Bathyarchaeia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
TACK is a group of
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoprote ...
), Aigarchaeota
The "Aigarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal phylum of which the main representative is '' Caldiarchaeum subterraneum''.. It is not yet clear if this represents a new phylum or a and order of the Nitrososphaerota, since the genome of ''Caldiarchaeu ...
, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
), and Korarchaeota
In alpha taxonomy, taxonomy, the Korarchaeota are a phylum (biology), phylum of the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning ''young man'' or ''young woman,'' and the Greek adjective archaios which means ''ancient.' ...
, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic
Acidophiles or acidophilic organisms are those that thrive under highly acidic conditions (usually at pH 5.0 or below). These organisms can be found in different branches of the tree of life, including Archaea, Bacteria,Becker, A.Types of Bacteria ...
thermophiles
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though they can be bacteria or fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earl ...
to mesophiles
A mesophile is an organism that grows best in moderate temperature, neither too hot nor too cold, with an optimum growth range from . The optimum growth temperature for these organisms is 37°C. The term is mainly applied to microorganisms. Organi ...
and psychrophiles
Psychrophiles or cryophiles (adj. ''psychrophilic'' or ''cryophilic'') are extremophilic organisms that are capable of growth and reproduction in low temperatures, ranging from to . They have an optimal growth temperature at . They are found in ...
and with different types of metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, predominantly anaerobic and chemosynthetic. TACK is a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
that is close to the branch that gave rise to the eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
. It has been proposed that the TACK clade be classified as Crenarchaeota and that the traditional "Crenarchaeota" (Thermoproteota) be classified as a class called "Sulfolobia", along with the other phyla with class rank or order.
Classification
*Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
(formerly Crenarchaeota). It is the best known edge and the most abundant archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
in the marine ecosystem. They were previously called sulfobacteria because of their dependence on sulfur and are important as carbon fixers. There are hyperthermophiles
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the doma ...
in hydrothermal vents and other groups are the most abundant at depths of less than 100 m.
* "Aigarchaeota
The "Aigarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal phylum of which the main representative is '' Caldiarchaeum subterraneum''.. It is not yet clear if this represents a new phylum or a and order of the Nitrososphaerota, since the genome of ''Caldiarchaeu ...
". It is a phylum proposed from the genome of the candidate species '' Caldiarchaeum'' subterraneum found deep within a gold mine in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. Genomic sequences of this group have also been found in geothermal environments, both terrestrial and marine.
* "Geoarchaeota
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic ther ...
". It includes thermophilic organisms that live in acidic environments reducing ferric iron. Alternatively it has been proposed that this and earlier group actually belong to the phylum Nitrososphaerota.
* Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoprote ...
(formerly Thaumarchaeota). It includes mesophilic or psychrophilic organisms (medium and low temperatures), of ammonia-oxidant chemolytoautotrophic metabolism (nitrifying) and that can play an important role in biochemical cycles, such as the nitrogen and carbon cycles.
* "Bathyarchaeota
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic th ...
". It is abundant in the sediments of the seabed with a shortage of nutrients. At least some lineages develop through homoacetogenesis, a type of metabolism hitherto thought unique to bacteria.
* "Korarchaeota
In alpha taxonomy, taxonomy, the Korarchaeota are a phylum (biology), phylum of the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning ''young man'' or ''young woman,'' and the Greek adjective archaios which means ''ancient.' ...
". They have only been found in hydrothermal environments and in low abundance. They seem diversified at different phylogenetic levels according to temperature, salinity (fresh or marine water) and geography.
Phylogeny
The relationships are roughly as follows:
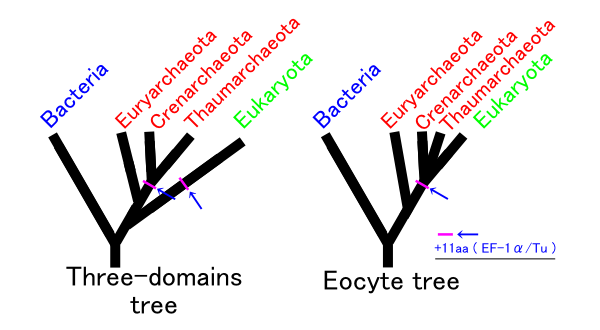
Eocyte hypothesis
Theeocyte hypothesis
The eocyte hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposes the origin of eukaryotes from a group of prokaryotes called eocytes (later classified as Thermoproteota, a group of archaea). After his team at the University of California, Los Angeles disc ...
proposed in the 1980s by James Lake
James A. Lake (born August 10, 1941, Kearney, Nebraska) is an American evolutionary biologist and a Distinguished Professor of Molecular, Cell, and Developmental Biology and of Human Genetics at UCLA. Lake is best known for the New Animal Phyloge ...
suggests that eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
emerged within the prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a Unicellular organism, single-celled organism that lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:πρό#Ancient Greek, πρό (, 'before') a ...
eocytes.
One possible piece of evidence supporting a close relationship between TACK and eukaryotes is the presence of a homolog of the RNA polymerase subunit Rbp-8 in Thermoproteota but not in Euryarchaea
See also
*List of Archaea genera
This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
Phylogeny
National Center for ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q47002232 Archaea