Bristol MMB «L9 Filton Junction 43366 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bristol () is a
 The port developed in the 11th century around the confluence of the Rivers Frome and
The port developed in the 11th century around the confluence of the Rivers Frome and
 During the 15th century, Bristol was the second most important port in the country, trading with Ireland, Iceland and
During the 15th century, Bristol was the second most important port in the country, trading with Ireland, Iceland and
 Fishermen from Bristol, who had fished the
Fishermen from Bristol, who had fished the  The 18th century saw an expansion of Bristol's population (45,000 in 1750) and its role in the Atlantic trade in Africans taken for slavery to the Americas. Bristol and later Liverpool became centres of the Triangular Trade. Manufactured goods were shipped to West Africa and exchanged for Africans; the enslaved captives were transported across the Atlantic to the Americas in the
The 18th century saw an expansion of Bristol's population (45,000 in 1750) and its role in the Atlantic trade in Africans taken for slavery to the Americas. Bristol and later Liverpool became centres of the Triangular Trade. Manufactured goods were shipped to West Africa and exchanged for Africans; the enslaved captives were transported across the Atlantic to the Americas in the
 From a population of about 330,000 in 1901, Bristol grew steadily during the 20th century, peaking at 428,089 in 1971. Its Avonmouth docklands were enlarged during the early 1900s by the Royal Edward Dock. Another new dock, the
From a population of about 330,000 in 1901, Bristol grew steadily during the 20th century, peaking at 428,089 in 1971. Its Avonmouth docklands were enlarged during the early 1900s by the Royal Edward Dock. Another new dock, the  Bristol was heavily damaged by Luftwaffe raids during World War II; about 1,300 people living or working in the city were killed and nearly 100,000 buildings were damaged, at least 3,000 beyond repair. The original central shopping area, near the bridge and castle, is now a park containing two bombed churches and fragments of the castle. A third bomb-damaged church nearby,
Bristol was heavily damaged by Luftwaffe raids during World War II; about 1,300 people living or working in the city were killed and nearly 100,000 buildings were damaged, at least 3,000 beyond repair. The original central shopping area, near the bridge and castle, is now a park containing two bombed churches and fragments of the castle. A third bomb-damaged church nearby,  The rebuilding of Bristol city centre was characterised by 1960s and 1970s
The rebuilding of Bristol city centre was characterised by 1960s and 1970s
 Bristol City council consists of 70 councillors representing 35 wards, with between one and three per ward serving four-year terms. Councillors are elected in thirds, with elections held in three years out of every four-year period. Thus, since wards do not have both councillors up for election at the same time, two-thirds of the wards participate in each election. Although the council was long dominated by the Labour Party, the Liberal Democrats have grown strong in the city and (as the largest party) took minority control of the council after the
Bristol City council consists of 70 councillors representing 35 wards, with between one and three per ward serving four-year terms. Councillors are elected in thirds, with elections held in three years out of every four-year period. Thus, since wards do not have both councillors up for election at the same time, two-thirds of the wards participate in each election. Although the council was long dominated by the Labour Party, the Liberal Democrats have grown strong in the city and (as the largest party) took minority control of the council after the
 Bristol's boundaries can be defined in several ways, including those of the city itself, the developed area, or Greater Bristol.
The city council boundary is the narrowest definition of the city itself. However, it unusually includes a large, roughly rectangular section of the western Severn Estuary ending at (but not including) the islands of Flat Holm (in Cardiff, Wales) and Steep Holm. This "seaward extension" can be traced back to the original boundary of the County of Bristol laid out in the charter granted to the city by
Bristol's boundaries can be defined in several ways, including those of the city itself, the developed area, or Greater Bristol.
The city council boundary is the narrowest definition of the city itself. However, it unusually includes a large, roughly rectangular section of the western Severn Estuary ending at (but not including) the islands of Flat Holm (in Cardiff, Wales) and Steep Holm. This "seaward extension" can be traced back to the original boundary of the County of Bristol laid out in the charter granted to the city by 
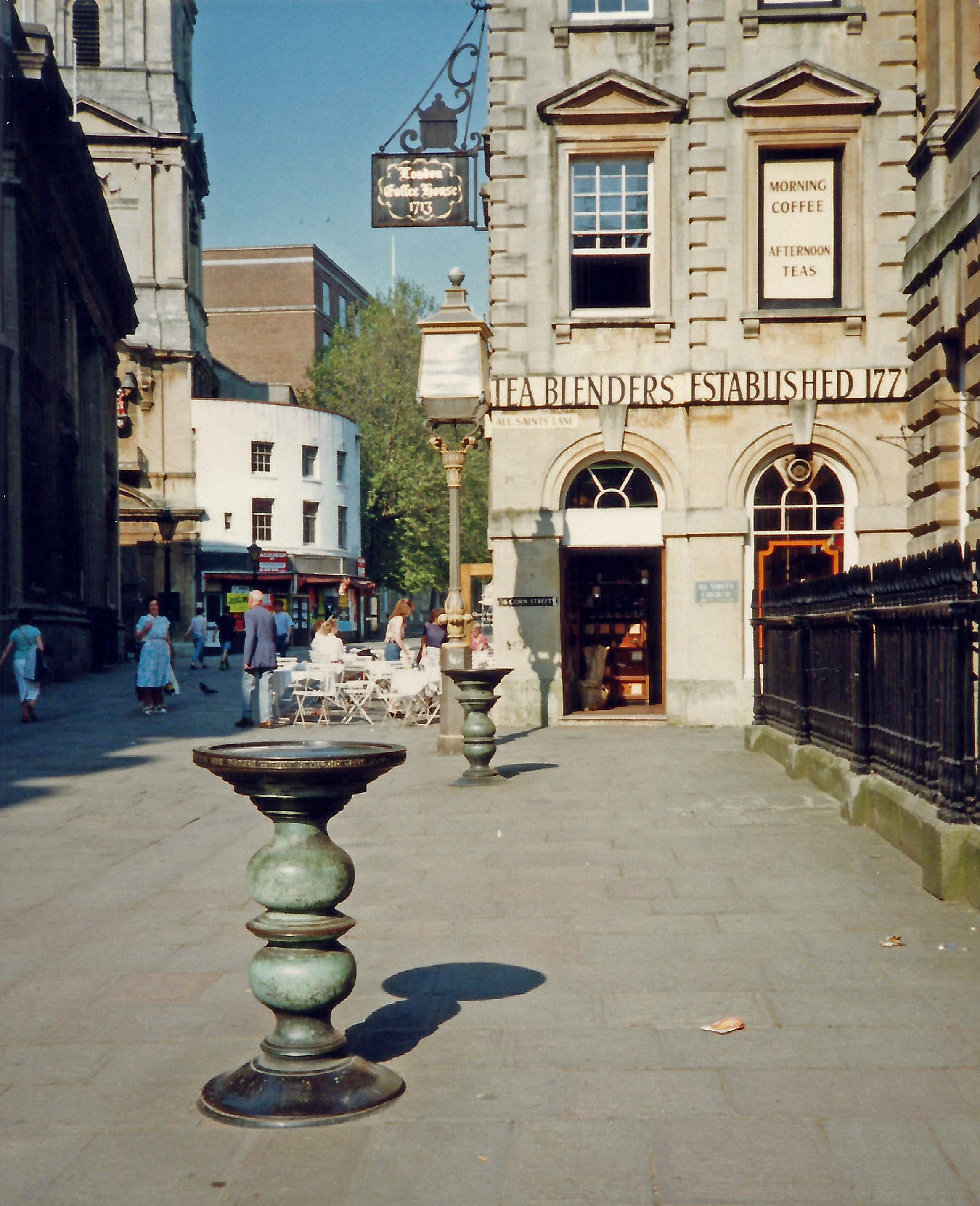 Bristol has a long history of trade, originally exporting wool cloth and importing fish, wine, grain and dairy products; later imports were tobacco, tropical fruits and plantation goods. Major imports are motor vehicles, grain, timber, produce and petroleum products. Since the 13th century, the rivers have been modified for docks; during the 1240s, the Frome was diverted into a deep, man-made channel (known as Saint Augustine's Reach) which flowed into the River Avon.
Ships occasionally departed Bristol for Iceland as early as 1420, and speculation exists that sailors (fishermen who landed on the Canadian coast to salt/ smoke their catch) from Bristol made landfall in the Americas before Christopher Columbus or John Cabot. Beginning in the early 1480s, the Bristol
Bristol has a long history of trade, originally exporting wool cloth and importing fish, wine, grain and dairy products; later imports were tobacco, tropical fruits and plantation goods. Major imports are motor vehicles, grain, timber, produce and petroleum products. Since the 13th century, the rivers have been modified for docks; during the 1240s, the Frome was diverted into a deep, man-made channel (known as Saint Augustine's Reach) which flowed into the River Avon.
Ships occasionally departed Bristol for Iceland as early as 1420, and speculation exists that sailors (fishermen who landed on the Canadian coast to salt/ smoke their catch) from Bristol made landfall in the Americas before Christopher Columbus or John Cabot. Beginning in the early 1480s, the Bristol  Filton played a key role in the Anglo-French Concorde supersonic airliner project during the 1960s. The British Concorde prototype made its maiden flight from Filton to RAF Fairford on 9 April 1969, five weeks after the French test flight. In 2003 British Airways and Air France decided to discontinue Concorde flights, retiring the aircraft to locations (primarily museums) worldwide. On 26 November 2003 Concorde 216 made the final Concorde flight, returning to Bristol Filton Airport as the centrepiece of a proposed air museum which is planned to include the existing Bristol Aero collection (including a Bristol Britannia).
The aerospace industry remains a major sector of the local economy. Major aerospace companies in Bristol include
Filton played a key role in the Anglo-French Concorde supersonic airliner project during the 1960s. The British Concorde prototype made its maiden flight from Filton to RAF Fairford on 9 April 1969, five weeks after the French test flight. In 2003 British Airways and Air France decided to discontinue Concorde flights, retiring the aircraft to locations (primarily museums) worldwide. On 26 November 2003 Concorde 216 made the final Concorde flight, returning to Bristol Filton Airport as the centrepiece of a proposed air museum which is planned to include the existing Bristol Aero collection (including a Bristol Britannia).
The aerospace industry remains a major sector of the local economy. Major aerospace companies in Bristol include
 Bristol has a thriving current and historical arts scene. Some of the modern venues and modern digital production companies have merged with legacy production companies based in old buildings around the city. In 2008 the city was a finalist for the 2008 European Capital of Culture, although the title was awarded to Liverpool. The city was designated "City of Film" by UNESCO in 2017 and has been a member of the Creative Cities Network since then.
The Bristol Old Vic, founded in 1946 as an offshoot of The Old Vic in London, occupies the 1766 Theatre Royal (607 seats) on King Street; the 150-seat New Vic (a studio-type theatre), and a foyer and bar in the adjacent Coopers' Hall (built in 1743). The Theatre Royal, a grade I listed building, is the oldest continuously operating theatre in England. The Bristol Old Vic Theatre School (which originated in King Street) is a separate company, and the Bristol Hippodrome is a 1,951-seat theatre for national touring productions. Other smaller theatres include the Tobacco Factory, QEH, the Redgrave Theatre at Clifton College, The Wardrobe Theatre, Bristol Improv Theatre, and the Alma Tavern. Bristol's theatre scene features several companies as well as the Old Vic, including Show of Strength, Shakespeare at the Tobacco Factory and Travelling Light. Theatre Bristol is a partnership between the city council,
Bristol has a thriving current and historical arts scene. Some of the modern venues and modern digital production companies have merged with legacy production companies based in old buildings around the city. In 2008 the city was a finalist for the 2008 European Capital of Culture, although the title was awarded to Liverpool. The city was designated "City of Film" by UNESCO in 2017 and has been a member of the Creative Cities Network since then.
The Bristol Old Vic, founded in 1946 as an offshoot of The Old Vic in London, occupies the 1766 Theatre Royal (607 seats) on King Street; the 150-seat New Vic (a studio-type theatre), and a foyer and bar in the adjacent Coopers' Hall (built in 1743). The Theatre Royal, a grade I listed building, is the oldest continuously operating theatre in England. The Bristol Old Vic Theatre School (which originated in King Street) is a separate company, and the Bristol Hippodrome is a 1,951-seat theatre for national touring productions. Other smaller theatres include the Tobacco Factory, QEH, the Redgrave Theatre at Clifton College, The Wardrobe Theatre, Bristol Improv Theatre, and the Alma Tavern. Bristol's theatre scene features several companies as well as the Old Vic, including Show of Strength, Shakespeare at the Tobacco Factory and Travelling Light. Theatre Bristol is a partnership between the city council,
 Manor houses include
Manor houses include
 Bristol Rovers, the oldest professional football team in the city, were formed in 1883 and promoted back into the football league in 2015. They were third-tier champions twice (
Bristol Rovers, the oldest professional football team in the city, were formed in 1883 and promoted back into the football league in 2015. They were third-tier champions twice (
 Bristol is home to the regional headquarters of BBC West and the BBC Natural History Unit based at Broadcasting House, which produces television, radio and online content with a natural history or wildlife theme. These include nature documentaries, including '' The Blue Planet'' and '' Planet Earth''. The city has a long association with
Bristol is home to the regional headquarters of BBC West and the BBC Natural History Unit based at Broadcasting House, which produces television, radio and online content with a natural history or wildlife theme. These include nature documentaries, including '' The Blue Planet'' and '' Planet Earth''. The city has a long association with
 Bristol has two major institutions of higher education: the University of Bristol, a Red brick university, redbrick chartered in 1909; and the University of the West of England, opened as Bristol Institute of technology, Polytechnic in 1969, which became a university in 1992. The University of Law also has a campus in the city. Bristol has two further education institutions (City of Bristol College and South Gloucestershire and Stroud College) and two Theology, theological colleges: Trinity College, Bristol, Trinity College, and Baptists Together, Bristol Baptist College. The city has 129 Infant school, infant, Junior school, junior and primary schools,
List of schools in Bristol, 17 secondary schools, and three learning centres. After a section of north London, Bristol has England's second-highest number of Independent school (United Kingdom), independent school places. Independent schools in the city include Clifton College, Clifton High School, Bristol, Clifton High School, Badminton School, Bristol Grammar School, Queen Elizabeth's Hospital (the only all-boys school) and the Redmaids' High School, Redmaids' School (founded in 1634 by John Whitson, which claims to be England's oldest girls' school).
Bristol has two major institutions of higher education: the University of Bristol, a Red brick university, redbrick chartered in 1909; and the University of the West of England, opened as Bristol Institute of technology, Polytechnic in 1969, which became a university in 1992. The University of Law also has a campus in the city. Bristol has two further education institutions (City of Bristol College and South Gloucestershire and Stroud College) and two Theology, theological colleges: Trinity College, Bristol, Trinity College, and Baptists Together, Bristol Baptist College. The city has 129 Infant school, infant, Junior school, junior and primary schools,
List of schools in Bristol, 17 secondary schools, and three learning centres. After a section of north London, Bristol has England's second-highest number of Independent school (United Kingdom), independent school places. Independent schools in the city include Clifton College, Clifton High School, Bristol, Clifton High School, Badminton School, Bristol Grammar School, Queen Elizabeth's Hospital (the only all-boys school) and the Redmaids' High School, Redmaids' School (founded in 1634 by John Whitson, which claims to be England's oldest girls' school).
 In 2005, Chancellor of the Exchequer Gordon Brown named Bristol one of six English 'science cities',
and a £300million science park was planned at Emersons Green. Research is conducted at the two universities, the Bristol Royal Infirmary and Southmead Hospital, and science outreach is practised at We The Curious, the Bristol Zoo, the Bristol Festival of Nature and the CREATE Centre.
The city has produced a number of scientists, including 19th-century chemist Humphry Davy (who worked in Hotwells). Physicist Paul Dirac (from Bishopston, Bristol, Bishopston) received the 1933 Nobel Prize for his contributions to quantum mechanics. C. F. Powell, Cecil Frank Powell was the Melvill Wills Professor of Physics at the University of Bristol when he received the 1950 Nobel Prize for, among other discoveries, his photographic method of studying nuclear processes. Colin Pillinger was the planetary scientist behind the Beagle 2 project, and neuropsychologist Richard Gregory founded the Exploratory (a hands-on science centre which was the predecessor of At-Bristol/We The Curious).
Initiatives such as the Flying Start Challenge encourage an interest in science and engineering in Bristol secondary-school pupils; links with aerospace companies impart technical information and advance student understanding of design.
The Bloodhound SSC project to break the land speed record is based at the Bloodhound Technology Centre on the city's harbourside.
In 2005, Chancellor of the Exchequer Gordon Brown named Bristol one of six English 'science cities',
and a £300million science park was planned at Emersons Green. Research is conducted at the two universities, the Bristol Royal Infirmary and Southmead Hospital, and science outreach is practised at We The Curious, the Bristol Zoo, the Bristol Festival of Nature and the CREATE Centre.
The city has produced a number of scientists, including 19th-century chemist Humphry Davy (who worked in Hotwells). Physicist Paul Dirac (from Bishopston, Bristol, Bishopston) received the 1933 Nobel Prize for his contributions to quantum mechanics. C. F. Powell, Cecil Frank Powell was the Melvill Wills Professor of Physics at the University of Bristol when he received the 1950 Nobel Prize for, among other discoveries, his photographic method of studying nuclear processes. Colin Pillinger was the planetary scientist behind the Beagle 2 project, and neuropsychologist Richard Gregory founded the Exploratory (a hands-on science centre which was the predecessor of At-Bristol/We The Curious).
Initiatives such as the Flying Start Challenge encourage an interest in science and engineering in Bristol secondary-school pupils; links with aerospace companies impart technical information and advance student understanding of design.
The Bloodhound SSC project to break the land speed record is based at the Bloodhound Technology Centre on the city's harbourside.
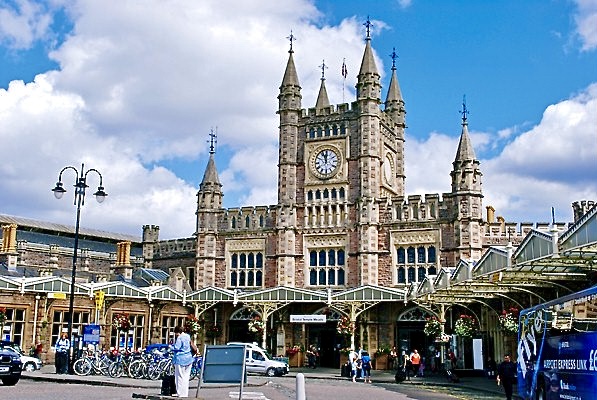 Bristol's principal surviving suburban railway is the Severn Beach Line to Avonmouth and Severn Beach. Although Portishead Railway, Portishead Railway's passenger service was a casualty of the Beeching cuts, freight service to the Royal Portbury Dock was restored from 2000 to 2002 with a Strategic Rail Authority rail-freight grant. The MetroWest (Bristol), MetroWest scheme, formerly known as The Greater Bristol Metro, proposes to increase the city's rail capacity including the restoration of a further of track on the Portishead Railway, line to Portishead, Somerset, Portishead (a Commuter town, dormitory town with one connecting road), and a further commuter rail line from Bristol Temple Meads to Henbury, on an Henbury Loop Line, existing freight line. Following numerous delays, the two lines are due to be opened in 2026.
Bristol's principal surviving suburban railway is the Severn Beach Line to Avonmouth and Severn Beach. Although Portishead Railway, Portishead Railway's passenger service was a casualty of the Beeching cuts, freight service to the Royal Portbury Dock was restored from 2000 to 2002 with a Strategic Rail Authority rail-freight grant. The MetroWest (Bristol), MetroWest scheme, formerly known as The Greater Bristol Metro, proposes to increase the city's rail capacity including the restoration of a further of track on the Portishead Railway, line to Portishead, Somerset, Portishead (a Commuter town, dormitory town with one connecting road), and a further commuter rail line from Bristol Temple Meads to Henbury, on an Henbury Loop Line, existing freight line. Following numerous delays, the two lines are due to be opened in 2026.
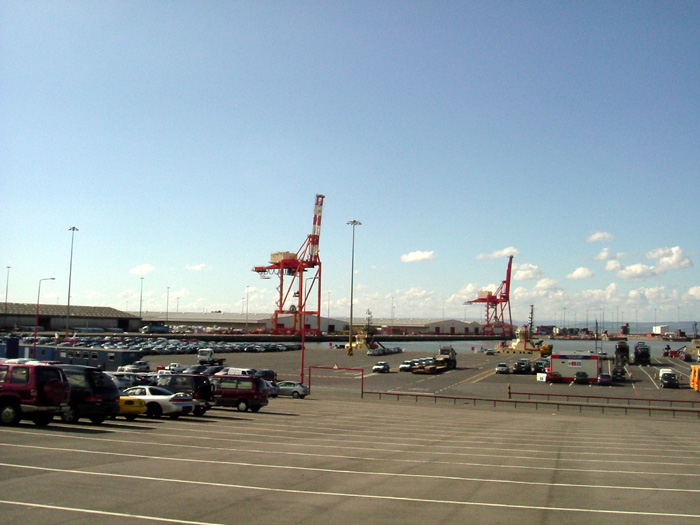 Private car use is high in the city, leading to traffic congestion costing an estimated £350million per year.
Bristol allows motorcycles to use most of the city's bus lanes and provides secure, free parking for them.
Private car use is high in the city, leading to traffic congestion costing an estimated £350million per year.
Bristol allows motorcycles to use most of the city's bus lanes and provides secure, free parking for them.
 The runway, terminal and other facilities at
The runway, terminal and other facilities at
 Bristol was among the first cities to adopt Twin towns and sister cities, town twinning after World War II. Twin towns include:
* Bordeaux, France (since 1947)
* Hanover, Germany (since 1947; one of the first post-war twinnings of British and German cities)
* Porto, Portugal (since 1984)
* Tbilisi, Georgia (since 1988)
* Puerto Morazán, Nicaragua (since 1989)
* Beira, Mozambique (since 1990)
* Guangzhou, China (since 2001)
Bristol was among the first cities to adopt Twin towns and sister cities, town twinning after World War II. Twin towns include:
* Bordeaux, France (since 1947)
* Hanover, Germany (since 1947; one of the first post-war twinnings of British and German cities)
* Porto, Portugal (since 1984)
* Tbilisi, Georgia (since 1988)
* Puerto Morazán, Nicaragua (since 1989)
* Beira, Mozambique (since 1990)
* Guangzhou, China (since 2001)
Visit Bristol
official tourism website
Bristol City Council
*
Know your Place: Bristol
historic maps website. {{Coord, 51, 27, N, 2, 35, W, type:city_region:GB-BST, display=title Bristol, Populated places on the River Severn Unitary authority districts of England Port cities and towns in South West England Staple ports County towns in England Cities in South West England Populated places in Bristol (county) Local government districts of South West England River Avon, Bristol Counties of England established in 1373 Counties of England disestablished in 1974 Counties of England established in 1996 Counties in South West England Unparished areas Boroughs in England
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England.
The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom.
Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the rivers Frome and Avon
Avon may refer to:
* River Avon (disambiguation), several rivers
Organisations
*Avon Buses, a bus operating company in Wirral, England
*Avon Coachworks, a car body builder established in 1919 at Warwick, England, relaunched in 1922, following ...
. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate
A county corporate or corporate county was a type of subnational division used for local government in England, Wales, and Ireland.
Counties corporate were created during the Middle Ages, and were effectively small self-governing county, county-e ...
. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts.
A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot
John Cabot ( it, Giovanni Caboto ; 1450 – 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest-known European exploration of coastal North ...
, a Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
, became the first European to land on mainland North America. In 1499, William Weston, a Bristol merchant, was the first Englishman to lead an exploration to North America. At the height of the Bristol slave trade, from 1700 to 1807, more than 2,000 slave ships carried an estimated 500,000 people from Africa to slavery in the Americas. The Port of Bristol has since moved from Bristol Harbour
Bristol Harbour is the harbour in the city of Bristol, England. The harbour covers an area of . It is the former natural tidal river Avon through the city but was made into its current form in 1809 when the tide was prevented from going out per ...
in the city centre to the Severn Estuary at Avonmouth and Royal Portbury Dock
The Royal Portbury Dock is part of the Port of Bristol, in England. It is situated near the village of Portbury on the southern side of the mouth of the River Avon, Bristol, Avon, where the river joins the Severn estuary — the Avonmouth ...
.
Bristol's modern economy is built on the creative media, electronics and aerospace industries; the city-centre docks have been redeveloped as centres of heritage and culture. The city has the largest circulating community currency in the UK, the Bristol Pound
The Bristol pound (£B) was a form of local, complementary, and/or community currency launched in Bristol, UK on 19 September 2012. Its objective is to encourage people to spend their money with local, independent businesses in Bristol, and f ...
, which is pegged to the pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
. The city has two universities: the University of Bristol and the University of the West of England (UWE Bristol). There are a variety of artistic and sporting organisations and venues including the Royal West of England Academy, the Arnolfini, Spike Island, Ashton Gate and the Memorial Stadium. It is connected to London and other major UK cities by road and rail, and to the world by sea and air: road, by the M5 and M4 (which connect to the city centre by the Portway and M32); rail, via Bristol Temple Meads and Bristol Parkway
Bristol Parkway, on the South Wales Main Line, is in the Stoke Gifford area in the northern suburbs of the Bristol conurbation. It is from London Paddington. The station was opened in 1972 by British Rail, and was the first in a new gener ...
mainline rail stations; and Bristol Airport
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on ...
.
Bristol was named the best city in Britain in which to live in 2014 and 2017; it won the European Green Capital Award in 2015.
Etymology
Early recorded place names in the Bristol area include the Roman-era British Celtic ''Abona'' (derived from the name of theAvon
Avon may refer to:
* River Avon (disambiguation), several rivers
Organisations
*Avon Buses, a bus operating company in Wirral, England
*Avon Coachworks, a car body builder established in 1919 at Warwick, England, relaunched in 1922, following ...
) and the archaic Welsh ('fort on the chasm'), which may have been calqued as the modern English ''Clifton''.
The current name "Bristol" derives from the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
form , which is typically etymologised as 'place at the bridge'. It has also been suggested that means "the place called Bridge by the place called Stow", the Stow in question referring to an early religious meeting place at what is now College Green. However, other derivations have been proposed. It appears that the form prevailed until 1204, and the '' Bristolian 'L''' (the tendency for the local dialect to add the sound "L" to many words ending in a neutral vowel) is what eventually changed the name to ''Bristol''. The original form of the name survives as the surname Bristow, which is derived from the city.
History
Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
finds, including flint tools believed to be between 300,000 and 126,000years old made with the Levallois technique, indicate the presence of Neanderthals in the Shirehampton and St Annes areas of Bristol during the Middle Palaeolithic. Iron Age hill forts near the city are at Leigh Woods and Clifton Down, on the side of the Avon Gorge, and on Kings Weston Hill near Henbury. A Roman settlement, Abona, existed at what is now Sea Mills (connected to Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
by a Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
); another was at the present-day Inns Court. Isolated Roman villas and small forts
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and settlements were also scattered throughout the area.
Middle Ages
Bristol was founded by 1000; by about 1020, it was a trading centre with a mint producing silver pennies bearing its name. By 1067, Brycgstow was a well-fortified '' burh'', and that year the townsmen beat back a raiding party from Ireland led by three of Harold Godwinson's sons. Under Norman rule, the town had one of the strongest castles in southern England. Bristol was the place of exile for Diarmait Mac Murchada, the Irish king of Leinster, after being overthrown. The Bristol merchants subsequently played a prominent role in fundingRichard Strongbow de Clare
Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke (of the first creation), Lord of Leinster, Justiciar of Ireland (113020 April 1176), also known as Richard FitzGilbert, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasion ...
and the Norman invasion of Ireland.
 The port developed in the 11th century around the confluence of the Rivers Frome and
The port developed in the 11th century around the confluence of the Rivers Frome and Avon
Avon may refer to:
* River Avon (disambiguation), several rivers
Organisations
*Avon Buses, a bus operating company in Wirral, England
*Avon Coachworks, a car body builder established in 1919 at Warwick, England, relaunched in 1922, following ...
, adjacent to Bristol Bridge just outside the town walls. By the 12th century, there was an important Jewish community in Bristol which survived through to the late 13th century when all Jews were expelled from England. The stone bridge built in 1247 was replaced by the current bridge during the 1760s. The town incorporated neighbouring suburbs and became a county in 1373, the first town in England to be given this status. During this period, Bristol became a shipbuilding and manufacturing centre. By the 14th century, Bristol, York and Norwich were England's largest medieval towns after London. One-third to one-half of the population died in the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of 1348–49, which checked population growth, and its population remained between 10,000 and 12,000 for most of the 15th and 16th centuries.
15th and 16th centuries
 During the 15th century, Bristol was the second most important port in the country, trading with Ireland, Iceland and
During the 15th century, Bristol was the second most important port in the country, trading with Ireland, Iceland and Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
. It was the starting point for many voyages, including Robert Sturmy
Robert Sturmy was a 15th-century Bristol merchant.
In 1445 he sponsored a voyage conveying 200 pilgrims to Santiago de Compostela in Galicia and in 1447 his ship the ''Cog Anne'' took pilgrims to Jaffa in Palestine but was wrecked off Greece on t ...
's (1457–58) unsuccessful attempt to break the Italian monopoly of Eastern Mediterranean trade. New exploration voyages were launched by Venetian John Cabot
John Cabot ( it, Giovanni Caboto ; 1450 – 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest-known European exploration of coastal North ...
, who in 1497 made landfall in North America. A 1499 voyage, led by merchant William Weston of Bristol, was the first expedition commanded by an Englishman to North America. During the first decade of the 16th century Bristol's merchants undertook a series of exploration voyages to North America and even founded a commercial organisation, 'The Company Adventurers to the New Found Land', to assist their endeavours. However, they seem to have lost interest in North America after 1509, having incurred great expenses and made little profit.
During the 16th century, Bristol merchants concentrated on developing trade with Spain and its American colonies. This included the smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are various ...
of prohibited goods, such as food and guns, to Iberia during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
The Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) was an intermittent conflict between the Habsburg Kingdom of Spain and the Kingdom of England. It was never formally declared. The war included much English privateering against Spanish ships, and several wid ...
. Bristol's illicit trade grew enormously after 1558, becoming integral to its economy.
The original Diocese of Bristol was founded in 1542, when the former Abbey of St. Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afri ...
(founded by Robert Fitzharding four hundred years earlier) became Bristol Cathedral. Bristol also gained city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
status that year. During the English Civil War in the 1640s the city was occupied by Royalists, who built the Royal Fort House
The Royal Fort House is a historic house in Tyndalls Park, Bristol. The building currently houses the University of Bristol's Faculty of Science offices, the Brigstow Institute, Elizabeth Blackwell Institute for Health Research, the Cabot Institu ...
on the site of an earlier Parliamentarian stronghold.
17th and 18th centuries
 Fishermen from Bristol, who had fished the
Fishermen from Bristol, who had fished the Grand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
since the 16th century, began settling Newfoundland permanently in larger numbers during the 17th century, establishing colonies at Bristol's Hope and Cuper's Cove. Growth of the city and trade came with the rise of England's American colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centur ...
in the 17th century. Bristol's location on the west side of Great Britain gave its ships an advantage in sailing to and from the New World, and the city's merchants made the most of it, with the city becoming one of the two leading outports in all of England by the middle of the 18th century. Bristol was the slave capital of England: In 1755, it had the largest number of slave traders in the country with 237, as against London's 147. It was a major supplier of slaves to South Carolina before 1750.
 The 18th century saw an expansion of Bristol's population (45,000 in 1750) and its role in the Atlantic trade in Africans taken for slavery to the Americas. Bristol and later Liverpool became centres of the Triangular Trade. Manufactured goods were shipped to West Africa and exchanged for Africans; the enslaved captives were transported across the Atlantic to the Americas in the
The 18th century saw an expansion of Bristol's population (45,000 in 1750) and its role in the Atlantic trade in Africans taken for slavery to the Americas. Bristol and later Liverpool became centres of the Triangular Trade. Manufactured goods were shipped to West Africa and exchanged for Africans; the enslaved captives were transported across the Atlantic to the Americas in the Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods (first ...
under brutal conditions. Plantation goods such as sugar, tobacco, rum, rice, cotton and a few slaves (sold to the aristocracy as house servants) returned across the Atlantic to England. Some household slaves were baptised in the hope this would lead them to be freed. The Somersett Case
''Somerset v Stewart'' (177298 ER 499(also known as ''Somersett's case'', ''v. XX Sommersett v Steuart and the Mansfield Judgment)'' is a judgment of the English Court of King's Bench in 1772, relating to the right of an enslaved person on En ...
of 1772 clarified that slavery was illegal in England. At the height of the Bristol slave trade from 1700 to 1807, more than 2,000 slave ships carried a conservatively estimated 500,000 people from Africa to slavery in the Americas.
In 1739, John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The soci ...
founded the first Methodist chapel, the New Room
John Wesley's New Room is a historic building in Broadmead, Bristol, England. Opened in 1739, it housed the earliest Methodist societies, and was enlarged in 1748. As the oldest purpose-built Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist meeting ...
, in Bristol. Wesley, along with his brother Charles Wesley and George Whitefield
George Whitefield (; 30 September 1770), also known as George Whitfield, was an Anglican cleric and evangelist who was one of the founders of Methodism and the evangelical movement.
Born in Gloucester, he matriculated at Pembroke College at th ...
, preached to large congregations in Bristol and the neighbouring village of Kingswood, often in the open air.
Wesley published a pamphlet on slavery, titled ''Thoughts Upon Slavery,'' in 1774 and the Society of Friends
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
began lobbying against slavery in Bristol in 1783. The city's scions remained nonetheless strongly anti-abolitionist. Thomas Clarkson came to Bristol to study the slave trade and gained access to the Society of Merchant Venturers
The Society of Merchant Venturers is a charitable organisation in the English city of Bristol.
The society can be traced back to a 13th-century guild which funded the voyage of John Cabot to Canada. In 1552, it gained a monopoly on sea trading ...
records. One of his contacts was the owner of the Seven Stars public house, who boarded sailors Clarkson sought to meet. Through these sailors he was able to observe how slaver captains and first mates "plied and stupefied seamen with drink" to sign them up. Other informants included ship surgeons and seamen seeking redress. When William Wilberforce began his parliamentary abolition campaign on 12 May 1788, he recalled the history of the Irish slave trade
Slavery had already existed in Ireland for centuries by the time the Vikings began to establish their coastal settlements, but it was under the Norse-Gael Kingdom of Dublin that it reached its peak, in the 11th century.
History
Gaelic Ireland
...
from Bristol, which he provocatively claimed continued into the reign of Henry VII. Hannah More, originally from Bristol, and a good friend of both Wilberforce and Clarkson, published "Slavery, A Poem" in 1788, just as Wilberforce began his parliamentary campaign. His major speech on 2 April 1792 likewise described the Bristol slave trade specifically, and led to the arrest, trial and subsequent acquittal of a local slaver captain named Kimber.
19th century
The city was associated with Victorian engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who designed theGreat Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
between Bristol and London Paddington, two pioneering Bristol-built oceangoing steamships ( and ), and the Clifton Suspension Bridge. The new railway replaced the Kennet and Avon Canal
The Kennet and Avon Canal is a waterway in southern England with an overall length of , made up of two lengths of navigable river linked by a canal. The name is used to refer to the entire length of the navigation rather than solely to the cent ...
, which had fully opened in 1810 as the main route for the transport of goods between Bristol and London. Competition from Liverpool (beginning around 1760), disruptions of maritime commerce due to war with France (1793) and the abolition of the slave trade (1807) contributed to Bristol's failure to keep pace with the newer manufacturing centres of Northern England and the West Midlands. The tidal Avon Gorge, which had secured the port during the Middle Ages, had become a liability. An 1804–09 plan to improve the city's port with a floating harbour designed by William Jessop was a costly error, requiring high harbour fees.
During the 19th century, Samuel Plimsoll, known as "the sailor's friend," campaigned to make the seas safer; shocked by overloaded vessels, he successfully fought for a compulsory load line on ships.
By 1867, ships were getting larger and the meanders in the river Avon prevented boats over from reaching the harbour, resulting in falling trade. The port facilities were migrating downstream to Avonmouth and new industrial complexes were founded there. Some of the traditional industries including copper and brass manufacture went into decline, but the import and processing of tobacco flourished with the expansion of the W.D. & H.O. Wills business.
Supported by new industry and growing commerce, Bristol's population (66,000 in 1801), quintupled during the 19th century, resulting in the creation of new suburbs such as Clifton
Clifton may refer to:
People
*Clifton (surname)
*Clifton (given name)
Places
Australia
* Clifton, Queensland, a town
**Shire of Clifton
*Clifton, New South Wales, a suburb of Wollongong
*Clifton, Western Australia
Canada
*Clifton, Nova Scotia ...
and Cotham. These provide architectural examples from the Georgian to the Regency style, with many fine terraces and villas facing the road, and at right angles to it. In the early 19th century, the romantic medieval gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
style appeared, partially as a reaction against the symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definit ...
of Palladianism, and can be seen in buildings such as the Bristol City Museum and Art Gallery, the Royal West of England Academy, and The Victoria Rooms. Riots
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted ...
broke out in 1793 and 1831; the first over the renewal of tolls on Bristol Bridge, and the second against the rejection of the second Reform Bill by the House of Lords. The population by 1841 had reached 140,158.
The Diocese of Bristol had undergone several boundary changes by 1897 when it was "reconstituted" into the configuration which has lasted into the 21st century.
20th century
 From a population of about 330,000 in 1901, Bristol grew steadily during the 20th century, peaking at 428,089 in 1971. Its Avonmouth docklands were enlarged during the early 1900s by the Royal Edward Dock. Another new dock, the
From a population of about 330,000 in 1901, Bristol grew steadily during the 20th century, peaking at 428,089 in 1971. Its Avonmouth docklands were enlarged during the early 1900s by the Royal Edward Dock. Another new dock, the Royal Portbury Dock
The Royal Portbury Dock is part of the Port of Bristol, in England. It is situated near the village of Portbury on the southern side of the mouth of the River Avon, Bristol, Avon, where the river joins the Severn estuary — the Avonmouth ...
, opened across the river from Avonmouth during the 1970s. As air travel grew in the first half of the century, aircraft manufacturers built factories. The unsuccessful Bristol International Exhibition was held on Ashton Meadows in the Bower Ashton area in 1914. After the premature closure of the exhibition the site was used, until 1919, as barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
for the Gloucestershire Regiment
The Gloucestershire Regiment, commonly referred to as the Glosters, was a line infantry regiment of the British Army from 1881 until 1994. It traced its origins to Colonel Gibson's Regiment of Foot, which was raised in 1694 and later became the ...
during World War I.
 Bristol was heavily damaged by Luftwaffe raids during World War II; about 1,300 people living or working in the city were killed and nearly 100,000 buildings were damaged, at least 3,000 beyond repair. The original central shopping area, near the bridge and castle, is now a park containing two bombed churches and fragments of the castle. A third bomb-damaged church nearby,
Bristol was heavily damaged by Luftwaffe raids during World War II; about 1,300 people living or working in the city were killed and nearly 100,000 buildings were damaged, at least 3,000 beyond repair. The original central shopping area, near the bridge and castle, is now a park containing two bombed churches and fragments of the castle. A third bomb-damaged church nearby, St Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-da ...
was restored and after a period as a museum has now re-opened as a church. It houses a 1756 William Hogarth triptych painted for the high altar of St Mary Redcliffe
St Mary Redcliffe is an Anglican parish church located in the Redcliffe district of Bristol, England. The church is a short walk from Bristol Temple Meads station. The church building was constructed from the 12th to the 15th centuries, and it ...
. The church also has statues of King Edward I (moved from Arno's Court Triumphal Arch) and King Edward III (taken from Lawfords' Gate in the city walls when they were demolished about 1760), and 13th-century statues of Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester (builder of Bristol Castle) and Geoffrey de Montbray (who built the city's walls) from Bristol's Newgate.
 The rebuilding of Bristol city centre was characterised by 1960s and 1970s
The rebuilding of Bristol city centre was characterised by 1960s and 1970s skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
s, mid-century modern architecture and road building. Beginning in the 1980s some main roads were closed, the Georgian-era Queen Square and Portland Square were restored, the Broadmead
Broadmead is a street in the Bristol city centre, central area of Bristol, England, which has given its name to the principal shopping district of the city. It is part of Bristol Shopping Quarter.
History
The name of the street was first rec ...
shopping area regenerated, and one of the city centre's tallest mid-century towers was demolished. Bristol's road infrastructure changed dramatically during the 1960s and 1970s with the development of the M4 and M5 motorways, which meet at the Almondsbury Interchange just north of the city and link Bristol with London (M4 eastbound), Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
(M4 westbound across the Severn Estuary), Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
(M5 southbound) and Birmingham (M5 northbound). Bristol was bombed twice by the IRA, in 1974
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; f ...
and again in 1978
Events January
* January 1 – Air India Flight 855, a Boeing 747 passenger jet, crashes off the coast of Bombay, killing 213.
* January 5 – Bülent Ecevit, of Republican People's Party, CHP, forms the new government of Turkey (42nd go ...
.
The 20th-century relocation of the docks to Avonmouth Docks and Royal Portbury Dock
The Royal Portbury Dock is part of the Port of Bristol, in England. It is situated near the village of Portbury on the southern side of the mouth of the River Avon, Bristol, Avon, where the river joins the Severn estuary — the Avonmouth ...
, downstream from the city centre, has allowed the redevelopment of the old dock area (the Floating Harbour). Although the docks' existence was once in jeopardy (since the area was seen as a derelict industrial site), the inaugural 1996 International Festival of the Sea
The International Festivals of the Sea were a series of maritime festivals, which were held in various British port cities between 1996 and 2005. The festivals were intended to be celebrations of the sea, bringing together sailors, musicians, art ...
held in and around the docks affirmed the area as a leisure asset of the city.
21st century
From 2018, there were lively discussions about a new explicative plaque under a commemorative statue of one of the city's major benefactors in the 17th and 18th centuries. The plaque was meant to replace an original which made no reference to Edward Colston's past with theRoyal Africa Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile (trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the west coast of Africa. It was led by the Duke of York, who was the brother o ...
and the Bristol Slave Trade. On 7 June 2020 a statue of Colston was pulled down from its plinth by protestors and pushed into Bristol Harbour. The statue was recovered on 11 June and has become a museum exhibit.
Government
 Bristol City council consists of 70 councillors representing 35 wards, with between one and three per ward serving four-year terms. Councillors are elected in thirds, with elections held in three years out of every four-year period. Thus, since wards do not have both councillors up for election at the same time, two-thirds of the wards participate in each election. Although the council was long dominated by the Labour Party, the Liberal Democrats have grown strong in the city and (as the largest party) took minority control of the council after the
Bristol City council consists of 70 councillors representing 35 wards, with between one and three per ward serving four-year terms. Councillors are elected in thirds, with elections held in three years out of every four-year period. Thus, since wards do not have both councillors up for election at the same time, two-thirds of the wards participate in each election. Although the council was long dominated by the Labour Party, the Liberal Democrats have grown strong in the city and (as the largest party) took minority control of the council after the 2005 United Kingdom general election
The 2005 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 5 May 2005, to elect List of MPs elected in the 2005 United Kingdom general election, 646 members to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. The Labour Party (U ...
. In 2007, Labour and the Conservatives united to defeat the Liberal Democrat administration; Labour ruled the council as a minority administration, with Helen Holland as council leader.
In February 2009, the Labour group resigned and the Liberal Democrats re-entered office with a minority administration. In the June 2009 council elections the Liberal Democrats gained four seats and, for the first time, overall control of the city council. In 2010
File:2010 Events Collage New.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2010 Chile earthquake was one of the strongest recorded in history; The Eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland disrupts air travel in Europe; A scene from the opening ceremony of ...
they increased their representation to 38 seats, giving them a majority of 6. In 2011, they lost their majority; leading to a hung council. In the 2013 local elections, in which a third of the city's wards were up for election, Labour gained 7seats and the Green Party doubled their seats from 2to 4. The Liberal Democrats lost 10 seats.
These trends were continued into the next election in May 2014, in which Labour gained three seats to take their total to 31, the Green Party won two more seats, the Conservative party gained one seat, and UKIP won their first-ever seat on the council. The Liberal Democrats lost a further seven seats.
On 3 May 2012, Bristol held a referendum on the question of a directly elected mayor replacing one elected by the council. There were 41,032 votes in favour of a directly elected mayor and 35,880 votes against, with a 24% turnout. An election for the new post was held on 15 November 2012, and Independent candidate George Ferguson became Mayor of Bristol. In May 2022 the city voted to abolish the position in a referendum, replacing it with a committee system. Marvin Rees, mayor in 2022, will hold the post until 2024.
The Lord Mayor of Bristol, not to be confused with the Mayor of Bristol, is a figurehead elected each May by the city council. Councillor Faruk Choudhury was selected by his fellow councillors for the position in 2013. At 38, he was the youngest person to serve as Lord Mayor of Bristol and the first Muslim elected to the office. The current Lord Mayor is Councillor Paula O'Rourke.
Bristol constituencies in the House of Commons also included parts of other local authority areas until the 2010 general election, when their boundaries were aligned with the county boundary. The city is divided into Bristol West, East, South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and North West. At the 2017 general election
This national electoral calendar for 2017 lists the national/federal elections held in 2017 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*5 November ...
, Labour won all four of the Bristol constituencies, gaining the Bristol North West seat, seven years after losing it to the Conservatives.
The city has a tradition of political activism. Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_ NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style"> ...
, MP for the Bristol constituency for six years beginning in 1774, insisted that he was a Member of Parliament first and a representative of his constituents' interests second. Women's-rights advocate Emmeline Pethick-Lawrence (1867–1954) was born in Bristol, and the left-winger Tony Benn served as MP for Bristol South East
Bristol South East was a constituency in the city of Bristol that returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
The constituency was created for the 1950 general election, mainly fro ...
in 1950–1960 and again from 1963 to 1983. In 1963 the Bristol Bus Boycott
The Bristol Bus Boycott of 1963 arose from the refusal of the Bristol Omnibus Company to employ Black or Asian bus crews in the city of Bristol, England. In line with many other British cities at the time, there was widespread racial discrimin ...
, following the Bristol Omnibus Company's refusal to hire black drivers and conductors, drove the passage of the UK's 1965 Race Relations Act. The 1980 St. Pauls riot
The St Pauls riot occurred in St Pauls, Bristol, England on 2 April 1980 when police raided the Black and White Café on Grosvenor Road in the heart of the area. After several hours of disturbance in which fire engines and police cars were damag ...
protested against racism and police harassment and showed mounting dissatisfaction with the socioeconomic circumstances of the city's Afro-Caribbean residents. Local support of fair trade
Fair trade is an arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. The fair trade movement combines the payment of higher prices to exporters with improved social and enviro ...
was recognised in 2005, when Bristol became a fairtrade zone
The Fair Trade Towns campaign is the result of a grass-roots citizens movement that started in the UK in 2001 (see below). It allows citizens to get together in order to self-proclaim their town (or other local geographical area) as a region that ...
.
Bristol is both a city and a county, since King Edward III granted it a county charter in 1373. The county was expanded in 1835 to include suburbs such as Clifton
Clifton may refer to:
People
*Clifton (surname)
*Clifton (given name)
Places
Australia
* Clifton, Queensland, a town
**Shire of Clifton
*Clifton, New South Wales, a suburb of Wollongong
*Clifton, Western Australia
Canada
*Clifton, Nova Scotia ...
, and it was named a county borough in 1889 when that designation was introduced.
Former county of Avon
On 1 April 1974, Bristol became a local government district of the county ofAvon
Avon may refer to:
* River Avon (disambiguation), several rivers
Organisations
*Avon Buses, a bus operating company in Wirral, England
*Avon Coachworks, a car body builder established in 1919 at Warwick, England, relaunched in 1922, following ...
. On 1 April 1996, Avon was abolished and Bristol became a unitary authority.
The former Avon area, called Greater Bristol by the Government Office of the South West (now abolished) and others, refers to the city and the three neighbouring local authorities Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire previously in Avon.
The North Fringe of Bristol, a developed area between the Bristol city boundary and the M4, M5 and M32 motorways (now in South Gloucestershire) was so named as part of a 1987 plan prepared by the Northavon
Northavon was a district in the English county of Avon from 1974 to 1996.
The district was formed by the Local Government Act 1972 on 1 April 1974 as part of a reform of local authorities throughout England and Wales. Under the reorganisation, ...
District Council of Avon county.
West of England Combined Authority
The West of England Combined Authority was created on 9 February 2017. Covering Bristol and the rest of the old Avon county with the exception of North Somerset, the new combined authority has responsibility for regional planning, roads, and local transport, and to a lesser extent, education and business investment. The authority's first mayor, Tim Bowles, was elected in May 2017. One of the first actions of the new authority was the announcement of a new train station to be built at Portway.Geography and environment
Boundaries
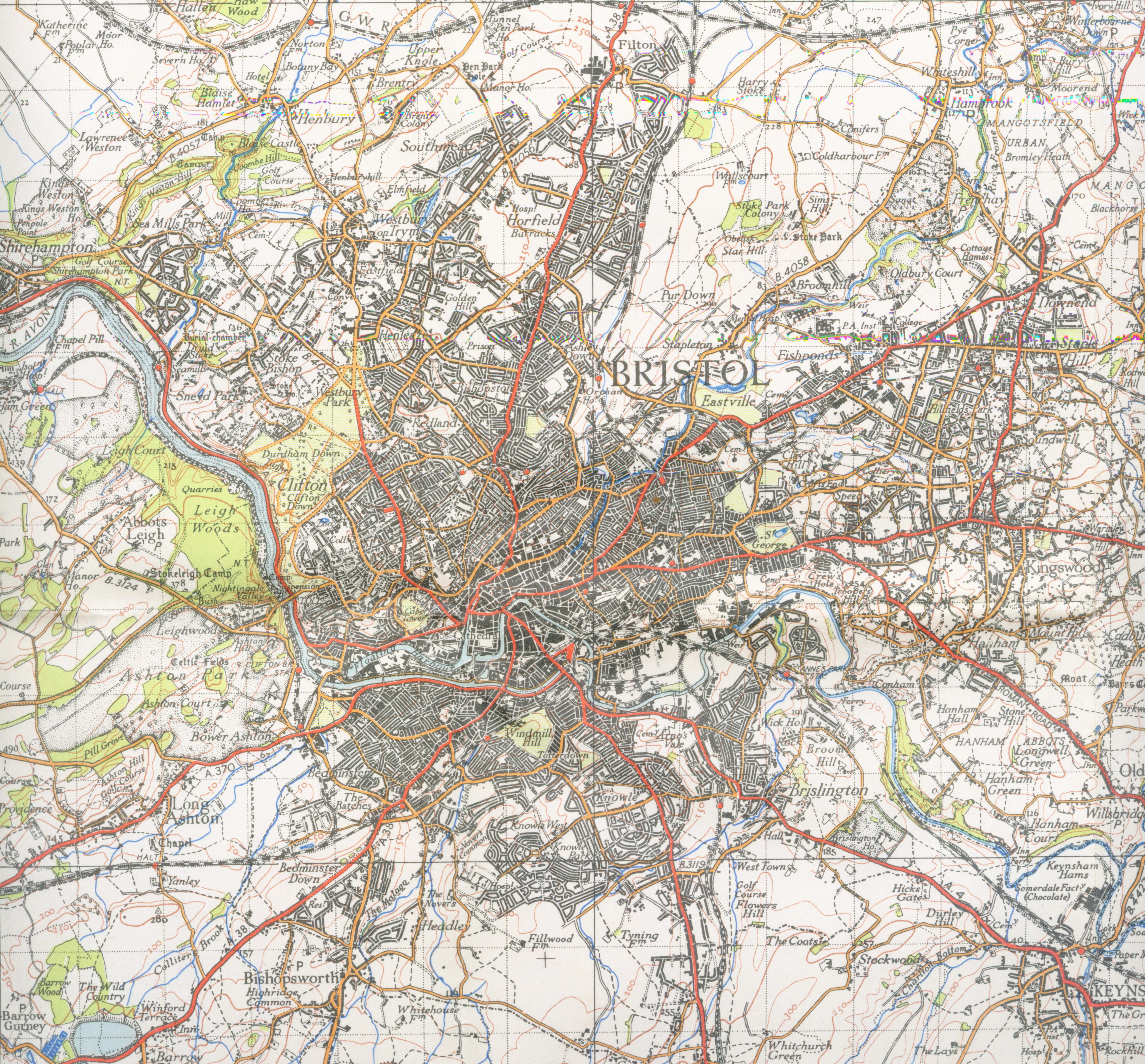
 Bristol's boundaries can be defined in several ways, including those of the city itself, the developed area, or Greater Bristol.
The city council boundary is the narrowest definition of the city itself. However, it unusually includes a large, roughly rectangular section of the western Severn Estuary ending at (but not including) the islands of Flat Holm (in Cardiff, Wales) and Steep Holm. This "seaward extension" can be traced back to the original boundary of the County of Bristol laid out in the charter granted to the city by
Bristol's boundaries can be defined in several ways, including those of the city itself, the developed area, or Greater Bristol.
The city council boundary is the narrowest definition of the city itself. However, it unusually includes a large, roughly rectangular section of the western Severn Estuary ending at (but not including) the islands of Flat Holm (in Cardiff, Wales) and Steep Holm. This "seaward extension" can be traced back to the original boundary of the County of Bristol laid out in the charter granted to the city by Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
in 1373.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) has defined a Bristol Urban Area, which includes developed areas adjoining Bristol but outside the city-council boundary, such as Kingswood, Mangotsfield, Stoke Gifford, Winterbourne, Almondsbury, Easton in Gordano, Whitchurch village, Filton, Patchway and Bradley Stoke, but excludes undeveloped areas within that boundary.

Geography
Bristol lies within a limestone area running from theMendip Hills
The Mendip Hills (commonly called the Mendips) is a range of limestone hills to the south of Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. Running from Weston-super-Mare and the Bristol Channel in the west to the Frome valley in the east, the hills ...
in the south to the Cotswolds
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale.
The area is defined by the bedrock of Jur ...
in the northeast. The rivers Avon and Frome cut through the limestone to the underlying clay, creating Bristol's characteristically hilly landscape. The Avon flows from Bath in the east, through flood plains and areas which were marshes before the city's growth. To the west the Avon cuts through the limestone to form the Avon Gorge, formed largely by glacial meltwater after the last ice age.
The gorge, which helped protect Bristol Harbour, has been quarried for stone to build the city, and its surrounding land has been protected from development as The Downs and Leigh Woods. The Avon estuary and the gorge form the county boundary with North Somerset, and the river flows into the Severn Estuary at Avonmouth. A smaller gorge, cut by the Hazel Brook which flows into the River Trym
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
, crosses the Blaise Castle
Blaise Castle is a folly built in 1766 near Henbury in Bristol, England. The castle sits within the Blaise Castle Estate, which also includes Blaise Castle House, a Grade II* listed 18th-century mansion house. The folly castle is also Grade I ...
estate in northern Bristol.
Bristol is sometimes described, by its inhabitants, as being built on seven hills. From 18th century guidebooks, these 7 hills were known as simply Bristol (the Old Town), Castle Hill, College Green, Kingsdown, St Michaels Hill, Brandon Hill
Brandon Hill () is the highest mountain in County Kilkenny, Ireland, with an elevation of and prominence at . The South Leinster Way, a long-distance trail, meandering through the Barrow Valley and traverses Brandon Hill. The village of ...
and Redcliffe Hill. Other local hills include Red Lion Hill, Barton Hill, Lawrence Hill, Black Boy Hill, Constitution Hill, Staple Hill, Windmill Hill, Malborough Hill, Nine Tree Hill, Talbot, Brook Hill and Granby Hill.
Bristol is west of London, south-southwest of Birmingham and east of the Welsh capital Cardiff. Areas adjoining the city fall within a loosely defined area known as Greater Bristol. Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
is located south east of the city centre, Weston-super-Mare is to the south west, and the Welsh city of Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
is to the north west.
Climate
The climate is oceanic ( Köppen: ''Cfb)'', milder than most places in England and United Kingdom. Located in southern England, Bristol is one of the warmest cities in the UK with a mean annual temperature of approximately . It is among the sunniest, with 1,541–1,885hours of sunshine per year. Although the city is partially sheltered by the Mendip Hills, it is exposed to the Severn Estuary and theBristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
. Annual rainfall increases from north to south, with totals north of the Avon in the range and south of the river. Rain is fairly evenly distributed throughout the year, with autumn and winter the wetter seasons. The Atlantic Ocean influences Bristol's weather, keeping its average temperature above freezing throughout the year, but winter frosts are frequent and snow occasionally falls from early November to late April. Summers are warm and drier, with variable sunshine, rain and clouds, and spring weather is unsettled.
The weather stations nearest Bristol for which long-term climate data are available are Long Ashton (about south west of the city centre) and Bristol Weather Station, in the city centre. Data collection at these locations ended in 2002 and 2001, respectively, and Filton Airfield is currently the nearest weather station to the city. Temperatures at Long Ashton from 1959 to 2002 ranged from in July 1976 to in January 1982. Monthly high temperatures since 2002 at Filton exceeding those recorded at Long Ashton include in April 2003, in July 2006 and in October 2011. The lowest recent temperature at Filton was in December 2010. Although large cities in general experience an urban heat island effect, with warmer temperatures than their surrounding rural areas, this phenomenon is minimal in Bristol.
Environment
Bristol was ranked as Britain's most sustainable city (based on its environmental performance, quality of life,future-proofing
Future-proofing is the process of anticipating the future and developing methods of minimizing the effects of shocks and stresses of future events. Future-proofing is used in industries such as electronics, medical industry, industrial design ...
and approaches to climate change, recycling and biodiversity), topping environmental charity Forum for the Future
Forum for the Future is a registered charity and non-profit organisation that works in partnership with business, government and civil society to accelerate the shift toward a sustainable future. It works by catalysing change in key global systems ...
's 2008 Sustainable Cities
The sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact (commonly referred to as the triple bottom line), and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromisi ...
Index. Local initiatives include Sustrans (creators of the National Cycle Network, founded as Cyclebag in 1977) and Resourcesaver, a non-profit business established in 1988 by Avon Friends of the Earth. In 2014 '' The Sunday Times'' named it as the best city in Britain in which to live. The city received the 2015 European Green Capital Award, becoming the first UK city to receive this award.
In 2019 Bristol City Council voted in favour of banning all privately owned diesel cars from the city centre. Since then, the plans have been revised in favour of a clean air zone whereby older and more polluting vehicles will be charged to drive through the city centre. The Clean Air Zone is currently due to come into effect in Summer 2022.
Green belt
The city has green belt mainly along its southern fringes, taking in small areas within theAshton Court Estate
Ashton may refer to:
Names
* Ashton (given name)
* Ashton (surname)
Places Australia
* Ashton, Elizabeth Bay, a heritage-listed house in Sydney, New South Wales
* Ashton, South Australia
Canada
*Ashton, Ontario
New Zealand
*Ashton, New Zealan ...
, South Bristol crematorium and cemetery, High Ridge common and Whitchurch, with a further area around Frenchay Farm. The belt extends outside the city boundaries into surrounding counties and districts, for several miles in places, to afford a protection from urban sprawl to surrounding villages and towns.
Demographics
In 2014, the Office for National Statistics estimated the Bristol unitary authority's population at 442,474, making it the 43rd-largestceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
in England. The ONS, using Census 2001 data, estimated the city's population at 441,556.
According to the 2011 census, 84% of the population was White (77.9% White British, 0.9% White Irish, 0.1% Gypsy or Irish Travellers and 5.1% Other White); 3.6% mixed-race (1.7% white-and-black Caribbean, 0.4% white-and-black African, 0.8% white and Asian and 0.7% other mixed); 5.5% Asian (1.6% Pakistani, 1.5% Indian, 0.9% Chinese, 0.5% Bangladeshi
Bangladeshis ( bn, বাংলাদেশী ) are the citizens of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centered on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the eponymous bay.
Bangladeshi citizenship was formed in 1971, when the ...
, and 1% other Asian); 6% Black (2.8% African, 1.6% Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
, 1.6% Other Black), 0.3% Arab and 0.6% with other heritage. Bristol is unusual among major British towns and cities in its larger black than Asian population. These statistics apply to the Bristol Unitary Authority area, excluding areas of the urban area (2006 estimated population 587,400) in South Gloucestershire, Bath and North East Somerset (BANES) and North Somerset—such as Kingswood, Mangotsfield, Filton and Warmley. 56.2% of the 209,995 Bristol residents who are employed commute to work using either a car, van, motorbike or taxi, 2.2% commute by rail and 9.8% by bus, while 19.6% walk.
Inequality
The Runnymede Trust found in 2017 that Bristol "ranked 7th out of the 348 districts of England & Wales (1=worst) on the Index of Multiple Inequality." In terms of employment, the report found that "ethnic minorities are disadvantaged compared to white British people nationally, but this is to a greater extent in Bristol, particularly for black groups." Black people in Bristol experience the 3rd highest level of educational inequality in England and Wales.Bristol conurbation
The population of Bristol's contiguous urban area was put at 551,066 by the ONS based on Census 2001 data. In 2006 the ONS estimated Bristol's urban-area population at 587,400, making it England's sixth-most populous city and tenth-most populous urban area. At it has the seventh-highest population density of any English district. According to data from 2019, the urban area has the 11th-largest population in the UK with a population of 670,000. In 2007 the European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON) defined Bristol's functional urban area as including Weston-super-Mare, Bath and Clevedon with a total population of 1.04 million, the twelfth largest of the UK.Economy
 Bristol has a long history of trade, originally exporting wool cloth and importing fish, wine, grain and dairy products; later imports were tobacco, tropical fruits and plantation goods. Major imports are motor vehicles, grain, timber, produce and petroleum products. Since the 13th century, the rivers have been modified for docks; during the 1240s, the Frome was diverted into a deep, man-made channel (known as Saint Augustine's Reach) which flowed into the River Avon.
Ships occasionally departed Bristol for Iceland as early as 1420, and speculation exists that sailors (fishermen who landed on the Canadian coast to salt/ smoke their catch) from Bristol made landfall in the Americas before Christopher Columbus or John Cabot. Beginning in the early 1480s, the Bristol
Bristol has a long history of trade, originally exporting wool cloth and importing fish, wine, grain and dairy products; later imports were tobacco, tropical fruits and plantation goods. Major imports are motor vehicles, grain, timber, produce and petroleum products. Since the 13th century, the rivers have been modified for docks; during the 1240s, the Frome was diverted into a deep, man-made channel (known as Saint Augustine's Reach) which flowed into the River Avon.
Ships occasionally departed Bristol for Iceland as early as 1420, and speculation exists that sailors (fishermen who landed on the Canadian coast to salt/ smoke their catch) from Bristol made landfall in the Americas before Christopher Columbus or John Cabot. Beginning in the early 1480s, the Bristol Society of Merchant Venturers
The Society of Merchant Venturers is a charitable organisation in the English city of Bristol.
The society can be traced back to a 13th-century guild which funded the voyage of John Cabot to Canada. In 1552, it gained a monopoly on sea trading ...
sponsored exploration of the North Atlantic in search of trading opportunities. In 1552, Edward VI granted a royal charter to the Merchant Venturers to manage the port. Among explorers to depart from the port after Cabot were Martin Frobisher
Sir Martin Frobisher (; c. 1535 – 22 November 1594) was an English seaman and privateer who made three voyages to the New World looking for the North-west Passage. He probably sighted Resolution Island near Labrador in north-eastern Canada ...
, Thomas James, after whom James Bay, on southern coast of Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
is named, and Martin Pring, who discovered Cape Cod and the southern New England coast in 1603.
By 1670 the city had 6,000tons of shipping (of which half was imported tobacco), and by the late 17th and early 18th centuries shipping played a significant role in the slave trade. During the 18th century, Bristol was Britain's second-busiest port; business was conducted in the trading area around The Exchange in Corn Street over bronze tables known as Nails. Although the Nails are cited as originating the phrase "cash on the nail" (immediate payment), the phrase was probably in use before their installation.
The city's economy also relies on the aerospace, defence, media, information technology, financial services and tourism industries. The Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
(MoD)'s Procurement Executive, later known as the Defence Procurement Agency and Defence Equipment and Support, moved to its headquarters to Abbey Wood, Filton, in 1995. This organisation, with a staff of 12,000 to 13,000, procures and supports MoD equipment. One of the UK's most popular tourist destinations, Bristol was selected in 2009 as one of the world's top-ten cities by international travel publishers Dorling Kindersley in their ''Eyewitness
Eyewitness or eye witness may refer to:
Witness
* Witness, someone who has knowledge acquired through first-hand experience
** Eyewitness memory
** Eyewitness testimony
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Eyewitness'' (1956 film), a Britis ...
'' guides for young adults.
Bristol is one of the eight-largest regional English cities that make up the Core Cities Group, and is ranked as a Gamma level global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, the fourth-highest-ranked English city. In 2017 Bristol's gross domestic product was £88.448billion. Its per capita GDP was £46,000 ($65,106, €57,794), which was some 65% above the national average, the third-highest of any English city (after London and Nottingham) and the sixth-highest of any city in the United Kingdom (behind London, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Belfast and Nottingham). According to the 2011 census, Bristol's unemployment rate (claiming Jobseeker's Allowance) was three per cent, compared with two per cent for South West England and the national average of four per cent.
Although Bristol's economy no longer relies upon its port, which was moved to docks at Avonmouth during the 1870s and to the Royal Portbury Dock in 1977 as ship size increased, it is the largest importer of cars to the UK. Until 1991, the port was publicly owned; it is leased, with £330million invested and its annual tonnage increasing from 3.9million long tons (4million tonnes) to 11.8million (12million). Tobacco importing and cigarette manufacturing have ceased, but the importation of wine and spirits continues.
The financial services sector employs 59,000 in the city, and 50 micro-electronics and silicon design companies employ about 5,000. In 1983 Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
opened its national research laboratory in Bristol. In 2014 the city was ranked seventh in the "top 10 UK destinations" by TripAdvisor.
During the 20th century, Bristol's manufacturing activities expanded to include aircraft production at Filton by the Bristol Aeroplane Company
The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable a ...
and aircraft-engine manufacturing by Bristol Aero Engines (later Rolls-Royce) at Patchway. Bristol Aeroplane was known for their World War I Bristol Fighter and World War II Blenheim and Beaufighter
The Bristol Type 156 Beaufighter (often called the Beau) is a British multi-role aircraft developed during the Second World War by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was originally conceived as a heavy fighter variant of the Bristol Beaufort ...
planes. During the 1950s they were a major English manufacturer of civilian aircraft, known for the Freighter, Britannia and Brabazon. The company diversified into automobile manufacturing during the 1940s, producing hand-built, luxury Bristol Cars
Bristol Cars were manufacturers of hand-built luxury cars headquartered in Bristol, England. After being placed in receivership and being taken over in 2011, it entered liquidation in February 2020.
After the Second World War, the car division ...
at their factory in Filton, and the Bristol Cars company was spun off in 1960. The city also gave its name to Bristol buses, which were manufactured in the city from 1908 to 1983: by Bristol Tramways until 1955, and from 1955 to 1983 by Bristol Commercial Vehicles.
 Filton played a key role in the Anglo-French Concorde supersonic airliner project during the 1960s. The British Concorde prototype made its maiden flight from Filton to RAF Fairford on 9 April 1969, five weeks after the French test flight. In 2003 British Airways and Air France decided to discontinue Concorde flights, retiring the aircraft to locations (primarily museums) worldwide. On 26 November 2003 Concorde 216 made the final Concorde flight, returning to Bristol Filton Airport as the centrepiece of a proposed air museum which is planned to include the existing Bristol Aero collection (including a Bristol Britannia).
The aerospace industry remains a major sector of the local economy. Major aerospace companies in Bristol include
Filton played a key role in the Anglo-French Concorde supersonic airliner project during the 1960s. The British Concorde prototype made its maiden flight from Filton to RAF Fairford on 9 April 1969, five weeks after the French test flight. In 2003 British Airways and Air France decided to discontinue Concorde flights, retiring the aircraft to locations (primarily museums) worldwide. On 26 November 2003 Concorde 216 made the final Concorde flight, returning to Bristol Filton Airport as the centrepiece of a proposed air museum which is planned to include the existing Bristol Aero collection (including a Bristol Britannia).
The aerospace industry remains a major sector of the local economy. Major aerospace companies in Bristol include BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
, a merger of Marconi Electronic Systems and BAe (the latter a merger of BAC, Hawker Siddeley and Scottish Aviation). Airbus and Rolls-Royce are also based at Filton, and aerospace engineering is an area of research at the University of the West of England. Another aviation company in the city is Cameron Balloons, who manufacture hot air balloons; each August the city hosts the Bristol International Balloon Fiesta, one of Europe's largest hot-air balloon festivals.
In 2005 Bristol was named by the UK government one of England's six science cities. A £500million shopping centre, Cabot Circus, opened in 2008 amidst predictions by developers and politicians that the city would become one of England's top ten retail destinations. The Bristol Temple Quarter Enterprise Zone, focused on creative, high-tech and low-carbon industries around Bristol Temple Meads railway station
Bristol Temple Meads is the oldest and largest railway station in Bristol, England. It is located away from London Paddington. It is an important transport hub for public transport in the city; there are bus services to many parts of the city ...
, was announced in 2011 and launched the following year. The Urban Enterprise Zone has streamlined planning procedures and reduced business rates. Rates generated by the zone are channelled to five other designated enterprise areas in the region: Avonmouth, Bath, Bristol and Bath Science Park
Bristol and Bath Science Park (BBSP) is a science park in Emersons Green, South Gloucestershire, England, north-east of Bristol and north-west of Bath. It cost £300 million to build and is expected to employ about 6,000 when fully developed. The ...
in Emersons Green, Filton, and Weston-super-Mare. Bristol is the only big city whose wealth per capita is higher than that of Britain as a whole. With a highly skilled workforce drawn from its universities, Bristol claims to have the largest cluster of computer chip designers and manufacturers outside Silicon Valley . The wider region has one of the biggest aerospace hubs in the UK, centred on Airbus, Rolls-Royce and GKN at Filton airfield.
Culture
Arts
 Bristol has a thriving current and historical arts scene. Some of the modern venues and modern digital production companies have merged with legacy production companies based in old buildings around the city. In 2008 the city was a finalist for the 2008 European Capital of Culture, although the title was awarded to Liverpool. The city was designated "City of Film" by UNESCO in 2017 and has been a member of the Creative Cities Network since then.
The Bristol Old Vic, founded in 1946 as an offshoot of The Old Vic in London, occupies the 1766 Theatre Royal (607 seats) on King Street; the 150-seat New Vic (a studio-type theatre), and a foyer and bar in the adjacent Coopers' Hall (built in 1743). The Theatre Royal, a grade I listed building, is the oldest continuously operating theatre in England. The Bristol Old Vic Theatre School (which originated in King Street) is a separate company, and the Bristol Hippodrome is a 1,951-seat theatre for national touring productions. Other smaller theatres include the Tobacco Factory, QEH, the Redgrave Theatre at Clifton College, The Wardrobe Theatre, Bristol Improv Theatre, and the Alma Tavern. Bristol's theatre scene features several companies as well as the Old Vic, including Show of Strength, Shakespeare at the Tobacco Factory and Travelling Light. Theatre Bristol is a partnership between the city council,
Bristol has a thriving current and historical arts scene. Some of the modern venues and modern digital production companies have merged with legacy production companies based in old buildings around the city. In 2008 the city was a finalist for the 2008 European Capital of Culture, although the title was awarded to Liverpool. The city was designated "City of Film" by UNESCO in 2017 and has been a member of the Creative Cities Network since then.
The Bristol Old Vic, founded in 1946 as an offshoot of The Old Vic in London, occupies the 1766 Theatre Royal (607 seats) on King Street; the 150-seat New Vic (a studio-type theatre), and a foyer and bar in the adjacent Coopers' Hall (built in 1743). The Theatre Royal, a grade I listed building, is the oldest continuously operating theatre in England. The Bristol Old Vic Theatre School (which originated in King Street) is a separate company, and the Bristol Hippodrome is a 1,951-seat theatre for national touring productions. Other smaller theatres include the Tobacco Factory, QEH, the Redgrave Theatre at Clifton College, The Wardrobe Theatre, Bristol Improv Theatre, and the Alma Tavern. Bristol's theatre scene features several companies as well as the Old Vic, including Show of Strength, Shakespeare at the Tobacco Factory and Travelling Light. Theatre Bristol is a partnership between the city council, Arts Council England
Arts Council England is an arm's length non-departmental public body of the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is also a registered charity. It was formed in 1994 when the Arts Council of Great Britain was divided into three s ...
and local residents to develop the city's theatre industry. Several organisations support Bristol theatre; the Residence (an artist-led community) provides office, social and rehearsal space for theatre and performance companies, and Equity
Equity may refer to:
Finance, accounting and ownership
* Equity (finance), ownership of assets that have liabilities attached to them
** Stock, equity based on original contributions of cash or other value to a business
** Home equity, the dif ...
has a branch in the city.
The city has many venues for live music, its largest the 2,000-seat Bristol Beacon, previously Colston Hall, named after Edward Colston. Others include the Bristol Academy, The Fleece
''The'' () is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speak ...
, The Croft
The Croft is a large detached house on Totteridge Green in Totteridge, Barnet. It has been Grade II listed on the National Heritage List for England since November 1974.
The house was designed by the English architect T.E. Collcutt as his persona ...
, the Exchange, Fiddlers, the Victoria Rooms
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seych ...
, Rough Trade, Trinity Centre, St George's Bristol
St George's is a former church in Great George Street, off Park Street, on the lower slopes of Brandon Hill in Bristol, England. Since 1999 it has been used as a music venue known as St George's Bristol. It was built in the 1820s by Sir Robert ...
and several pubs, from the jazz-oriented The Old Duke to rock at the Fleece and indie bands at the Louisiana. In 2010 PRS for Music called Bristol the UK's most musical city, based on the number of its members born there relative to the city's population. Since the late 1970s Bristol has been home to bands combining punk, funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African Americans in the m ...
, dub and political consciousness. With trip hop and Bristol Sound artists such as Tricky, Portishead and Massive Attack, the list of bands from Bristol is extensive. The city is a stronghold of drum and bass
Drum and bass (also written as drum & bass or drum'n'bass and commonly abbreviated as D&B, DnB, or D'n'B) is a genre of electronic dance music characterized by fast breakbeats (typically 165–185 beats per minute) with heavy bass and sub-ba ...
, with artists such as Roni Size's Mercury Prize-winning Reprazent
Roni Size & Reprazent (stylised as Roni Size / Reprazent) are a British drum and bass group fronted by Roni Size. Their debut album ''New Forms'' won the Mercury Music Prize in 1997. Their follow-up album ''In the Møde'' featured artists inclu ...
, as DJ Krust, More Rockers
Rob Smith is an English DJ, musician and remixer from Bristol, England. Previously on the now defunct Grand Central Records independent record label, playing breakbeat Hip hop music, hip-hop, Dub music, dub and reggae-influenced music, more rece ...
and TC. Trip hop and drum & bass music, in particular, is part of the Bristol urban-culture scene which received international media attention during the 1990s. The Downs Festival is also a yearly occurrence where both local and well-known bands play. Since its inception in 2016, it has become a major event in the city.
The Bristol Museum and Art Gallery houses a collection encompassing natural history, archaeology, local glassware, Chinese ceramics and art. The M Shed museum opened in 2011 on the site of the former Bristol Industrial Museum
The Bristol Industrial Museum was a museum in Bristol, England, located on Prince's Wharf beside the Floating Harbour and which closed in 2006. On display were items from Bristol's industrial past – including aviation, car and bus manufactur ...
. Both are operated by Bristol Culture and Creative Industries, which also runs three historic housesthe Tudor Red Lodge, the Georgian House and Blaise Castle House; and Bristol Archives. The 18th- and 19th-century portrait painter Thomas Lawrence, 19th-century architect Francis Greenway (designer of many of Sydney's first buildings) were born in the city. The graffiti artist Banksy is believed to be from Bristol, and many of his works are on display in the city.
The Watershed Media Centre and Arnolfini gallery (both in dockside warehouses) exhibit contemporary art, photography and cinema, and the city's oldest gallery is at the Royal West of England Academy in Clifton. The nomadic Antlers Gallery opened in 2010, moving into empty spaces on Park Street, on Whiteladies Road
Whiteladies Road is a main road in Bristol, England. It runs north from the Victoria Rooms to Durdham Down, and separates Clifton on the west side from Redland and Cotham on the east. It forms part of the A4018.
Significant buildings on ...
and in the Purifier House on Bristol's Harbourside. Stop-motion
Stop motion is an animated filmmaking technique in which objects are physically manipulated in small increments between individually photographed frames so that they will appear to exhibit independent motion or change when the series of frames i ...
animation films and commercials (produced by Aardman Animations) are made in Bristol. Robert Newton, Bobby Driscoll and other cast members of the 1950 Walt Disney film '' Treasure Island'' (some scenes were filmed along the harbourside) were visitors to the city along with Walt Disney himself. Bristol is home to the regional headquarters of BBC West and the BBC Natural History Unit. Locations in and around Bristol have featured in the BBC's natural-history programmes, including '' Animal Magic'' (filmed at Bristol Zoo).
Bristol is the birthplace of 18th-century poets Robert Southey and Thomas Chatterton. Southey (born on Wine Street in 1774) and his friend, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, married the Fricker sisters from the city. William Wordsworth spent time in Bristol, where Joseph Cottle
Joseph Cottle (1770–1853) was an English publisher and author.
Cottle started business in Bristol. He published the works of Samuel Taylor Coleridge and Robert Southey on generous terms. He then wrote in his ''Early Recollections'' an expos ...
published '' Lyrical Ballads'' in 1798. Actor Cary Grant was born in Bristol, and comedians from the city include Justin Lee Collins, Lee Evans, Russell Howard and writer-comedian Stephen Merchant.
The author John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architecture, ...
wrote a poem called "Bristol".
It begins:
Architecture
Bristol has 51 Grade I, 500 Grade II* and over 3,800Grade II listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
buildings
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and funct ...
in a variety of architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings o ...
styles, from medieval to modern. During the mid-19th century Bristol Byzantine, a style unique to the city, was developed, and several examples have survived. Buildings from most architectural periods of the United Kingdom can be seen in the city. Surviving elements of the fortifications and castle date to the medieval period, and the Church of St James dates back to the 12th century.
The oldest Grade I listed buildings in Bristol are religious. St James' Priory was founded in 1129 as a Benedictine priory by Earl Robert of Gloucester, the illegitimate son of Henry I. The second-oldest is Bristol Cathedral and its associated Great Gatehouse. Founded in 1140, the church became the seat of the bishop and cathedral of the new Diocese of Bristol in 1542. Most of the medieval stonework, particularly the Elder Lady Chapel, is made from limestone taken from quarries around Dundry and Felton with Bath stone
Bath Stone is an oolitic limestone comprising granular fragments of calcium carbonate. Originally obtained from the Combe Down and Bathampton Down Mines under Combe Down, Somerset, England. Its honey colouring gives the World Heritage City of ...
being used in other areas. Amongst the other churches included in the list is the 12th-century St Mary Redcliffe which is the tallest building in Bristol. The church was described by Queen Elizabeth I as "the fairest, goodliest, and most famous parish church in England."
Secular buildings include The Red Lodge
The Red Lodge was a fraternal organization that traced its lineage back to 1912 with the creation of the Red Lodge or Medicine Lodge by Ernest Thompson Seton within the Woodcraft Movement. They describe themselves as a Brotherhood of men who have ...
, built in 1580 for John Yonge as a lodge for a larger house that once stood on the site of the present Bristol Beacon (previously known as Colston Hall). It was subsequently added to in Georgian times and restored in the early 20th century. St Bartholomew's Hospital is a 12th-century town house which was incorporated into a monastery hospital founded in 1240 by Sir John la Warr, 2nd Baron De La Warr (), and became Bristol Grammar School from 1532 to 1767, and then Queen Elizabeth's Hospital 1767–1847. The round piers predate the hospital, and may come from an aisled hall, the earliest remains of domestic architecture in the city, which was then adapted to form the hospital chapel. Three 17th-century town houses which were attached to the hospital were incorporated into model workers' flats in 1865, and converted to offices in 1978. St Nicholas's Almshouses
St Nicholas' Almshouses () is a historic building on King Street, Bristol, England.
It was built in 1652 to 1656, extended in the 19th century and restored 1961 by Donald Insall. The foundations of a bastion of the City Wall were revealed durin ...
were built in 1652 to provide care for the poor. Several public houses were also built in this period, including the Llandoger Trow on King Street and the Hatchet Inn.
 Manor houses include
Manor houses include Goldney Hall
Goldney Hall is a self-catered hall of residence in the University of Bristol. It is one of three in the Clifton area of Bristol, England.
The hall occupies part of the grounds of Goldney House, built in the 18th century and remodelled in th ...
, where the highly decorated Grotto
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave used by humans in both modern times and antiquity, and historically or prehistorically. Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high ti ...
dates from 1739. Commercial buildings such as the Exchange and Old Post Office from the 1740s are also included in the list. Residential buildings include the Georgian Portland Square and the complex of small cottages around a green at Blaise Hamlet
Blaise Hamlet is a group of nine small cottages around a green in Henbury, now a district in the north of Bristol, England. All the cottages, and the sundial on the green are Grade I listed buildings. Along with Blaise Castle the Hamlet is list ...
, which was built around 1811 for retired employees of Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
banker and philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private goo ...
John Scandrett Harford
John Scandrett Harford, FRS (8 October 1785 – 16 April 1866) was a British banker, benefactor and abolitionist.
Early life and background
Harford was the son of John Scandrett Harford, a prominent banker in Bristol. By the end of the 18th c ...
, who owned Blaise Castle House. The 18th-century Kings Weston House, in northern Bristol, was designed by John Vanbrugh
Sir John Vanbrugh (; 24 January 1664 (baptised) – 26 March 1726) was an English architect, dramatist and herald, perhaps best known as the designer of Blenheim Palace and Castle Howard. He wrote two argumentative and outspoken Restora ...
and is the only Vanbrugh building in any UK city outside London. Almshouse
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) was charitable housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the medieval era. They were often targeted at the poor of a locality, at those from certain ...
s and pubs from the same period intermingle with modern development. Several Georgian squares were designed for the middle class as prosperity increased during the 18th century. During World War II, the city centre was heavily bombed during the Bristol Blitz. The central shopping area near Wine Street and Castle Street was particularly hard-hit, and the Dutch House and St Peter's Hospital were destroyed. Nevertheless, in 1961 John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architecture, ...
called Bristol "the most beautiful, interesting and distinguished city in England".
Sport
Bristol is represented by professional teams in all the major national sports. Bristol City and Bristol Rovers are the city's mainfootball
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
clubs. Bristol Bears ( rugby union) and Gloucestershire County Cricket Club
Gloucestershire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Gloucestershire. Founded in 1870, Gloucestershire have always ...
are also based in the city.
The two Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engla ...
clubs are Bristol City and Bristol Roversthe former being the only club from the city to play in the precursor to the Premier League. Non-league clubs include Bristol Manor Farm, Hengrove Athletic, Brislington, Roman Glass St George and Bristol Telephones. Bristol City, formed in 1894, were Division One runners-up in 1907 and lost the FA Cup final in 1909. In the First Division in 1976, they then sank to the bottom professional tier before reforming after a 1982 bankruptcy. 28 October 2000 is a date of significance in the city as it is the last time Bristol Rovers were above Bristol City in the Football league. Bristol City were promoted to the second tier of English football in 2007, losing to Hull City in the playoff for promotion to the Premier League that season. Bristol City Women
Bristol City Women's Football Club is a women's association football team from the city of Bristol. Formed in 1998 as Bristol Rovers W.F.C., they were renamed Bristol Academy W.F.C. in 2005 following increased involvement of the Bristol Acad ...
are based at Twerton Park
Twerton Park is a football stadium in the Twerton suburb of Bath, England. The stadium is named after the surrounding area, Twerton. The stadium has a physical capacity of 8,884, 1,066 of which are seats. It has been the home of Bath City F.C. ...
.
 Bristol Rovers, the oldest professional football team in the city, were formed in 1883 and promoted back into the football league in 2015. They were third-tier champions twice (
Bristol Rovers, the oldest professional football team in the city, were formed in 1883 and promoted back into the football league in 2015. They were third-tier champions twice (Division Three South
The Third Division South of The Football League was a tier in the English football league system from 1921 to 1958. It ran in parallel with the Third Division North with clubs elected to the League or relegated from Division Two allocated to ...
in 1952–53 and Division Three in 1989–90), Watney Cup Winners (1972) and runners-up for the Johnstone's Paint Trophy
The English Football League Trophy, known for sponsorship purposes as the Papa Johns Trophy after restaurant chain Papa John's Pizza, is an annual English association football knockout competition open to all clubs in EFL League One and EFL Leag ...
(2006–07) although have never played in England's top Division. The club has planning permission for a new 21,700-capacity all-seater stadium at the University of the West of England's Frenchay campus. Construction was due to begin in mid-2014, but in March 2015 the sale of the Memorial Stadium site (needed to finance the new stadium) was in jeopardy.
Bristol Manor Farm are the highest-ranked non-league club within the city boundaries. They play their games at The Creek, Sea Mills, in the north of Bristol. Formed in 1960, the club currently play in the Southern League Division One South having finished the 2016–17 Western League season as champions. They reached the quarter finals of the FA Vase
The Football Association Challenge Vase, usually referred to as the FA Vase, is an annual football competition for teams playing in Steps 5 and 6 of the English National League System (or equivalently, tier 9 or 10 of the overall English footbal ...
in 2015–16.
The city is also home to Bristol Bears, formed in 1888 as Bristol Football Club by the merger of the Carlton club with rival Redland Park. Westbury Park declined the merger and folded, with many of its players joining what was then Bristol Rugby. Bristol Rugby has often competed at the highest level of the sport since its formation in 1888. The club played at the Memorial Ground, which it shared with Bristol Rovers from 1996. Although Bristol Rugby owned the stadium when the football club arrived, a decline in the rugby club's fortunes led to a transfer of ownership to Bristol Rovers. In 2014 Bristol Rugby moved to their new home, Ashton Gate Stadium (home to Bristol Rovers' rivals Bristol City), for the 2014–15 season. They changed their name from Bristol Rugby to Bristol Bears to coincide with their return to Premiership Rugby in 2018–19.
Dating from 1901, the Bristol Combination and its 53 clubs promote rugby union in the city and help support Bristol Bears. The most prominent of Bristol's smaller rugby clubs include Clifton Rugby
Clifton Rugby Football Club is an English rugby union club founded in Clifton, Bristol. Over the years the club's home games have been played in a variety of locations in northern Bristol, though never in Clifton itself; since 1976 they h ...
, Dings Crusaders, and Cleve. Rugby league is represented in Bristol by the Bristol Sonics
Bristol Sonics are a rugby league club based in Bristol in the South West of England.
The Sonics' first team plays in the Conference League South competition, having previously played in the now defunct Rugby League Conference Midlands Prem ...
.
The first-class cricket club Gloucestershire County Cricket Club
Gloucestershire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Gloucestershire. Founded in 1870, Gloucestershire have always ...
has its headquarters and plays the majority of its home games at the Bristol County Ground, the only major international sports venue in the south-west of England. It was formed by the family of W. G. Grace. The club is arguably Bristol's most successful, achieving a period of success between 1999 and 2006 when it won nine trophies and became the most formidable one-day outfit in England, including winning a "double double" in 1999 and 2000 (both the Benson and Hedges Cup and the C&G Trophy), and the Sunday League in 2000. Gloucestershire CCC also won the Royal London One-Day Cup in 2015.
The Bristol Flyers
The Bristol Flyers are a British professional basketball team based in the city of Bristol, England. The Flyers compete in the British Basketball League, after promotion from the English Basketball League in 2014. The team play their home game ...
basketball team have competed in the British Basketball League, the UK's premier professional basketball league, since 2014. Bristol Aztecs play in Britain's premier American football competition, the BAFA National Leagues
The BAFANL (BAFA National Leagues) are the primary American football domestic League competition in Great Britain. The League is run by the British American Football Association to coordinate contact football within England, Scotland and Wales. ...
. In 2009 ice hockey returned to Bristol after a 17-year absence, with the Bristol Pitbulls playing at Bristol Ice Rink; after its closure, it shared a venue with Oxford City Stars
The Oxford City Stars are an ice hockey team based in Oxford, England. They currently play in the NIHL South Division 1
The NIHL South Division 1 is the top-level league in the Southern Region of the British National Ice Hockey League setup.
...
. Bristol sponsors an annual half marathon and hosted the 2001 IAAF World Half Marathon Championships
The 10th IAAF World Half Marathon Championships was held on 7 October 2001 in the city of Bristol, UK, and was run immediately before that year's Bristol Half Marathon. A total of 200 athletes, 125 men and 75 women, from 52 countries took part.
D ...
. Athletic clubs in Bristol include Bristol and West AC, Bitton Road Runners and Westbury Harriers. Bristol has staged finishes and starts of the Tour of Britain cycle race and facilities in the city were used as training camps for the 2012 London Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
. The Bristol International Balloon Fiesta, a major UK hot-air ballooning event, is held each summer at Ashton Court.
Dialect
A dialect of English ( West Country English), known as Bristolian, is spoken by longtime residents, who are known as Bristolians. Bristol natives have arhotic accent
Rhoticity in English is the pronunciation of the historical rhotic consonant by English speakers. The presence or absence of rhoticity is one of the most prominent distinctions by which varieties of English can be classified. In rhotic varieti ...
, in which the post-vocalic ''r'' in ''car'' and ''card'' is pronounced (unlike in Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the Accent (sociolinguistics), accent traditionally regarded as the Standard language, standard and most Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestigious form of spoken British English. For over a century, there has been ...
). The unique feature of this accent is the 'Bristol (or terminal) l', in which ''l'' is appended to words ending in ''a'' or ''o''. Whether this is a broad ''l'' or a ''w'' is a subject of debate, with ''area'' pronounced 'areal' or 'areaw'. The ending of ''Bristol'' is another example of the Bristol ''l''. Bristolians pronounce ''-a'' and ''-o'' at the end of a word as ''-aw'' (''cinemaw''). To non-natives, the pronunciation suggests an ''l'' after the vowel.
Until recently, Bristolese was characterised by retention of the second-person singular, as in the doggerel "Cassn't see what bist looking at? Cassn't see as well as couldst, casst? And if couldst, 'ouldn't, 'ouldst?" The West Saxon ''bist'' is used for the English ''art'', and children were admonished with "Thee and thou, the Welshman's cow". In Bristolian, as in French and German, the second-person singular was not used when speaking to a superior (except by the egalitarian Quakers). The pronoun ''thee'' is also used in the subject position ("What bist thee doing?"), and ''I'' or ''he'' in the object position ("Give he to I."). Linguist Stanley Ellis, who found that many dialect words in the Filton area were linked to aerospace work, described Bristolian as "a cranky, crazy, crab-apple tree of language and with the sharpest, juiciest flavour that I've heard for a long time".
Religion
In the 2011 United Kingdom census, 46.8% of Bristol's population identified asChristian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
and 37.4% said they were not religious; the English averages were 59.4% and 24.7%, respectively. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is observed by 5.1% of the population, Buddhism by 0.6%, Hinduism by 0.6%, Sikhism by 0.5%, Judaism by 0.2% and other religions by 0.7%; 8.1% did not identify with a religion.
Among the notable Christian churches are the Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
Bristol Cathedral and St Mary Redcliffe
St Mary Redcliffe is an Anglican parish church located in the Redcliffe district of Bristol, England. The church is a short walk from Bristol Temple Meads station. The church building was constructed from the 12th to the 15th centuries, and it ...
and the Roman Catholic Clifton Cathedral. Nonconformist chapels include Buckingham Baptist Chapel
Buckingham Baptist Chapel is a Gothic Revival church in Queens Road, Clifton, Bristol, England.
History
The church was built in 1842 to the designs of Richard Shackleton Pope. It is one of the earliest Baptist chapels built in this style.
Th ...
and John Wesley's New Room
John Wesley's New Room is a historic building in Broadmead, Bristol, England. Opened in 1739, it housed the earliest Methodist societies, and was enlarged in 1748. As the oldest purpose-built Methodist preaching house (chapel), it has been des ...
in Broadmead. After St James' Presbyterian Church was bombed on 24 November 1940, it was never again used as a church; although its bell tower
A bell tower is a tower that contains one or more bells, or that is designed to hold bells even if it has none. Such a tower commonly serves as part of a Christian church, and will contain church bells, but there are also many secular bell tower ...
remains, its nave was converted into offices. The city has eleven mosques, several Buddhist meditation centres, a Hindu temple, Reform and Orthodox-Jewish synagogues and four Sikh temples.
Bars and nightlife
Bristol has been awarded Purple Flag status on many of its districts, which shows that it meets or surpasses the standards of excellence in managing the evening and night-time economy. ''DJ Mag'' top 100 club list ranked Motion as the 19th-best club in the world in 2016. This is up 5 spots from 2015. Motion is host to some of the world's top DJs, and leading producers. Motion is a complex made up of different rooms, outdoor space and a terrace that looks over the river Avon. In 2011, Motion was transformed from a skate park into the rave spot it is today. In:Motion is an annual series which takes place each autumn and delivers 12 weeks of music and dancing. The club, on Avon Street, behind Temple Meads train station, does not limit itself to playing one genre of music. Party-goers can hear everything from disco, house, techno, grime, drum and bass or hip hop, depending on the night. In 2020 and 2021, Motion adapted many of its indoor events into outdoor events. Some of these included Bingo Lingdo. Other famous clubs in the city include Lakota and Thekla. The Attic Bar is a venue located inStokes Croft
Stokes Croft is a road in Bristol, England. It is part of the A38, a main road north of the city centre. Locals refer to the area around the road by the same name.
The road became a centre of industry during the mid-19th century, including the ...
. Equipped with a sound system and stage which are used every weekend for gigs of every genre, the bar and the connected Full Moon Pub were rated by ''The Guardian'', a British daily paper, as one of the top ten clubs in the UK. Located by Bristol's harbourside, The Apple is a cider bar which opened in 2004, in a converted Dutch barge, offering a range of 40 different ciders. In 2014, the Great British Pub Awards ranked The Apple as the best cider bar in the UK. Bristol is also home to the pie chain Pieminster started in the Stokes Croft area of the city.
Media
 Bristol is home to the regional headquarters of BBC West and the BBC Natural History Unit based at Broadcasting House, which produces television, radio and online content with a natural history or wildlife theme. These include nature documentaries, including '' The Blue Planet'' and '' Planet Earth''. The city has a long association with
Bristol is home to the regional headquarters of BBC West and the BBC Natural History Unit based at Broadcasting House, which produces television, radio and online content with a natural history or wildlife theme. These include nature documentaries, including '' The Blue Planet'' and '' Planet Earth''. The city has a long association with David Attenborough
Sir David Frederick Attenborough (; born 8 May 1926) is an English broadcaster, biologist, natural historian and author. He is best known for writing and presenting, in conjunction with the BBC Natural History Unit, the nine natural histor ...
's authored documentaries, including ''Life on Earth (TV series), Life on Earth''. It was made public in 2021 that the BBC was moving the production of many of its programmes from Broadcasting House to Bridgewater House in Finzels Reach in Bristol City Centre.
Bristol has two daily newspapers, the ''Western Daily Press'' and the ''Bristol Post'', (both owned by Reach plc); and a Bristol edition of the free Metro (British newspaper), ''Metro'' newspaper (owned by Daily Mail and General Trust, DMGT). ''The Bristol Cable'' specialises in investigative journalism with a quarterly print edition and website.
Aardman Animations is an Academy Awards, Oscar-winning animation studio founded and still based in Bristol. They created famous characters such as Wallace and Gromit and Morph (animation), Morph. Its Aardman filmography, films include ''Chicken Run'' (2000), ''Early Man (film), Early Man (2018)'', shorts such as ''Creature Comforts'' and ''Adam (1992 film), Adam'' and TV series like ''Shaun the Sheep'' and ''Timmy Time''.
The city has several radio stations, including BBC Radio Bristol. Bristol's television productions include ''BBC Points West, Points West'' for BBC West, Endemol productions such as ''Deal or No Deal'', ''The Crystal Maze'', and ''ITV News West Country'' for ITV West Country. The hospital drama ''Casualty (TV series), Casualty'', formerly filmed in Bristol, moved to Cardiff in 2012. In October 2018, Channel 4 announced that Bristol would be home to one of its 'Creative Hubs', as part of their move to produce more content outside of London.
Publishers in the city have included 18th-century Bristolian Joseph Cottle, who helped introduce Romanticism by publishing the works of William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge. During the 19th century, J.W. Arrowsmith published the Victorian comedies ''Three Men in a Boat'' (by Jerome K. Jerome) and ''The Diary of a Nobody'' by George Grossmith, George and Weedon Grossmith. The contemporary Redcliffe Press has published over 200 books covering all aspects of the city. Bristol is home to YouTube video developers and stylists The Yogscast, with founders Simon Lane and Lewis Brindley moving their operations from Reading, Berkshire, Reading to Bristol in 2012.
Education
 Bristol has two major institutions of higher education: the University of Bristol, a Red brick university, redbrick chartered in 1909; and the University of the West of England, opened as Bristol Institute of technology, Polytechnic in 1969, which became a university in 1992. The University of Law also has a campus in the city. Bristol has two further education institutions (City of Bristol College and South Gloucestershire and Stroud College) and two Theology, theological colleges: Trinity College, Bristol, Trinity College, and Baptists Together, Bristol Baptist College. The city has 129 Infant school, infant, Junior school, junior and primary schools,
List of schools in Bristol, 17 secondary schools, and three learning centres. After a section of north London, Bristol has England's second-highest number of Independent school (United Kingdom), independent school places. Independent schools in the city include Clifton College, Clifton High School, Bristol, Clifton High School, Badminton School, Bristol Grammar School, Queen Elizabeth's Hospital (the only all-boys school) and the Redmaids' High School, Redmaids' School (founded in 1634 by John Whitson, which claims to be England's oldest girls' school).
Bristol has two major institutions of higher education: the University of Bristol, a Red brick university, redbrick chartered in 1909; and the University of the West of England, opened as Bristol Institute of technology, Polytechnic in 1969, which became a university in 1992. The University of Law also has a campus in the city. Bristol has two further education institutions (City of Bristol College and South Gloucestershire and Stroud College) and two Theology, theological colleges: Trinity College, Bristol, Trinity College, and Baptists Together, Bristol Baptist College. The city has 129 Infant school, infant, Junior school, junior and primary schools,
List of schools in Bristol, 17 secondary schools, and three learning centres. After a section of north London, Bristol has England's second-highest number of Independent school (United Kingdom), independent school places. Independent schools in the city include Clifton College, Clifton High School, Bristol, Clifton High School, Badminton School, Bristol Grammar School, Queen Elizabeth's Hospital (the only all-boys school) and the Redmaids' High School, Redmaids' School (founded in 1634 by John Whitson, which claims to be England's oldest girls' school).
 In 2005, Chancellor of the Exchequer Gordon Brown named Bristol one of six English 'science cities',
and a £300million science park was planned at Emersons Green. Research is conducted at the two universities, the Bristol Royal Infirmary and Southmead Hospital, and science outreach is practised at We The Curious, the Bristol Zoo, the Bristol Festival of Nature and the CREATE Centre.
The city has produced a number of scientists, including 19th-century chemist Humphry Davy (who worked in Hotwells). Physicist Paul Dirac (from Bishopston, Bristol, Bishopston) received the 1933 Nobel Prize for his contributions to quantum mechanics. C. F. Powell, Cecil Frank Powell was the Melvill Wills Professor of Physics at the University of Bristol when he received the 1950 Nobel Prize for, among other discoveries, his photographic method of studying nuclear processes. Colin Pillinger was the planetary scientist behind the Beagle 2 project, and neuropsychologist Richard Gregory founded the Exploratory (a hands-on science centre which was the predecessor of At-Bristol/We The Curious).
Initiatives such as the Flying Start Challenge encourage an interest in science and engineering in Bristol secondary-school pupils; links with aerospace companies impart technical information and advance student understanding of design.
The Bloodhound SSC project to break the land speed record is based at the Bloodhound Technology Centre on the city's harbourside.
In 2005, Chancellor of the Exchequer Gordon Brown named Bristol one of six English 'science cities',
and a £300million science park was planned at Emersons Green. Research is conducted at the two universities, the Bristol Royal Infirmary and Southmead Hospital, and science outreach is practised at We The Curious, the Bristol Zoo, the Bristol Festival of Nature and the CREATE Centre.
The city has produced a number of scientists, including 19th-century chemist Humphry Davy (who worked in Hotwells). Physicist Paul Dirac (from Bishopston, Bristol, Bishopston) received the 1933 Nobel Prize for his contributions to quantum mechanics. C. F. Powell, Cecil Frank Powell was the Melvill Wills Professor of Physics at the University of Bristol when he received the 1950 Nobel Prize for, among other discoveries, his photographic method of studying nuclear processes. Colin Pillinger was the planetary scientist behind the Beagle 2 project, and neuropsychologist Richard Gregory founded the Exploratory (a hands-on science centre which was the predecessor of At-Bristol/We The Curious).
Initiatives such as the Flying Start Challenge encourage an interest in science and engineering in Bristol secondary-school pupils; links with aerospace companies impart technical information and advance student understanding of design.
The Bloodhound SSC project to break the land speed record is based at the Bloodhound Technology Centre on the city's harbourside.
Transport
Rail
Bristol has two principal railway stations. Bristol Temple Meads (near the city centre) has Great Western Railway (train operating company), Great Western Railway services which include high-speed trains to Paddington railway station, London Paddington and local, regional and CrossCountry trains.Bristol Parkway
Bristol Parkway, on the South Wales Main Line, is in the Stoke Gifford area in the northern suburbs of the Bristol conurbation. It is from London Paddington. The station was opened in 1972 by British Rail, and was the first in a new gener ...
, north of the city centre, has high-speed Great Western Railway services to Swansea railway station, Swansea, Cardiff Central railway station, Cardiff Central and London Paddington and CrossCountry services to Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham and Northern England, east of Northern England. A limited service to London Waterloo railway station, London Waterloo, via Clapham Junction railway station, Clapham Junction, from Temple Meads is operated by South Western Railway (train operating company), South Western Railway and there are scheduled coach links to most major UK cities.
 Bristol's principal surviving suburban railway is the Severn Beach Line to Avonmouth and Severn Beach. Although Portishead Railway, Portishead Railway's passenger service was a casualty of the Beeching cuts, freight service to the Royal Portbury Dock was restored from 2000 to 2002 with a Strategic Rail Authority rail-freight grant. The MetroWest (Bristol), MetroWest scheme, formerly known as The Greater Bristol Metro, proposes to increase the city's rail capacity including the restoration of a further of track on the Portishead Railway, line to Portishead, Somerset, Portishead (a Commuter town, dormitory town with one connecting road), and a further commuter rail line from Bristol Temple Meads to Henbury, on an Henbury Loop Line, existing freight line. Following numerous delays, the two lines are due to be opened in 2026.
Bristol's principal surviving suburban railway is the Severn Beach Line to Avonmouth and Severn Beach. Although Portishead Railway, Portishead Railway's passenger service was a casualty of the Beeching cuts, freight service to the Royal Portbury Dock was restored from 2000 to 2002 with a Strategic Rail Authority rail-freight grant. The MetroWest (Bristol), MetroWest scheme, formerly known as The Greater Bristol Metro, proposes to increase the city's rail capacity including the restoration of a further of track on the Portishead Railway, line to Portishead, Somerset, Portishead (a Commuter town, dormitory town with one connecting road), and a further commuter rail line from Bristol Temple Meads to Henbury, on an Henbury Loop Line, existing freight line. Following numerous delays, the two lines are due to be opened in 2026.
Roads
The M4 motorway connects the city on an east–west axis from London to West Wales, and the M5 is a north–south west axis from Birmingham to Exeter. The M49 motorway is a shortcut between the M5 in the south and the M4 Second Severn Crossing, Severn Crossing in the west, and the M32 is a spur from the M4 to the city centre. The Portway connects the M5 to the city centre, and was the most expensive road in Britain when opened in 1926. As of 2019, Bristol is working on plans for a Clean Air Zone to reduce pollution, which could involve charging the most polluting vehicles to enter the city centre. Several road-construction plans, including re-routing and improving the South Bristol (UK), South Bristol A4174 road, Ring Road, are supported by the city council. Private car use is high in the city, leading to traffic congestion costing an estimated £350million per year.
Bristol allows motorcycles to use most of the city's bus lanes and provides secure, free parking for them.
Private car use is high in the city, leading to traffic congestion costing an estimated £350million per year.
Bristol allows motorcycles to use most of the city's bus lanes and provides secure, free parking for them.
Public transport
Public transport in the city consists primarily of a First West of England Buses in Bristol, bus network. Other providers are Abus, Stagecoach West, Stagecoach South West and until its sale to Stagecoach West, Wessex Bus. Bristol's bus service has been criticised as unreliable and expensive, and in 2005 FirstGroup was fined for delays and safety violations. Although the city council has included a light rail system in its local transport plan since 2000, it has not yet funded the project; Bristol was offered European Union funding for the system, but the Department for Transport did not provide the required additional funding. As of 2019, a four-line Light rail in Bristol, mass transit network with potential underground sections radiating from Bristol Temple Meads is proposed; a southern line toBristol Airport
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on ...
, a northern line to Aztec West, a northeastern line Bristol & Bath Science Park and a southeastern line to Brislington or Keynsham.
In 2006, a project to develop a bus rapid transit system (BRT) named MetroBus (Bristol), MetroBus was started, with the purpose of providing a faster and more reliable service than buses, improving transport infrastructure and reducing congestion. The project was approved by the Department for Transport, government in December 2013, and in June 2017, it was announced that First West of England, First would operate the buses. MetroBus services commenced in 2018, with the opening of a route from Emersons Green to Bristol city centre, Bristol City Centre (route m3). Further routes were subsequently introduced from Cribbs Causeway to Hengrove Park (route m1), and from Long Ashton Park and ride bus services in the United Kingdom, Park and Ride to Bristol city centre, Bristol City Centre (route m2). In May 2022, it was announced that a fourth route would open in Spring the following year to connect Cribbs Causeway with Bristol Parkway railway station, Bristol Parkway Railway Station (route m4).
Three park and ride sites serve Bristol.
The city centre has water transport operated by Bristol Ferry Boats, Bristol Packet Boat Trips and Number Seven Boat Trips, providing leisure and commuter service in the harbour.
Cycling
Bristol was designated as England's first "cycling city" in 2008 and one of England's 12 "Cycling demonstration" areas. It is home to Sustrans, the sustainable transport charity. The Bristol and Bath Railway Path links it to Bath, and was the first part of the National Cycle Network. The city also has urban cycle routes and links with National Cycle Network routes to The rest of the Country. Cycling trips increased by 21% from 2001 to 2005.Air
 The runway, terminal and other facilities at
The runway, terminal and other facilities at Bristol Airport
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on ...
(BRS), Lulsgate Plateau, Lulsgate, have been upgraded since 2001. In 2019 it was ranked the eighth Busiest airports in the United Kingdom by total passenger traffic, busiest airport in the United Kingdom, handling nearly 8.9 million passengers, an over 3% increase compared with 2018.
International relations
 Bristol was among the first cities to adopt Twin towns and sister cities, town twinning after World War II. Twin towns include:
* Bordeaux, France (since 1947)
* Hanover, Germany (since 1947; one of the first post-war twinnings of British and German cities)
* Porto, Portugal (since 1984)
* Tbilisi, Georgia (since 1988)
* Puerto Morazán, Nicaragua (since 1989)
* Beira, Mozambique (since 1990)
* Guangzhou, China (since 2001)
Bristol was among the first cities to adopt Twin towns and sister cities, town twinning after World War II. Twin towns include:
* Bordeaux, France (since 1947)
* Hanover, Germany (since 1947; one of the first post-war twinnings of British and German cities)
* Porto, Portugal (since 1984)
* Tbilisi, Georgia (since 1988)
* Puerto Morazán, Nicaragua (since 1989)
* Beira, Mozambique (since 1990)
* Guangzhou, China (since 2001)
Freedom of the City
People and military units receiving the Freedom of the City of Bristol include: * Billy Hughes: 20 May 1916. * Kipchoge Keino: 5 July 2012. * Peter Higgs: 4 July 2013. * Sir David Attenborough: 17 December 2013. * The Rifles: 2007, 2015. * 39 (Skinners) Signal Regiment, 39 Signal Regiment: 20 March 2019.See also
*Atlantic history *Bristol Christian Fellowship *Bristol Pound
The Bristol pound (£B) was a form of local, complementary, and/or community currency launched in Bristol, UK on 19 September 2012. Its objective is to encourage people to spend their money with local, independent businesses in Bristol, and f ...
*Bristol power stations
*Healthcare in Bristol
*Parks of Bristol
*Subdivisions of Bristol
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Visit Bristol
official tourism website
Bristol City Council
*
Know your Place: Bristol
historic maps website. {{Coord, 51, 27, N, 2, 35, W, type:city_region:GB-BST, display=title Bristol, Populated places on the River Severn Unitary authority districts of England Port cities and towns in South West England Staple ports County towns in England Cities in South West England Populated places in Bristol (county) Local government districts of South West England River Avon, Bristol Counties of England established in 1373 Counties of England disestablished in 1974 Counties of England established in 1996 Counties in South West England Unparished areas Boroughs in England