|
King Street, Bristol
King Street is a 17th-century street in the historic city centre of Bristol, England. The street lies just south of the old town wall and was laid out in 1650 to develop the Town Marsh, the area then lying between the south or Marsh Wall and the Avon. The north side was developed first and the south side in 1663, when the street was named after Charles II. The section of the city wall is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Historic buildings Among the historic buildings in the street are: * The Llandoger Trow, originally merchants' houses, now a historic public house (1664) * The Old Duke, a public house (1780s) * St Nicholas' Almshouses (1652) * Theatre Royal (1766) and Coopers' Hall (1743), both now part of the Bristol Old Vic. * Number 6 an example of an early Georgian frontage. It dates from c. 1665, but the present early Georgian frontage dates from about 1720. It is thought that the original roof had gables, like those seen on the neighbouring 7 and 8, which were cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Street, Bristol (June2010)
King Street is a 17th-century street in the historic city centre of Bristol, England. The street lies just south of the old town wall and was laid out in 1650 to develop the Town Marsh, the area then lying between the south or Marsh Wall and the Avon. The north side was developed first and the south side in 1663, when the street was named after Charles II. The section of the city wall is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Historic buildings Among the historic buildings in the street are: * The Llandoger Trow, originally merchants' houses, now a historic public house (1664) * The Old Duke, a public house (1780s) * St Nicholas' Almshouses (1652) * Theatre Royal (1766) and Coopers' Hall (1743), both now part of the Bristol Old Vic. * Number 6 an example of an early Georgian frontage. It dates from c. 1665, but the present early Georgian frontage dates from about 1720. It is thought that the original roof had gables, like those seen on the neighbouring 7 and 8, which were cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriel Window
An oriel window is a form of bay window which protrudes from the main wall of a building but does not reach to the ground. Supported by corbels, bracket (architecture), brackets, or similar cantilevers, an oriel window is most commonly found projecting from an upper floor but is also sometimes used on the ground floor. Oriel windows are seen in Arab architecture in the form of mashrabiya and in Turkish are known as ''şahnişin'' or ''cumba''. In Islamic culture, these windows and balconies project from the street-front of a house, providing an area in which women could peer out and see the activities below while remaining invisible. Origins According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the term ''oriel'' is derived from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ' and Late Latin ', both meaning "gallery" or "porch", perhaps from Classical Latin ' ("curtain"). * Oriel College, Oxford, took its name from a balcony or oriel window forming a feature of a building which occupied the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Byzantine
Bristol Byzantine is a variety of Byzantine Revival architecture that was popular in the city of Bristol from about 1850 to 1880. Many buildings in the style have been destroyed or demolished, but notable surviving examples include the Colston Hall, the Granary on Welsh Back, the Carriage Works on Stokes Croft and several of the buildings around Victoria Street. Several of the warehouses around the harbour have survived including the Arnolfini, which now houses an art gallery. Clarks Wood Company warehouse and the St Vincent's Works in Silverthorne Lane and the Wool Hall in St Thomas Street are other survivors from the 19th century. Style Bristol Byzantine has influences from Byzantine and Moorish architecture applied mainly to industrial buildings such as warehouses and factories. The style is characterised by a robust and simple outline, materials with character and coloured polychrome brickwork including red, yellow, black and white brick primarily from the Cattybrook Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35 King Street, Bristol
The 35 King Street () is a former cork warehouse in King Street, Bristol, England, currently housing an Indian restaurant and serviced office space. It was built around 1870 and is an example of the Bristol Byzantine style. It has been designated by English Heritage as a grade II listed building. References See also * Grade II listed buildings in Bristol There are many Grade II listed buildings in Bristol, United Kingdom. In England and Wales the authority for listing is granted by the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 and is administered by English Heritage, an agency ... Grade II listed buildings in Bristol Commercial buildings completed in 1870 Byzantine Revival architecture in the United Kingdom {{Bristol-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32 King Street, Bristol
32 King Street is the address of a historic warehouse building in King Street, Bristol, England. It was built around 1860 and is now occupied by a restaurant. The contemporary 14 and 15 King Street are of similar design. It has been designated by English Heritage as a grade II listed building. References See also * Grade II listed buildings in Bristol There are many Grade II listed buildings in Bristol, United Kingdom. In England and Wales the authority for listing is granted by the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 and is administered by English Heritage, an agency ... Grade II listed buildings in Bristol {{Bristol-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King William Ale House
The King William Ale House is a historic public house situated on King Street in Bristol, England. It dates from 1670 and was originally part of a row of three houses. The three have been designated by English Heritage as a grade II* listed building since 8 January 1959. It includes a mixture of 17th-century and 18th-century features, but currently serves as a public house owned and operated by Samuel Smith Old Brewery. History The King William Ale House stands as part of a group of three houses, which were built in approximately 1670; originally built as a refuge for poor women, the buildings were later converted into public houses. The three buildings were designated as a Grade II* listed building on 8 January 1959, and currently include two public houses, the ''King William Ale House'' as well as ''The Famous Royal Navy Volunteer'', with a restaurant between them. The building is timber-framed, with brick stacks; the front of the building is gabled with three jettied floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", "taverns" and "inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17 King Street, Bristol
17 King Street is a historic building on King Street in the English city of Bristol. Along with the adjacent 18 King Street, it houses a public house called The Famous Royal Naval Volunteer. 17 King Street dates from 1665 and has been designated by English Heritage as a grade II* listed building In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern I .... References Houses completed in 1665 Grade II* listed pubs in Bristol 1665 establishments in England {{pub-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
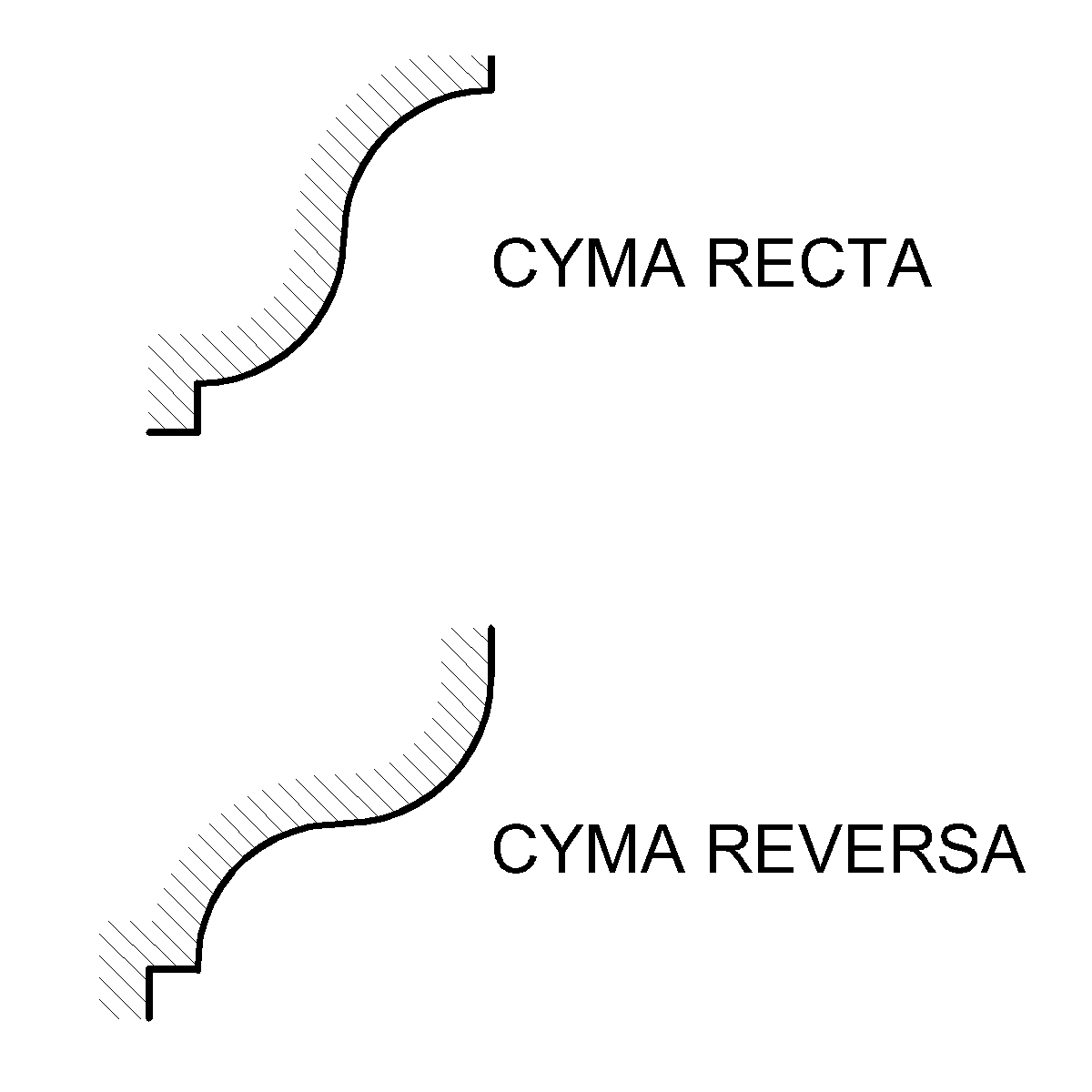
Molding (decorative)
Moulding (spelled molding in the United States), or coving (in United Kingdom, Australia), is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the moulding is often carved in marble or other stones. A "plain" moulding has right-angled upper and lower edges. A "sprung" moulding has upper and lower edges that bevel towards its rear, allowing mounting between two non-parallel planes (such as a wall and a ceiling), with an open space behind. Mouldings may be decorated with paterae as long, uninterrupted elements may be boring for eyes. Types Decorative mouldings have been made of wood, stone and cement. Recently mouldings have been made of extruded PVC and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) as a core with a cement-based protective coating. Synthetic mouldings are a cost-effective alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovolo
The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle. The 1911 edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' says:adapted from Ital. ''uovolo'', diminutive of ''uovo'', an egg; other foreign equivalents are Fr. ''ove'', ''échine'', ''quart de rond''; Lat. ''echinus''... s usedin architecture, ora convex moulding known also as the echinus, which in Classic architecture was invariably carved with the egg and tongue. In Roman and Italian work the moulding is called by workmen a quarter round. The "egg and tongue" referred to, also known as egg-and-dart, egg-and-anchor, or egg-and-star, refers to alternating egg and V-shapes enriching the surface of the concave ovolo in many early cases. The description of ovolo as the fundamental convex quarter-round element underlying or being combined with other elements to compose molding, details on column capitals, and other archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finial
A finial (from '' la, finis'', end) or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature. In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the Apex (geometry), apex of a dome, spire, tower, roof, or gable or any of various distinctive ornaments at the top, end, or corner of a building or structure. A finial is typically carved in stone. Where there are several such elements they may be called pinnacles. The very top of a finial can be a floral or foliated element called a bouquet. Smaller finials in materials such as metal or wood are used as a decorative ornament on the tops or ends of poles or rods such as tent-poles or curtain rods or any object such as a piece of furniture. These are frequently seen on top of bed posts or clocks. Decorative finials are also commonly used to fasten lampshades, and as an ornamental element at the end of the handles of souvenir spoons. The charm at the end of a pull chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newel
A newel, also called a central pole or support column, is the central supporting pillar of a staircase. It can also refer to an upright post that supports and/or terminates the handrail of a stair banister (the "newel post"). In stairs having straight flights it is the principal post at the foot of the staircase, but the term can also be used for the intermediate posts on landings and at the top of a staircase. Although its primary purpose is structural, newels have long been adorned with decorative trim and designed in different architectural styles. Newel posts turned on a lathe are solid pieces that can be highly decorative, and they typically need to be fixed to a square newel base for installation. These are sometimes called solid newels in distinction from hollow newels due to varying techniques of construction. Hollow newels are known more accurately as box newel posts. In historic homes, folklore holds that the house plans were placed in the newel upon completion of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |