Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium Chloride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is the
chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
with the formula , often abbreviated , where Ph is phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen ...
, or even abbreviated PNl or NPl or PPNCl or PNPCl, where PPN or PNP stands for . This color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
less salt is a source of the cation (abbreviated or ), which is used as an unreactive and weakly coordinating cation to isolate reactive anions. is a phosphazene Phosphazenes refer to classes of organophosphorus compounds featuring phosphorus(V) with a double bond between P and N. One class of phosphazenes have the formula . These phosphazenes are also known as iminophosphoranes and phosphine imides. They ar ...
.
Synthesis and structure
is prepared in two steps fromtriphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists a ...
:
:
This triphenylphosphine dichloride
Triphenylphosphine dichloride, Ph3PCl2, is a Halogenation, chlorinating agent widely used in organic chemistry. Applications include the conversion of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and ethers to alkyl chlorides, the cleavage of epoxides to vicinal ...
is related to phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moist ...
. Treatment of this species with hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula . The material is a white crystalline, hygroscopic compound.Greenwood and Earnshaw. ''Chemistry of the Elements.'' 2nd Edition. Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd. pp. 431–43 ...
in the presence of results in replacement of the two single P–Cl bonds in by one double P=N bond:
:
Triphenylphosphine oxide
Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = phenyl, C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste prod ...
is a by-product.
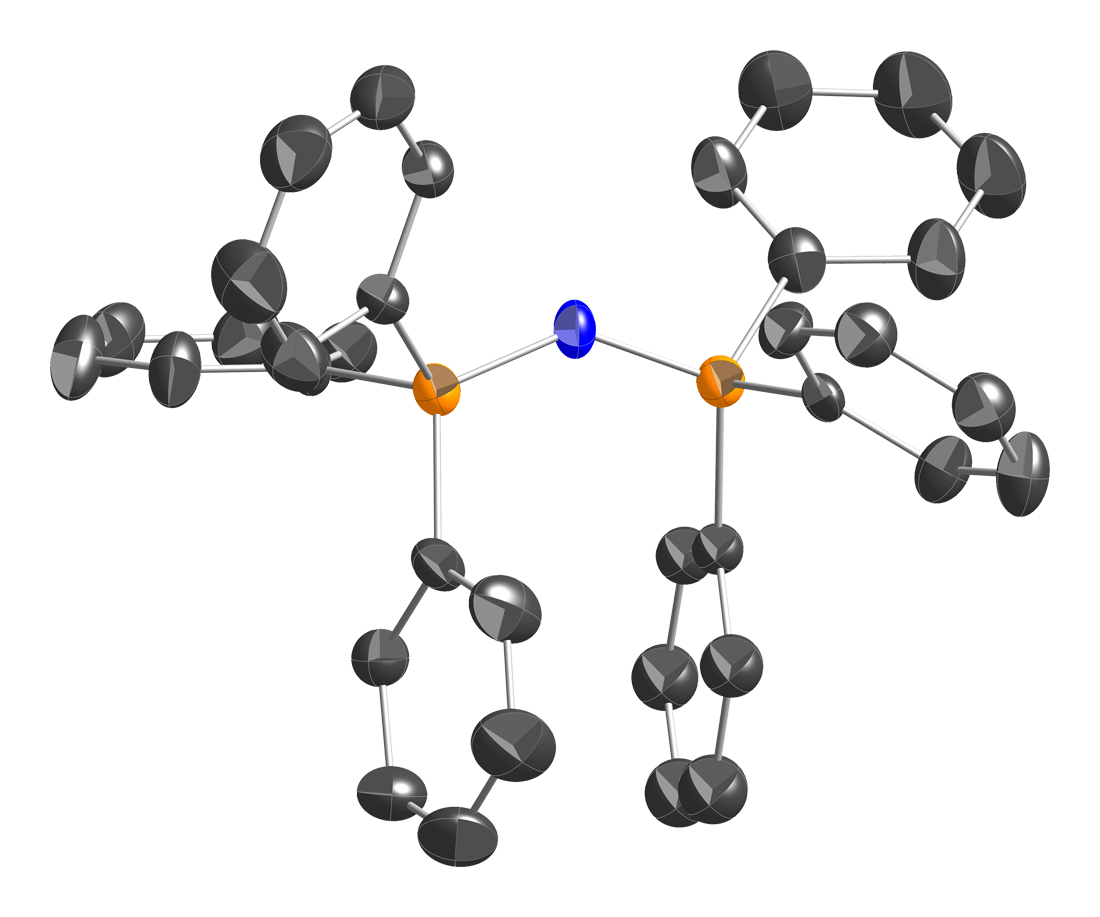
Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is described as . The structure of the bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium cation is . The P=N=P angle in the cation is flexible, ranging from ~130 to 180° depending on the salt. Bent and linear forms of the P=N=P connections have been observed in the same unit cell. The same shallow potential well for bending is observed in the isoelectronic species bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)methane, , as well as the more distantly related molecule carbon suboxide
Carbon suboxide, or tricarbon dioxide, is an organic, oxygen-containing chemical compound with formula and structure . Its four cumulative double bonds make it a cumulene. It is one of the stable members of the series of linear oxocarbons , whi ...
, . For the solvent-free chloride salt , the P=N=P bond angle was determined to be 133°. The two P=N bonds are equivalent, and their length is 1.597(2) Å.

Use as reagent
In the laboratory, is the main precursor to salts. Using salt metathesis reactions,nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
, azide
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant applic ...
, and other small inorganic anions can be obtained with cations. The resulting salts , , etc. are soluble in polar organic solvents.
forms crystalline salts with a range of anions that are otherwise difficult to crystallize. Its effectiveness is partially attributable to its rigidity, reflecting the presence of six phenyl rings. Often forms salts that are more air-stable than salts with smaller cations such as those containing quaternary ammonium
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations ...
cation , or alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
cations. This effect is attributed to the steric shielding provided by this voluminous cation. Illustrative salts of reactive anions include , , (M = Cr, Mo, W), and . The role of ion pair
In chemistry, ion association is a chemical reaction whereby ions of opposite electric charge come together in solution to form a distinct chemical entity. Ion associates are classified, according to the number of ions that associate with each ot ...
ing in chemical reactions is often clarified by examination of the related salt derived from .
Related cations
A phosphazenium cation related to is .References
{{reflist Organophosphorus compounds Chlorides Phosphazenes Phenyl compounds