Capella Antiqua Bambergensis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Capella is the brightest
 ''α Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Aurigae'') is the star system's
''α Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Aurigae'') is the star system's
 Building J of the pre-Columbian site Monte Albán in Oaxaca state in Mexico was built around 275 BC, at a different orientation to other structures in the complex. Its steps are aligned perpendicular to the rising of Capella at that time, so that a person looking out a doorway on the building would have faced it directly. Capella is significant as its
Building J of the pre-Columbian site Monte Albán in Oaxaca state in Mexico was built around 275 BC, at a different orientation to other structures in the complex. Its steps are aligned perpendicular to the rising of Capella at that time, so that a person looking out a doorway on the building would have faced it directly. Capella is significant as its
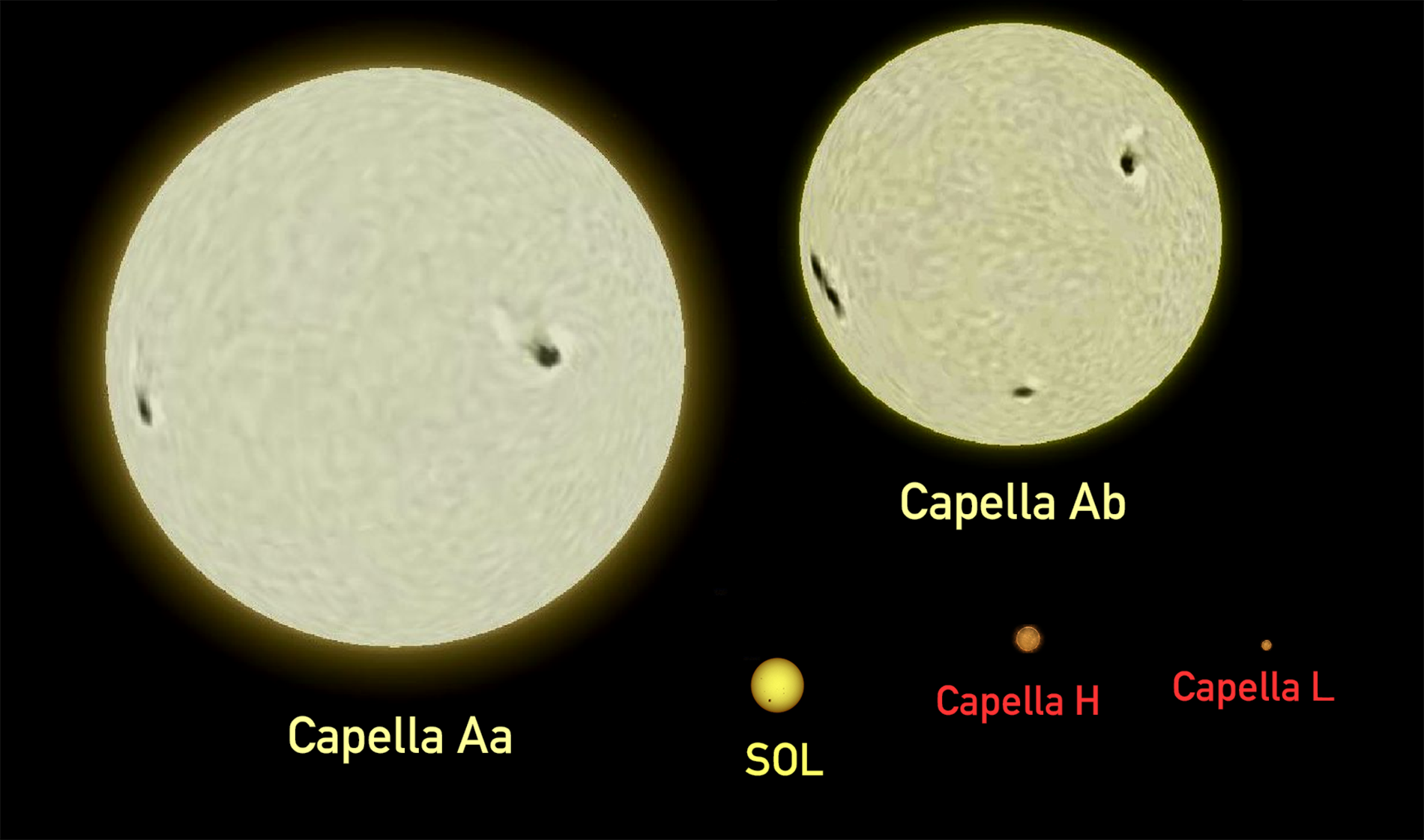 There are several stars within a few
There are several stars within a few
 Capella A consists of two yellow evolved stars that have been calculated to orbit each other every 104.02128 ± 0.00016 days, with a semimajor axis of 111.11 ± 0.10 million km (0.74272 ± 0.00069 AU), roughly the distance between Venus and the Sun. The pair is not an eclipsing binary—that is, as seen from Earth, neither star passes in front of the other. The orbit is known extremely accurately and can be used to derive an orbital parallax with far better precision than the one measured directly. The stars are not near enough to each other for the Roche lobe of either star to have been filled and any significant mass transfer to have taken place, even during the
Capella A consists of two yellow evolved stars that have been calculated to orbit each other every 104.02128 ± 0.00016 days, with a semimajor axis of 111.11 ± 0.10 million km (0.74272 ± 0.00069 AU), roughly the distance between Venus and the Sun. The pair is not an eclipsing binary—that is, as seen from Earth, neither star passes in front of the other. The orbit is known extremely accurately and can be used to derive an orbital parallax with far better precision than the one measured directly. The stars are not near enough to each other for the Roche lobe of either star to have been filled and any significant mass transfer to have taken place, even during the
star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in the northern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Auriga. It has the Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
α Aurigae, which is Latinised to Alpha Aurigae and abbreviated Alpha Aur or α Aur. Capella is the sixth-brightest star in the night sky, and the third-brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere after Arcturus and Vega. A prominent object in the northern winter sky, it is circumpolar to observers north of 44°N
The 44th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 44 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the s ...
. Its name meaning "little goat" in Latin, Capella depicted the goat Amalthea that suckled Zeus in classical mythology. Capella is relatively close, at from the Sun. It is one of the brightest X-ray sources in the sky, thought to come primarily from the corona of Capella Aa.
Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, Capella is actually a quadruple star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speak ...
organized in two binary pairs, made up of the stars Capella Aa, Capella Ab, Capella H and Capella L. The primary pair, Capella Aa and Capella Ab, are two bright-yellow giant stars, both of which are around 2.5 times as massive as the Sun. The secondary pair, Capella H and Capella L, are around 10,000 astronomical units (AU)the distance between the Earth and the Sun is one astronomical unit from the first and are two faint, small and relatively cool red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
s.
Capella Aa and Capella Ab have exhausted their core hydrogen, and cooled and expanded, moving off the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
. They are in a very tight circular orbit about 0.74 AU apart, and orbit each other every 104 days. Capella Aa is the cooler and more luminous of the two with spectral class K0III; it is 78.7 ± 4.2 times the Sun's luminosity and 11.98 ± 0.57 times its radius. An aging red clump star, it is fusing helium to carbon and oxygen in its core. Capella Ab is slightly smaller and hotter and of spectral class G1III; it is 72.7 ± 3.6 times as luminous as the Sun and 8.83 ± 0.33 times its radius. It is in the Hertzsprung gap, corresponding to a brief subgiant evolutionary phase as it expands and cools to become a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
. Several other stars in the same visual field have been catalogued as companions but are physically unrelated.
Nomenclature
 ''α Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Aurigae'') is the star system's
''α Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Aurigae'') is the star system's Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
. It also has the Flamsteed designation 13 Aurigae. It is listed in several multiple star catalogues as ADS 3841, CCDM J05168+4559, and WDS J05167+4600. As a relatively nearby star system, Capella is listed in the Gliese-Jahreiss Catalogue with designations GJ 194 for the bright pair of giants and GJ 195 for the faint pair of red dwarfs.
The traditional name ''Capella'' is Latin for ''(small) female goat''; the alternative name ''Capra'' was more commonly used in classical times. It is the translation of the Greek star name Aἴξ (aix) meaning "the Goat". As the sound of the Greek term for the goat (aἴξ) is similar to the sound of the name for the Aegaean Sea, this star has been used for weather rules and determining the seasonal wind direction. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Capella'' for this star. It is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names. The catalogue of star names lists ''Capella'' as applying to the star α Aurigae Aa.
Observational history
Capella was the brightest star in the night sky from 210,000 years ago to 160,000 years ago, at about −1.8 in apparent magnitude. At −1.1, Aldebaran was brightest before this period; it and Capella were situated rather close to each other in the sky and approximated boreal pole stars at the time. Capella is thought to be mentioned in an Akkadian inscription dating to the 20th century BC. Its goat-associated symbolism dates back to Mesopotamia as a constellation called "GAM", "Gamlum" or "MUL.GAM" in the 7th-century BC document MUL.APIN. GAM represented a scimitar or crook and may have represented the star alone or the constellation of Auriga as a whole. Later,Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
astronomers created constellations that were groups of animals, where each star represented one animal. The stars of Auriga comprised a herd of goats, an association also present in Greek mythology. It is sometimes called the ''Shepherd's Star'' in English literature. Capella was seen as a portent of rain in classical times.
 Building J of the pre-Columbian site Monte Albán in Oaxaca state in Mexico was built around 275 BC, at a different orientation to other structures in the complex. Its steps are aligned perpendicular to the rising of Capella at that time, so that a person looking out a doorway on the building would have faced it directly. Capella is significant as its
Building J of the pre-Columbian site Monte Albán in Oaxaca state in Mexico was built around 275 BC, at a different orientation to other structures in the complex. Its steps are aligned perpendicular to the rising of Capella at that time, so that a person looking out a doorway on the building would have faced it directly. Capella is significant as its heliacal rising
The heliacal rising ( ) or star rise of a star occurs annually, or the similar phenomenon of a planet, when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon at dawn just before sunrise (thus becoming "the morning star") after a complete orbit of ...
took place within a day of the Sun passing directly overhead over Monte Albán.
Multiple status
Professor William Wallace Campbell of theLick Observatory
The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by th ...
announced that Capella was binary in 1899, based on spectroscopic observations—he noted on photographic plates taken from August 1896 to February 1897 that a second spectrum appeared superimposed over the first, and that there was a doppler shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who d ...
to violet in September and October and to red in November and February—showing that the components were moving toward and away from the Earth (and hence orbiting each other). Almost simultaneously, British astronomer Hugh Newall
Hugh Frank Newall, FRS FRAS (21 June 1857 – 22 February 1944) was a British astrophysicist. He was Professor of Astrophysics (1909) at Cambridge. He was the son of Robert Stirling Newall FRS and his wife Mary, daughter of Hugh Lee Patti ...
had observed its composite spectrum with a four prism spectroscope attached to a telescope at Cambridge in July 1899, concluding that it was a binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
system.
Many observers tried to discern the component stars without success. Known as "The Interferometrist's Friend", it was first resolved interferometrically
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opti ...
in 1919 by John Anderson and Francis Pease at Mount Wilson Observatory, who published an orbit in 1920 based on their observations. This was the first interferometric measurement of any object outside the Solar System. A high-precision orbit was published in 1994 based on observations by the Mark III Stellar Interferometer The Mark III Stellar Interferometer was a long-baseline optical astronomical interferometer, located at the Mount Wilson Observatory, California, United States.The Mark III stellar interferometer, M. Shao et al., ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'' 193 ...
, again at Mount Wilson Observatory. See §1 for spectral types, Table 1 for orbit, Table 5 for stellar parameters, and §6.3 for the age of the system. Capella also became the first astronomical object to be imaged by a separate element optical interferometer when it was imaged by the Cambridge Optical Aperture Synthesis Telescope in September 1995.
In 1914, Finnish astronomer Ragnar Furuhjelm
Elis Ragnar Furuhjelm (12 October 1879 – 15 November 1944) was a Finnish astronomer and politician, born in Oulu. He was Deputy Minister of Finance from 14 December 1932 to 21 April 1933. He was a member of the Parliament of Finland from 1917 un ...
observed that the spectroscopic binary had a faint companion star, which, as its proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
was similar to that of the spectroscopic binary, was probably physically bound to it. In February 1936, Carl L. Stearns observed that this companion appeared to be double itself;. this was confirmed in September that year by Gerard Kuiper. This pair are designated Capella H and L.
X-ray source
Two Aerobee-Hi rocket flights on September 20, 1962, and March 15, 1963, detected and confirmed an X-ray source in Auriga at RA Dec , identified as Capella. Stellar X-ray astronomy started on April 5, 1974, with the detection of X-rays from Capella. A rocket flight on that date briefly calibrated its attitude control system when a star sensor pointed the payload axis at Capella. During this period, X-rays in the range 0.2–1.6 keV were detected by an X-ray reflector system co-aligned with the star sensor. The X-ray luminosity (''L''x) of ~1024 W (1031 erg s−1) is four orders of magnitude above the Sun's X-ray luminosity. Capella's X-rays are thought to be primarily from the corona of the most massive star. Capella is ROSAT X-ray source 1RXS J051642.2+460001. The high temperature of Capella's corona as obtained from the first coronal X-ray spectrum of Capella using HEAO 1 would require magnetic confinement, unless it is a free-flowing coronal wind.Observation
With an average apparent magnitude of +0.08, Capella is the brightest object in theconstellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Auriga, the sixth-brightest star in the night sky, the third-brightest in the northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
celestial hemisphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
(after Arcturus and Vega), and the fourth-brightest visible to the naked eye from the latitude 40°N
The 40th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 40 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the su ...
. It appears to be a rich yellowish-white colour, although the yellow colour is more apparent during daylight observation with a telescope, due to the contrast against the blue sky.
Capella is closer to the north celestial pole than any other first-magnitude star
First-magnitude stars are the brightest stars in the night sky, with apparent magnitudes lower (i.e. brighter) than +1.50. Hipparchus, in the 1st century B.C., introduced the magnitude scale. He allocated first magnitude to the 20 brightest stars ...
.Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that ...
is only second magnitude. Its northern declination is such that it is actually invisible south of latitude 44°S—this includes southernmost New Zealand, Argentina and Chile as well as the Falkland Islands. Conversely it is circumpolar north of 44°N
The 44th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 44 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the s ...
: for the whole of the United Kingdom and Canada (except for part of Southern Ontario), most of Europe, and the northernmost fringes of the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
, the star never sets. Capella and Vega are on opposite sides of the pole, at about the same distance from it, such that an imaginary line between the two stars will nearly pass through Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that ...
. Visible halfway between Orion's Belt and Polaris, Capella is at its highest in the night sky at midnight in early December and is regarded as a prominent star of the northern winter sky.
A few degrees to the southwest of Capella lie three stars, Epsilon Aurigae, Zeta Aurigae
Zeta Aurigae, or ζ Aurigae, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this system is approximately distant from the sun. It has a combined appa ...
and Eta Aurigae
Eta Aurigae (η Aurigae, abbreviated Eta Aur, η Aur), officially named Haedus , is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.18, it is visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measuremen ...
, the latter two of which are known as "The Kids", or Haedi. The four form a familiar pattern, or asterism, in the sky.
Distance
Based on an annualparallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
shift of 76.20 milliarcseconds (with a margin of error of 0.46 milliarcseconds) as measured by the Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
satellite, this system is estimated to be from Earth, with a margin of error of 0.3 light-year (0.09 parsec). An alternative method to determine the distance is via the orbital parallax, which gives a distance of with a margin of error of only 0.1%. Capella is estimated to have been a little closer to the Solar System in the past, passing within 29 light-years distant around 237,000 years ago. At this range, it would have shone at apparent magnitude −0.82, comparable to Canopus today.
In a 1960 paper, American astronomer Olin J. Eggen
Olin Jeuck Eggen (July 9, 1919 – October 2, 1998) was an American astronomer.
Biography
Olin Jeuck Eggen was born to Olin Eggen and Bertha Clare Jeuck in the village of Orfordville in Rock County, Wisconsin. Both of his parents were of Norw ...
concluded that Capella was a member of the Hyades moving group, a group of stars moving in the same direction as the Hyades cluster
The Hyades (; Greek Ὑάδες, also known as Caldwell 41, Collinder 50, or Melotte 25) is the nearest open cluster and one of the best-studied star clusters. Located about away from the Sun, it consists of a roughly spherical group of hundreds ...
, after analysing its proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
and parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
. Members of the group are of a similar age, and those that are around 2.5 times as massive as the Sun have moved off the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
after exhausting their core hydrogen reserves and are expanding and cooling into red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
s.
Stellar system
 There are several stars within a few
There are several stars within a few arcminutes
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
of Capella and some have been listed as companions in various multiple star catalogues. The Washington Double Star Catalog lists components A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, L, M, N, O, P, Q, and R, with A being the naked-eye star. Most are only line-of-sight companions, but the close pair of red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
s H and L are at the same distance as the bright component A and moving through space along with it. Capella A is itself a spectroscopic binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separa ...
with components Aa and Ab, both giant stars. The pair of giants is separated from the pair of red dwarfs by 723 ".
American astronomer Robert Burnham Jr.
Robert Burnham Jr. (June 16, 1931 – March 20, 1993) was an American astronomer, best known for writing the classic three-volume ''Burnham's Celestial Handbook''. He is the discoverer of numerous asteroids including the Mars crossing asteroid 3 ...
described a scale model of the system where Capella A was represented by spheres 13 and 7 inches across, separated by ten feet. The red dwarfs were then each 0.7 inch across and they were separated by 420 feet. At this scale, the two pairs are 21 miles apart.
Capella A
red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
stage of the primary star.
Modern convention designates the more luminous cooler star as component Aa and its spectral type has been usually measured between G2 and K0. The hotter secondary Ab has been given various spectral types of late (cooler) F or early (warmer) G. The MK spectral types of the two stars have been measured a number of times, and they are both consistently assigned a luminosity class of III indicating a giant star. The composite spectrum appears to be dominated by the primary star due to its sharper absorption line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
s; the lines from the secondary are broadened and blurred by its rapid rotation. The composite spectral class is given as approximately G3III, but with a specific mention of features due to a cooler component. The most recent specific published types are K0III and G1III, although older values are still widely quoted such as G5IIIe + G0III from the Bright Star Catalogue or G8III + G0III by Eggen. Where the context is clear, these two components have been referred to as A and B.
The individual apparent magnitudes of the two component stars cannot be directly measured, but their relative brightness has been measured at various wavelengths. They have very nearly equal brightness in the visible light spectrum, with the hotter secondary component generally being found to be a few tenths of a magnitude brighter. A 2016 measurement gives the magnitude difference between the two stars at a wavelength of 700 nm as 0.00 ± 0.1.
The physical properties of the two stars can be determined with high accuracy. The masses are derived directly from the orbital solution, with Aa being and Ab being . Their angular radii have been directly measured; in combination with the very accurate distance, this gives and for Aa and Ab, respectively. Their surface temperatures can be calculated by comparison of observed and synthetic spectra, direct measurement of their angular diameters and brightnesses, calibration against their observed colour indices
In astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature. The lower the color index, the more blue (or hotter) the object is. Conversely, the large ...
, and disentangling of high resolution spectra. Weighted averages of these four methods give 4,970 ± 50 K for Aa and 5,730 ± 60 for Ab. Their bolometric luminosities
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a st ...
are most accurately derived from their apparent magnitudes and bolometric corrections, but are confirmed by calculation from the temperatures and radii of the stars. Aa is 78.7 ± 4.2 times as luminous as the Sun and Ab 72.7 ± 3.6 times as luminous, so the star defined as the primary component is the more luminous when all wavelengths are considered but very slightly less bright at visual wavelengths.
Estimated to be 590 to 650 million years old, the stars were probably at the hot end of spectral class A
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
during their main-sequence lifetime, similar to Vega. They have now exhausted their core hydrogen and evolved off the main sequence, their outer layers expanding and cooling. Despite the giant luminosity class, the secondary component is very clearly within the Hertzsprung gap on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosity, luminosities versus their stellar classifications or eff ...
, still expanding and cooling towards the red giant branch, making it a subgiant in evolutionary terms. The more massive primary has already passed through this stage, when it reached a maximum radius of 36 to 38 times that of the Sun. It is now a red clump star which is fusing helium to carbon and oxygen in its core, a process that has not yet begun for the less massive star. Detailed analysis shows that it is nearing the end of this stage and starting to expand again which will lead it to the asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
. Isotope abundance
In physics, natural abundance (NA) refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass (a weighted average, weighted by mole-fraction abundance figures) of these isotopes is the atomic ...
sThe lithium abundance, C12/C13 ratio and C/N ratio have all declined in Capella Aa but not in Capella Ab. and spin rates confirm this evolutionary difference between the two stars. Heavy element abundances are broadly comparable to those of the Sun and the overall metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a ...
is slightly less than the Sun's.
The rotational period of each star can be measured by observing periodic variations in the doppler shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who d ...
s of their spectral lines. The absolute rotational velocities of the two stars are known from their inclinations, rotation periods, and sizes, but the projected equatorial rotational velocities measured using doppler broadening of spectral lines are a standard measure and these are generally quoted. Capella Aa has a projected rotational velocity of 4.1 ± 0.4 km per second, taking 104 ± 3 days to complete one rotation, while Capella Ab spins much more rapidly at 35.0 ± 0.5 km per second, completing a full rotation in only 8.5 ± 0.2 days. Rotational braking occurs in all stars when they expand into giants, and binary stars are also tidally braked. Capella Aa has slowed until it is rotationally locked to the orbital period, although theory predicts that it should still be rotating more quickly from a starting point of a rapidly-spinning main sequence A star.
Capella has long been suspected to be slightly variable. Its amplitude of about 0.1 magnitudes means that it may at times be brighter or fainter than Rigel, Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is a red supergiant of spectral type M1-2 and one of the largest stars visible to the naked eye. It is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and, after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion ...
and Vega, which are also variable. The system has been classified as an RS Canum Venaticorum variable, a class of binary stars with active chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color") is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively.
In the Su ...
s that cause huge starspots, but it is still only listed as a suspected variable in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars. Unusually for RS CVn systems, the hotter star, Capella Ab, has the more active atmosphere because it is located in the Hertzsprung gap—a stage where it is changing its angular momentum and deepening its convection zone.
The active atmospheres and closeness of these stars means that they are among the brightest X-ray sources in the sky. However the X-ray emission is due to stable coronal structures and not eruptive flaring activity. Coronal loops larger than the Sun and with temperatures of several million kelvin are likely to be responsible for the majority of the X-rays.
Capella HL
The seventh companion published for Capella, component H, is physically associated with the bright primary star. It is ared dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
separated from the pair of G-type giants by a distance of around .
It has its own close companion, an even fainter red dwarf that was 1.8″ away when it was discovered in 1935. It is component L in double star catalogues. In 2015 the separation had increased to 3.5″, which was sufficient to allow ''tentative'' orbital parameters to be derived, 80 years after its discovery.
The Gliese-Jahreiss Catalogue of nearby stars designates the binary system as GJ 195. The two components are then referred to individually as GJ 195 A and B.
The two stars are reported to have a 3.5-visual-magnitude difference (2.3 mag in the passband of the ''Gaia'' spacecraft) although the difference is much smaller at infrared wavelengths. This is unexpected and may indicate further unseen companions.
The mass of the stars can, in principle, be determined from the orbital motion, but uncertainties in the orbit have led to widely varying results. In 1975, an eccentric 388-year orbit gave masses of and . A smaller near-circular orbit published in 2015 had a 300-year orbit, benefitting from mass constraints of and , respectively, for GJ 195 A and B, based on their infrared magnitudes.
Visual companions
Six visual companions to Capella were discovered before Capella H and are generally known only as Capella B through G. None are thought to be physically associated with Capella, although all appear closer in the sky than the HL pair. Component F is also known as TYC 3358-3142-1. It is listed with a spectral type of K although it is included in a catalogue of OB stars as a distant luminous star. Component G is BD+45 1076, with a spectral type of F0, at a distance of . It is identified as a variable member of theGuide Star Catalogue
The Guide Star Catalog (GSC), also known as the ''Hubble Space Telescope, Guide Catalog'' (''HSTGC''), is a star catalog compiled to support the Hubble Space Telescope with targeting off-axis stars. GSC-I contained approximately 20,000,000 stars w ...
from Chandra observations although it is not known what type of variability. It is known to be an X-ray source with an active corona.
Several other stars have also been catalogued as companions to Capella. Components I, Q and R are 13th-magnitude stars at distances of 92″, 133″ and 134″.
V538 Aurigae
V538 Aurigae is a single star in the northern constellation of Auriga. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.23, this star requires good dark sky conditions to view with the naked eye. It is located at a distance of from Sun based on ...
and its close companion HD 233153 are red dwarfs ten degrees away from Capella; they have very similar space motions but the small difference makes it possible that this is just a coincidence.
Two faint stars have been discovered by speckle imaging in the Capella HL field, around 10″ distant from that pair. These have been catalogued as Capella O and P. It is not known whether they are physically associated with the red dwarf binary.
Etymology and culture
Capella traditionally marks the left shoulder of the constellation's eponymous charioteer, or, according to the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy's ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'', the goat that the charioteer is carrying. In Bayer's 1603 work '' Uranometria'', Capella marks the charioteer's back. The three '' Haedi'' had been identified as a separate constellation by Pliny the Elder and Manilius, and were called ''Capra'', ''Caper'', or ''Hircus'', all of which relate to its status as the "goat star". Ptolemy merged the Charioteer and the Goats in the 2nd-century ''Almagest''.
In Greek mythology, the star represented the goat Amalthea that suckled Zeus. It was this goat whose horn, after accidentally being broken off by Zeus, was transformed into the Cornucopia, or "horn of plenty", which would be filled with whatever its owner desired. Though most often associated with Amalthea, Capella has sometimes been associated with Amalthea's owner, a nymph. The myth of the nymph says that the goat's hideous appearance, resembling a Gorgon, was partially responsible for the Titans' defeat, after Zeus skinned the goat and wore it as his aegis.
In medieval accounts, it bore the uncommon name ''Alhajoth'' (also spelled ''Alhaior'', ''Althaiot'', ''Alhaiset'', ''Alhatod'', ''Alhojet'', ''Alanac'', ''Alanat'', ''Alioc''), which (especially the last) may be a corruption of its Arabic name, , ''al-cayyūq.'' ''cAyyūq'' has no clear significance in Arabic, but may be an Arabized form of the Greek αίξ ''aiks'' "goat"; cf. the modern Greek Αίγα ''Aiga'', the feminine of goat. To the Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
of the Negev and Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
, Capella ''al-'Ayyūq ath-Thurayyā'' "Capella of the Pleiades", from its role as pointing out the position of that asterism. Another name in Arabic was ''Al-Rākib'' "the driver", a translation of the Greek.
To the ancient Balts, Capella was known as ''Perkūno Ožka'' "Thunder's Goat", or ''Tikutis''. Conversely in Slavic Macedonian folklore, Capella was ''Jastreb'' "the hawk", flying high above and ready to pounce on Mother Hen (the Pleiades) and the Rooster (Nath).
Astrologically, Capella portends civic and military honors and wealth. In the Middle Ages, it was considered a Behenian fixed star, with the stone sapphire and the plants horehound, mint, mugwort and mandrake as attributes. Cornelius Agrippa listed its kabbalistic
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and Jewish theology, school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "rece ...
sign with the name ''Hircus'' (Latin for ''goat'').
In Hindu mythology
Hindu mythology is the body of myths and literature attributed to, and espoused by, the adherents of the Hindu religion, found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'', the Puranas, and reg ...
, Capella was seen as the heart of Brahma, ''Brahma Hṛdaya''. In traditional Chinese astronomy, Capella was part of the asterism (; English: ''Five Chariots Five Chariots (五車, pinyin: Wǔ Ju) is a constellation in Chinese astronomy.
Introduction
A five-star Chinese constellation equivalent to Auriga minus δ Aur ( Delta Aurigae). Also known in Japanese as Gosha (Five Chariots; 五車).
Stars
* ...
''), which consisted of Capella together with Beta Aurigae, Theta Aurigae
Theta Aurigae ( Latinized from θ Aurigae, abbreviated Theta Aur, θ Aur) is a binary star in the constellation of Auriga. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to this system is about .
The two components are designated Thet ...
and Iota Aurigae
Iota Aurigae (ι Aurigae, abbreviated Iota Aur, ι Aur), officially named Hassaleh , is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga (constellation), Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.7, which is bright enough to be Bortle ...
, as well as Beta Tauri. Since it was the second star in this asterism, it has the Chinese name (; English: ''Second of the Five Chariots'').
In Quechua it was known as ''Colça''; the Incas held the star in high regard. The Hawaiians saw Capella as part of an asterism ''Ke ka o Makali'i'' ("The canoe bailer of Makali'i") that helped them navigate at sea. Called ''Hoku-lei'' "star wreath", it formed this asterism with Procyon, Sirius, Castor and Pollux. In Tahitian folklore, Capella was ''Tahi-ari'i'', the wife of ''Fa'a-nui'' (Auriga) and mother of prince ''Ta'urua'' ( Venus) who sails his canoe across the sky. In Inuit astronomy
Inuit astronomy is centered around the ''Qilak,'' the Inuit name for the celestial sphere and the home for souls of departed people. Inuit beliefs about astronomy are the shaped by the harsh climate in the Arctic and the resulting difficulties o ...
, Capella, along with Menkalinan ( Beta Aurigae), Pollux (Beta Geminorum) and Castor (Alpha Geminorum), formed a constellation Quturjuuk, "collar-bones", the two pairs of stars denoting a bone each. Used for navigation and time-keeping at night, the constellation was recognised from Alaska to western Greenland. The Gwich'in saw Capella and Menkalinan has forming ''shreets'ą įį vidzee'', the right ear of the large circumpolar constellation ''Yahdii'', which covered much of the night sky, and whose orientation facilitated navigation and timekeeping.
In Australian Aboriginal mythology for the Boorong
The Wergaia or Werrigia people are an Aboriginal Australian group in the Mallee and Wimmera regions of north-Western Victoria, made up of a number of clans. The people were also known as the Maligundidj (in the Wotjobaluk language) which means ...
people of Victoria, Capella was ''Purra'', the kangaroo, pursued and killed by the nearby Gemini twins, ''Yurree'' ( Castor) and ''Wanjel'' ( Pollux). The Wardaman people
The Wardaman people are a small group of Aboriginal Australians living about South-West of Katherine, on Menngen Aboriginal Land Trust in the Northern Territory of Australia.
Language
Wardaman is a non Pama-Nyungan language. Though close to ...
of northern Australia knew the star as ''Yagalal'', a ceremonial fish scale, related to Guwamba the barramundi ( Aldebaran).
Namesakes
* Capella, a lunar crater to the north of the Mare Nectaris, not named after the star * and USNS ''Capella'' (T-AKR-293), both U.S. Navy ships * Mazda Capella, a model of automobile manufactured by MazdaSee also
*Capella in fiction
The planetary systems of stars other than the Sun and the Solar System are a staple element in many works of the science fiction genre.
Overview
The notion that there might be inhabited extrasolar planets can be traced at least as far back as G ...
* List of brightest stars
* List of nearest bright stars
* Historical brightest stars
The Solar System and all of the visible stars are in different orbits about the core of the Milky Way galaxy. Thus, their relative positions change over time, and for the nearer stars this movement can be measured. As a star moves toward or away ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Capella G-type giants K-type giants M-type main-sequence stars RS Canum Venaticorum variables Spectroscopic binaries 4 Hyades Stream Auriga (constellation) Aurigae, Alpha BD+45 1077 Aurigae, 13 0194 034029 0246081708
In the Swedish calendar it was a leap year starting on Wednesday, one day ahead of the Julian and ten days behind the Gregorian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 1 – Charles XII of Sweden invades Russia, by crossing th ...
Stars with proper names