Calcium Channel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to
Other calcium channels can also be regulated by both voltage and ligands to provide precise control over ion flow. Some cation channels allow calcium as well as other cations to pass through the membrane. Calcium channels can participate in the creation of
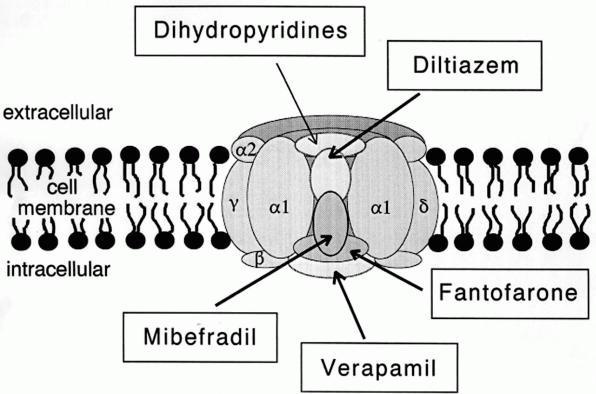 L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body,
L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body,
calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeabili ...
, which are a type of calcium channel regulated by changes in membrane potential. Some calcium channels are regulated by the binding of a ligand.Striggow F, Ehrlich BE (August 1996). "Ligand-gated calcium channels inside and out". ''Current Opinion in Cell Biology''. 8 (4): 490–495. doi: 10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80025-1. PMID
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintain the ...
br>8791458Other calcium channels can also be regulated by both voltage and ligands to provide precise control over ion flow. Some cation channels allow calcium as well as other cations to pass through the membrane. Calcium channels can participate in the creation of
action potentials
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells ...
across cell membranes. Calcium channels can also be used to release calcium ions as second messengers within the cell, affecting downstream signaling pathways.
Comparison tables
The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated.Voltage-gated
* ''voltage-operated calcium channels''Ligand-gated
*''receptor-operated calcium channels''Non-selective Channels Permeable to Calcium
There are several cation channel families that allow positively charged ions including calcium to pass through. These includeP2X receptors
The ATP-gated P2X receptor cation channel familyTC# 1.A.7, or simply P2X receptor family, consists of cation-permeable ligand-gated ion channels that open in response to the binding of extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate ( ATP). They belong ...
, Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels, Cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels, Acid-sensing ion channels, and SOC channels Store-operated channels (SOCs) are ion channels located in the plasma membrane of cells. These channels are most studied in regard to their role in calcium entry into the cytoplasm from extracellular milieu. There are other SOC channels selective ...
. These channels can be regulated by membrane voltage potentials, ligands, and/or other cellular conditions. Cat-Sper channels, found in mammalian sperm, are one example of this as they are voltage gated and ligand regulated.
Pharmacology
 L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body,
L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is ess ...
is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypertension.
T-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
. Increased calcium conductance in the neurons leads to increased depolarization and excitability. This leads to a greater predisposition to epileptic episodes. Calcium channel blockers reduce the neuronal calcium conductance and reduce the likelihood of experiencing epileptic attacks.
See also
* .References
External links
* * * * {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels Electrophysiology Integral membrane proteins Calcium channels