|
Aigarchaeota
The "Aigarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal phylum of which the main representative is '' Caldiarchaeum subterraneum''.. It is not yet clear if this represents a new phylum or a and order of the Nitrososphaerota, since the genome of ''Caldiarchaeum subterraneum'' encodes several Nitrososphaerota-like features. The name "''Aigarchaeota''" comes from the Greek , ''avgí'', meaning "dawn" or "aurora", for the intermediate features of hyperthermophilic and mesophilic life during the evolution of its lineage. Taxonomy * Genus "''Candidatus'' Caldarchaeum" corrig. Nunoura et al. 2011 ** "''Ca.'' C. subterraneum" corrig. Nunoura et al. 2011 * Genus "''Candidatus'' Calditenuis" Beam et al. 2016 ** "''Ca.'' C. aerorheumensis" Beam et al. 2016 See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TACK
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic thermophiles to mesophiles and psychrophiles and with different types of metabolism, predominantly anaerobic and chemosynthetic. TACK is a clade that is close to the branch that gave rise to the eukaryotes. It has been proposed that the TACK clade be classified as Crenarchaeota and that the traditional "Crenarchaeota" (Thermoproteota) be classified as a class called "Sulfolobia", along with the other phyla with class rank or order. Classification * Thermoproteota (formerly Crenarchaeota). It is the best known edge and the most abundant archaea in the marine ecosystem. They were previously called sulfobacteria because of their dependence on sulfur and are important as carbon fixers. There are hyperthermophiles in hydrothermal vents and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
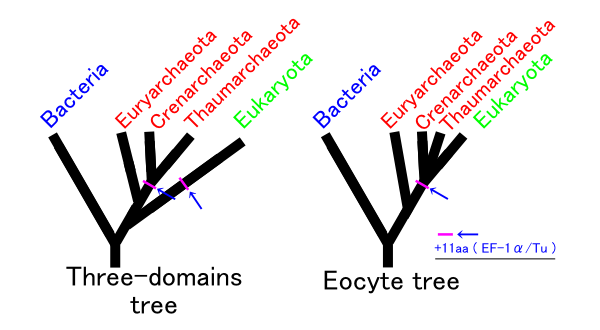
Proteoarchaeota
"Proteoarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal kingdom thought to be closely related to the Eukaryotes.Approximately the same group is sometimes referred to as TACK after the initial letters of its early-found daughter clades: Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), "Aigarchaeota", Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and "Korarchaeota". Because of the unsettled phylogeny A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ... of the group, the names "Proteoarchaeota" and TACK may become distinct after further re-organization. Classification The phylogenetic relationship of this group is still under discussion. The relationship of the members is approximately as follows: Notes References Archaea Kingdoms (biology) {{Archaea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldiarchaeum Subterraneum
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaea Genera
This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy was initially used to decorate the genome tree via tax2tree. The 16S rRNA-based Greengenes taxonomy is used to supplement the taxonomy particularly in regions of the tree with no cultured representatives. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is used as the primary taxonomic authority for establishing naming priorities. Taxonomic ranks are normalised using phylorank and the taxonomy manually curated to remove polyphyletic groups. Cladogram was taken from the GTDB release 07-RS207 (8th April 2022). The position of clades with a "question mark" are based on the additional phylogeny of the 16S rRNA-based LTP_12_2021 by The All-Species Living Tree Project. Phylum " Altarcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoproteota (formerly Crenarchaeota). Three described species in addition to ''C. symbiosum'' are ''Nitrosopumilus maritimus'', ''Nitrososphaera viennensis'', and ''Nitrososphaera gargensis''. The phylum was proposed in 2008 based on phylogenetic data, such as the sequences of these organisms' ribosomal RNA genes, and the presence of a form of type I topoisomerase that was previously thought to be unique to the eukaryotes. This assignment was confirmed by further analysis published in 2010 that examined the genomes of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea ''Nitrosopumilus maritimus'' and ''Nitrososphaera gargensis'', concluding that these species form a distinct lineage that includes ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum''. The lipid crenarchaeol has been found only i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
