|
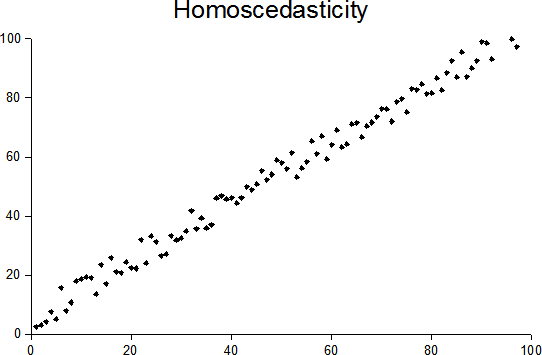
Homoscedastic
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical tests of significance that assume that the modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is still unbiased in the presence of heteroscedasticity, it is inefficient and generalized least squares should be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical tests of significance that assume that the modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is still unbiased in the presence of heteroscedasticity, it is inefficient and generalized least squares should be used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, where the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the ''t''-test beyond two means. In other words, the ANOVA is used to test the difference between two or more means. History While the analysis of variance reached fruition in the 20th century, antecedents extend centuries into the past according to Stigler. These include hypothesis testing, the partitioning of sums of squares, experimental techniques and the additive model. Laplace was performing hypothesis testi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauss–Markov Theorem
In statistics, the Gauss–Markov theorem (or simply Gauss theorem for some authors) states that the ordinary least squares (OLS) estimator has the lowest sampling variance within the class of linear unbiased estimators, if the errors in the linear regression model are uncorrelated, have equal variances and expectation value of zero. The errors do not need to be normal, nor do they need to be independent and identically distributed (only uncorrelated with mean zero and homoscedastic with finite variance). The requirement that the estimator be unbiased cannot be dropped, since biased estimators exist with lower variance. See, for example, the James–Stein estimator (which also drops linearity), ridge regression, or simply any degenerate estimator. The theorem was named after Carl Friedrich Gauss and Andrey Markov, although Gauss' work significantly predates Markov's. But while Gauss derived the result under the assumption of independence and normality, Markov reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinary Least Squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the principle of least squares: minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed dependent variable (values of the variable being observed) in the input dataset and the output of the (linear) function of the independent variable. Geometrically, this is seen as the sum of the squared distances, parallel to the axis of the dependent variable, between each data point in the set and the corresponding point on the regression surface—the smaller the differences, the better the model fits the data. The resulting estimator can be expressed by a simple formula, especially in the case of a simple linear regression, in which there is a single regressor on the right side of the regression equation. The OLS estimator is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Least Squares
In statistics, generalized least squares (GLS) is a technique for estimating the unknown parameters in a linear regression model when there is a certain degree of correlation between the residuals in a regression model. In these cases, ordinary least squares and weighted least squares can be statistically inefficient, or even give misleading inferences. GLS was first described by Alexander Aitken in 1936. Method outline In standard linear regression models we observe data \_ on ''n'' statistical units. The response values are placed in a vector \mathbf = \left( y_, \dots, y_ \right)^, and the predictor values are placed in the design matrix \mathbf = \left( \mathbf_^, \dots, \mathbf_^ \right)^, where \mathbf_ = \left( 1, x_, \dots, x_ \right) is a vector of the ''k'' predictor variables (including a constant) for the ''i''th unit. The model forces the conditional mean of \mathbf given \mathbf to be a linear function of \mathbf, and assumes the conditional variance of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals In Statistics
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its " true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the '' estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression Analysis
In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable (often called the 'outcome' or 'response' variable, or a 'label' in machine learning parlance) and one or more independent variables (often called 'predictors', 'covariates', 'explanatory variables' or 'features'). The most common form of regression analysis is linear regression, in which one finds the line (or a more complex linear combination) that most closely fits the data according to a specific mathematical criterion. For example, the method of ordinary least squares computes the unique line (or hyperplane) that minimizes the sum of squared differences between the true data and that line (or hyperplane). For specific mathematical reasons (see linear regression), this allows the researcher to estimate the conditional expectation (or population average value) of the dependent variable when the independent variables take on a given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Memorial Prize For Economics
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered by the Nobel Foundation. Although not one of the five Nobel Prizes which were established by Alfred Nobel's will in 1895, it is commonly referred to as the Nobel Prize in Economics. The winners of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences are chosen in a similar way, are announced along with the Nobel Prize recipients, and the prize is presented at the Nobel Prize Award Ceremony. The award was established in 1968 by an endowment "in perpetuity" from Sweden's central bank, Sveriges Riksbank, to commemorate the bank's 300th anniversary. It is administered and referred to along with the Nobel Prizes by the Nobel Foundation. Laureates in the Memorial Prize in Economics are selected by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Best Linear Unbiased Estimator
Best or The Best may refer to: People * Best (surname), people with the surname Best * Best (footballer, born 1968), retired Portuguese footballer Companies and organizations * Best & Co., an 1879–1971 clothing chain * Best Lock Corporation, a lock manufacturer * Best Manufacturing Company, a farm machinery company * Best Products, a chain of catalog showroom retail stores * Brihanmumbai Electric Supply and Transport, a public transport and utility provider * Best High School (other) Acronyms * Berkeley Earth Surface Temperature, a project to assess global temperature records * BEST Robotics, a student competition * BioEthanol for Sustainable Transport * Bootstrap error-adjusted single-sample technique, a statistical method * Bringing Examination and Search Together, a European Patent Office initiative * Bronx Environmental Stewardship Training, a program of the Sustainable South Bronx organization * Smart BEST, a Japanese experimental train * Brihanmumbai Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scedastic Function
In probability theory and statistics, a conditional variance is the variance of a random variable given the value(s) of one or more other variables. Particularly in econometrics, the conditional variance is also known as the scedastic function or skedastic function. Conditional variances are important parts of autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity (ARCH) models. Definition The conditional variance of a random variable ''Y'' given another random variable ''X'' is :\operatorname(Y, X) = \operatorname\Big(\big(Y - \operatorname(Y\mid X)\big)^\mid X\Big). The conditional variance tells us how much variance is left if we use \operatorname(Y\mid X) to "predict" ''Y''. Here, as usual, \operatorname(Y\mid X) stands for the conditional expectation of ''Y'' given ''X'', which we may recall, is a random variable itself (a function of ''X'', determined up to probability one). As a result, \operatorname(Y, X) itself is a random variable (and is a function of ''X''). Explanation, rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |