Basf 1865 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
BASF SE () is a German multinational chemical company and the largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters is located in
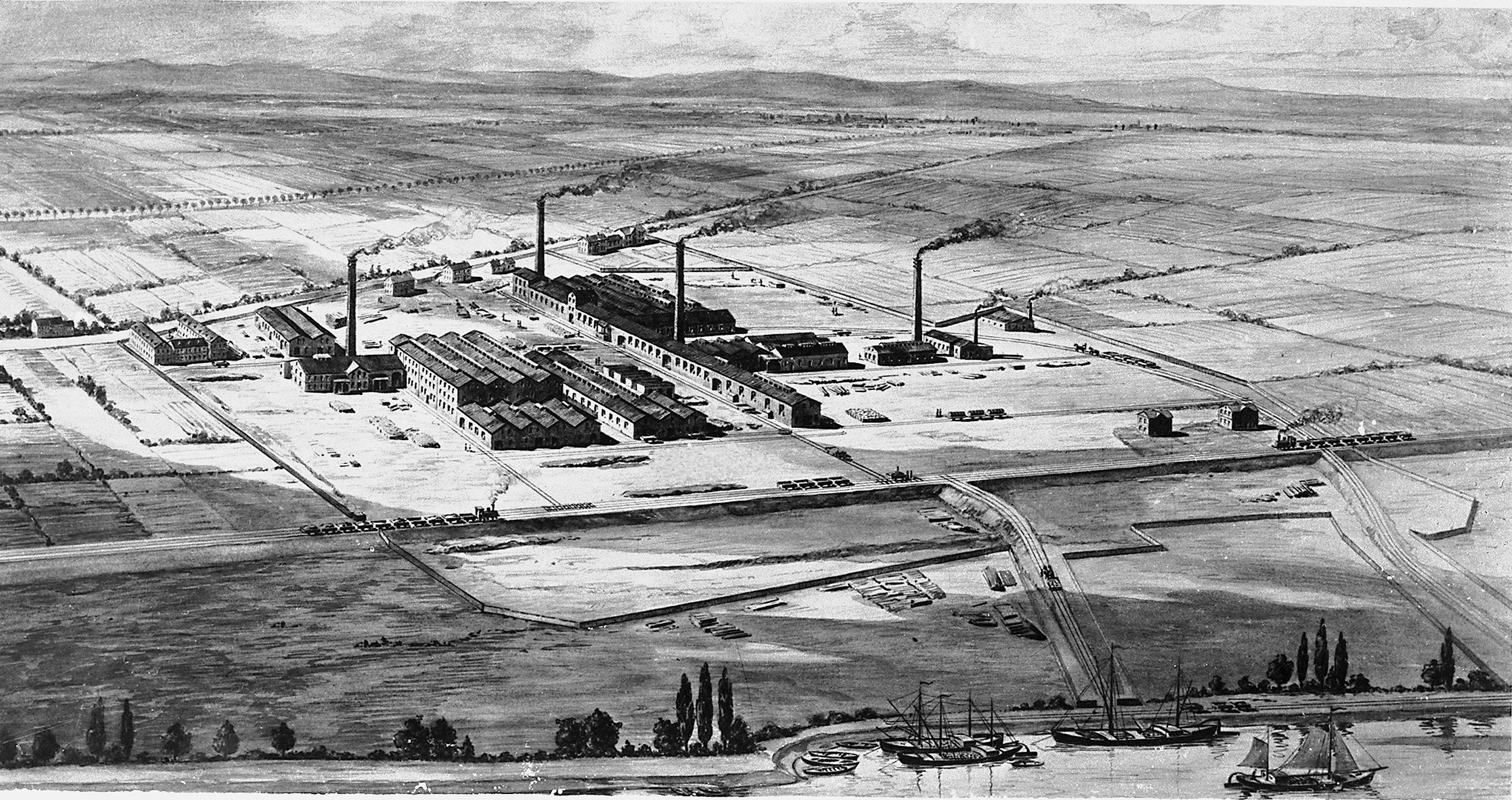 BASF is an
BASF is an
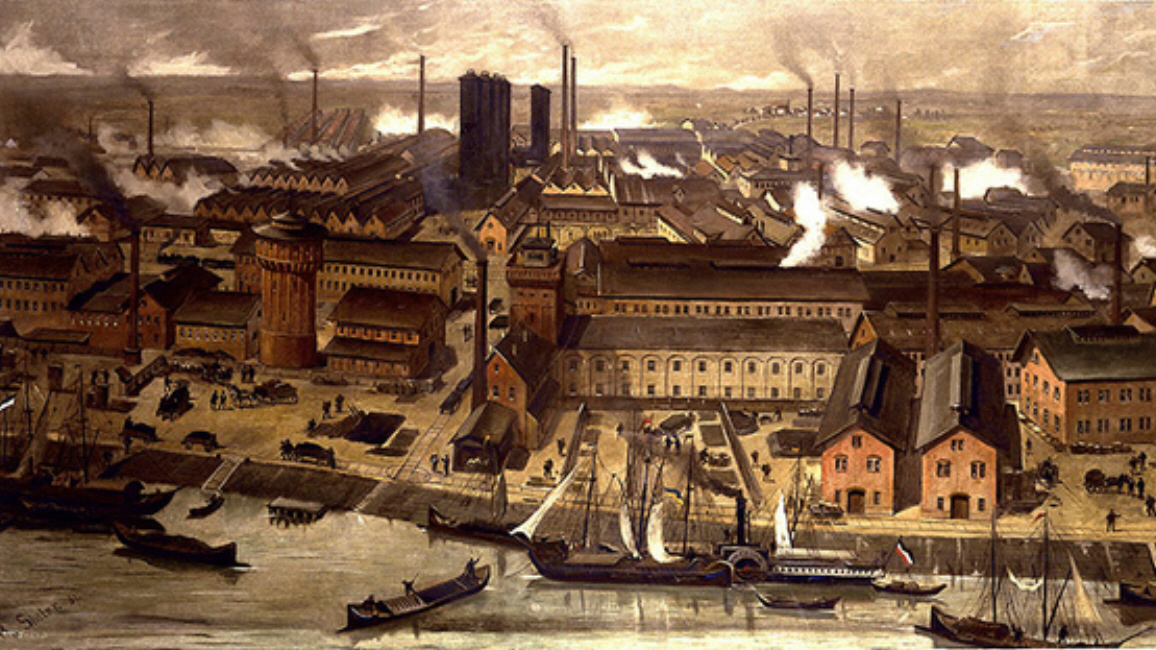 The discovery in 1857 by
The discovery in 1857 by



Beating BASF: OCAW Busts Union-Buster
. ''Labor Research Review'' 1(16): 39–49. The plant produced plastics, herbicides, and antifreeze. BASF soon tried to operate union-free, having already reduced or eliminated union membership in several other US plants. Challenging the Geismar OCAW union resulted in a labor dispute that saw members locked out from 1984 to 1989 and eventually winning their case. A worker solidarity committee at BASF's headquarters plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany, took donations from German workers to support the American strikers and organized rallies and publicity in support. The dispute was the subject of an academic study. The union also exposed major accidental releases of phosgene, toluene and other toxic gases, these being publicized in the local media and through a video, ''Out of Control''. A court threw out a $66,700 fine against BASF for five environmental violations as "too small". BASF's European coatings business was taken over by The acquisition of Degussa AG's construction chemicals business was completed in 2006. The purchase price for equity was about €2.2 billion. In addition, the transaction was associated with a debt of €500 million.
The company agreed to acquire Ciba (formerly part of
The acquisition of Degussa AG's construction chemicals business was completed in 2006. The purchase price for equity was about €2.2 billion. In addition, the transaction was associated with a debt of €500 million.
The company agreed to acquire Ciba (formerly part of
 BASF operates in a variety of markets. Its business is organized in the segments of Chemicals, Plastics, Performance Products, Functional Solutions, Agricultural Solutions, and Oil and Gas.
BASF operates in a variety of markets. Its business is organized in the segments of Chemicals, Plastics, Performance Products, Functional Solutions, Agricultural Solutions, and Oil and Gas.
BASF's Engineering Plastics consists of the "4 Ultras" – Ultramid
BASF Styrenics consists of the Foams and Copolymers. BASF's styrenic copolymers have applications in electronics, building and construction, and automotive components. In 2011 BASF and
BASF's
Foams like Styropor are generally used as insulating materials. They are eco-efficient and offer advantages over other materials in terms of cost-effectiveness, preservation of resources and environmental protection. Investments made for insulating materials usually pay for themselves within a short time and contribute to retaining and even enhancing the value of buildings. Polyamides and Intermediates
BASF manufactures polyamide precursors and
BASF developed a

 BASF's Functional Solutions segment consists of the Catalysts, Construction Chemicals and Coatings divisions. These divisions develop customer-specific products, in particular for the automotive and construction industries.
BASF's Functional Solutions segment consists of the Catalysts, Construction Chemicals and Coatings divisions. These divisions develop customer-specific products, in particular for the automotive and construction industries.
 BASF's recent success is characterized by a focus on creating resource efficient product lines after completely abandoning consumer products. This strategy was reflected in production by a re-focus towards integrated production sites. The largest such integrated production site is located in
BASF's recent success is characterized by a focus on creating resource efficient product lines after completely abandoning consumer products. This strategy was reflected in production by a re-focus towards integrated production sites. The largest such integrated production site is located in
Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it form ...
, Germany.
The BASF Group comprises subsidiaries
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a sa ...
and joint ventures in more than 80 countries and operates six integrated production sites and 390 other production sites in Europe, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Africa. BASF has customers in over 190 countries and supplies products to a wide variety of industries. Despite its size and global presence, BASF has received relatively little public attention since it abandoned the manufacture and sale of BASF-branded consumer electronics
Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic (analog or digital) equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for entertainment, communications and recreation. Usually r ...
products in the 1990s.
At the end of 2019, the company employed 117,628 people, with over 54,000 in Germany. , BASF posted sales of €59.3 billion and income from operations before special items of about €4.5 billion. Between 1990 and 2005, the company invested €5.6 billion in Asia, specifically in sites near Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
and Shanghai in China and Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka–Ker ...
in India.
BASF is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange
The Frankfurt Stock Exchange (german: link=no, Börse Frankfurt, former German name – FWB) is the world's 12th largest stock exchange by market capitalization. It has operations from 8:00 am to 10:00 pm ( German time).
Organisation
Locat ...
, London Stock Exchange
London Stock Exchange (LSE) is a stock exchange in the City of London, England, United Kingdom. , the total market value of all companies trading on LSE was £3.9 trillion. Its current premises are situated in Paternoster Square close to St Pau ...
, and Zurich Stock Exchange
SIX Swiss Exchange (formerly SWX Swiss Exchange), based in Zurich, is Switzerland's principal stock exchange (the other being Berne eXchange). SIX Swiss Exchange also trades other securities such as Swiss government bonds and derivatives such a ...
. The company delisted its ADR ADR or adr may refer to:
Computing
* Asynchronous DRAM refresh, an approach for persistent memory found in some Intel Xeon processors
* The adr microformat, part of the hCard microformat
* Architectural decision record
* Action–domain–respond ...
from the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed c ...
in September 2007. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index
In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures a stock market, or a subset of the stock market, that helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
Two of the ...
.
History
 BASF is an
BASF is an acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as ...
for Badische Anilin- und Sodafabrik (). It was founded by Friedrich Engelhorn
Friedrich Engelhorn (17 July 1821 – 11 March 1902) was a German industrialist and founder of BASF in Ludwigshafen.
Curriculum Vitae
Friedrich Engelhorn was born on 17 July 1821 in Mannheim, where his father was a brewery master and pub ow ...
on 6 April 1865 in Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 2 ...
, in the German-speaking state of Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden is ...
. Engelhorn had been responsible for setting up a gasworks
A gasworks or gas house is an industrial plant for the production of flammable gas. Many of these have been made redundant in the developed world by the use of natural gas, though they are still used for storage space.
