factions or against the external threat of Islamic factions.
End of Christendom
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
and the formation of the great colonial empire
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early mode ...
s together with the beginning decline of the Ottoman Empire
In the late eighteenth century, the Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Old Regime) faced numerous enemies. In response to these threats, the empire initiated a period of internal reform which came to be known as the Tanzimat, which succeeded in significan ...
mark the end of the geopolitical "history of Christendom". Instead, the focus of Western history shifts to the development of the nation-state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
, accompanied by increasing atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
and secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on Secularity, secular, Naturalism (philosophy), naturalistic considerations.
Secularism is most commonly defined as the Separation of church and state, separation of relig ...
, culminating with the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
and the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
at the turn of the 19th century.
Writing in 1997, Canadian theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
professor Douglas John Hall
Douglas John Hall (born 1928) is an emeritus professor of theology at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, and a minister of the United Church of Canada. Prior to joining the McGill Faculty of Religious Studies in 1975 he was MacDougald Professo ...
argued that Christendom had either fallen already or was in its death throes; although its end was gradual and not as clear to pin down as its 4th-century establishment, the "transition to the post-Constantinian, or post-Christendom, situation (...) has already been in process for a century or two," beginning with the 18th-century rationalist Enlightenment and the French Revolution (the first attempt to topple the Christian establishment). American Catholic bishop Thomas John Curry stated (2001) that the end of Christendom came about because modern governments refused to "uphold the teachings, customs, ethos, and practice of Christianity." He argued the First Amendment to the United States Constitution
The First Amendment (Amendment I) to the United States Constitution prevents the government from making laws that regulate an establishment of religion, or that prohibit the free exercise of religion, or abridge the freedom of speech, the ...
(1791) and the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st Catholic ecumenical councils, ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions) ...
's Declaration on Religious Freedom (1965) are two of the most important documents setting the stage for its end. According to British historian Diarmaid MacCulloch (2010), Christendom was 'killed' by the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–18), which led to the fall of the three main Christian empires ( Russian, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
and Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
) of Europe, as well as the Ottoman Empire, rupturing the Eastern Christian communities that had existed on its territory. The Christian empires were replaced by secular, even anti-clerical republics seeking to definitively keep the churches out of politics. The only surviving monarchy with an established church, Britain, was severely damaged by the war, lost most of Ireland due to Catholic–Protestant infighting, and was starting to lose grip on its colonies.MacCulloch (2010), p. 1024–1030.
Changes in worldwide Christianity over the last century have been significant, since 1900, Christianity has spread rapidly in the Global South
The concept of Global North and Global South (or North–South divide in a global context) is used to describe a grouping of countries along socio-economic and political characteristics. The Global South is a term often used to identify region ...
and Third World countries. The late 20th century has shown the shift of Christian adherence to the Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
and the Southern Hemisphere in general, by 2010 about 157 countries and territories in the world had Christian majorities.
Classical culture
Western culture
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
, throughout most of its history, has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture, and many of the population of the Western hemisphere could broadly be described as cultural Christians. The notion of "Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
" and the "Western World
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christianity and Christendom"; many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity
Pan-European identity is the sense of personal identification with Europe, in a cultural or political sense. The concept is discussed in the context of European integration, historically in connection with hypothetical proposals, but since th ...
. Historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the stu ...
Paul Legutko of Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
said the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
is "at the center of the development of the values, ideas, science, laws, and institutions which constitute what we call Western civilization."
Though Western culture contained several polytheistic religions during its early years under the Greek and Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
s, as the centralized Roman power waned, the dominance of the Catholic Church was the only consistent force in Western Europe. Until the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, Christian culture guided the course of philosophy, literature, art, music and science. Christian disciplines of the respective arts have subsequently developed into Christian philosophy
Christian philosophy includes all philosophy carried out by Christians, or in relation to the religion of Christianity.
Christian philosophy emerged with the aim of reconciling science and faith, starting from natural rational explanations wit ...
, Christian art, Christian music, Christian literature etc. Art and literature, law, education, and politics were preserved in the teachings of the Church, in an environment that, otherwise, would have probably seen their loss. The Church founded many cathedrals
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
, universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
, monasteries and seminaries, some of which continue to exist today. Medieval Christianity
Christianity in the Middle Ages covers the history of Christianity from the fall of the Western Roman Empire (). The end of the period is variously defined. Depending on the context, events such as the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman ...
created the first modern universities. The Catholic Church established a hospital system in Medieval Europe that vastly improved upon the Roman ''valetudinaria''. These hospitals were established to cater to "particular social groups marginalized by poverty, sickness, and age," according to historian of hospitals, Guenter Risse. Christianity also had a strong impact on all other aspects of life: marriage and family, education, the humanities and sciences, the political and social order, the economy, and the arts.
Christianity had a significant impact on education and science and medicine as the church created the bases of the Western system of education, and was the sponsor of founding universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
in the Western world as the university is generally regarded as an institution that has its origin in the Medieval Christian
Christianity in the Middle Ages covers the history of Christianity from the fall of the Western Roman Empire (). The end of the period is variously defined. Depending on the context, events such as the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman ...
setting.Rüegg, Walter: "Foreword. The University as a European Institution", in: ''A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages'', Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. XIX–XX Many clerics
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
throughout history have made significant contributions to science and Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
in particular have made numerous significant contributions to the development of science. The cultural influence of Christianity includes social welfare, founding hospitals
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
, economics (as the Protestant work ethic
The Protestant work ethic, also known as the Calvinist work ethic or the Puritan work ethic, is a work ethic concept in theology, sociology, economics and history which emphasizes that diligence, discipline, and frugality are a result of a person ...
), natural law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacte ...
(which would later influence the creation of international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
), politics, architecture,Sir Banister Fletcher, ''History of Architecture on the Comparative Method''. literature, personal hygiene, and family life. Christianity played a role in ending practices common among pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
societies, such as human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein ...
, slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose is the prevention of reso ...
and polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married ...
.
Art and literature
Writings and poetry
Christian literature is writing that deals with Christian themes and incorporates the Christian world view. This constitutes a huge body of extremely varied writing. Christian poetry is anypoetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
that contains Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
teachings, theme
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
s, or references. The influence of Christianity on poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
has been great in any area that Christianity has taken hold. Christian poems often directly reference the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
, while others provide allegory
As a literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a hidden meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory th ...
.
Supplemental arts
Christian art is art produced in an attempt to illustrate, supplement and portray in tangible form the principles ofChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
. Virtually all Christian groupings use or have used art to some extent. The prominence of art and the media, style, and representations change; however, the unifying theme is ultimately the representation of the life and times of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
and in some cases the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
. Depictions of saints are also common, especially in Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
, Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, and Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first m ...
.
Illumination
 An
An illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
is a manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printing, printed or repr ...
in which the text is supplemented by the addition of decoration. The earliest surviving substantive illuminated manuscripts are from the period AD 400 to 600, primarily produced in Ireland, Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
and Italy. The majority of surviving manuscripts are from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, although many illuminated manuscripts survive from the 15th century Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, along with a very limited number from Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
.
Most illuminated manuscripts were created as codices
The codex (plural codices ) was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term ''codex'' is often used for ancient manuscript books, with ...
, which had superseded scrolls; some isolated single sheets survive. A very few illuminated manuscript fragments survive on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
. Most medieval manuscripts, illuminated or not, were written on parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves, and goats. It has been used as a writing medium for over two millennia. Vellum is a finer quality parchment made from the skins of ...
(most commonly of calf
Calf most often refers to:
* Calf (animal), the young of domestic cattle.
* Calf (leg), in humans (and other primates), the back portion of the lower leg
Calf or calves may also refer to:
Biology and animal byproducts
* Veal, meat from calves
* ...
, sheep, or goat skin), but most manuscripts important enough to illuminate were written on the best quality of parchment, called vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. Parchment is another term for this material, from which vellum is sometimes distinguished, when it is made from calfskin, as opposed to that made from other anima ...
, traditionally made of unsplit calfskin
Calfskin or calf leather is a leather or membrane produced from the hide of a calf, or juvenile domestic cattle. Calfskin is particularly valuable because of its softness and fine grain, as well as durability. It is commonly used for high-quality ...
, though high quality parchment from other skins was also called ''parchment''.
Iconography
 Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from
Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
imagery
Imagery is visual symbolism, or figurative language that evokes a mental image or other kinds of sense impressions, especially in a literary work, but also in other activities such as psychotherapy.
Forms
There are five major types of sensory ima ...
, classical Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
and Roman religion and popular art. Religious images
A religious image is a work of visual art that is representational and has a religious purpose, subject or connection. All major historical religions have made some use of religious images, although their use is strictly controlled and often cont ...
are used to some extent by the Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
Christian faith, and often contain highly complex iconography, which reflects centuries of accumulated tradition. In the Late Antique
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
period iconography began to be standardised, and to relate more closely to Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
texts, although many gaps in the canonical Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
narratives were plugged with matter from the apocryphal gospels
The New Testament apocrypha (singular apocryphon) are a number of writings by early Christians that give accounts of Jesus and his teachings, the nature of God, or the teachings of his apostles and of their lives. Some of these writings were cite ...
. Eventually the Church would succeed in weeding most of these out, but some remain, like the ox and ass in the Nativity of Christ.
An icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most ...
is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
. Christianity has used symbolism
Symbolism or symbolist may refer to:
Arts
* Symbolism (arts), a 19th-century movement rejecting Realism
** Symbolist movement in Romania, symbolist literature and visual arts in Romania during the late 19th and early 20th centuries
** Russian sy ...
from its very beginnings. In both East and West, numerous iconic types of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, names and titles), was ...
, Mary and saints and other subjects were developed; the number of named types of icons of Mary, with or without the infant Christ, was especially large in the East, whereas Christ Pantocrator was much the commonest image of Christ.
Christian symbolism
Christian symbolism is the use of symbols, including archetypes, acts, artwork or events, by Christianity. It invests objects or actions with an inner meaning expressing Christian ideas.
The symbolism of the early Church was characterized by bei ...
invests objects or actions with an inner meaning expressing Christian ideas. Christianity has borrowed from the common stock of significant symbols known to most periods and to all regions of the world. Religious symbolism
A religious symbol is an iconic representation intended to represent a specific religion, or a specific concept within a given religion.
Religious symbols have been used in the military in many countries, such as the United States military chapl ...
is effective when it appeals to both the intellect and the emotions. Especially important depictions of Mary include the Hodegetria
A Hodegetria , ; russian: Одиги́трия, Odigítria ; Romanian: Hodighitria, or Virgin Hodegetria, is an iconographic depiction of the Theotokos (Virgin Mary) holding the Child Jesus at her side while pointing to him as the source of s ...
and Panagia
Panagia ( el, Παναγία, fem. of , + , the ''All-Holy'', or the ''Most Holy''; pronounced ) (also transliterated Panaghia or Panajia), in Medieval and Modern Greek, is one of the titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, used especially in Eastern ...
types. Traditional models evolved for narrative paintings, including large cycles covering the events of the Life of Christ, the Life of the Virgin
The Life of the Virgin, showing narrative scenes from the life of Mary, the mother of Jesus, is a common subject for pictorial cycles in Christian art, often complementing, or forming part of, a cycle on the Life of Christ. In both cases the nu ...
, parts of the Old Testament, and, increasingly, the lives of popular saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
s. Especially in the West, a system of attributes developed for identifying individual figures of saints by a standard appearance and symbolic objects held by them; in the East they were more likely to identified by text labels.
Each saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
has a story and a reason why he or she led an exemplary life. Symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
have been used to tell these stories throughout the history of the Church. A number of Christian saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
s are traditionally represented by a symbol or iconic motif associated with their life, termed an attribute or emblem
An emblem is an abstract or representational pictorial image that represents a concept, like a moral truth, or an allegory, or a person, like a king or saint.
Emblems vs. symbols
Although the words ''emblem'' and '' symbol'' are often use ...
, in order to identify them. The study of these forms part of iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
in Art history
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today ...
.
Architecture

Christian architecture
Church architecture refers to the architecture of buildings of churches, convents, seminaries etc. It has evolved over the two thousand years of the Christian religion, partly by innovation and partly by borrowing other architectural styles as ...
encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Christianity to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Christian culture.
Buildings were at first adapted from those originally intended for other purposes but, with the rise of distinctively ecclesiastical architecture, church buildings came to influence secular ones which have often imitated religious architecture. In the 20th century, the use of new materials, such as concrete, as well as simpler styles has had its effect upon the design of churches and arguably the flow of influence has been reversed. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant period of transformation for Christian architecture
Church architecture refers to the architecture of buildings of churches, convents, seminaries etc. It has evolved over the two thousand years of the Christian religion, partly by innovation and partly by borrowing other architectural styles as ...
in the west was the Gothic cathedral. In the east, Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire.
The Byzantine era is usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great moved the Roman capital to Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until th ...
was a continuation of Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered on ...
.
Philosophy
Christian philosophy
Christian philosophy includes all philosophy carried out by Christians, or in relation to the religion of Christianity.
Christian philosophy emerged with the aim of reconciling science and faith, starting from natural rational explanations wit ...
is a term to describe the fusion of various fields of philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
with the theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
doctrines of Christianity. Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translate ...
, which means "that hichbelongs to the school", and was a method of learning taught by the academics (or ''school people'') of medieval universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
c. 1100–1500. Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translate ...
originally started to reconcile the philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
of the ancient classical philosophers with medieval Christian theology. Scholasticism is not a philosophy or theology in itself but a tool and method for learning which places emphasis on dialectical reasoning
Dialectic ( grc-gre, διαλεκτική, ''dialektikḗ''; related to dialogue; german: Dialektik), also known as the dialectical method, is a discourse between two or more people holding different Opinion, points of view about a subject but wi ...
.
Christian civilization

Medieval conditions
TheByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, which was the most sophisticated culture during antiquity, suffered under Muslim conquests limiting its scientific prowess during the Medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Christian Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
had suffered a catastrophic loss of knowledge following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. But thanks to the Church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chris ...
scholars such as Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wit ...
and Buridan
Jean Buridan (; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14th-century French philosopher.
Buridan was a teacher in the faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career who focused in particular on logic and the wo ...
, the West carried on at least the spirit of scientific inquiry which would later lead to Europe's taking the lead in science during the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
using Latin translations of the 12th century, translations of medieval works.
Medieval technology refers to the technology used in medieval Europe under Christian rule. After the Renaissance of the 12th century, medieval Europe saw a radical change in the rate of new inventions, innovations in the ways of managing traditional means of production, and economic growth. The period saw major technology, technological advances, including the adoption of gunpowder and the astrolabe, the invention of spectacles, and greatly improved water mills, building techniques, agriculture in general, clocks, and ships. The latter advances made possible the dawn of the Age of Exploration. The development of water mills was impressive, and extended from agriculture to sawmills both for timber and stone, probably derived from Roman technology. By the time of the Domesday Book, most large villages in Great Britain, Britain had mills. They also were widely used in mining, as described by Georg Agricola in De Re Metallica for raising ore from shafts, crushing ore, and even powering bellows.
Significant in this respect were advances within the fields of navigation. The compass and astrolabe along with advances in shipbuilding, enabled the navigation of the Ocean, World Oceans and thus domination of the worlds economic trade. Johann Gutenberg, Gutenberg’s printing press made possible a dissemination of knowledge to a wider population, that would not only lead to a gradually more egalitarian society, but one more able to dominate other cultures, drawing from a vast reserve of knowledge and experience.
Renaissance innovations
During theRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, great advances occurred in geography, astronomy, chemistry, physics, math, manufacturing, and engineering. The rediscovery of ancient scientific texts was accelerated after the Fall of Constantinople, and the invention of printing which would democratize learning and allow a faster propagation of new ideas. ''Renaissance technology'' is the set of artifacts and customs, spanning roughly the 14th through the 16th century. The era is marked by such profound technical advancements like the printing press, Perspective (graphical), linear perspectivity, patent law, Santa Maria del Fiore, double shell domes or Bastion fortresses. Draw-books of the Renaissance artist-engineers such as Taccola and Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
give a deep insight into the mechanical technology then known and applied.
History of science in the Renaissance, Renaissance science spawned the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
; science and technology began a cycle of mutual advancement. The ''Scientific Renaissance'' was the early phase of the Scientific Revolution. In the two-phase model of early modern science: a ''Scientific Renaissance'' of the 15th and 16th centuries, focused on the restoration of the natural knowledge of the ancients; and a ''Scientific Revolution'' of the 17th century, when scientists shifted from recovery to innovation. Some scholars and historians attributes Christianity to having contributed to the rise of the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
.
Demographics
Geographic spread
 In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%, Latin America with 92%, North America with 81%, and Oceania with 79%. There are also large Christian communities in other parts of the world, such as China, India and Central Asia, where Christianity is the second-largest religion after Islam. The United States is home to the world's largest Christian population, followed by Brazil and Mexico.
Many Christians not only live under, but also have an official status in, a state religion of the following nations: Argentina (Roman Catholic Church), Armenia (Armenian Apostolic Church), Costa Rica (Roman Catholic Church), Denmark (Church of Denmark), El Salvador (Roman Catholic Church), England (Church of England), Georgia (country), Georgia (Georgian Orthodox Church), Greece (Church of Greece), Iceland (Church of Iceland), Liechtenstein (Roman Catholic Church), Malta (Roman Catholic Church), Monaco (Roman Catholic Church), Romania (Romanian Orthodox Church), Norway (Church of Norway), Vatican City (Roman Catholic Church), Switzerland (Roman Catholic Church, Swiss Reformed Church and Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland).
In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%, Latin America with 92%, North America with 81%, and Oceania with 79%. There are also large Christian communities in other parts of the world, such as China, India and Central Asia, where Christianity is the second-largest religion after Islam. The United States is home to the world's largest Christian population, followed by Brazil and Mexico.
Many Christians not only live under, but also have an official status in, a state religion of the following nations: Argentina (Roman Catholic Church), Armenia (Armenian Apostolic Church), Costa Rica (Roman Catholic Church), Denmark (Church of Denmark), El Salvador (Roman Catholic Church), England (Church of England), Georgia (country), Georgia (Georgian Orthodox Church), Greece (Church of Greece), Iceland (Church of Iceland), Liechtenstein (Roman Catholic Church), Malta (Roman Catholic Church), Monaco (Roman Catholic Church), Romania (Romanian Orthodox Church), Norway (Church of Norway), Vatican City (Roman Catholic Church), Switzerland (Roman Catholic Church, Swiss Reformed Church and Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland).
Number of adherents
The estimated number ofChristians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
in the world ranges from 2.2 billion33.39% of ~7.2 billion world population (under the section 'People') to 2.4 billion people. The faith represents approximately one-third of the world's population and is the largest religion in the world, with the List of Christian denominations, three largest groups of Christians being the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Protestantism, and the Eastern Orthodox Church. The largest Christian denomination is the Catholic Church, with an estimated 1.2 billion adherents.
Notable Christian organizations
A religious order is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious practice. In contrast, the term Holy Orders is used by many Christian churches to refer to ordination or to a group of individuals who are set apart for a special role or ministry. Historically, the word "order" designated an established civil body or corporation with a hierarchy, and ordination meant legal incorporation into an ordo. The word "holy" refers to the Church. In context, therefore, a holy order is set apart for ministry in the Church. Religious orders are composed of initiates (laity) and, in some traditions, ordained clergies. Various organizations include: * In the Roman Catholic Church, religious institutes and secular institutes are the major forms of institute of consecrated life, institutes of consecrated life, similar to which are society of apostolic life, societies of apostolic life. They are organizations of laity or clergy who live a common life under the guidance of a fixed rule and the leadership of a superior. (ed., see : Catholic orders and societies for a particular listing.) * Anglican religious orders are communities of laity or clergy in the Anglican churches who live under a common rule of life. (ed., see : Anglican organizations for a particular listing)Christianity law and ethics
Church and state framing
Within the framework of Christianity, there are at least three possible definitions for Church law. One is the Torah/Mosaic Law (from what Christians consider to be theOld Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
) also called Divine Law or Biblical law. Another is the instructions of Jesus, Jesus of Nazareth in the Gospel (sometimes referred to as the Law of Christ or the New Commandment or the New Covenant). A third is canon law which is the internal ecclesiastical law governing the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches, and the Anglicanism, Anglican Communion of churches. The way that such church law is legislative power, legislated, interpreted and at times court, adjudicated varies widely among these three bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon was initially a rule adopted by a ecumenical council, council (From Greek ''kanon'' / κανών, Hebrew kaneh / קנה, for rule, standard, or measure); these canons formed the foundation of canon law.
Christian ethics in general has tended to stress the need for divine grace, grace, mercy, and forgiveness because of human weakness and developed while Early Christians were subjects of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. From the time Nero blamed Christians for setting Rome ablaze (64 AD) until Galerius (311 AD), persecutions against Christians erupted periodically. Consequently, Early Christian ethics included discussions of how believers should relate to Roman authority and to the empire.
Under the Constantine I and Christianity, Emperor Constantine I (312-337), Christianity became a legal religion. While some scholars debate whether Constantine's conversion to Christianity was authentic or simply matter of political expediency, Edict of Milan, Constantine's decree made the empire safe for Christian practice and belief. Consequently, issues of Christian doctrine, ethics and church practice were debated openly, see for example the First Council of Nicaea and the First seven Ecumenical Councils. By the time of Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
(379-395), Christianity had become the state religion of the empire. With Christianity in power, ethical concerns broaden and included discussions of the proper role of the state.
Render unto Caesar… is the beginning of a phrase attributed to Jesus in the synoptic gospels which reads in full, "''Render unto Caesar the things which are Caesar’s, and unto God the things that are God’s''". This phrase has become a widely quoted summary of the relationship between Christianity and secular authority. The gospels say that when Jesus gave his response, his interrogators "marvelled, and left him, and went their way." Time has not resolved an ambiguity in this phrase, and people continue to interpret this passage to support various positions that are poles apart. The traditional division, carefully determined, in Christian thought is the Sovereign state, state and Christian Church, church have separate sphere of influence, spheres of influence.
Thomas Aquinas thoroughly discussed that ''human law'' is positive law which means that it is natural law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacte ...
applied by governments to societies. All human laws were to be judged by their conformity to the natural law. An unjust law was in a sense no law at all. At this point, the natural law was not only used to pass judgment on the moral worth of various laws, but also to determine what the law said in the first place. This could result in some tension.Burns, "Aquinas's Two Doctrines of Natural Law." Late ecclesiastical writers followed in his footsteps.
Democratic ideology
Christian democracy is a political ideology that seeks to apply Christian principles to public policy. It emerged in 19th-century Europe, largely under the influence of Catholic social teaching. In a number of countries, the democracy's Christian ethos has been diluted by secularisation. In practice, Christian democracy is often considered social conservatism, conservative on cultural, social and moral issues and progressivism, progressive on fiscal and economic issues. In places, where their opponents have traditionally been secularist socialism, socialists and social democracy, social democrats, Christian democratic parties are moderately conservatism, conservative, whereas in other cultural and political environments they can lean to the left.Women's roles
Attitudes and beliefs about the roles and responsibilities of women in Christianity vary considerably today as they have throughout the last two millennia — evolving along with or counter to the societies in which Christians have lived. The Bible and Christianity historically have been interpreted as excluding women from church leadership and placing them in submissive roles in marriage. Male leadership has been assumed in the church and within marriage, society and government.Blevins, Carolyn DeArmond, ''Women in Christian History: A Bibliography.'' Macon, Georgia: Mercer Univ Press, 1995. Some contemporary writers describe the role of women in the life of the church as having been downplayed, overlooked, or denied throughout much of Christian history. Paradigm shifts in gender roles in society and also many churches has inspired reevaluation by many Christians of some long-held attitudes to the contrary. Christian egalitarianism, Christian egalitarians have increasingly argued for equal roles for men and women in Christian views of marriage, marriage, as well as for the ordination of women to theclergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
. Contemporary conservatives meanwhile have reasserted what has been termed a "Complementarianism, complementarian" position, promoting the traditional belief that the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
ordains different roles and responsibilities for women and men in the Church and family.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * Union of Christendom, a traditional Catholic view of ecumenismNotes
References
Bibliography
;21st century Sources * * ;20th century sources * * * * ;19th century sources * Hull, MosesEncyclopedia of Biblical Spiritualism; Or, A Concordance to the Principal Passages of the Old and New Testament Scriptures Which Prove or Imply Spiritualism; Together with a Brief History of the Origin of Many of the Important Books of the Bible
Chicago: M. Hull, 1895. (ed.
reprint version
is available) * Bosanquet, Bernard
The Civilization of Christendom, And Other Studies
London: S. Sonnenschein, 1893. * * * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* Bainton, Roland H. (1966). ''Christendom: a Short History of Christianity and Its Impact on Western Civilization'', in series, ''Harper Colophon Books''. New York: Harper & Row. 2 vol., ill. *Molland, Einar (1959) ''Christendom: the Christian churches, their doctrines, constitutional forms and ways of worship''. London: A. & R. Mowbray & Co. (first published in Norwegian in 1953 as ''Konfesjonskunnskap''). * Whalen, Brett Edward (2009). ''Dominion of God: Christendom and Apocalypse in the Middle Ages''. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press.External links
;Websites * {{Authority control Christian terminology Christian organizations Cultural regions Ecclesiology European civilizations Historical regions World Christianity