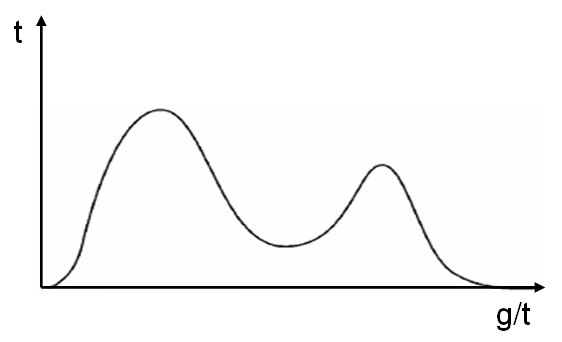

In
statistics, a multimodal distribution is a
probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomeno ...
with more than one
mode. These appear as distinct peaks (local maxima) in the
probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) c ...
, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Categorical, continuous, and discrete data can all form multimodal distributions. Among univariate analyses, multimodal distributions are commonly bimodal.
Terminology
When the two modes are unequal the larger mode is known as the major mode and the other as the minor mode. The least frequent value between the modes is known as the
antimode. The difference between the major and minor modes is known as the
amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of a ...
. In time series the major mode is called the
acrophase and the antimode the
batiphase.
Galtung's classification
Galtung introduced a classification system (AJUS) for distributions:
*A: unimodal distribution – peak in the middle
*J: unimodal – peak at either end
*U: bimodal – peaks at both ends
*S: bimodal or multimodal – multiple peaks
This classification has since been modified slightly:
*J: (modified) – peak on right
*L: unimodal – peak on left
*F: no peak (flat)
Under this classification bimodal distributions are classified as type S or U.
Examples
Bimodal distributions occur both in mathematics and in the natural sciences.
Probability distributions
Important bimodal distributions include the
arcsine distribution
In probability theory, the arcsine distribution is the probability distribution whose cumulative distribution function involves the arcsine and the square root:
:F(x) = \frac\arcsin\left(\sqrt x\right)=\frac+\frac
for 0 ≤ ''x'' ...
and the
beta distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the beta distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval , 1in terms of two positive parameters, denoted by ''alpha'' (''α'') and ''beta'' (''β''), that appear as ...
(iff both parameters are less than 1). Others include the
U-quadratic distribution.
The ratio of two normal distributions is also bimodally distributed. Let
:
where ''a'' and ''b'' are constant and ''x'' and ''y'' are distributed as normal variables with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. ''R'' has a known density that can be expressed as a
confluent hypergeometric function
In mathematics, a confluent hypergeometric function is a solution of a confluent hypergeometric equation, which is a degenerate form of a hypergeometric differential equation where two of the three regular singularities merge into an irregular ...
.
The distribution of the
reciprocal
Reciprocal may refer to:
In mathematics
* Multiplicative inverse, in mathematics, the number 1/''x'', which multiplied by ''x'' gives the product 1, also known as a ''reciprocal''
* Reciprocal polynomial, a polynomial obtained from another pol ...
of a ''t'' distributed random variable is bimodal when the degrees of freedom are more than one. Similarly the reciprocal of a normally distributed variable is also bimodally distributed.
A ''t'' statistic generated from data set drawn from a
Cauchy distribution
The Cauchy distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy, is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among physicists, as the Lorentz distribution (after Hendrik Lorentz), Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, Lorentz(ian) fu ...
is bimodal.
Occurrences in nature
Examples of variables with bimodal distributions include the time between eruptions of certain
geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only ...
s, the
color of galaxies, the size of worker
weaver ants, the age of incidence of
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition w ...
, the speed of inactivation of the drug
isoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. For ...
in US adults, the absolute magnitude of
nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
e, and the
circadian activity patterns of those
crepuscular
In zoology, a crepuscular animal is one that is active primarily during the twilight period, being matutinal, vespertine, or both. This is distinguished from diurnal and nocturnal behavior, where an animal is active during the hours of dayli ...
animals that are active both in morning and evening twilight. In fishery science multimodal length distributions reflect the different year classes and can thus be used for age distribution- and growth estimates of the fish population. Sediments are usually distributed in a bimodal fashion. When sampling mining galleries crossing either the host rock and the mineralized veins, the distribution of geochemical variables would be bimodal. Bimodal distributions are also seen in traffic analysis, where traffic peaks in during the AM rush hour and then again in the PM rush hour. This phenomenon is also seen in daily water distribution, as water demand, in the form of showers, cooking, and toilet use, generally peak in the morning and evening periods.
Econometrics
In
econometric
Econometrics is the application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships. M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8� ...
models, the parameters may be bimodally distributed.
Origins
Mathematical
A bimodal distribution most commonly arises as a mixture of two different
unimodal
In mathematics, unimodality means possessing a unique mode. More generally, unimodality means there is only a single highest value, somehow defined, of some mathematical object.
Unimodal probability distribution
In statistics, a unimodal pr ...
distributions (i.e. distributions having only one mode). In other words, the bimodally distributed random variable X is defined as
with probability
or
with probability
where ''Y'' and ''Z'' are unimodal random variables and
is a mixture coefficient.
Mixtures with two distinct components need not be bimodal and two component mixtures of unimodal component densities can have more than two modes. There is no immediate connection between the number of components in a mixture and the number of modes of the resulting density.
Particular distributions
Bimodal distributions, despite their frequent occurrence in data sets, have only rarely been studied. This may be because of the difficulties in estimating their parameters either with frequentist or Bayesian methods. Among those that have been studied are
* Bimodal exponential distribution.
* Alpha-skew-normal distribution.
* Bimodal skew-symmetric normal distribution.
* A mixture of
Conway-Maxwell-Poisson distributions has been fitted to bimodal count data.
Bimodality also naturally arises in the
cusp catastrophe distribution.
Biology
In biology five factors are known to contribute to bimodal distributions of population sizes:
*the initial distribution of individual sizes
*the distribution of growth rates among the individuals
*the size and time dependence of the growth rate of each individual
* mortality rates that may affect each size class differently
* the DNA methylation in human and mouse genome.
The bimodal distribution of sizes of
weaver ant workers arises due to existence of two distinct classes of workers, namely major workers and minor workers.
The
distribution of fitness effects
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
of mutations for both whole
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
s and individual
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s is also frequently found to be bimodal with most
mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
being either neutral or lethal with relatively few having intermediate effect.
General properties
A mixture of two unimodal distributions with differing means is not necessarily bimodal. The combined distribution of heights of men and women is sometimes used as an example of a bimodal distribution, but in fact the difference in mean heights of men and women is too small relative to their
standard deviations to produce bimodality.
Bimodal distributions have the peculiar property that – unlike the unimodal distributions – the mean may be a more robust sample estimator than the median.
This is clearly the case when the distribution is U shaped like the arcsine distribution. It may not be true when the distribution has one or more long tails.
Moments of mixtures
Let
:
where ''g''
''i'' is a probability distribution and ''p'' is the mixing parameter.
The moments of ''f''(''x'') are
:
:

 In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a
In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a  In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a
In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a