Early gasworks
Coal ...
and street lighting for the town council in 1861. The gasworks produced tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black bit ...
as a by-product, and Engelhorn used this for the production of dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution an ...
s. BASF was set up in 1865 to produce other chemicals necessary for dye production, notably soda and acids. The plant, however, was erected on the other side of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
river at Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it form ...
because the town council of Mannheim was afraid that the air pollution from the chemical plant could bother the inhabitants of the town. In 1866, the dye production processes were also moved to the BASF site.W. Ludewig (1966) ''Trans Inst Chem Engrs'' vol 44 ppT237-252 "Highlights in the History of BASF"
Dyes
William Henry Perkin
Sir William Henry Perkin (12 March 1838 – 14 July 1907) was a British chemist and entrepreneur best known for his serendipitous discovery of the first commercial synthetic organic dye, mauveine, made from aniline. Though he failed in trying ...
that aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine
In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aroma ...
could be used to make intense colouring agents had led to the commercial production of synthetic dyes in England from aniline extracted from coal tar. BASF recruited Heinrich Caro
Heinrich Caro (February 13, 1834 in Posen, Prussia Germany now Poznań, Poland – September 11, 1910 in Dresden), was a German chemist.
He was a Sephardic Jew. He started his study of chemistry at the Friedrich Wilhelms University and later ...
, a German chemist with experience of the dyestuff industry in England, to be the first head of research. Caro developed a synthesis for alizarin
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Histori ...
(a natural pigment in madder
''Rubia'' is the type genus of the Rubiaceae family of flowering plants, which also contains coffee. It contains around 80 species of perennial scrambling or climbing herbs and subshrubs native to the Old World. The genus and its best-known spe ...
), and applied for a British patent on 25 June 1869. Coincidentally, Perkin applied for a virtually identical patent on 26 June 1869, and the two companies came to a mutual commercial agreement about the process.
Further patents were granted for the synthesis of methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobin ...
and eosin
Eosin is the name of several fluorescent acidic compounds which bind to and form salts with basic, or eosinophilic, compounds like proteins containing amino acid residues such as arginine and lysine, and stains them dark red or pink as a resul ...
, and in 1880, research began to try to find a synthetic process for indigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the ''Indigofera'' genus, in particular ''Indigofera tinctoria''; dye-bearing ''Indigofera'' pla ...
, though this was not successfully brought to the market until 1897. In 1901, some 80% of the BASF production was dyestuffs.
Soda

Sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
(soda) was produced by the Leblanc process
The Leblanc process (pronounced leh-blaank) was an early industrial process for making ''soda ash'' (sodium carbonate) used throughout the 19th century, named after its inventor, Nicolas Leblanc. It involved two stages: making sodium sulfate from ...
until 1880 when the much cheaper Solvay process
The Solvay process or ammonia-soda process is the major industrial process for the production of sodium carbonate (soda ash, Na2CO3). The ammonia-soda process was developed into its modern form by the Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay during the 1860s. ...
became available. BASF ceased to make its own and bought it from the Solvay company thereafter.
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
was initially produced by the lead chamber process
The lead chamber process was an industrial method used to produce sulfuric acid in large quantities. It has been largely supplanted by the contact process.
In 1746 in Birmingham, England, John Roebuck began producing sulfuric acid in lead-lined ...
, but in 1890, a unit using the contact process
The contact process is the current method of producing sulfuric acid in the high concentrations needed for industrial processes. Platinum was originally used as the catalyst for this reaction; however, as it is susceptible to reacting with arsenic ...
was brought on stream, producing the acid at higher concentration (98% instead of 80%) and a lower cost. This development followed extensive research and development by Rudolf Knietsch, for which he received the Liebig Medal
The Liebig Medal (German: ''Liebig-Denkmünze'') was established by the (''Verein Deutscher Chemiker'') in 1903 to celebrate the centenary of Justus von Liebig. Since 1946 it has been awarded by the Society of German Chemists (''Gesellschaft Deut ...
in 1904.
Ammonia
The development of theHaber process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is an artificial nitrogen fixation process and is the main industrial procedure for the production of ammonia today. It is named after its inventors, the German chemists Fritz Haber and C ...
from 1908 to 1912 made it possible to synthesize ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
(a major industrial chemical as the primary source of nitrogen), and, after acquiring exclusive rights to the process, in 1913 BASF started a new production plant in Oppau, adding fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s to its product range. BASF also acquired and began mining anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the ...
for gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
at the Kohnstein in 1917.
