Cambridge And Arrington Roads Act 1797 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the


 Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain around 410, the location may have been abandoned by the Britons, although the site is usually identified as ,
Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain around 410, the location may have been abandoned by the Britons, although the site is usually identified as ,
The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Evidence exists that the invading Anglo-Saxons had begun occupying the area by the end of the century. Their settlement – also on and around Castle Hill – became known as Grantebrycge. (" Granta-bridge"). (By Middle English, the settlement's name had changed to "Cambridge", deriving from the word 'Camboricum', meaning 'Passage' or 'ford' of stream in a town or settlement, and the lower stretches of the Granta changed their name to match.)
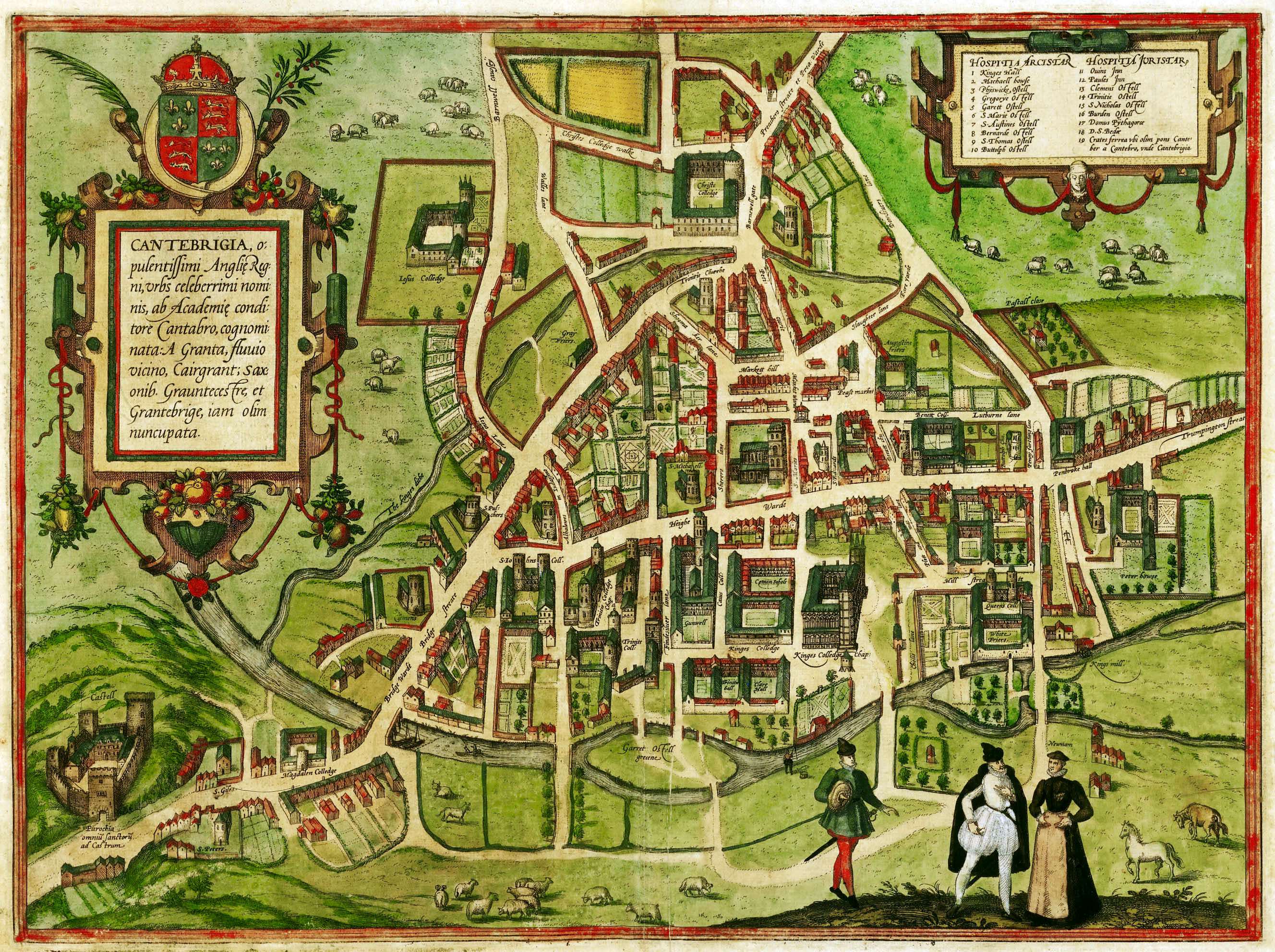 Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of Hobson's Conduit in the early 1600s. Water was brought from Nine Wells, at the foot of the Gog Magog Hills to the southeast of Cambridge, into the centre of the town.
Cambridge played a significant role in the early part of the English Civil War as it was the headquarters of the Eastern Counties Association, an organisation administering a regional East Anglian army, which became the mainstay of the Parliamentarian military effort before the formation of the
Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of Hobson's Conduit in the early 1600s. Water was brought from Nine Wells, at the foot of the Gog Magog Hills to the southeast of Cambridge, into the centre of the town.
Cambridge played a significant role in the early part of the English Civil War as it was the headquarters of the Eastern Counties Association, an organisation administering a regional East Anglian army, which became the mainstay of the Parliamentarian military effort before the formation of the
 Cambridge is a non-metropolitan district – one of six districts within the county of Cambridgeshire – and is administered by Cambridge City Council. The district covers most of the city's urban area, although some suburbs extend into the surrounding South Cambridgeshire district. The city council's headquarters are in the Guildhall, a large building in the market square. Cambridge was granted a Royal Charter by King John in 1207, which permitted the appointment of a mayor, although the first recorded mayor, Harvey FitzEustace, served in 1213. City councillors now elect a mayor annually.
For electoral purposes the city is divided into 14 wards: Abbey, Arbury, Castle, Cherry Hinton, Coleridge,
Cambridge is a non-metropolitan district – one of six districts within the county of Cambridgeshire – and is administered by Cambridge City Council. The district covers most of the city's urban area, although some suburbs extend into the surrounding South Cambridgeshire district. The city council's headquarters are in the Guildhall, a large building in the market square. Cambridge was granted a Royal Charter by King John in 1207, which permitted the appointment of a mayor, although the first recorded mayor, Harvey FitzEustace, served in 1213. City councillors now elect a mayor annually.
For electoral purposes the city is divided into 14 wards: Abbey, Arbury, Castle, Cherry Hinton, Coleridge,

 Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between
Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between
 At the 2011 Census, the population of the Cambridge contiguous built-up area (urban area) was 158,434, while that of the City Council area was 123,867.
In the 2001 Census held during University term, 89.44% of Cambridge residents identified themselves as white, compared with a national average of 92.12%. Within the university, 84% of undergraduates and 80% of post-graduates identified as white (including overseas students).
Cambridge has a much higher than average proportion of people in the highest paid professional, managerial or administrative jobs (32.6% vs. 23.5%)ONS 2001 Census (Approximated Social Grade – Workplace Population, Cambridge local authority) and a much lower than average proportion of manual workers (27.6% vs. 40.2%). In addition, 41.2% have a higher-level qualification (e.g. degree, Higher National Diploma, Master's or PhD), much higher than the national average proportion (19.7%).
Centre for Cities identified Cambridge as the UK's most unequal city in 2017 and 2018. Residents' income was the least evenly distributed of 57 British cities measured, with its top 6% earners accounting for 19% of its total income and the bottom 20% for only 2%, and a Gini coefficient of 0.460 in 2018.
At the 2011 Census, the population of the Cambridge contiguous built-up area (urban area) was 158,434, while that of the City Council area was 123,867.
In the 2001 Census held during University term, 89.44% of Cambridge residents identified themselves as white, compared with a national average of 92.12%. Within the university, 84% of undergraduates and 80% of post-graduates identified as white (including overseas students).
Cambridge has a much higher than average proportion of people in the highest paid professional, managerial or administrative jobs (32.6% vs. 23.5%)ONS 2001 Census (Approximated Social Grade – Workplace Population, Cambridge local authority) and a much lower than average proportion of manual workers (27.6% vs. 40.2%). In addition, 41.2% have a higher-level qualification (e.g. degree, Higher National Diploma, Master's or PhD), much higher than the national average proportion (19.7%).
Centre for Cities identified Cambridge as the UK's most unequal city in 2017 and 2018. Residents' income was the least evenly distributed of 57 British cities measured, with its top 6% earners accounting for 19% of its total income and the bottom 20% for only 2%, and a Gini coefficient of 0.460 in 2018.
 The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and
The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and
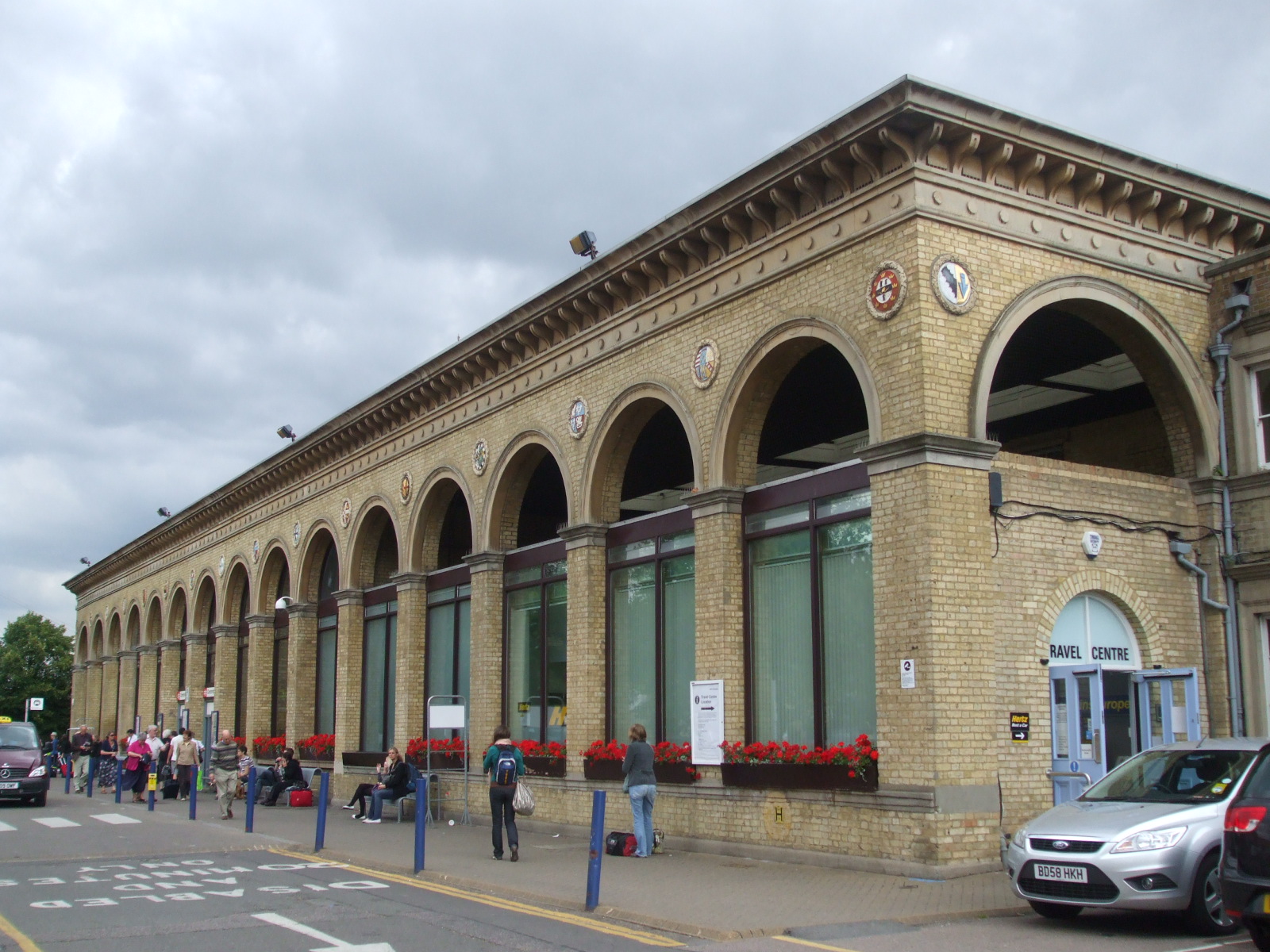
 Cambridge railway station was opened in 1845, initially linking to Bishopsgate station in London, via Bishops Stortford. Further lines opened throughout the 19th century, including the Cambridge and St Ives branch line, the Stour Valley Railway, the Cambridge to Mildenhall railway, and the Varsity Line to Oxford. Another station was opened in Cherry Hinton though, at the time, this was a separate village to Cambridge. Several of these lines were closed during the 1960s.
Today, Cambridge station has direct rail links to London with termini at (via the Cambridge Line and the
Cambridge railway station was opened in 1845, initially linking to Bishopsgate station in London, via Bishops Stortford. Further lines opened throughout the 19th century, including the Cambridge and St Ives branch line, the Stour Valley Railway, the Cambridge to Mildenhall railway, and the Varsity Line to Oxford. Another station was opened in Cherry Hinton though, at the time, this was a separate village to Cambridge. Several of these lines were closed during the 1960s.
Today, Cambridge station has direct rail links to London with termini at (via the Cambridge Line and the
 Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate University of Cambridge and the local campus of Anglia Ruskin University, serve around 30,000 students, by some estimates. Cambridge University estimated its 2007/08 student population at 17,662, and Anglia Ruskin reports 24,000 students across its two campuses (one of which is outside Cambridge, in Chelmsford) for the same period. ARU now (2019) has additional campuses in London and Peterborough. State provision in the
Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate University of Cambridge and the local campus of Anglia Ruskin University, serve around 30,000 students, by some estimates. Cambridge University estimated its 2007/08 student population at 17,662, and Anglia Ruskin reports 24,000 students across its two campuses (one of which is outside Cambridge, in Chelmsford) for the same period. ARU now (2019) has additional campuses in London and Peterborough. State provision in the
 Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern
Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern
 The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for rowing and the
The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for rowing and the



 Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer.
Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer.
 Cambridge is served by Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, with several smaller medical centres in the city and a teaching hospital at
Cambridge is served by Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, with several smaller medical centres in the city and a teaching hospital at
Cambridge City Council
Greater Cambridge Partnership
Cambridgeshire Association for Local History
Cambridgeshire Community Archives
Visit Cambridge
the official tourism website for Cambridge {{authority control Cities in the East of England County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Cambridgeshire Towns in Cambridgeshire Unparished areas in Cambridgeshire Boroughs in England
county town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam
The River Cam () is the main river flowing through Cambridge in eastern England. After leaving Cambridge, it flows north and east before joining the River Great Ouse to the south of Ely, at Pope's Corner. The total distance from Cambridge to ...
approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census
The decennial 2021 censuses of England and Wales and of Northern Ireland took place on 21 March 2021, and the census of Scotland took place on 20 March 2022. The censuses were administered by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in England an ...
, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951.
The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory
The Cavendish Laboratory is the Department of Physics at the University of Cambridge, and is part of the School of Physical Sciences. The laboratory was opened in 1874 on the New Museums Site as a laboratory for experimental physics and is named ...
, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs Church, and the chimney of Addenbrooke's Hospital. Anglia Ruskin University, which evolved from the Cambridge School of Art and the Cambridgeshire College of Arts and Technology, also has its main campus in the city.
Cambridge is at the heart of the high-technology Silicon Fen, which contains industries such as software and bioscience
''BioScience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Institute of Biological Sciences. It was established in 1964 and was preceded by the ''AIBS Bulletin'' (1951–19 ...
and many start-up companies born out of the university. Over 40 per cent of the workforce have a higher education qualification, more than twice the national average. The Cambridge Biomedical Campus, one of the largest biomedical research clusters in the world includes the headquarters of AstraZeneca, a hotel, and the relocated Royal Papworth Hospital.
The first game of association football took place at Parker's Piece
Parker's Piece is a flat and roughly square green common located near the centre of Cambridge, England, regarded by some as the birthplace of the rules of association football. The two main walking and cycling paths across it run diagonally, an ...
. The Strawberry Fair
Strawberry Fair is a local festival of music, entertainments, arts and crafts which has been held in Cambridge, England, since 1974. The fair is held on Midsummer Common on the first Saturday in June. It is completely run and organised by volun ...
music and arts festival and Midsummer Fair are held on Midsummer Common, and the annual Cambridge Beer Festival takes place on Jesus Green. The city is adjacent to the M11 and A14 roads. Cambridge station is less than an hour from London King's Cross railway station
King's Cross railway station, also known as London King's Cross, is a passenger railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, on the edge of Central London. It is in the London station group, one of the List of busiest railway stations in ...
.
History
Prehistory
Settlements have existed around the Cambridge area since prehistoric times. The earliest clear evidence of occupation is the remains of a year-old farmstead discovered at the site of Fitzwilliam College. Archaeological evidence of occupation through the Iron Age is a settlement on Castle Hill from the 1st century BC, perhaps relating to wider cultural changes occurring in southeastern Britain linked to the arrival of theBelgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
.
Roman
The principal Roman site is a small fort (') Duroliponte on Castle Hill, just northwest of the city centre around the location of the earlier British village. The fort was bounded on two sides by the lines formed by the present Mount Pleasant, continuing across Huntingdon Road into Clare Street. The eastern side followed Magrath Avenue, with the southern side running near to Chesterton Lane and Kettle's Yard before turning northwest at Honey Hill. It was constructed around AD 70 and converted to civilian use around 50 years later. Evidence of more widespread Roman settlement has been discovered including numerous farmsteads and a village in the Cambridge district of Newnham. A Roman coffin for Etheldreda was found next to the Roman town, and taken back by river for her burial in Ely. (Bede)Medieval


 Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain around 410, the location may have been abandoned by the Britons, although the site is usually identified as ,
Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain around 410, the location may have been abandoned by the Britons, although the site is usually identified as ,Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
(). Theodor Mommsen (). ''Historia Brittonum'', VI. Composed after AD 830. Hosted at Latin Wikisource. as listed among the 28 cities of Britain in the '' History of the Britons'' attributed to Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
.Ford, David Nash.The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Evidence exists that the invading Anglo-Saxons had begun occupying the area by the end of the century. Their settlement – also on and around Castle Hill – became known as Grantebrycge. (" Granta-bridge"). (By Middle English, the settlement's name had changed to "Cambridge", deriving from the word 'Camboricum', meaning 'Passage' or 'ford' of stream in a town or settlement, and the lower stretches of the Granta changed their name to match.)
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
grave goods have been found in the area. During this period, Cambridge benefited from good trade links across the hard-to-travel fenlands. By the 7th century, the town was less significant and described by Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
as a "little ruined city" containing the burial site of Æthelthryth (Etheldreda). Cambridge was on the border between the East and Middle Anglia
The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxon period.
Origins and territory
It is likely that Angles broke into the Midlands from East Anglia and the Wash e ...
n kingdoms and the settlement slowly expanded on both sides of the river.
The arrival of the Vikings was recorded in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' in 875. Viking rule, the Danelaw, had been imposed by 878 Their vigorous trading habits caused the town to grow rapidly. During this period the centre of the town shifted from Castle Hill on the left bank of the river to the area now known as the Quayside on the right bank. After the Viking period, the Saxons enjoyed a return to power, building churches such as St Bene't's Church, wharves, merchant houses and a mint, which produced coins with the town's name abbreviated to "Grant".
In 1068, two years after the Norman Conquest of England, William the Conqueror built a castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
on Castle Hill, the motte of which survives. Like the rest of the newly conquered kingdom, Cambridge fell under the control of the King and his deputies.
The first town charter was granted by Henry I between 1120 and 1131. It gave Cambridge monopoly of waterborne traffic and hithe tolls and recognised the borough court. The distinctive Round Church dates from this period. In 1209, Cambridge University was founded by Oxford students fleeing from hostility. The oldest existing college, Peterhouse, was founded in 1284.
In 1349 Cambridge was affected by the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
. Few records survive but 16 of 40 scholars at King's Hall died. The town north of the river was severely affected being almost wiped out. Following further depopulation after a second national epidemic in 1361, a letter from the Bishop of Ely suggested that two parishes in Cambridge be merged as there were not enough people to fill even one church. With more than a third of English clergy dying in the Black Death, four new colleges were established at the university over the following years to train new clergymen, namely Gonville Hall, Trinity Hall, Corpus Christi and Clare Clare may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Clare Range, a mountain range in Victoria Land
Australia
* Clare, South Australia, a town in the Clare Valley
* Clare Valley, South Australia
Canada
* Clare (electoral district), an electoral district
* Cl ...
.
In 1382 a revised town charter effects a "diminution of the liberties that the community had enjoyed", due to Cambridge's participation in the Peasants' Revolt. The charter transfers supervision of baking and brewing, weights and measures, and forestalling and regrating, from the town to the university.
King's College Chapel, was begun in 1446 by King Henry VI
Henry VI (6 December 1421 – 21 May 1471) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1422 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471, and disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. The only child of Henry V, he succeeded to the English throne a ...
. The chapel was built in phases by a succession of kings of England from 1446 to 1515, its history intertwined with the Wars of the Roses, and completed during the reign of King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disag ...
. The building would become synonymous with Cambridge, and currently is used in the logo for the Cambridge City Council.
Early modern
 Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of Hobson's Conduit in the early 1600s. Water was brought from Nine Wells, at the foot of the Gog Magog Hills to the southeast of Cambridge, into the centre of the town.
Cambridge played a significant role in the early part of the English Civil War as it was the headquarters of the Eastern Counties Association, an organisation administering a regional East Anglian army, which became the mainstay of the Parliamentarian military effort before the formation of the
Following repeated outbreaks of pestilence throughout the 16th century, sanitation and fresh water were brought to Cambridge by the construction of Hobson's Conduit in the early 1600s. Water was brought from Nine Wells, at the foot of the Gog Magog Hills to the southeast of Cambridge, into the centre of the town.
Cambridge played a significant role in the early part of the English Civil War as it was the headquarters of the Eastern Counties Association, an organisation administering a regional East Anglian army, which became the mainstay of the Parliamentarian military effort before the formation of the New Model Army
The New Model Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Th ...
. In 1643 control of the town was given by Parliament to Oliver Cromwell, who had been educated at Sidney Sussex College in Cambridge. The town's castle was fortified and garrisoned with troops and some bridges were destroyed to aid its defence. Although Royalist forces came within of the town in 1644, the defences were never used, and the garrison was stood down the following year.
Early-industrial era
In the 19th century, in common with many other English towns, Cambridge expanded rapidly, due in part to increased life expectancy and improved agricultural production leading to increased trade in town markets. The Inclosure Acts of 1801 and 1807 enabled the town to expand over surrounding open fields and in 1912 and again in 1935 its boundaries were extended to include Chesterton, Cherry Hinton, and Trumpington. The railway came to Cambridge in 1845 after initial resistance, with the opening of theGreat Eastern Railway
The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern R ...
's London to Norwich line. The station was outside the town centre following pressure from the university to restrict travel by undergraduates. With the arrival of the railway and associated employment came development of areas around the station, such as Romsey Town. The rail link to London stimulated heavier industries, such as the production of brick, cement and malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, wh ...
.
20th and 21st centuries
From the 1930s to the 1980s, the size of the city was increased by several large council estates. The biggest impact has been on the area north of the river, which are now the estates ofEast Chesterton
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sunrise, Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from ...
, King's Hedges, and Arbury where Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Rowan Williams lived and worked as an assistant priest in the early 1980s.
During World War II, Cambridge was an important centre for defence of the east coast. The town became a military centre, with an R.A.F. training centre and the regional headquarters for Norfolk, Suffolk, Essex, Cambridgeshire, Huntingdonshire, Hertfordshire, and Bedfordshire established during the conflict. The town itself escaped relatively lightly from German bombing raids, which were mainly targeted at the railway. 29 people were killed and no historic buildings were damaged. In 1944, a secret meeting of military leaders held in Trinity College laid the foundation for the allied invasion of Europe. During the war Cambridge served as an evacuation centre for over 7,000 people from London, as well as for parts of the University of London.
Cambridge was granted its city charter in 1951 in recognition of its history, administrative importance and economic success. Cambridge does not have a cathedral, traditionally a prerequisite for city status, instead falling within the Church of England Diocese of Ely
The Diocese of Ely is a Church of England diocese in the Province of Canterbury. It is headed by the Bishop of Ely, who sits at Ely Cathedral in Ely. There is one suffragan (subordinate) bishop, the Bishop of Huntingdon. The diocese now co ...
. In 1962 Cambridge's first shopping arcade, Bradwell's Court, opened on Drummer Street, though this was demolished in 2006. Other shopping arcades followed at Lion Yard, which housed a relocated Central Library for the city, and the Grafton Centre which replaced Victorian housing stock which had fallen into disrepair in the Kite area of the city. This latter project was controversial at the time.
The city gained its second University in 1992 when Anglia Polytechnic became Anglia Polytechnic University. Renamed Anglia Ruskin University in 2005, the institution has its origins in the Cambridge School of Art opened in 1858 by John Ruskin. The Open University also has a presence in the city, with an office operating on Hills Road.
Governance
Local government
East Chesterton
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sunrise, Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from ...
, King's Hedges, Market, Newnham, Petersfield, Queen Edith's, Romsey
Romsey ( ) is a historic market town in the county of Hampshire, England. Romsey was home to the 17th-century philosopher and economist William Petty and the 19th-century British prime minister, Lord Palmerston, whose statue has stood in the t ...
, Trumpington, and West Chesterton. At the 2019 election, Labour retained its majority.
Each of the 14 wards also elects councillors to Cambridgeshire County Council, which is responsible for services including school education, social care and highways.
Since 2017, Cambridge has also been within the area of the Cambridgeshire and Peterborough Combined Authority, which is led by a directly elected Mayor. The city is represented on the authority by the leader of the City Council.
Westminster
The parliamentary constituency of Cambridge covers most of the city; Daniel Zeichner ( Labour) has represented the seat since the 2015 general election. The seat was generally held by the Conservatives until it was won by Labour in 1992, then taken by the Liberal Democrats in 2005 and 2010, before returning to Labour in 2015. A southern area of the city, Queen Edith's ward, falls within the South Cambridgeshire constituency, whose MP is Anthony Browne (Conservative), first elected in 2019. The University of Cambridge formerly had two seats in the House of Commons; Sir Isaac Newton was one of the most notable MPs. The Cambridge University constituency was abolished under 1948 legislation, and ceased at the dissolution of Parliament for the 1950 general election, along with the other university constituencies.Geography and environment

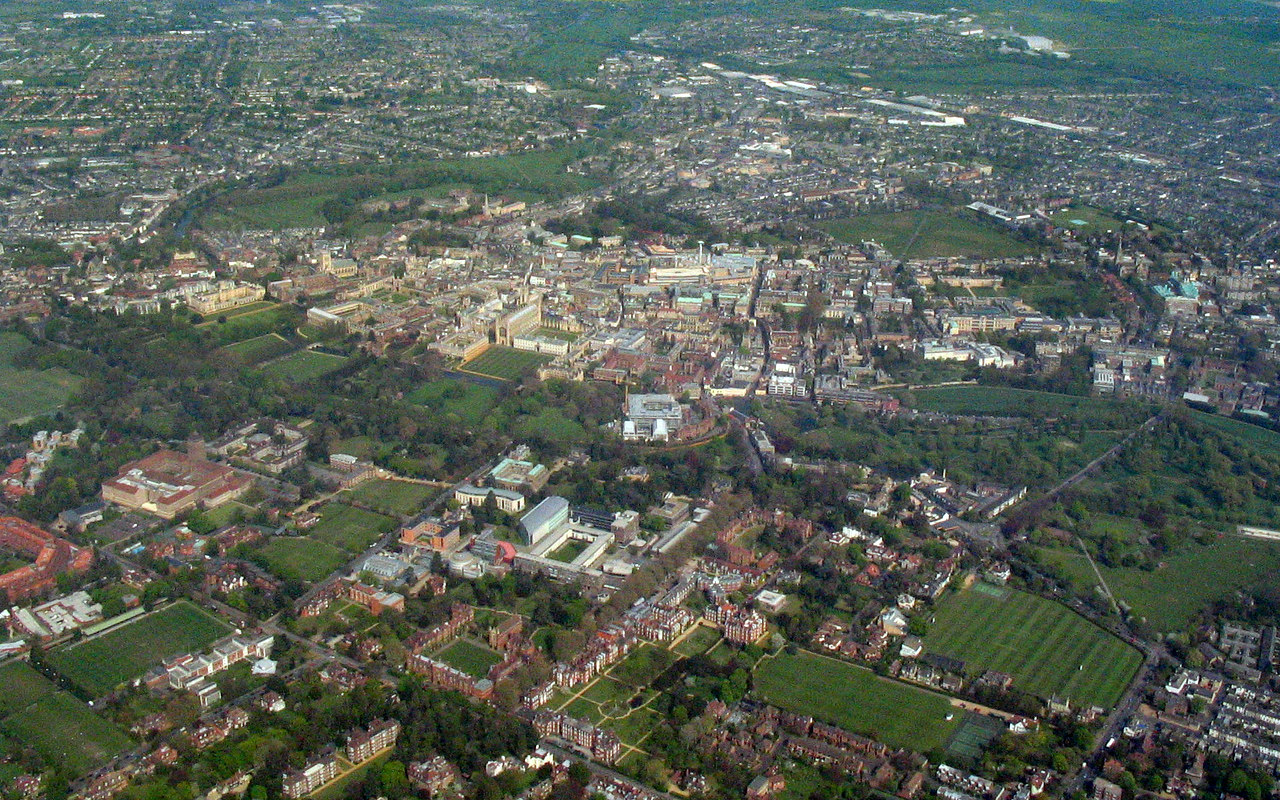
 Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between
Cambridge is situated about north-by-east of London and 95 miles (152 kilometres) east of Birmingham. The city is located in an area of level and relatively low-lying terrain just south of the Fens, which varies between above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The town was thus historically surrounded by low-lying wetlands that have been drained as the town has expanded.
The underlying geology of Cambridge consists of gault clay and Chalk Marl, known locally as Cambridge Greensand, partly overlaid by terrace gravel. A layer of phosphatic nodules ( coprolites) under the marl was mined in the 19th century for fertiliser; this became a major industry in the county, and its profits yielded buildings such as the Corn Exchange, Fulbourn Hospital
Fulbourn Hospital is a mental health facility located between the Cambridgeshire village of Fulbourn and the Cambridge city boundary at Cherry Hinton, about south-east of the city centre. It is managed by the Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS ...
, and St. John's Chapel until the Quarries Act 1894 and competition from America ended production.
The River Cam
The River Cam () is the main river flowing through Cambridge in eastern England. After leaving Cambridge, it flows north and east before joining the River Great Ouse to the south of Ely, at Pope's Corner. The total distance from Cambridge to ...
flows through the city from the village of Grantchester, to the southwest. It is bordered by water meadows within the city such as Sheep's Green as well as residential development. Like most cities, modern-day Cambridge has many suburbs and areas of high-density housing. The city centre of Cambridge is mostly commercial, historic buildings, and large green areas such as Jesus Green, Parker's Piece
Parker's Piece is a flat and roughly square green common located near the centre of Cambridge, England, regarded by some as the birthplace of the rules of association football. The two main walking and cycling paths across it run diagonally, an ...
and Midsummer Common. Many of the roads in the centre are pedestrianised.
Population growth has seen new housing developments in the 21st century, with estates such as the CB1 and Accordia schemes near the station, and developments such as Great Kneighton Great Kneighton is a large housing development and residential area in the southern part of the Cambridge, City of Cambridge district of Cambridgeshire, adjacent to, and integrated with, the neighbouring village of Trumpington. Together with nearby ...
, formally known as Clay Farm, and Trumpington Meadows currently under construction in the south of the city. Other major developments currently being constructed in the city are Darwin Green (formerly NIAB), and University-led developments at West Cambridge and North West Cambridge, (Eddington Eddington or Edington may refer to:
People
* Eddington Varmah, Liberian politician
* Eddington (surname), people with the surname
Places
Australia
* Eddington, Victoria
United Kingdom
* Eddington, Berkshire
* Eddington, Cambridge
* E ...
).
The entire city centre, as well as parts of Chesterton, Petersfield, West Cambridge, Newnham, and Abbey, are covered by an Air Quality Management Area, implemented to counter high levels of nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere.
Climate
The city has anoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
. ( Köppen: ''Cfb''). Cambridge has an official weather observing station, at the Cambridge University Botanic Garden, about south of the city centre. In addition, the Digital Technology Group of the university's Department of Computer Science and Technology maintains a weather station on the West Cambridge site, displaying current weather conditions online via web browsers or an app
App, Apps or APP may refer to:
Computing
* Application software
* Mobile app, software designed to run on smartphones and other mobile devices
* Web application or web app, software designed to run inside a web browser
* Adjusted Peak Performan ...
, and also an archive dating back to 1995.
The city, like most of the UK, has a maritime climate highly influenced by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
. Located in the driest region of Britain, Cambridge's rainfall averages around per year, around half the national average, The driest recent year was in 2011 with of rain at the Botanic Garden and at the NIAB site. This is just below the semi-arid precipitation threshold for the area, which is 350mm of annual precipitation. Conversely, 2012 was the wettest year on record, with reported. Snowfall accumulations are usually small, in part because of Cambridge's low elevation, and low precipitation tendency during transitional snow events.
Owing to its low-lying, inland, and easterly position within the British Isles, summer temperatures tend to be somewhat higher than areas further west, and often rival or even exceed those recorded in the London area. Cambridge also often records the annual highest national temperature in any given year – in July 2008 at NIAB and in August 2007 at the Botanic Garden are two recent examples. Other years include 1876, 1887, 1888, 1892, 1897, 1899 and 1900. The absolute maximum stands at recorded on 19 July 2022 at Cambridge University Botanic Garden. Before this date, Cambridge held the record for the all-time maximum temperature in the UK, after recording on 25 July 2019. Typically the temperature will reach or higher on over 25 days of the year over the 1981–2010 period, with the annual warmest day averaging over the same period.
The absolute minimum temperature recorded at the Botanic Garden site was , recorded in February 1947, although a minimum of was recorded at the now defunct observatory site in December 1879. More recently the temperature fell to on 11 February 2012, on 22 January 2013 and on 20 December 2010. The average frequency of air frosts ranges from 42.8 days at the NIAB site, to 48.3 days at the Botanic Garden per year over the 1981–2010 period. Typically the coldest night of the year at the Botanic Garden will fall to . Such minimum temperatures and frost averages are typical for inland areas across much of southern and central England.
Sunshine averages around 1,500 hours a year or around 35% of possible, a level typical of most locations in inland central England.
Ecology
The city contains three Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs), at Cherry Hinton East Pit, Cherry Hinton West Pit, and Travellers Pit, and ten Local Nature Reserves (LNRs): Sheep's Green and Coe Fen, Coldham's Common, Stourbridge Common, Nine Wells, Byron's Pool, West Pit, Paradise, Barnwell West, Barnwell East, and Logan's Meadow.Green belt
Cambridge is completely enclosed by green belt as a part of a wider environmental and planning policy first defined in 1965 and formalised in 1992. While some small tracts of green belt exist on the fringes of the city's boundary, much of the protection is in the surrounding South Cambridgeshire and nearby East Cambridgeshire districts, helping to maintain local green space, prevent further urban sprawl and unplanned expansion of the city, as well as protecting smaller outlying villages from further convergence with each other as well as the city.Demography
Historical population
Local census 1749 Census: Regional District 1801–1901 Civil Parish 1911–1961 District 1971–2011Ethnicity
Religion
Economy
 The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and
The town's river link to the surrounding agricultural land, and good road connections to London in the south meant Cambridge has historically served as an important regional trading post. King Henry I granted Cambridge a monopoly on river trade, privileging this area of the economy of Cambridge The town market provided for trade in a wide variety of goods and annual trading fairs such as Stourbridge Fair and Midsummer Fair
Midsummer Common is an area of common land in Cambridge, England. It lies northeast of the city centre on the south bank of the River Cam.
The common borders the River Cam and houseboats are often moored on the common's bank. The boathouse ...
were visited by merchants from across the country. The river was described in an account of 1748 as being "often so full of erchant boatsthat the navigation thereof is stopped for some time". For example, 2000 firkins of butter were brought up the river every Monday from the agricultural lands to the North East, particularity Norfolk, to be unloaded in the town for road transportation to London. Changing patterns of retail distribution and the advent of the railways led to a decline in Cambridge's importance as a market town.
Cambridge today has a diverse economy with strength in sectors such as research and development, software consultancy, high value engineering, creative industries, pharmaceuticals and tourism. Described as one of the "most beautiful cities in the world" by '' Forbes'' in 2010, with the view from The Backs being selected as one of the 10 greatest in England by National Trust chair Simon Jenkins
Sir Simon David Jenkins (born 10 June 1943) is a British author, a newspaper columnist and editor. He was editor of the ''Evening Standard'' from 1976 to 1978 and of ''The Times'' from 1990 to 1992.
Jenkins chaired the National Trust from 20 ...
, tourism generates over £750 million for the city's economy.
Cambridge and its surrounds are sometimes referred to as Silicon Fen, an allusion to Silicon Valley, because of the density of high-tech businesses and technology incubators that have developed on science parks around the city. Many of these parks and buildings are owned or leased by university colleges, and the companies often have been spun out of the university. Cambridge Science Park, which is the largest commercial R&D centre in Europe, is owned by Trinity College; St John's is the landlord of St John's Innovation Centre
St John's Innovation Centre (SJIC) is a business incubator in Cambridge, England. It houses a concentration of science and technology related businesses.
History
The idea for the innovation centre was first proposed by Dr Chris Johnson, who was ...
. Technology companies include Abcam, CSR, ARM Limited, CamSemi, Jagex and Sinclair. Microsoft has located its Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technologi ...
UK offices in West Cambridge, separate from the main Microsoft UK campus in Reading, and also has an office on Station Road.
Cambridge was also the home of Pye Ltd, founded in 1898 by W. G. Pye, who worked in the Cavendish Laboratory
The Cavendish Laboratory is the Department of Physics at the University of Cambridge, and is part of the School of Physical Sciences. The laboratory was opened in 1874 on the New Museums Site as a laboratory for experimental physics and is named ...
; it began by supplying the university and later specialised in wireless telegraphy equipment, radios, televisions and also defence equipment. Pye Ltd evolved into several other companies including TETRA radio equipment manufacturer Sepura. Another major business is Marshall Aerospace located on the eastern edge of the city. The Cambridge Network keeps businesses in touch with each other.
Transport

Road
Due to its rapid growth in the 20th century, Cambridge has a congested road network. TheM11 motorway
The M11 is a motorway that runs north from the North Circular Road (A406) in South Woodford to the A14, northwest of Cambridge, England. Originally proposed as a trunk road as early as 1915, various plans were considered throughout the 1960s ...
from east London terminates to the north-west of the city where it joins the A14, a major freight route which connects the port of Felixstowe on the east coast with the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Ind ...
. The A428 connects the city with the A1 at St Neots
St NeotsPronunciation of the town name: Most commonly, but variations that ''saint'' is said as in most English non-georeferencing speech, the ''t'' is by a small minority of the British pronounced and higher traces of in the final syllable ...
: the route continues westwards towards Oxford (as the A421) via Bedford and Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
. The A10 connects the city to King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, no ...
to the north via Ely Ely or ELY may refer to:
Places Ireland
* Éile, a medieval kingdom commonly anglicised Ely
* Ely Place, Dublin, a street
United Kingdom
* Ely, Cambridgeshire, a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, England
** Ely Cathedral
Ely Cathedral, formal ...
and is the historic route south to the City of London.
, the Greater Cambridge Parternship is consulting on plans comprising: transforming the bus network; investing in other sustainable travel scheme; and creating a sustainable travel zone, which includes the introduction of a congestion charge.
Cycling
As a university town lying on fairly flat ground and withtraffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
, Cambridge has the highest level of cycle use in the UK. According to the 2001 census, 25% of residents travelled to work by bicycle. Furthermore, a survey in 2013 found that 47% of residents travel by bike at least once a week.
Park and ride
Cambridge has five Park and Ride sites, all of which operate seven days a week and are aimed at encouraging motorists to park near the city's edge. Since 2011, the Cambridgeshire Guided Busway has carried bus services into the centre of Cambridge from St Ives, Huntingdon and other towns and villages along the routes, operated byStagecoach in the Fens
Stagecoach East is the divisional name for the bus operations of the Stagecoach Group in eastern England.
History
Under the control of the National Bus Company, ''Cambus Ltd.'' was set up when the Eastern Counties Omnibus Company was split in ...
and Whippet. The A service continues on to the railway station and Addenbrookes, before terminating at a new Park and Ride in Trumpington. Since 2017, it has also linked to Cambridge North railway station.
Air
Although Cambridge has its own airport,Cambridge City Airport
Cambridge City Airport , previously Marshall Airport Cambridge UK, is a regional airport in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the eastern outskirts of Cambridge, south of Newmarket Road and west of the village of Teversham, from the ...
, it has no scheduled services and is used mainly by charter and training flights and by Marshall Aerospace for aircraft maintenance. London Stansted Airport, about south via the M11 or direct rail, offers a broad range of international destinations.
Metro
In February 2020, consultations opened for a transport system known as the Cambridgeshire Autonomous Metro. It would have connected the historic city centre and the existing busway route with the mainline railway stations, Cambridge Science Park, and Haverhill. In May 2021 the newly elected mayor said he was focused instead on a "revamped bus network" but would not yet abandon the work done.Rail
East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
), (on the West Anglia Main Line) and St Pancras (on the Thameslink line). Commuter trains to King's Cross run every half-hour during peak hours, with a journey time of 53 minutes. Trains also run to and (via the Fen Line), (via the Breckland Line), , Birmingham, , , , Stansted Airport, Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
and Gatwick Airport railway stations.
A second railway station, Cambridge North, opened on 21 May 2017, having originally planned to open in March 2015. A third railway station, , near Addenbrooke's Hospital, has been proposed; it is expected to open in 2025.
Education
 Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate University of Cambridge and the local campus of Anglia Ruskin University, serve around 30,000 students, by some estimates. Cambridge University estimated its 2007/08 student population at 17,662, and Anglia Ruskin reports 24,000 students across its two campuses (one of which is outside Cambridge, in Chelmsford) for the same period. ARU now (2019) has additional campuses in London and Peterborough. State provision in the
Cambridge's two universities, the collegiate University of Cambridge and the local campus of Anglia Ruskin University, serve around 30,000 students, by some estimates. Cambridge University estimated its 2007/08 student population at 17,662, and Anglia Ruskin reports 24,000 students across its two campuses (one of which is outside Cambridge, in Chelmsford) for the same period. ARU now (2019) has additional campuses in London and Peterborough. State provision in the further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is education in addition to that received at secondary school, that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. I ...
sector includes Hills Road Sixth Form College, Long Road Sixth Form College, and Cambridge Regional College.
Both state and independent schools serve Cambridge pupils from nursery to secondary school age. State schools are administered by Cambridgeshire County Council, which maintains 251 schools in total, 35 of them in Cambridge city. Netherhall School, Chesterton Community College, the Parkside Federation (comprising Parkside Community College
Parkside Community College is a secondary academy school with 600 places for children aged 11–16, situated in Cambridge, Cambridgeshire. It is part of the United Learning Cambridge Cluster, along with Parkside Sixth, Coleridge Community Colleg ...
and Coleridge Community College), North Cambridge Academy
North Cambridge Academy is a small secondary school with academy status, located in North Cambridge, England. Founded in 1959 the school has also been known as Manor Community College, and The Manor.
Partner schools
Associate primary schools ...
and the Christian inter-denominational St Bede's School
Saint Bede's School is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form in the English town of Redhill, Surrey. In the most recent Ofsted inspection, the school was graded as "outstanding" in all areas. It now has over 1700 male and female pupi ...
provide comprehensive secondary education. Many other pupils from the Cambridge area attend village colleges, an educational institution unique to Cambridgeshire, which serve as secondary schools during the day and adult education centres outside of school hours. Independent schools in the city include The Perse School, Stephen Perse Foundation
The Stephen Perse Foundation is a family of independent schools in Cambridge and Saffron Walden for students aged 1 to 18.
The Foundation is made up of 3 nurseries (2 in Cambridge and 1 in Saffron Walden, Essex) for ages 1–5, 2 Junior Schoo ...
, Sancton Wood School
Sancton Wood School is a mixed private day school for children aged 1 to 16 located in Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, England. The school was founded as an independent primary school in 1976 and opened a senior school department in 1979.
The sch ...
, St Mary's School, Heritage School and The Leys School. The city has one university technical college, Cambridge Academy for Science and Technology, which opened in September 2014.
Sport
Football
 Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern
Cambridge played a unique role in the invention of modern football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
: the game's first set of rules were drawn up by members of the university in 1848. The Cambridge Rules were first played on Parker's Piece
Parker's Piece is a flat and roughly square green common located near the centre of Cambridge, England, regarded by some as the birthplace of the rules of association football. The two main walking and cycling paths across it run diagonally, an ...
and had a 'defining influence on the 1863 Football Association
The Football Association (also known as The FA) is the governing body of association football in England and the Crown Dependencies of Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man. Formed in 1863, it is the oldest football association in the world an ...
rules' which again were first played on Parker's Piece.
The city is home to Cambridge United FC
Cambridge United Football Club is a professional association football club based in the city of Cambridge, England. They compete in EFL League one , the 3rd tier of the English football league system. The club is based at the Abbey Stadium on ...
, who play at the Abbey Stadium. Formed in 1912, as Abbey United, they were elected to the Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engla ...
in 1970 and reached the Football League Second Division in 1978, although a serious decline in them in the mid-1980s saw them drop back down to the Football League Fourth Division
The Football League Fourth Division was the fourth-highest division in the English football league system from the 1958–59 season until the creation of the Premier League prior to the 1992–93 season. Whilst the division disappeared in name ...
and almost go out of business. Success returned to the club in the early 1990s when they won two successive promotions and reached the FA Cup quarter finals in both of those seasons and, in 1992, they came close to becoming the first English team to win three successive Football League promotions which would have taken them into the newly created FA Premier League
The Premier League (legal name: The Football Association Premier League Limited) is the highest level of the men's English football league system. Contested by 20 clubs, it operates on a system of promotion and relegation with the English Foo ...
; however, they were beaten in the play-offs and another decline set in. In 2005, they were relegated from the Football League and, for the second time in 20 years, narrowly avoided going out of business. After nine years of non-league football, they returned to the Football League in 2014 by winning the Conference National
The National League, known as the Vanarama National League for sponsorship reasons, is the highest level of the National League System and fifth-highest of the overall English football league system. It is the highest league that is semi-profes ...
play-offs.
Cambridge United WFC
Cambridge United WFC is a women's only football club based in the city of Cambridge, England. The team compete in the FA Women's National Division One South East
FA, Fa or fa may refer to:
People
* Fa of Xia, King of China 1747–1728 BC
* F ...
is a women's only football club based in Cambridge. The team compete in the FA Women's National League South East. The club plays home games at St Neots Town F.C.
St Neots Town Football Club is an English semi-professional football club based in St Neots, Cambridgeshire. The club are currently members of the . Founded in 1879 and known as "The Saints", St Neots Town play their home matches at Premier Pl ...
and the Abbey Stadium.
Cambridge City FC
Cambridge City Football Club is a association football, football club based in Cambridgeshire, England who currently play in the . Formed in 1908 as Cambridge Town F.C. in Cambridge, they played their home games at the City Ground (Cambridge), ...
of the Southern Football League Premier Division now play in the adjoining village of Histon. Formed in Cambridge in 1908, as Cambridge Town, the club were Southern Premier League Southern Premier League may refer to: Association football
* Southern Football League, premier division, in England
* Southern Championship, formerly known as the Southern Premier League, in Tasmania, Australia
* FootballSouth Premier League, also k ...
champions in 1962–63, the highest they have finished in the English football pyramid
The English football league system, also known as the football pyramid, is a series of interconnected leagues for men's association football clubs in England, with five teams from Wales, one from Guernsey, one from Jersey and one from the Isl ...
. After a legal dispute with their landlords, the club left their home ground in Cambridge in order to groundshare with fellow Southern League Premier club Histon FC
Histon Football Club is a football club based in the village of Histon, Cambridgeshire, England. The club are currently members of the and play at Bridge Road in Impington. Nicknamed 'the Stutes', originating from the club's previous name His ...
in 2013-14 and intend to construct a new ground outside the city, in Sawston.
Cricket
Parker's Piece was used for first-class cricket matches from 1817 to 1864. The University of Cambridge's cricket ground, Fenner's, is located in the city and is one of the home grounds for minor counties team Cambridgeshire CCC. The Cambridgeshire Cricket Association operates an amateur club cricket league with six adult divisions, including numerous clubs in the city, plus junior divisions. Most of the university colleges also operate their own teams, and there are several casual village cricket teams that play in the city suburbs.Rugby
The city is represented in both codes of Rugby football. Rugby union clubCambridge R.U.F.C.
Cambridge Rugby Union Football Club or CRUFC ('The Blood & Sand') is a rugby union club representing the city of Cambridge, England. Formed in 1923 the club currently competes in the third tier of the English rugby union system, National Leag ...
were founded in 1923 and play in National League 1 at their home ground, Grantchester Road
Grantchester Road is a rugby stadium in Cambridge, England. Situated on Grantchester Road, off Barton Road in the southwest of Cambridge, it is the home ground of Cambridge R.U.F.C., and is also used by University of Cambridge
The University o ...
, in the south-west corner of the city. Cambridge Lions represent the city in rugby league and are members of East Rugby League.
Watersports
 The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for rowing and the
The River Cam, which runs through the city centre, is used for boating. The university and its colleges are well known for rowing and the Cambridgeshire Rowing Association
The Cambridgeshire Rowing Association (CRA) is based in Cambridge, United Kingdom, UK. It is the administrative body for non-college sport rowing, rowing in Cambridge and since 1868 has organised races such as the CRA Bumps race, Bumps as well as ...
, formed in 1868, organises competitive rowing on the river outside of the university. Rowing clubs based in the city include City of Cambridge RC, Cambridge '99 RC
Cambridge '99 Rowing Club, generally referred to as 'Nines', is based on Kimberley Road in the historic City of Cambridge, UK.
Club history
Cambridge '99 Rowing Club was formed in 1899 and is the third oldest of the 'Town' clubs in Cambridge. ...
, Cantabrigian RC and Rob Roy BC. Parts of the Cam are used for recreational punting, a type of boating in which the craft is propelled by pushing against the river bed with a quant pole.
Cambridge Swimming Club, Cambridge Dive team and City of Cambridge Water Polo Club are all based at Parkside Swimming Pool.
Parkour/freerunning
Home and training ground to many influential traceurs, Cambridge is well known for its vibrant, and at times high-profile,parkour
Parkour () is an athletic training discipline or sport in which practitioners (called ''traceurs'') attempt to get from point A to point B in the fastest and most efficient way possible, without assisting equipment and often while performing a ...
and freerunning scene.
Other sports
Cambridge is home to tworeal tennis
Real tennis – one of several games sometimes called "the sport of kings" – is the original racquet sport from which the modern game of tennis (also called "lawn tennis") is derived. It is also known as court tennis in the United Sta ...
courts (out of about 50 in the world) at Cambridge University Real Tennis Club. Cambridgeshire Cats
The Cambridgeshire Cats are an American football team competing in Southern Football Conference 1, East Division of the BAFA National Leagues (BAFA NL), with their home games played at Coldhams Common in Cambridge. The club was first formed in 1 ...
play American football at Coldham's Common. Cambridge Royals are members of the British Baseball Federation's Triple-A South Division. Cambridge has two cycling clubs: Team Cambridge and Cambridge Cycling Club. Cambridge & Coleridge Athletic Club is the city's track and field club, based at the University of Cambridge's Wilberforce Road track. Cambridge Handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball or Olympic handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the g ...
Club compete in the men's England Handball National Super 8 League and the women's England Handball National Super 7 League. There are three field hockey clubs; Cambridge City Hockey Club, Cambridge South Hockey Club and Cambridge Nomads.
The city is also represented in polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ...
by Cambridge Polo Club, based in Barton, just outside the city. The Romsey Town Rollerbillies play roller derby
Roller derby is a roller skating contact sport played by two teams of fifteen members. Roller derby is played by approximately 1,250 amateur leagues worldwide, mostly in the United States.
Game play consists of a series of short scrimmages (jam ...
in Cambridge. Speedway racing was formerly staged at a greyhound stadium in Coldhams Lane.
Varsity sports
Cambridge is known for the sporting events between the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford, especially the rugby union Varsity Match and the Boat Race, though many of these do not take place within either Cambridge or Oxford.Culture


Theatre
Cambridge's main traditional theatre is the Arts Theatre, a venue with 666 seats in the town centre. The theatre often has touring shows, as well as those by local companies. The largest venue in the city to regular hold theatrical performances is the Cambridge Corn Exchange with a capacity of 1,800 standing or 1,200 seated. Housed within the city's 19th century former corn exchange building the venue was used for a variety of additional functions throughout the 20th century including tea parties, motor shows, sports matches and a music venue with temporary stage. The City Council renovated the building in the 1980s, turning it into a full-time arts venue, hosting theatre, dance and music performances. The newest theatre venue in Cambridge is the 220-seat J2, part of Cambridge Junction in Cambridge Leisure Park. The venue was opened in 2005 and hosts theatre, dance, live music and comedy The ADC Theatre is managed by the University of Cambridge, and typically has 3 shows a week during term time. It hosts the Cambridge University Footlights Dramatic Club which has produced many notable figures in British comedy. The Mumford Theatre is part of Anglia Ruskin University, and hosts shows by both student and non-student groups. There are also a number of venues within the colleges.Museums
Within the city there are several notable museums, some run by theUniversity of Cambridge Museums
University of Cambridge Museums is a consortium of the eight museums of the University of Cambridge, which came into being in 2012 following awarding of Major Partner Museums status by Arts Council England. The consortium works in partnership w ...
consortium and others independent of it.
The Fitzwilliam Museum is the city's largest, and is the lead museum of the University of Cambridge Museums. Founded in 1816 from the bequeathment and collections of Richard, Viscount FitzWilliam, the museum was originally located in the building of the Perse Grammar School
(He who does things for others does them for himself)
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public schoolIndependent day school
, religion = Nondenominational Christian
, president =
, head_label = Head
, h ...
in Free School Lane. After a brief housing in the University of Cambridge library, it moved to its current, purpose-built building on Trumpington Street in 1848. The museum has five departments: Antiquities; Applied Arts; Coins and Medals; Manuscripts and Printed Books; and Paintings, Drawings and Prints. Other members of the University of Cambridge Museums are the Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, The Polar Museum, The Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences, Museum of Classical Archaeology, The Whipple Museum of the History of Science, and the University Museum of Zoology.
The Museum of Cambridge, formerly known as the Cambridge & County Folk Museum, is a social history
Social history, often called the new social history, is a field of history that looks at the lived experience of the past. In its "golden age" it was a major growth field in the 1960s and 1970s among scholars, and still is well represented in his ...
museum located in a former pub on Castle Street. The Centre for Computing History, a museum dedicated to the story of the Information age, moved to Cambridge from Haverhill in 2013. Housed in a former sewage pumping station, the Cambridge Museum of Technology has a collection of large exhibits related to the city's industrial heritage.
Music
Popular music
Pink Floyd
Pink Floyd are an English rock band formed in London in 1965. Gaining an early following as one of the first British psychedelic music, psychedelic groups, they were distinguished by their extended compositions, sonic experimentation, philo ...
are the most notable band with roots in Cambridge. The band's former songwriter, guitarist and vocalist Syd Barrett
Roger Keith "Syd" Barrett (6 January 1946 – 7 July 2006) was an English singer, songwriter, and musician who co-founded the rock band Pink Floyd in 1965. Barrett was their original frontman and primary songwriter, becoming known for his ...
was born and lived in the city, and he and another founding member, Roger Waters
George Roger Waters (born 6 September 1943) is an English musician, singer-songwriter and composer. In 1965, he co-founded the progressive rock band Pink Floyd. Waters initially served as the bassist, but following the departure of singer-so ...
, went to school together at Cambridgeshire High School for Boys. David Gilmour
David Jon Gilmour ( ; born 6 March 1946) is an English guitarist, singer, songwriter, and member of the rock band Pink Floyd. He joined as guitarist and co-lead vocalist in 1967, shortly before the departure of founding member Syd Barrett. P ...
, the guitarist who replaced Barrett, was also a Cambridge resident and attended the nearby Perse School
(He who does things for others does them for himself)
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public schoolIndependent day school
, religion = Nondenominational Christian
, president =
, head_label = Head
, he ...
. Bands that were formed in Cambridge include Clean Bandit, Henry Cow, The Movies, Katrina and the Waves
Katrina and the Waves were a British rock band widely known for the 1985 hit " Walking on Sunshine". They also won the 1997 Eurovision Song Contest with the song "Love Shine a Light".
History Pre-history (1975–1980)
The band's earliest inc ...
, The Soft Boys, Ezio The Broken Family Band
The Broken Family Band was a British rock band from Cambridge and London.
The band was formed in Cambridge, England by Steven Adams, Jay Williams, Micky Roman and Gavin Johnson in 2001, following the break-up of Adams and Williams' indie ro ...
, Uncle Acid & the Deadbeats
Uncle Acid & the Deadbeats (written as Uncle Acid and the deadbeats or simply Uncle Acid) are an English rock band, formed in Cambridge by Kevin Starrs. The band have released five albums – the most recent, ''Wasteland'', was released in Octob ...
, and the pop-classical group the King's Singers, who were formed at the university. Solo artist Boo Hewerdine is from Cambridge, as are drum and bass
Drum and bass (also written as drum & bass or drum'n'bass and commonly abbreviated as D&B, DnB, or D'n'B) is a genre of electronic dance music characterized by fast breakbeats (typically 165–185 beats per minute) with heavy bass and sub-ba ...
artists (and brothers) Nu:Tone and Logistics. Singers Matthew Bellamy, of the rock band Muse, Tom Robinson, Olivia Newton-John and Charli XCX were born in the city. 2012 Mercury Prize winners Alt-J
Alt-J (stylised as alt-J, real name Δ) are an English indie rock band formed in 2007 in Leeds. Their lineup includes Joe Newman (guitar/lead vocals), Thom Sonny Green (drums), Gus Unger-Hamilton (keyboards/vocals), and formerly Gwilym Sainsbur ...
are based in Cambridge.
Live music venues hosting popular music in the city include the Cambridge Corn Exchange, Cambridge Junction and the Portland Arms, as well as The Blue Moon.
Classical music
Started in 1991, the annual Cambridge Music Festival takes place each November. The Cambridge Summer Music Festival takes place in July.Contemporary art
Cambridge contains Kettle's Yard gallery of modern and contemporary art and the Heong Gallery which opened to the public in 2016 at Downing College. Anglia Ruskin University operates the publicly accessible Ruskin Gallery within the Cambridge School of Art.Wysing Arts Centre
Wysing Arts Centre is a contemporary arts residency centre and campus for artistic production, experimentation and learning in South Cambridgeshire, England. The centre was established in 1989 and completed a £1.7 million capital developm ...
, one of the leading research centres for the visual arts in Europe, is associated with the city, though is located several miles west of Cambridge. Artist-run organisations including Aid & Abet, Cambridge Art Salon, Changing Spaces and Motion Sickness also run exhibitions, events and artists' studios in the city, often in short-term or temporary spaces.
Festivals and events

 Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer.
Several fairs and festivals take place in Cambridge, mostly during the British summer. Midsummer Fair
Midsummer Common is an area of common land in Cambridge, England. It lies northeast of the city centre on the south bank of the River Cam.
The common borders the River Cam and houseboats are often moored on the common's bank. The boathouse ...
dates back to 1211, when it was granted a charter by King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
. Today it exists primarily as an annual funfair with the vestige of a market attached and is held over several days around or close to midsummers day. On the first Saturday in June Midsummer Common is the site for Strawberry Fair
Strawberry Fair is a local festival of music, entertainments, arts and crafts which has been held in Cambridge, England, since 1974. The fair is held on Midsummer Common on the first Saturday in June. It is completely run and organised by volun ...
, a free music and children's fair, with various market stalls. For one week in May, on Jesus Green, the annual Cambridge Beer Festival has been held since 1974.
Cambridge Folk Festival is held annually in the grounds of Cherry Hinton Hall. The festival has been organised by the city council since its inception in 1964. The Cambridge Summer Music Festival is an annual festival of classical music, held in the university's colleges and chapels. The Cambridge Shakespeare Festival is an eight-week season of open-air performances of the works of William Shakespeare, held in the gardens of various colleges of the university. Started in 1977, the Cambridge Film Festival was held annually in July, moving to September in 2008 to avoid a clash with the rescheduled Edinburgh Film Festival
The Edinburgh International Film Festival (EIFF) is a film festival that runs for two weeks in June each year. Established in 1947, it is the world's oldest continually running film festival. EIFF presents both UK and international films (all ti ...
.
The Cambridge Science Festival, typically held annually in March, is the United Kingdom's largest free science festival. The Cambridge Literary Festival, which focusses on contemporary literary fiction and non-fiction, is held bi-annually in April and November. Between 1975 and 1985 the Cambridge Poetry Festival was held biannually. Other festivals include the annual Mill Road Winter Fair, held the first Saturday of December, the E-luminate Festival, which took place every February from 2013 to 2018, and The Big Weekend, a city outdoor event organised by the City Council every July.
Three Cambridge Free Festivals held in 1969, 1970, and 1971 that featured artists including David Bowie, King Crimson, Roy Harper, Spontaneous Combustion, UFO and others are believed by the festival organiser to have been the first free multiple-day rock music festivals held in the UK.
Literature and film
The city has been the setting for all or part of several novels, including Douglas Adams' '' Dirk Gently's Holistic Detective Agency'', Rose Macaulay's ''They Were Defeated
''They Were Defeated'' is a historical novel by Rose Macaulay, first published in 1932. It was published in the USA under the title ''The Shadow Flies''. It was through the publication of the American edition that Macaulay got back in touch with ...
'', Kate Atkinson Kate Atkinson may refer to:
* Kate Atkinson (actress) (born 1972), Australian actress
* Kate Atkinson (writer)
Kate Atkinson (born 20 December 1951) is an English writer of novels, plays and short stories. She is known for creating the Jac ...
's '' Case Histories'', Rebecca Stott's ''Ghostwalk'' and Robert Harris' ''Enigma'', while Susanna Gregory
Susanna Gregory is the pseudonym of Elizabeth Cruwys, a Cambridge academic who was previously a coroner's officer. She writes detective fiction, and is noted for her series of mediaeval mysteries featuring Matthew Bartholomew, a teacher of medici ...
wrote a series of novels set in 14th century Cambridge. Gwen Raverat, the granddaughter of Charles Darwin, talked about her late Victorian Cambridge childhood in her memoir '' Period Piece'', and '' The Night Climbers of Cambridge'' is a book written by Noel Symington
''The Night Climbers of Cambridge'' is a book, written under the pseudonym "Whipplesnaith", about nocturnal climbing on the colleges and town buildings of Cambridge, England, in the 1930s. The book remains popular among Cambridge University stud ...
under the pseudonym "Whipplesnaith" about nocturnal climbing on the colleges and town buildings of Cambridge in the 1930s.
Fictionalised versions of Cambridge appear in Philippa Pearce's '' Tom's Midnight Garden'' and '' Minnow on the Say'', the city renamed as Castleford, and as the home of Tom Sharpe's fictional college in '' Porterhouse Blue''.
ITV
ITV or iTV may refer to:
ITV
*Independent Television (ITV), a British television network, consisting of:
** ITV (TV network), a free-to-air national commercial television network covering the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man, and the Channel Islan ...
TV series ''Granchester'' was partly filmed in Cambridge.
Television
News and television programmes are broadcast from the BBC East studio in Cambridge that is home to BBC Look East (West) which covers the city, Cambridgeshire, Northamptonshire, Bedfordshire,Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
(Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (), abbreviated Bucks, is a ceremonial county in South East England that borders Greater London to the south-east, Berkshire to the south, Oxfordshire to the west, Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-ea ...
) and parts of Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For govern ...
. ITV Anglia is another TV news which broadcasts from Norwich.
Public services
Addenbrooke's
Addenbrooke's Hospital is an internationally renowned large teaching hospital and research centre in Cambridge, England, with strong affiliations to the University of Cambridge. Addenbrooke's Hospital is based on the Cambridge Biomedical Campu ...
. Located on the Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Addenbrooke's is one of the largest hospitals in the United Kingdom and is a designated regional trauma centre.
The East of England Ambulance Service covers the city and has an ambulance station on Hills Road. The smaller Brookfields Hospital stands on Mill Road. Cambridgeshire Constabulary
Cambridgeshire Constabulary is the local territorial police force that covers the county of Cambridgeshire and Peterborough unitary authority. It provides law enforcement and security for an area of and population of 856,000 people, in a pred ...
provides the city's policing; the main police station is at Parkside, adjacent to the city's fire station, operated by Cambridgeshire Fire and Rescue Service.
Cambridge Water Company supplies water services to the city, while Anglian Water provides sewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff (stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drainage, drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, a ...
services. For the supply of electricity, Cambridge is part of the East of England
The East of England is one of the nine official regions of England. This region was created in 1994 and was adopted for statistics purposes from 1999. It includes the ceremonial counties of Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire, Essex, Hertfordshire ...
region, for which the distribution network operator is UK Power Networks. The city has no power stations, though a five-metre wind turbine, part of a Cambridge Regional College development, can be seen in King's Hedges. The Cambridge Electric Supply Company had provided the city with electricity since the early twentieth century from Cambridge power station. Upon nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
of the electricity industry in 1948 ownership passed to the British Electricity Authority
The British Electricity Authority (BEA) was established as the central British electricity authority in 1948 under the nationalisation of Great Britain's electricity supply industry enacted by the Electricity Act 1947. The BEA was responsible for ...
and later to the Central Electricity Generating Board. Electricity connections to the national grid rendered the small 7.26 megawatt (MW) coal fired power station redundant. It closed in 1965 and was subsequently demolished; in its final year of operation it delivered 2771 MWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
of electricity to the city.
Following the Public Libraries Act 1850 the city's first public library, located on Jesus Lane, was opened in 1855. It was moved to the Guildhall in 1862, and is now located in the Grand Arcade shopping centre. The library was reopened in September 2009, after having been closed for refurbishment for 33 months, more than twice as long as was forecast when the library closed for redevelopment in January 2007. As of 2018 the city contains six public libraries, run by the County Council.
The Cambridge City Cemetery is located to the north of Newmarket Road.
Religion
Cambridge has a number of churches, some of which form a significant part of the city's architectural landscape. Like the rest of Cambridgeshire it is part of theAnglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
Diocese of Ely
The Diocese of Ely is a Church of England diocese in the Province of Canterbury. It is headed by the Bishop of Ely, who sits at Ely Cathedral in Ely. There is one suffragan (subordinate) bishop, the Bishop of Huntingdon. The diocese now co ...
.
Great St Mary's Church has the status of "University Church". Many of the university colleges contain chapels that hold services according to the rites and ceremonies of the Church of England, while the chapel of St Edmund's College is Roman Catholic. The city also has a number of theological colleges
A seminary, school of theology, theological seminary, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called ''seminarians'') in scripture, theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy, ...
training clergy for ordination into a number of denominations, with affiliations to both the University of Cambridge and Anglia Ruskin University.
Cambridge is in the Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia and is served by the large Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
Our Lady and the English Martyrs Church at the junction of Hills Road and Lensfield Road, St Laurence's on Milton Road, St Vincent De Paul Church on Ditton Lane and by the church of St Philip Howard, in Cherry Hinton Road.
There is a Russian Orthodox church under the Diocese of Sourozh who worship at the chapel of Westcott House, the Greek Orthodox Church holds services at the purpose-built St Athanasios church under the Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain, while the Romanian Orthodox Church share St Giles' with the Church of England.
There are two Methodist churches in the city. Wesley Methodist Church was built in 1913, and is located next to
Christ's Pieces. The Castle Street Methodist Church is the oldest of the two, having been built in 1823, and was formerly a Primitive Methodist
The Primitive Methodist Church is a Methodist Christian denomination with the holiness movement. It began in England in the early 19th century, with the influence of American evangelist Lorenzo Dow (1777–1834).
In the United States, the Primiti ...
church.
There are three Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
Meetings in Cambridge, located on Jesus Lane, Hartington Grove, and a Meeting called "Oast House" that meets in Pembroke College.
An Orthodox synagogue and Jewish student centre is located on Thompson's Lane, operated jointly by the Cambridge Traditional Jewish Congregation and the Cambridge University Jewish Society, which is affiliated to the Union of Jewish Students. The Beth Shalom Reform synagogue which previously met at a local school, opened a purpose-built synagogue in 2015. There is also a student-led egalitarian minyan
In Judaism, a ''minyan'' ( he, מניין \ מִנְיָן ''mīnyān'' , lit. (noun) ''count, number''; pl. ''mīnyānīm'' ) is the quorum of ten Jewish adults required for certain religious obligations. In more traditional streams of Jud ...
which holds services on Friday evenings.
Cambridge Central Mosque
The Cambridge Central Mosque is Europe's first eco-friendly mosque and the first purpose-built mosque within the city of Cambridge, England. Its mandate is to meet the needs of the Muslim community in the UK and beyond by facilitating good pract ...
is the main place of worship for Cambridge's community of around 4,000 Muslims. Opened in 2019, it is described as Europe's first eco-friendly mosque and is the first purpose-built mosque within the city. The Abu Bakr Jamia Islamic Centre on Mawson Road and the Omar Faruque Mosque and Cultural Centre in Kings Hedges are additional places of Muslim worship.
Cambridge Buddhist Centre, which belongs to Triratna Buddhist Community, was opened in the former Barnwell Theatre on Newmarket Road in 1998. There are also several local Buddhist meditation groups from various Buddhist including Samatha Trust and Buddha Mettā Society.
A Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
shrine was opened in 2010 at the Bharat Bhavan Indian cultural centre off Mill Road.
A Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
community has met in the city since 1982, and a Gurdwara was opened in Arbury in 2013.
Twinned cities
Cambridge is twinned with two cities. Like Cambridge, both have universities and are also similar in population; Heidelberg, Germany since 1965, and Szeged, Hungary since 1987.Panoramic gallery
See also
* List of bridges in Cambridge *List of churches in Cambridge
The following is a list of churches in Cambridge, England:
Active churches and chapels, other than college and school chapels
College and school chapels
Disused churches
Demolished churches
Maps
References
{{Lists of churche ...
* Cambridgeshire Archives and Local Studies
Cambridgeshire Archives and Local Studies Service (CALS) is a UK local government institution which collects and preserves archives, other historical documents and printed material relating to the modern county of Cambridgeshire, which includes th ...
* :Buildings and structures in Cambridge
* :Organisations based in Cambridge
* :People from Cambridge
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * Rawle, Tim (author and photographer), John Adamson (editor). '' Cambridge'' (new ed. with foreword by William Bortrick). Cambridge: The Oxbridge Portfolio (2016), 204 pp.External links
Cambridge City Council
Greater Cambridge Partnership
Cambridgeshire Association for Local History
Cambridgeshire Community Archives
Visit Cambridge
the official tourism website for Cambridge {{authority control Cities in the East of England County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Cambridgeshire Towns in Cambridgeshire Unparished areas in Cambridgeshire Boroughs in England