Biology is the
scientific study of
life.
It is a
natural science
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeatab ...
with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field.
For instance, all
organisms are made up of
cells that process hereditary information encoded in
genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is
evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life.
is also important to life as it allows organisms to
move, grow, and
reproduce.
Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own
internal environment
The internal environment (or ''milieu intérieur'' in French) was a concept developed by Claude Bernard, a French physiologist in the 19th century, to describe the interstitial fluid and its physiological capacity to ensure protective stability f ...
s.
Biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize in ...
s are able to study life at multiple
levels of organization,
from the
molecular biology of a cell to the
anatomy and
physiology of
plants and
animals, and evolution of
populations.
[Based on definition from: ] Hence, there are multiple
subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their
research questions and the
tools that they use.
Like other
scientists, biologists use the
scientific method to make
observation
Observation is the active acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The ...
s, pose questions, generate
hypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
, perform
experiments, and form conclusions about the world around them.
Life on
Earth, which emerged more than 3.7 billion years ago,
is immensely diverse. Biologists have sought to study and classify the various forms of life, from
prokaryotic organisms such as
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
and
bacteria to
eukaryotic organisms such as
protists,
fungi, plants, and animals. These various organisms contribute to the
biodiversity of an
ecosystem, where they play specialized roles in the
cycling of
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s and
energy through their
biophysical environment
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
.
History

The earliest of roots of
science, which included
medicine, can be traced to
ancient Egypt and
Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200
BCE.
Their contributions later entered and shaped Greek
natural philosophy of
classical antiquity.
philosophers such as
Aristotle (384–322 BCE) contributed extensively to the development of biological knowledge. His works such as ''
History of Animals'' were especially important because they revealed his naturalist leanings, and later more empirical works that focused on biological causation and the diversity of life. Aristotle's successor at the
Lyceum,
Theophrastus, wrote a series of books on
botany that survived as the most important contribution of antiquity to the plant sciences, even into the
Middle Ages.
Scholars of the
medieval Islamic world
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
who wrote on biology included
al-Jahiz (781–869),
Al-Dīnawarī
Abū Ḥanīfa Aḥmad ibn Dāwūd Dīnawarī ( fa, ابوحنيفه دينوری; died 895) was a Persian Islamic Golden Age polymath, astronomer, agriculturist, botanist, metallurgist, geographer, mathematician, and historian.
Life
Dinawar ...
(828–896), who wrote on botany,
and
Rhazes (865–925) who wrote on
anatomy and
physiology.
Medicine was especially well studied by Islamic scholars working in Greek philosopher traditions, while natural history drew heavily on Aristotelian thought, especially in upholding a fixed hierarchy of life.
Biology began to quickly develop and grow with
Anton van Leeuwenhoek's dramatic improvement of the
microscope. It was then that scholars discovered
spermatozoa,
bacteria,
infusoria and the diversity of microscopic life. Investigations by
Jan Swammerdam led to new interest in
entomology
Entomology () is the science, scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such ...
and helped to develop the basic techniques of microscopic
dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause o ...
and
staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the ...
.
Advances in
microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
also had a profound impact on biological thinking. In the early 19th century, a number of biologists pointed to the central importance of the
cell. Then, in 1838,
Schleiden and
Schwann began promoting the now universal ideas that (1) the basic unit of organisms is the cell and (2) that individual cells have all the characteristics of
life, although they opposed the idea that (3) all cells come from the division of other cells. However,
Robert Remak and
Rudolf Virchow were able to reify the third tenet, and by the 1860s most biologists accepted all three tenets which consolidated into
cell theory.
Meanwhile, taxonomy and classification became the focus of natural historians.
Carl Linnaeus published a basic
taxonomy for the natural world in 1735 (variations of which have been in use ever since), and in the 1750s introduced
scientific names for all his species.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, treated species as artificial categories and living forms as malleable—even suggesting the possibility of
common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
. Although he was opposed to evolution, Buffon is a key figure in the
history of evolutionary thought; his work influenced the evolutionary theories of both
Lamarck and
Darwin
Darwin may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charles Darwin (1809–1882), English naturalist and writer, best known as the originator of the theory of biological evolution by natural selection
* Darwin, Northern Territory, a territorial capital city i ...
.

Serious evolutionary thinking originated with the works of
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who was the first to present a coherent theory of evolution.
[ Gould, Stephen Jay. ''The Structure of Evolutionary Theory''. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: Cambridge, 2002. . p. 187.] He posited that evolution was the result of environmental stress on properties of animals, meaning that the more frequently and rigorously an organ was used, the more complex and efficient it would become, thus adapting the animal to its environment. Lamarck believed that these acquired traits could then be passed on to the animal's offspring, who would further develop and perfect them.
[ Lamarck (1914)] However, it was the British naturalist
Charles Darwin, combining the biogeographical approach of
Humboldt Humboldt may refer to:
People
* Alexander von Humboldt, German natural scientist, brother of Wilhelm von Humboldt
* Wilhelm von Humboldt, German linguist, philosopher, and diplomat, brother of Alexander von Humboldt
Fictional characters
* ...
, the uniformitarian geology of
Lyell,
Malthus's writings on population growth, and his own morphological expertise and extensive natural observations, who forged a more successful evolutionary theory based on
natural selection; similar reasoning and evidence led
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
to independently reach the same conclusions. Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection quickly spread through the scientific community and soon became a central axiom of the rapidly developing science of biology.
The basis for modern genetics began with the work of
Gregor Mendel, who presented his paper, "''Versuche über Pflanzenhybriden''" ("
Experiments on Plant Hybridization"), in 1865, which outlined the principles of biological inheritance, serving as the basis for modern genetics.
However, the significance of his work was not realized until the early 20th century when evolution became a unified theory as the
modern synthesis reconciled Darwinian evolution with
classical genetics.
In the 1940s and early 1950s, a
series of experiments by
Alfred Hershey
Alfred Day Hershey (December 4, 1908 – May 22, 1997) was an American Nobel Prize–winning bacteriologist and geneticist.
He was born in Owosso, Michigan and received his B.S. in chemistry at Michigan State University in 1930 and his Ph.D. ...
and
Martha Chase pointed to
DNA as the component of
chromosomes that held the trait-carrying units that had become known as
genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
. A focus on new kinds of model organisms such as
viruses and
bacteria, along with the discovery of the double-helical structure of DNA by
James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
and
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
in 1953, marked the transition to the era of
molecular genetics. From the 1950s onwards, biology has been vastly extended in the
molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
domain. The
genetic code was cracked by
Har Gobind Khorana,
Robert W. Holley and
Marshall Warren Nirenberg after DNA was understood to contain
codons
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
. Finally, the
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
was launched in 1990 with the goal of mapping the general human
genome. This project was essentially completed in 2003, with further analysis still being published. The Human Genome Project was the first step in a globalized effort to incorporate accumulated knowledge of biology into a functional, molecular definition of the human body and the bodies of other organisms.
Chemical basis
Atoms and molecules
All organisms are made up of
chemical elements;
,
carbon,
hydrogen, and
nitrogen account for 96% of all organisms, with
calcium,
phosphorus,
sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
,
sodium,
chlorine, and
magnesium constituting essentially all the remainder. Different elements can combine to form
compounds such as water, which is fundamental to life.
is the study of
chemical processes
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
within and relating to living
organisms.
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including
molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions.
Water
Life arose from the Earth's first
ocean, which was formed approximately 3.8 billion years ago.
Since then,
water continues to be the most abundant molecule in every organism. Water is important to life because it is an effective
solvent, capable of dissolving solutes such as
sodium and
chloride ions or other small molecules to form an
aqueous solution. Once dissolved in water, these solutes are more likely to come in contact with one another and therefore take part in
chemical reactions that sustain life.
In terms of its
molecular structure, water is a small
polar molecule with a bent shape formed by the polar covalent bonds of two hydrogen (H) atoms to one oxygen (O) atom (H
2O).
Because the O–H bonds are polar, the oxygen atom has a slight negative charge and the two hydrogen atoms have a slight positive charge.
This polar
property of water allows it to attract other water molecules via hydrogen bonds, which makes water
cohesive
Cohesion may refer to:
* Cohesion (chemistry), the intermolecular attraction between like-molecules
* Cohesion (computer science), a measure of how well the lines of source code within a module work together
* Cohesion (geology), the part of shear ...
.
Surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
results from the cohesive force due to the attraction between molecules at the surface of the liquid.
Water is also
adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
as it is able to adhere to the surface of any polar or charged non-water molecules.
Water is
denser
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek language, Greek letter Rho (letter), rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' ca ...
as a
liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
than it is as a solid (or
ice).
This unique property of water allows ice to float above liquid water such as ponds, lakes, and oceans, thereby
insulating the liquid below from the cold air above.
The lower density of ice compared to liquid water is due to the lower number of water molecules that form the
crystal lattice structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns t ...
of ice, which leaves a large amount of space between water molecules.
In contrast, there is no crystal lattice structure in liquid water, which allows more water molecules to occupy the same amount of volume.
Water also has the capacity to absorb energy, giving it a higher
specific heat capacity than other solvents such as
ethanol.
Thus, a large amount of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules to convert liquid water into
water vapor.
As a molecule, water is not completely stable as each water molecule continuously dissociates into
hydrogen and
hydroxyl ions before reforming into a water molecule again.
In
pure water, the number of hydrogen ions balances (or equals) the number of hydroxyl ions, resulting in a
pH that is neutral.
Organic compounds
Organic compounds are molecules that contain carbon bonded to another element such as hydrogen.
With the exception of water, nearly all the molecules that make up each organism contain carbon.
Carbon can form
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
s with up to four other atoms, enabling it to form diverse, large, and complex molecules.
For example, a single carbon atom can form four single covalent bonds such as in
methane, two
double covalent bonds such as in
carbon dioxide (), or a
triple covalent bond such as in
carbon monoxide (CO). Moreover, carbon can form very long chains of interconnecting
carbon–carbon bonds such as
octane
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula , and the condensed structural formula . Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-Tri ...
or ring-like structures such as
glucose.
The simplest form of an organic molecule is the
hydrocarbon, which is a large family of organic compounds that are composed of
hydrogen atoms bonded to a chain of carbon atoms. A hydrocarbon backbone can be substituted by other elements such as
oxygen (O),
hydrogen (H),
phosphorus (P), and
sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
(S), which can change the chemical behavior of that compound.
Groups of atoms that contain these elements (O-, H-, P-, and S-) and are bonded to a central carbon atom or skeleton are called
functional groups.
There are six prominent functional groups that can be found in organisms:
amino group,
carboxyl group,
carbonyl group,
hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
,
phosphate group, and
sulfhydryl group.
In 1953, the
Miller-Urey experiment showed that organic compounds could be synthesized abiotically within a closed system mimicking the conditions of
early Earth, thus suggesting that complex organic molecules could have arisen spontaneously in early Earth (see
abiogenesis).
Macromolecules

Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The ...
s are large molecules made up of smaller molecular subunits that are joined.
Small molecules such as sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides can act as single repeating units called
monomers to form chain-like molecules called
polymers via a chemical process called
condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
.
For example, amino acids can form
polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
s whereas nucleotides can form strands of nucleic acid. Polymers make up three of the four macromolecules (
polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s,
lipids,
proteins, and
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s) that are found in all organisms. Each of these macromolecules plays a specialized role within any given cell.
Carbohydrates (or
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
) are molecules with the molecular formula , with ''n'' being the number of carbon-hydrate groups.
They include monosaccharides (monomer), oligosaccharides (small polymers), and polysaccharides (large polymers). Monosaccharides can be linked together by
glycosidic linkages, a type of covalent bond.
When two monosaccharides such as
glucose and
fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
are linked together, they can form a
disaccharide such as
sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
.
When many monosaccharides are linked together, they can form an oligosaccharide or a polysaccharide, depending on the number of monosaccharides. Polysaccharides can vary in function. Monosaccharides such as glucose can be a source of energy and some polysaccharides can serve as storage material that can be
hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
to provide cells with sugar.
Lipids are the only class of macromolecules that are not made up of polymers. The most biologically important lipids are
steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s,
phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s, and
fats.
These lipids are organic compounds that are largely nonpolar and hydrophobic.
Steroids are organic compounds that consist of four fused rings.
Phospholipids consist of glycerol that is linked to a phosphate group and two hydrocarbon chains (or
fatty acids).
The glycerol and phosphate group together constitute the polar and
hydrophilic (or head) region of the molecule whereas the fatty acids make up the nonpolar and hydrophobic (or tail) region.
Thus, when in water, phospholipids tend to form a
phospholipid bilayer whereby the hydrophobic heads face outwards to interact with water molecules. Conversely, the hydrophobic tails face inwards towards other hydrophobic tails to avoid contact with water.

Proteins are the most diverse of the macromolecules, which include
enzymes,
transport proteins, large
signaling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
molecules,
antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
, and
structural proteins. The basic unit (or monomer) of a protein is an amino acid, which has a central carbon atom that is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, an
amino group, a
carboxyl group, and a
side chain (or R-group, "R" for residue).
There are twenty amino acids that make up the building blocks of proteins, with each amino acid having its own unique side chain.
The polarity and charge of the side chains affect the solubility of amino acids. An amino acid with a side chain that is polar and electrically charged is soluble as it is hydrophilic whereas an amino acid with a side chain that lacks a charged or an electronegative atom is hydrophobic and therefore tends to coalesce rather than dissolve in water.
Proteins have four distinct levels of organization (
primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
,
secondary
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature
* Secondary emission, of particles
** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products
* The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding i ...
,
tertiary, and
quartenary). The primary structure consists of a unique sequence of amino acids that are covalently linked together by
peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
s.
The side chains of the individual amino acids can then interact with each other, giving rise to the secondary structure of a protein.
The two common types of secondary structures are
alpha helices and
beta sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a g ...
s.
The folding of alpha helices and beta sheets gives a protein its three-dimensional or tertiary structure. Finally, multiple tertiary structures can combine to form the quaternary structure of a protein.
Nucleic acids are polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides.
Their function is to store, transmit, and express hereditary information.
Nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Ribonucleotides, which contain ribose as the sugar, are the monomers of
ribonucleic acid (RNA). In contrast, deoxyribonucleotides contain deoxyribose as the sugar and are constitute the monomers of
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). RNA and DNA also differ with respect to one of their bases.
There are two types of bases:
purines and
pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other ...
s.
The purines include
guanine (G) and
adenine (A) whereas the pyrimidines consist of
cytosine (C),
uracil (U), and
thymine (T). Uracil is used in RNA whereas thymine is used in DNA. Taken together, when the different sugar and bases are take into consideration, there are eight distinct nucleotides that can form two types of nucleic acids: DNA (A, G, C, and T) and RNA (A, G, C, and U).
Cells
Cell theory states that
cells are the fundamental units of life, that all living things are composed of one or more cells, and that all cells arise from preexisting cells through
cell division.
Most cells are very small, with diameters ranging from 1 to 100
micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* American spelling of micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; ...
s and are therefore only visible under a
light or
electron microscope. There are generally two types of cells:
eukaryotic cells, which contain a
nucleus, and
prokaryotic cells, which do not. Prokaryotes are
single-celled organisms such as
bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be single-celled or
multicellular. In
multicellular organisms, every cell in the organism's body is derived ultimately from a
single cell Single cell and similar can mean:
Biology
*Single-cell organism
*Single-cell protein
*Single-cell recording, a neuro-electric monitoring technique
*Single-cell sequencing
**Single cell epigenomics
*Single-cell transcriptomics
Other
* Single-cell th ...
in a fertilized
egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
.
Cell structure

Every cell is enclosed within a
cell membrane that separates its
cytoplasm from the
extracellular space.
A cell membrane consists of a
lipid bilayer, including
cholesterols that sit between
phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s to maintain their
fluidity at various temperatures. Cell membranes are
semipermeable
Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecul ...
, allowing small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water to pass through while restricting the movement of larger molecules and charged particles such as
ions.
Cell membranes also contains
membrane proteins, including
integral membrane proteins that go across the membrane serving as
membrane transporter
A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Transport proteins are integral transmembrane ...
s, and
peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer side of the cell membrane, acting as
enzymes shaping the cell.
Cell membranes are involved in various cellular processes such as
cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indir ...
,
storing electrical energy, and
cell signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures such as a
cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
,
glycocalyx, and
cytoskeleton.

Within the
cytoplasm of a cell, there are many
biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large ...
s such as
proteins and
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s.
[Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body](_blank)
in Chapter 21 of
Molecular Biology of the Cell
'' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science.
The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s. It is also common to describe small molecules such as amino acids as
molecular building blocks
". In addition to biomolecules, eukaryotic cells have specialized structures called
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s that have their own lipid bilayers or are spatially units.
These organelles include the
cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
, which contains most of the cell's DNA, or
mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, which generates
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to power cellular processes. Other organelles such as
endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
and
Golgi apparatus play a role in the synthesis and packaging of proteins, respectively. Biomolecules such as proteins can be engulfed by
lysosomes, another specialized organelle.
Plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
s have additional organelles that distinguish them from
animal cells such as a
cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
that provides support for the plant cell,
chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s that harvest sunlight energy to produce sugar, and
vacuoles that provide storage and structural support as well as being involved in reproduction and breakdown of plant seeds.
Eukaryotic cells also have cytoskeleton that is made up of
microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 an ...
s,
intermediate filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''.
Intermedia ...
s, and
microfilaments, all of which provide support for the cell and are involved in the movement of the cell and its organelles.
In terms of their structural composition, the microtubules are made up of
tubulin (e.g.,
α-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
and
β-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
whereas intermediate filaments are made up of fibrous proteins.
Microfilaments are made up of
actin molecules that interact with other strands of proteins.
Metabolism

All cells require
energy to sustain cellular processes. Energy is the capacity to do
work, which, in
thermodynamics, can be calculated using
Gibbs free energy. According to the
first law of thermodynamics, energy is
conserved, i.e., cannot be created or destroyed. Hence,
chemical reactions in a cell do not create new energy but are involved instead in the transformation and transfer of energy.
Nevertheless, all energy transfers lead to some loss of usable energy, which increases
entropy (or state of disorder) as stated by the
second law of thermodynamics. As a result, an organism requires continuous input of energy to maintain a low state of entropy. In cells, energy can be transferred as electrons during
redox (reduction–oxidation) reactions, stored in covalent bonds, and generated by the movement of ions (e.g., hydrogen, sodium, potassium) across a membrane.
Metabolism is the set of
life-sustaining
chemical reactions in
organisms. The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of food to
energy to run cellular processes; the conversion of food/fuel to building blocks for
proteins,
lipids,
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s, and some
carbohydrates; and the elimination of
metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, ...
s. These
enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as
catabolic—the breaking down of compounds (for example, the breaking down of glucose to pyruvate by
cellular respiration); or
anabolic—the building up (
synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organ ...
) of compounds (such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids). Usually, catabolism releases energy, and anabolism consumes energy.
The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into
metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, each step being facilitated by a specific
enzyme. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require
energy that will not occur by themselves, by
coupling them to
spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as
catalysts—they allow a reaction to proceed more rapidly without being consumed by it—by reducing the amount of
activation energy needed to convert
reactants into
products. Enzymes also allow the
regulation of the rate of a metabolic reaction, for example in response to changes in the
cell's environment or to
signals from other cells.
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is a set of
metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
reactions and processes that take place in the
cells of
organisms to convert
chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
from
nutrients into
adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are
catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are
redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a
combustion reaction
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combusti ...
, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a cell because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions.
Sugar in the form of
glucose is the main nutrient used by animal and plant cells in respiration. Cellular respiration involving oxygen is called aerobic respiration, which has four stages:
glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
,
citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle),
electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
, and
oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (UK , US ) or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine tri ...
.
Glycolysis is a metabolic process that occurs in the cytoplasm whereby glucose is converted into two
pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
s, with two net molecules of ATP being produced at the same time.
Each pyruvate is then oxidized into
acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
by the
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and t ...
, which also generates
NADH and carbon dioxide. Acetyl-Coa enters the citric acid cycle, which takes places inside the mitochondrial matrix. At the end of the cycle, the total yield from 1 glucose (or 2 pyruvates) is 6 NADH, 2 FADH
2, and 2 ATP molecules. Finally, the next stage is oxidative phosphorylation, which in eukaryotes, occurs in the
mitochondrial cristae. Oxidative phosphorylation comprises the
electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
, which is a series of four
protein complexes that transfer electrons from one complex to another, thereby releasing energy from NADH and FADH
2 that is coupled to the pumping of protons (hydrogen ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane (
chemiosmosis), which generates a
proton motive force.
Energy from the proton motive force drives the enzyme
ATP synthase
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation ...
to synthesize more ATPs by
phosphorylating
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, whi ...
ADP
Adp or ADP may refer to:
Aviation
* Aéroports de Paris, airport authority for the Parisian region in France
* Aeropuertos del Perú, airport operator for airports in northern Peru
* SLAF Anuradhapura, an airport in Sri Lanka
* Ampara Air ...
s. The transfer of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen being the final
electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
.
If oxygen were not present, pyruvate would not be metabolized by cellular respiration but undergoes a process of
fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
. The pyruvate is not transported into the mitochondrion but remains in the cytoplasm, where it is converted to
waste products that may be removed from the cell. This serves the purpose of oxidizing the electron carriers so that they can perform glycolysis again and removing the excess pyruvate. Fermentation oxidizes NADH to NAD
+ so it can be re-used in glycolysis. In the absence of oxygen, fermentation prevents the buildup of NADH in the cytoplasm and provides NAD
+ for glycolysis. This waste product varies depending on the organism. In skeletal muscles, the waste product is
lactic acid. This type of fermentation is called
lactic acid fermentation. In strenuous exercise, when energy demands exceed energy supply, the respiratory chain cannot process all of the hydrogen atoms joined by NADH. During anaerobic glycolysis, NAD
+ regenerates when pairs of hydrogen combine with pyruvate to form lactate. Lactate formation is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase in a reversible reaction. Lactate can also be used as an indirect precursor for liver glycogen. During recovery, when oxygen becomes available, NAD
+ attaches to hydrogen from lactate to form ATP. In yeast, the waste products are
ethanol and
carbon dioxide. This type of fermentation is known as alcoholic or
ethanol fermentation. The ATP generated in this process is made by
substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP by the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate directly to ADP or GDP. Transferring from a higher energy (whether phosphate group atta ...
, which does not require oxygen.
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to
convert light energy into
chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
that can later be released to fuel the organism's metabolic activities via
cellular respiration. This chemical energy is stored in
carbohydrate molecules, such as
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
s, which are synthesized from
carbon dioxide and
water.
In most cases,
oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most
plants,
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, and
cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
perform photosynthesis, which is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the
oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for
life on Earth.
Photosynthesis has four stages:
Light absorption, electron transport, ATP synthesis, and
carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
.
Light absorption is the initial step of photosynthesis whereby light energy is absorbed by
chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
pigments attached to proteins in the
thylakoid membranes. The absorbed light energy is used to remove electrons from a donor (water) to a primary electron acceptor, a
quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds uch as benzene or naphthalene
Uch ( pa, ;
ur, ), frequently referred to as Uch Sharīf ( pa, ;
ur, ; ''"Noble Uch"''), is a historic city in the southern part of Pakistan's Punjab province. Uch may have been founded as Alexandria on the Indus, a town founded by Alexand ...
by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double ...
designated as Q. In the second stage, electrons move from the quinone primary electron acceptor through a series of electron carriers until they reach a final electron acceptor, which is usually the oxidized form of NADP
+, which is
reduced to NADPH, a process that takes place in a protein complex called
photosystem I (PSI). The transport of electrons is coupled to the movement of protons (or hydrogen) from the stroma to the thylakoid membrane, which forms a pH gradient across the membrane as hydrogen becomes more concentrated in the lumen than in the stroma. This is analogous to the proton-motive force generated across the inner mitochondrial membrane in aerobic respiration.
During the third stage of photosynthesis, the movement of protons down their
concentration gradients from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma through the ATP synthase is coupled to the synthesis of ATP by that same ATP synthase.
The NADPH and ATPs generated by the
light-dependent reactions in the second and third stages, respectively, provide the energy and electrons to drive the synthesis of glucose by fixing atmospheric carbon dioxide into existing organic carbon compounds, such as
ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in a sequence of light-independent (or dark) reactions called the
Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
.
Cell signaling
Cell signaling (or communication) is the ability of
cells to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself.
Signals can be non-chemical such as light,
electrical impulses
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
, and heat, or chemical signals (or
ligands) that interact with
receptors, which can be found
embedded in the
cell membrane of another cell or
located deep inside a cell.
There are generally four types of chemical signals:
autocrine,
paracrine,
juxtacrine, and
hormones.
In autocrine signaling, the ligand affects the same cell that releases it.
Tumor cells, for example, can reproduce uncontrollably because they release signals that initiate their own self-division. In paracrine signaling, the ligand diffuses to nearby cells and affects them. For example, brain cells called
neurons release ligands called
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
s that diffuse across a
synaptic cleft to bind with a receptor on an adjacent cell such as another neuron or
muscle cell
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscl ...
. In juxtacrine signaling, there is direct contact between the signaling and responding cells. Finally, hormones are ligands that travel through the
circulatory systems of animals or
vascular systems of plants to reach their target cells. Once a ligand binds with a receptor, it can influence the behavior of another cell, depending on the type of receptor. For instance, neurotransmitters that bind with an
inotropic receptor can alter the
excitability of a target cell. Other types of receptors include
protein kinase receptors (e.g.,
receptor for the hormone
insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
) and
G protein-coupled receptors. Activation of G protein-coupled receptors can initiate
second messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first me ...
cascades. The process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a
series of molecular events is called
signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
Cell cycle

The cell cycle is a series of events that take place in a
cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the
duplication of its DNA and some of its
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s, and the subsequent partitioning of its cytoplasm into two daughter cells in a process called
cell division. In
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s (i.e.,
animal,
plant,
fungal, and
protist cells), there are two distinct types of cell division:
mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
and
meiosis.
Mitosis is part of the cell cycle, in which replicated
chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of
interphase (during which the DNA is replicated) and is often followed by
telophase and
cytokinesis; which divides the
cytoplasm,
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s and
cell membrane of one cell into two new
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis all together define the mitotic phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. The cell cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled
fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which
hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
,
skin,
blood cells, and some
internal organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the
interphase of a new cycle. In contrast to mitosis, meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells by undergoing one round of DNA replication followed by two divisions.
s are separated in the first division (
meiosis I), and sister chromatids are separated in the second division (
meiosis II). Both of these cell division cycles are used in the process of sexual reproduction at some point in their life cycle. Both are believed to be present in the last eukaryotic common ancestor.
Prokaryotes (i.e.,
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
and
bacteria) can also undergo cell division (or
binary fission). Unlike the processes of
mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
and
meiosis in eukaryotes, binary fission takes in prokaryotes takes place without the formation of a
spindle apparatus on the cell. Before binary fission, DNA in the bacterium is tightly coiled. After it has uncoiled and duplicated, it is pulled to the separate poles of the bacterium as it increases the size to prepare for splitting. Growth of a new cell wall begins to separate the bacterium (triggered by
FtsZ polymerization and "Z-ring" formation)
The new cell wall (
septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
* Interatri ...
) fully develops, resulting in the complete split of the bacterium. The new daughter cells have tightly coiled DNA rods,
ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
s, and
plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; how ...
s.
Genetics
Inheritance
 Genetics
Genetics is the scientific study of inheritance.
, specifically, is the process by which genes and traits are passed on from parents to offspring.
It was formulated by
Gregor Mendel, based on his work with pea plants in the mid-nineteenth century. Mendel established several principles of inheritance. The first is that genetic characteristics, which are now called
alleles, are discrete and have alternate forms (e.g., purple vs. white or tall vs. dwarf), each inherited from one of two parents. Based on his
law of dominance and uniformity, which states that some alleles are
dominant while others are
recessive; an organism with at least one dominant allele will display the
phenotype of that dominant allele.
[Rutgers]
Mendelian Principles
Exceptions to this rule include
penetrance and
expressivity.
Mendel noted that during gamete formation, the alleles for each gene segregate from each other so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene, which is stated by his
law of segregation.
Heterozygotic
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
individuals produce gametes with an equal frequency of two alleles. Finally, Mendel formulated the
law of independent assortment, which states that genes of different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes, i.e., genes are unlinked. An exception to this rule would include traits that are
sex-linked
Sex linked describes the sex-specific patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation ( allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome (autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked rece ...
.
Test crosses can be performed to experimentally determine the underlying
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
of an organism with a dominant phenotype.
A
Punnett square
The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach in 1905. The diagram is used by biologists to determine ...
can be used to predict the results of a test cross. The
chromosome theory of inheritance
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
, which states that genes are found on chromosomes, was supported by
Thomas Morgans's experiments with
fruit flies, which established the
sex linkage between eye color and
sex in these insects.
In humans and other mammals (e.g., dogs), it is not feasible or practical to conduct test cross experiments. Instead,
pedigree
Pedigree may refer to:
Breeding
* Pedigree chart, a document to record ancestry, used by genealogists in study of human family lines, and in selective breeding of other animals
** Pedigree, a human genealogy (ancestry chart)
** Pedigree (animal ...
s, which are genetic representations of family trees,
are used instead to trace the inheritance of a specific trait or disease through multiple generations.
DNA

A gene is a unit of
heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
that corresponds to a region of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that carries genetic information that influences the form or function of an organism in specific ways. DNA is a
molecule composed of two
polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a
double helix, which was first described by
James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
and
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
in 1953.
It is found as linear
chromosomes in
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s, and circular chromosomes in
prokaryotes. A chromosome is an organized structure consisting of DNA and
histones. The set of chromosomes in a cell and any other hereditary information found in the
mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
,
chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s, or other locations is collectively known as a cell's
genome. In eukaryotes, genomic DNA is localized in the
cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
, or with small amounts in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
In prokaryotes, the DNA is held within an irregularly shaped body in the cytoplasm called the
nucleoid
The nucleoid (meaning ''nucleus-like'') is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dim ...
. The genetic information in a genome is held within genes, and the complete assemblage of this information in an organism is called its
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
. Genes encode the information needed by cells for the synthesis of proteins, which in turn play a central role in influencing the final
phenotype of the organism.
The two polynucleotide strands that make up DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are thus
antiparallel. Each strand is composed of
nucleotides, with each nucleotide containing one of four nitrogenous
bases (
cytosine guanine adenine or
thymine , a
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
called
deoxyribose, and a
phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
s between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating
sugar-phosphate backbone. It is the
sequence of these four bases along the backbone that encodes genetic information. Bases of the two polynucleotide strands are bound together by
hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s, according to
base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
ing rules (A with T and C with G), to make double-stranded DNA. The bases are divided into two groups:
pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other ...
s and
purines. In DNA, the pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine whereas the purines are adenine and guanine.
There are
grooves
Groove or Grooves may refer to:
Music
* Groove (music)
* Groove (drumming)
* The Groove (band), an Australian rock/pop band of the 1960s
* The Groove (Sirius XM), a US radio station
* Groove 101.7FM, a former Perth, Australia, radio station
* ...
that run along the entire length of the double helix due to the uneven spacing of the DNA strands relative to each other.
Both grooves differ in size, with the major groove being larger and therefore more accessible to the binding of proteins than the minor groove.
The outer edges of the bases are exposed to these grooves and are therefore accessible for additional hydrogen bonding.
Because each groove can have two possible base-pair configurations (G-C and A-T), there are four possible base-pair configurations within the entire double helix, each of which is chemically distinct from another.
As a result, protein molecules are able to recognize and bind to specific base-pair sequences, which is the basis of specific DNA-protein interactions.
DNA replication is a
semiconservative
Semiconservative replication describe the mechanism of DNA replication in all known cells. DNA replication occurs on multiple origins of replication along the DNA template strand (antinsense strand). As the DNA double helix is unwound by helicase, ...
process whereby each strand serves as a template for a new strand of DNA.
The process begins with the unwounding of the double helix at an
origin of replication, which separates the two strands, thereby making them available as two templates. This is then followed by the binding of the enzyme
primase to the template to synthesize a starter RNA (or DNA in some viruses) strand called a
primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a t ...
from the 5' to 3' location.
Once the primer is completed, the primase is released from the template, followed by the binding of the enzyme
DNA polymerase to the same template to synthesize new DNA. The rate of DNA replication in a living cell was measured as 749 nucleotides added per second under ideal conditions.
DNA replication is not perfect as the DNA polymerase sometimes insert bases that are not complementary to the template (e.g., putting in A in the strand opposite to G in the template strand).
In eukaryotes, the initial error or
mutation rate is about 1 in 100,000.
Proofreading
Proofreading is the reading of a galley proof or an electronic copy of a publication to find and correct reproduction errors of text or art. Proofreading is the final step in the editorial cycle before publication.
Professional
Traditional ...
and
mismatch repair are the two mechanisms that repair these errors, which reduces the mutation rate to 10
−10, particularly before and after a cell cycle.
Mutations are heritable changes in DNA.
They can arise Mutation#Spontaneous mutation, spontaneously as a result of replication errors that were not corrected by proofreading or can be Mutation#Induced mutation, induced by an environmental mutagen such as a chemical (e.g., nitrous acid, benzopyrene) or radiation (e.g., x-ray, gamma ray, Ultraviolet, ultraviolet radiation, particles emitted by unstable isotopes).
Mutations can appear as a change in single base or at a larger scale involving chromosomal mutations such as Deletion (genetics), deletions, Chromosomal inversion, inversions, or Chromosomal translocation, translocations.
In multicellular organisms, mutations can occur in Somatic cell, somatic or germline cells.
In somatic cells, the mutations are passed on to daughter cells during mitosis.
In a germline cell such as a sperm or an egg, the mutation will appear in an organism at fertilization.
Mutations can lead to several types of phenotypic effects such as silent, loss-of-function, Gain-of-function research, gain-of-function, and conditional mutations.
Some mutations can be beneficial, as they are a source of genetic variation for evolution.
Others can be harmful if they were to result in a loss of function of genes needed for survival.
Mutagens such as carcinogens are typically avoided as a matter of health policy, public health policy goals.
One example is the banning of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) by the Montreal Protocol, as CFCs tend to deplete the ozone layer, resulting in more ultraviolet radiation from the sun passing through the Earth's upper atmosphere, thereby causing somatic mutations that can lead to skin cancer.
Similarly, smoking bans have been enforced throughout the world in an effort to reduce the incidence of lung cancer.
Gene expression

Gene expression is the molecular process by which a
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
gives rise to a
phenotype, i.e., observable trait. The genetic information stored in
DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the synthesis of proteins that control an organism's structure and development, or that act as
enzymes catalyzing specific metabolic pathways. This process is summarized by the central dogma of molecular biology, which was formulated by
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
in 1958. According to the Central Dogma, genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. Hence, there are two gene expression processes: transcription (genetics), transcription (DNA to RNA) and translation (genetics), translation (RNA to protein).
These processes are used by all life—eukaryotes (including
multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (
bacteria and
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
), and are exploited by viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life.
During transcription, messenger RNA (mRNA) strands are created using DNA strands as a template, which is initiated when RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence called a Promoter (genetics), promoter, which instructs the RNA to begin transcription of one of the two DNA strands.
The DNA bases are exchanged for their corresponding bases except in the case of thymine (T), for which RNA substitutes
uracil (U). In eukaryotes, a large part of DNA (e.g., >98% in humans) contain non-coding DNA, non-coding called introns, which do not serve as patterns for Primary protein structure, protein sequences. The coding regions or exons are interspersed along with the introns in the primary transcript (or pre-mRNA).
Before translation, the pre-mRNA undergoes further processing whereby the introns are removed (or spliced out), leaving only the spliced exons in the mature mRNA strand.
The translation of mRNA to protein occurs in
ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
s, whereby the transcribed mRNA strand specifies the sequence of
amino acids within proteins using the
genetic code. Gene products are often
proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA.
Gene regulation

The regulation of gene expression (or gene regulation) by environmental factors and during different stages of Developmental biology, development can occur at each step of the process such as Transcription (biology), transcription, RNA splicing, Translation (biology), translation, and post-translational modification of a protein.
The ability of gene transcription to be regulated allows for the conservation of energy as cells will only make proteins when needed.
Gene expression can be influenced by positive or negative regulation, depending on which of the two types of regulatory proteins called transcription factors bind to the DNA sequence close to or at a promoter.
A cluster of genes that share the same promoter is called an operon, found mainly in prokaryotes and some lower eukaryotes (e.g., ''Caenorhabditis elegans'').
It was first identified in ''Escherichia coli''—a prokaryotic cell that can be found in the intestines of humans and other animals—in the 1960s by François Jacob and Jacques Monod.
They studied the prokaryotic cell's lac operon, ''lac'' operon, which is part of three genes (''lacZ'', ''lacY'', and ''lacA'') that encode three lactose-metabolizing enzymes (Beta-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, Beta-galactoside permease, β-galactoside permease, and Galactoside acetyltransferase, β-galactoside transacetylase).
In positive regulation of gene expression, the Activator (genetics), activator is the transcription factor that stimulates transcription when it binds to the sequence near or at the promoter. In contrast, negative regulation occurs when another transcription factor called a repressor binds to a DNA sequence called an Operon#Operator, operator, which is part of an operon, to prevent transcription. When a repressor binds to a repressible operon (e.g., trp operon, ''trp'' operon), it does so only in the presence of a corepressor. Repressors can be inhibited by compounds called inducers (e.g., allolactose), which exert their effects by binding to a repressor to prevent it from binding to an operator, thereby allowing transcription to occur.
Specific genes that can be activated by inducers are called Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, inducible genes (e.g., ''lacZ'' or ''lacA'' in ''E. coli''), which are in contrast to Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, constitutive genes that are almost always active.
In contrast to both, structural genes encode proteins that are not involved in gene regulation.
In prokaryotic cells, transcription is regulated by proteins called sigma factors, which bind to RNA polymerase and direct it to specific promoters.
Similarly, transcription factors in eukaryotic cells can also coordinate the expression of a group of genes, even if the genes themselves are located on different chromosomes.
Coordination of these genes can occur as long as they share the same regulatory DNA sequence that bind to the same transcription factors.
Promoters in eukaryotic cells are more diverse but tend to contain a core sequence that RNA polymerase can bind to, with the most common sequence being the TATA box, which contains multiple repeating A and T bases.
Specifically, RNA polymerase II is the RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter to initiate transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes, but only in the presence of multiple general transcription factors, which are distinct from the transcription factors that have regulatory effects, i.e., activators and repressors.
In eukaryotic cells, DNA sequences that bind with activators are called enhances whereas those sequences that bind with repressors are called silencers.
Transcription factors such as NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) are able to identify specific nucleotide sequence based on the base sequence (e.g., CGAGGAAAATTG for NFAT) of the binding site, which determines the arrangement of the chemical groups within that sequence that allows for specific DNA-protein interactions.
The expression of transcription factors is what underlies cellular differentiation in a developing
embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
.
In addition to regulatory events involving the promoter, gene expression can also be regulated by Epigenetics, epigenetic changes to chromatin, which is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells.
Post-transcriptional control of mRNA can involve the alternative splicing of primary transcript, primary mRNA transcripts, resulting in a single gene giving rise to different mature mRNAs that encode a family of different proteins.
A well-studied example is the ''Sxl'' gene in ''Drosophila'', which determines the
sex in these animals. The gene itself contains four exons and alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA transcript can generate two active forms of the Sxl protein in female flies and one in inactive form of the protein in males.
Another example is the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which has a single pre-mRNA transcript that can generate up to nine proteins as a result of alternative splicing.
In humans, eighty percent of all 21,000 genes are alternatively spliced.
Given that both chimpanzees and humans have a similar number of genes, it is thought that alternative splicing might have contributed to the latter's complexity due to the greater number of alternative splicing in the human brain than in the brain of chimpanzees.
Translation can be regulated in three known ways, one of which involves the binding of tiny RNA molecules called microRNA (miRNA) to a target mRNA transcript, which inhibits its translation and causes it to degrade.
Translation can also be inhibited by the modification of the 5' cap by substituting the modified guanosine triphosphate (GTP) at the 5' end of an mRNA for an unmodified GTP molecule.
Finally, translational repressor proteins can bind to mRNAs and prevent them from attaching to a ribosome, thereby blocking translation.
Once translated, the stability of proteins can be regulated by being targeted for degradation.
A common example is when an enzyme attaches a regulatory protein called ubiquitin to the lysine Amino acid, residue of a targeted protein.
Other ubiquitins then attached to the primary ubiquitin to form a polyubiquitinated protein, which then enters a much larger protein complex called proteasome.
Once the polyubiquitinated protein enters the proteasome, the polyubiquitin detaches from the target protein, which is unfolded by the proteasome in an ATP-dependent manner, allowing it to be hydrolyzed by three proteases.
Genomes

A
genome is an organism's complete set of
DNA, including all of its genes. Sequencing and analysis of genomes can be done using high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes.
The genomes of prokaryotes are small, compact, and diverse. In contrast, the genomes of eukaryotes are larger and more complex such as having more regulatory sequences and much of its genome are made up of non-coding DNA sequences for functional RNA (Ribosomal RNA, rRNA, Transfer RNA, tRNA, and Messenger RNA, mRNA) or regulatory sequences. The genomes of various model organisms such as arabidopsis, Drosophila melanogaster, fruit fly, mice, Caenorhabditis elegans, nematodes, and yeast have been sequenced. The
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
was a major undertaking by the international scientific community to sequence the entire human genome, which was completed in 2003.
The sequencing of the human genome has yielded practical applications such as DNA fingerprinting, which can be used for DNA paternity testing, paternity testing and forensics. In
medicine, sequencing of the entire human genome has allowed for the identification of mutations that cause neoplasm, tumors as well as genes that cause a specific genetic disorder.
The sequencing of genomes from various organisms has led to the emergence of comparative genomics, which aims to draw comparisons of genes from the genomes of those different organisms.
Many genes encode more than one protein, with posttranslational modifications increasing the diversity of proteins within a cell. An organism's proteome is its entire set of proteins expressed by its genome and proteomics seeks to study the complete set of proteins produced by an organism.
Because many proteins are enzymes, their activities tend to affects the concentrations of substrates and products. Thus, as the proteome changes, so do the amount of small molecules or metabolites.
The complete set of small molecules in a cell or organism is called a metabolome and metabolomics is the study of the metabolome in relation to the physiological activity of a cell or organism.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the use of cells or organisms to develop products for humans.
One commonly used technology with wide applications is the creation of recombinant DNA, which is a DNA molecule assembled from two or more sources in a laboratory. Before the advent of polymerase chain reaction, biologists would manipulate DNA by cutting it into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes. They would then purify and analyze the fragments using gel electrophoresis and then later recombine the fragments into a novel DNA sequence using DNA ligase.
The recombinant DNA is then molecular cloning, cloned by inserting it into a host cell, a process known as Transformation (genetics), transformation if the host cells were bacteria such as ''Escherichia coli, E. coli'', or transfection if the host cells were eukaryotic cells like yeast, plant, or animal cells. Once the host cell or organism has received and integrated the recombinant DNA, it is described as transgene, transgenic.
A recombinant DNA can be inserted in one of two ways. A common method is to insert the DNA into a host chromosome, with the site of insertion being random.
Another approach would be to insert the recombinant DNA as part of another DNA sequence called a Vector (molecular biology), vector, which then integrates into the host chromosome or has its own origin of DNA replication, thereby allowing to replicate independently of the host chromosome.
Plasmids from bacterial cells such as ''E. coli'' are typically used as vectors due to their relatively small size (e.g. 2000–6000 base pairs in ''E. coli''), presence of restriction enzymes, genes that are resistant to antibiotics, and the presence of an origin of replication.
A gene coding for a selectable marker such as antibiotic resistance is also incorporated into the vector.
Inclusion of this market allows for the selection of only those host cells that contained the recombinant DNA while discarding those that do not.
Moreover, the marker also serves as a reporter gene that once expressed, can be easily detected and measured.
Once the recombinant DNA is inside individual bacterial cells, those cells are then Culture plate, plated and allowed to grow into a Colony (biology), colony that contains millions of transgenic cells that carry the same recombinant DNA.
These transgenic cells then produce large quantities of the transgene product such as human
insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
, which was the first medicine to be made using recombinant DNA technology.
One of the goals of molecular cloning is to identify the function of specific DNA sequences and the proteins they encode.
For a specific DNA sequence to be studied and manipulated, millions of copies of DNA fragments containing that DNA sequence need to be made.
This involves breaking down an intact genome, which is much too large to be introduced into a host cell, into smaller DNA fragments. Although no longer intact, the collection of these DNA fragments still make up an organism's genome, with the collection itself being referred to as a genomic library, due to the ability to search and retrieve specific DNA fragments for further study, analogous to the process of retrieving a book from a regular library.
DNA fragments can be obtained using restriction enzymes and other processes such as DNA fragmentation, mechanical shearing. Each obtained fragment is then inserted into a vector that is taken up by a bacterial host cell. The host cell is then allowed to proliferate on a selective Growth medium, medium (e.g., antibiotic resistance), which produces a colony of these recombinant cells, each of which contains many copies of the same DNA fragment.
These colonies can be grown by spreading them over a solid medium in Petri dishes, which are Incubator (culture), incubated at a suitable temperature. One dish alone can hold thousands of bacterial colonies, which can be easily screened for a specific DNA sequence.
The sequence can be identified by first duplicating a Petri dish with bacterial colonies and then exposing the DNA of the duplicated colonies for Nucleic acid hybridization, hybridization, which involves labeling them with complementary Isotopic labeling, radioactive or Fluorophore, fluorescent nucleotides.
Smaller DNA libraries that contain genes from a specific tissue can be created using complementary DNA (cDNA).
The collection of these cDNAs from a specific tissue at a particular time is called a cDNA library, which provides a "snapshot" of transcription patterns of cells at a specific location and time.
Other biotechnology tools include DNA microarrays, expression vectors, synthetic genomics, and CRISPR gene editing.
Other approaches such as Pharming (genetics), pharming can produce large quantities of medically useful products through the use of genetically modified organisms.
Many of these other tools also have wide applications such as creating medically useful proteins, or improving Plant#Cultivation, plant cultivation and animal husbandry.
Genes, development, and evolution

Developmental biology, Development is the process by which a multicellular organism (
plant or
animal) goes through a series of a changes, starting from a single cell, and taking on various forms that are characteristic of its life cycle.
There are four key processes that underlie development: Cell fate determination, Determination, Cellular differentiation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and growth. Determination sets the developmental fate of a cell, which becomes more restrictive during development. Differentiation is the process by which specialized cells from less specialized cells such as stem cells. Stem cells are Cellular differentiation, undifferentiated or partially differentiated
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
that can differentiate into various types of cells and Cell proliferation, proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell.
Cellular differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolism, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals, which are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the
DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same
genome. Morphogenesis, or the development of body form, is the result of spatial differences in gene expression.
Specially, the organization of differentiated tissues into specific structures such as arms or wings, which is known as Pattern formation#Biology, pattern formation, is governed by morphogens, signaling molecules that move from one group of cells to surrounding cells, creating a morphogen gradient as described by the French flag model. Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, also occurs during morphogenesis, such as the death of cells between digits in human embryonic development, which frees up individual fingers and toes. Expression of transcription factor genes can determine organ placement in a plant and a cascade of transcription factors themselves can establish body segmentation in a fruit fly.
A small fraction of the genes in an organism's genome called the Evo-devo gene toolkit, developmental-genetic toolkit control the development of that organism. These toolkit genes are highly conserved among Phylum, phyla, meaning that they are ancient and very similar in widely separated groups of animals. Differences in deployment of toolkit genes affect the body plan and the number, identity, and pattern of body parts. Among the most important toolkit genes are the Hox gene, ''Hox'' genes. Hox genes determine where repeating parts, such as the many vertebrae of snakes, will grow in a developing embryo or larva.
Variations in the toolkit may have produced a large part of the morphological evolution of animals. The toolkit can drive evolution in two ways. A toolkit gene can be expressed in a different pattern, as when the beak of Darwin's large ground-finch was enlarged by the ''Bone morphogenetic protein, BMP'' gene, or when snakes lost their legs as ''DLX gene family, Distal-less (Dlx)'' genes became under-expressed or not expressed at all in the places where other reptiles continued to form their limbs. Or, a toolkit gene can acquire a new function, as seen in the many functions of that same gene, ''distal-less'', which controls such diverse structures as the mandible in vertebrates,
legs and antennae in the fruit fly, and eyespot (mimicry), eyespot pattern in butterfly wings. Given that small changes in toolbox genes can cause significant changes in body structures, they have often enabled Convergent evolution, convergent or parallel evolution.
Evolution
Evolutionary processes

A central organizing concept in biology is that life changes and develops through
evolution, which is the change in Heredity, heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of
populations over successive generations. Evolution is now used to explain the great variations of life on Earth. The term ''evolution'' was introduced into the scientific lexicon by Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck in 1809.
He proposed that evolution occurred as a result of Lamarckism, inheritance of acquired characteristics, which was unconvincing but there were no alternative explanations at the time.
, an English naturalist, had returned to England in 1836 from his second voyage of HMS Beagle, five-year travels on the HMS Beagle where he studied rocks and collected plants and animals from various parts of the world such as the Galápagos Islands.
He had also read ''Principles of Geology'' by Charles Lyell and ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'' by Thomas Robert Malthus, Thomas Malthus and was influenced by them.
Based on his observations and readings, Darwin began to formulate his Natural selection, theory of evolution by natural selection to explain the diversity of plants and animals in different parts of the world.
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
, another English naturalist who had studied plants and animals in the Malay Archipelago, also came to the same idea, but later and independently of Darwin.
Both Darwin and Wallace jointly presented their essay and manuscript, respectively, at the Linnaean Society of London in 1858, giving them both credit for their discovery of evolution by natural selection.
Darwin would later publish his book ''On the Origin of Species'' in 1859, which explained in detail how the process of evolution by natural selection works.
To explain natural selection, Darwin drew an analogy with humans modifying animals through artificial selection, whereby animals were selectively bred for specific Phenotypic trait, traits, which has given rise to individuals that no longer resemble their wild ancestors.
Darwin argued that in the natural world, it was nature that played the role of humans in selecting for specific traits. He came to this conclusion based on two observations and two inferences.
First, members of any population tend to vary with respect to their heredity, heritable traits. Second, all species tend to produce more offspring than can be supported by their respective environments, resulting in many individuals not surviving and reproducing.
Based on these observations, Darwin inferred that those individuals who possessed heritable traits that are better adapted to their environments are more likely to survive and produce more offspring than other individuals.
He further inferred that the unequal or differential survival and reproduction of certain individuals over others will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits over successive generations, thereby increasing the match between the organisms and their environment.
Thus, taken together, natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals in subsequent generations due to differences in or more heritable traits.
Darwin was not aware of Mendel's work of inheritance and so the exact mechanism of inheritance that underlie natural selection was not well-understood
until the early 20th century when the
modern synthesis reconciled Darwinism, Darwinian evolution with
classical genetics, which established a Neo-Darwinism, neo-Darwinian perspective of evolution by natural selection.
This perspective holds that evolution occurs when there are changes in the allele frequency, allele frequencies within a population of interbreeding organisms. In the absence of any evolutionary process acting on a large random mating population, the allele frequencies will remain constant across generations as described by the Hardy–Weinberg principle.
Another process that drives evolution is genetic drift, which is the random fluctuations of allele frequencies within a population from one generation to the next.
When selective forces are absent or relatively weak, allele frequencies are equally likely to ''drift'' upward or downward at each successive generation because the alleles are subject to sampling error.
This drift halts when an allele eventually becomes fixed, either by disappearing from the population or replacing the other alleles entirely. Genetic drift may therefore eliminate some alleles from a population due to chance alone.
Speciation

A species is a group of organisms that mate with one another and speciation is the process by which one lineage splits into two lineages as a result of having evolved independently from each other.
For speciation to occur, there has to be reproductive isolation.
Reproductive isolation can result from incompatibilities between genes as described by Bateson–Dobzhansky–Muller model. Reproductive isolation also tends to increase with genetic divergence. Speciation can occur when there are physical barriers that divide an ancestral species, a process known as allopatric speciation.
In contrast, sympatric speciation occurs in the absence of physical barriers.
Reproductive isolation#Pre-zygotic isolation, Pre-zygotic isolation such as Reproductive isolation#Mechanical isolation, mechanical, Reproductive isolation#Mechanical isolation, temporal, Reproductive isolation#Behavioral isolation, behavioral, habitat, and Reproductive isolation#Gametic isolation, gametic isolations can prevent different species from Hybrid (biology), hybridizing.
Similarly, Reproductive isolation#Post-zygotic isolation, post-zygotic isolations can result in hybridization being selected against due to the lower viability of hybrids or hybrid infertility (e.g., mule). Hybrid zones can emerge if there were to be incomplete reproductive isolation between two closely related species.
Phylogeny
A phylogeny is an evolutionary history of a specific group of organisms or their genes.
It can be represented using a phylogenetic tree, which is a diagram showing lines of descent among organisms or their genes. Each line drawn on the time axis of a tree represents a Lineage (evolution), lineage of descendants of a particular species or population. When a lineage divides into two, it is represented as a node (or split) on the phylogenetic tree. The more splits there are over time, the more branches there will be on the tree, with the common ancestor of all the organisms in that tree being represented by the root of that tree. Phylogenetic trees may portray the evolutionary history of all life forms, a major evolutionary group (e.g., insects), or an even smaller group of closely related species. Within a tree, any group of species designated by a name is a taxon (e.g., humans, primates, mammals, or vertebrates) and a taxon that consists of all its evolutionary descendants is a clade, otherwise known as a monophyletic taxon.
Closely related species are referred to as Sister group, sister species and closely related clades are sister clades. In contrast to a monophyletic group, a polyphyly, polyphyletic group does not include its common ancestor whereas a paraphyly, paraphyletic group does not include all the descendants of a common ancestor.
Phylogenetic trees are the basis for comparing and grouping different species.
Different species that share a feature inherited from a common ancestor are described as having Homology (biology), homologous features (or Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphy).
[)] Homologous features may be any Heredity, heritable Phenotypic trait, traits such as Nucleic acid sequence, DNA sequence, protein structures, anatomical features, and behavior patterns. A vertebral column is an example of a homologous feature shared by all vertebrate animals. Traits that have a similar form or function but were not derived from a common ancestor are described as analogous structures, analogous features. Phylogenies can be reconstructed for a group of organisms of primary interests, which are called the ingroup. A species or group that is closely related to the ingroup but is phylogenetically outside of it is called the Outgroup (cladistics), outgroup, which serves a reference point in the tree. The root of the tree is located between the ingroup and the outgroup.
When phylogenetic trees are reconstructed, multiple trees with different evolutionary histories can be generated. Based on the principle of Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics), Parsimony (or Occam's razor), the tree that is favored is the one with the fewest evolutionary changes needed to be assumed over all traits in all groups. Computational phylogenetics, Computational algorithms can be used to determine how a tree might have evolved given the evidence.
Phylogeny provides the basis of biological classification, which is based on Linnaean taxonomy that was developed by
Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century.
This classification system is rank-based, with the highest rank being the Domain (biology), domain followed by Kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum, Class (biology), class, Order (biology), order, Family (biology), family, genus, and species.
All organisms can be classified as belonging to one of three-domain system, three domains: Archaea (originally Archaebacteria);
bacteria (originally eubacteria), or Eukaryote, eukarya (includes the
protist,
fungi,
plant, and
animal kingdoms).
A binomial nomenclature is used to classify different species. Based on this system, each species is given two names, one for its genus and another for its species.
For example, humans are ''Homo sapiens'', with ''Homo'' being the genus and ''sapiens'' being the species. By convention, the scientific names of organisms are italicized, with only the first letter of the genus capitalized.
History of life
The history of life on
Earth traces the processes by which
organisms have evolved from the earliest emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago and all life on
Earth, both living and extinct, descended from a last universal common ancestor that lived about Timeline of evolution, 3.5 billion years ago.
The dating of the Earth's history can be done using several geological methods such as stratigraphy, radiometric dating, and Geochronology#Paleomagnetic dating, paleomagnetic dating.
Based on these methods, geologists have developed a geologic time scale that divides the history of the Earth into major divisions, starting with four eons (Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic), the first three of which are collectively known as the Precambrian, which lasted approximately 4 billion years.
Each eon can be divided into eras, with the Phanerozoic eon that began 539 million years ago being subdivided into Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras.
These three eras together comprise eleven Geologic time scale#Terminology, periods (Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, Permian, Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous, Tertiary, and Quaternary) and each period into epochs.
The similarities among all known present-day species indicate that they have diverged through the process of
evolution from their common ancestor. Biologists regard the ubiquity of the
genetic code as evidence of universal
common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
for all
bacteria,
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, and
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s.
Microbial mat, Microbal mats of coexisting bacteria and archaea were the dominant form of life in the early Archean epoch and many of the major steps in early evolution are thought to have taken place in this environment.
The earliest evidence of
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s dates from 1.85 billion years ago,
and while they may have been present earlier, their diversification accelerated when they started using oxygen in their metabolism. Later, around 1.7 billion years ago, multicellular organisms began to appear, with Cellular differentiation, differentiated cells performing specialised functions.
Algae-like multicellular land plants are dated back even to about 1 billion years ago, although evidence suggests that microorganisms formed the earliest terrestrial ecosystems, at least 2.7 billion years ago. Microorganisms are thought to have paved the way for the inception of land plants in the Ordovician period. Land plants were so successful that they are thought to have contributed to the Late Devonian extinction, Late Devonian extinction event.
Ediacara biota appear during the Ediacaran period, while vertebrates, along with most other modern phylum, phyla originated about 525 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion.
During the Permian period, synapsids, including the ancestors of mammals, dominated the land, but most of this group became extinct in the Permian–Triassic extinction event 252 million years ago. During the recovery from this catastrophe, archosaurs became the most abundant land vertebrates;
one archosaur group, the dinosaurs, dominated the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. After the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago killed off the non-avian dinosaurs, mammals Adaptive radiation, increased rapidly in size and diversity. Such Extinction event, mass extinctions may have accelerated evolution by providing opportunities for new groups of organisms to diversify.
Diversity
Bacteria and Archaea

Bacteria are a type of
cell that constitute a large domain (biology), domain of
prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few
micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* American spelling of micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; ...
s in length, bacteria have a Bacterial cell structure#Cell morphology, number of shapes, ranging from coccus, spheres to bacillus (shape), rods and spiral bacteria, spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on
Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of the earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. Most bacteria have not been characterised, and only about 27 percent of the bacterial phyla have species that can be microbiological culture, grown in the laboratory.
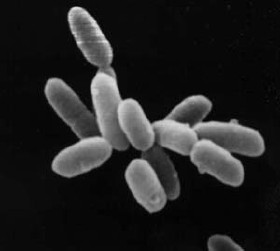
Archaea constitute the other domain of prokaryotic cells and were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as
bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), a term that has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other three-domain system, two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat and square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this Morphology (biology), morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess
genes and several
metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the
enzymes involved in transcription (genetics), transcription and translation (biology), translation. Other aspects of archaeal biochemistry are unique, such as their reliance on ether lipids in their
cell membranes, including archaeols. Archaea use more energy sources than eukaryotes: these range from organic compounds, such as sugars, to ammonia, ion, metal ions or even hydrogen, hydrogen gas. Halophile, Salt-tolerant archaea (the Haloarchaea) use sunlight as an energy source, and other species of archaea carbon fixation, fix carbon, but unlike plants and
cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, no known species of archaea does both. Archaea asexual reproduction, reproduce asexually by
binary fission, Fragmentation (reproduction), fragmentation, or budding; unlike bacteria, no known species of Archaea form endospores.
The first observed archaea were extremophiles, living in extreme environments, such as hot springs and salt lakes with no other organisms. Improved molecular detection tools led to the discovery of archaea in almost every habitat, including soil, oceans, and marshlands. Archaea are particularly numerous in the oceans, and the archaea in plankton may be one of the most abundant groups of organisms on the planet.
Archaea are a major part of Life, Earth's life. They are part of the microbiota of all organisms. In the human microbiome, they are important in the Colon (anatomy), gut, mouth, and on the skin.
Their morphological, metabolic, and geographical diversity permits them to play multiple ecological roles: carbon fixation; nitrogen cycling; organic compound turnover; and maintaining microbial symbiotic and Syntrophy, syntrophic communities, for example.
Protists

Eukaryotes are hypothesized to have split from archaea, which was followed by their Endosymbiont, endosymbioses with bacteria (or symbiogenesis) that gave rise to mitochondria and chloroplasts, both of which are now part of modern-day eukaryotic cells.
The major lineages of eukaryotes diversified in the Precambrian about 1.5 billion years ago and can be classified into eight major clades: alveolates, Excavata, excavates, stramenopiles,
plants, rhizarians, amoebozoans, fungus, fungi, and
animals.
Five of these clades are collectively known as
protists, which are mostly microscopic
eukaryotic organisms that are not plants, fungi, or animals.
While it is likely that protists share a Common descent, common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor),
protists by themselves do not constitute a separate clade as some protists may be more closely related to plants, fungi, or animals than they are to other protists. Like groupings such as
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, invertebrates, or protozoans, the protist grouping is not a formal taxonomic group but is used for convenience.
Most protists are unicellular, which are also known as microbial eukaryotes.
The alveolates are mostly photosynthetic unicellular protists that possess sacs called alveoli (hence their name alveolates) that are located beneath their cell membrane, providing support for the cell surface.
Alveolates comprise several groups such as dinoflagellates, apicomplexans, and ciliates. Dinoflagellates are photosynthetic and can be found in the ocean where they play a role as Autotroph, primary producers of organic matter.
Apicomplexans are parasitic alveolates that possess an apical complex, which is a group of organelles located in the apical end of the cell.
This complex allows apicomplexans to invade their hosts' tissues. Ciliates are alveolates that possess numerous hair-like structure called cilia. A defining characteristic of ciliates is the presence of two types of nuclei in each ciliate cell. A commonly studied ciliate is the ''paramecium''.
The excavates are groups of protists that began to diversify approximately 1.5 billion years ago shortly after the origin of the eukaryotes.
Some excavates do not possess mitochondria, which are thought to have been lost over the course of evolution as these protists still possess nuclear genes that are associated with mitochondria.
The excavates comprise several groups such as diplomonads, parabasalids, Percolozoa, heteroloboseans, euglenids, and Kinetoplastida, kinetoplastids.
Stramenopiles, most of which can be characterized by the presence of tubular hairs on the longer of their two flagella, include diatoms and brown algae.
Diatoms are primary producers and contribute about one-fifth of all photosynthetic
carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
, making them a major component of phytoplankton.
Rhizarians are mostly unicellular and aquatic protists that typically contain long, thin Pseudopodia, pseudopods.
The rhizarians comprise three main groups: cercozoans, foraminiferans, and radiolarians.
Amoebozoans are protists with a body form characterized by the presence lobe-shaped pseudopods, which help them to move.
They include groups such as lobosa, loboseans and slime molds (e.g., Myxogastria, plasmodial slime mold and cellular slime molds).
Plant diversity

Plants are mainly multicellular organisms, predominantly photosynthetic
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae, which would exclude
fungi and some
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
. A shared derived trait (or Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphy) of Plantae is the primary endosymbiosis of a cyanobacterium into an early eukaryote about one billion years ago, which gave rise to chloroplasts.
The first several clades that emerged following primary endosymbiosis were aquatic and most of the aquatic photosynthesis, photosynthetic
eukaryotic organisms are collectively described as algae, which is a term of convenience as not all algae are closely related.
Algae comprise several distinct clades such as glaucophytes, which are microscopic freshwater algae that may have resembled in form to the early unicellular ancestor of Plantae.
Unlike glaucophytes, the other algal clades such as Red algae, red and green algae are multicellular. Green algae comprise three major clades: chlorophytes, Coleochaetophyceae, coleochaetophytes, and stoneworts.
Land plants (embryophytes) first appeared in terrestrial environments approximately 450 to 500 million years ago.
A synapomorphy of land plants is an embryo that develops under the protection of tissues of its parent plant.
Land plants comprise ten major clades, seven of which constitute a single clade known as vascular plants (or tracheophytes) as they all have tracheids, which are fluid-conducting cells, and a well-developed system that transports materials throughout their bodies.
In contrast, the other three clades are Non-vascular plant, nonvascular plants as they do not have tracheids.
They also do not constitute a single clade.
Nonvascular plants include liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. They tend to be found in areas where water is readily available.
Most live on soil or even on vascular plants themselves. Some can grow on bare rock, tree trunks that are dead or have fallen, and even buildings.
Most nonvascular plants are terrestrial, with a few living in freshwater environments and none living in the oceans.
The seven clades (or Division (biology), divisions) that make up vascular plants include Equisetum, horsetails and ferns, which together can be grouped as a single clade called monilophytes.
Seed plants (or spermatophyte) comprise the other five divisions, four of which are grouped as gymnosperms and one is angiosperms. Gymnosperms includes Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophyta, gnetophytes. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form Conifer cone, cones, or solitary as in Taxus, yew, ''Torreya'', ''Ginkgo''.
Angiosperms are the most diverse group of Embryophyte, land plants, with 64 Order (biology), orders, 416 Family (biology), families, approximately 13,000 known Genus, genera and 300,000 known species.
Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are Spermatophyte, seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by having characteristics such as flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and production of fruits that contain the seeds.
Fungi
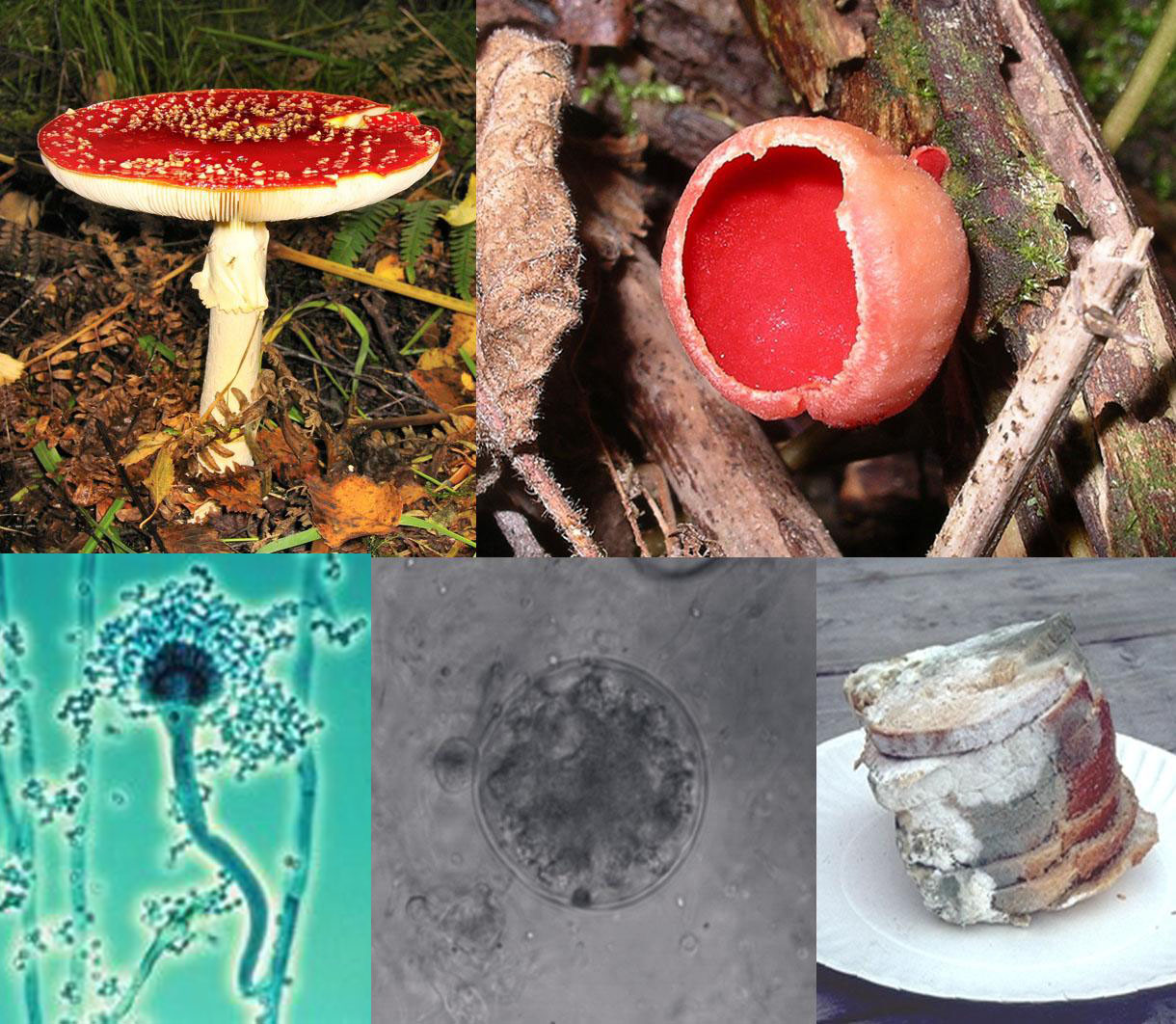

Fungus, Fungi are
eukaryotic organisms that digest foods outside of their bodies.
They do so through a process called absorptive heterotrophy whereby they would first secrete digestive enzymes that break down large food molecules before absorbing them through their cell membranes. Many fungi are also saprobes as they are able to take in nutrients from dead organic matter and are hence, the principal decomposers in ecological systems.
Some fungi are parasites by absorbing nutrients from living hosts while others are mutualists.
Fungi, along with two other lineages, choanoflagellates and animals, can be grouped as opisthokonts. A synapomorphy that distinguishes fungi from other two opisthokonts is the presence of chitin in their
cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
s.
Most fungi are multicellular but some are unicellular such as yeasts, which live in liquid or moist environments and are able to absorb nutrients directly into their cell surfaces.
Multicellular fungi, on the other hand, have a body called mycelium, which is composed of a mass of individual tubular filaments called hyphae that allows for nutrient absorption to occur.
Fungi can be divided into six major groups based on their life cycles: microsporidia, Chytridiomycota, chytrids, zygospore fungi (Zygomycota), arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota), sac fungi (Ascomycota), and Clavarioid fungi, club fungi (Basidiomycota).
Fungi are classified by the particular processes of sexual reproduction they use. The usual cellular products of
meiosis during sexual reproduction are spores that are adapted to survive inclement times and to spread. A principal adaptive benefit of meiosis during sexual reproduction in the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota was proposed to be the repair of DNA damage through meiotic recombination.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxon, taxa with varied ecologies, biological life cycle, life cycle strategies, and morphology (biology), morphologies ranging from unicellular aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true
biodiversity of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at 2.2 million to 3.8 million species.
Of these, only about 148,000 have been described,
with over 8,000 species known to be detrimental to plants and at least 300 that can be pathogenic to humans.
Animal diversity
File:Animal diversity.png , right , Diversity of animals. From top to bottom, first column: Echinoderm, cnidaria, bivalve, tardigrade, crustacean, and arachnid. Second column: Sponge, insect, mammal, bryozoa, acanthocephala, and flatworm. Third column: Cephalopod, annelid, tunicate, fish, bird, and phoronida.
rect 0 0 118 86 Echinoderm
rect 0 86 118 172 Cnidaria
rect 0 172 118 258 Bivalve
rect 0 258 118 344 Tardigrade
rect 0 344 118 430 Crustacean
rect 0 430 118 516 Arachnid
rect 118 0 236 86 Sponge
rect 118 86 236 172 Insect
rect 118 172 236 258 Mammal
rect 118 258 236 344 Bryozoa
rect 118 344 236 430 Acanthocephala
rect 118 430 236 620 Flatworm
rect 236 0 354 86 Cephalopod
rect 236 86 354 172 Annelid
rect 236 172 354 258 Tunicate
rect 236 258 354 344 Fish
rect 236 344 354 430 Bird
rect 236 430 354 620 Phoronida
Animals are multicellular eukaryotic organisms that form the kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs.
Animals can be distinguished into two groups based on their developmental characteristics.
For instance, embryos of Eumetazoa, diploblastic animals such as ctenophores, placeozoans, and cnidarians have two cell layers (ectoderm and endoderm) whereas the embryos of Triploblasty, triploblastic animals have three tissue layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), which is a synapomorphy of these animals.
Triploblastic animals can be further divided into two major clades based on based on the pattern of gastrulation, whereby a cavity called a blastopore is formed from the indentation of a blastula. In protostomes, the blastopore gives rise to the mouth, which is then followed by the formation of the anus.
In deuterostomes, the blastopore gives rise to the anus, followed by the formation of the mouth.
Animals can also be differentiated based on their body plan, specifically with respect to four key features: Symmetry in biology, symmetry, body cavity, Segmentation (biology), segmentation, and appendages.
The bodies of most animals are symmetrical, with symmetry being either Symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radial or Symmetry in biology#Bilateral symmetry, bilateral.
Triploblastic animals can be divided into three types based on their body cavity: acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, and coelomate.
Segmentation can be observed in the bodies of many animals, which allows for specialization of different parts of the body as well as allowing the animal to change the shape of its body to control its movements.
Finally, animals can be distinguished based on the type and location of their appendages such as Antenna (biology), antennae for sensing the environment or claws for capturing prey.
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal Metazoa (animal) clade as a sister of the diploblasts.
They are Multicellular organism, multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of
cells.
The majority (~97%) of animal species are invertebrates, which are animals that do not have a vertebral column (or backbone or spine), derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum vertebrate, Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include sponges, cnidarians (hydras, jellyfishes, sea anemones, and corals), mollusks (chitons, snail, bivalves, squids, and octopuses), annelids (earthworms and leeches), and arthropods (insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and myriapods). Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.
In contrast, vertebrates comprise all species of animals within the subphylum Vertebrata, which are chordates with vertebral columns. These animals have four key features, which are an anterior skull with a brain, a rigid internal skeleton supported by a vertebral column that encloses a spinal cord, internal organs suspended in a coelom, and a well-developed circulatory system driven by a single large heart.
Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise different major groups that include Agnatha, jawless fishes (not including hagfishes), Gnathostomata, jawed vertebrates such as Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fishes (sharks, Batoidea, rays, and ratfish), Osteichthyes, bony fishes, tetrapods such as amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
The two remaining groups of jawless fishes that have survived beyond the Devonian Geologic time scale#Terminology, period are hagfishes and lamprey, which are collectively known as Cyclostomi, cyclostomes (for ''circled mouths'').
Both groups of animals have elongated eel-like bodies with no paired fins.
However, because hagfishes have a weak circulatory system with three accessory hearts, a partial skull with no cerebellum, no jaws or stomach, and no jointed vertebrae, some biologists do not classify them as vertebrates but instead as a sister group of vertebrates.
In contrast, lampreys have a complete skull and a distinct vertebrae that is cartilaginous.
Mammals have four key features that distinguish them from other animals such as sweat glands, mammary glands, hair, and a four-chambered heart.
Small and medium-sized mammals used to co-exist with large dinosaurs in much of the Mesozoic era but soon Evolutionary radiation, radiated following the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, mass extinction of dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous period.
There are approximately 57,000 mammal species, which can be divided into two primary groups: Yinotheria, prototherians and therians. Prototherians do not possess nipples on their mammary but instead secrete milk onto their skin, allowing their offspring to lap if off their furs.
They also lack a placenta, lays eggs, and have sprawling legs. Currently, there only five known species of prototherians (platypus and four species of echidnas).
The therian clade is Viviparity, viviparous and can be further divided into two groups: marsupials and eutherians.
Marsupial females have a ventral pouch to carry and feed their offspring. Eutherians form the majority of mammals and include major groups such as rodents, bats, even-toed ungulates and cetaceans, shrews and Mole (animal), moles, primates, carnivores, rabbits, Afrosoricida, African insectivores, Erinaceidae, spiny insectivores, armadillos, treeshrews, odd-toed ungulates, Elephant shrew, long-nosed insectivores, anteaters and sloths, pangolins, hyraxes, sirenians, elephants, colugos, and aardvark.
A split in the primate lineage occurred approximately 90 million years ago during the Cretaceous, which brought about two major clades: prosimians and simian, anthropoids.
The prosimians include lemurs, lorises, and galagos whereas the anthropoids comprise tarsiers, New World monkeys, Old World monkeys, and apes.
Apes separated from Old World monkeys about 35 million years ago, with various species living in Africa, Europe, and Asia between 22 and 5.5 million years ago.
The modern descendants of these animals include chimpanzees and gorillas in Africa, gibbons and orangutans in Asia, and humans worldwide. A split in the ape lineage occurred about six million years ago in Africa, which resulted in the emergence of chimpanzees as one group and a hominid clade as another group that includes humans and their extinct relatives.
Bipedalism emerged in the earliest Human evolution, protohominids known as Ardipithecus, ardipithecines. As an adaptation, bipedalism conferred three advantages. First, it enabled the ardipithecines to use their forelimbs to manipulate and carry objects while working.
Second, it elevated the animal's eyes to spot preys or predators over tall vegetation.
Finally, bipedalism is more energetically efficient than quadrupedal locomotion.
Viruses
Viruses are wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agents that Viral replication, replicate inside the
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
of
organisms.
Viruses infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including
bacteria and
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
.
More than 6,000 virus species have been described in detail.
Viruses are found in almost every
ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity.
When infected, a host cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of the genetic material (
DNA or RNA), a
protein coat called ''capsid'', and in some cases an outside viral envelope, envelope of
lipids. The shapes of these virus particles range from simple helix, helical and icosahedron, icosahedral forms to more complex structures. Most virus species have virions too small to be seen with an optical microscope, as they are one-hundredth the size of most bacteria.
The origins of viruses in the evolutionary history of life are unclear: some may have evolution, evolved from
plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; how ...
s—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria. In evolution, viruses are an important means of horizontal gene transfer, which increases genetic diversity in a way analogous to sexual reproduction.
Because viruses possess some but not all characteristics of life, they have been described as "organisms at the edge of life",
and as Self-replication, self-replicators.
Viruses can spread in many ways. One transmission pathway is through disease-bearing organisms known as Vector (epidemiology), vectors: for example, viruses are often transmitted from plant to plant by insects that feed on plant sap, such as aphids; and viruses in animals can be carried by Hematophagy, blood-sucking insects. influenza, Influenza viruses are spread by coughing and sneezing. Norovirus and rotavirus, common causes of viral gastroenteritis, are transmitted by the fecal–oral route, faecal–oral route, passed by hand-to-mouth contact or in food or water. Viral infections in animals provoke an immune response that usually eliminates the infecting virus. Immune responses can also be produced by vaccines, which confer an immunity (medical), artificially acquired immunity to the specific viral infection.
Plant form and function
Plant body

The plant body is made up of Organ (biology), organs that can be organized into two major organ systems: a root , root system and a shoot , shoot system.
The root system anchors the plants into place. The roots themselves absorb water and minerals and store photosynthetic products. The shoot system is composed of Plant stem, stem, Leaf, leaves, and flowers. The stems hold and orient the leaves to the sun, which allow the leaves to conduct photosynthesis. The flowers are shoots that have been modified for reproduction. Shoots are composed of phytomers, which are functional units that consist of a node carrying one or more leaves, internode, and one or more buds.
A plant body has two basic patterns (apical–basal and radial axes) that been established during Plant embryogenesis, embryogenesis.
Cells and tissues are arranged along the apical-basal axis from root to shoot whereas the three tissue systems (Dermal tissue system, dermal, Ground tissue, ground, and Vascular tissue, vascular) that make up a plant's body are arranged concentrically around its radial axis.
The dermal tissue system forms the epidermis (or outer covering) of a plant, which is usually a single cell layer that consists of cells that have differentiated into three specialized structures: stomata for gas exchange in leaves, trichomes (or leaf hair) for protection against insects and Solar irradiance, solar radiation, and root hairs for increased surface areas and absorption of water and nutrients. The ground tissue makes up virtually all the tissue that lies between the dermal and vascular tissues in the shoots and roots. It consists of three cell types: Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells. Finally, the vascular tissues are made up of two constituent tissues: xylem and phloem. The xylem is made up of two conducting cells called tracheids and vessel elements whereas the phloem is characterized by the presence of sieve tube elements and companion cells.
Plant nutrition and transport

Like all other organisms, plants are primarily made up of water and other molecules containing chemical element, elements that are essential to life.
The absence of specific nutrients (or Mineral (nutrient), essential elements), many of which have been identified in Hydroponics, hydroponic experiments, can disrupt plant development, plant growth and Plant reproduction, reproduction. The majority of plants are able to obtain these nutrients from
solutions that surrounds their roots in the soil.
Continuous Leaching (agriculture), leaching and harvesting of crops can deplete the soil of its nutrients, which can be restored with the use of fertilizers. Carnivorous plants such as Venus flytraps are able to obtain nutrients by digesting other arthropods whereas parasitic plants such as mistletoes can parasitize other plants for water and nutrients.
Plants need water to conduct photosynthesis, transport solutes between organs, cool their leaves by evaporation, and maintain internal pressures that support their bodies.
Water is able to diffusion, diffuse in and out of plant cells by osmosis. The direction of water movement across a semipermeable membrane is determined by the water potential across that membrane.
Water is able to diffuse across a root cell's membrane through aquaporins whereas solutes are transported across by the membrane by ion channels and Ion transporter, pumps. In vascular plants, water and solutes are able to enter the xylem, a vascular tissue, by way of an apoplast and symplast. Once in the xylem, the water and minerals are distributed upward by transpiration from the soil to the aerial parts of the plant.
In contrast, the phloem, another vascular tissue, distributes
carbohydrates (e.g.,
sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
) and other solutes such as hormones by Phloem#Function, translocation from a Pressure flow hypothesis#Sources and sinks, source (e.g., mature leaf or root) in which they were produced to a Pressure flow hypothesis#Sources and sinks, sink (e.g., root, flower, or developing fruit) in which they will be used and stored.
Sources and sinks can switch roles, depending on the amount of carbohydrates accumulated or mobilized for the nourishment of other organs.
Plant development
Plant development is regulated by environmental cues and the plant's own Receptor (biochemistry), receptors,
hormones, and
genome.
Morever, they have several characteristics that allow them to obtain resources for growth and reproduction such as meristems, post-embryonic organ formation, and differential growth.
Development begins with a seed, which is an Plant embryogenesis, embryonic
plant enclosed in a testa (botany), protective outer covering. Most plant seeds are usually Seed dormancy, dormant, a condition in which the seed's normal activity is suspended.
Seed dormancy may last may last weeks, months, years, and even centuries. Dormancy is broken once conditions are favorable for growth, and the seed will begin to sprout, a process called germination. Imbibition is the first step in germination, whereby water is absorbed by the seed. Once water is absorbed, the seed undergoes metabolic changes whereby
enzymes are activated and RNA and
proteins are synthesized. Once the seed germinates, it obtains
carbohydrates,
amino acids, and small
lipids that serve as building blocks for its development. These
monomers are obtained from the hydrolysis of starch,
proteins, and lipids that are stored in either the cotyledons or endosperm. Germination is completed once embryonic roots called radicle have emerged from the Seed#Seed coat, seed coat. At this point, the developing plant is called a seedling and its growth is regulated by its own photoreceptor protein#Photoreceptors in plants, photoreceptor proteins and hormones.
Unlike
animals in which growth is determinate, i.e., ceases when the adult state is reached, plant growth is indeterminate as it is an open-ended process that could potentially be lifelong.
Plants grow in two ways: secondary growth, primary and secondary growth, secondary. In primary growth, the shoots and roots are formed and lengthened. The Meristem#Apical meristems, apical meristem produces the primary plant body, which can be found in all Spermatophyte, seed plants. During secondary growth, the thickness of the plant increases as the Meristem#Secondary meristems, lateral meristem produces the secondary plant body, which can be found in woody eudicots such as trees and shrubs. Monocotyledon, Monocots do not go through secondary growth.
The plant body is generated by a hierarchy of meristems. The apical meristems in the root and shoot systems give rise to primary meristems (protoderm, ground meristem, and Meristem#Primary meristems, procambium), which in turn, give rise to the three tissue systems (Dermal tissue system, dermal, Ground tissue, ground, and Vascular tissue, vascular).
Plant reproduction

Most angiosperms (or flowering plants) engage in sexual reproduction.
Their flowers are organs that facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happened in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positioned so that the pollen can land on the flower's stigma. This pollination does not require an investment from the plant to provide nectar and pollen as food for pollinators.
Plant responses
Like animals, plants produce plant hormone, hormones in one part of its body to signal cells in another part to respond. The ripening of fruit and loss of leaves in the winter are controlled in part by the production of the gas Ethylene as a plant hormone, ethylene by the plant. Stress from water loss, changes in air chemistry, or crowding by other plants can lead to changes in the way a plant functions. These changes may be affected by genetic, chemical, and physical factors.
To function and survive, plants produce a wide array of chemical compounds not found in other organisms. Because they cannot move, plants must also defend themselves chemically from herbivores, pathogens and competition from other plants. They do this by producing toxins and foul-tasting or smelling chemicals. Other compounds defend plants against disease, permit survival during drought, and prepare plants for dormancy, while other compounds are used to attract pollinators or herbivores to spread ripe seeds.
Many plant organs contain different types of photoreceptor protein#Photoreceptors in plants, photoreceptor proteins, each of which reacts very specifically to certain wavelengths of light.
The photoreceptor proteins relay information such as whether it is day or night, duration of the day, intensity of light available, and the source of light. Shoots generally grow towards light, while roots grow away from it, responses known as phototropism and skototropism, respectively. They are brought about by light-sensitive pigments like phototropins and phytochromes and the plant hormone auxin. Many flowering plants bloom at the appropriate time because of light-sensitive compounds that respond to the length of the night, a phenomenon known as photoperiodism.
In addition to light, plants can respond to other types of stimuli. For instance, plants can sense the direction of gravity to orient themselves correctly. They can respond to mechanical stimulation.
Animal form and function
General features

The cells in each animal body are bathed in interstitial fluid, which make up the cell's environment. This fluid and all its characteristics (e.g., temperature, ionic composition) can be described as the animal's
internal environment
The internal environment (or ''milieu intérieur'' in French) was a concept developed by Claude Bernard, a French physiologist in the 19th century, to describe the interstitial fluid and its physiological capacity to ensure protective stability f ...
, which is in contrast to the external environment that encompasses the animal's outside world.
Animals can be classified as either regulators or conformers. Animals such as mammals and birds are regulators as they are able to maintain a constant internal environment such as body temperature despite their environments changing. These animals are also described as homeotherms as they exhibit thermoregulation by keeping their internal body temperature constant. In contrast, animals such as fishes and frogs are conformers as they adapt their internal environment (e.g., body temperature) to match their external environments. These animals are also described as poikilotherms or ectotherms as they allow their body temperatures to match their external environments. In terms of energy, regulation is more costly than conformity as an animal expands more energy to maintain a constant internal environment such as increasing its basal metabolic rate, which is the rate of energy consumption.
Similarly, homeothermy is more costly than poikilothermy. Homeostasis is the stability of an animal's internal environment, which is maintained by Negative feedback#Biology, negative feedback loops.
The body size of terrestrial animals vary across different species but their use of energy does not Allometry#Physiological scaling, scale linearly according to their size.
Mice, for example, are able to consume three times more food than rabbits in proportion to their weights as the basal metabolic rate per unit weight in mice is greater than in rabbits.
Physical activity can also increase an animal's metabolic rate. When an animal runs, its metabolic rate increases linearly with speed.
However, the relationship is non-linear in animals that Aquatic locomotion, swim or Flight, fly. When a fish swims faster, it encounters greater water resistance and so its metabolic rates increases exponential.
Alternatively, the relationship of flight speeds and metabolic rates is U-shaped in birds.
At low flight speeds, a bird must maintain a high metabolic rates to remain airborne. As it speeds up its flight, its metabolic rate decreases with the aid of air rapidly flows over its wings. However, as it increases in its speed even further, its high metabolic rates rises again due to the increased effort associated with rapid flight speeds. Basal metabolic rates can be measured based on an animal's rate of heat production.
Water and salt balance
An animal's body fluids have three properties: osmotic pressure,
ionic composition, and volume.
Osmotic pressures determine the direction of the diffusion of water (or osmosis), which moves from a region where osmotic pressure (total solute concentration) is low to a region where osmotic pressure (total solute concentration) is high. Aquatic animals are diverse with respect to their body fluid compositions and their environments. For example, most invertebrate animals in the ocean have body fluids that are Tonicity#Isotonicity, isosmotic with seawater. In contrast, ocean Osteichthyes, bony fishes have body fluids that are Tonicity#Hypotonic solution, hyposmotic to seawater. Finally, freshwater animals have body fluids that are Tonicity#Hypertonic solution, hyperosmotic to fresh water. Typical ions that can be found in an animal's body fluids are
sodium, potassium,
calcium, and
chloride. The volume of body fluids can be regulated by excretion. Vertebrate animals have kidneys, which are excretory organs made up of tiny tubular structures called nephrons, which make urine from blood plasma. The kidneys' primary function is to regulate the composition and volume of blood plasma by selectively removing material from the blood plasma itself. The ability of Deserts and xeric shrublands, xeric animals such as kangaroo rats to minimize water loss by producing urine that is 10–20 times concentrated than their blood plasma allows them to adapt in desert environments that receive very little precipitation.
Nutrition and digestion

Animals are heterotrophs as they feed on other organisms to obtain energy and organic compounds.
They are able to obtain food in three major ways such as targeting visible food objects, collecting tiny food particles, or depending on microbes for critical food needs. The amount of Food energy, energy stored in food can be quantified based on the amount of heat (measured in calories or joule, kilojoules) emitted when the food is burnt in the presence of oxygen. If an animal were to consume food that contains an excess amount of chemical energy, it will store most of that energy in the form of
lipids for future use and some of that energy as glycogen for more immediate use (e.g., meeting the brain's energy needs).
The molecules in food are chemical building blocks that are needed for growth and development. These molecules include nutrients such as
carbohydrates,
fats, and
proteins. Vitamins and Mineral (nutrient), minerals (e.g., calcium, magnesium, sodium, and phosphorus) are also essential. The digestive system, which typically consist of a tubular tract that extends from the mouth to the anus, is involved in the breakdown (or digestion) of food into small molecules as it travels down peristalsis, peristaltically through the Gastrointestinal tract, gut lumen shortly after it has been ingestion, ingested. These small food molecules are then Absorption (biology), absorbed into the blood from the lumen, where they are then distributed to the rest of the body as building blocks (e.g., amino acids) or sources of energy (e.g., glucose).
In addition to their digestive tracts, vertebrate animals have accessory glands such as a liver and pancreas as part of their digestive systems.
The processing of food in these animals begins in the foregut, which includes the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. Mechanical digestion of food starts in the mouth with the esophagus serving as a passageway for food to reach the stomach, where it is stored and disintegrated (by the stomach's acid) for further processing. Upon leaving the stomach, food enters into the midgut, which is the first part of the intestine (or small intestine in mammals) and is the principal site of digestion and absorption. Food that does not get absorbed are stored as indigestible waste (or feces) in the hindgut, which is the second part of the intestine (or large intestine in mammals). The hindgut then completes the reabsorption of needed water and salt prior to eliminating the feces from the rectum.
Breathing

The respiratory system consists of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in
animals. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In terrestrial animal, land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs.
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, and in birds they are known as Bird anatomy#Respiratory system, atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood.
These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchus, bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed Bird anatomy#Respiratory system, parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic pulmonary alveolus, alveoli in mammals and Bird anatomy#Respiratory system, atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing, which involves the muscles of respiration.
Circulation

A circulatory system usually consists of a muscular pump such as a heart, a fluid (blood), and system of blood vessels that deliver it.
Its principal function is to transport blood and other substances to and from
cells and Tissue (biology), tissues. There are two types of circulatory systems: Open circulatory system, open and Closed circulatory system, closed. In open circulatory systems, blood exits blood vessels as it circulates throughout the body whereas in closed circulatory system, blood is contained within the blood vessels as it circulates. Open circulatory systems can be observed in invertebrate animals such as arthropods (e.g., insects, spiders, and lobsters) whereas closed circulatory systems can be found in vertebrate animals such as fishes, amphibians, and mammals. Circulation in animals occur between two types of tissues: Circulatory system#Systemic circulation, systemic tissues and Respiratory system, breathing (or pulmonary) organs.
Systemic tissues are all the tissues and organs that make up an animal's body other than its breathing organs. Systemic tissues take up oxygen but adds carbon dioxide to the blood whereas a breathing organs takes up carbon dioxide but add oxygen to the blood.
In birds and mammals, the systemic and pulmonary systems are connected in series.
In the circulatory system, blood is important because it is the means by which
oxygen,
carbon dioxide,
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s,
hormones, agents of immune system, heat, wastes, and other commodities are transported.
In annelids such as earthworms and leeches, blood is propelled by Peristalsis, peristaltic waves of Muscle contraction, contractions of the heart muscles that make up the blood vessels. Other animals such as crustaceans (e.g., crayfish and lobsters), have more than one heart to propel blood throughout their bodies. Vertebrate hearts are Heart#Chambers, multichambered and are able to pump blood when their ventricle (heart), ventricles contract at each cardiac cycle, which propels blood through the blood vessels.
Although vertebrate hearts are Myogenic mechanism, myogenic, their rate of contraction (or heart rate) can be modulated by neural input from the body's autonomic nervous system.
Muscle and movement

In vertebrates, the muscular system consists of skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscle, cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture and circulates blood throughout the body.
Together with the skeletal system, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of vertebrate animals. Skeletal muscle contractions are neurogenic as they require Synapse, synaptic input from motor neurons. A single motor neuron is able to innervate multiple muscle fibers, thereby causing the fibers to contract at the same time. Once innervated, the protein filaments within each skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction, which is explained by the sliding filament theory. The contraction produced can be described as a twitch, summation, or tetanus, depending on the frequency of action potentials. Unlike skeletal muscles, contractions of smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscles are Myogenic contraction, myogenic as they are initiated by the smooth or heart muscle cells themselves instead of a motor neuron. Nevertheless, the strength of their contractions can be modulated by input from the autonomic nervous system. The mechanisms of contraction are similar in all three muscle tissues.
In invertebrates such as earthworms and leeches, Muscle contraction#Circular and longitudinal muscles, circular and longitudinal muscles cells form the body wall of these animals and are responsible for their movement.
In an earthworm that is moving through a soil, for example, contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles occur reciprocally while the Coelom#Coelomic fluid, coelomic fluid serves as a Hydrostatic skeleton, hydroskeleton by maintaining turgidity of the earthworm.
Other animals such as Mollusca, mollusks, and nematodes, possess obliquely striated muscles, which contain bands of thick and thin filaments that are arranged helically rather than transversely, like in vertebrate skeletal or cardiac muscles.
Advanced insects such as wasps, Fly, flies, bees, and beetles possess asynchronous muscles that constitute the flight muscles in these animals.
These flight muscles are often called ''fibrillar muscles'' because they contain myofibrils that are thick and conspicuous.
Nervous system

Most multicellular animals have nervous systems
that allow them to sense from and respond to their environments. A nervous system is a network of cells that processes Sense, sensory information and generates behaviors. At the cellular level, the nervous system is defined by the presence of
neurons, which are cells specialized to handle information.
They can transmit or receive information at sites of contacts called synapses.
More specifically, neurons can conduct nerve impulses (or action potentials) that travel along their thin fibers called axons, which can then be transmitted directly to a neighboring cell through electrical synapses or cause chemicals called
neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
s to be released at chemical synapses. According to the sodium theory, these action potentials can be generated by the increased permeability of the neuron's
cell membrane to sodium ions.
Cells such as neurons or muscle cells may be excited or inhibited upon receiving a signal from another neuron. The connections between neurons can form neural pathways, neural circuits, and large scale brain networks, larger networks that generate an organism's perception of the world and determine its behavior. Along with neurons, the nervous system contains other specialized cells called glia or glial cells, which provide structural and metabolic support.
In vertebrates, the nervous system comprises the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of nerves that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the CNS are called motor nerves or Efferent nerve fiber, efferent nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or Afferent nerve fiber, afferent nerves. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both functions. The PNS is divided into three separate subsystems, the somatic nervous system, somatic, autonomic nervous system, autonomic, and enteric nervous system, enteric nervous systems. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nervous system is further subdivided into the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is activated in cases of emergencies to mobilize energy, while the parasympathetic nervous system is activated when organisms are in a relaxed state. The enteric nervous system functions to control the gastrointestinal system. Both autonomic and enteric nervous systems function involuntarily. Nerves that exit directly from the brain are called cranial nerves while those exiting from the spinal cord are called spinal nerves.
Many animals have Sensory nervous system, sense organs that can detect their environment. These sense organs contain sensory receptors, which are sensory neurons that convert stimuli into electrical signals.
Mechanoreceptors, for example, which can be found in skin, muscle, and hearing organs, generate action potentials in response to changes in pressures.
Photoreceptor cells such as Rod cell, rods and Cone cell, cones, which are part of the vertebrate retina, can respond to specific Electromagnetic spectrum, wavelengths of light.
Chemoreceptors detect chemicals in the mouth (taste) or in the air (sense of smell, smell).
Hormonal control
Hormones are signaling molecules transported in the blood to distant organs to regulate their function.
Hormones are secreted by internal glands that are part of an
animal's endocrine system. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans specifically, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. Many other organs that are part of other body systems have secondary endocrine functions, including bone, kidneys, liver, heart and gonads. For example, kidneys secrete the endocrine hormone erythropoietin. Hormones can be amino acid complexes,
steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins.
The endocrine system can be contrasted to both exocrine glands, which secrete hormones to the outside of the body, and paracrine signaling between cells over a relatively short distance. Endocrine glands have no Duct (anatomy), ducts, are vascular, and commonly have intracellular vacuoles or granules that store their hormones. In contrast, exocrine glands, such as salivary glands, sweat glands, and glands within the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, tend to be much less vascular and have ducts or a hollow Lumen (anatomy), lumen.
Animal reproduction

Animals can Reproduction, reproduce in one of two ways: Asexual reproduction#Examples in animals, asexual and Sexual reproduction#Animals, sexual. Nearly all animals engage in some form of sexual reproduction. They produce haploid gametes by
meiosis. The smaller, motile gametes are Spermatozoon, spermatozoa and the larger, non-motile gametes are Egg cell, ova. These fuse to form zygotes, which develop via
mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
into a hollow sphere, called a blastula. In sponges, blastula larvae swim to a new location, attach to the seabed, and develop into a new sponge. In most other groups, the blastula undergoes more complicated rearrangement. It first Invagination, invaginates to form a gastrula with a digestive chamber and two separate germ layers, an external ectoderm and an internal endoderm. In most cases, a third germ layer, the mesoderm, also develops between them. These germ layers then differentiate to form tissues and organs. Some animals are capable of asexual reproduction, which often results in a genetic clone of the parent. This may take place through Fragmentation (reproduction), fragmentation; budding, such as in Hydra (genus), ''Hydra'' and other cnidarians; or parthenogenesis, where fertile eggs are produced without mating, such as in aphids.
Animal development

Animal development begins with the formation of a zygote that results from the fusion of a sperm and egg cell, egg during fertilization. The zygote undergoes a rapid multiple rounds of mitotic cell period of cell divisions called cleavage (embryo), cleavage, which forms a ball of similar cells called a blastula. Gastrulation occurs, whereby morphogenetic movements convert the cell mass into a three germ layers that comprise the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
The end of gastrulation signals the beginning of organogenesis, whereby the three germ layers form the internal organs of the organism.
The cells of each of the three germ layers undergo Cellular differentiation, differentiation, a process where less-specialized cells become more-specialized through the expression of a specific set of genes. Cellular differentiation is influenced by extracellular signals such as growth factors that are exchanged to adjacent cells, which is called Juxtacrine signalling, juxtracrine signaling, or to neighboring cells over short distances, which is called paracrine signaling. Intracellular signals consist of a cell signaling itself (autocrine signaling), also play a role in organ formation. These signaling pathways allows for cell rearrangement and ensures that organs form at specific sites within the organism.
Immune system

The immune system is a network of biological processes that detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions.
Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of
enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryote, plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt to recognize pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates an immunological memory leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.
Animal behavior

Behaviors play a central a role in animals' interaction with each other and with their environment.
They are able to use their muscles to approach one another, Animal communication, vocalize, seek shelter, and migration (ecology), migrate. An animal's nervous system activates and coordinates its behaviors. Fixed action patterns, for instance, are genetically determined and stereotyped behaviors that occur without learning.
These behaviors are under the control of the nervous system and can be quite elaborate.
Examples include the pecking of kelp gull chicks at the red dot on their mother's beak. Other behaviors that have emerged as a result of
natural selection include foraging, mating, and Altruism (biology), altruism.
In addition to evolved behavior, animals have evolved the ability to learn by modifying their behaviors as a result of early individual experiences.
Ecology
Ecology is the study of the distribution and abundance of
life, the interaction between organisms and their natural environment, environment.
Ecosystems

The community (ecology), community of living (Biotic component, biotic) organisms in conjunction with the nonliving (Abiotic component, abiotic) components (e.g., water, light, radiation, temperature, humidity, atmosphere, acidity, and soil) of their environment is called an
ecosystem.
These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
Energy from the sun enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and
energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and Microbe, microbial Biomass (ecology), biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release
carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.
The Earth's physical environment is shaped by solar energy and topography.
The amount of solar energy input varies in space and time due to the spherical shape of the Earth and its axial Earth#Axial tilt and seasons, tilt. Variation in solar energy input drives weather and climate patterns. Weather is the day-to-day temperature and precipitation (meteorology), precipitation activity, whereas climate is the long-term average of weather, typically averaged over a period of 30 years.
Variation in topography also produces environmental heterogeneity. On the Windward and leeward, windward side of a mountain, for example, air rises and cools, with water changing from gaseous to liquid or solid form, resulting in precipitation such as rain or snow.
As a result, wet environments allow for lush vegetation to grow. In contrast, conditions tend to be dry on the leeward side of a mountain due to the lack of precipitation as air descends and warms, and moisture remains as water vapor in the atmosphere. Temperature and precipitation are the main factors that shape terrestrial biomes.
Populations

A
population is the number of
organisms of the same species that occupy an geographical area, area and Sexual reproduction, reproduce from generation to generation.
Its abundance can be measured using population density, which is the number of individuals per unit area (e.g., land or tree) or volume (e.g., sea or air).
Given that it is usually impractical to count every individual within a large population to determine its size, population size can be estimated by multiplying population density by the area or volume. Population growth during short-term intervals can be determined using the Population growth#Population growth rate, population growth rate equation, which takes into consideration Birth rate, birth, Death Rate, death, and immigration rates. In the longer term, the exponential growth of a population tends to slow down as it reaches its carrying capacity, which can be modeled using the Logistic function, logistic equation.
The carrying capacity of an Natural environment, environment is the maximum population size of a species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, Drinking water, water, and other resources that are available.
The carrying capacity of a population can be affected by changing environmental conditions such as changes in the availability resources and the cost of maintaining them. In human populations, new technology, technologies such as the Green revolution have helped increase the Earth's carrying capacity for humans over time, which has stymied the attempted predictions of impending population decline, the famous of which was by Thomas Robert Malthus, Thomas Malthus in the 18th century.
Communities

A community is a group of
populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time. A biological interaction is the effect that a pair of
organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the
evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from Mutualism (biology), mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition (biology), competition, harmful to both partners.
Every species participates as a consumer, resource, or both in consumer–resource interactions, which form the core of food chains or food webs.
There are different trophic levels within any food web, with the lowest level being the primary producers (or autotrophs) such as plants and algae that convert energy and inorganic material into organic compounds, which can then be used by the rest of the community.
[ At the next level are the heterotrophs, which are the species that obtain energy by breaking apart organic compounds from other organisms.]
Biosphere
 In the global ecosystem (or biosphere), matter exist as different interacting compartments, which can be biotic or abiotic as well as accessible or inaccessible, depending on their forms and locations.
In the global ecosystem (or biosphere), matter exist as different interacting compartments, which can be biotic or abiotic as well as accessible or inaccessible, depending on their forms and locations.
Conservation
Conservation biology is the study of the conservation of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions.[Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005). ''Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Biodiversity Synthesis.'' World Resources Institute, Washington, D.]
See also
* Biology in fiction
* Glossary of biology
* List of biological websites
* List of biologists
* List of biology journals
* List of biology topics
* List of life sciences
* List of omics topics in biology
* National Association of Biology Teachers
* Outline of biology
* Periodic table of life sciences in Tinbergen's four questions
* Reproduction
* Science tourism
* :Biology terminology, Terminology of biology
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* .
**
*
Global Warming of 1.5 ºC —
**
*
External links
*
OSU's Phylocode
Biology Online – Wiki Dictionary
MIT video lecture series on biology
OneZoom Tree of Life
Journal links
PLOS Biology
A peer-reviewed, open-access journal published by the Public Library of Science
''Current Biology''
General journal publishing original research from all areas of biology
*
Biology Letters
': A Impact factor, high-impact Royal Society journal publishing peer-reviewed biology papers of general interest
*
Science
': Internationally renowned American Association for the Advancement of Science, AAAS science journal – see sections of the life sciences
*
International Journal of Biological Sciences
': A biological journal publishing significant peer-reviewed scientific papers
*
Perspectives in Biology and Medicine
': An interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary scholarly method, scholarly journal publishing essays of broad relevance
{{Good article
Biology,
Biology terminology,
 The earliest of roots of science, which included medicine, can be traced to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions later entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE) contributed extensively to the development of biological knowledge. His works such as '' History of Animals'' were especially important because they revealed his naturalist leanings, and later more empirical works that focused on biological causation and the diversity of life. Aristotle's successor at the Lyceum, Theophrastus, wrote a series of books on botany that survived as the most important contribution of antiquity to the plant sciences, even into the Middle Ages.
Scholars of the
The earliest of roots of science, which included medicine, can be traced to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions later entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE) contributed extensively to the development of biological knowledge. His works such as '' History of Animals'' were especially important because they revealed his naturalist leanings, and later more empirical works that focused on biological causation and the diversity of life. Aristotle's successor at the Lyceum, Theophrastus, wrote a series of books on botany that survived as the most important contribution of antiquity to the plant sciences, even into the Middle Ages.
Scholars of the  Serious evolutionary thinking originated with the works of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who was the first to present a coherent theory of evolution. Gould, Stephen Jay. ''The Structure of Evolutionary Theory''. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: Cambridge, 2002. . p. 187. He posited that evolution was the result of environmental stress on properties of animals, meaning that the more frequently and rigorously an organ was used, the more complex and efficient it would become, thus adapting the animal to its environment. Lamarck believed that these acquired traits could then be passed on to the animal's offspring, who would further develop and perfect them. Lamarck (1914) However, it was the British naturalist Charles Darwin, combining the biogeographical approach of
Serious evolutionary thinking originated with the works of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who was the first to present a coherent theory of evolution. Gould, Stephen Jay. ''The Structure of Evolutionary Theory''. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: Cambridge, 2002. . p. 187. He posited that evolution was the result of environmental stress on properties of animals, meaning that the more frequently and rigorously an organ was used, the more complex and efficient it would become, thus adapting the animal to its environment. Lamarck believed that these acquired traits could then be passed on to the animal's offspring, who would further develop and perfect them. Lamarck (1914) However, it was the British naturalist Charles Darwin, combining the biogeographical approach of 
 Proteins are the most diverse of the macromolecules, which include enzymes, transport proteins, large
Proteins are the most diverse of the macromolecules, which include enzymes, transport proteins, large  A gene is a unit of
A gene is a unit of  Gene expression is the molecular process by which a
Gene expression is the molecular process by which a  The regulation of gene expression (or gene regulation) by environmental factors and during different stages of Developmental biology, development can occur at each step of the process such as Transcription (biology), transcription, RNA splicing, Translation (biology), translation, and post-translational modification of a protein.
The ability of gene transcription to be regulated allows for the conservation of energy as cells will only make proteins when needed. Gene expression can be influenced by positive or negative regulation, depending on which of the two types of regulatory proteins called transcription factors bind to the DNA sequence close to or at a promoter. A cluster of genes that share the same promoter is called an operon, found mainly in prokaryotes and some lower eukaryotes (e.g., ''Caenorhabditis elegans''). It was first identified in ''Escherichia coli''—a prokaryotic cell that can be found in the intestines of humans and other animals—in the 1960s by François Jacob and Jacques Monod. They studied the prokaryotic cell's lac operon, ''lac'' operon, which is part of three genes (''lacZ'', ''lacY'', and ''lacA'') that encode three lactose-metabolizing enzymes (Beta-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, Beta-galactoside permease, β-galactoside permease, and Galactoside acetyltransferase, β-galactoside transacetylase). In positive regulation of gene expression, the Activator (genetics), activator is the transcription factor that stimulates transcription when it binds to the sequence near or at the promoter. In contrast, negative regulation occurs when another transcription factor called a repressor binds to a DNA sequence called an Operon#Operator, operator, which is part of an operon, to prevent transcription. When a repressor binds to a repressible operon (e.g., trp operon, ''trp'' operon), it does so only in the presence of a corepressor. Repressors can be inhibited by compounds called inducers (e.g., allolactose), which exert their effects by binding to a repressor to prevent it from binding to an operator, thereby allowing transcription to occur. Specific genes that can be activated by inducers are called Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, inducible genes (e.g., ''lacZ'' or ''lacA'' in ''E. coli''), which are in contrast to Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, constitutive genes that are almost always active. In contrast to both, structural genes encode proteins that are not involved in gene regulation.
In prokaryotic cells, transcription is regulated by proteins called sigma factors, which bind to RNA polymerase and direct it to specific promoters. Similarly, transcription factors in eukaryotic cells can also coordinate the expression of a group of genes, even if the genes themselves are located on different chromosomes. Coordination of these genes can occur as long as they share the same regulatory DNA sequence that bind to the same transcription factors. Promoters in eukaryotic cells are more diverse but tend to contain a core sequence that RNA polymerase can bind to, with the most common sequence being the TATA box, which contains multiple repeating A and T bases. Specifically, RNA polymerase II is the RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter to initiate transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes, but only in the presence of multiple general transcription factors, which are distinct from the transcription factors that have regulatory effects, i.e., activators and repressors. In eukaryotic cells, DNA sequences that bind with activators are called enhances whereas those sequences that bind with repressors are called silencers. Transcription factors such as NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) are able to identify specific nucleotide sequence based on the base sequence (e.g., CGAGGAAAATTG for NFAT) of the binding site, which determines the arrangement of the chemical groups within that sequence that allows for specific DNA-protein interactions. The expression of transcription factors is what underlies cellular differentiation in a developing
The regulation of gene expression (or gene regulation) by environmental factors and during different stages of Developmental biology, development can occur at each step of the process such as Transcription (biology), transcription, RNA splicing, Translation (biology), translation, and post-translational modification of a protein.
The ability of gene transcription to be regulated allows for the conservation of energy as cells will only make proteins when needed. Gene expression can be influenced by positive or negative regulation, depending on which of the two types of regulatory proteins called transcription factors bind to the DNA sequence close to or at a promoter. A cluster of genes that share the same promoter is called an operon, found mainly in prokaryotes and some lower eukaryotes (e.g., ''Caenorhabditis elegans''). It was first identified in ''Escherichia coli''—a prokaryotic cell that can be found in the intestines of humans and other animals—in the 1960s by François Jacob and Jacques Monod. They studied the prokaryotic cell's lac operon, ''lac'' operon, which is part of three genes (''lacZ'', ''lacY'', and ''lacA'') that encode three lactose-metabolizing enzymes (Beta-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, Beta-galactoside permease, β-galactoside permease, and Galactoside acetyltransferase, β-galactoside transacetylase). In positive regulation of gene expression, the Activator (genetics), activator is the transcription factor that stimulates transcription when it binds to the sequence near or at the promoter. In contrast, negative regulation occurs when another transcription factor called a repressor binds to a DNA sequence called an Operon#Operator, operator, which is part of an operon, to prevent transcription. When a repressor binds to a repressible operon (e.g., trp operon, ''trp'' operon), it does so only in the presence of a corepressor. Repressors can be inhibited by compounds called inducers (e.g., allolactose), which exert their effects by binding to a repressor to prevent it from binding to an operator, thereby allowing transcription to occur. Specific genes that can be activated by inducers are called Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, inducible genes (e.g., ''lacZ'' or ''lacA'' in ''E. coli''), which are in contrast to Gene expression#Regulation of gene expression, constitutive genes that are almost always active. In contrast to both, structural genes encode proteins that are not involved in gene regulation.
In prokaryotic cells, transcription is regulated by proteins called sigma factors, which bind to RNA polymerase and direct it to specific promoters. Similarly, transcription factors in eukaryotic cells can also coordinate the expression of a group of genes, even if the genes themselves are located on different chromosomes. Coordination of these genes can occur as long as they share the same regulatory DNA sequence that bind to the same transcription factors. Promoters in eukaryotic cells are more diverse but tend to contain a core sequence that RNA polymerase can bind to, with the most common sequence being the TATA box, which contains multiple repeating A and T bases. Specifically, RNA polymerase II is the RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter to initiate transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes, but only in the presence of multiple general transcription factors, which are distinct from the transcription factors that have regulatory effects, i.e., activators and repressors. In eukaryotic cells, DNA sequences that bind with activators are called enhances whereas those sequences that bind with repressors are called silencers. Transcription factors such as NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) are able to identify specific nucleotide sequence based on the base sequence (e.g., CGAGGAAAATTG for NFAT) of the binding site, which determines the arrangement of the chemical groups within that sequence that allows for specific DNA-protein interactions. The expression of transcription factors is what underlies cellular differentiation in a developing  A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. Sequencing and analysis of genomes can be done using high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. The genomes of prokaryotes are small, compact, and diverse. In contrast, the genomes of eukaryotes are larger and more complex such as having more regulatory sequences and much of its genome are made up of non-coding DNA sequences for functional RNA (Ribosomal RNA, rRNA, Transfer RNA, tRNA, and Messenger RNA, mRNA) or regulatory sequences. The genomes of various model organisms such as arabidopsis, Drosophila melanogaster, fruit fly, mice, Caenorhabditis elegans, nematodes, and yeast have been sequenced. The
A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. Sequencing and analysis of genomes can be done using high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. The genomes of prokaryotes are small, compact, and diverse. In contrast, the genomes of eukaryotes are larger and more complex such as having more regulatory sequences and much of its genome are made up of non-coding DNA sequences for functional RNA (Ribosomal RNA, rRNA, Transfer RNA, tRNA, and Messenger RNA, mRNA) or regulatory sequences. The genomes of various model organisms such as arabidopsis, Drosophila melanogaster, fruit fly, mice, Caenorhabditis elegans, nematodes, and yeast have been sequenced. The  Developmental biology, Development is the process by which a multicellular organism ( plant or animal) goes through a series of a changes, starting from a single cell, and taking on various forms that are characteristic of its life cycle. There are four key processes that underlie development: Cell fate determination, Determination, Cellular differentiation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and growth. Determination sets the developmental fate of a cell, which becomes more restrictive during development. Differentiation is the process by which specialized cells from less specialized cells such as stem cells. Stem cells are Cellular differentiation, undifferentiated or partially differentiated
Developmental biology, Development is the process by which a multicellular organism ( plant or animal) goes through a series of a changes, starting from a single cell, and taking on various forms that are characteristic of its life cycle. There are four key processes that underlie development: Cell fate determination, Determination, Cellular differentiation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and growth. Determination sets the developmental fate of a cell, which becomes more restrictive during development. Differentiation is the process by which specialized cells from less specialized cells such as stem cells. Stem cells are Cellular differentiation, undifferentiated or partially differentiated  Bacteria are a type of cell that constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few
Bacteria are a type of cell that constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few  Archaea constitute the other domain of prokaryotic cells and were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), a term that has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other three-domain system, two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat and square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this Morphology (biology), morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved in transcription (genetics), transcription and translation (biology), translation. Other aspects of archaeal biochemistry are unique, such as their reliance on ether lipids in their cell membranes, including archaeols. Archaea use more energy sources than eukaryotes: these range from organic compounds, such as sugars, to ammonia, ion, metal ions or even hydrogen, hydrogen gas. Halophile, Salt-tolerant archaea (the Haloarchaea) use sunlight as an energy source, and other species of archaea carbon fixation, fix carbon, but unlike plants and
Archaea constitute the other domain of prokaryotic cells and were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), a term that has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other three-domain system, two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat and square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this Morphology (biology), morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved in transcription (genetics), transcription and translation (biology), translation. Other aspects of archaeal biochemistry are unique, such as their reliance on ether lipids in their cell membranes, including archaeols. Archaea use more energy sources than eukaryotes: these range from organic compounds, such as sugars, to ammonia, ion, metal ions or even hydrogen, hydrogen gas. Halophile, Salt-tolerant archaea (the Haloarchaea) use sunlight as an energy source, and other species of archaea carbon fixation, fix carbon, but unlike plants and  Eukaryotes are hypothesized to have split from archaea, which was followed by their Endosymbiont, endosymbioses with bacteria (or symbiogenesis) that gave rise to mitochondria and chloroplasts, both of which are now part of modern-day eukaryotic cells. The major lineages of eukaryotes diversified in the Precambrian about 1.5 billion years ago and can be classified into eight major clades: alveolates, Excavata, excavates, stramenopiles, plants, rhizarians, amoebozoans, fungus, fungi, and animals. Five of these clades are collectively known as protists, which are mostly microscopic eukaryotic organisms that are not plants, fungi, or animals. While it is likely that protists share a Common descent, common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), protists by themselves do not constitute a separate clade as some protists may be more closely related to plants, fungi, or animals than they are to other protists. Like groupings such as
Eukaryotes are hypothesized to have split from archaea, which was followed by their Endosymbiont, endosymbioses with bacteria (or symbiogenesis) that gave rise to mitochondria and chloroplasts, both of which are now part of modern-day eukaryotic cells. The major lineages of eukaryotes diversified in the Precambrian about 1.5 billion years ago and can be classified into eight major clades: alveolates, Excavata, excavates, stramenopiles, plants, rhizarians, amoebozoans, fungus, fungi, and animals. Five of these clades are collectively known as protists, which are mostly microscopic eukaryotic organisms that are not plants, fungi, or animals. While it is likely that protists share a Common descent, common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), protists by themselves do not constitute a separate clade as some protists may be more closely related to plants, fungi, or animals than they are to other protists. Like groupings such as  Plants are mainly multicellular organisms, predominantly photosynthetic
Plants are mainly multicellular organisms, predominantly photosynthetic  Fungus, Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that digest foods outside of their bodies. They do so through a process called absorptive heterotrophy whereby they would first secrete digestive enzymes that break down large food molecules before absorbing them through their cell membranes. Many fungi are also saprobes as they are able to take in nutrients from dead organic matter and are hence, the principal decomposers in ecological systems. Some fungi are parasites by absorbing nutrients from living hosts while others are mutualists. Fungi, along with two other lineages, choanoflagellates and animals, can be grouped as opisthokonts. A synapomorphy that distinguishes fungi from other two opisthokonts is the presence of chitin in their
Fungus, Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that digest foods outside of their bodies. They do so through a process called absorptive heterotrophy whereby they would first secrete digestive enzymes that break down large food molecules before absorbing them through their cell membranes. Many fungi are also saprobes as they are able to take in nutrients from dead organic matter and are hence, the principal decomposers in ecological systems. Some fungi are parasites by absorbing nutrients from living hosts while others are mutualists. Fungi, along with two other lineages, choanoflagellates and animals, can be grouped as opisthokonts. A synapomorphy that distinguishes fungi from other two opisthokonts is the presence of chitin in their  Viruses are wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agents that Viral replication, replicate inside the
Viruses are wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agents that Viral replication, replicate inside the  Most angiosperms (or flowering plants) engage in sexual reproduction. Their flowers are organs that facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happened in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positioned so that the pollen can land on the flower's stigma. This pollination does not require an investment from the plant to provide nectar and pollen as food for pollinators.
Most angiosperms (or flowering plants) engage in sexual reproduction. Their flowers are organs that facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happened in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positioned so that the pollen can land on the flower's stigma. This pollination does not require an investment from the plant to provide nectar and pollen as food for pollinators.
 The cells in each animal body are bathed in interstitial fluid, which make up the cell's environment. This fluid and all its characteristics (e.g., temperature, ionic composition) can be described as the animal's
The cells in each animal body are bathed in interstitial fluid, which make up the cell's environment. This fluid and all its characteristics (e.g., temperature, ionic composition) can be described as the animal's  Animals are heterotrophs as they feed on other organisms to obtain energy and organic compounds. They are able to obtain food in three major ways such as targeting visible food objects, collecting tiny food particles, or depending on microbes for critical food needs. The amount of Food energy, energy stored in food can be quantified based on the amount of heat (measured in calories or joule, kilojoules) emitted when the food is burnt in the presence of oxygen. If an animal were to consume food that contains an excess amount of chemical energy, it will store most of that energy in the form of lipids for future use and some of that energy as glycogen for more immediate use (e.g., meeting the brain's energy needs). The molecules in food are chemical building blocks that are needed for growth and development. These molecules include nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Vitamins and Mineral (nutrient), minerals (e.g., calcium, magnesium, sodium, and phosphorus) are also essential. The digestive system, which typically consist of a tubular tract that extends from the mouth to the anus, is involved in the breakdown (or digestion) of food into small molecules as it travels down peristalsis, peristaltically through the Gastrointestinal tract, gut lumen shortly after it has been ingestion, ingested. These small food molecules are then Absorption (biology), absorbed into the blood from the lumen, where they are then distributed to the rest of the body as building blocks (e.g., amino acids) or sources of energy (e.g., glucose).
In addition to their digestive tracts, vertebrate animals have accessory glands such as a liver and pancreas as part of their digestive systems. The processing of food in these animals begins in the foregut, which includes the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. Mechanical digestion of food starts in the mouth with the esophagus serving as a passageway for food to reach the stomach, where it is stored and disintegrated (by the stomach's acid) for further processing. Upon leaving the stomach, food enters into the midgut, which is the first part of the intestine (or small intestine in mammals) and is the principal site of digestion and absorption. Food that does not get absorbed are stored as indigestible waste (or feces) in the hindgut, which is the second part of the intestine (or large intestine in mammals). The hindgut then completes the reabsorption of needed water and salt prior to eliminating the feces from the rectum.
Animals are heterotrophs as they feed on other organisms to obtain energy and organic compounds. They are able to obtain food in three major ways such as targeting visible food objects, collecting tiny food particles, or depending on microbes for critical food needs. The amount of Food energy, energy stored in food can be quantified based on the amount of heat (measured in calories or joule, kilojoules) emitted when the food is burnt in the presence of oxygen. If an animal were to consume food that contains an excess amount of chemical energy, it will store most of that energy in the form of lipids for future use and some of that energy as glycogen for more immediate use (e.g., meeting the brain's energy needs). The molecules in food are chemical building blocks that are needed for growth and development. These molecules include nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Vitamins and Mineral (nutrient), minerals (e.g., calcium, magnesium, sodium, and phosphorus) are also essential. The digestive system, which typically consist of a tubular tract that extends from the mouth to the anus, is involved in the breakdown (or digestion) of food into small molecules as it travels down peristalsis, peristaltically through the Gastrointestinal tract, gut lumen shortly after it has been ingestion, ingested. These small food molecules are then Absorption (biology), absorbed into the blood from the lumen, where they are then distributed to the rest of the body as building blocks (e.g., amino acids) or sources of energy (e.g., glucose).
In addition to their digestive tracts, vertebrate animals have accessory glands such as a liver and pancreas as part of their digestive systems. The processing of food in these animals begins in the foregut, which includes the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. Mechanical digestion of food starts in the mouth with the esophagus serving as a passageway for food to reach the stomach, where it is stored and disintegrated (by the stomach's acid) for further processing. Upon leaving the stomach, food enters into the midgut, which is the first part of the intestine (or small intestine in mammals) and is the principal site of digestion and absorption. Food that does not get absorbed are stored as indigestible waste (or feces) in the hindgut, which is the second part of the intestine (or large intestine in mammals). The hindgut then completes the reabsorption of needed water and salt prior to eliminating the feces from the rectum.
 In vertebrates, the muscular system consists of skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscle, cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture and circulates blood throughout the body. Together with the skeletal system, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of vertebrate animals. Skeletal muscle contractions are neurogenic as they require Synapse, synaptic input from motor neurons. A single motor neuron is able to innervate multiple muscle fibers, thereby causing the fibers to contract at the same time. Once innervated, the protein filaments within each skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction, which is explained by the sliding filament theory. The contraction produced can be described as a twitch, summation, or tetanus, depending on the frequency of action potentials. Unlike skeletal muscles, contractions of smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscles are Myogenic contraction, myogenic as they are initiated by the smooth or heart muscle cells themselves instead of a motor neuron. Nevertheless, the strength of their contractions can be modulated by input from the autonomic nervous system. The mechanisms of contraction are similar in all three muscle tissues.
In invertebrates such as earthworms and leeches, Muscle contraction#Circular and longitudinal muscles, circular and longitudinal muscles cells form the body wall of these animals and are responsible for their movement. In an earthworm that is moving through a soil, for example, contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles occur reciprocally while the Coelom#Coelomic fluid, coelomic fluid serves as a Hydrostatic skeleton, hydroskeleton by maintaining turgidity of the earthworm. Other animals such as Mollusca, mollusks, and nematodes, possess obliquely striated muscles, which contain bands of thick and thin filaments that are arranged helically rather than transversely, like in vertebrate skeletal or cardiac muscles. Advanced insects such as wasps, Fly, flies, bees, and beetles possess asynchronous muscles that constitute the flight muscles in these animals. These flight muscles are often called ''fibrillar muscles'' because they contain myofibrils that are thick and conspicuous.
In vertebrates, the muscular system consists of skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscle, cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture and circulates blood throughout the body. Together with the skeletal system, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of vertebrate animals. Skeletal muscle contractions are neurogenic as they require Synapse, synaptic input from motor neurons. A single motor neuron is able to innervate multiple muscle fibers, thereby causing the fibers to contract at the same time. Once innervated, the protein filaments within each skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction, which is explained by the sliding filament theory. The contraction produced can be described as a twitch, summation, or tetanus, depending on the frequency of action potentials. Unlike skeletal muscles, contractions of smooth muscle, smooth and cardiac muscles are Myogenic contraction, myogenic as they are initiated by the smooth or heart muscle cells themselves instead of a motor neuron. Nevertheless, the strength of their contractions can be modulated by input from the autonomic nervous system. The mechanisms of contraction are similar in all three muscle tissues.
In invertebrates such as earthworms and leeches, Muscle contraction#Circular and longitudinal muscles, circular and longitudinal muscles cells form the body wall of these animals and are responsible for their movement. In an earthworm that is moving through a soil, for example, contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles occur reciprocally while the Coelom#Coelomic fluid, coelomic fluid serves as a Hydrostatic skeleton, hydroskeleton by maintaining turgidity of the earthworm. Other animals such as Mollusca, mollusks, and nematodes, possess obliquely striated muscles, which contain bands of thick and thin filaments that are arranged helically rather than transversely, like in vertebrate skeletal or cardiac muscles. Advanced insects such as wasps, Fly, flies, bees, and beetles possess asynchronous muscles that constitute the flight muscles in these animals. These flight muscles are often called ''fibrillar muscles'' because they contain myofibrils that are thick and conspicuous.
 Most multicellular animals have nervous systems that allow them to sense from and respond to their environments. A nervous system is a network of cells that processes Sense, sensory information and generates behaviors. At the cellular level, the nervous system is defined by the presence of neurons, which are cells specialized to handle information. They can transmit or receive information at sites of contacts called synapses. More specifically, neurons can conduct nerve impulses (or action potentials) that travel along their thin fibers called axons, which can then be transmitted directly to a neighboring cell through electrical synapses or cause chemicals called
Most multicellular animals have nervous systems that allow them to sense from and respond to their environments. A nervous system is a network of cells that processes Sense, sensory information and generates behaviors. At the cellular level, the nervous system is defined by the presence of neurons, which are cells specialized to handle information. They can transmit or receive information at sites of contacts called synapses. More specifically, neurons can conduct nerve impulses (or action potentials) that travel along their thin fibers called axons, which can then be transmitted directly to a neighboring cell through electrical synapses or cause chemicals called  Animals can Reproduction, reproduce in one of two ways: Asexual reproduction#Examples in animals, asexual and Sexual reproduction#Animals, sexual. Nearly all animals engage in some form of sexual reproduction. They produce haploid gametes by meiosis. The smaller, motile gametes are Spermatozoon, spermatozoa and the larger, non-motile gametes are Egg cell, ova. These fuse to form zygotes, which develop via
Animals can Reproduction, reproduce in one of two ways: Asexual reproduction#Examples in animals, asexual and Sexual reproduction#Animals, sexual. Nearly all animals engage in some form of sexual reproduction. They produce haploid gametes by meiosis. The smaller, motile gametes are Spermatozoon, spermatozoa and the larger, non-motile gametes are Egg cell, ova. These fuse to form zygotes, which develop via  Animal development begins with the formation of a zygote that results from the fusion of a sperm and egg cell, egg during fertilization. The zygote undergoes a rapid multiple rounds of mitotic cell period of cell divisions called cleavage (embryo), cleavage, which forms a ball of similar cells called a blastula. Gastrulation occurs, whereby morphogenetic movements convert the cell mass into a three germ layers that comprise the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
The end of gastrulation signals the beginning of organogenesis, whereby the three germ layers form the internal organs of the organism. The cells of each of the three germ layers undergo Cellular differentiation, differentiation, a process where less-specialized cells become more-specialized through the expression of a specific set of genes. Cellular differentiation is influenced by extracellular signals such as growth factors that are exchanged to adjacent cells, which is called Juxtacrine signalling, juxtracrine signaling, or to neighboring cells over short distances, which is called paracrine signaling. Intracellular signals consist of a cell signaling itself (autocrine signaling), also play a role in organ formation. These signaling pathways allows for cell rearrangement and ensures that organs form at specific sites within the organism.
Animal development begins with the formation of a zygote that results from the fusion of a sperm and egg cell, egg during fertilization. The zygote undergoes a rapid multiple rounds of mitotic cell period of cell divisions called cleavage (embryo), cleavage, which forms a ball of similar cells called a blastula. Gastrulation occurs, whereby morphogenetic movements convert the cell mass into a three germ layers that comprise the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
The end of gastrulation signals the beginning of organogenesis, whereby the three germ layers form the internal organs of the organism. The cells of each of the three germ layers undergo Cellular differentiation, differentiation, a process where less-specialized cells become more-specialized through the expression of a specific set of genes. Cellular differentiation is influenced by extracellular signals such as growth factors that are exchanged to adjacent cells, which is called Juxtacrine signalling, juxtracrine signaling, or to neighboring cells over short distances, which is called paracrine signaling. Intracellular signals consist of a cell signaling itself (autocrine signaling), also play a role in organ formation. These signaling pathways allows for cell rearrangement and ensures that organs form at specific sites within the organism.
 The immune system is a network of biological processes that detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions.
Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryote, plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt to recognize pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates an immunological memory leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.
The immune system is a network of biological processes that detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions.
Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryote, plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt to recognize pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates an immunological memory leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.
 Behaviors play a central a role in animals' interaction with each other and with their environment. They are able to use their muscles to approach one another, Animal communication, vocalize, seek shelter, and migration (ecology), migrate. An animal's nervous system activates and coordinates its behaviors. Fixed action patterns, for instance, are genetically determined and stereotyped behaviors that occur without learning. These behaviors are under the control of the nervous system and can be quite elaborate. Examples include the pecking of kelp gull chicks at the red dot on their mother's beak. Other behaviors that have emerged as a result of natural selection include foraging, mating, and Altruism (biology), altruism. In addition to evolved behavior, animals have evolved the ability to learn by modifying their behaviors as a result of early individual experiences.
Behaviors play a central a role in animals' interaction with each other and with their environment. They are able to use their muscles to approach one another, Animal communication, vocalize, seek shelter, and migration (ecology), migrate. An animal's nervous system activates and coordinates its behaviors. Fixed action patterns, for instance, are genetically determined and stereotyped behaviors that occur without learning. These behaviors are under the control of the nervous system and can be quite elaborate. Examples include the pecking of kelp gull chicks at the red dot on their mother's beak. Other behaviors that have emerged as a result of natural selection include foraging, mating, and Altruism (biology), altruism. In addition to evolved behavior, animals have evolved the ability to learn by modifying their behaviors as a result of early individual experiences.
 A community is a group of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time. A biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from Mutualism (biology), mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition (biology), competition, harmful to both partners.
Every species participates as a consumer, resource, or both in consumer–resource interactions, which form the core of food chains or food webs. There are different trophic levels within any food web, with the lowest level being the primary producers (or autotrophs) such as plants and algae that convert energy and inorganic material into organic compounds, which can then be used by the rest of the community. At the next level are the heterotrophs, which are the species that obtain energy by breaking apart organic compounds from other organisms. Heterotrophs that consume plants are primary consumers (or herbivores) whereas heterotrophs that consume herbivores are secondary consumers (or carnivores). And those that eat secondary consumers are tertiary consumers and so on. Omnivore, Omnivorous heterotrophs are able to consume at multiple levels. Finally, there are decomposers that feed on the waste products or dead bodies of organisms.
On average, the total amount of energy incorporated into the biomass of a trophic level per unit of time is about one-tenth of the energy of the trophic level that it consumes. Waste and dead material used by decomposers as well as heat lost from metabolism make up the other ninety percent of energy that is not consumed by the next trophic level.
A community is a group of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time. A biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from Mutualism (biology), mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition (biology), competition, harmful to both partners.
Every species participates as a consumer, resource, or both in consumer–resource interactions, which form the core of food chains or food webs. There are different trophic levels within any food web, with the lowest level being the primary producers (or autotrophs) such as plants and algae that convert energy and inorganic material into organic compounds, which can then be used by the rest of the community. At the next level are the heterotrophs, which are the species that obtain energy by breaking apart organic compounds from other organisms. Heterotrophs that consume plants are primary consumers (or herbivores) whereas heterotrophs that consume herbivores are secondary consumers (or carnivores). And those that eat secondary consumers are tertiary consumers and so on. Omnivore, Omnivorous heterotrophs are able to consume at multiple levels. Finally, there are decomposers that feed on the waste products or dead bodies of organisms.
On average, the total amount of energy incorporated into the biomass of a trophic level per unit of time is about one-tenth of the energy of the trophic level that it consumes. Waste and dead material used by decomposers as well as heat lost from metabolism make up the other ninety percent of energy that is not consumed by the next trophic level.
 In the global ecosystem (or biosphere), matter exist as different interacting compartments, which can be biotic or abiotic as well as accessible or inaccessible, depending on their forms and locations. For example, matter from terrestrial autotrophs are both biotic and accessible to other organisms whereas the matter in rocks and minerals are abiotic and inaccessible. A biogeochemical cycle is a pathway by which specific chemical element, elements of matter are turned over or moved through the biotic (biosphere) and the abiotic (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) compartments of Earth. There are biogeochemical cycles for nitrogen cycle, nitrogen, carbon cycle, carbon, and water cycle, water. In some cycles there are ''reservoirs'' where a substance remains or is :Wiktionary:sequestered, sequestered for a long period of time.
Climate change includes both global warming driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been Climate variability and change, previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale. The largest driver of warming is the Greenhouse gas emissions, emission of greenhouse gases, of which more than 90% are carbon dioxide and methane. Fossil fuel burning (coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas) for World energy consumption, energy consumption is the main source of these emissions, with additional contributions from agriculture, deforestation, and Industrial processes#Chemical processes by main basic material, manufacturing. Temperature rise is accelerated or tempered by Climate change feedback, climate feedbacks, such as loss of Albedo, sunlight-reflecting snow and ice cover, increased water vapor (a greenhouse gas itself), and changes to Carbon sink, land and ocean carbon sinks.
In the global ecosystem (or biosphere), matter exist as different interacting compartments, which can be biotic or abiotic as well as accessible or inaccessible, depending on their forms and locations. For example, matter from terrestrial autotrophs are both biotic and accessible to other organisms whereas the matter in rocks and minerals are abiotic and inaccessible. A biogeochemical cycle is a pathway by which specific chemical element, elements of matter are turned over or moved through the biotic (biosphere) and the abiotic (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) compartments of Earth. There are biogeochemical cycles for nitrogen cycle, nitrogen, carbon cycle, carbon, and water cycle, water. In some cycles there are ''reservoirs'' where a substance remains or is :Wiktionary:sequestered, sequestered for a long period of time.
Climate change includes both global warming driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been Climate variability and change, previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale. The largest driver of warming is the Greenhouse gas emissions, emission of greenhouse gases, of which more than 90% are carbon dioxide and methane. Fossil fuel burning (coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas) for World energy consumption, energy consumption is the main source of these emissions, with additional contributions from agriculture, deforestation, and Industrial processes#Chemical processes by main basic material, manufacturing. Temperature rise is accelerated or tempered by Climate change feedback, climate feedbacks, such as loss of Albedo, sunlight-reflecting snow and ice cover, increased water vapor (a greenhouse gas itself), and changes to Carbon sink, land and ocean carbon sinks.