Berlin is
the capital
''The Capital'' (also known as ''Capital Gazette'' as its online nameplate and informally), the Sunday edition is called ''The Sunday Capital'', is a daily newspaper published by Capital Gazette Communications in Annapolis, Maryland, to serv ...
and largest city of
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, both by area and
by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
's
most populous city, as measured by population within city limits
having gained this status after the United Kingdom's, and thus
London's
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major se ...
,
departure from the European Union. Simultaneously, the city is one of the
states of Germany, and is the
third smallest state in the country in terms of area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
, and Brandenburg's capital
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.5 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany.
The
Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million
inhabitants
Domicile is relevant to an individual's "personal law," which includes the law that governs a person's status and their property. It is independent of a person's nationality. Although a domicile may change from time to time, a person has only one ...
and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
after the
Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region (german: Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr) is the largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the region covers ...
region, and the
fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union.
Berlin was built along the banks of the
Spree river, which flows into the
Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
in the western borough of
Spandau
Spandau () is the westernmost of the 12 boroughs () of Berlin, situated at the confluence of the Havel and Spree rivers and extending along the western bank of the Havel. It is the smallest borough by population, but the fourth largest by la ...
. The city incorporates lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs, the largest of which is
Müggelsee
The Müggelsee (), also known as the Großer Müggelsee, is a natural lake in the eastern suburbs of Berlin, the capital city of Germany. It is the largest of the Berlin lakes by area, with an area of , a length of
The lake is in the Berlin d ...
. About one-third of the city's area is composed of forests,
parks and gardens, rivers, canals, and lakes.
First documented in the 13th century
and at the crossing of two important historic
trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sin ...
s,
Berlin was designated the capital of the
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
(1417–1701),
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: ...
(1701–1918),
German Empire (1871–1918),
Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also r ...
(1919–1933), and
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
(1933–1945). Berlin has served as a scientific, artistic, and philosophical hub during the
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
,
Neoclassicism, and the
German revolutions of 1848–1849
The German revolutions of 1848–1849 (), the opening phase of which was also called the March Revolution (), were initially part of the Revolutions of 1848 that broke out in many European countries. They were a series of loosely coordinated pro ...
. During the ''
Gründerzeit
(; "founders' period") was the economic phase in 19th-century Germany and Austria before the great stock market crash of 1873. In Central Europe, the age of industrialisation had been taking place since the 1840s. That period is not precisely ...
,'' an industrialization-induced economic boom triggered a rapid population increase in Berlin.
1920s Berlin
The Golden Twenties was a particular vibrant period in the history of Berlin. After the Greater Berlin Act the city became the third largest municipality in the world and experienced its heyday as a major world city. It was known for its leadersh ...
was the third-largest city in the world by population.
After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and following Berlin's occupation, the city was split into
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under m ...
and
East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 u ...
, divided by the
Berlin Wall. East Berlin was declared the capital of East Germany, while
Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ru ...
became the West German capital. Following
German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany. Due to its geographic location and history, Berlin has been called "the heart of Europe".
The
economy of Berlin is based on
high tech
High technology (high tech), also known as advanced technology (advanced tech) or exotechnology, is technology that is at the cutting edge: the highest form of technology available. It can be defined as either the most complex or the newest tec ...
and the
service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector ( raw materials) and the sec ...
, encompassing a diverse range of
creative industries,
startup companies
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an Entrepreneurship, entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses t ...
, research facilities, and media corporations.
Berlin serves as a continental hub for air and rail traffic and has a complex public transportation network.
Tourism in Berlin
Berlin grew out of the historical city centre, the Nikolai quarter and its adjacent town of Cölln, both situated along the River Spree. It expanded its territories with areas such as Dorotheenstadt and Friedrichstadt. The creation of Greater ...
makes the city a popular global destination. Significant industries include information technology, the
healthcare industry
The healthcare industry (also called the medical industry or health economy) is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, ...
,
biomedical engineering
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare purposes (e.g., diagnostic or therapeutic). BME is also traditionally logical sciences ...
,
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, the
automotive industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % su ...
, and
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
.
Berlin is home to several universities such as the
Humboldt University of Berlin
The Humboldt University of Berlin (german: link=no, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a public university, public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin, Germany.
The university was established ...
, the
Technical University of Berlin
The Technical University of Berlin (official name both in English and german: link=no, Technische Universität Berlin, also known as TU Berlin and Berlin Institute of Technology) is a public research university located in Berlin, Germany. It was ...
, the
Berlin University of the Arts
The Universität der Künste Berlin (UdK; also known in English as the Berlin University of the Arts), situated in Berlin, Germany, is the largest art school in Europe. It is a public art and design school, and one of the four research universit ...
and the
Free University of Berlin
The Free University of Berlin (, often abbreviated as FU Berlin or simply FU) is a public university, public research university in Berlin, Germany. It is consistently ranked among Germany's best universities, with particular strengths in poli ...
. The
Berlin Zoological Garden
The Berlin Zoological Garden (german: link=no, Zoologischer Garten Berlin) is the oldest surviving and best-known zoo in Germany. Opened in 1844, it covers and is located in Berlin's Tiergarten. With about 1,380 different species and over 20, ...
is the most visited zoo in Europe.
Babelsberg Studio
Babelsberg Film Studio (german: Filmstudio Babelsberg), located in Potsdam-Babelsberg outside Berlin, Germany, is the second oldest large-scale film studio in the world only preceded by the Danish Nordisk Film (est. 1906), producing films since ...
is the world's first large-scale movie studio complex and the
list of films set in Berlin is long.
Berlin is also home to three
World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Museum Island
The Museum Island (german: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Euro ...
, the
Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin, and the
Berlin Modernism Housing Estates.
Other landmarks include the
Brandenburg Gate
The Brandenburg Gate (german: Brandenburger Tor ) is an 18th-century neoclassical monument in Berlin, built on the orders of Prussian king Frederick William II after restoring the Orangist power by suppressing the Dutch popular unrest. One ...
, the
Reichstag building
The Reichstag (, ; officially: – ; en, Parliament) is a historic government building in Berlin which houses the Bundestag, the lower house of Germany's parliament.
It was constructed to house the Imperial Diet (german: Reichstag) of the ...
,
Potsdamer Platz
Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag ( German Parliament Building), and close to the southeast corn ...
, the
Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe
The Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe (german: Denkmal für die ermordeten Juden Europas), also known as the Holocaust Memorial (German: ''Holocaust-Mahnmal''), is a memorial in Berlin to the Jewish victims of the Holocaust, designed by arc ...
, and the
Berlin Wall Memorial
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituen ...
. Berlin has numerous museums, galleries, and libraries.
History
Etymology
Berlin lies in northeastern Germany. Most of the cities and villages in northeastern Germany bear
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavs, Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic language, Proto ...
-derived names. Typical
Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
for place name
suffixes of Slavic origin are and ,
prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particu ...
es are ' and '. The name ''Berlin'' has its roots in the language of the
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic la ...
, and may be related to the Old
Polabian stem ("swamp").
Of Berlin's
twelve boroughs, five bear a Slavic-derived name:
Pankow
Pankow () is the most populous and the second-largest borough by area of Berlin. In Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, it was merged with the former boroughs of Prenzlauer Berg and Weißensee; the resulting borough retained the name Pankow. ...
,
Steglitz-Zehlendorf
Steglitz-Zehlendorf () is the sixth borough of Berlin, formed in Berlin's 2001 administrative reform by merging the former boroughs of Steglitz and Zehlendorf.
Home to Free University of Berlin, the Berlin Botanical Garden, and a variety of m ...
,
Marzahn-Hellersdorf,
Treptow-Köpenick
Treptow-Köpenick () is the ninth borough of Berlin, Germany, formed in Berlin's 2001 administrative reform by merging the former boroughs of Treptow and Köpenick.
Overview
Among Berlin's boroughs it is the largest by area with the lowest po ...
, and
Spandau
Spandau () is the westernmost of the 12 boroughs () of Berlin, situated at the confluence of the Havel and Spree rivers and extending along the western bank of the Havel. It is the smallest borough by population, but the fourth largest by la ...
. Of Berlin's ninety-six neighborhoods, twenty-two bear a Slavic-derived name:
Altglienicke,
Alt-Treptow,
Britz,
Buch
Buch (the German word for book or a modification of the German word '' Buche'' for beech) may refer to:
People
* Buch (surname), a list of people with the surname Buch Geography
;Germany:
* Buch am Wald, a town in the district of Ansbach, Bavaria ...
,
Buckow,
Gatow
Gatow (), a district of south-western Berlin is located west of the ''Havelsee'' lake and has forested areas within its boundaries. It is within the borough of Spandau. On 31 December 2002, it had 5,532 inhabitants.
History
Gatow's existence was ...
,
Karow,
Kladow
Kladow () is the southernmost district of the Borough of Spandau in Berlin, Germany.
Geography
Located approximately 17 Km from central Berlin (Charlottenburg), the district of Kladow is bordered by the District of Gatow to the north, by the Hav ...
,
Köpenick
Köpenick () is a historic town and locality (''Ortsteil'') in Berlin, situated at the confluence of the rivers Dahme and Spree in the south-east of the German capital. It was formerly known as Copanic and then Cöpenick, only officially adop ...
,
Lankwitz,
Lübars,
Malchow
Malchow () is a municipality in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany.
Geography
It is situated on the river Elde, 25,5 km west of Waren, and 35 km north of Wittstock.
History
The ...
,
Marzahn,
Pankow
Pankow () is the most populous and the second-largest borough by area of Berlin. In Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, it was merged with the former boroughs of Prenzlauer Berg and Weißensee; the resulting borough retained the name Pankow. ...
,
Prenzlauer Berg
Prenzlauer Berg () is a locality of Berlin, forming the southerly and most urban district of the borough of Pankow. From its founding in 1920 until 2001, Prenzlauer Berg was a district of Berlin in its own right. However, that year it was incorp ...
,
Rudow,
Schmöckwitz
Schmöckwitz () is a German locality (''Ortsteil'') within the Berlin borough (''Bezirk'') of Treptow-Köpenick. Until 2001 it was part of the former borough of Köpenick.
History
The locality was founded in 1375 with the name of Smekewitz. In 19 ...
,
Spandau
Spandau () is the westernmost of the 12 boroughs () of Berlin, situated at the confluence of the Havel and Spree rivers and extending along the western bank of the Havel. It is the smallest borough by population, but the fourth largest by la ...
,
Stadtrandsiedlung Malchow
Stadtrandsiedlung Malchow () is a German locality (''Ortsteil'') within the Berlin borough (''Bezirk'') of Pankow. Until 2001 it was part of the former Weißensee borough.
History
The history of this locality is related to the neighboring quarte ...
,
Steglitz
Steglitz () is a locality of the Steglitz-Zehlendorf borough in Southwestern Berlin, the capital of Germany. is a Slavic name for the European goldfinch, similar to the German .
Steglitz was also a borough from 1920 to 2000. It contained th ...
,
Tegel
Tegel () is a locality (''Ortsteil'') in the Berlin borough of Reinickendorf on the shore of Lake Tegel. The Tegel locality, the second largest in area (after Köpenick) of the 96 Berlin districts, also includes the neighbourhood of ''Saatwinke ...
and
Zehlendorf.
Prehistory of Berlin
The earliest human settlements in the area of modern Berlin are dated around 60,000 BC. A deer mask, dated to 9,000 BC, is attributed to the
Maglemosian culture. In 2,000 BC dense human settlements along the
Spree and
Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
rivers gave rise to the
Lusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1700 BC – 500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III (early ...
. Starting around 500 BC Germanic tribes settled in a number of villages in the higher situated areas of today's Berlin. After the
Semnones
The Semnones were a Germanic and specifically a Suevian people, who were settled between the Elbe and the Oder in the 1st century when they were described by Tacitus in ''Germania'':
"The Semnones give themselves out to be the most ancient and ...
left around 200 AD, the
Burgundians followed. In the 7th century Slavic tribes, the later known
Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
and
Sprevane, reached the region.
12th century to 16th century
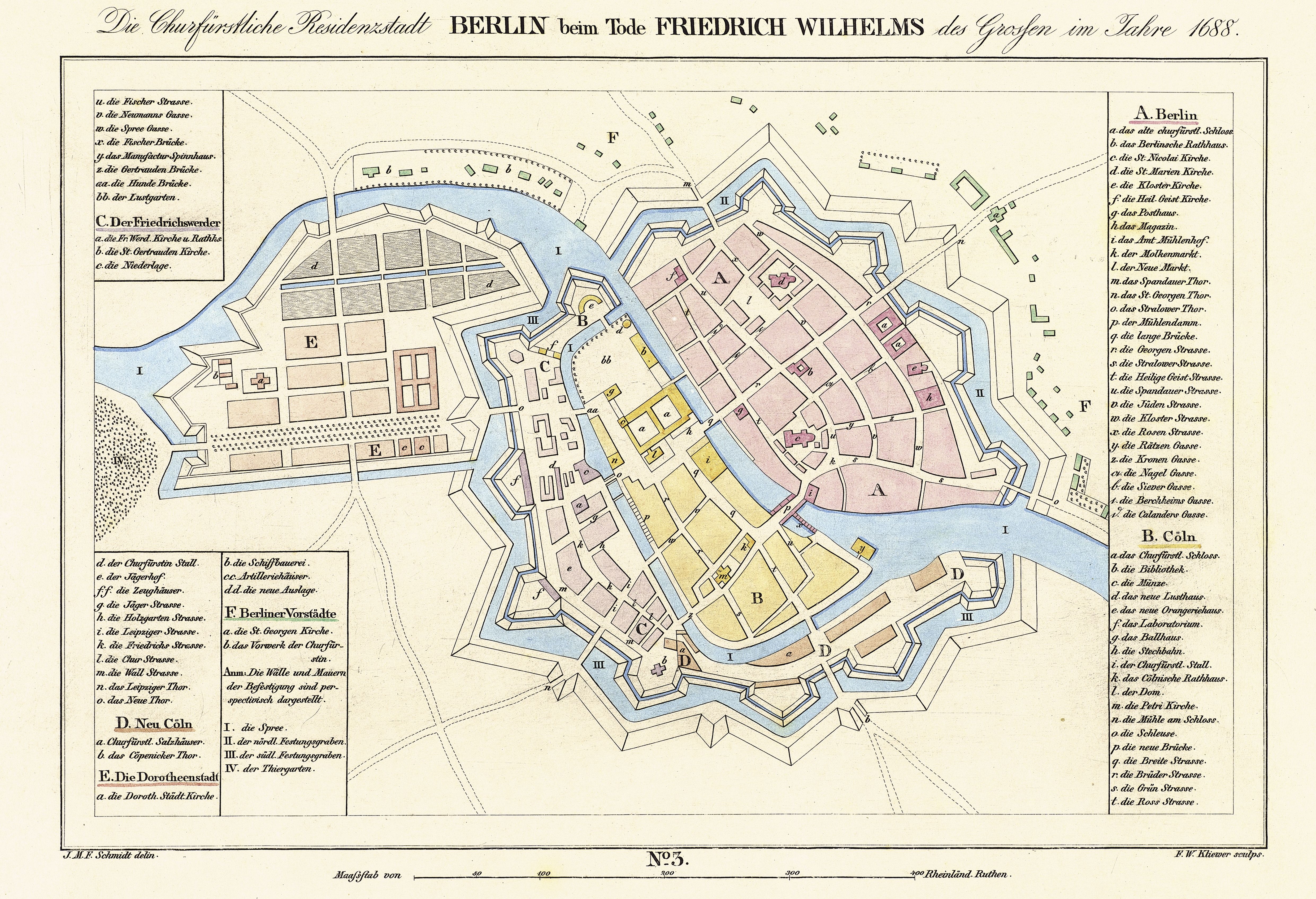

In the 12th century the region came under German rule as part of the
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
, founded by
Albert the Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142.
Life
Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Bal ...
in 1157. Early evidence of middle age settlements in the area of today's Berlin are remnants of a
house foundation dated 1270 to 1290, found in excavations in
Berlin Mitte. The first written records of towns in the area of present-day Berlin date from the late 12th century.
Spandau
Spandau () is the westernmost of the 12 boroughs () of Berlin, situated at the confluence of the Havel and Spree rivers and extending along the western bank of the Havel. It is the smallest borough by population, but the fourth largest by la ...
is first mentioned in 1197 and
Köpenick
Köpenick () is a historic town and locality (''Ortsteil'') in Berlin, situated at the confluence of the rivers Dahme and Spree in the south-east of the German capital. It was formerly known as Copanic and then Cöpenick, only officially adop ...
in 1209. 1237 is considered the founding date of the city.
The two towns over time formed close economic and social ties, and profited from the
staple right
The staple right, also translated stacking right or storage right, both from the Dutch language, Dutch ''stapelrecht'', was a medieval right accorded to certain ports, the staple ports. It required merchant barges or ships to unload their goods at ...
on the two important
trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sin ...
s, one was known as ''
Via Imperii
Via Imperii (Imperial Road) was one of the most important of a class of roads known collectively as imperial roads (''german: Reichsstraßen'') of the Holy Roman Empire. This old trade route ran in a south–north direction from Venice on the Ad ...
'', and the other trade route reached from Bruges to Novgorod.
In 1307 the two towns formed an alliance with a common external policy, their internal administrations still being separated.
[Stöver B. ''Geschichte Berlins'' Verlag CH Beck 2010 ]
Members of the Hohenzollern family ruled in Berlin until 1918, first as electors of Brandenburg, then as kings of Prussia, and eventually as German emperors. In 1443, Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg, Frederick II Irontooth started the construction of a new Stadtschloss, Berlin, royal palace in the twin city Berlin-Cölln. The protests of the town citizens against the building culminated in 1448, in the "Berlin Indignation" ("Berliner Unwille"). Officially, the Berlin-Cölln palace became permanent residence of the Brandenburg electors of the Hohenzollerns from 1486, when John Cicero, Elector of Brandenburg, John Cicero came to power. Berlin-Cölln, however, had to give up its status as a free Hanseatic League city. In 1539, the electors and the city officially became Lutheran.
17th to 19th centuries
The Thirty Years' War between 1618 and 1648 devastated Berlin. One third of its houses were damaged or destroyed, and the city lost half of its population. Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg, Frederick William, known as the "Great Elector", who had succeeded his father George William, Elector of Brandenburg, George William as ruler in 1640, initiated a policy of promoting immigration and religious tolerance.
With the Edict of Potsdam in 1685, Frederick William offered asylum to the French Huguenots.
By 1700, approximately 30 percent of Berlin's residents were French, because of the Huguenot immigration.
Many other immigrants came from Bohemia, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland, and Archbishopric of Salzburg, Salzburg.

Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: ...
, as Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg, crowned himself as king Frederick I of Prussia, Frederick I in Prussia. Berlin became the capital of the new Kingdom, replacing Königsberg. This was a successful attempt to centralise the capital in the very far-flung state, and it was the first time the city began to grow. In 1709, Berlin merged with the four cities of Cölln, Friedrichswerder, Friedrichstadt and Dorotheenstadt under the name Berlin, "Haupt- und Residenzstadt Berlin".
In 1740, Frederick II, known as Frederick the Great (1740–1786), came to power.
Under the rule of Frederick II, Berlin became a center of the Enlightenment, but also, was briefly occupied during the Seven Years' War by the Russian army.
Following France's victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition, Napoleon Bonaparte Fall of Berlin (1806), marched into Berlin in 1806, but granted self-government to the city.
In 1815, the city became part of the new Province of Brandenburg.
The Industrial Revolution transformed Berlin during the 19th century; the city's economy and population expanded dramatically, and it became the main railway hub and economic center of Germany. Additional suburbs soon developed and increased the area and population of Berlin. In 1861, neighboring suburbs including Wedding (Berlin), Wedding, Moabit and several others were incorporated into Berlin.
In 1871, Berlin became capital of the newly founded
German Empire.
In 1881, it became a city district separate from Brandenburg.
20th to 21st centuries
In the early 20th century, Berlin had become a fertile ground for the German Expressionism, German Expressionist movement.
In fields such as architecture, painting and cinema new forms of artistic styles were invented. At the end of the First World War in 1918, a Weimar Republic, republic was proclaimed by Philipp Scheidemann at the Reichstag (building), Reichstag building. In 1920, the Greater Berlin Act incorporated dozens of suburban cities, villages, and estates around Berlin into an expanded city. The act increased the area of Berlin from . The population almost doubled, and Berlin had a population of around four million. During the Weimar culture, Weimar era, Berlin underwent political unrest due to economic uncertainties but also became a renowned center of the Roaring Twenties. The metropolis experienced its heyday as a major world capital and was known for its leadership roles in science, technology, arts, the humanities, city planning, film, higher education, government, and industries. Albert Einstein rose to public prominence during his years in Berlin, being awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
In 1933, Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party Nazis came to power, came to power. Hitler was inspired by the architecture he had experienced in Vienna, and he wished for a German Empire with a capital city that had a monumental ensemble. The National Socialist regime embarked on monumental construction projects in Berlin as a way to express their power and authority through Nazi architecture, architecture. Adolf Hitler and Albert Speer developed architectural concepts for the conversion of the city into Germania (city), World Capital Germania; these were never implemented.
NSDAP rule diminished Berlin's Jewish community from 160,000 (one-third of all Jews in the country) to about 80,000 due to emigration between 1933 and 1939. After Kristallnacht in 1938, thousands of the city's Jews were imprisoned in the nearby Sachsenhausen concentration camp. Starting in early 1943, many were deported to Jewish ghettos established by Nazi Germany, ghettos like Łódź Ghetto, Łódź, and to concentration camp, concentration and extermination camps such as Auschwitz.
Berlin hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics for which the Olympiastadion (Berlin), Olympic stadium was built.

During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Berlin was the location of multiple Nazi prisons, Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour camps, 17 subcamps of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp for men and women, including teenagers, of various nationalities, including Polish, Jewish, French, Belgian, Czechoslovak, Russian, Ukrainian, Romani, Dutch, Greek, Norwegian, Spanish, Luxembourgish, German, Austrian, Italian, Yugoslavian, Bulgarian, Hungarian, a camp for Sinti and Romani people (see ''Romani Holocaust''), and the Stalag III-D German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war camp for Allied POWs of various nationalities.
During World War II, large parts of Berlin were destroyed during Allied air raids and the 1945 Battle of Berlin. The Allies dropped 67,607 tons of bombs on the city, destroying 6,427 acres of the built-up area. Around 125,000 civilians were killed. After the end of World War II in Europe in May 1945, Berlin received large numbers of refugees from the Eastern provinces. The victorious powers divided the city into four sectors, analogous to Allied-occupied Germany the sectors of the Allies of World War II (the United States, the United Kingdom, and France) formed
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under m ...
, while the Soviet Union formed
East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 u ...
.
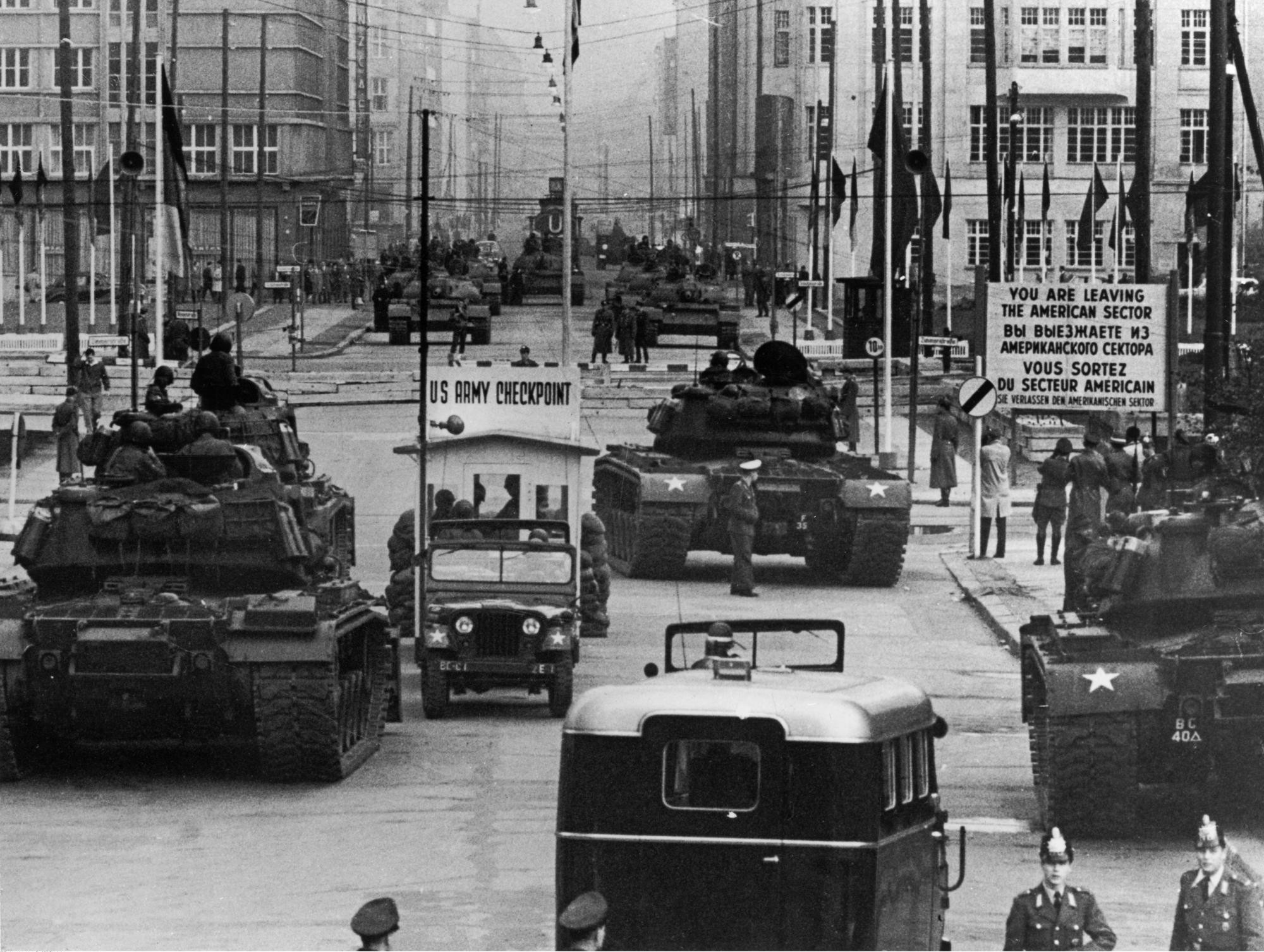


All four Allies of World War II shared administrative responsibilities for Berlin. However, in 1948, when the Western Allies extended the currency reform in the Western zones of Germany to the three western sectors of Berlin, the Soviet Union imposed the Berlin Blockade on the access routes to and from West Berlin, which lay entirely inside Soviet-controlled territory. The Berlin airlift, conducted by the three western Allies, overcame this blockade by supplying food and other supplies to the city from June 1948 to May 1949. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany was founded in West Germany and eventually included all of the American, British and French zones, excluding those three countries' zones in Berlin, while the Marxist–Leninist East Germany, German Democratic Republic was proclaimed in East Germany. West Berlin officially remained an occupied city, but it politically was aligned with the Federal Republic of Germany despite West Berlin's geographic isolation. Airline service to West Berlin was granted only to American, British and French airlines.

The founding of the two German states increased Cold War tensions. West Berlin was surrounded by East German territory, and East Germany proclaimed the Eastern part as its capital, a move the western powers did not recognize. East Berlin included most of the city's historic center. The West German government established itself in
Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ru ...
. In 1961, East Germany began to build the
Berlin Wall around West Berlin, and events escalated to a tank standoff at Checkpoint Charlie. West Berlin was now de facto a part of West Germany with a unique legal status, while East Berlin was de facto a part of East Germany. John F. Kennedy gave his "''Ich bin ein Berliner''" speech on 26 June 1963, in front of the Schöneberg city hall, located in the city's western part, underlining the US support for West Berlin. Berlin was completely divided. Although it was possible for Westerners to pass to the other side through strictly controlled checkpoints, for most Easterners, travel to West Berlin or West Germany was prohibited by the government of East Germany. In 1971, a Four Power Agreement on Berlin, Four-Power agreement guaranteed access to and from West Berlin by car or train through East Germany.
In 1989, with the end of the Cold War and pressure from the East German population, the Fall of the Berlin Wall, Berlin Wall fell on 9 November and was subsequently mostly demolished. Today, the East Side Gallery preserves a large portion of the wall. On 3 October 1990, the two parts of Germany were German reunification, reunified as the Federal Republic of Germany, and Berlin again became a reunified city. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, the city experienced significan
urban developmentand still impacts urban planning decisions.
Walter Momper, the mayor of West Berlin, became the first mayor of the reunified city in the interim. City-wide elections in December 1990 resulted in the first "all Berlin" mayor being elected to take office in January 1991, with the separate offices of mayors in East and West Berlin expiring by that time, and Eberhard Diepgen (a former mayor of West Berlin) became the first elected mayor of a reunited Berlin. On 18 June 1994, soldiers from the United States, France and Britain marched in a parade which was part of the ceremonies to mark the withdrawal of allied occupation troops allowing a German reunification#Unified Berlin, reunified Berlin
(the last Russian troops departed on 31 August, while the final departure of Western Allies forces was on 8 September 1994). On 20 June 1991, the Bundestag (German Parliament) Decision on the Capital of Germany, voted to move the seat of the German capital from Bonn to Berlin, which was completed in 1999, during the chancellorship of Gerhard Schröder.
Berlin's 2001 administrative reform merged several boroughs, reducing their number from 23 to 12.
In 2006, the 2006 FIFA World Cup Final, FIFA World Cup Final was held in Berlin.
Construction of the "Berlin Wall Trail" (Berliner Mauerweg) began in 2002 and was completed in 2006.
In a 2016 Berlin truck attack, 2016 terrorist attack linked to ISIL, a truck was deliberately driven into a Christmas market next to the Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church, leaving 13 people dead and 55 others injured.
In 2018, more than 200,000 protestors took to the streets in Berlin with demonstrations of solidarity against racism, in response to the emergence of Far-right politics in Germany (1945-present), far-right politics in Germany.
Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER) opened in 2020, nine years later than planned, with Terminal 1 coming into service at the end of October, and flights to and from Tegel Airport ending in November. Due to the fall in passenger numbers resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, plans were announced to temporarily close BER's Terminal 5, the former Schönefeld Airport, beginning in March 2021 for up to one year. The connecting link of U-Bahn line U5 from Alexanderplatz to Hauptbahnhof, along with the new stations Rotes Rathaus and Unter den Linden, opened on 4 December 2020, with the Museumsinsel U-Bahn station expected to open around March 2021, which would complete all new works on the U5.
A partial opening by the end of 2020 of the Humboldt Forum museum, housed in the reconstructed Berlin Palace, which had been announced in June, was postponed until March 2021. On 16 September 2022, the opening of the eastern wing, the last section of the Humboldt Forum museum, meant the Humboldt Forum museum was finally completed. It became Germany's currently most expensive cultural project.
Berlin-Brandenburg fusion attempt

The legal basis for a combined state of Berlin and
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
is different from other state fusion proposals. Normally, Article 29 of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, Basic Law stipulates that a state fusion requires a federal law. However, a clause added to the Basic Law in 1994, Article 118a, allows Berlin and Brandenburg to unify without federal approval, requiring a referendum and a ratification by both state parliaments.
In 1996, there was an unsuccessful attempt of unifying the states of Berlin and Brandenburg.
Both share a common history, dialect and culture and in 2020, there are over 225.000 residents of Brandenburg that commute to Berlin. The fusion had the near-unanimous support by a broad coalition of both state governments, political parties, media, business associations, trade unions and churches. Though Berlin voted in favor by a small margin, largely based on support in former
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under m ...
, Brandenburg voters disapproved of the fusion by a large margin. It failed largely due to Brandenburg voters not wanting to take on Berlin's large and growing public debt and fearing losing identity and influence to the capital.
Geography
Topography


Berlin is in northeastern Germany, in an area of low-lying marshy woodlands with a mainly flat topography, part of the vast Northern European Plain which stretches all the way from northern France to western Russia. The ''Berliner Urstromtal'' (an ice age glacial valley), between the low Barnim Plateau to the north and the Teltow plateau to the south, was formed by meltwater flowing from ice sheets at the end of the last Weichselian glaciation. The
Spree follows this valley now. In Spandau, a borough in the west of Berlin, the Spree empties into the river
Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
, which flows from north to south through western Berlin. The course of the Havel is more like a chain of lakes, the largest being the Tegeler See and the Großer Wannsee. A series of lakes also feeds into the upper Spree, which flows through the Müggelsee, Großer Müggelsee in eastern Berlin.
Substantial parts of present-day Berlin extend onto the low plateaus on both sides of the Spree Valley. Large parts of the boroughs Reinickendorf and
Pankow
Pankow () is the most populous and the second-largest borough by area of Berlin. In Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, it was merged with the former boroughs of Prenzlauer Berg and Weißensee; the resulting borough retained the name Pankow. ...
lie on the Barnim Plateau, while most of the boroughs of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf,
Steglitz-Zehlendorf
Steglitz-Zehlendorf () is the sixth borough of Berlin, formed in Berlin's 2001 administrative reform by merging the former boroughs of Steglitz and Zehlendorf.
Home to Free University of Berlin, the Berlin Botanical Garden, and a variety of m ...
, Tempelhof-Schöneberg, and Neukölln lie on the Teltow Plateau.
The borough of Spandau lies partly within the Berlin Glacial Valley and partly on the Nauen Plain, which stretches to the west of Berlin. Since 2015, the Arkenberge hills in Pankow at elevation, have been the highest point in Berlin. Through the disposal of construction debris they surpassed Teufelsberg (), which itself was made up of rubble from the ruins of the Second World War. The Müggelberge at elevation is the highest natural point and the lowest is the Spektesee in Spandau, at elevation.
Climate
Berlin has an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen: ''Cfb'') bordering on a humid continental climate (''Dfb''). This type of climate features mild to very warm summer temperatures and cold, though not very severe, winters. Annual precipitation is modest.
Frosts are common in winter, and there are larger temperature differences between seasons than typical for many oceanic climates. Summers are warm and sometimes humid with average high temperatures of and lows of . Winters are cold with average high temperatures of and lows of . Spring and autumn are generally chilly to mild. Berlin's built-up area creates a microclimate, with Urban heat island, heat stored by the city's buildings and pavement. Temperatures can be higher in the city than in the surrounding areas. Annual precipitation is with moderate rainfall throughout the year. Snowfall mainly occurs from December through March.
The hottest month in Berlin was July 1834, with a mean temperature of and the coldest was Great Frost of 1709, January 1709, with a mean temperature of . The wettest month on record was July 1907, with of rainfall, whereas the driest were October 1866, November 1902, October 1908 and September 1928, all with of rainfall.
Cityscape



Berlin's history has left the city with a polycentric metropolitan area and an eclectic mix of architecture. The city's appearance today has been predominantly shaped by German history during the 20th century. 17% of Berlin's buildings are
Gründerzeit
(; "founders' period") was the economic phase in 19th-century Germany and Austria before the great stock market crash of 1873. In Central Europe, the age of industrialisation had been taking place since the 1840s. That period is not precisely ...
or earlier and nearly 25% are of the 1920s and 1930s, when Berlin played a part in the origin of Berlin Modernism Housing Estates, modern architecture.
Devastated by the bombing of Berlin in World War II many of the buildings that had survived in both East and West were demolished during the postwar period. After the reunification, many important heritage structures have been Reconstruction (architecture), reconstructed, including the ''Forum Fridericianum'' along with, the Berlin State Opera, Charlottenburg Palace, Gendarmenmarkt, Alte Kommandantur, as well as the City Palace, Berlin, City Palace.
The list of tallest buildings in Berlin spreads across the urban area, they can be found for example at
Potsdamer Platz
Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag ( German Parliament Building), and close to the southeast corn ...
, the City West, and Alexanderplatz.
Over one-third of the city area consists of green space, woodlands, and water.
Berlin's second-largest and most popular park, the Großer Tiergarten, is located right in the center of the city.
Architecture


The Fernsehturm Berlin, Fernsehturm (TV tower) at Alexanderplatz in Mitte is among the tallest structures in the European Union at . Built in 1969, it is visible throughout most of the central districts of Berlin.

The city can be viewed from its observation floor. Starting here, the Karl-Marx-Allee heads east, an avenue lined by monumental residential buildings, designed in the Socialist Classicism style. Adjacent to this area is the Rotes Rathaus (City Hall), with its distinctive red-brick architecture. In front of it is the Neptunbrunnen, a fountain featuring a mythological group of Triton (mythology), Tritons, personifications of the four main Prussian rivers, and Neptune (mythology), Neptune on top of it.
The
Brandenburg Gate
The Brandenburg Gate (german: Brandenburger Tor ) is an 18th-century neoclassical monument in Berlin, built on the orders of Prussian king Frederick William II after restoring the Orangist power by suppressing the Dutch popular unrest. One ...
is an iconic landmark of Berlin and Germany; it stands as a symbol of eventful European history and of unity and peace. The
Reichstag building
The Reichstag (, ; officially: – ; en, Parliament) is a historic government building in Berlin which houses the Bundestag, the lower house of Germany's parliament.
It was constructed to house the Imperial Diet (german: Reichstag) of the ...
is the traditional seat of the German Parliament. It was remodeled by British architect Norman Foster (architect), Norman Foster in the 1990s and features a glass dome over the session area, which allows free public access to the parliamentary proceedings and magnificent views of the city.
The East Side Gallery is an open-air exhibition of art painted directly on the last existing portions of the Berlin Wall. It is the largest remaining evidence of the city's historical division.
The Gendarmenmarkt is a neoclassical architecture, neoclassical square in Berlin, the name of which derives from the headquarters of the famous Gens d'armes regiment located here in the 18th century. Two similarly designed cathedrals border it, the Französischer Dom with its observation platform and the Deutscher Dom. The Konzerthaus (Concert Hall), home of the Berlin Symphony Orchestra, stands between the two cathedrals.


The
Museum Island
The Museum Island (german: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Euro ...
in the Spree (river), River Spree houses #Museums, five museums built from 1830 to 1930 and is a UNESCO List of World Heritage Sites in Germany, World Heritage site. Restoration and construction of a main entrance to all museums, as well as reconstruction of the Stadtschloss, Berlin, Stadtschloss continues. Also on the island and next to the Lustgarten and palace is Berlin Cathedral, emperor William II's ambitious attempt to create a Protestant counterpart to St. Peter's Basilica in Rome. A large crypt houses the remains of some of the earlier Prussian royal family. St. Hedwig's Cathedral is Berlin's Roman Catholic cathedral.
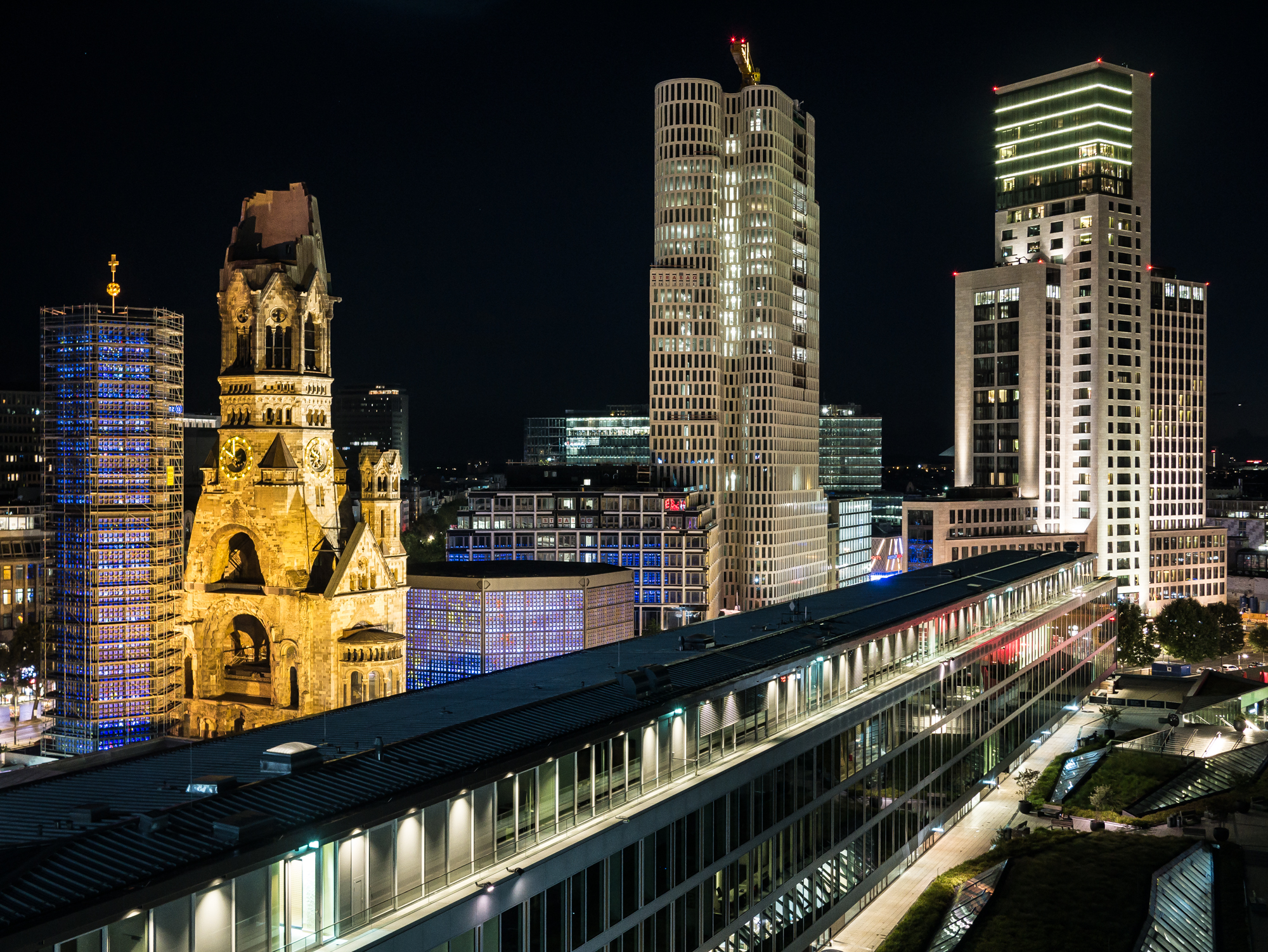

Unter den Linden is a tree-lined east–west avenue from the Brandenburg Gate to the site of the former Berliner Stadtschloss, and was once Berlin's premier promenade. Many Classical buildings line the street, and part of Humboldt University is there. Friedrichstraße was Berlin's legendary street during the Golden Twenties. It combines 20th-century traditions with the modern architecture of today's Berlin.
Potsdamer Platz
Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag ( German Parliament Building), and close to the southeast corn ...
is an entire quarter built from scratch after the Berlin Wall, Wall came down. To the west of Potsdamer Platz is the Kulturforum, which houses the Gemäldegalerie, Berlin, Gemäldegalerie, and is flanked by the Neue Nationalgalerie and the Berliner Philharmonie. The
Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe
The Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe (german: Denkmal für die ermordeten Juden Europas), also known as the Holocaust Memorial (German: ''Holocaust-Mahnmal''), is a memorial in Berlin to the Jewish victims of the Holocaust, designed by arc ...
, a Holocaust memorial, is to the north.
The area around Hackescher Markt is home to fashionable culture, with countless clothing outlets, clubs, bars, and galleries. This includes the Hackesche Höfe, a conglomeration of buildings around several courtyards, reconstructed around 1996. The nearby New Synagogue, Berlin, New Synagogue is the center of Jewish culture.
The Straße des 17. Juni, connecting the Brandenburg Gate and Ernst-Reuter-Platz, serves as the central east–west axis. Its name commemorates the Uprising of 1953 in East Germany, uprisings in East Berlin of 17 June 1953. Approximately halfway from the Brandenburg Gate is the Großer Stern, a circular traffic island on which the Berlin Victory Column, Siegessäule (Victory Column) is situated. This monument, built to commemorate Prussia's victories, was relocated in 1938–39 from its previous position in front of the Reichstag.
The Kurfürstendamm is home to some of Berlin's luxurious stores with the Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church at its eastern end on Breitscheidplatz. The church was destroyed in the Second World War and left in ruins. Nearby on Tauentzienstraße is KaDeWe, claimed to be continental Europe's largest department store. The Rathaus Schöneberg, where John F. Kennedy made his famous "Ich bin ein Berliner!" speech, is in Tempelhof-Schöneberg.
West of the center, Bellevue Palace (Germany), Bellevue Palace is the residence of the German President. Charlottenburg Palace, which was burnt out in the Second World War, is the largest historical palace in Berlin.
The Funkturm Berlin is a lattice radio tower in the fairground area, built between 1924 and 1926. It is the only observation tower which stands on insulators and has a restaurant and an observation deck above ground, which is reachable by a windowed elevator.
The Oberbaumbrücke over the Spree river is Berlin's most iconic bridge, connecting the now-combined boroughs of Friedrichshain and Kreuzberg. It carries vehicles, pedestrians, and the U1 Berlin U-Bahn line. The bridge was completed in a brick gothic style in 1896, replacing the former wooden bridge with an upper deck for the U-Bahn. The center portion was demolished in 1945 to stop the Red Army from crossing. After the war, the repaired bridge served as a Berlin border crossings, checkpoint and border crossing between the Soviet and American sectors, and later between East and West Berlin. In the mid-1950s, it was closed to vehicles, and after the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961, pedestrian traffic was heavily restricted. Following German reunification, the center portion was reconstructed with a steel frame, and U-Bahn service resumed in 1995.
Demographics


At the end of 2018, the city-state of Berlin had 3.75 million registered inhabitants
in an area of .
The city's population density was 4,206 inhabitants per km
2. Berlin is the Largest cities of the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city proper in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
. In 2019, the urban area of Berlin had about 4.5 million inhabitants.
, the Larger Urban Zones, functional urban area was home to about 5.2 million people. The entire
Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has a population of more than 6 million in an area of .
In 2014, the city-state Berlin had 37,368 live births (+6.6%), a record number since 1991. The number of deaths was 32,314. Almost 2.0 million households were counted in the city. 54 percent of them were single-person households. More than 337,000 families with children under the age of 18 lived in Berlin. In 2014, the German capital registered a migration surplus of approximately 40,000 people.
Nationalities
National and international migration into the city has a long history. In 1685, after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in France, the city responded with the Edict of Potsdam, which guaranteed religious freedom and tax-free status to French Huguenot refugees for ten years. The Greater Berlin Act in 1920 incorporated many suburbs and surrounding cities of Berlin. It formed most of the territory that comprises modern Berlin and increased the population from 1.9 million to 4 million.
Active immigration and asylum politics in West Berlin triggered waves of immigration in the 1960s and 1970s. Berlin is home to at least 180,000 Turkish people, Turkish and Turks in Germany, Turkish German residents,
making it the largest Turkish community outside of Turkey. In the 1990s the ''Aussiedlergesetze'' enabled immigration to Germany of some residents from the former Soviet Union. Today ethnic History of Germans in Russia and the Soviet Union, Germans from countries of the former Soviet Union make up the largest portion of the Russian-speaking community. The last decade experienced an influx from various Western countries and some African regions. A portion of the African immigrants have settled in the Afrikanisches Viertel. Young Germans, EU-Europeans and Israelis have also settled in the city.
In December 2019 there were 777,345 registered residents of foreign nationality and another 542,975 German citizens with a "migration background" ''(Migrationshintergrund, MH)'',
meaning they or one of their parents immigrated to Germany after 1955. Foreign residents of Berlin originate from about 190 countries. 48 percent of the residents under the age of 15 have a migration background in 2017. Berlin in 2009 was estimated to have 100,000 to 250,000 unregistered inhabitants. Boroughs of Berlin with a significant number of migrants or foreign born population are Mitte, Neukölln and Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg. The number of Arabic speakers in Berlin could be higher than 150,000. There are at least 40,000 Berliners with Syrian citizenship, third only behind Turkish and Polish citizens. The 2015 European migrant crisis, 2015 refugee crisis made Berlin Europe's capital of Arab culture. Berlin is among the cities in Germany that have received the biggest amount of refugees after the Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. As of November 2022, an estimated 85,000 Ukrainian refugees were registered in Berlin, making Berlin the most popular destination of Ukrainian refugees in Germany.
Berlin has a vibrant expatriate community involving precarious immigrants, illegal immigrants, seasonal workers, and refugees. Therefore, Berlin sustains a broad variety of English-based speakers. Speaking a particular type of English does attract prestige and cultural capital in Berlin.
Languages
German is the official and predominant spoken language in Berlin. It is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language that derives most of its vocabulary from the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. German is one of 24 languages of the European Union, and one of the three working languages of the European Commission.
Berlinerisch or Berlinisch is not a dialect linguistically. It is spoken in Berlin and the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, surrounding metropolitan area. It originates from a Brandenburgisch dialect, Brandenburgish variant. The dialect is now seen more like a sociolect, largely through increased immigration and trends among the educated population to speak standard German in everyday life.
The most commonly spoken foreign languages in Berlin are Turkish, Polish, English, Persian, Arabic, Italian, Bulgarian, Russian, Romanian, Kurdish, Serbo-Croatian, French, Spanish and Vietnamese. Turkish, Arabic, Kurdish, and Serbo-Croatian are heard more often in the western part due to the large Middle Eastern and former-Yugoslavian communities. Polish, English, Russian, and Vietnamese have more native speakers in East Berlin.
Religion
On the report of the 2011 census, approximately 37 percent of the population reported being members of a legally-recognized church or religious organization. The rest either did not belong to such an organization, or there was no information available about them.
The largest religious denomination recorded in 2010 was the Protestant Landeskirche, regional church body—the Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia, Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia (EKBO)—a united church. EKBO is a member of the Protestant Church in Germany, Protestant Church in Germany (EKD) and of the Union of Protestant Churches in the EKD, Union of Protestant Churches in the EKD (UEK). According to the EKBO, their membership accounted for 18.7 percent of the local population, while the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church had 9.1 percent of residents registered as its members.
About 2.7% of the population identify with other Christian denominations (mostly Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, but also various Protestants).
According to the Berlin residents register, in 2018 14.9 percent were members of the Evangelical Church, and 8.5 percent were members of the Catholic Church.
The government keeps a register of members of these churches for tax purposes, because it collects Church tax#Germany, church tax on behalf of the churches. It does not keep records of members of other religious organizations which may collect their own church tax, in this way.
In 2009, approximately 249,000 Muslims were reported by the Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg, Office of Statistics to be members of mosques and Islamic religious organizations in Berlin, while in 2016, the newspaper ''Der Tagesspiegel'' estimated that about 350,000 Muslims observed Ramadan in Berlin. In 2019, about 437,000 registered residents, 11.6% of the total, reported having a migration background from one of the Member states of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation.
Between 1992 and 2011 the Muslim population almost doubled.
About 0.9% of Berliners belong to other religions. Of the estimated population of 30,000–45,000 Jewish residents,
approximately 12,000 are registered members of religious organizations.
Berlin is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Berlin, Roman Catholic archbishop of Berlin and Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia, EKBO's elected chairperson is titled the bishop of EKBO. Furthermore, Berlin is the seat of many Orthodox cathedrals, such as the Cathedral of St. Boris the Baptist, one of the two seats of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church, Bulgarian Orthodox Diocese of Western and Central Europe, and the Resurrection of Christ Cathedral of the Diocese of Berlin (Patriarchate of Moscow).
The faithful of the different religions and denominations maintain many List of places of worship in Berlin, places of worship in Berlin. The Independent Evangelical Lutheran Church has eight parishes of different sizes in Berlin. There are 36 Baptist congregations (within Union of Evangelical Free Church Congregations in Germany), 29 New Apostolic Churches, 15 United Methodist churches, eight Free Evangelical Congregations, four Church of Christ, Scientist, Churches of Christ, Scientist (1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 11th), six congregations of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, an Old Catholic church, and an Anglican church in Berlin. Berlin has more than 80 mosques, ten synagogues, and two Buddhist as well as two Hinduism, Hindu temples.
Government and politics
German federal city state

Since the
German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
on 3 October 1990, Berlin has been one of the three city-
states of Germany among the present 16 federal states of Germany. The Abgeordnetenhaus von Berlin (''House of Representatives'') functions as the city and state parliament, which has 141 seats. Berlin's executive body is the Senate of Berlin (''Senat von Berlin''). The Senate consists of the Governing Mayor of Berlin (''Regierender Bürgermeister''), and up to ten senators holding ministerial positions, two of them holding the title of "Mayor" (''Bürgermeister'') as deputy to the Governing Mayor.
The total annual budget of Berlin in 2015 exceeded €24.5 ($30.0) billion including a budget surplus of €205 ($240) million. The German Federal city state of Berlin owns extensive assets, including administrative and government buildings, real estate companies, as well as stakes in the Olympic Stadium, swimming pools, housing companies, and numerous public enterprises and subsidiary companies. The federal state of Berlin runs a real estate portal to advertise commercial spaces or land suitable for redevelopment.
The Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) and The Left (Germany), The Left (Die Linke) took control of the city government after the Berlin state election, 2001, 2001 state election and won another term in the Berlin state election, 2006, 2006 state election. From the Berlin state election, 2016, 2016 state election until the 2023 Berlin state election, 2023 state election, there was a coalition between the Social Democratic Party, the Greens and the Left Party. Since April 2023, the government has been formed by a coalition between the Christian Democrats and the Social Democrats.
The Governing Mayor is simultaneously Lord Mayor of the City of Berlin (''Oberbürgermeister der Stadt'') and Minister President of the State of Berlin (''Ministerpräsident des Bundeslandes''). The office of the Governing Mayor is in the Rotes Rathaus, Rotes Rathaus (Red City Hall). Since 2023, this office has been held by Kai Wegner of the Christian Democrats. He is the first conservative mayor in Berlin in more than two decades.
Boroughs

Berlin is subdivided into 12 boroughs or districts (''Bezirke''). Each borough has several subdistricts or neighborhoods (''Ortsteile''), which have roots in much older municipalities that predate the formation of Greater Berlin on 1 October 1920. These subdistricts became urbanized and incorporated into the city later on. Many residents strongly identify with their neighborhoods, colloquially called ''Kiez''. At present, Berlin consists of 96 subdistricts, which are commonly made up of several smaller residential areas or quarters.
Each borough is governed by a borough council (''Bezirksamt'') consisting of five councilors (''Bezirksstadträte'') including the borough's mayor (''Bezirksbürgermeister''). The council is elected by the borough assembly (''Bezirksverordnetenversammlung''). However, the individual boroughs are not independent municipalities, but subordinate to the Senate of Berlin. The borough's mayors make up the council of mayors (''Rat der Bürgermeister''), which is led by the city's Governing Mayor and advises the Senate. The neighborhoods have no local government bodies.
City partnerships
Berlin to this day maintains official partnerships with 17 cities.
Sister city, Town twinning between
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under m ...
and other cities began with its sister city Los Angeles, California, in 1967.
East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 u ...
's partnerships were canceled at the time of
German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
.
Capital city
Berlin is the capital of the Federal Republic of Germany. The President of Germany, whose functions are mainly ceremonial under the Grundgesetz, German constitution, has their official residence in Bellevue Palace (Germany), Bellevue Palace. Berlin is the Seat of government, seat of the Chancellor of Germany (1949–), German Chancellor (Prime Minister), housed in the Federal Chancellery (Berlin), Chancellery building, the ''Bundeskanzleramt''. Facing the Chancellery is the Bundestag, the German Parliament, housed in the renovated
Reichstag building
The Reichstag (, ; officially: – ; en, Parliament) is a historic government building in Berlin which houses the Bundestag, the lower house of Germany's parliament.
It was constructed to house the Imperial Diet (german: Reichstag) of the ...
since the government's relocation to Berlin in 1998. The Bundesrat of Germany, Bundesrat ("federal council", performing the function of an upper house) is the federalism, representation of the States of Germany, 16 constituent states (''Länder'') of Germany and has its seat at the former Prussian House of Lords. The total annual federal budget managed by the German government exceeded €310 ($375) billion in 2013.
File:07.08.21.Bundeskanzleramt.jpg, The Federal Chancellery (Berlin), Federal Chancellery building, seat of the Chancellor of Germany (1949–), Chancellor of Germany
File:Berlin reichstag west panorama.jpg, The Reichstag building, Reichstag, seat of the Bundestag
File:Bellevue Palace Berlin 02-14.jpg, Schloss Bellevue, seat of the President of Germany
File:Bundesrat Gebäude, Berlin, Leipziger Strasse.jpg, Prussian House of Lords, seat of the Bundesrat of Germany
File:Zentrale des Bundesnachrichtendienst, Berlin.jpg, Headquarters of the Federal Intelligence Service
The relocation of the federal Cabinet of Germany, government and Bundestag to Berlin was mostly completed in 1999. However, some ministries, as well as some minor departments, stayed in the federal city
Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ru ...
, the former capital of West Germany. Berlin-Bonn Act, Discussions about moving the remaining ministries and departments to Berlin continue.
The Foreign Office (Germany), Federal Foreign Office and the ministries and departments of Federal Ministry of Defence (Germany), Defense, Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection, Justice and Consumer Protection, Federal Ministry of Finance (Germany), Finance, Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany), Interior, Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (Germany), Economic Affairs and Energy, Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs, Labor and Social Affairs, Federal Ministry of Family Affairs, Senior Citizens, Women and Youth, Family Affairs, Senior Citizens, Women and Youth, Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, Food and Agriculture, Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development, Economic Cooperation and Development, Federal Ministry of Health (Germany), Health, Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure, Transport and Digital Infrastructure and Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Germany), Education and Research are based in the capital.
Embassies
Berlin hosts in total 158 foreign embassies as well as the headquarters of many think tanks, trade unions, nonprofit organizations, lobbying groups, and professional associations. Frequent official visits and diplomatic consultations among governmental representatives and national leaders are common in contemporary Berlin.
Economy

In 2018, the GDP of Berlin totaled €147 billion, an increase of 3.1% over the previous year.
Berlin's economy is dominated by the
service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector ( raw materials) and the sec ...
, with around 84% of all companies doing business in services. In 2015, the total labor force in Berlin was 1.85 million. The unemployment rate reached a 24-year low in November 2015 and stood at 10.0%. From 2012 to 2015 Berlin, as a German state, had the highest annual employment growth rate. Around 130,000 jobs were added in this period.
Important economic sectors in Berlin include life sciences, transportation, information and communication technologies, media and music, advertising and design, biotechnology, environmental services, construction, e-commerce, retail, hotel business, and medical engineering.
Research and development have economic significance for the city.
Several major corporations like Volkswagen, Pfizer, and SAP operate innovation laboratories in the city.
The Science and Business Park in Adlershof is the largest technology park in Germany measured by revenue. Within the Eurozone, Berlin has become a center for business relocation and international investment (macroeconomics), investments.
Companies
Many German and international companies have business or service centers in the city. For several years Berlin has been recognized as a major center of Entrepreneurship, business founders. In 2015, Berlin generated the most venture capital for young Startup company, startup companies in Europe.
Among the 10 largest employers in Berlin are the City-State of Berlin, , largest railway company in the world, the hospital providers Charité and Vivantes, the Federal Government of Germany, the local public transport provider Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe, BVG, Siemens and Deutsche Telekom.
Siemens, a Fortune Global 500, Global 500 and DAX-listed company is partly headquartered in Berlin. Other DAX-listed companies headquartered in Berlin are the property company Deutsche Wohnen and the online food delivery service Delivery Hero. The national railway operator , Europe's largest digital publisher Axel Springer SE, Axel Springer as well as the MDAX-listed firms Zalando and HelloFresh and also have their main headquarters in the city. Among the largest international corporations who have their German or European headquarters in Berlin are Bombardier Transportation, Securing Energy for Europe, Coca-Cola, Pfizer, Sony and TotalEnergies.
As of 2023, Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, a network of public banks that together form the largest financial services group in Germany and in all of Europe, is headquartered in Berlin. The Bundesverband der Deutschen Volksbanken und Raiffeisenbanken has its headquarters in Berlin, managing around 1.200 trillion euros. The three largest banks in the capital are Deutsche Kreditbank, Landesbank Berlin and Berlin Hyp.
Mercedes-Benz Group manufactures cars, and BMW Motorrad, BMW builds motorcycles in Berlin. In 2022, American electric car manufacturer Tesla, Inc., Tesla opened its first European Gigafactory outside the city borders in Grünheide (Mark), Brandenburg. The Pharmaceuticals division of Bayer and Berlin Chemie are major pharmaceutical companies in the city.
Tourism and conventions
Berlin had 788 hotels with 134,399 beds in 2014.
The city recorded 28.7 million overnight hotel stays and 11.9 million hotel guests in 2014.
[ Tourism figures have more than doubled within the last ten years and Berlin has become the third-most-visited city destination in Europe. Some of the most visited places in Berlin include: ]Potsdamer Platz
Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag ( German Parliament Building), and close to the southeast corn ...
, Brandenburg Gate, Brandenburger Tor, Berlin Wall, the Berlin wall, Alexanderplatz, Museum Island, Museumsinsel, Fernsehturm Berlin, Fernsehturm, the East Side Gallery, East-Side Gallery, Charlottenburg Palace, Schloss-Charlottenburg, Berlin Zoological Garden, Zoologischer Garten, Berlin Victory Column, Siegessäule, Gedenkstätte Berliner Mauer, Mauerpark, Berlin-Dahlem Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum, Botanical Garden, French Cathedral, Berlin, Französischer Dom, Deutscher Dom and Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe, Holocaust-Mahnmal. The largest visitor groups are from Germany, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Italy, Spain and the United States.
According to figures from the International Congress and Convention Association in 2015, Berlin became the leading organizer of conferences globally, hosting 195 international meetings. Some of these congress events take place on venues such as CityCube Berlin or the Berlin Congress Center (bcc).
The Messe Berlin (also known as Berlin ExpoCenter City) is the main convention organizing company in the city. Its main exhibition area covers more than . Several large-scale trade fairs like the consumer electronics trade fair IFA Berlin, IFA, where the first practical audio Magnetophon, tape recorder and the first Manfred von Ardenne, completely electronic television system were first introduced to the public,
A brief history of magnetic tape from the BASF Historian and the founding curator of the Ampex museum.
Creative industries
 The Creative industries, creative arts and entertainment business is an important part of Berlin's economy. The sector comprises music, film, advertising, architecture, art, design, German fashion, fashion, performing arts, publishing, research and development, R&D, software, TV, radio, and Video gaming in Germany, video games.
In 2014, around 30,500 creative companies operated in the Berlin-Brandenburg metropolitan region, predominantly Small and medium-sized enterprises, SMEs. Generating a revenue of 15.6 billion Euro and 6% of all private economic sales, the culture industry grew from 2009 to 2014 at an average rate of 5.5% per year.
Berlin is an important European and Cinema of Germany, German film industry hub. It is home to more than 1,000 film and television production companies, 270 movie theaters, and around 300 national and international co-productions are filmed in the region every year.
The Creative industries, creative arts and entertainment business is an important part of Berlin's economy. The sector comprises music, film, advertising, architecture, art, design, German fashion, fashion, performing arts, publishing, research and development, R&D, software, TV, radio, and Video gaming in Germany, video games.
In 2014, around 30,500 creative companies operated in the Berlin-Brandenburg metropolitan region, predominantly Small and medium-sized enterprises, SMEs. Generating a revenue of 15.6 billion Euro and 6% of all private economic sales, the culture industry grew from 2009 to 2014 at an average rate of 5.5% per year.
Berlin is an important European and Cinema of Germany, German film industry hub. It is home to more than 1,000 film and television production companies, 270 movie theaters, and around 300 national and international co-productions are filmed in the region every year.Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
. The city is also home of the Deutsche Filmakademie, German Film Academy (Deutsche Filmakademie), founded in 2003, and the European Film Academy, founded in 1988.
Media
 Berlin is home to many magazine, newspaper, book, and scientific/academic publishers and their associated service industries. In addition, around 20 news agencies, more than 90 regional daily newspapers and their websites, as well as the Berlin offices of more than 22 national publications such as , and Die Zeit reinforce the capital's position as Germany's epicenter for influential debate. Therefore, many international journalists, bloggers, and writers live and work in the city.
Berlin is the central location to several international and regional television and radio stations. The public broadcaster Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg, RBB has its headquarters in Berlin as well as the commercial broadcasters MTV Europe and Welt (German TV channel), Welt. German international public broadcaster Deutsche Welle has its TV production unit in Berlin, and most national German broadcasters have a studio in the city, including ZDF and RTL Television, RTL.
Berlin has Germany's largest number of daily newspapers, with numerous local broadsheets (''Berliner Morgenpost'', ''Berliner Zeitung'', ''Der Tagesspiegel''), and three major Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloids, as well as national dailies of varying sizes, each with a different political affiliation, such as ''Die Welt'', ''Neues Deutschland'', and ''Die Tageszeitung''. The ''Exberliner'', a monthly magazine, is Berlin's English-language periodical and La Gazette de Berlin a French-language newspaper.
Berlin is also the headquarter of major German-language publishing houses like Walter de Gruyter, Axel Springer AG, Springer, the Ullstein Verlagsgruppe (publishing group), Suhrkamp, and Cornelsen are all based in Berlin. Each of which publishes books, periodicals, and multimedia products.
Berlin is home to many magazine, newspaper, book, and scientific/academic publishers and their associated service industries. In addition, around 20 news agencies, more than 90 regional daily newspapers and their websites, as well as the Berlin offices of more than 22 national publications such as , and Die Zeit reinforce the capital's position as Germany's epicenter for influential debate. Therefore, many international journalists, bloggers, and writers live and work in the city.
Berlin is the central location to several international and regional television and radio stations. The public broadcaster Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg, RBB has its headquarters in Berlin as well as the commercial broadcasters MTV Europe and Welt (German TV channel), Welt. German international public broadcaster Deutsche Welle has its TV production unit in Berlin, and most national German broadcasters have a studio in the city, including ZDF and RTL Television, RTL.
Berlin has Germany's largest number of daily newspapers, with numerous local broadsheets (''Berliner Morgenpost'', ''Berliner Zeitung'', ''Der Tagesspiegel''), and three major Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloids, as well as national dailies of varying sizes, each with a different political affiliation, such as ''Die Welt'', ''Neues Deutschland'', and ''Die Tageszeitung''. The ''Exberliner'', a monthly magazine, is Berlin's English-language periodical and La Gazette de Berlin a French-language newspaper.
Berlin is also the headquarter of major German-language publishing houses like Walter de Gruyter, Axel Springer AG, Springer, the Ullstein Verlagsgruppe (publishing group), Suhrkamp, and Cornelsen are all based in Berlin. Each of which publishes books, periodicals, and multimedia products.
Quality of life
According to Mercer (consulting firm), Mercer, Berlin ranked number 13 in the Quality of Living City Ranking in 2019.
Also in 2019, according to Monocle (UK magazine), ''Monocle'', Berlin occupied the position of the 6th-most-livable city in the world. Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Berlin number 21 of all global cities for ''livability''. In 2019 Berlin was also number 8 on the Global Power City Index. In the same year Berlin was honored for having the best future prospects of all cities in Germany.
Transport in Berlin
Roads
Berlin's transport infrastructure provides a diverse range of urban mobility.
A total of 979 bridges cross 197 km (122 miles) the inner-city waterways. Berlin roads total 5,422 km (3,369 miles) of which 77 km (48 miles) are motorways (known as Autobahn).
Cycling
 Berlin is well known for its highly developed bicycle lane system. It is estimated that Berlin has 710 bicycles per 1,000 residents. Around 500,000 daily bike riders accounted for 13 percent of total traffic in 2010.
Cyclists in Berlin have access to 620 km of bicycle paths including approximately 150 km of mandatory bicycle paths, 190 km of off-road bicycle routes, 60 km of bicycle lanes on roads, 70 km of shared bus lanes which are also open to cyclists, 100 km of combined pedestrian/bike paths and 50 km of marked bicycle lanes on roadside pavements or sidewalks. Riders are allowed to carry their bicycles on Regionalbahn (RE), S-Bahn and U-Bahn trains, on trams, and on night buses if a bike ticket is purchased.
Berlin is well known for its highly developed bicycle lane system. It is estimated that Berlin has 710 bicycles per 1,000 residents. Around 500,000 daily bike riders accounted for 13 percent of total traffic in 2010.
Cyclists in Berlin have access to 620 km of bicycle paths including approximately 150 km of mandatory bicycle paths, 190 km of off-road bicycle routes, 60 km of bicycle lanes on roads, 70 km of shared bus lanes which are also open to cyclists, 100 km of combined pedestrian/bike paths and 50 km of marked bicycle lanes on roadside pavements or sidewalks. Riders are allowed to carry their bicycles on Regionalbahn (RE), S-Bahn and U-Bahn trains, on trams, and on night buses if a bike ticket is purchased.
Taxicabs
 Taxicabs in Berlin are yellow or beige. In 2024, around 8,000 taxicabs were in service. Like in most of Europe, app-based Ridesharing company, sharing cab services are available but limited.
Taxicabs in Berlin are yellow or beige. In 2024, around 8,000 taxicabs were in service. Like in most of Europe, app-based Ridesharing company, sharing cab services are available but limited.
Rail

 Long-distance rail lines directly connect Berlin with all of the major cities of Germany. the regional rail lines of the Verkehrsverbund Berlin-Brandenburg provide access to
Long-distance rail lines directly connect Berlin with all of the major cities of Germany. the regional rail lines of the Verkehrsverbund Berlin-Brandenburg provide access to Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
and to the Baltic Sea. The Berlin Hauptbahnhof is the largest grade separation, grade-separated railway station in Europe. The Deutsche Bahn runs the high speed Intercity-Express (ICE) to domestic destinations, including Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Stuttgart, and Frankfurt am Main.
Water transport
The Spree and the Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
rivers cross Berlin. There are no frequent passenger connections to and from Berlin by water. Berlin's largest harbour, the Westhafen, is located in the district of Moabit. It is a transhipment and storage site for inland shipping with a growing importance.
Intercity buses
There is an increasing quantity of intercity bus services. Berlin city has more than 10 stations that run buses to destinations throughout Berlin. Destinations in Germany and Europe are connected via the intercity bus exchange ''Zentraler Omnibusbahnhof Berlin''.
Urban public transport

 The ''Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe'' (BVG) and the German State-owned Deutsche Bahn (DB) manage several extensive urban public transport systems.
Public transport in Berlin has a long and complicated history because of the 20th-century division of the city, where movement between the two halves was not served. Since 1989, the transport network has been developed extensively. However, it still contains early 20th century traits, such as the U1.
The ''Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe'' (BVG) and the German State-owned Deutsche Bahn (DB) manage several extensive urban public transport systems.
Public transport in Berlin has a long and complicated history because of the 20th-century division of the city, where movement between the two halves was not served. Since 1989, the transport network has been developed extensively. However, it still contains early 20th century traits, such as the U1.
Airports
 Berlin is served by one commercial international airport: Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER), located just outside Berlin's south-eastern border, in the state of Brandenburg. It began construction in 2006, with the intention of replacing Berlin Tegel Airport, Airport (TXL) and Berlin Schönefeld Airport, Airport (SXF) as the single commercial airport of Berlin.
Berlin is served by one commercial international airport: Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER), located just outside Berlin's south-eastern border, in the state of Brandenburg. It began construction in 2006, with the intention of replacing Berlin Tegel Airport, Airport (TXL) and Berlin Schönefeld Airport, Airport (SXF) as the single commercial airport of Berlin.
Rohrpost
From 1865 to 1976, Berlin operated an expansive Pneumatic tube, pneumatic postal network, reaching a maximum length of 400 kilometers (roughly 250 miles) by 1940. The system was divided into two distinct networks after 1949. The West Berlin system remained in public use until 1963, and continued to be utilized for government correspondence until 1972. Conversely, the East Berlin system, which incorporated the ''Hauptelegraphenamt''—the central hub of the operation—remained functional until 1976.
Energy
 Berlin's two largest energy provider for private households are the Swedish firm Vattenfall and the Berlin-based company GASAG. Both offer electric power and natural gas supply. Some of the city's electric energy is imported from nearby power plants in southern
Berlin's two largest energy provider for private households are the Swedish firm Vattenfall and the Berlin-based company GASAG. Both offer electric power and natural gas supply. Some of the city's electric energy is imported from nearby power plants in southern Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
.
the five List of power stations in Germany, largest power plants measured by capacity are the Heizkraftwerk Reuter West, the Heizkraftwerk Lichterfelde, the Heizkraftwerk Mitte, the Heizkraftwerk Wilmersdorf, and the Heizkraftwerk Charlottenburg. All of these power stations generate electricity generation, electricity and Heat, useful heat at the same time to facilitate buffering during load peaks.
In 1993 the power grid connections in the Berlin-Brandenburg capital region were renewed. In most of the inner districts of Berlin power lines are underground cables; only a 380 kV and a 110 kV line, which run from Reuter substation to the urban Autobahn, use overhead lines. The Berlin 380-kV electric line is the backbone of the city's energy grid.
Health
 Berlin has a long history of discoveries in medicine and innovations in medical technology. The modern history of medicine has been significantly influenced by scientists from Berlin. Rudolf Virchow was the founder of cellular pathology, while Robert Koch developed vaccines for anthrax, cholera, and tuberculosis. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine.
The Charité complex (Universitätsklinik Charité) is the largest university hospital in Europe, tracing back its origins to the year 1710. More than half of all German Nobel Prize winners in Physiology or Medicine, including Emil von Behring, Robert Koch and Paul Ehrlich, have worked at the Charité. The Charité is spread over four campuses and comprises around 3,000 beds, 15,500 staff, 8,000 students, and more than 60 operating theaters, and it has a turnover of two billion euros annually.
Berlin has a long history of discoveries in medicine and innovations in medical technology. The modern history of medicine has been significantly influenced by scientists from Berlin. Rudolf Virchow was the founder of cellular pathology, while Robert Koch developed vaccines for anthrax, cholera, and tuberculosis. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine.
The Charité complex (Universitätsklinik Charité) is the largest university hospital in Europe, tracing back its origins to the year 1710. More than half of all German Nobel Prize winners in Physiology or Medicine, including Emil von Behring, Robert Koch and Paul Ehrlich, have worked at the Charité. The Charité is spread over four campuses and comprises around 3,000 beds, 15,500 staff, 8,000 students, and more than 60 operating theaters, and it has a turnover of two billion euros annually.
Telecommunication
 Since 2017, the digital television standard in Berlin and Germany is DVB-T2. This system transmits video compression, compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream.
Berlin has installed several hundred free public Wireless LAN sites across the capital since 2016. The wireless networks are concentrated mostly in central districts; 650 hotspots (325 indoor and 325 outdoor access points) are installed.
The UMTS (3G) and LTE (telecommunication), LTE (4G) networks of the three major cellular operators Vodafone, T-Mobile International AG, T-Mobile and Telefónica Germany, O2 enable the use of mobile broadband applications citywide.
Since 2017, the digital television standard in Berlin and Germany is DVB-T2. This system transmits video compression, compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream.
Berlin has installed several hundred free public Wireless LAN sites across the capital since 2016. The wireless networks are concentrated mostly in central districts; 650 hotspots (325 indoor and 325 outdoor access points) are installed.
The UMTS (3G) and LTE (telecommunication), LTE (4G) networks of the three major cellular operators Vodafone, T-Mobile International AG, T-Mobile and Telefónica Germany, O2 enable the use of mobile broadband applications citywide.
Education and research
 , Berlin had 878 schools, teaching 340,658 students in 13,727 classes and 56,787 trainees in businesses and elsewhere.
, Berlin had 878 schools, teaching 340,658 students in 13,727 classes and 56,787 trainees in businesses and elsewhere.
Higher education
 The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region is one of the most prolific centers of higher education and research in Germany and Europe. Historically, 67 Nobel Prize winners are affiliated with the Berlin-based universities.
The city has four public research universities and more than 30 private, professional, and technical colleges ''(Hochschulen)'', offering a wide range of disciplines. A record number of 175,651 students were enrolled in the winter term of 2015/16. Among them around 18% have an international background.
The three largest universities combined have approximately 103,000 enrolled students. There are the Free University of Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin ''(Free University of Berlin, FU Berlin)'' with about 33,000 students, the Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin ''(HU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students, and the Technical University of Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin ''(TU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students. The Charité Medical School has around 8,000 students.
The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region is one of the most prolific centers of higher education and research in Germany and Europe. Historically, 67 Nobel Prize winners are affiliated with the Berlin-based universities.
The city has four public research universities and more than 30 private, professional, and technical colleges ''(Hochschulen)'', offering a wide range of disciplines. A record number of 175,651 students were enrolled in the winter term of 2015/16. Among them around 18% have an international background.
The three largest universities combined have approximately 103,000 enrolled students. There are the Free University of Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin ''(Free University of Berlin, FU Berlin)'' with about 33,000 students, the Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin ''(HU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students, and the Technical University of Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin ''(TU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students. The Charité Medical School has around 8,000 students.[ The FU, the HU, the TU, and the Charité make up the Berlin University Alliance, which has received funding from the German Universities Excellence Initiative, Excellence Strategy program of the German government. The Berlin University of the Arts, Universität der Künste ''(UdK)'' has about 4,000 students and ESMT Berlin is only one of four business schools in Germany with triple accreditation. The Hertie School, a private public policy school located in Mitte, has more than 900 students and doctoral students. The Berlin School of Economics and Law has an enrollment of about 11,000 students, the Berliner Hochschule für Technik, Berlin University of Applied Sciences and Technology of about 12,000 students, and the HTW Berlin, Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft (University of Applied Sciences for Engineering and Economics) of about 14,000 students.
]
Research
 The city has a high density of internationally renowned research institutions, such as the Fraunhofer Society, the DLR Institute for Planetary Research, the Leibniz Association, the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres, Helmholtz Association, and the Max Planck Society, which are independent of, or only loosely connected to its universities. In 2012, around 65,000 professional scientists were working in research and development in the city.
The city has a high density of internationally renowned research institutions, such as the Fraunhofer Society, the DLR Institute for Planetary Research, the Leibniz Association, the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres, Helmholtz Association, and the Max Planck Society, which are independent of, or only loosely connected to its universities. In 2012, around 65,000 professional scientists were working in research and development in the city.
Culture


 Berlin is known for its numerous cultural institutions, many of which enjoy international reputation.
Berlin is known for its numerous cultural institutions, many of which enjoy international reputation.[
Many German and International films were shot in Berlin, including M (1931 film), M, One, Two, Three, Cabaret (1972 film), Cabaret, Christiane F. (film), Christiane F., Possession (1981 film), Possession, Octopussy, Wings of Desire, Run Lola Run, Bourne (film series), The Bourne Trilogy, Good Bye, Lenin!, The Lives of Others, Inglourious Basterds, Hanna (film), Hanna, Unknown (2011 film), Unknown and Bridge of Spies (film), Bridge of Spies.
]
Galleries and museums
 Berlin is home to 138 museums and more than 400 art galleries.
Berlin is home to 138 museums and more than 400 art galleries.Museum Island
The Museum Island (german: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Euro ...
is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is in the northern part of the Spree Island between the Spree and the Kupfergraben.[ As early as 1841 it was designated a "district dedicated to art and antiquities" by a royal decree. Subsequently, the Altes Museum was built in the Lustgarten. The Neues Museum, which displays the Nefertiti Bust, bust of Queen Nefertiti, Alte Nationalgalerie, Pergamon Museum, and Bode Museum were built there.
Apart from the Museum Island, there are many additional museums in the city. The Gemäldegalerie, Berlin, Gemäldegalerie (Painting Gallery) focuses on the paintings of the "old masters" from the 13th to the 18th centuries, while the Neue Nationalgalerie (New National Gallery, built by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe) specializes in 20th-century European painting. The Hamburger Bahnhof, in Moabit, exhibits a major collection of modern and contemporary art. The expanded Deutsches Historisches Museum reopened in the Zeughaus with an overview of German history spanning more than a millennium. The Bauhaus Archive is a museum of 20th-century design from the famous Bauhaus school. Museum Berggruen houses the collection of noted 20th century collector Heinz Berggruen, and features an extensive assortment of works by Picasso, Matisse, Cézanne, and Giacometti, among others. The Kupferstichkabinett Berlin, Kupferstichkabinett Berlin (Museum of Prints and Drawings) is part of the Berlin State Museums, Staatlichen Museen zu Berlin (Berlin State Museums) and the Kulturforum, Kulturforum at Potsdamer Platz in the Tiergarten district of Berlin's Mitte district. It is the largest museum of the graphic arts in Germany and at the same time one of the four most important collections of its kind in the world. The collection includes Friedrich Gilly's design for the monument to Frederick II of Prussia.
] The Jewish Museum Berlin, Jewish Museum has a standing exhibition on two millennia of German-Jewish history. The German Museum of Technology (Berlin), German Museum of Technology in Kreuzberg has a large collection of historical technical artifacts. The ''Natural History Museum, Berlin, Museum für Naturkunde'' (Berlin's natural history museum) exhibits natural history near Berlin Hauptbahnhof. It has the largest mounted dinosaur in the world (a ''Giraffatitan'' skeleton). A well-preserved specimen of ''Tyrannosaurus, Tyrannosaurus rex'' and the early bird ''Archaeopteryx'' are at display as well.
In Dahlem (Berlin), Dahlem, there are several museums of world art and culture, such as the Museum of Asian Art, the Ethnological Museum of Berlin, Ethnological Museum, the Museum Europäischer Kulturen, Museum of European Cultures, as well as the Allied Museum. The Brücke Museum features one of the largest collection of works by artist of the early 20th-century expressionist movement. In Lichtenberg, on the grounds of the former Stasi, East German Ministry for State Security, is the Stasi Museum. The site of Checkpoint Charlie, one of the most renowned crossing points of the Berlin Wall, is still preserved. A private Checkpoint Charlie Museum, museum venture exhibits a comprehensive documentation of detailed plans and strategies devised by people who tried to flee from the East.
The Beate Uhse Erotic Museum claimed to be the largest erotic museum in the world until it closed in 2014.
The cityscape of Berlin displays large quantities of urban street art. It has become a significant part of the city's cultural heritage and has its roots in the graffiti scene of Kreuzberg of the 1980s. The Berlin Wall graffiti art, Berlin Wall itself has become one of the largest open-air canvasses in the world. The leftover stretch along the Spree river in Friedrichshain remains as the East Side Gallery. Berlin today is consistently rated as an important world city for street art culture.
Berlin has galleries which are quite rich in contemporary art. Located in Mitte, KW Institute for Contemporary Art, KOW, Sprüth Magers; Kreuzberg there are a few galleries as well such as Blain Southern, Esther Schipper, Future Gallery, König Gallerie.
The Jewish Museum Berlin, Jewish Museum has a standing exhibition on two millennia of German-Jewish history. The German Museum of Technology (Berlin), German Museum of Technology in Kreuzberg has a large collection of historical technical artifacts. The ''Natural History Museum, Berlin, Museum für Naturkunde'' (Berlin's natural history museum) exhibits natural history near Berlin Hauptbahnhof. It has the largest mounted dinosaur in the world (a ''Giraffatitan'' skeleton). A well-preserved specimen of ''Tyrannosaurus, Tyrannosaurus rex'' and the early bird ''Archaeopteryx'' are at display as well.
In Dahlem (Berlin), Dahlem, there are several museums of world art and culture, such as the Museum of Asian Art, the Ethnological Museum of Berlin, Ethnological Museum, the Museum Europäischer Kulturen, Museum of European Cultures, as well as the Allied Museum. The Brücke Museum features one of the largest collection of works by artist of the early 20th-century expressionist movement. In Lichtenberg, on the grounds of the former Stasi, East German Ministry for State Security, is the Stasi Museum. The site of Checkpoint Charlie, one of the most renowned crossing points of the Berlin Wall, is still preserved. A private Checkpoint Charlie Museum, museum venture exhibits a comprehensive documentation of detailed plans and strategies devised by people who tried to flee from the East.
The Beate Uhse Erotic Museum claimed to be the largest erotic museum in the world until it closed in 2014.
The cityscape of Berlin displays large quantities of urban street art. It has become a significant part of the city's cultural heritage and has its roots in the graffiti scene of Kreuzberg of the 1980s. The Berlin Wall graffiti art, Berlin Wall itself has become one of the largest open-air canvasses in the world. The leftover stretch along the Spree river in Friedrichshain remains as the East Side Gallery. Berlin today is consistently rated as an important world city for street art culture.
Berlin has galleries which are quite rich in contemporary art. Located in Mitte, KW Institute for Contemporary Art, KOW, Sprüth Magers; Kreuzberg there are a few galleries as well such as Blain Southern, Esther Schipper, Future Gallery, König Gallerie.
Nightlife and festivals
 Berlin's nightlife has been celebrated as one of the most diverse and vibrant of its kind. In the 1970s and 80s, the SO36 in Kreuzberg was a center for punk music and culture. The ''SOUND'' and the ''Dschungel'' gained notoriety. Throughout the 1990s, people in their 20s from all over the world, particularly those in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, made Berlin's club scene a premier nightlife venue. After the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, many historic buildings in Mitte, the former city center of East Berlin, were illegally occupied and re-built by young squatters and became a fertile ground for underground and counterculture gatherings. The central boroughs are home to many nightclubs, including the Watergate, Tresor (club), Tresor and Berghain. The KitKatClub and several other locations are known for their sexually uninhibited parties.
Clubs are not required to close at a fixed time during the weekends, and many parties last well into the morning or even all weekend. The ''Weekend Club'' near Alexanderplatz features a roof terrace that allows partying at night. Several venues have become a popular stage for the Neo-Burlesque scene.
Berlin's nightlife has been celebrated as one of the most diverse and vibrant of its kind. In the 1970s and 80s, the SO36 in Kreuzberg was a center for punk music and culture. The ''SOUND'' and the ''Dschungel'' gained notoriety. Throughout the 1990s, people in their 20s from all over the world, particularly those in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, made Berlin's club scene a premier nightlife venue. After the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, many historic buildings in Mitte, the former city center of East Berlin, were illegally occupied and re-built by young squatters and became a fertile ground for underground and counterculture gatherings. The central boroughs are home to many nightclubs, including the Watergate, Tresor (club), Tresor and Berghain. The KitKatClub and several other locations are known for their sexually uninhibited parties.
Clubs are not required to close at a fixed time during the weekends, and many parties last well into the morning or even all weekend. The ''Weekend Club'' near Alexanderplatz features a roof terrace that allows partying at night. Several venues have become a popular stage for the Neo-Burlesque scene.

 Berlin has a long history of gay culture, and is an important Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, birthplace of the LGBT rights movement. Same-sex bars and dance halls operated freely as early as the 1880s, and the first gay magazine, ''Der Eigene'', started in 1896. By the 1920s, gays and lesbians had an unprecedented visibility.
Berlin has a long history of gay culture, and is an important Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, birthplace of the LGBT rights movement. Same-sex bars and dance halls operated freely as early as the 1880s, and the first gay magazine, ''Der Eigene'', started in 1896. By the 1920s, gays and lesbians had an unprecedented visibility.
Performing arts
 Berlin is home to 44 theaters and stages.
Berlin is home to 44 theaters and stages.
Cuisine
The German cuisine, cuisine and culinary offerings of Berlin vary greatly. 23 restaurants in Berlin have been awarded one or more Michelin Guide#Stars, Michelin stars in the Michelin Guide of 2021, which ranks the city at the top for the number of restaurants having this distinction in Germany.
Recreation
 Berlin Zoological Garden, Zoologischer Garten Berlin, the older of two zoos in the city, was founded in 1844. It is the most visited zoo in Europe and presents the most diverse range of species in the world. It was the home of the captive-born celebrity polar bear Knut (polar bear), Knut.
Berlin Zoological Garden, Zoologischer Garten Berlin, the older of two zoos in the city, was founded in 1844. It is the most visited zoo in Europe and presents the most diverse range of species in the world. It was the home of the captive-born celebrity polar bear Knut (polar bear), Knut. The Tiergarten (park), Tiergarten park in Mitte, with landscape design by Peter Joseph Lenné, is one of Berlin's largest and most popular parks. In Kreuzberg, the Viktoriapark provides a viewing point over the southern part of inner-city Berlin. Treptower Park, beside the Spree in Treptow, features a large Soviet War Memorial (Treptower Park), Soviet War Memorial. The Volkspark in Friedrichshain, which opened in 1848, is the oldest park in the city, with monuments, a summer outdoor cinema and several sports areas. Tempelhofer Feld, the site of the former Berlin Tempelhof Airport, city airport, is the world's largest inner-city open space.
The Tiergarten (park), Tiergarten park in Mitte, with landscape design by Peter Joseph Lenné, is one of Berlin's largest and most popular parks. In Kreuzberg, the Viktoriapark provides a viewing point over the southern part of inner-city Berlin. Treptower Park, beside the Spree in Treptow, features a large Soviet War Memorial (Treptower Park), Soviet War Memorial. The Volkspark in Friedrichshain, which opened in 1848, is the oldest park in the city, with monuments, a summer outdoor cinema and several sports areas. Tempelhofer Feld, the site of the former Berlin Tempelhof Airport, city airport, is the world's largest inner-city open space.
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
is on the southwestern periphery of Berlin. The city was a residence of the Prussian kings and the German Emperor, German Kaiser, until 1918. The area around Potsdam in particular Sanssouci is known for a series of interconnected lakes and cultural landmarks. The Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin are the largest World Heritage Site in Germany.
Berlin is also well known for its numerous cafés, street musicians, beach bars along the Spree River, flea markets, boutique shops and pop-up stores, which are a source for recreation and leisure.
Sports

 Berlin has established a high-profile as a host city of major international sporting events. The city hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics and was the host city for the 2006 FIFA World Cup final. The World Athletics Championships was held at Olympiastadion (Berlin), Olympiastadion in 2009 World Athletics Championships, 2009 and 2025 World Athletics Championships, 2025. The city hosted the Euroleague Final Four basketball competition in 2009 Euroleague Final Four, 2009 and 2016 Euroleague Final Four, 2016, and was one of the hosts of FIBA EuroBasket 2015. In 2015 Berlin was the venue for the 2015 UEFA Champions League Final, UEFA Champions League Final. The city bid to host the 2000 Summer Olympics but lost to Sydney.
Berlin hosted the 2023 Special Olympics World Summer Games. This is the first time Germany has ever hosted the Special Olympics World Games.
The annual Berlin Marathona course that holds the most top-10 world record runsand the Internationales Stadionfest, ISTAF are well-established athletic events in the city. The Mellowpark in Köpenick is one of the biggest skate and BMX parks in Europe. A fan fest at Brandenburg Gate, which attracts several hundreds of thousands of spectators, has become popular during international football competitions, such as the UEFA European Championship.
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, who is often hailed as the "father of modern gymnastics", invented the horizontal bar, parallel bars, Rings (gymnastics), rings, and the Vault (gymnastics), vault around 1811 in Berlin. Jahn's Turners movement, first realized at Volkspark Hasenheide, was the origin of modern sports clubs. In 2013, around 600,000 Berliners were registered in one of the more than 2,300 sport and fitness clubs. The city of Berlin operates more than 60 public indoor and outdoor swimming pools. Berlin is the largest Olympic training center in Germany, with around 500 top athletes (15% of all German top athletes) being based there. Forty-seven elite athletes participated in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Berliners would achieve seven gold, twelve silver, and three bronze medals.
Berlin has established a high-profile as a host city of major international sporting events. The city hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics and was the host city for the 2006 FIFA World Cup final. The World Athletics Championships was held at Olympiastadion (Berlin), Olympiastadion in 2009 World Athletics Championships, 2009 and 2025 World Athletics Championships, 2025. The city hosted the Euroleague Final Four basketball competition in 2009 Euroleague Final Four, 2009 and 2016 Euroleague Final Four, 2016, and was one of the hosts of FIBA EuroBasket 2015. In 2015 Berlin was the venue for the 2015 UEFA Champions League Final, UEFA Champions League Final. The city bid to host the 2000 Summer Olympics but lost to Sydney.
Berlin hosted the 2023 Special Olympics World Summer Games. This is the first time Germany has ever hosted the Special Olympics World Games.
The annual Berlin Marathona course that holds the most top-10 world record runsand the Internationales Stadionfest, ISTAF are well-established athletic events in the city. The Mellowpark in Köpenick is one of the biggest skate and BMX parks in Europe. A fan fest at Brandenburg Gate, which attracts several hundreds of thousands of spectators, has become popular during international football competitions, such as the UEFA European Championship.
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, who is often hailed as the "father of modern gymnastics", invented the horizontal bar, parallel bars, Rings (gymnastics), rings, and the Vault (gymnastics), vault around 1811 in Berlin. Jahn's Turners movement, first realized at Volkspark Hasenheide, was the origin of modern sports clubs. In 2013, around 600,000 Berliners were registered in one of the more than 2,300 sport and fitness clubs. The city of Berlin operates more than 60 public indoor and outdoor swimming pools. Berlin is the largest Olympic training center in Germany, with around 500 top athletes (15% of all German top athletes) being based there. Forty-seven elite athletes participated in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Berliners would achieve seven gold, twelve silver, and three bronze medals.
See also
* List of fiction set in Berlin
* List of honorary citizens of Berlin
* List of people from Berlin
* List of songs about Berlin
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
* Andreas Daum, Daum, Andreas. ''Kennedy in Berlin''. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2008, .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
berlin.de
– official website
*
{{Authority control
Berlin,
German state capitals
Capitals in Europe
City-states
Members of the Hanseatic League
Populated places established in the 13th century
Turkish communities outside Turkey
1230s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1237 establishments in Europe
States of Germany
NUTS 2 statistical regions of Germany
NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union

 In the 12th century the region came under German rule as part of the
In the 12th century the region came under German rule as part of the  Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the
Since 1618, the Margraviate of Brandenburg had been in personal union with the Duchy of Prussia. In 1701, the dual state formed the  During
During 
 All four Allies of World War II shared administrative responsibilities for Berlin. However, in 1948, when the Western Allies extended the currency reform in the Western zones of Germany to the three western sectors of Berlin, the Soviet Union imposed the Berlin Blockade on the access routes to and from West Berlin, which lay entirely inside Soviet-controlled territory. The Berlin airlift, conducted by the three western Allies, overcame this blockade by supplying food and other supplies to the city from June 1948 to May 1949. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany was founded in West Germany and eventually included all of the American, British and French zones, excluding those three countries' zones in Berlin, while the Marxist–Leninist East Germany, German Democratic Republic was proclaimed in East Germany. West Berlin officially remained an occupied city, but it politically was aligned with the Federal Republic of Germany despite West Berlin's geographic isolation. Airline service to West Berlin was granted only to American, British and French airlines.
All four Allies of World War II shared administrative responsibilities for Berlin. However, in 1948, when the Western Allies extended the currency reform in the Western zones of Germany to the three western sectors of Berlin, the Soviet Union imposed the Berlin Blockade on the access routes to and from West Berlin, which lay entirely inside Soviet-controlled territory. The Berlin airlift, conducted by the three western Allies, overcame this blockade by supplying food and other supplies to the city from June 1948 to May 1949. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany was founded in West Germany and eventually included all of the American, British and French zones, excluding those three countries' zones in Berlin, while the Marxist–Leninist East Germany, German Democratic Republic was proclaimed in East Germany. West Berlin officially remained an occupied city, but it politically was aligned with the Federal Republic of Germany despite West Berlin's geographic isolation. Airline service to West Berlin was granted only to American, British and French airlines.
 The founding of the two German states increased Cold War tensions. West Berlin was surrounded by East German territory, and East Germany proclaimed the Eastern part as its capital, a move the western powers did not recognize. East Berlin included most of the city's historic center. The West German government established itself in
The founding of the two German states increased Cold War tensions. West Berlin was surrounded by East German territory, and East Germany proclaimed the Eastern part as its capital, a move the western powers did not recognize. East Berlin included most of the city's historic center. The West German government established itself in 
 Berlin is in northeastern Germany, in an area of low-lying marshy woodlands with a mainly flat topography, part of the vast Northern European Plain which stretches all the way from northern France to western Russia. The ''Berliner Urstromtal'' (an ice age glacial valley), between the low Barnim Plateau to the north and the Teltow plateau to the south, was formed by meltwater flowing from ice sheets at the end of the last Weichselian glaciation. The Spree follows this valley now. In Spandau, a borough in the west of Berlin, the Spree empties into the river
Berlin is in northeastern Germany, in an area of low-lying marshy woodlands with a mainly flat topography, part of the vast Northern European Plain which stretches all the way from northern France to western Russia. The ''Berliner Urstromtal'' (an ice age glacial valley), between the low Barnim Plateau to the north and the Teltow plateau to the south, was formed by meltwater flowing from ice sheets at the end of the last Weichselian glaciation. The Spree follows this valley now. In Spandau, a borough in the west of Berlin, the Spree empties into the river 

 Berlin's history has left the city with a polycentric metropolitan area and an eclectic mix of architecture. The city's appearance today has been predominantly shaped by German history during the 20th century. 17% of Berlin's buildings are
Berlin's history has left the city with a polycentric metropolitan area and an eclectic mix of architecture. The city's appearance today has been predominantly shaped by German history during the 20th century. 17% of Berlin's buildings are 
 The Fernsehturm Berlin, Fernsehturm (TV tower) at Alexanderplatz in Mitte is among the tallest structures in the European Union at . Built in 1969, it is visible throughout most of the central districts of Berlin.
The Fernsehturm Berlin, Fernsehturm (TV tower) at Alexanderplatz in Mitte is among the tallest structures in the European Union at . Built in 1969, it is visible throughout most of the central districts of Berlin.  The city can be viewed from its observation floor. Starting here, the Karl-Marx-Allee heads east, an avenue lined by monumental residential buildings, designed in the Socialist Classicism style. Adjacent to this area is the Rotes Rathaus (City Hall), with its distinctive red-brick architecture. In front of it is the Neptunbrunnen, a fountain featuring a mythological group of Triton (mythology), Tritons, personifications of the four main Prussian rivers, and Neptune (mythology), Neptune on top of it.
The
The city can be viewed from its observation floor. Starting here, the Karl-Marx-Allee heads east, an avenue lined by monumental residential buildings, designed in the Socialist Classicism style. Adjacent to this area is the Rotes Rathaus (City Hall), with its distinctive red-brick architecture. In front of it is the Neptunbrunnen, a fountain featuring a mythological group of Triton (mythology), Tritons, personifications of the four main Prussian rivers, and Neptune (mythology), Neptune on top of it.
The 
 The
The  Unter den Linden is a tree-lined east–west avenue from the Brandenburg Gate to the site of the former Berliner Stadtschloss, and was once Berlin's premier promenade. Many Classical buildings line the street, and part of Humboldt University is there. Friedrichstraße was Berlin's legendary street during the Golden Twenties. It combines 20th-century traditions with the modern architecture of today's Berlin.
Unter den Linden is a tree-lined east–west avenue from the Brandenburg Gate to the site of the former Berliner Stadtschloss, and was once Berlin's premier promenade. Many Classical buildings line the street, and part of Humboldt University is there. Friedrichstraße was Berlin's legendary street during the Golden Twenties. It combines 20th-century traditions with the modern architecture of today's Berlin.
 Since the
Since the  In 2018, the GDP of Berlin totaled €147 billion, an increase of 3.1% over the previous year. Berlin's economy is dominated by the
In 2018, the GDP of Berlin totaled €147 billion, an increase of 3.1% over the previous year. Berlin's economy is dominated by the  Berlin is home to many magazine, newspaper, book, and scientific/academic publishers and their associated service industries. In addition, around 20 news agencies, more than 90 regional daily newspapers and their websites, as well as the Berlin offices of more than 22 national publications such as , and Die Zeit reinforce the capital's position as Germany's epicenter for influential debate. Therefore, many international journalists, bloggers, and writers live and work in the city.
Berlin is the central location to several international and regional television and radio stations. The public broadcaster Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg, RBB has its headquarters in Berlin as well as the commercial broadcasters MTV Europe and Welt (German TV channel), Welt. German international public broadcaster Deutsche Welle has its TV production unit in Berlin, and most national German broadcasters have a studio in the city, including ZDF and RTL Television, RTL.
Berlin has Germany's largest number of daily newspapers, with numerous local broadsheets (''Berliner Morgenpost'', ''Berliner Zeitung'', ''Der Tagesspiegel''), and three major Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloids, as well as national dailies of varying sizes, each with a different political affiliation, such as ''Die Welt'', ''Neues Deutschland'', and ''Die Tageszeitung''. The ''Exberliner'', a monthly magazine, is Berlin's English-language periodical and La Gazette de Berlin a French-language newspaper.
Berlin is also the headquarter of major German-language publishing houses like Walter de Gruyter, Axel Springer AG, Springer, the Ullstein Verlagsgruppe (publishing group), Suhrkamp, and Cornelsen are all based in Berlin. Each of which publishes books, periodicals, and multimedia products.
Berlin is home to many magazine, newspaper, book, and scientific/academic publishers and their associated service industries. In addition, around 20 news agencies, more than 90 regional daily newspapers and their websites, as well as the Berlin offices of more than 22 national publications such as , and Die Zeit reinforce the capital's position as Germany's epicenter for influential debate. Therefore, many international journalists, bloggers, and writers live and work in the city.
Berlin is the central location to several international and regional television and radio stations. The public broadcaster Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg, RBB has its headquarters in Berlin as well as the commercial broadcasters MTV Europe and Welt (German TV channel), Welt. German international public broadcaster Deutsche Welle has its TV production unit in Berlin, and most national German broadcasters have a studio in the city, including ZDF and RTL Television, RTL.
Berlin has Germany's largest number of daily newspapers, with numerous local broadsheets (''Berliner Morgenpost'', ''Berliner Zeitung'', ''Der Tagesspiegel''), and three major Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloids, as well as national dailies of varying sizes, each with a different political affiliation, such as ''Die Welt'', ''Neues Deutschland'', and ''Die Tageszeitung''. The ''Exberliner'', a monthly magazine, is Berlin's English-language periodical and La Gazette de Berlin a French-language newspaper.
Berlin is also the headquarter of major German-language publishing houses like Walter de Gruyter, Axel Springer AG, Springer, the Ullstein Verlagsgruppe (publishing group), Suhrkamp, and Cornelsen are all based in Berlin. Each of which publishes books, periodicals, and multimedia products.
 Berlin is well known for its highly developed bicycle lane system. It is estimated that Berlin has 710 bicycles per 1,000 residents. Around 500,000 daily bike riders accounted for 13 percent of total traffic in 2010.
Cyclists in Berlin have access to 620 km of bicycle paths including approximately 150 km of mandatory bicycle paths, 190 km of off-road bicycle routes, 60 km of bicycle lanes on roads, 70 km of shared bus lanes which are also open to cyclists, 100 km of combined pedestrian/bike paths and 50 km of marked bicycle lanes on roadside pavements or sidewalks. Riders are allowed to carry their bicycles on Regionalbahn (RE), S-Bahn and U-Bahn trains, on trams, and on night buses if a bike ticket is purchased.
Berlin is well known for its highly developed bicycle lane system. It is estimated that Berlin has 710 bicycles per 1,000 residents. Around 500,000 daily bike riders accounted for 13 percent of total traffic in 2010.
Cyclists in Berlin have access to 620 km of bicycle paths including approximately 150 km of mandatory bicycle paths, 190 km of off-road bicycle routes, 60 km of bicycle lanes on roads, 70 km of shared bus lanes which are also open to cyclists, 100 km of combined pedestrian/bike paths and 50 km of marked bicycle lanes on roadside pavements or sidewalks. Riders are allowed to carry their bicycles on Regionalbahn (RE), S-Bahn and U-Bahn trains, on trams, and on night buses if a bike ticket is purchased.
 Taxicabs in Berlin are yellow or beige. In 2024, around 8,000 taxicabs were in service. Like in most of Europe, app-based Ridesharing company, sharing cab services are available but limited.
Taxicabs in Berlin are yellow or beige. In 2024, around 8,000 taxicabs were in service. Like in most of Europe, app-based Ridesharing company, sharing cab services are available but limited.

 Long-distance rail lines directly connect Berlin with all of the major cities of Germany. the regional rail lines of the Verkehrsverbund Berlin-Brandenburg provide access to
Long-distance rail lines directly connect Berlin with all of the major cities of Germany. the regional rail lines of the Verkehrsverbund Berlin-Brandenburg provide access to 
 The ''Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe'' (BVG) and the German State-owned Deutsche Bahn (DB) manage several extensive urban public transport systems.
Public transport in Berlin has a long and complicated history because of the 20th-century division of the city, where movement between the two halves was not served. Since 1989, the transport network has been developed extensively. However, it still contains early 20th century traits, such as the U1.
The ''Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe'' (BVG) and the German State-owned Deutsche Bahn (DB) manage several extensive urban public transport systems.
Public transport in Berlin has a long and complicated history because of the 20th-century division of the city, where movement between the two halves was not served. Since 1989, the transport network has been developed extensively. However, it still contains early 20th century traits, such as the U1.
 Berlin is served by one commercial international airport: Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER), located just outside Berlin's south-eastern border, in the state of Brandenburg. It began construction in 2006, with the intention of replacing Berlin Tegel Airport, Airport (TXL) and Berlin Schönefeld Airport, Airport (SXF) as the single commercial airport of Berlin. Previously set to open in 2012, after extensive delays and cost overruns, it opened for commercial operations in October 2020. The planned initial capacity of around 27 million passengers per year is to be further developed to bring the terminal capacity to approximately 55 million per year by 2040.
Before the opening of the BER in Brandenburg, Berlin was served by Tegel Airport and Schönefeld Airport. Tegel Airport was within the city limits, and Schönefeld Airport was located at the same site as the BER. Both airports together handled 29.5 million passengers in 2015. In 2014, 67 airlines served 163 destinations in 50 countries from Berlin. Airport was a focus city for Lufthansa and Eurowings while Schönefeld served as an important destination for airlines like , easyJet and Ryanair. Until 2008, Berlin was also served by the smaller Tempelhof Airport, which functioned as a city airport, with a convenient location near the city center, allowing for quick transit times between the central business district and the airport. The airport grounds have since been turned into a city park.
Berlin is served by one commercial international airport: Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER), located just outside Berlin's south-eastern border, in the state of Brandenburg. It began construction in 2006, with the intention of replacing Berlin Tegel Airport, Airport (TXL) and Berlin Schönefeld Airport, Airport (SXF) as the single commercial airport of Berlin. Previously set to open in 2012, after extensive delays and cost overruns, it opened for commercial operations in October 2020. The planned initial capacity of around 27 million passengers per year is to be further developed to bring the terminal capacity to approximately 55 million per year by 2040.
Before the opening of the BER in Brandenburg, Berlin was served by Tegel Airport and Schönefeld Airport. Tegel Airport was within the city limits, and Schönefeld Airport was located at the same site as the BER. Both airports together handled 29.5 million passengers in 2015. In 2014, 67 airlines served 163 destinations in 50 countries from Berlin. Airport was a focus city for Lufthansa and Eurowings while Schönefeld served as an important destination for airlines like , easyJet and Ryanair. Until 2008, Berlin was also served by the smaller Tempelhof Airport, which functioned as a city airport, with a convenient location near the city center, allowing for quick transit times between the central business district and the airport. The airport grounds have since been turned into a city park.
 Berlin's two largest energy provider for private households are the Swedish firm Vattenfall and the Berlin-based company GASAG. Both offer electric power and natural gas supply. Some of the city's electric energy is imported from nearby power plants in southern
Berlin's two largest energy provider for private households are the Swedish firm Vattenfall and the Berlin-based company GASAG. Both offer electric power and natural gas supply. Some of the city's electric energy is imported from nearby power plants in southern  Berlin has a long history of discoveries in medicine and innovations in medical technology. The modern history of medicine has been significantly influenced by scientists from Berlin. Rudolf Virchow was the founder of cellular pathology, while Robert Koch developed vaccines for anthrax, cholera, and tuberculosis. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine.
The Charité complex (Universitätsklinik Charité) is the largest university hospital in Europe, tracing back its origins to the year 1710. More than half of all German Nobel Prize winners in Physiology or Medicine, including Emil von Behring, Robert Koch and Paul Ehrlich, have worked at the Charité. The Charité is spread over four campuses and comprises around 3,000 beds, 15,500 staff, 8,000 students, and more than 60 operating theaters, and it has a turnover of two billion euros annually.
Berlin has a long history of discoveries in medicine and innovations in medical technology. The modern history of medicine has been significantly influenced by scientists from Berlin. Rudolf Virchow was the founder of cellular pathology, while Robert Koch developed vaccines for anthrax, cholera, and tuberculosis. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine.
The Charité complex (Universitätsklinik Charité) is the largest university hospital in Europe, tracing back its origins to the year 1710. More than half of all German Nobel Prize winners in Physiology or Medicine, including Emil von Behring, Robert Koch and Paul Ehrlich, have worked at the Charité. The Charité is spread over four campuses and comprises around 3,000 beds, 15,500 staff, 8,000 students, and more than 60 operating theaters, and it has a turnover of two billion euros annually.
 Since 2017, the digital television standard in Berlin and Germany is DVB-T2. This system transmits video compression, compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream.
Berlin has installed several hundred free public Wireless LAN sites across the capital since 2016. The wireless networks are concentrated mostly in central districts; 650 hotspots (325 indoor and 325 outdoor access points) are installed.
The UMTS (3G) and LTE (telecommunication), LTE (4G) networks of the three major cellular operators Vodafone, T-Mobile International AG, T-Mobile and Telefónica Germany, O2 enable the use of mobile broadband applications citywide.
Since 2017, the digital television standard in Berlin and Germany is DVB-T2. This system transmits video compression, compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream.
Berlin has installed several hundred free public Wireless LAN sites across the capital since 2016. The wireless networks are concentrated mostly in central districts; 650 hotspots (325 indoor and 325 outdoor access points) are installed.
The UMTS (3G) and LTE (telecommunication), LTE (4G) networks of the three major cellular operators Vodafone, T-Mobile International AG, T-Mobile and Telefónica Germany, O2 enable the use of mobile broadband applications citywide.
 , Berlin had 878 schools, teaching 340,658 students in 13,727 classes and 56,787 trainees in businesses and elsewhere. The city has a 6-year primary education program. After completing primary school, students continue to the (a comprehensive school) or (college preparatory school). Berlin has a special bilingual school program in the , in which children are taught the curriculum in German and a foreign language, starting in primary school and continuing in high school.
The Französisches Gymnasium Berlin, which was founded in 1689 to teach the children of Huguenot refugees, offers (German/French) instruction. The John F. Kennedy School, Berlin, John F. Kennedy School, a bilingual German–American public school in Zehlendorf, is particularly popular with children of diplomats and the English-speaking expatriate community. 82 teach Latin and 8 teach Classical Greek.
, Berlin had 878 schools, teaching 340,658 students in 13,727 classes and 56,787 trainees in businesses and elsewhere. The city has a 6-year primary education program. After completing primary school, students continue to the (a comprehensive school) or (college preparatory school). Berlin has a special bilingual school program in the , in which children are taught the curriculum in German and a foreign language, starting in primary school and continuing in high school.
The Französisches Gymnasium Berlin, which was founded in 1689 to teach the children of Huguenot refugees, offers (German/French) instruction. The John F. Kennedy School, Berlin, John F. Kennedy School, a bilingual German–American public school in Zehlendorf, is particularly popular with children of diplomats and the English-speaking expatriate community. 82 teach Latin and 8 teach Classical Greek.
 The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region is one of the most prolific centers of higher education and research in Germany and Europe. Historically, 67 Nobel Prize winners are affiliated with the Berlin-based universities.
The city has four public research universities and more than 30 private, professional, and technical colleges ''(Hochschulen)'', offering a wide range of disciplines. A record number of 175,651 students were enrolled in the winter term of 2015/16. Among them around 18% have an international background.
The three largest universities combined have approximately 103,000 enrolled students. There are the Free University of Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin ''(Free University of Berlin, FU Berlin)'' with about 33,000 students, the Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin ''(HU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students, and the Technical University of Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin ''(TU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students. The Charité Medical School has around 8,000 students. The FU, the HU, the TU, and the Charité make up the Berlin University Alliance, which has received funding from the German Universities Excellence Initiative, Excellence Strategy program of the German government. The Berlin University of the Arts, Universität der Künste ''(UdK)'' has about 4,000 students and ESMT Berlin is only one of four business schools in Germany with triple accreditation. The Hertie School, a private public policy school located in Mitte, has more than 900 students and doctoral students. The Berlin School of Economics and Law has an enrollment of about 11,000 students, the Berliner Hochschule für Technik, Berlin University of Applied Sciences and Technology of about 12,000 students, and the HTW Berlin, Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft (University of Applied Sciences for Engineering and Economics) of about 14,000 students.
The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region is one of the most prolific centers of higher education and research in Germany and Europe. Historically, 67 Nobel Prize winners are affiliated with the Berlin-based universities.
The city has four public research universities and more than 30 private, professional, and technical colleges ''(Hochschulen)'', offering a wide range of disciplines. A record number of 175,651 students were enrolled in the winter term of 2015/16. Among them around 18% have an international background.
The three largest universities combined have approximately 103,000 enrolled students. There are the Free University of Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin ''(Free University of Berlin, FU Berlin)'' with about 33,000 students, the Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin ''(HU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students, and the Technical University of Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin ''(TU Berlin)'' with 35,000 students. The Charité Medical School has around 8,000 students. The FU, the HU, the TU, and the Charité make up the Berlin University Alliance, which has received funding from the German Universities Excellence Initiative, Excellence Strategy program of the German government. The Berlin University of the Arts, Universität der Künste ''(UdK)'' has about 4,000 students and ESMT Berlin is only one of four business schools in Germany with triple accreditation. The Hertie School, a private public policy school located in Mitte, has more than 900 students and doctoral students. The Berlin School of Economics and Law has an enrollment of about 11,000 students, the Berliner Hochschule für Technik, Berlin University of Applied Sciences and Technology of about 12,000 students, and the HTW Berlin, Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft (University of Applied Sciences for Engineering and Economics) of about 14,000 students.
 The city has a high density of internationally renowned research institutions, such as the Fraunhofer Society, the DLR Institute for Planetary Research, the Leibniz Association, the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres, Helmholtz Association, and the Max Planck Society, which are independent of, or only loosely connected to its universities. In 2012, around 65,000 professional scientists were working in research and development in the city.
Berlin is one of the knowledge and innovation communities (KIC) of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT). The KIC is based at the Center for Entrepreneurship at TU Berlin and has a focus in the development of IT industries. It partners with major multinational companies such as Siemens, Deutsche Telekom, and SAP SE, SAP.
One of Europe's successful research, business and technology List of technology centers, clusters is based at WISTA in Berlin-Adlershof, with more than 1,000 affiliated firms, university departments and scientific institutions.
In addition to the university-affiliated libraries, the Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin is a major research library. Its two main locations are on Potsdamer Straße and on Unter den Linden. There are also 86 public libraries in the city. ResearchGate, a global social networking site for scientists, is based in Berlin.
The city has a high density of internationally renowned research institutions, such as the Fraunhofer Society, the DLR Institute for Planetary Research, the Leibniz Association, the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres, Helmholtz Association, and the Max Planck Society, which are independent of, or only loosely connected to its universities. In 2012, around 65,000 professional scientists were working in research and development in the city.
Berlin is one of the knowledge and innovation communities (KIC) of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT). The KIC is based at the Center for Entrepreneurship at TU Berlin and has a focus in the development of IT industries. It partners with major multinational companies such as Siemens, Deutsche Telekom, and SAP SE, SAP.
One of Europe's successful research, business and technology List of technology centers, clusters is based at WISTA in Berlin-Adlershof, with more than 1,000 affiliated firms, university departments and scientific institutions.
In addition to the university-affiliated libraries, the Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin is a major research library. Its two main locations are on Potsdamer Straße and on Unter den Linden. There are also 86 public libraries in the city. ResearchGate, a global social networking site for scientists, is based in Berlin.


 Berlin is known for its numerous cultural institutions, many of which enjoy international reputation. The diversity and vivacity of the metropolis led to a trendsetting atmosphere. An innovative music, dance and art scene has developed in the 21st century.
Young people, international artists and entrepreneurs continued to settle in the city and made Berlin a popular entertainment center in the world.
The expanding cultural performance of the city was underscored by the relocation of the Universal Music Group who decided to move their headquarters to the banks of the River Spree. In 2005, Berlin was named "City of Design" by UNESCO and has been part of the Creative Cities Network ever since.
Many German and International films were shot in Berlin, including M (1931 film), M, One, Two, Three, Cabaret (1972 film), Cabaret, Christiane F. (film), Christiane F., Possession (1981 film), Possession, Octopussy, Wings of Desire, Run Lola Run, Bourne (film series), The Bourne Trilogy, Good Bye, Lenin!, The Lives of Others, Inglourious Basterds, Hanna (film), Hanna, Unknown (2011 film), Unknown and Bridge of Spies (film), Bridge of Spies.
Berlin is known for its numerous cultural institutions, many of which enjoy international reputation. The diversity and vivacity of the metropolis led to a trendsetting atmosphere. An innovative music, dance and art scene has developed in the 21st century.
Young people, international artists and entrepreneurs continued to settle in the city and made Berlin a popular entertainment center in the world.
The expanding cultural performance of the city was underscored by the relocation of the Universal Music Group who decided to move their headquarters to the banks of the River Spree. In 2005, Berlin was named "City of Design" by UNESCO and has been part of the Creative Cities Network ever since.
Many German and International films were shot in Berlin, including M (1931 film), M, One, Two, Three, Cabaret (1972 film), Cabaret, Christiane F. (film), Christiane F., Possession (1981 film), Possession, Octopussy, Wings of Desire, Run Lola Run, Bourne (film series), The Bourne Trilogy, Good Bye, Lenin!, The Lives of Others, Inglourious Basterds, Hanna (film), Hanna, Unknown (2011 film), Unknown and Bridge of Spies (film), Bridge of Spies.
 Berlin is home to 138 museums and more than 400 art galleries. The ensemble on the
Berlin is home to 138 museums and more than 400 art galleries. The ensemble on the  The Jewish Museum Berlin, Jewish Museum has a standing exhibition on two millennia of German-Jewish history. The German Museum of Technology (Berlin), German Museum of Technology in Kreuzberg has a large collection of historical technical artifacts. The ''Natural History Museum, Berlin, Museum für Naturkunde'' (Berlin's natural history museum) exhibits natural history near Berlin Hauptbahnhof. It has the largest mounted dinosaur in the world (a ''Giraffatitan'' skeleton). A well-preserved specimen of ''Tyrannosaurus, Tyrannosaurus rex'' and the early bird ''Archaeopteryx'' are at display as well.
In Dahlem (Berlin), Dahlem, there are several museums of world art and culture, such as the Museum of Asian Art, the Ethnological Museum of Berlin, Ethnological Museum, the Museum Europäischer Kulturen, Museum of European Cultures, as well as the Allied Museum. The Brücke Museum features one of the largest collection of works by artist of the early 20th-century expressionist movement. In Lichtenberg, on the grounds of the former Stasi, East German Ministry for State Security, is the Stasi Museum. The site of Checkpoint Charlie, one of the most renowned crossing points of the Berlin Wall, is still preserved. A private Checkpoint Charlie Museum, museum venture exhibits a comprehensive documentation of detailed plans and strategies devised by people who tried to flee from the East.
The Beate Uhse Erotic Museum claimed to be the largest erotic museum in the world until it closed in 2014.
The cityscape of Berlin displays large quantities of urban street art. It has become a significant part of the city's cultural heritage and has its roots in the graffiti scene of Kreuzberg of the 1980s. The Berlin Wall graffiti art, Berlin Wall itself has become one of the largest open-air canvasses in the world. The leftover stretch along the Spree river in Friedrichshain remains as the East Side Gallery. Berlin today is consistently rated as an important world city for street art culture.
Berlin has galleries which are quite rich in contemporary art. Located in Mitte, KW Institute for Contemporary Art, KOW, Sprüth Magers; Kreuzberg there are a few galleries as well such as Blain Southern, Esther Schipper, Future Gallery, König Gallerie.
The Jewish Museum Berlin, Jewish Museum has a standing exhibition on two millennia of German-Jewish history. The German Museum of Technology (Berlin), German Museum of Technology in Kreuzberg has a large collection of historical technical artifacts. The ''Natural History Museum, Berlin, Museum für Naturkunde'' (Berlin's natural history museum) exhibits natural history near Berlin Hauptbahnhof. It has the largest mounted dinosaur in the world (a ''Giraffatitan'' skeleton). A well-preserved specimen of ''Tyrannosaurus, Tyrannosaurus rex'' and the early bird ''Archaeopteryx'' are at display as well.
In Dahlem (Berlin), Dahlem, there are several museums of world art and culture, such as the Museum of Asian Art, the Ethnological Museum of Berlin, Ethnological Museum, the Museum Europäischer Kulturen, Museum of European Cultures, as well as the Allied Museum. The Brücke Museum features one of the largest collection of works by artist of the early 20th-century expressionist movement. In Lichtenberg, on the grounds of the former Stasi, East German Ministry for State Security, is the Stasi Museum. The site of Checkpoint Charlie, one of the most renowned crossing points of the Berlin Wall, is still preserved. A private Checkpoint Charlie Museum, museum venture exhibits a comprehensive documentation of detailed plans and strategies devised by people who tried to flee from the East.
The Beate Uhse Erotic Museum claimed to be the largest erotic museum in the world until it closed in 2014.
The cityscape of Berlin displays large quantities of urban street art. It has become a significant part of the city's cultural heritage and has its roots in the graffiti scene of Kreuzberg of the 1980s. The Berlin Wall graffiti art, Berlin Wall itself has become one of the largest open-air canvasses in the world. The leftover stretch along the Spree river in Friedrichshain remains as the East Side Gallery. Berlin today is consistently rated as an important world city for street art culture.
Berlin has galleries which are quite rich in contemporary art. Located in Mitte, KW Institute for Contemporary Art, KOW, Sprüth Magers; Kreuzberg there are a few galleries as well such as Blain Southern, Esther Schipper, Future Gallery, König Gallerie.

 Berlin has a long history of gay culture, and is an important Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, birthplace of the LGBT rights movement. Same-sex bars and dance halls operated freely as early as the 1880s, and the first gay magazine, ''Der Eigene'', started in 1896. By the 1920s, gays and lesbians had an unprecedented visibility. Today, in addition to a positive atmosphere in the wider club scene, the city again has a huge number of queer clubs and festivals. The most famous and largest are Berlin Pride, the Christopher Street Day, the Lesbian and Gay City Festival in Berlin-Schöneberg, the Kreuzberg Pride.
The annual Berlin International Film Festival (Berlinale) with around 500,000 admissions is considered to be the largest publicly attended film festival in the world. The Karneval der Kulturen (''Carnival of Cultures''), a multi-ethnic street parade, is celebrated every Pentecost weekend. Berlin is also well known for the cultural festival Berliner Festspiele, which includes the jazz festival JazzFest Berlin, and Young Euro Classic, the largest international festival of youth orchestras in the world. Several technology and media art festivals and conferences are held in the city, including Transmediale and Chaos Communication Congress. The annual Berlin Festival focuses on indie rock, electronic music and synthpop and is part of the International Berlin Music Week. Every year Berlin hosts one of the largest New Year's Eve celebrations in the world, attended by well over a million people. The focal point is the Brandenburg Gate, where midnight fireworks are centered, but various private fireworks displays take place throughout the entire city. Partygoers in Germany often toast the New Year with a glass of Sekt, sparkling wine.
Berlin has a long history of gay culture, and is an important Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, birthplace of the LGBT rights movement. Same-sex bars and dance halls operated freely as early as the 1880s, and the first gay magazine, ''Der Eigene'', started in 1896. By the 1920s, gays and lesbians had an unprecedented visibility. Today, in addition to a positive atmosphere in the wider club scene, the city again has a huge number of queer clubs and festivals. The most famous and largest are Berlin Pride, the Christopher Street Day, the Lesbian and Gay City Festival in Berlin-Schöneberg, the Kreuzberg Pride.
The annual Berlin International Film Festival (Berlinale) with around 500,000 admissions is considered to be the largest publicly attended film festival in the world. The Karneval der Kulturen (''Carnival of Cultures''), a multi-ethnic street parade, is celebrated every Pentecost weekend. Berlin is also well known for the cultural festival Berliner Festspiele, which includes the jazz festival JazzFest Berlin, and Young Euro Classic, the largest international festival of youth orchestras in the world. Several technology and media art festivals and conferences are held in the city, including Transmediale and Chaos Communication Congress. The annual Berlin Festival focuses on indie rock, electronic music and synthpop and is part of the International Berlin Music Week. Every year Berlin hosts one of the largest New Year's Eve celebrations in the world, attended by well over a million people. The focal point is the Brandenburg Gate, where midnight fireworks are centered, but various private fireworks displays take place throughout the entire city. Partygoers in Germany often toast the New Year with a glass of Sekt, sparkling wine.
 Berlin is home to 44 theaters and stages. The Deutsches Theater (Berlin), Deutsches Theater in Mitte was built in 1849–50 and has operated almost continuously since then. The Volksbühne at Rosa-Luxemburg-Platz was built in 1913–14, though the company had been founded in 1890. The Berliner Ensemble, famous for performing the works of Bertolt Brecht, was established in 1949. The Schaubühne was founded in 1962 and moved to the building of the former Universum Cinema on Kurfürstendamm in 1981. With a seating capacity of 1,895 and a stage floor of , the Friedrichstadt-Palast in Berlin Mitte is the largest show palace in Europe. For Berlin's independent dance and theatre scene, venues such as the Sophiensäle in Mitte and the three houses of the Hebbel-Theater, Hebbel am Ufer (HAU) in Kreuzberg are important. Most productions there are also accessible to an English-speaking audience. Some of the dance and theatre groups that also work internationally (Gob Squad, Rimini Protokoll) are based there, as well as festivals such as the international festival Tanz im August, Dance in August.
Berlin has three major opera houses: the Deutsche Oper, the Berlin State Opera, and the Komische Oper. The Berlin State Opera on Unter den Linden opened in 1742 and is the oldest of the three. Its musical director is Daniel Barenboim. The Komische Oper has traditionally specialized in operettas and is also at Unter den Linden. The Deutsche Oper opened in 1912 in Charlottenburg.
The city's main venue for musical theater performances are the Theater am Potsdamer Platz and Theater des Westens (built in 1895). Contemporary dance can be seen at the ''Radialsystem V''. The Tempodrom is host to concerts and circus-inspired entertainment. It also houses a multi-sensory spa experience. The Admiralspalast in Mitte has a vibrant program of variety and music events.
There are seven symphony orchestras in Berlin. The Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra is one of the preeminent orchestras in the world; it is housed in the Berliner Philharmonie near Potsdamer Platz on a street named for the orchestra's longest-serving conductor, Herbert von Karajan. Simon Rattle was its principal conductor from 1999 to 2018, a position now held by Kirill Petrenko. The Konzerthausorchester Berlin was founded in 1952 as the orchestra for East Berlin. Christoph Eschenbach is its principal conductor. The Haus der Kulturen der Welt presents exhibitions dealing with intercultural issues and stages world music and conferences. The ''Kookaburra'' and the ''Quatsch Comedy Club'' are known for satire and comedy shows. In 2018, the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described Berlin as "arguably the world capital of underground electronic music".
Berlin is home to 44 theaters and stages. The Deutsches Theater (Berlin), Deutsches Theater in Mitte was built in 1849–50 and has operated almost continuously since then. The Volksbühne at Rosa-Luxemburg-Platz was built in 1913–14, though the company had been founded in 1890. The Berliner Ensemble, famous for performing the works of Bertolt Brecht, was established in 1949. The Schaubühne was founded in 1962 and moved to the building of the former Universum Cinema on Kurfürstendamm in 1981. With a seating capacity of 1,895 and a stage floor of , the Friedrichstadt-Palast in Berlin Mitte is the largest show palace in Europe. For Berlin's independent dance and theatre scene, venues such as the Sophiensäle in Mitte and the three houses of the Hebbel-Theater, Hebbel am Ufer (HAU) in Kreuzberg are important. Most productions there are also accessible to an English-speaking audience. Some of the dance and theatre groups that also work internationally (Gob Squad, Rimini Protokoll) are based there, as well as festivals such as the international festival Tanz im August, Dance in August.
Berlin has three major opera houses: the Deutsche Oper, the Berlin State Opera, and the Komische Oper. The Berlin State Opera on Unter den Linden opened in 1742 and is the oldest of the three. Its musical director is Daniel Barenboim. The Komische Oper has traditionally specialized in operettas and is also at Unter den Linden. The Deutsche Oper opened in 1912 in Charlottenburg.
The city's main venue for musical theater performances are the Theater am Potsdamer Platz and Theater des Westens (built in 1895). Contemporary dance can be seen at the ''Radialsystem V''. The Tempodrom is host to concerts and circus-inspired entertainment. It also houses a multi-sensory spa experience. The Admiralspalast in Mitte has a vibrant program of variety and music events.
There are seven symphony orchestras in Berlin. The Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra is one of the preeminent orchestras in the world; it is housed in the Berliner Philharmonie near Potsdamer Platz on a street named for the orchestra's longest-serving conductor, Herbert von Karajan. Simon Rattle was its principal conductor from 1999 to 2018, a position now held by Kirill Petrenko. The Konzerthausorchester Berlin was founded in 1952 as the orchestra for East Berlin. Christoph Eschenbach is its principal conductor. The Haus der Kulturen der Welt presents exhibitions dealing with intercultural issues and stages world music and conferences. The ''Kookaburra'' and the ''Quatsch Comedy Club'' are known for satire and comedy shows. In 2018, the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described Berlin as "arguably the world capital of underground electronic music".
 Berlin Zoological Garden, Zoologischer Garten Berlin, the older of two zoos in the city, was founded in 1844. It is the most visited zoo in Europe and presents the most diverse range of species in the world. It was the home of the captive-born celebrity polar bear Knut (polar bear), Knut. The city's other zoo, Tierpark Berlin, Tierpark Friedrichsfelde, was founded in 1955.
Berlin-Dahlem Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum, Berlin's Botanischer Garten includes the Botanic Museum Berlin. With an area of and around 22,000 different plant species, it is one of the largest and most diverse collections of botanical life in the world. Other gardens in the city include the Britzer Garten, and the Erholungspark Marzahn, Gärten der Welt (Gardens of the World) in Marzahn.
Berlin Zoological Garden, Zoologischer Garten Berlin, the older of two zoos in the city, was founded in 1844. It is the most visited zoo in Europe and presents the most diverse range of species in the world. It was the home of the captive-born celebrity polar bear Knut (polar bear), Knut. The city's other zoo, Tierpark Berlin, Tierpark Friedrichsfelde, was founded in 1955.
Berlin-Dahlem Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum, Berlin's Botanischer Garten includes the Botanic Museum Berlin. With an area of and around 22,000 different plant species, it is one of the largest and most diverse collections of botanical life in the world. Other gardens in the city include the Britzer Garten, and the Erholungspark Marzahn, Gärten der Welt (Gardens of the World) in Marzahn.
 The Tiergarten (park), Tiergarten park in Mitte, with landscape design by Peter Joseph Lenné, is one of Berlin's largest and most popular parks. In Kreuzberg, the Viktoriapark provides a viewing point over the southern part of inner-city Berlin. Treptower Park, beside the Spree in Treptow, features a large Soviet War Memorial (Treptower Park), Soviet War Memorial. The Volkspark in Friedrichshain, which opened in 1848, is the oldest park in the city, with monuments, a summer outdoor cinema and several sports areas. Tempelhofer Feld, the site of the former Berlin Tempelhof Airport, city airport, is the world's largest inner-city open space.
The Tiergarten (park), Tiergarten park in Mitte, with landscape design by Peter Joseph Lenné, is one of Berlin's largest and most popular parks. In Kreuzberg, the Viktoriapark provides a viewing point over the southern part of inner-city Berlin. Treptower Park, beside the Spree in Treptow, features a large Soviet War Memorial (Treptower Park), Soviet War Memorial. The Volkspark in Friedrichshain, which opened in 1848, is the oldest park in the city, with monuments, a summer outdoor cinema and several sports areas. Tempelhofer Feld, the site of the former Berlin Tempelhof Airport, city airport, is the world's largest inner-city open space.


 Berlin has established a high-profile as a host city of major international sporting events. The city hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics and was the host city for the 2006 FIFA World Cup final. The World Athletics Championships was held at Olympiastadion (Berlin), Olympiastadion in 2009 World Athletics Championships, 2009 and 2025 World Athletics Championships, 2025. The city hosted the Euroleague Final Four basketball competition in 2009 Euroleague Final Four, 2009 and 2016 Euroleague Final Four, 2016, and was one of the hosts of FIBA EuroBasket 2015. In 2015 Berlin was the venue for the 2015 UEFA Champions League Final, UEFA Champions League Final. The city bid to host the 2000 Summer Olympics but lost to Sydney.
Berlin hosted the 2023 Special Olympics World Summer Games. This is the first time Germany has ever hosted the Special Olympics World Games.
The annual Berlin Marathona course that holds the most top-10 world record runsand the Internationales Stadionfest, ISTAF are well-established athletic events in the city. The Mellowpark in Köpenick is one of the biggest skate and BMX parks in Europe. A fan fest at Brandenburg Gate, which attracts several hundreds of thousands of spectators, has become popular during international football competitions, such as the UEFA European Championship.
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, who is often hailed as the "father of modern gymnastics", invented the horizontal bar, parallel bars, Rings (gymnastics), rings, and the Vault (gymnastics), vault around 1811 in Berlin. Jahn's Turners movement, first realized at Volkspark Hasenheide, was the origin of modern sports clubs. In 2013, around 600,000 Berliners were registered in one of the more than 2,300 sport and fitness clubs. The city of Berlin operates more than 60 public indoor and outdoor swimming pools. Berlin is the largest Olympic training center in Germany, with around 500 top athletes (15% of all German top athletes) being based there. Forty-seven elite athletes participated in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Berliners would achieve seven gold, twelve silver, and three bronze medals.
Several professional clubs representing the most important spectator team sports in Germany are based in Berlin. The oldest and most popular first-division team based in Berlin is the football club Hertha BSC. The team represented Berlin as a founding member of the Bundesliga in 1963. Other professional team sport clubs include:
Berlin has established a high-profile as a host city of major international sporting events. The city hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics and was the host city for the 2006 FIFA World Cup final. The World Athletics Championships was held at Olympiastadion (Berlin), Olympiastadion in 2009 World Athletics Championships, 2009 and 2025 World Athletics Championships, 2025. The city hosted the Euroleague Final Four basketball competition in 2009 Euroleague Final Four, 2009 and 2016 Euroleague Final Four, 2016, and was one of the hosts of FIBA EuroBasket 2015. In 2015 Berlin was the venue for the 2015 UEFA Champions League Final, UEFA Champions League Final. The city bid to host the 2000 Summer Olympics but lost to Sydney.
Berlin hosted the 2023 Special Olympics World Summer Games. This is the first time Germany has ever hosted the Special Olympics World Games.
The annual Berlin Marathona course that holds the most top-10 world record runsand the Internationales Stadionfest, ISTAF are well-established athletic events in the city. The Mellowpark in Köpenick is one of the biggest skate and BMX parks in Europe. A fan fest at Brandenburg Gate, which attracts several hundreds of thousands of spectators, has become popular during international football competitions, such as the UEFA European Championship.
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, who is often hailed as the "father of modern gymnastics", invented the horizontal bar, parallel bars, Rings (gymnastics), rings, and the Vault (gymnastics), vault around 1811 in Berlin. Jahn's Turners movement, first realized at Volkspark Hasenheide, was the origin of modern sports clubs. In 2013, around 600,000 Berliners were registered in one of the more than 2,300 sport and fitness clubs. The city of Berlin operates more than 60 public indoor and outdoor swimming pools. Berlin is the largest Olympic training center in Germany, with around 500 top athletes (15% of all German top athletes) being based there. Forty-seven elite athletes participated in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Berliners would achieve seven gold, twelve silver, and three bronze medals.
Several professional clubs representing the most important spectator team sports in Germany are based in Berlin. The oldest and most popular first-division team based in Berlin is the football club Hertha BSC. The team represented Berlin as a founding member of the Bundesliga in 1963. Other professional team sport clubs include: