|
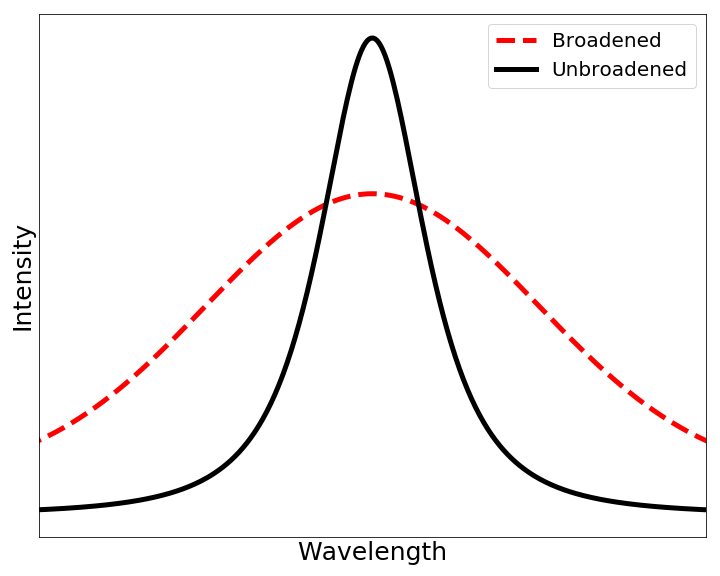
Doppler Broadening
In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting (or absorbing) particles result in different Doppler shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the emission (absorption) line broadening. This resulting line profile is known as a Doppler profile. A particular case is the thermal Doppler broadening due to the thermal motion of the particles. Then, the broadening depends only on the frequency of the spectral line, the mass of the emitting particles, and their temperature, and therefore can be used for inferring the temperature of an emitting (or absorbing) body being spectroscopically investigated. Derivation When a particle moves (e.g., due to the thermal motion) towards the observer, the emitted radiation is shifted to a higher frequency. Likewise, when the emitter moves away, the frequency is lowered. For non-relativistic thermal ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Broadening Example
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Water Reactor
The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light-water reactors are the most common type of thermal-neutron reactor. There are three varieties of light-water reactors: the pressurized water reactor (PWR), the boiling water reactor (BWR), and (most designs of) the supercritical water reactor (SCWR). History Early concepts and experiments After the discoveries of fission, moderation and of the theoretical possibility of a nuclear chain reaction, early experimental results rapidly showed that natural uranium could only undergo a sustained chain reaction using graphite or heavy water as a moderator. While the world's first reactors ( CP-1, X10 etc.) were successfully reaching criticality, uranium enrichment began to develop from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas-cooled Reactor
A gas-cooled reactor (GCR) is a nuclear reactor that uses graphite as a neutron moderator and a gas (carbon dioxide or helium in extant designs) as coolant. Although there are many other types of reactor cooled by gas, the terms ''GCR'' and to a lesser extent ''gas cooled reactor'' are particularly used to refer to this type of reactor. The GCR was able to use natural uranium as fuel, enabling the countries that developed them to fabricate their own fuel without relying on other countries for supplies of enriched uranium, which was at the time of their development in the 1950s only available from the United States or the Soviet Union. The Canadian CANDU reactor, using heavy water as a moderator, was designed with the same goal of using natural uranium fuel for similar reasons. Design considerations Historically thermal spectrum graphite moderated gas cooled reactors mostly competed with light water reactors, ultimately losing out to them after having seen some deployment in Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Nuclear Safety
Passive nuclear safety is a design approach for safety features, implemented in a nuclear reactor, that does not require any active intervention on the part of the operator or electrical/electronic feedback in order to bring the reactor to a safe shutdown state, in the event of a particular type of emergency (usually overheating resulting from a loss of coolant or loss of coolant flow). Such design features tend to rely on the engineering of components such that their predicted behaviour would slow down, rather than accelerate the deterioration of the reactor state; they typically take advantage of natural forces or phenomena such as gravity, buoyancy, pressure differences, conduction or natural heat convection to accomplish safety functions without requiring an active power source. Many older common reactor designs use passive safety systems to a limited extent, rather, relying on active safety systems such as diesel powered motors. Some newer reactor designs feature more passive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
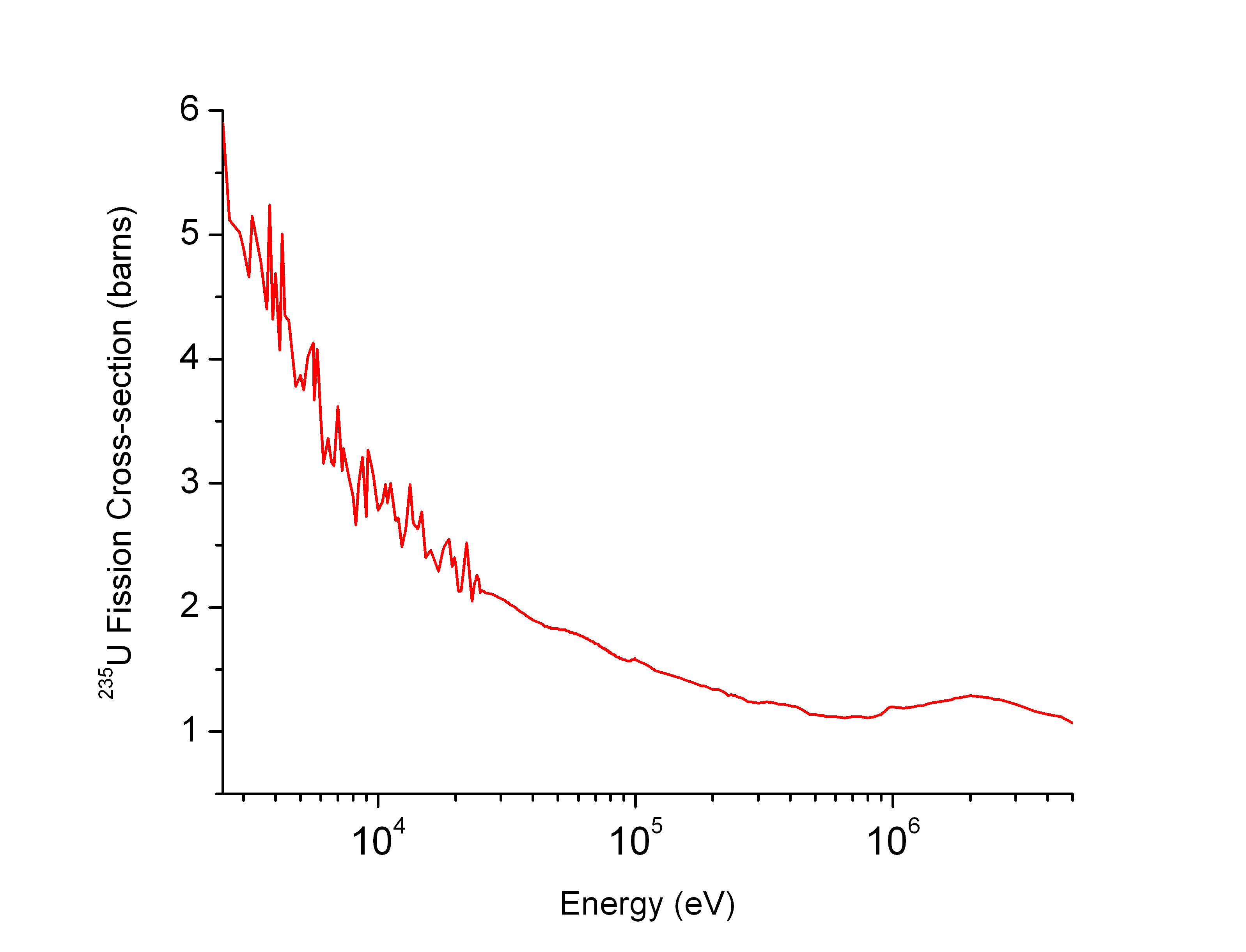
Neutron Cross Section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reactors
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid (water or gas), which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. , the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world. In the early era of nuclear reactors (1940s), a reactor was known as a nuclear pile or atomic pile (so-called because the graphite moderator blocks of the first reactor were placed into a tall pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Temperature Coefficient Of Reactivity
Fuel temperature coefficient of reactivity is the change in reactivity of the nuclear fuel per degree change in the fuel temperature. The coefficient quantifies the amount of neutrons that the nuclear fuel (such as uranium-238) absorbs from the fission process as the fuel temperature increases. It is a measure of the stability of the reactor operations. This coefficient is also known as the Doppler coefficient due to the contribution of Doppler broadening, which is the dominant effect in thermal systems. Contributing effects Doppler broadening Thermal Doppler motion of atoms within the fuel results in a broader neutron spectrum and, consequently, in a decreased neutron capture rate. Thermal expansion Thermal expansion of the fuel at higher temperatures results in a lower density which reduces the likelihood of a neutron interacting with the fuel. See also *Nuclear fission *Nuclear reactor physics *Void coefficient In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient (more properl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stark Broadening
The Stark effect is the shifting and splitting of spectral lines of atoms and molecules due to the presence of an external electric field. It is the electric-field analogue of the Zeeman effect, where a spectral line is split into several components due to the presence of the magnetic field. Although initially coined for the static case, it is also used in the wider context to describe the effect of time-dependent electric fields. In particular, the Stark effect is responsible for the pressure broadening (Stark broadening) of spectral lines by charged particles in plasmas. For most spectral lines, the Stark effect is either linear (proportional to the applied electric field) or quadratic with a high accuracy. The Stark effect can be observed both for emission and absorption lines. The latter is sometimes called the inverse Stark effect, but this term is no longer used in the modern literature. History The effect is named after the German physicist Johannes Stark, who discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Density
The number density (symbol: ''n'' or ''ρ''N) is an intensive quantity used to describe the degree of concentration of countable objects (particles, molecules, phonons, cells, galaxies, etc.) in physical space: three-dimensional volumetric number density, two-dimensional areal number density, or one-dimensional linear number density. ''Population density'' is an example of areal number density. The term number concentration (symbol: lowercase ''n'', or ''C'', to avoid confusion with amount of substance indicated by uppercase '' N'') is sometimes used in chemistry for the same quantity, particularly when comparing with other concentrations. Definition Volume number density is the number of specified objects per unit volume: :n = \frac, where ''N'' is the total number of objects in a volume ''V''. Here it is assumed that ''N'' is large enough that rounding of the count to the nearest integer does not introduce much of an error, however ''V'' is chosen to be small enough that the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion Disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other forces induce instabilities causing orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology. Manifestations Accretion disks are a ubiquitous phenomenon in astrophysics; active galactic nuclei, protoplanetary disks, and gamma ray bursts all involve accretion disks. These disks very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. This increases the energy needed to pump fluid through a pipe. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |