Belarus Route P81 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a
' ''. An ethno-religious theory suggests that the name used to describe the part of old  The name ''Rus'' is often conflated with its Latin forms ''Russia'' and ''Ruthenia'', thus Belarus is often referred to as ''White Russia'' or ''White Ruthenia''. The name first appeared in
The name ''Rus'' is often conflated with its Latin forms ''Russia'' and ''Ruthenia'', thus Belarus is often referred to as ''White Russia'' or ''White Ruthenia''. The name first appeared in
 In the 9th century the territory of modern Belarus became part of
In the 9th century the territory of modern Belarus became part of
 On 2 February 1386, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the
On 2 February 1386, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the
 The union between Poland and Lithuania ended in 1795 with the
The union between Poland and Lithuania ended in 1795 with the
 In 1919 a part of Belarus under Russian rule emerged as the
In 1919 a part of Belarus under Russian rule emerged as the
 In 1939,
In 1939,
 After the war, Belarus was among the 51 founding member states of the
After the war, Belarus was among the 51 founding member states of the
 In March 1990,
In March 1990,
United Nations (October 13, 2015). Mass protests erupted across the country following the disputed
Mass protests erupted across the country following the disputed
 The highest point is
The highest point is
 Belarus, by constitution, is a
Belarus, by constitution, is a  The House of Representatives has the power to appoint the
The House of Representatives has the power to appoint the
 Belarus has often been described as "Europe's last dictatorship" by some media outlets, politicians and authors due to its authoritarian government. The
Belarus has often been described as "Europe's last dictatorship" by some media outlets, politicians and authors due to its authoritarian government. The  In the 2006 presidential election, Lukashenko was opposed by
In the 2006 presidential election, Lukashenko was opposed by
 The Byelorussian SSR was one of the two Soviet republics that joined the
The Byelorussian SSR was one of the two Soviet republics that joined the  Bilateral relations with the United States are strained; the United States had not had an ambassador in Minsk since 2007 and Belarus never had an ambassador in Washington since 2008. Diplomatic relations remained tense, and in 2004, the United States passed the Belarus Democracy Act, which authorized funding for anti-government Belarusian NGOs, and prohibited loans to the Belarusian government, except for humanitarian purposes.
Sino-Belarusian relations have improved, strengthened by the visit of President Lukashenko to China in October 2005. Belarus also has strong ties with
Bilateral relations with the United States are strained; the United States had not had an ambassador in Minsk since 2007 and Belarus never had an ambassador in Washington since 2008. Diplomatic relations remained tense, and in 2004, the United States passed the Belarus Democracy Act, which authorized funding for anti-government Belarusian NGOs, and prohibited loans to the Belarusian government, except for humanitarian purposes.
Sino-Belarusian relations have improved, strengthened by the visit of President Lukashenko to China in October 2005. Belarus also has strong ties with
 Lieutenant General
Lieutenant General
 Belarus's
Belarus's
 Belarus is divided into six regions called oblasts ( be, вобласць; russian: область), which are named after the cities that serve as their administrative centers:
Belarus is divided into six regions called oblasts ( be, вобласць; russian: область), which are named after the cities that serve as their administrative centers:

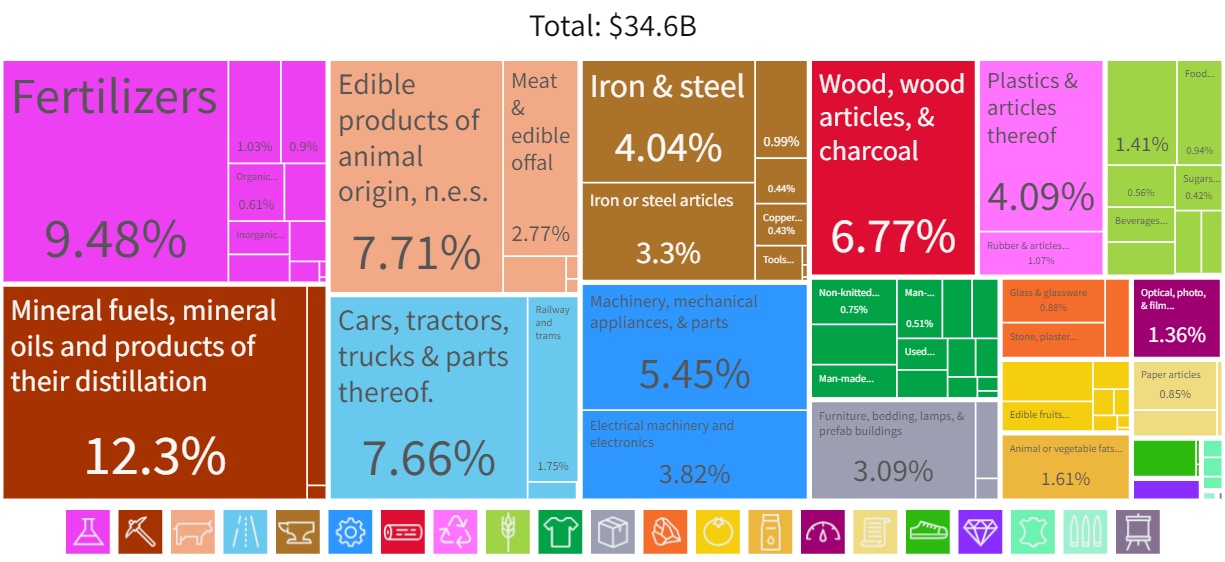 In 2019 the share of manufacturing in GDP was 31%, over two-thirds of this amount falls on manufacturing industries. The number of people employed in the industry is 34.7% of the working population. The growth rate is much lower than for the economy as a whole—about 2.2% in 2021. At the time of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Belarus was one of the world's most industrially developed states by percentage of GDP as well as the richest CIS member-state.World Bank. "Belarus: Prices, Markets, and Enterprise Reform,
In 2019 the share of manufacturing in GDP was 31%, over two-thirds of this amount falls on manufacturing industries. The number of people employed in the industry is 34.7% of the working population. The growth rate is much lower than for the economy as a whole—about 2.2% in 2021. At the time of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Belarus was one of the world's most industrially developed states by percentage of GDP as well as the richest CIS member-state.World Bank. "Belarus: Prices, Markets, and Enterprise Reform,
p. 1
World Bank, 1997; In 2015, 39.3% of Belarusians were employed by state-controlled companies, 57.2% were employed by private companies (in which the government has a 21.1% stake) and 3.5% were employed by foreign companies. The country relies on Russia for various imports, including petroleum. Important agricultural products include potatoes and cattle byproducts, including meat. In 1994, Belarus's main exports included heavy machinery (especially Belarus (tractor), tractors), agricultural products, and energy products. Economically, Belarus involved itself in the CIS, Due to its failure to protect labor rights, including passing laws forbidding unemployment or working outside of state-controlled sectors, Belarus lost its EU Generalized System of Preferences status on 21 June 2007, which raised tariff rates to their prior most favored nation levels. Belarus applied to become a member of the World Trade Organization in 1993.
The labor force consists of more than four million people, among whom women hold slightly more jobs than men. In 2005, nearly a quarter of the population was employed by industrial factories. Employment is also high in agriculture, manufacturing sales, trading goods, and education. The unemployment rate, according to government statistics, was 1.5% in 2005. There were 679,000 unemployed Belarusians, two-thirds of whom were women. The unemployment rate has been in decline since 2003, and the overall rate of employment is the highest since statistics were first compiled in 1995.
The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble. The currency was introduced in May 1992 to replace the Soviet ruble and it has undergone redenomination twice since then. The first coins of the Republic of Belarus were issued on 27 December 1996. The ruble was reintroduced with new values in 2000 and has been in use ever since. As part of the Union State, Union of Russia and Belarus, both states have discussed using a single currency along the same lines as the Euro. This led to a proposal that the Belarusian ruble be discontinued in favor of the Russian ruble (RUB), starting as early as 1 January 2008. The National Bank of the Republic of Belarus, National Bank of Belarus abandoned pegging the Belarusian ruble to the Russian rouble in August 2007.
On 23 May 2011, the ruble depreciated 56% against the United States dollar. The depreciation was even steeper on the black market and financial collapse seemed imminent as citizens rushed to exchange their rubles for dollars, euros, durable goods, and canned goods. On 1 June 2011, Belarus requested an economic rescue package from the International Monetary Fund. A new currency, the new Belarusian ruble (ISO 4217 code: BYN) was introduced in July 2016, replacing the Belarusian ruble in a rate of 1:10,000 (10,000 old ruble = 1 new ruble). From 1 July until 31 December 2016, the old and new currencies were in parallel circulation and series 2000 notes and coins can be exchanged for series 2009 from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2021. This redenomination can be considered an effort to fight the high inflation rate.
The banking system of Belarus consists of two levels: Central Bank (National Bank of the Republic of Belarus) and 25 commercial banks.
Due to its failure to protect labor rights, including passing laws forbidding unemployment or working outside of state-controlled sectors, Belarus lost its EU Generalized System of Preferences status on 21 June 2007, which raised tariff rates to their prior most favored nation levels. Belarus applied to become a member of the World Trade Organization in 1993.
The labor force consists of more than four million people, among whom women hold slightly more jobs than men. In 2005, nearly a quarter of the population was employed by industrial factories. Employment is also high in agriculture, manufacturing sales, trading goods, and education. The unemployment rate, according to government statistics, was 1.5% in 2005. There were 679,000 unemployed Belarusians, two-thirds of whom were women. The unemployment rate has been in decline since 2003, and the overall rate of employment is the highest since statistics were first compiled in 1995.
The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble. The currency was introduced in May 1992 to replace the Soviet ruble and it has undergone redenomination twice since then. The first coins of the Republic of Belarus were issued on 27 December 1996. The ruble was reintroduced with new values in 2000 and has been in use ever since. As part of the Union State, Union of Russia and Belarus, both states have discussed using a single currency along the same lines as the Euro. This led to a proposal that the Belarusian ruble be discontinued in favor of the Russian ruble (RUB), starting as early as 1 January 2008. The National Bank of the Republic of Belarus, National Bank of Belarus abandoned pegging the Belarusian ruble to the Russian rouble in August 2007.
On 23 May 2011, the ruble depreciated 56% against the United States dollar. The depreciation was even steeper on the black market and financial collapse seemed imminent as citizens rushed to exchange their rubles for dollars, euros, durable goods, and canned goods. On 1 June 2011, Belarus requested an economic rescue package from the International Monetary Fund. A new currency, the new Belarusian ruble (ISO 4217 code: BYN) was introduced in July 2016, replacing the Belarusian ruble in a rate of 1:10,000 (10,000 old ruble = 1 new ruble). From 1 July until 31 December 2016, the old and new currencies were in parallel circulation and series 2000 notes and coins can be exchanged for series 2009 from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2021. This redenomination can be considered an effort to fight the high inflation rate.
The banking system of Belarus consists of two levels: Central Bank (National Bank of the Republic of Belarus) and 25 commercial banks.
 According to the census of November 2011, 58.9% of all Belarusians adhered to some kind of religion; out of those, Eastern Orthodoxy made up about 82%: Eastern Orthodox in Belarus are mainly part of the Belarusian Exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church, though a small Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church also exists. Roman Catholicism in Belarus, Roman Catholicism is practiced mostly in the western regions, and there are also different denominations of Protestantism. Minorities also practice Belarusian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism, Judaism, Islam and Modern paganism, neo-paganism. Overall, 48.3% of the population is Orthodox Christian, 41.1% is not religious, 7.1% is Roman Catholic and 3.3% follows other religions.
Belarus's Catholic minority is concentrated in the western part of the country, especially around Hrodna, is made up of a mixture of Belarusians and the country's Poles, Polish and Lithuanian people, Lithuanian minorities. President Lukashenko has stated that Orthodox and Catholic believers are the "two main confessions in our country".
Belarus was once a major center of European Jews, with 10% of the population being history of the Jews in Belarus, Jewish. But since the mid-20th century, the number of Jews has been reduced by the Holocaust, deportation, and emigration, so that today it is a very small minority of less than one percent. The Lipka Tatars, numbering over 15,000, are predominantly Islam in Belarus, Muslims. According to Article 16 of the Constitution of Belarus, Constitution, Belarus has no official religion. While the freedom of religion, freedom of worship is granted in the same article, religious organizations deemed harmful to the government or social order can be prohibited.
Belarus's two official languages are Russian and Belarusian language, Belarusian; Russian is the most common language spoken at home, used by 70% of the population, while Belarusian, the official first language, is spoken at home by 23%. Minorities also speak Polish language, Polish, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and Eastern Yiddish. Belarusian, although not as widely used as Russian, is the mother tongue of 53.2% of the population, whereas Russian is the mother tongue of only 41.5%.
According to the census of November 2011, 58.9% of all Belarusians adhered to some kind of religion; out of those, Eastern Orthodoxy made up about 82%: Eastern Orthodox in Belarus are mainly part of the Belarusian Exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church, though a small Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church also exists. Roman Catholicism in Belarus, Roman Catholicism is practiced mostly in the western regions, and there are also different denominations of Protestantism. Minorities also practice Belarusian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism, Judaism, Islam and Modern paganism, neo-paganism. Overall, 48.3% of the population is Orthodox Christian, 41.1% is not religious, 7.1% is Roman Catholic and 3.3% follows other religions.
Belarus's Catholic minority is concentrated in the western part of the country, especially around Hrodna, is made up of a mixture of Belarusians and the country's Poles, Polish and Lithuanian people, Lithuanian minorities. President Lukashenko has stated that Orthodox and Catholic believers are the "two main confessions in our country".
Belarus was once a major center of European Jews, with 10% of the population being history of the Jews in Belarus, Jewish. But since the mid-20th century, the number of Jews has been reduced by the Holocaust, deportation, and emigration, so that today it is a very small minority of less than one percent. The Lipka Tatars, numbering over 15,000, are predominantly Islam in Belarus, Muslims. According to Article 16 of the Constitution of Belarus, Constitution, Belarus has no official religion. While the freedom of religion, freedom of worship is granted in the same article, religious organizations deemed harmful to the government or social order can be prohibited.
Belarus's two official languages are Russian and Belarusian language, Belarusian; Russian is the most common language spoken at home, used by 70% of the population, while Belarusian, the official first language, is spoken at home by 23%. Minorities also speak Polish language, Polish, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and Eastern Yiddish. Belarusian, although not as widely used as Russian, is the mother tongue of 53.2% of the population, whereas Russian is the mother tongue of only 41.5%.
Britannica.com
accessed 4 March 2016. The modern era of Belarusian literature began in the late 19th century; one prominent writer was Yanka Kupala. Many Belarusian writers of the time, such as Uładzimir Žyłka, Kazimir Svayak, Yakub Kolas, Źmitrok Biadula, and Maksim Haretski, wrote for ''Nasha Niva'', a Belarusian-language paper published that was previously published in Vilnius but now is published in Minsk. After Belarus was incorporated into the Soviet Union, the Soviet government took control of the Republic's cultural affairs. At first, a policy of "Belarusianization" was followed in the newly formed Byelorussian SSR. This policy was reversed in the 1930s, and the majority of prominent Belarusian intellectuals and nationalist advocates were either exiled or killed in Stalinist purges. The free development of literature occurred only in Polish-held territory until Soviet occupation in 1939. Several poets and authors went into exile after the Nazi occupation of Belarus and would not return until the 1960s. The last major revival of Belarusian literature occurred in the 1960s with novels published by Vasil Bykaŭ and Uladzimir Karatkievich. An influential author who devoted his work to awakening the awareness of the catastrophes the country has suffered, was Ales Adamovich. He was named by Svetlana Alexievich, the Belarusian winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature 2015, as "her main teacher, who helped her to find a path of her own".
Music of Belarus, Music in Belarus largely comprises a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the
The last major revival of Belarusian literature occurred in the 1960s with novels published by Vasil Bykaŭ and Uladzimir Karatkievich. An influential author who devoted his work to awakening the awareness of the catastrophes the country has suffered, was Ales Adamovich. He was named by Svetlana Alexievich, the Belarusian winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature 2015, as "her main teacher, who helped her to find a path of her own".
Music of Belarus, Music in Belarus largely comprises a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the
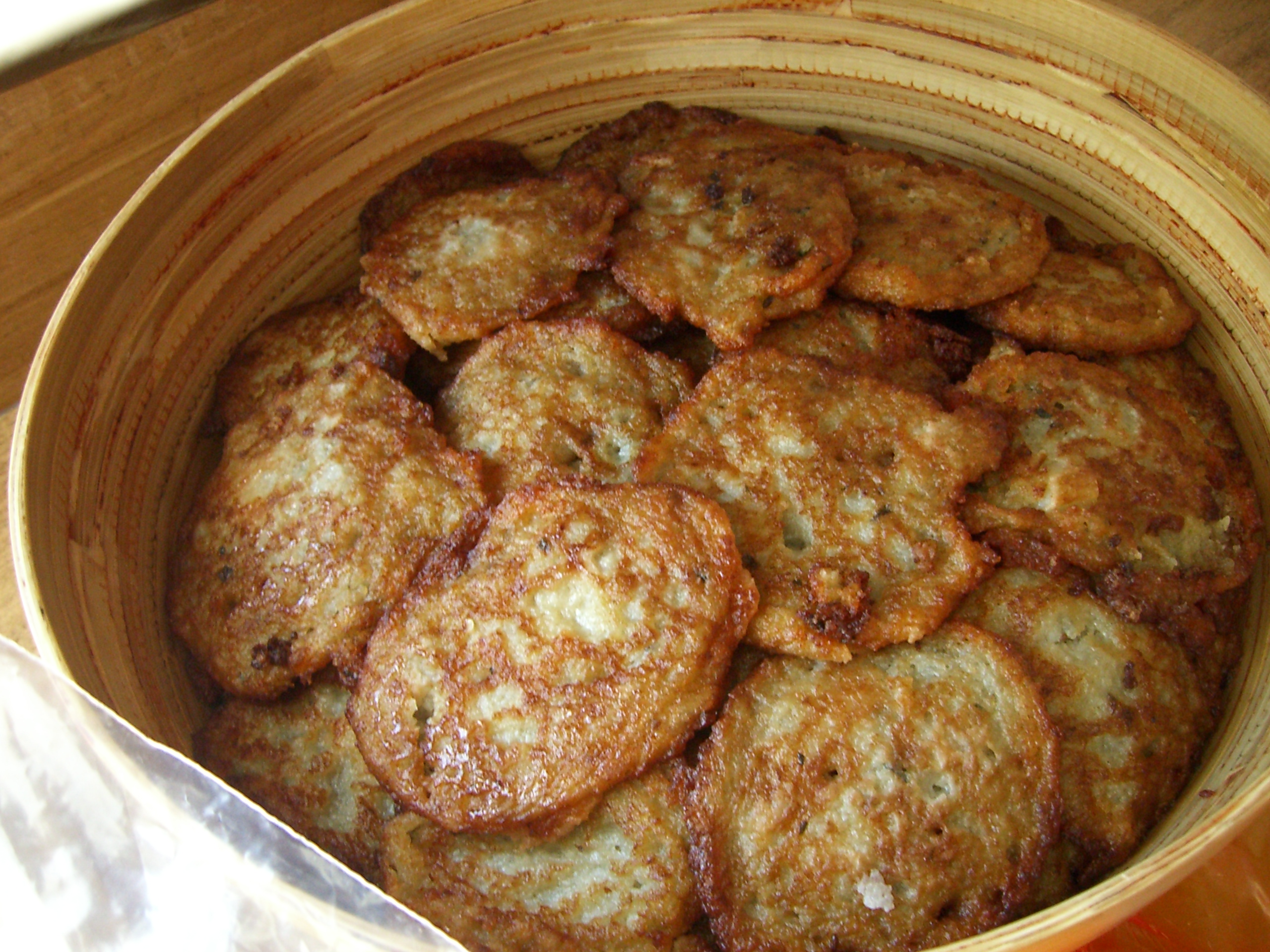 Belarusian cuisine consists mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Belarusians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals later in the day. Wheat and rye bread are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. To show hospitality, a host traditionally presents an offering of bread and salt when greeting a guest or visitor.
Belarusian cuisine consists mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Belarusians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals later in the day. Wheat and rye bread are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. To show hospitality, a host traditionally presents an offering of bread and salt when greeting a guest or visitor.
 Darya Domracheva is a leading biathlon, biathlete whose honours include three gold medals at the 2014 Winter Olympics. Tennis player Victoria Azarenka became the first Belarusian to win a Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam singles title at the Australian Open in 2012. She also won the gold medal in mixed doubles at the Tennis at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 Summer Olympics with Max Mirnyi, who holds ten Grand Slam titles in Singles tennis, doubles.
Other notable Belarusian sportspeople include cyclist Vasil Kiryienka, who won the 2015 UCI Road World Championships – Men's time trial, 2015 Road World Time Trial Championship, and middle-distance runner Maryna Arzamasava, who won the gold medal in the 2015 World Championships in Athletics – Women's 800 metres, 800m at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics.
Andrei Arlovski, who was born in Babruysk,
Darya Domracheva is a leading biathlon, biathlete whose honours include three gold medals at the 2014 Winter Olympics. Tennis player Victoria Azarenka became the first Belarusian to win a Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam singles title at the Australian Open in 2012. She also won the gold medal in mixed doubles at the Tennis at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 Summer Olympics with Max Mirnyi, who holds ten Grand Slam titles in Singles tennis, doubles.
Other notable Belarusian sportspeople include cyclist Vasil Kiryienka, who won the 2015 UCI Road World Championships – Men's time trial, 2015 Road World Time Trial Championship, and middle-distance runner Maryna Arzamasava, who won the gold medal in the 2015 World Championships in Athletics – Women's 800 metres, 800m at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics.
Andrei Arlovski, who was born in Babruysk,
OpenNet Initiative, 18 November 2010
"The European Union and Belarus: Democracy Promotion by Technocratic Means?"
''Democratization'' 23: 4 pp. 678–698. . * * * Marples, David. Our Glorious Past': Lukashenka's Belarus and the Great Patriotic War'' (Columbia University Press, 2014) * Parker, Stewart. ''The Last Soviet Republic: Alexander Lukashenko's Belarus'' (Trafford Publishing, 2007) * Rudling, Pers Anders. ''The Rise and Fall of Belarusian Nationalism, 1906–1931'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2014) 436 pages * * * Snyder, Timothy (2004)
''The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999''
* * * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: The Making of a Nation: A Case Study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A Bibliographical Guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956)
Website of the Republic of Belarus
by BelTA news agency
Belarus
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. *
FAO Country Profiles: Belarus
{{Authority control Belarus, Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Landlocked countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the United Nations Member States of the Collective Security Treaty Organization Member States of the Eurasian Economic Union Republics Russian-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1991 States and territories established in the 980s Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basin, endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked list of states with limited recogni ...
in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
. It is bordered by Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
to the east and northeast, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
to the south, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
to the west, and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
to the northwest. Covering an area of and with a population of 9.4 million, Belarus is the 13th-largest and the 20th-most populous country in Europe. The country has a hemiboreal
Hemiboreal means halfway between the temperate and subarctic (or boreal) zones. The term is most frequently used in the context of climates and ecosystems.
Botany
A hemiboreal forest has some characteristics of a boreal forest to the north, and ...
climate and is administratively divided into seven regions. Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
is the capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
.
Until the 20th century, different states at various times controlled the lands of modern-day Belarus, including Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
, the Principality of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk ( be, По́лацкае кня́ства, ''Polackaje kniastva''; la, Polocensis Ducatus), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs. The origin and ...
, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
in 1917, different states arose competing for legitimacy amid the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, ultimately ending in the rise of the Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
, which became a founding constituent republic
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in 1922. After the Polish-Soviet War, Belarus lost almost half of its territory to Poland. Much of the borders of Belarus took their modern shape in 1939, when some lands of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
were reintegrated into it after the Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subse ...
, and were finalized after World War II. During World War II, military operations devastated Belarus, which lost about a quarter of its population and half of its economic resources. The republic was redeveloped in the post-war years. In 1945, the Byelorussian SSR became a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, along with the Soviet Union.
The parliament of the republic proclaimed the sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
of Belarus on 27 July 1990, and during the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, Belarus declared independence on 25 August 1991. Following the adoption of a new constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
in 1994, Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (as transliterated from Russian language, Russian; also transliterated from Belarusian language, Belarusian as Alyaksand(a)r Ryhoravich Lukashenka;, ; rus, Александр Григорьевич Лука� ...
was elected Belarus's first president in the country's first and only free election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
post-independence, serving as president ever since. Lukashenko heads a highly centralized authoritarian
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic votin ...
government, and has referred to himself as the "last dictator" in Europe. Belarus ranks low in international measurements of freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic News media, media, especially publication, published materials, should be conside ...
and civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
. It has continued a number of Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownershi ...
of large sections of the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
. Belarus is the only European country using capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
. In 2000, Belarus and Russia signed a treaty for greater cooperation, forming the Union State
The Union State,; be, Саю́зная дзяржа́ва Расі́і і Белару́сі, Sajuznaja dziaržava Rasii i Bielarusi, links=no. or Union State of Russia and Belarus,; be, Саю́зная дзяржа́ва, Sajuznaja dziar� ...
.
Belarus is a developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, ranking 60th in the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
. It has been a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
since its founding and has joined the CIS
Cis or cis- may refer to:
Places
* Cis, Trentino, in Italy
* In Poland:
** Cis, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central
** Cis, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, north
Math, science and biology
* cis (mathematics) (cis(''θ'')), a trigonome ...
, the CSTO
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has ...
, the EAEU
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of some post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The Treaty on the Eurasian Econo ...
, the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, and the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
. It has shown no aspirations of joining the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
but nevertheless maintains a bilateral relationship with the bloc and also participates in two EU projects, the Baku Initiative
The Baku Initiative is an international initiative of the European Union.
It is a policy dialogue on energy and transport cooperation between the European Union, Turkey, and the former Soviet republics, undertaken as part of the INOGATE energy ...
and the Eastern Partnership
The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European External Action Service of the European Union (EU) together with the EU, its member states, and six Eastern European partners governing the EU's relationship with the post-Sovi ...
. Belarus suspended its participation in the latter on 28 June 2021, after the EU imposed more sanctions against the country.
Etymology
The name ''Belarus'' is closely related with the term ''Belaya Rus'', i.e., ''White Rus'
White Ruthenia ( cu, Бѣла Роусь, Bela Rous'; be, Белая Русь, Biełaja Ruś; pl, Ruś Biała; russian: Белая Русь, Belaya Rus'; ukr, Біла Русь, Bila Rus') alternatively known as Russia Alba, White Rus' or W ...
''. There are several claims to the origin of the name ''White RusRuthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
n lands within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
that had been populated mostly by Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
who had been Christianized early, as opposed to Black Ruthenia
Black Ruthenia ( la, Ruthenia Nigra), or Black Rus' ( be, Чорная Русь, translit=Čornaja Ruś; lt, Juodoji Rusia; pl, Ruś Czarna), is a historical region on the Upper Nemunas, including Novogrudok (Naugardukas), Grodno (Gardinas) a ...
, which was predominantly inhabited by pagan Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
. An alternative explanation for the name comments on the white clothing worn by the local Slavic population. A third theory suggests that the old Rus' lands that were not conquered by the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
(i.e., Polotsk, Vitebsk and Mogilev) had been referred to as ''White Rus. A fourth theory suggests that the color white was associated with the west, and Belarus was the western part of in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Rus
Rus or RUS may refer to:
People and places
* Rus (surname), a Romanian-language surname
* East Slavic historical territories and peoples (). See Names of Rus', Russia and Ruthenia
** Rus' people, the people of Rus'
** Rus' territories
*** Kievan ...
in the 9th to 13th centuries.
 The name ''Rus'' is often conflated with its Latin forms ''Russia'' and ''Ruthenia'', thus Belarus is often referred to as ''White Russia'' or ''White Ruthenia''. The name first appeared in
The name ''Rus'' is often conflated with its Latin forms ''Russia'' and ''Ruthenia'', thus Belarus is often referred to as ''White Russia'' or ''White Ruthenia''. The name first appeared in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
medieval literature
Medieval literature is a broad subject, encompassing essentially all written works available in Europe and beyond during the Middle Ages (that is, the one thousand years from the fall of the Western Roman Empire ca. AD 500 to the beginning of t ...
; the chronicles of Jan of Czarnków
Jan(ko) of Czarnków ( pl, Jan(ko) z Czarnkowa) (ca. 1320–1387), of Nałęcz coat of arms, was a Polish chronicler, Deputy Chancellor of the Crown and Archdeacon of Gniezno.
He started his career as a diplomat in service of one of Polish bishops ...
mention the imprisonment of Lithuanian grand duke Jogaila and his mother at "" in 1381. The first known use of ''White Russia'' to refer to Belarus was in the late-16th century by Englishman Sir Jerome Horsey
Sir Jerome Horsey (c. 1550 – 1626), of Great Kimble, Buckinghamshire, was an English explorer, diplomat and politician in the 16th and 17th centuries.
He spent much time in Russia over the course of seventeen years, first arriving in 1573 a ...
, who was known for his close contacts with the Russian royal court. During the 17th century, the Russian tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
s used ''White Rus'' to describe the lands added from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
The term ''Belorussia'' (russian: link=no, Белору́ссия, the latter part similar but spelled and stressed differently from Росси́я, ''Russia'') first rose in the days of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, and the Russian Tsar was usually styled "the Tsar of All the Russias", as ''Russia'' or the ''Russian Empire'' was formed by three parts of Russia—the Great
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
, Little
Little is a synonym for small size and may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Little'' (album), 1990 debut album of Vic Chesnutt
* ''Little'' (film), 2019 American comedy film
*The Littles, a series of children's novels by American author John P ...
, and White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
. This asserted that the territories are all Russian and all the peoples are also Russian; in the case of the Belarusians, they were variants of the Russian people.
After the Bolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was ...
in 1917, the term ''White Russia'' caused some confusion, as it was also the name of the military force that opposed the red Bolsheviks. During the period of the Byelorussian SSR, the term ''Byelorussia'' was embraced as part of a national consciousness. In western Belarus under Polish control, ''Byelorussia'' became commonly used in the regions of Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok Up ...
and Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
during the interwar period.
The term ''Byelorussia'' (its names in other languages such as English being based on the Russian form) was only used officially until 1991. Officially, the full name of the country is ''Republic of Belarus'' (, , ). In Russia, the usage of ''Belorussia'' is still very common.
In Lithuanian, besides ''Baltarusija'' (White Russia), Belarus is also called ''Gudija''. The etymology of the word ''Gudija'' is not clear. By one hypothesis the word derives from the Old Prussian name ''Gudwa'', which, in turn, is related to the form ''Żudwa'', which is a distorted version of ''Sudwa, Sudovia. Sudovia'', in its turn, is one of the names of the Yotvingians
Yotvingians (also called: Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians; Yotvingian: ''Jotvingai''; lt, Jotvingiai, ; lv, Jātvingi; pl, Jaćwingowie, be, Яцвягі, ger, Sudauer) were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prus ...
. Another hypothesis connects the word with the Gothic Kingdom that occupied parts of the territory of modern Belarus and Ukraine in the 4th and 5th centuries. The self-naming of Goths was ''Gutans'' and ''Gytos'', which are close to Gudija. Yet another hypothesis is based on the idea that ''Gudija'' in Lithuanian means "the other" and may have been used historically by Lithuanians to refer to any people who did not speak Lithuanian.
History
Early history
From 5000 to 2000 BC, theBandkeramik
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
predominated in what now constitutes Belarus, and the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West A ...
as well as other pastoralists roamed through the area by 1,000 BC. The Zarubintsy culture
The Zarubintsy or Zarubinets culture was a culture that, from the 3rd century BC until the 1st century AD, flourished in the area north of the Black Sea along the upper and middle Dnieper and Pripyat Rivers, stretching west towards the Southern B ...
later became widespread at the beginning of the 1st millennium
File:1st millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: Depiction of Jesus, the central figure in Christianity; The Colosseum, a landmark of the once-mighty Roman Empire; Kaaba, the Great Mosque of Mecca, the holiest site of Islam; Chess, a new ...
. In addition, remains from the Dnieper–Donets culture
The Dnieper–Donets culture (ca. 5th—4th millennium BC) was a Mesolithic and later Neolithic culture which flourished north of the Black Sea ca. 5000-4200 BC. It has many parallels with the Samara culture, and was succeeded by the Sredny ...
were found in Belarus and parts of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. The region was first permanently settled by Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
tribes in the 3rd century. Around the 5th century, the area was taken over by the Slavs. The takeover was partially due to the lack of military coordination of the Balts, but their gradual assimilation into Slavic culture was peaceful in nature. Invaders from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, among whom were the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
and Avars, swept through c. 400–600 AD, but were unable to dislodge the Slavic presence.
Kievan Rus'
 In the 9th century the territory of modern Belarus became part of
In the 9th century the territory of modern Belarus became part of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
, a vast East Slavic state ruled by the Rurikid
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
dynasty. Upon the death of Kievan Rus' ruler Yaroslav I the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was als ...
in 1054, the state split into independent principalities. The Battle on the Nemiga River
The Battle on the Nemiga River ( be, Бітва на Нямізе, russian: Сраже́ние на Неми́ге) was a battle of the Kievan Rus' feudal period that occurred on March 3, 1067 on the Niamiha River. The description of the battle is ...
in 1067 was one of the more notable events of the period, the date of which is considered the founding date of Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
.
Many early Rus' principalities were virtually razed or severely affected by a major Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
in the 13th century, but the lands of modern-day Belarus avoided the brunt of the invasion and eventually joined the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
. There are no sources of military seizure, but the annals affirm the alliance and united foreign policy of Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Distr ...
and Lithuania for decades. Trying to avoid the Tatar Yoke
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, destroying numerous southern cities, including the largest cities, Kiev (50,000 inhabitants) and Chernihiv (30,000 inhabitants), with the only major cities escaping destr ...
, the Principality of Minsk
The Principality of Minsk was an appanage principality of the Duchy of Polotsk and centered on the city of Minsk (today in Belarus). It existed from its founding in 1101 until it was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242, and only no ...
sought protection from Lithuanian princes further north and in 1242, the Principality of Minsk
The Principality of Minsk was an appanage principality of the Duchy of Polotsk and centered on the city of Minsk (today in Belarus). It existed from its founding in 1101 until it was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242, and only no ...
became a part of the expanding Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Incorporation into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania resulted in an economic, political and ethno-cultural unification of Belarusian lands. Of the principalities held by the duchy, nine of them were settled by a population that would eventually become the Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
. During this time, the duchy was involved in several military campaigns, including fighting on the side of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
against the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
at the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
in 1410; the joint victory allowed the duchy to control the northwestern borderlands of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
.
The Muscovites, led by Ivan III of Moscow
Ivan III Vasilyevich (russian: Иван III Васильевич; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was a Grand Prince of Moscow and Grand Prince of all Rus'. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his blin ...
, began military campaigns in 1486 in an attempt to incorporate the former lands of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
, specifically the territories of modern-day Belarus, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
 On 2 February 1386, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the
On 2 February 1386, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
*Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
*Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exist ...
were joined in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
through a marriage of their rulers. This union set in motion the developments that eventually resulted in the formation of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
, created in 1569 by the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the pe ...
.
The Lithuanian nobles were forced to seek rapprochement with the Poles because of a potential threat from Muscovy Muscovy is an alternative name for the Grand Duchy of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
* Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata'') and Domes ...
. To strengthen their independence within the format of the union, three editions of the Statutes of Lithuania
The Statutes of Lithuania, originally known as the Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, were a 16th-century codification of all the legislation of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and its successor, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Stat ...
were issued in the second half of the 16th century. The third Article of the Statutes established that all lands of the duchy will be eternally within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and never enter as a part of other states. The Statutes allowed the right to own land only to noble families of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Anyone from outside the duchy gaining rights to a property would actually own it only after swearing allegiance to the Grand Duke of Lithuania (a title dually held by the King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
). These articles were aimed to defend the rights of the Lithuanian nobility within the duchy against Polish and other nobles of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
.
In the years following the union, the process of gradual Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
of both Lithuanians and Ruthenians gained steady momentum. In culture and social life, both the Polish language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In a ...
and Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
became dominant, and in 1696, Polish replaced Ruthenian as the official language, with Ruthenian being banned from administrative use. However, the Ruthenian peasants continued to speak their native language. Also, the Belarusian Byzantine Catholic Church
The Belarusian Greek Catholic Church ( be, Беларуская грэка-каталіцкая царква, ''Bielaruskaja hreka-katalickaja carkva'' BHKC; la, Ecclesiae Graecae Catholico Belarusica) sometimes called in reference to its By ...
was formed by the Poles in order to bring Orthodox Christians into the See of Rome
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome ...
. The Belarusian church entered into a full communion with the Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
through the Union of Brest
The Union of Brest (; ; ; ) was the 1595–96 decision of the Ruthenian Orthodox Church eparchies (dioceses) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth to break relations with the Eastern Orthodox Church and to enter into communion with, and place i ...
in 1595, while keeping its Byzantine liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
in the Church Slavonic
Church Slavonic (, , literally "Church-Slavonic language"), also known as Church Slavic, New Church Slavonic or New Church Slavic, is the conservative Slavic liturgical language used by the Eastern Orthodox Church in Belarus, Bosnia and Herzeg ...
language.
The Statutes were initially issued in the Ruthenian language
Ruthenian ( Belarusian: руская мова; Ukrainian: руська мова; Ruthenian: руска(ѧ) мова; also see other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely-related group of East Slavic linguistic varieties, particularly th ...
alone and later also in Polish. Around 1840 the Statutes were banned by the Russian tsar following the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
. Ukrainian lands used them until 1860s.
Russian Empire
 The union between Poland and Lithuania ended in 1795 with the
The union between Poland and Lithuania ended in 1795 with the Third Partition of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish ...
by Imperial Russia, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
, and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. The Belarusian territories acquired by the Russian Empire under the reign of Catherine II were included into the Belarusian Governorate
The Belarusian Governorate (russian: Белорусская губерния, be, Беларуская губерня) was an administrative division of the Russian Empire established on December 12, 1796. It included the lands acquired after th ...
( rus, Белорусское генерал-губернаторство) in 1796 and held until their occupation by the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
Under Nicholas I and Alexander III the national cultures were repressed. Policies of Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
changed by Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
,Żytko, ''Russian policy ...'', p. 551. which included the return to Orthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Late antiquity, A ...
of Belarusian Uniates
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of t ...
. Belarusian language was banned in schools while in neighboring Samogitia
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
primary school education with Samogitian literacy was allowed.
In a Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
drive in the 1840s, Nicholas I prohibited use of the Belarusian language in public schools, campaigned against Belarusian publications and tried to pressure those who had converted to Catholicism under the Poles to reconvert to the Orthodox faith. In 1863, economic and cultural pressure exploded in a revolt
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
, led by Konstanty Kalinowski
Wincenty Konstanty Kalinowski, also known as Kastuś Kalinoŭski ( be, Касту́сь Каліно́ўскі also be, Вінцэ́нт Канстанці́н Каліно́ўскі, lit=Vincent Kanstancin Kalinoŭski, lt, Konstantinas Kalinau ...
(also known as Kastus). After the failed revolt, the Russian government reintroduced the use of Cyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
to Belarusian in 1864 and no documents in Belarusian were permitted by the Russian government until 1905.
During the negotiations of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
, Belarus first declared independence under German occupation on 25 March 1918, forming the Belarusian People's Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; be, Беларуская Народная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Narodnaja Respublika, ), or Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic R ...
. Immediately afterwards, the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
ignited, and the territory of Belarus was divided between Poland and Soviet Russia. The Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic exists as a government in exile
A government in exile (abbreviated as GiE) is a political group that claims to be a country or semi-sovereign state's legitimate government, but is unable to exercise legal power and instead resides in a foreign country. Governments in exile us ...
ever since then; in fact, it is currently the world's longest serving government in exile.
Early states and interwar period
TheBelarusian People's Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; be, Беларуская Народная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Narodnaja Respublika, ), or Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic R ...
was the first attempt to create an independent Belarusian state under the name "Belarus". Despite significant efforts, the state ceased to exist, primarily because the territory was continually dominated by the German Imperial Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (german: Deutsches Heer), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the l ...
and the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and then the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
. It existed from only 1918 to 1919 but created prerequisites for the formation of a Belarusian state. The choice of name was probably based on the fact that core members of the newly formed government were educated in tsarist universities, with corresponding emphasis on the ideology of West-Russianism.
The Republic of Central Lithuania
The Republic of Central Lithuania ( pl, Republika Litwy Środkowej, ), commonly known as the Central Lithuania, and the Middle Lithuania ( pl, Litwa Środkowa, , be, Сярэдняя Літва, translit=Siaredniaja Litva), was an unrecognize ...
was a short-lived political entity, which was the last attempt to restore Lithuania in the historical confederacy state (it was also supposed to create Lithuania Upper and Lithuania Lower). The republic was created in 1920 following the staged rebellion of soldiers of the 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division
The 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division ( pl, 1. Dywizja Litewsko-Białoruska, 1.DL-B; be, 1-ая Літоўска-Беларуская дывізія; lt, 1-oji Lietuvos-Baltarusijos divizija) was a volunteer unit of the Polish Army formed aro ...
of the Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stret ...
under Lucjan Żeligowski
Lucjan Żeligowski (; 17 October 1865 – 9 July 1947) was a Polish-Lithuanian general, politician, military commander and veteran of World War I, the Polish-Soviet War and World War II. He is mostly remembered for his role in Żeligowski's M ...
. Centered on the historical capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
, Vilna
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional u ...
( lt, Vilnius, pl, Wilno), for 18 months the entity served as a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between t ...
between Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, upon which it depended, and Lithuania, which claimed the area. After a variety of delays, a disputed election took place on 8 January 1922, and the territory was annexed to Poland. Żeligowski later in his memoir which was published in London in 1943 condemned the annexation of the Republic by Poland, as well as the policy of closing Belarusian schools and general disregard of Marshal Józef Piłsudski
), Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire (now Lithuania)
, death_date =
, death_place = Warsaw, Poland
, constituency =
, party = None (formerly PPS)
, spouse =
, children = Wan ...
's confederation plans by Polish ally.
 In 1919 a part of Belarus under Russian rule emerged as the
In 1919 a part of Belarus under Russian rule emerged as the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
(Byelorussian SSR). Soon thereafter it merged to form the Lithuanian-Byelorussian SSR. The contested lands were divided between Poland and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
after the war ended in 1921, and the Byelorussian SSR became a founding member of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922. In the 1920s and 1930s, Soviet agricultural and economic policies, including collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member ...
and five-year plans for the national economy, led to famine and political repression.
The western part of modern Belarus remained part of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
. After an early period of liberalization, tensions between increasingly nationalistic Polish government and various increasingly separatist ethnic minorities started to grow, and the Belarusian minority was no exception.Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a Welsh-Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Professor at ...
, ''God's Playground
''God's Playground: A History of Poland'' is a history book in two volumes written by Norman Davies, covering a 1000-year history of Poland. Volume 1: ''The origins to 1795'', and Volume 2: ''1795 to the present'' first appeared as the Oxford Cla ...
'' (Polish edition), second tome, pp. 512–513 The polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
drive was inspired and influenced by the Polish National Democracy National Democracy may refer to:
* National Democracy (Czech Republic)
* National Democracy (Italy)
* National Democracy (Philippines)
* National Democracy (Poland)
* National Democracy (Spain)
See also
* Civic nationalism, a general concept
* Na ...
, led by Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
, who advocated refusing Belarusians and Ukrainians the right for a free national development. A Belarusian organization, the ''Belarusian Peasants' and Workers' Union
The Belarusian Peasants' and Workers' Union or the Hramada ( be, Беларуская Сялянска-Работніцкая Грамада ( Lacinka: ''Biełaruskaja Sialanska-Rabotnickaja Hramada''), pl, Białoruska Włościańsko-Robotnicza H ...
'', was banned in 1927, and opposition to Polish government was met with state repressions. Nonetheless, compared to the (larger) Ukrainian minority, Belarusians were much less politically aware and active, and thus suffered fewer repressions than the Ukrainians. In 1935, after the death of Piłsudski, a new wave of repressions was released upon the minorities, with many Orthodox churches and Belarusian schools being closed. Use of the Belarusian language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some p ...
was discouraged. Belarusian leadership was sent to Bereza Kartuska prison
Bereza Kartuska Prison (, "Place of Isolation at Bereza Kartuska") was operated by Poland's Sanation government from 1934 to 1939 in Bereza Kartuska, Polesie Voivodeship (today, Biaroza, Belarus). Because the inmates were detained without trial ...
.
World War II
 In 1939,
In 1939, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Soviet Union invaded and occupied Poland, marking the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The Soviets invaded and annexed much of eastern Poland, which had been part of the country since the Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet War.
...
two decades earlier. Much of the northern section of this area was added to the Byelorussian SSR, and now constitutes West Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus ( be, Заходняя Беларусь, translit=Zachodniaja Bielaruś; pl, Zachodnia Białoruś; russian: Западная Белоруссия, translit=Zapadnaya Belorussiya) is a historical region of mod ...
.
* Клоков В. Я. Великий освободительный поход Красной Армии. (Освобождение Западной Украины и Западной Белоруссии).-Воронеж, 1940.
* Минаев В. Западная Белоруссия и Западная Украина под гнетом панской Польши.—М., 1939.
* Трайнин И.Национальное и социальное освобождение Западной Украины и Западной Белоруссии.—М., 1939.—80 с.
* Гiсторыя Беларусі. Том пяты.—Мінск, 2006.—с. 449–474
The Soviet-controlled Byelorussian People's Council officially took control of the territories, whose populations consisted of a mixture of Poles, Ukrainians, Belarusians and Jews, on 28 October 1939 in Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok Up ...
. Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. The defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
of Brest Fortress
Brest Fortress ( be, Брэсцкая крэпасць, '; pl, Twierdza brzeska, russian: Брестская крепость), formerly known as Brest-Litoŭsk Fortress, is a 19th-century fortress in Brest, Belarus. In 1965, the title "H ...
was the first major battle of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
.
The Byelorussian SSR was the hardest-hit Soviet republic in World War II; it remained in Nazi hands until 1944. The German called for the extermination, expulsion, or enslavement of most or all Belarusians for the purpose of providing more living space
Housing, or more generally, living spaces, refers to the construction and assigned usage of houses or buildings individually or collectively, for the purpose of shelter. Housing ensures that members of society have a place to live, whether i ...
in the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
for Germans. Most of Western Belarus became part of the ''Reichskommissariat Ostland
The Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and the western part of Byelorussian SSR. German planning documents initia ...
'' in 1941, but in 1943 the German authorities allowed local collaborators to set up a client state, the Belarusian Central Council
The Belarusian Central Council ( be, Беларуская цэнтральная рада, in lacinka: Biełaruskaja centralnaja rada; german: Weißruthenischer Zentralrat) was a puppet administrative body in German-occupied Belarus during Worl ...
.
The German occupation in 1941–1944 and war on the Eastern Front devastated Belarus. During that time, 209 out of 290 towns and cities were destroyed, 85% of the republic's industry, and more than one million buildings. After the war, it was estimated that 2.2 million local inhabitants had died and of those some 810,000 were combatants—some foreign. This figure represented a staggering quarter of the prewar population. In the 1990s some raised the estimate even higher, to 2.7 million. The Jewish population of Belarus was devastated during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
and never recovered. The population of Belarus did not regain its pre-war level until 1971.
Post-war
 After the war, Belarus was among the 51 founding member states of the
After the war, Belarus was among the 51 founding member states of the United Nations Charter
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the ...
and as such it was allowed an additional vote at the UN, on top of the Soviet Union's vote. Vigorous postwar reconstruction promptly followed the end of the war and the Byelorussian SSR became a major center of manufacturing in the western USSR, creating jobs and attracting ethnic Russians. The borders of the Byelorussian SSR and Poland were redrawn, in accord with the 1919-proposed Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by George Curzon, 1st Marque ...
.
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
implemented a policy of Sovietization
Sovietization (russian: Советизация) is the adoption of a political system based on the model of soviets (workers' councils) or the adoption of a way of life, mentality, and culture modelled after the Soviet Union. This often included ...
to isolate the Byelorussian SSR from Western influences. This policy involved sending Russians from various parts of the Soviet Union and placing them in key positions in the Byelorussian SSR government. After Stalin's death in 1953, Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
continued his predecessor's cultural hegemony
In Marxist philosophy, cultural hegemony is the dominance of a culturally diverse society by the ruling class who manipulate the culture of that society—the beliefs and explanations, perceptions, values, and mores—so that the worldview of t ...
program, stating, "The sooner we all start speaking Russian, the faster we shall build communism."
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Belarusian communist politician Andrei Gromyko
Andrei Andreyevich Gromyko (russian: Андрей Андреевич Громыко; be, Андрэй Андрэевіч Грамыка; – 2 July 1989) was a Soviet communist politician and diplomat during the Cold War. He served as ...
, who served as Soviet foreign minister (1957–1985) and as Chairman
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the grou ...
of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet
The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet (russian: Президиум Верховного Совета, Prezidium Verkhovnogo Soveta) was a body of state power in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR).Eduard Shevardnadze
Eduard Ambrosis dze Shevardnadze ( ka, ედუარდ ამბროსის ძე შევარდნაძე}, romanized: ; 25 January 1928 – 7 July 2014) was a Soviet and Georgian politician and diplomat who governed Georgia for ...
. In 1986, the Byelorussian SSR was contaminated with most (70%) of the nuclear fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioac ...
from the explosion at the Chernobyl
Chernobyl ( , ; russian: Чернобыль, ) or Chornobyl ( uk, Чорнобиль, ) is a partially abandoned city in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, situated in the Vyshhorod Raion of northern Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. Chernobyl is about no ...
power plant located 16 km beyond the border in the neighboring Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
.
By the late 1980s, political liberalization led to a national revival, with the Belarusian Popular Front
The Belarusian Popular Front "Revival" (BPF, be, Беларускі Народны Фронт "Адраджэньне", БНФ; ''Biełaruski Narodny Front "Adradžeńnie"'', ''BNF'') was a social and political movement in Belarus in the late 1 ...
becoming a major pro-independence force.
Independence
 In March 1990,
In March 1990, elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operate ...
for seats in the Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet (russian: Верховный Совет, Verkhovny Sovet, Supreme Council) was the common name for the legislative bodies (parliaments) of the Soviet socialist republics (SSR) in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) ...
of the Byelorussian SSR took place. Though the opposition candidates, mostly associated with the pro-independence Belarusian Popular Front
The Belarusian Popular Front "Revival" (BPF, be, Беларускі Народны Фронт "Адраджэньне", БНФ; ''Biełaruski Narodny Front "Adradžeńnie"'', ''BNF'') was a social and political movement in Belarus in the late 1 ...
, took only 10% of the seats, Belarus declared itself sovereign on 27 July 1990 by issuing the Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic was a formal document issued by the Supreme Soviet of Belarus to assert its independence from the Soviet Union. Passed on July 27, 1990, the Declaration started th ...
.
Mass protests erupted in spring 1991 and became known as the Belarusian revolution. With the support of the Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of ''The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. A ...
, the country's name was changed to the Republic of Belarus on 25 August 1991. Stanislau Shushkevich
Stanislav Stanislavovich Shushkevich ( be, Станісла́ў Станісла́вавіч Шушке́віч, translit=Stanisłáŭ Stanisłávavič Šuškiévič,; russian: Станисла́в Станисла́вович Шушке́вич; ...
, the chairman of the Supreme Soviet of Belarus, met with Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
of Russia and Leonid Kravchuk
Leonid Makarovych Kravchuk ( uk, Леонід Макарович Кравчук; 10 January 1934 – 10 May 2022) was a Ukrainian politician and the first president of Ukraine, serving from 5 December 1991 until 19 July 1994. In 1992, he signed ...
of Ukraine on 8 December 1991 in Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest; lt, Baltvyžių giria; pl, Puszcza Białowieska ; russian: Беловежская пуща, Belovezhskaya Pushcha is a forest on the border between Belarus and Poland. It is one of the last and largest remaining pa ...
to formally declare the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
.
Lukashenko era
Anational constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
was adopted in March 1994 in which the functions of prime minister were given to the President of Belarus
The president of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Прэзідэнт Рэспублікі Беларусь; russian: Президент Республики Беларусь) is the head of state and head of government of Belarus. The office was cre ...
. A two-round election for the presidency on 24 June 1994 and 10 July 1994 catapulted the formerly unknown Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (as transliterated from Russian language, Russian; also transliterated from Belarusian language, Belarusian as Alyaksand(a)r Ryhoravich Lukashenka;, ; rus, Александр Григорьевич Лука� ...
into national prominence. He garnered 45% of the vote in the first round and 80% in the second, defeating Vyacheslav Kebich
Vyacheslav Frantsevich Kebich ( be, Вячаслаў Францавіч Кебіч, Vjačaslaŭ Francavič Kjebič , russian: Вячесла́в Фра́нцевич Ке́бич; 10 June 1936 – 9 December 2020) was a Belarusian politician and ...
who received 14% of the vote.
Lukashenko was officially re-elected in 2001, in 2006, in 2010, in 2015 and again in 2020, although none of those elections were considered free or fair nor democratic.Belarus election 'neither free nor fair,' says UN human rights expertUnited Nations (October 13, 2015).
Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and sup ...
, and Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
have criticized Lukashenko's violations of human rights.
The 2000s saw a number of economic disputes between Belarus and its primary economic partner, Russia. The first one was the 2004 Russia–Belarus energy dispute when Russian energy giant Gazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the larges ...
ceased the import of gas into Belarus because of price disagreements. The 2007 Russia–Belarus energy dispute
The Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia. It escala ...
centered on accusations by Gazprom that Belarus was siphoning oil off of the Druzhba pipeline
The Druzhba pipeline (russian: нефтепровод «Дружба»; also has been referred to as the Friendship Pipeline and the Comecon Pipeline) is one of the world's longest oil pipelines and one of the largest oil pipeline networks in th ...
that runs through Belarus. Two years later the so-called Milk War
The Milk War was a trade conflict between Russia and Belarus in June 2009. Russia and Belarus have close relations and the conflict stemmed from Russia allegedly attempting to pay Belarus US$500 million to recognize the independence o ...
, a trade dispute, started when Russia wanted Belarus to recognize the independence of Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which vi ...
and South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
and through a series of events ended up banning the import of dairy products from Belarus.
In 2011, Belarus suffered a severe economic crisis attributed to Lukashenko's government's centralized control of the economy, with inflation reaching 108.7%. Around the same time the 2011 Minsk Metro bombing
The 2011 Minsk Metro bombing took place on 11 April 2011 when 15 people were killed and 204 were injured when a bomb exploded within the Minsk Metro, Belarus. The explosion happened at the central Kastryčnickaja (Minsk Metro), Kastryčnickaja s ...
occurred in which 15 people were killed and 204 were injured. Two suspects, who were arrested within two days, confessed to being the perpetrators and were executed by shooting in 2012. The official version of events as publicised by the Belarusian government was questioned in the unprecedented wording of the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
statement condemning "the apparent terrorist attack" intimating the possibility that the Belarusian government itself was behind the bombing.
 Mass protests erupted across the country following the disputed
Mass protests erupted across the country following the disputed 2020 Belarusian presidential election
Presidential elections were held in Belarus on Sunday, 9 August 2020. Early voting began on 4 August and ran until 8 August.
Incumbent Alexander Lukashenko was announced by the Central Election Commission (CEC) to have won a sixth term in offi ...
, in which Lukashenko sought a sixth term in office. Neighbouring countries Poland and Lithuania do not recognize Lukashenko as the legitimate president of Belarus and the Lithuanian government has allotted a residence for main opposition candidate Sviatlana Tsikhanouskaya
Sviatlana Heorhiyeuna Tsikhanouskaya (' Pilipchuk;, , ; russian: Светлана Георгиевна Тихановская, , Svetlana Georgiyevna Tikhanovskaya, , , born 11 September 1982) is a Belarusian educator and the leader of the Bel ...
and other members of the Belarusian opposition in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
. Neither is Lukashenko recognized as the legitimate president of Belarus by the European Union, Canada, the United Kingdom nor the United States. The European Union, Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States have all imposed sanctions against Belarus because of the rigged election and political oppression during the ongoing protests in the country. Further sanctions were imposed in 2022 following the country's role in the invasion of Ukraine
The territory of present-day Ukraine has been Invasion, invaded or Military occupation, occupied a number of times throughout History of Ukraine, its history.
List
See also
*List of invasions
*List of wars involving Ukraine
References
...
.
Geography
Belarus lies between latitudes 51° and 57° N, and longitudes 23° and 33° E. Its extension from north to south is , from west to east is . It islandlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
, relatively flat, and contains large tracts of marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
y land. About 40% of Belarus is covered by forests. The country lies within two ecoregions: Sarmatic mixed forests
The Sarmatic mixed forests constitute an ecoregion within the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome, according to the World Wide Fund for Nature classification (ecoregion PA0436). The term comes from the word "Sarmatia".
Distribution
This e ...
and Central European mixed forests
The Central European mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0412) is a temperate hardwood forest covering much of northeastern Europe, from Germany to Russia. The area is only about one-third forested, with pressure from human agriculture leaving the r ...
.
Many streams and 11,000 lakes are found in Belarus. Three major rivers run through the country: the Neman
The Neman, Nioman, Nemunas or MemelTo bankside nations of the present: Lithuanian: be, Нёман, , ; russian: Неман, ''Neman''; past: ger, Memel (where touching Prussia only, otherwise Nieman); lv, Nemuna; et, Neemen; pl, Niemen; ...
, the Pripyat
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 19 ...
, and the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
. The Neman flows westward towards the Baltic sea and the Pripyat flows eastward to the Dnieper; the Dnieper flows southward towards the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
.
 The highest point is
The highest point is Dzyarzhynskaya Hara
Dzyarzhynskaya Hara ( Belarusian: Дзяржынская гара - ''Dziaržynskaja hara'' ) is the highest point in Belarus. The hill is 345 meters (1,130 ft) above sea level and is located west of Minsk, near Dzyarzhynsk, in the village ...
(Dzyarzhynsk Hill) at , and the lowest point is on the Neman River at . The average elevation of Belarus is above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The climate features mild to cold winters, with January minimum temperatures ranging from in southwest (Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
) to in northeast (Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
), and cool and moist summers with an average temperature of . Belarus has an average annual rainfall of . The country is in the transitional zone between continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
s and maritime climates.
Natural resources include peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
, dolomite (limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
), marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
, chalk, sand, gravel, and clay. About 70% of the radiation from neighboring Ukraine's 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR in the Sov ...
entered Belarusian territory, and about a fifth of Belarusian land (principally farmland and forests in the southeastern regions) was affected by radiation fallout. The United Nations and other agencies have aimed to reduce the level of radiation in affected areas, especially through the use of caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
binders and rapeseed
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus ''subsp.'' napus''), also known as rape, or oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains a ...
cultivation, which are meant to decrease soil levels of caesium-137
Caesium-137 (), cesium-137 (US), or radiocaesium, is a radioactive isotope of caesium that is formed as one of the more common fission products by the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and other fissionable isotopes in nuclear reactors and nucl ...
.
Belarus borders five countries: Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
to the north, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
to the northwest, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
to the west, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
to the north and the east, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
to the south. Treaties in 1995 and 1996 demarcated Belarus's borders with Latvia and Lithuania, and Belarus ratified a 1997 treaty establishing the Belarus-Ukraine border in 2009. Belarus and Lithuania ratified final border demarcation documents in February 2007.
Government and politics
 Belarus, by constitution, is a
Belarus, by constitution, is a presidential republic
A presidential system, or single executive system, is a form of government in which a head of government, typically with the title of president, leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch in systems that use separation ...
with separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typic ...
, governed by a president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
and the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
.
Under Lukashenko, Belarus has been considered an autocracy
Autocracy is a system of government in which absolute power over a state is concentrated in the hands of one person, whose decisions are subject neither to external legal restraints nor to regularized mechanisms of popular control (except perh ...
where power is ultimately concentrated in the hands of the president, elections are not free and judicial independence Judicial independence is the concept that the judiciary should be independent from the other branches of government. That is, courts should not be subject to improper influence from the other branches of government or from private or partisan inte ...
is weak.
The term
Term may refer to:
* Terminology, or term, a noun or compound word used in a specific context, in particular:
**Technical term, part of the specialized vocabulary of a particular field, specifically:
***Scientific terminology, terms used by scient ...
for each presidency is five years. Under the 1994 constitution, the president could serve for only two terms as president, but a change in the constitution in 2004 eliminated term limits. Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (as transliterated from Russian language, Russian; also transliterated from Belarusian language, Belarusian as Alyaksand(a)r Ryhoravich Lukashenka;, ; rus, Александр Григорьевич Лука� ...
has been the president of Belarus since 1994. In 1996, Lukashenko called for a controversial vote to extend the presidential term from five to seven years, and as a result the election
''The Election'' () is a political drama series produced by Hong Kong Television Network (HKTV). With a budget of HK$15 million, filming started in July 2014 and wrapped up on 28 October 2014. Popularly voted to be the inaugural drama of ...
that was supposed to occur in 1999 was pushed back to 2001. The referendum on the extension was denounced as a "fantastic" fake by the chief electoral officer, Viktar Hanchar
Viktar Hanchar, or Viktar Hančar ( be, Віктар Ганчар, russian: Виктор Гончар, Viktor Gonchar, September 7, 1957 – September 16, 1999?) was a Belarusian politician who disappeared and was presumably murdered in 1999. He w ...
, who was removed from the office for official matters only during the campaign. The National Assembly is a bicameral parliament
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
comprising the 110-member House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
(the lower house) and the 64-member Council of the Republic (the upper house).
 The House of Representatives has the power to appoint the
The House of Representatives has the power to appoint the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, make constitutional amendments, call for a vote of confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
on the prime minister, and make suggestions on foreign and domestic policy. The Council of the Republic has the power to select various government officials, conduct an impeachment trial of the president, and accept or reject the bills passed by the House of Representatives. Each chamber has the ability to veto any law passed by local officials if it is contrary to the constitution.
The government includes a Council of Ministers, headed by the prime minister and five deputy prime ministers. The members of this council need not be members of the legislature and are appointed by the president. The judiciary comprises the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
and specialized courts such as the Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ...
, which deals with specific issues related to constitutional and business law. The judges of national courts are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Council of the Republic. For criminal cases, the highest court of appeal is the Supreme Court. The Belarusian Constitution forbids the use of special extrajudicial courts.
In the 2012 parliamentary election, 105 of the 110 members elected to the House of Representatives were not affiliated with any political party. The Communist Party of Belarus
The Communist Party of Belarus (CPB; russian: Коммунисти́ческая па́ртия Белару́си, Kommunisticheskaya Partiya Belarusi; be, Камуністы́чная па́ртыя Белару́сі, Kamunistyčnaja Partyja B ...
won 3 seats, and the Agrarian Party and Republican Party of Labour and Justice
)
, seats1_title = House of Representatives
, seats1 =
, seats2_title = Council of the Republic
, seats2 =
, seats3_title = Local seats
, seats3 =
, colours = Red, Green (official) Pi ...
, one each. Most non-partisans represent a wide scope of social organizations such as workers' collectives, public associations, and civil society organizations, similar to the composition of the Soviet legislature.
Elections
 Belarus has often been described as "Europe's last dictatorship" by some media outlets, politicians and authors due to its authoritarian government. The
Belarus has often been described as "Europe's last dictatorship" by some media outlets, politicians and authors due to its authoritarian government. The Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
removed Belarus from its observer status since 1997 as a response for election irregularities in the November 1996 constitutional referendum and parliament by-elections. Re-admission of the country into the council is dependent on the completion of benchmarks set by the council, including the improvement of human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
, rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannica ...
, and democracy.
Neither the pro-Lukashenko parties, such as the Belarusian Socialist Sporting Party and the Republican Party of Labour and Justice
)
, seats1_title = House of Representatives
, seats1 =
, seats2_title = Council of the Republic
, seats2 =
, seats3_title = Local seats
, seats3 =
, colours = Red, Green (official) Pi ...
nor the People's Coalition 5 Plus
The People's Coalition 5 Plus (''Narodnaja Kaalicyja Piaciorka Plus'') was a political alliance in Belarus, that opposed the regime of president Alexander Lukashenko.
At the legislative elections, 13–17 October 2004, the alliance won no seats. ...
opposition parties, such as the Belarusian People's Front
The Belarusian Popular Front "Revival" (BPF, be, Беларускі Народны Фронт "Адраджэньне", БНФ; ''Biełaruski Narodny Front "Adradžeńnie"'', ''BNF'') was a social and political movement in Belarus in the late 1 ...
and the United Civil Party of Belarus
The United Civic Party (UCP; be, Аб'яднаная грамадзянская партыя; АГП, Abjadnanaja hramadzianskaja partyja; AHP; russian: Объединённая гражданская партия; ОГП, Obyedinonnaya grazhdans ...
, won any seats in the 2004 elections
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest c ...
. The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
(OSCE) ruled that the elections were unfair because opposition candidates were arbitrarily denied registration and the election process was designed to favor the ruling party.
 In the 2006 presidential election, Lukashenko was opposed by
In the 2006 presidential election, Lukashenko was opposed by Alaksandar Milinkievič
Alaksandar Uladzimyeravič Milinkyevič ( be, Аляксандар Уладзімеравіч Мілінкевіч, translit=Alyaksandar Uladzimyeravich Milinkyevich, russian: Александр Владимирович Милинкевич, trans ...
, who represented a coalition of opposition parties, and by Alaksandar Kazulin
Alyaksandr Kazulin ( be, Аляксандр Уладзіслававіч Казулін, russian: Александр Владиславович Козулин, born 25 November 1955 in
Minsk) is the former leader of the Belarusian Social Democr ...
of the Social Democrats. Kazulin was detained and beaten by police during protests surrounding the All Belarusian People's Assembly
The All Belarusian People's Assembly ( be, Усебеларускі народны сход, russian: Всебелорусское народное собрание) is a general meeting of the Belarusian Government with industry leaders and other ...
. Lukashenko won the election with 80% of the vote; the Russian Federation and the CIS
Cis or cis- may refer to:
Places
* Cis, Trentino, in Italy
* In Poland:
** Cis, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central
** Cis, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, north
Math, science and biology
* cis (mathematics) (cis(''θ'')), a trigonome ...
deemed the vote open and fair while the OSCE and other organizations called the election unfair.
After the December completion of the 2010 presidential election, Lukashenko was elected to a fourth straight term with nearly 80% of the vote in elections. The runner-up opposition leader Andrei Sannikov
Andrei Olegovich Sannikov (or Andrei Sannikau, be, Андрэй Алегавіч Саннікаў, russian: Андрей Олегович Санников, born 8 March 1954) is a Belarusian politician and activist. In the early 1990s, he headed ...
received less than 3% of the vote; independent observers criticized the election as fraudulent. When opposition protesters took to the streets in Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, many people, including most rival presidential candidates, were beaten and arrested by the state militia. Many of the candidates, including Sannikov, were sentenced to prison or house arrest for terms which are mainly and typically over four years.Belarus opposition leader Andrei Sannikov jailedBBC News Online
BBC News Online is the website of BBC News, the division of the BBC responsible for newsgathering and production. It is one of the most popular news websites, with 1.2 billion website visits in April 2021, as well as being used by 60% of the U ...
(14 May 2011) Six months later amid an unprecedented economic crisis, activists utilized social networking to initiate a fresh round of protests characterized by wordless hand-clapping.
In the 2020 presidential election
This national electoral calendar for 2020 lists the national/federal elections held in 2020 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 January:
**C ...
, Lukashenko won again with official results giving him 80% of the vote, leading to mass protests and numerous countries not recognizing the result, with the EU imposing sanctions.
Foreign relations
 The Byelorussian SSR was one of the two Soviet republics that joined the
The Byelorussian SSR was one of the two Soviet republics that joined the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
along with the Ukrainian SSR as one of the original 51 members in 1945. Belarus and Russia have been close trading partners and diplomatic allies since the breakup of the Soviet Union. Belarus is dependent on Russia for imports of raw materials and for its export market.
The union of Russia and Belarus
The Union State,; be, Саю́зная дзяржа́ва Расі́і і Белару́сі, Sajuznaja dziaržava Rasii i Bielarusi, links=no. or Union State of Russia and Belarus,; be, Саю́зная дзяржа́ва, Sajuznaja dziar� ...
, a supranational confederation, was established in a 1996–99 series of treaties that called for monetary union, equal rights, single citizenship, and a common foreign and defense policy. However, the future of the union has been placed in doubt because of Belarus's repeated delays of monetary union, the lack of a referendum date for the draft constitution, and a dispute over the petroleum trade. Belarus was a founding member of the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
(CIS). Belarus has trade agreements with several European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
member states (despite other member states' travel ban on Lukashenko and top officials), including neighboring Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland. Travel bans imposed by the European Union have been lifted in the past in order to allow Lukashenko to attend diplomatic meetings and also to engage his government and opposition groups in dialogue.
 Bilateral relations with the United States are strained; the United States had not had an ambassador in Minsk since 2007 and Belarus never had an ambassador in Washington since 2008. Diplomatic relations remained tense, and in 2004, the United States passed the Belarus Democracy Act, which authorized funding for anti-government Belarusian NGOs, and prohibited loans to the Belarusian government, except for humanitarian purposes.
Sino-Belarusian relations have improved, strengthened by the visit of President Lukashenko to China in October 2005. Belarus also has strong ties with
Bilateral relations with the United States are strained; the United States had not had an ambassador in Minsk since 2007 and Belarus never had an ambassador in Washington since 2008. Diplomatic relations remained tense, and in 2004, the United States passed the Belarus Democracy Act, which authorized funding for anti-government Belarusian NGOs, and prohibited loans to the Belarusian government, except for humanitarian purposes.
Sino-Belarusian relations have improved, strengthened by the visit of President Lukashenko to China in October 2005. Belarus also has strong ties with Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, considered a key partner in the Middle East. In addition to the CIS, Belarus is a member of the Eurasian Economic Union
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of some post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The Treaty on the Eurasian Econo ...
(previously the Eurasian Economic Community
The Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC or EurAsEC) was a regional organisation between 2000 and 2014 which aimed for the economic integration of its member states.
The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on ...
), the Collective Security Treaty Organisation
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has ...
, the international Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
since 1998, and the Organization on Security and Cooperation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
(OSCE). As an OSCE member state, Belarus's international commitments are subject to monitoring under the mandate of the U.S. Helsinki Commission
The Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), also known as the U.S. Helsinki Commission, is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent U.S. government agency created by U.S. Congress, Congress in 1975 t ...
. Belarus is included in the European Union's Eastern Partnership
The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European External Action Service of the European Union (EU) together with the EU, its member states, and six Eastern European partners governing the EU's relationship with the post-Sovi ...
program, part of the EU's European Neighbourhood Policy
The European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) is a foreign relations instrument of the European Union (EU) which seeks to tie those countries to the east and south of the European territory of the EU to the Union. These countries, primarily developing ...
(ENP), which aims to bring the EU and its neighbours closer in economic and geopolitical terms. However, Belarus suspended its participation in the Eastern Partnership program on 28 June 2021, after the EU imposed more sanctions against the country.
Military
 Lieutenant General
Lieutenant General Viktor Khrenin
Viktor Gennadievich Khrenin ( be, Віктар Генадзевіч Хрэнін, russian: Виктор Геннадиевич Хренин) is a senior leader in the Belarusian Armed Forces and the current Minister of Defense. Lieutenant Gener ...
heads the Ministry of Defence, and Alexander Lukashenko (as president) serves as Commander-in-Chief. The armed forces were formed in 1992 using parts of the former Soviet Armed Forces
The Soviet Armed Forces, the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union and as the Red Army (, Вооружённые Силы Советского Союза), were the armed forces of the Russian SFSR (1917–1922), the Soviet Union (1922–1991), and th ...
on the new republic's territory. The transformation of the ex-Soviet forces into the Armed Forces of Belarus, which was completed in 1997, reduced the number of its soldiers by 30,000 and restructured its leadership and military formations.
Most of Belarus's service members are conscripts
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
, who serve for 12 months if they have higher education or 18 months if they do not. Demographic decreases in the Belarusians of conscription age have increased the importance of contract soldiers, who numbered 12,000 in 2001. In 2005, about 1.4% of Belarus's gross domestic product was devoted to military expenditure.
Belarus has not expressed a desire to join NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
but has participated in the Individual Partnership Program since 1997, and Belarus provides refueling and airspace support for the ISAF
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
mission in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. Belarus first began to cooperate with NATO upon signing documents to participate in their Partnership for Peace Program in 1995. However, Belarus cannot join NATO because it is a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has ...
. Tensions between NATO and Belarus peaked after the March 2006 presidential election in Belarus.
Human rights and corruption
 Belarus's
Belarus's Democracy Index
The ''Democracy Index'' is an index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), the research division of the Economist Group, a UK-based private company which publishes the weekly newspaper ''The Economist''. Akin to a Human Development I ...
rating is the lowest in Europe, the country is labelled as "not free" by Freedom House, as "repressed" in the Index of Economic Freedom, and in the Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders, Belarus is ranked 153th out of 180 countries for 2022. The Belarusian government is also criticized for human rights violations and its persecution of non-governmental organisations, independent journalists, national minorities, and opposition politicians. Lukashenko announced a new law in 2014 that will prohibit kolkhoz workers (around 9% of total work force) from leaving their jobs at will—a change of job and living location will require permission from governors. The law was compared with serfdom by Lukashenko himself. Similar regulations were introduced for the forestry industry in 2012. Belarus is the only European country still using capital punishment having carried out executions in 2011.
The judicial system in Belarus lacks independence and is subject to political interference. Corrupt practices such as bribery often took place during tender processes, and whistleblower protection and national ombudsman are lacking in Belarus's anti-corruption system.
On 1 September 2020, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights declared that its experts received reports of 450 documented cases of torture and ill-treatment of people who were arrested during the 2020–2021 Belarusian protests, protests following the presidential election. The experts also received reports of violence against women and children, including sexual abuse and rape with rubber batons. At least three detainees suffered injuries indicative of sexual violence in Okrestino prison in Minsk or on the way there. The victims were hospitalized with intramuscular bleeding of the rectum, anal fissure and bleeding, and damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum. In an interview from September 2020 Lukashenko claimed that detainees faked their bruises, saying, "Some of the girls there had their butts painted in blue".
On 23 May 2021, Belarusian authorities Ryanair Flight 4978, forcibly diverted a Ryanair flight from Athens to Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
in order to detain opposition activist and journalist Roman Protasevich along with his girlfriend; in response, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
imposed stricter sanctions on Belarus. In May 2021, Lukashenko threatened that he will flood the European Union with migrants and drugs as a response to the sanctions. In July 2021, Belarusian authorities launched a hybrid warfare by human trafficking of 2021 Belarus–European Union border crisis, migrants to the European Union. Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
n authorities and top European officials Ursula von der Leyen, Josep Borrell condemned the usage of migrants as a weapon and suggested that Belarus could be subject to further sanctions. In August 2021, Belarusian officials, wearing uniforms, riot shields and helmets, were recorded on camera near the Belarus–Lithuania border pushing and urging the migrants to cross the European Union border. Following the granting of humanitarian visas to an Olympic athlete Krystsina Tsimanouskaya and her husband, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
also accused Belarus for organizing a hybrid warfare as the number of migrants crossing the Belarus–Poland border sharply increased multiple times when compared to the 2020 statistics. Illegal migrants numbers also exceeded the previous annual numbers in Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
. On 2 December 2021, the United States, European Union, United Kingdom and Canada imposed new sanctions on Belarus.
Administrative divisions
 Belarus is divided into six regions called oblasts ( be, вобласць; russian: область), which are named after the cities that serve as their administrative centers:
Belarus is divided into six regions called oblasts ( be, вобласць; russian: область), which are named after the cities that serve as their administrative centers: Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
, Gomel, Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
, Mogilev, Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, and Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
. Each region has a provincial legislative authority, called a region council ( be, link=no, абласны Савет Дэпутатаў; russian: link=no, Областной Совет депутатов), which is elected by its residents, and a provincial executive authority called a region administration ( be, link=no, абласны выканаўчы камітэт; russian: link=no, областной исполнительный комитет), whose chairman is appointed by the president. The Regions are further subdivided into 118 raions, commonly translated as districts ( be, link=no, раён; russian: link=no, район). Each raion has its own legislative authority, or raion council, ( be, link=no, раённы Савет Дэпутатаў; russian: link=no, районный Совет депутатов) elected by its residents, and an executive authority or raion administration appointed by oblast executive powers. The city of Minsk is split into nine districts and enjoys special status as the nation's capital at the same administration level as the oblasts. It is run by an executive committee and has been granted a charter of self-rule.
Local government
Local government in Belarus is administered by administrative-territorial units ( be, адміністрацыйна-тэрытарыяльныя адзінкі; russian: административно-территориальные единицы), and occurs on two levels: basic and primary. At the basic level are 118 raions councils and 10 cities of oblast subordination councils, which are supervised by the governments of the oblasts. At the primary level are 14 cities of raion subordination councils, 8 Urban-type settlements in Belarus, urban-type settlements councils, and 1,151 village councils. The councils are elected by their residents, and have executive committees appointed by their executive committee chairs. The chairs of executive committees for raions and city of oblast subordinations are appointed by the regional executive committees at the level above; the chairs of executive committees for towns of raion subordination, settlements and villages are appointed by their councils, but upon the recommendation of the raion executive committees. In either case, the councils have the power to approve or reject a nonimee for executive committee chair. Human settlement, Settlements without their own local council and executive committee are called territorial units ( be, тэрытарыяльныя адзінкі; russian: территориальные единицы). These territorial units may also be classified as a city of regional or raion subordination, urban-type settlement or rural settlement, but whose government is administered by the council of another primary or basic unit. In October 1995, a decree, presidential decree abolished the local governments of cities of raion subordination and urban-type settlements which served as the administrative centre, administrative center of raions, demoting them from administrative-territorial units to territorial units. As for 2019, the administrative-territorial and territorial units include 115 cities, 85 urban-type settlements, and 23,075 rural settlements.Economy
Belarus has trade relations with over 180 countries. The main trading partners are Russia, which accounts for about 45% of Belarusian exports and 55% of imports, and the EU countries, which account for 25% of exports and 20% of imports. In 2019 the share of manufacturing in GDP was 31%, over two-thirds of this amount falls on manufacturing industries. The number of people employed in the industry is 34.7% of the working population. The growth rate is much lower than for the economy as a whole—about 2.2% in 2021. At the time of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Belarus was one of the world's most industrially developed states by percentage of GDP as well as the richest CIS member-state.World Bank. "Belarus: Prices, Markets, and Enterprise Reform,
In 2019 the share of manufacturing in GDP was 31%, over two-thirds of this amount falls on manufacturing industries. The number of people employed in the industry is 34.7% of the working population. The growth rate is much lower than for the economy as a whole—about 2.2% in 2021. At the time of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Belarus was one of the world's most industrially developed states by percentage of GDP as well as the richest CIS member-state.World Bank. "Belarus: Prices, Markets, and Enterprise Reform,p. 1
World Bank, 1997; In 2015, 39.3% of Belarusians were employed by state-controlled companies, 57.2% were employed by private companies (in which the government has a 21.1% stake) and 3.5% were employed by foreign companies. The country relies on Russia for various imports, including petroleum. Important agricultural products include potatoes and cattle byproducts, including meat. In 1994, Belarus's main exports included heavy machinery (especially Belarus (tractor), tractors), agricultural products, and energy products. Economically, Belarus involved itself in the CIS,
Eurasian Economic Community
The Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC or EurAsEC) was a regional organisation between 2000 and 2014 which aimed for the economic integration of its member states.
The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on ...
, and Union State, Union with Russia.
In the 1990s, however, industrial production plunged due to decreases in imports, investment, and demand for Belarusian products from its trading partners. GDP only began to rise in 1996; the country was the fastest-recovering former Soviet republic in the terms of its economy. In 2006, GDP amounted to US$83.1 billion in purchasing power parity (PPP) dollars (estimate), or about $8,100 per capita. In 2005, GDP increased by 9.9%; the inflation rate averaged 9.5%.
Since the disintegration of the Soviet Union, under Lukashenko's leadership, Belarus has maintained government control over key industries and eschewed the large-scale privatizations seen in other former Soviet republics.
 Due to its failure to protect labor rights, including passing laws forbidding unemployment or working outside of state-controlled sectors, Belarus lost its EU Generalized System of Preferences status on 21 June 2007, which raised tariff rates to their prior most favored nation levels. Belarus applied to become a member of the World Trade Organization in 1993.
The labor force consists of more than four million people, among whom women hold slightly more jobs than men. In 2005, nearly a quarter of the population was employed by industrial factories. Employment is also high in agriculture, manufacturing sales, trading goods, and education. The unemployment rate, according to government statistics, was 1.5% in 2005. There were 679,000 unemployed Belarusians, two-thirds of whom were women. The unemployment rate has been in decline since 2003, and the overall rate of employment is the highest since statistics were first compiled in 1995.
The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble. The currency was introduced in May 1992 to replace the Soviet ruble and it has undergone redenomination twice since then. The first coins of the Republic of Belarus were issued on 27 December 1996. The ruble was reintroduced with new values in 2000 and has been in use ever since. As part of the Union State, Union of Russia and Belarus, both states have discussed using a single currency along the same lines as the Euro. This led to a proposal that the Belarusian ruble be discontinued in favor of the Russian ruble (RUB), starting as early as 1 January 2008. The National Bank of the Republic of Belarus, National Bank of Belarus abandoned pegging the Belarusian ruble to the Russian rouble in August 2007.
On 23 May 2011, the ruble depreciated 56% against the United States dollar. The depreciation was even steeper on the black market and financial collapse seemed imminent as citizens rushed to exchange their rubles for dollars, euros, durable goods, and canned goods. On 1 June 2011, Belarus requested an economic rescue package from the International Monetary Fund. A new currency, the new Belarusian ruble (ISO 4217 code: BYN) was introduced in July 2016, replacing the Belarusian ruble in a rate of 1:10,000 (10,000 old ruble = 1 new ruble). From 1 July until 31 December 2016, the old and new currencies were in parallel circulation and series 2000 notes and coins can be exchanged for series 2009 from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2021. This redenomination can be considered an effort to fight the high inflation rate.
The banking system of Belarus consists of two levels: Central Bank (National Bank of the Republic of Belarus) and 25 commercial banks.
Due to its failure to protect labor rights, including passing laws forbidding unemployment or working outside of state-controlled sectors, Belarus lost its EU Generalized System of Preferences status on 21 June 2007, which raised tariff rates to their prior most favored nation levels. Belarus applied to become a member of the World Trade Organization in 1993.
The labor force consists of more than four million people, among whom women hold slightly more jobs than men. In 2005, nearly a quarter of the population was employed by industrial factories. Employment is also high in agriculture, manufacturing sales, trading goods, and education. The unemployment rate, according to government statistics, was 1.5% in 2005. There were 679,000 unemployed Belarusians, two-thirds of whom were women. The unemployment rate has been in decline since 2003, and the overall rate of employment is the highest since statistics were first compiled in 1995.
The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble. The currency was introduced in May 1992 to replace the Soviet ruble and it has undergone redenomination twice since then. The first coins of the Republic of Belarus were issued on 27 December 1996. The ruble was reintroduced with new values in 2000 and has been in use ever since. As part of the Union State, Union of Russia and Belarus, both states have discussed using a single currency along the same lines as the Euro. This led to a proposal that the Belarusian ruble be discontinued in favor of the Russian ruble (RUB), starting as early as 1 January 2008. The National Bank of the Republic of Belarus, National Bank of Belarus abandoned pegging the Belarusian ruble to the Russian rouble in August 2007.
On 23 May 2011, the ruble depreciated 56% against the United States dollar. The depreciation was even steeper on the black market and financial collapse seemed imminent as citizens rushed to exchange their rubles for dollars, euros, durable goods, and canned goods. On 1 June 2011, Belarus requested an economic rescue package from the International Monetary Fund. A new currency, the new Belarusian ruble (ISO 4217 code: BYN) was introduced in July 2016, replacing the Belarusian ruble in a rate of 1:10,000 (10,000 old ruble = 1 new ruble). From 1 July until 31 December 2016, the old and new currencies were in parallel circulation and series 2000 notes and coins can be exchanged for series 2009 from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2021. This redenomination can be considered an effort to fight the high inflation rate.
The banking system of Belarus consists of two levels: Central Bank (National Bank of the Republic of Belarus) and 25 commercial banks.
Demographics
According to the 2019 census the population was 9.41 million with ethnicBelarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
constituting 84.9% of Belarus's total population. Minority groups include: Russians (7.5%), Poles (3.1%), and Ukrainians (1.7%).
Belarus has a population density of about 50 people per square kilometre (127 per sq mi); 70% of its total population is concentrated in urban areas. Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, the nation's capital and largest city, was home to 1,937,900 residents . Gomel, with a population of 481,000, is the second-largest city and serves as the capital of the Homiel Voblast. Other large cities are Mogilev (365,100), Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
(342,400), Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
(314,800) and Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
(298,300).
Like many other Eastern European countries, Belarus has a negative population growth rate and a negative natural growth rate. In 2007, Belarus's population declined by 0.41% and its Total fertility rate, fertility rate was 1.22, well Sub-replacement fertility, below the replacement rate. Its net migration rate is +0.38 per 1,000, indicating that Belarus experiences slightly more immigration than emigration. , 69.9% of Belarus's population is aged 14 to 64; 15.5% is under 14, and 14.6% is 65 or older. Its population is also aging; the median age of 30–34 is estimated to rise to between 60 and 64 in 2050. There are about 0.87 males per female in Belarus. The average life expectancy is 72.15 (66.53 years for men and 78.1 years for women). Over 99% of Belarusians aged 15 and older are literate.
Religion and languages
 According to the census of November 2011, 58.9% of all Belarusians adhered to some kind of religion; out of those, Eastern Orthodoxy made up about 82%: Eastern Orthodox in Belarus are mainly part of the Belarusian Exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church, though a small Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church also exists. Roman Catholicism in Belarus, Roman Catholicism is practiced mostly in the western regions, and there are also different denominations of Protestantism. Minorities also practice Belarusian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism, Judaism, Islam and Modern paganism, neo-paganism. Overall, 48.3% of the population is Orthodox Christian, 41.1% is not religious, 7.1% is Roman Catholic and 3.3% follows other religions.
Belarus's Catholic minority is concentrated in the western part of the country, especially around Hrodna, is made up of a mixture of Belarusians and the country's Poles, Polish and Lithuanian people, Lithuanian minorities. President Lukashenko has stated that Orthodox and Catholic believers are the "two main confessions in our country".
Belarus was once a major center of European Jews, with 10% of the population being history of the Jews in Belarus, Jewish. But since the mid-20th century, the number of Jews has been reduced by the Holocaust, deportation, and emigration, so that today it is a very small minority of less than one percent. The Lipka Tatars, numbering over 15,000, are predominantly Islam in Belarus, Muslims. According to Article 16 of the Constitution of Belarus, Constitution, Belarus has no official religion. While the freedom of religion, freedom of worship is granted in the same article, religious organizations deemed harmful to the government or social order can be prohibited.
Belarus's two official languages are Russian and Belarusian language, Belarusian; Russian is the most common language spoken at home, used by 70% of the population, while Belarusian, the official first language, is spoken at home by 23%. Minorities also speak Polish language, Polish, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and Eastern Yiddish. Belarusian, although not as widely used as Russian, is the mother tongue of 53.2% of the population, whereas Russian is the mother tongue of only 41.5%.
According to the census of November 2011, 58.9% of all Belarusians adhered to some kind of religion; out of those, Eastern Orthodoxy made up about 82%: Eastern Orthodox in Belarus are mainly part of the Belarusian Exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church, though a small Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church also exists. Roman Catholicism in Belarus, Roman Catholicism is practiced mostly in the western regions, and there are also different denominations of Protestantism. Minorities also practice Belarusian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism, Judaism, Islam and Modern paganism, neo-paganism. Overall, 48.3% of the population is Orthodox Christian, 41.1% is not religious, 7.1% is Roman Catholic and 3.3% follows other religions.
Belarus's Catholic minority is concentrated in the western part of the country, especially around Hrodna, is made up of a mixture of Belarusians and the country's Poles, Polish and Lithuanian people, Lithuanian minorities. President Lukashenko has stated that Orthodox and Catholic believers are the "two main confessions in our country".
Belarus was once a major center of European Jews, with 10% of the population being history of the Jews in Belarus, Jewish. But since the mid-20th century, the number of Jews has been reduced by the Holocaust, deportation, and emigration, so that today it is a very small minority of less than one percent. The Lipka Tatars, numbering over 15,000, are predominantly Islam in Belarus, Muslims. According to Article 16 of the Constitution of Belarus, Constitution, Belarus has no official religion. While the freedom of religion, freedom of worship is granted in the same article, religious organizations deemed harmful to the government or social order can be prohibited.
Belarus's two official languages are Russian and Belarusian language, Belarusian; Russian is the most common language spoken at home, used by 70% of the population, while Belarusian, the official first language, is spoken at home by 23%. Minorities also speak Polish language, Polish, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and Eastern Yiddish. Belarusian, although not as widely used as Russian, is the mother tongue of 53.2% of the population, whereas Russian is the mother tongue of only 41.5%.
Culture
Arts and literature
The Belarusian government sponsors annual cultural festivals such as the Slavianski Bazaar in Vitebsk, which showcases Belarusian performers, artists, writers, musicians, and actors. Several state holidays, such as List of countries by Independence Day, Independence Day and Victory Day (9 May), Victory Day, draw big crowds and often include displays such as fireworks and military parades, especially in Vitebsk and Minsk. The government's Ministry of Culture finances events promoting Belarusian arts and culture both inside and outside the country. Belarusian literature began with 11th- to 13th-century religious scripture, such as the 12th-century poetry of Cyril of Turaw. By the 16th century, Polotsk resident Francysk Skaryna translated the Bible into Belarusian. It was published in Prague andVilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
sometime between 1517 and 1525, making it the first book printed in Belarus or anywhere in Eastern Europe."Belarus: history"Britannica.com
accessed 4 March 2016. The modern era of Belarusian literature began in the late 19th century; one prominent writer was Yanka Kupala. Many Belarusian writers of the time, such as Uładzimir Žyłka, Kazimir Svayak, Yakub Kolas, Źmitrok Biadula, and Maksim Haretski, wrote for ''Nasha Niva'', a Belarusian-language paper published that was previously published in Vilnius but now is published in Minsk. After Belarus was incorporated into the Soviet Union, the Soviet government took control of the Republic's cultural affairs. At first, a policy of "Belarusianization" was followed in the newly formed Byelorussian SSR. This policy was reversed in the 1930s, and the majority of prominent Belarusian intellectuals and nationalist advocates were either exiled or killed in Stalinist purges. The free development of literature occurred only in Polish-held territory until Soviet occupation in 1939. Several poets and authors went into exile after the Nazi occupation of Belarus and would not return until the 1960s.
 The last major revival of Belarusian literature occurred in the 1960s with novels published by Vasil Bykaŭ and Uladzimir Karatkievich. An influential author who devoted his work to awakening the awareness of the catastrophes the country has suffered, was Ales Adamovich. He was named by Svetlana Alexievich, the Belarusian winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature 2015, as "her main teacher, who helped her to find a path of her own".
Music of Belarus, Music in Belarus largely comprises a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the
The last major revival of Belarusian literature occurred in the 1960s with novels published by Vasil Bykaŭ and Uladzimir Karatkievich. An influential author who devoted his work to awakening the awareness of the catastrophes the country has suffered, was Ales Adamovich. He was named by Svetlana Alexievich, the Belarusian winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature 2015, as "her main teacher, who helped her to find a path of her own".
Music of Belarus, Music in Belarus largely comprises a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Li ...
. In the 19th century, Polish composer Stanisław Moniuszko composed operas and chamber music pieces while living in Minsk. During his stay, he worked with Belarusian poet Vintsent Dunin-Martsinkyevich and created the opera ''Sialanka'' (''Peasant Woman''). At the end of the 19th century, major Belarusian cities formed their own opera and ballet companies. The ballet ''Nightingale (ballet), Nightingale'' by M. Kroshner was composed during the Soviet era and became the first Belarusian ballet showcased at the National Academic Vialiki Ballet Theatre in Minsk.
After the Second World War, music focused on the hardships of the Belarusian people or on those who took up arms in defense of the homeland. During this period, Anatoly Bogatyrev, creator of the opera ''In Polesye Virgin Forest'', served as the "tutor" of Belarusian composers. The National Academic Theatre of Ballet in Minsk was awarded the Prix Benois de la Danse, Benois de la Dance Prize in 1996 as the top ballet company in the world. Rock music has become increasingly popular in recent years, though the Belarusian government has attempted to limit the amount of foreign music aired on the radio in favor of traditional Belarusian music. Since 2004, Belarus has been sending artists to the Eurovision Song Contest.
Marc Chagall was born in Liozna (near Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
) in 1887. He spent the World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
years in Soviet Belarus, becoming one of the country's most distinguished artists and a member of the modernist avant-garde and was a founder of the Vitebsk Arts College.
Dress
The traditional Belarusian dress originates from theKievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
period. Due to the cool climate, clothes were designed to conserve body heat and were usually made from flax or wool. They were decorated with ornate patterns influenced by the neighboring cultures: Poles, Lithuanians, Latvians, Russians, and other European nations. Each region of Belarus has developed specific design patterns. One ornamental pattern common in early dresses currently decorates the hoist of the Flag of Belarus, Belarusian national flag, adopted in a 1995 Belarusian referendum, disputed referendum in 1995.
Cuisine
 Belarusian cuisine consists mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Belarusians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals later in the day. Wheat and rye bread are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. To show hospitality, a host traditionally presents an offering of bread and salt when greeting a guest or visitor.
Belarusian cuisine consists mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Belarusians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals later in the day. Wheat and rye bread are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. To show hospitality, a host traditionally presents an offering of bread and salt when greeting a guest or visitor.
Sport
Belarus has competed in the Olympic Games since the 1994 Winter Olympics as an independent nation. Receiving heavy sponsorship from the government, ice hockey is the nation's second most popular sport after Association football, football. The Belarus national football team, national football team has never qualified for a major tournament; however, FC BATE Borisov, BATE Borisov has played in the UEFA Champions League, Champions League. The Belarus national men's ice hockey team, national hockey team finished fourth at the Ice hockey at the 2002 Winter Olympics, 2002 Salt Lake City Olympics following a memorable upset win over Sweden in the quarterfinals and regularly competes in the Ice Hockey World Championships, World Championships, often making the quarterfinals. Numerous Belarusian players are present in the Kontinental Hockey League in Eurasia, particularly for Belarusian club HC Dinamo Minsk, and several have also played in the National Hockey League in North America. The 2014 IIHF World Championship was hosted in Belarus and the 2021 IIHF World Championship was supposed to be co-hosted in Latvia and Belarus but it was cancelled due to widespread protests and security concerns. The 2021 UEC European Track Championships in cycling was also cancelled because Belarus was not considered a safe host. Darya Domracheva is a leading biathlon, biathlete whose honours include three gold medals at the 2014 Winter Olympics. Tennis player Victoria Azarenka became the first Belarusian to win a Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam singles title at the Australian Open in 2012. She also won the gold medal in mixed doubles at the Tennis at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 Summer Olympics with Max Mirnyi, who holds ten Grand Slam titles in Singles tennis, doubles.
Other notable Belarusian sportspeople include cyclist Vasil Kiryienka, who won the 2015 UCI Road World Championships – Men's time trial, 2015 Road World Time Trial Championship, and middle-distance runner Maryna Arzamasava, who won the gold medal in the 2015 World Championships in Athletics – Women's 800 metres, 800m at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics.
Andrei Arlovski, who was born in Babruysk,
Darya Domracheva is a leading biathlon, biathlete whose honours include three gold medals at the 2014 Winter Olympics. Tennis player Victoria Azarenka became the first Belarusian to win a Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam singles title at the Australian Open in 2012. She also won the gold medal in mixed doubles at the Tennis at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 Summer Olympics with Max Mirnyi, who holds ten Grand Slam titles in Singles tennis, doubles.
Other notable Belarusian sportspeople include cyclist Vasil Kiryienka, who won the 2015 UCI Road World Championships – Men's time trial, 2015 Road World Time Trial Championship, and middle-distance runner Maryna Arzamasava, who won the gold medal in the 2015 World Championships in Athletics – Women's 800 metres, 800m at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics.
Andrei Arlovski, who was born in Babruysk, Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
, is a current Ultimate Fighting Championship, UFC fighter and the former List of UFC champions, UFC heavyweight champion of the world.
Belarus is also known for its strong rhythmic gymnasts. Noticeable gymnasts include Inna Zhukova, who earned silver at the 2008 Beijing Olympics, Liubov Charkashyna, who earned bronze at the 2012 London Olympics and Melitina Staniouta, Bronze All-Around Medalist of the 2015 World Championships. The Belorussian senior group earned bronze at the 2012 London Olympics.
Telecommunications
* Country code: .by The state telecom monopoly, Beltelecom, holds the exclusive interconnection with Internet providers outside of Belarus. Beltelecom owns all the backbone channels that linked to the Lattelecom, TEO LT, Tata Communications (former Teleglobe), Synterra, Rostelecom, Transtelekom and MTS ISPs. Beltelecom is the only operator licensed to provide commercial VoIP services in Belarus."ONI Country Profile: Belarus"OpenNet Initiative, 18 November 2010
World Heritage Sites
Belarus has four UNESCO-designated World Heritage Sites: the Mir Castle Complex, the Nesvizh Castle, the Białowieża Forest, Belovezhskaya Pushcha (shared withPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
), and the Struve Geodetic Arc (shared with nine other countries).
See also
* List of Belarus-related topics * Outline of Belarus * Republican Scientific Medical LibraryReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
* Bennett, Brian M. ''The Last Dictatorship in Europe: Belarus under Lukashenko'' (Columbia University Press, 2011) * Frear, Matthew. ''Belarus Under Lukashenka: Adaptive Authoritarianism'' (Routledge, 2015) * Korosteleva, Elena A. (June 2016)"The European Union and Belarus: Democracy Promotion by Technocratic Means?"
''Democratization'' 23: 4 pp. 678–698. . * * * Marples, David. Our Glorious Past': Lukashenka's Belarus and the Great Patriotic War'' (Columbia University Press, 2014) * Parker, Stewart. ''The Last Soviet Republic: Alexander Lukashenko's Belarus'' (Trafford Publishing, 2007) * Rudling, Pers Anders. ''The Rise and Fall of Belarusian Nationalism, 1906–1931'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2014) 436 pages * * * Snyder, Timothy (2004)
''The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999''
* * * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: The Making of a Nation: A Case Study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A Bibliographical Guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956)
External links
Website of the Republic of Belarus
by BelTA news agency
Belarus
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. *
FAO Country Profiles: Belarus
{{Authority control Belarus, Countries in Europe Eastern European countries Landlocked countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States Member states of the United Nations Member States of the Collective Security Treaty Organization Member States of the Eurasian Economic Union Republics Russian-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1991 States and territories established in the 980s Countries of Europe with multiple official languages