IG Farben
In 1916, BASF started operations at a new site in Leuna, whereexplosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
s were produced during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. On 21 September 1921, an explosion occurred in Oppau, killing 565 people. The Oppau explosion
The Oppau explosion occurred on September 21, 1921, when approximately 4,500 tonnes of a mixture of ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate fertilizer stored in a tower silo exploded at a BASF plant in Oppau, now part of Ludwigshafen, Germany, kil ...
was the biggest industrial accident in German history. Under the leadership of Carl Bosch
Carl Bosch (; 27 August 1874 – 26 April 1940) was a German chemist and engineer and Nobel Laureate in Chemistry. He was a pioneer in the field of high-pressure industrial chemistry and founder of IG Farben, at one point the world's largest ...
, BASF founded IG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate (company), conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies—BASF, ...
with Hoechst Hoechst, Hochst, or Höchst may refer to:
* Hoechst AG, a former German life-sciences company
* Hoechst stain, one of a family of fluorescent DNA-binding compounds
* Höchst (Frankfurt am Main), a city district of Frankfurt am Main, Germany
** Fra ...
, Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of busi ...
, and three other companies, thus losing its independence. BASF was the nominal survivor, as all shares were exchanged for BASF shares before the merger. Rubber, fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
s, and coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the Substrate (materials science), substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquid ...
s were added to the range of products. In 1935, IG Farben and AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG (AEG; ) was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in Berlin as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität'' in 1883 by Emil Rathenau. During the Second World War, AEG ...
presented the magnetophon
Magnetophone, or simply Magnetophon, was the brand or model name of the pioneering reel-to-reel tape recorder developed by engineers of the German electronics company AEG in the 1930s, based on the magnetic tape invention by Fritz Pfleumer
Fr ...
– the first tape recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present- ...
– at the Radio Exhibition in Berlin.
World War II
After the appointment ofAdolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
as Chancellor in 1933, IG Farben co-operated with the National Socialist government, profiting from guaranteed volumes and prices and, in time, from slave labour
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
provided through governmental concentration camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
. BASF (leader of the chemical industry of the IG Farben) built a chemical factory in Auschwitz named "IG Auschwitz"; with a width of 3 km and length of 8 km (resulting in a size of 24 km2), it was the largest chemical factory in the world to that time. IG Farben became notorious through its production of Zyklon-B, the lethal gas used to kill prisoners in German extermination camps during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
.
The Ludwigshafen site was almost completely destroyed during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
but was subsequently rebuilt. The allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
dissolved IG Farben in November 1945.
Both the Ludwigshafen and Oppau plants were of strategic importance for the war because the German military needed many of their products (''e.g.'', synthetic rubber and gasoline). As a result, they were major targets for air raids. During the war, Allied bombers attacked the plants a total of 65 times.
Bombing
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanica ...
took place from the autumn of 1943 and saturation bombing inflicted extensive damage. Production virtually stopped by the end of 1944.
Due to a shortage of male workers during the war, women were conscript
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
ed to work in the factories, joined later by prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
and foreign civilians. Concentration camp inmates did not work at the Ludwigshafen and Oppau plants.
In July 1945, the American military administration confiscated all IG Farben assets. That same year, the Allied Commission decreed that IG Farben should be dissolved. The sites at Ludwigshafen and Oppau were controlled by French authorities.
BASF refounded
On 28 July 1948, an explosion occurred at a BASF site inLudwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it form ...
, killing 207 people and injuring 3818. In 1952, BASF was refounded under its name following the efforts of former Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that crea ...
member Carl Wurster, who served in Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
as ''Wehrwirtschaftsführer
''Wehrwirtschaftsführer'' (WeWiFü) were, during the time of Nazi Germany (1933–1945), executives of companies or big factories called ''rüstungswichtiger Betrieb'' (company important for the production of war materials). ''Wehrwirtschaft ...
'' (war economy leader). With the German economic miracle
The ''Wirtschaftswunder'' (, "economic miracle"), also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II (adopting an ordoliberalism-based social marke ...
in the 1950s, BASF added synthetics such as nylon to its product range. BASF developed Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
in the 1930s and invented Styropor in 1951.
Production abroad
In the 1960s, production abroad was expanded and plants were built inArgentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, Australia, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Brazil, France, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Spain, United Kingdom and the United States. Following a change in corporate strategy in 1965, greater emphasis was placed on higher-value products such as coatings, pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
s, pesticides
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampric ...
and fertilizers. Following German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
, BASF acquired a site in Schwarzheide
Schwarzheide ( dsb, Carny Gózd) is a town in the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district, in Lower Lusatia, Brandenburg, Germany. It is situated on the river Schwarze Elster, 11 km southwest of Senftenberg, 110 km south of Berlin and 40 km n ...
, Eastern Germany, on 25 October 1990. It expanded to Podolsk
Podolsk ( rus, Подольск, p=pɐˈdolʲsk) is an industrial city, center of Podolsk Urban Okrug, Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Pakhra River (a tributary of the Moskva River).
History
The first mentions of the village of Podol, w ...
, Russia, in 2012, and to Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering a ...
in 2013.
The company announced the start of a US$10 billion investment project at Zhanjiang
Zhanjiang (), historically spelled Tsamkong, is a prefecture-level city at the southwestern end of Guangdong province, People's Republic of China, facing Haikou city to the south.
As of the 2020 census, its population was 6,981,236 (6,994,832 ...
, China, in November 2019. This ″Verbund″ site is intended for the production of engineering plastics and TPU. The site would be the third-largest BASF site worldwide, following Ludwigshafen, Germany, and Antwerp, Belgium, and is expected to be operational by 2022.

Takeovers
In 1968 BASF (together withBayer AG
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutica ...
) bought the German coatings company Herbol
Herbol is one of the oldest German brands for professional coatings. It has its origins in the ''Lackfabrik Herbig-Haarhaus'' that was founded in Cologne in 1844. The product range contains façade paints, interior wall paints, lacquers and glazin ...
. BASF completely took over the Herbol branches in Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 m ...
and Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg is ...
in 1970. Under new management, the renewal and expansion of the trademark continued. After an extensive reorganisation and an increasing international orientation of the coatings business, Herbol became part of the new founded Deco GmbH in 1997.
BASF bought the Wyandotte Chemical Company, and its Geismar, Louisiana chemical plant in the early 1970s.Richard Leonard and Zack Nauth. 1990Beating BASF: OCAW Busts Union-Buster
. ''Labor Research Review'' 1(16): 39–49. The plant produced plastics, herbicides, and antifreeze. BASF soon tried to operate union-free, having already reduced or eliminated union membership in several other US plants. Challenging the Geismar OCAW union resulted in a labor dispute that saw members locked out from 1984 to 1989 and eventually winning their case. A worker solidarity committee at BASF's headquarters plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany, took donations from German workers to support the American strikers and organized rallies and publicity in support. The dispute was the subject of an academic study. The union also exposed major accidental releases of phosgene, toluene and other toxic gases, these being publicized in the local media and through a video, ''Out of Control''. A court threw out a $66,700 fine against BASF for five environmental violations as "too small". BASF's European coatings business was taken over by
AkzoNobel
Akzo Nobel N.V., stylized as AkzoNobel, is a Dutch multinational company which creates paints and performance coatings for both industry and consumers worldwide. Headquartered in Amsterdam, the company has activities in more than 80 countries, ...
in 1999. BASF bought the Engelhard
Engelhard Corporation was an American ''Fortune'' 500 company headquartered in Iselin, New Jersey, United States. It is credited with developing the first production catalytic converter. In 2006, the German chemical manufacturer BASF bough ...
Corporation for $4.8 billion in 2006. Other acquisitions in 2006 were the purchase of Johnson Polymer and the construction chemicals business of Degussa
Evonik Industries AG is a stock-listed German specialty chemicals company headquartered in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the second largest chemicals company in Germany, and one of the largest specialty chemicals companies in the ...
.
The acquisition of Johnson Polymer was completed on 1 July 2006. The purchase price was $470 million on a cash and debt-free basis. It provided BASF with a range of water-based resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on natu ...
s that complements its portfolio of high solids and UV resins for the coatings and paints industry and strengthened the company's market presence, particularly in North America.
Ciba-Geigy
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
) in September 2008. The proposed deal was reviewed by the European Commissioner for Competition
The Commissioner for Competition is the member of the European Commission responsible for competition. The current commissioner is Margrethe Vestager ( ALDE).
Responsibilities
The portfolio has responsibility for such matters as commercial co ...
. On 9 April 2009, the acquisition was officially completed.
On 19 December 2008, BASF acquired U.S.-based Whitmire Micro-Gen together with U.K.-based Sorex Ltd, Widnes, Great Britain. Sorex is a manufacturer of branded chemical and non-chemical products for professional pest management. In March 2007 Sorex was put up for sale with a price tag of about £100 million.
In December 2010, BASF completed the acquisition of Cognis
Cognis was a worldwide supplier of specialty chemicals and nutritional ingredients, headquartered in Monheim am Rhein, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The company employs about 5,600 people and operates production or service centers in almost 3 ...
.
In May 2015, BASF agreed to sell parts of its pharmaceutical ingredients business to Swiss drug manufacturer Siegfried Holding for a fee of €270 million, including assumed debt.
In October 2017, BASF announced it would buy seed and herbicide businesses from Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of busi ...
for €5.9 billion ($7 billion), as part of its acquisition of Monsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in th ...
.
In August 2019, BASF agreed to sell its global pigments business to Japanese fine chemical company DIC for €1.15 billion ($1.28 billion) on a cash and debt-free basis.
In September 2019, BASF signed an agreement with DuPont Safety & Construction, a subsidiary business unit of DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
Co., to sell its ultrafiltration membrane business, Inge GmbH. According to BASF executives, Inge GmbH and its products fit better with DuPont and their business strategy.
Dicamba lawsuit
On 27 January 2020, the first-ever lawsuit concerningDicamba
Dicamba (3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid) is a broad-spectrum herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated de ...
-related products began in Cape Girardeau, Missouri. The lawsuit involves a peach farmer who alleged that Dicamba-based herbicides caused significant damage to his crops and trees. It had also been filed in November 2016, when Dicamba was still owned by Monsanto. On 14 February 2020, the jury involved in the lawsuit ruled against BASF its co-defendant Bayer, which had acquired Monsanto and its products, and found in favor of the peach grower, Bader Farms owner Bill Bader. BASF and Bayer were also ordered to pay Bader $15 million in damages. On 15 February 2020, Monsanto and BASF were ordered to pay an additional $250 million in punitive damages.
Finances
For the fiscal year 2017, BASF reported earnings of EUR€6.1 billion, with an annual revenue of EUR€64.5 billion, an increase of 12% over the previous fiscal cycle. BASF's shares traded at over €69 per share, and its market capitalization was valued at US€63.7 billion in November 2018. In October 2019, BASF reported a drop of operating income for July to September amounting to 24 percent, along with a drop in EBIT earnings of €1.1 billion ($1.2 billion). The US-China trade war as well as uncertainties related toBrexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or ...
were identified as contributing factors. However, overall third quarter profit beat expectations as the acquisition of Bayer AG
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutica ...
's agrochemical
An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of ''agricultural chemical'', is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical refers to biocides ( pesticides including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and nematicides) an ...
and seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
business help to offset some of the effects of the trade war.
Business segments
 BASF operates in a variety of markets. Its business is organized in the segments of Chemicals, Plastics, Performance Products, Functional Solutions, Agricultural Solutions, and Oil and Gas.
BASF operates in a variety of markets. Its business is organized in the segments of Chemicals, Plastics, Performance Products, Functional Solutions, Agricultural Solutions, and Oil and Gas.
Chemicals
BASF produces a wide range of chemicals such as solvents, amines, resins, glues, electronic-grade chemicals,industrial gas
Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also avail ...
es, basic petrochemicals, and inorganic chemicals (such as Z-Cote Z-Cote is a commercial zinc oxide line manufactured and owned by BASF. Due to Z-Cote's photo-protective properties it is commonly used in personal care products and sunscreens. It is available in nano, non-nano, coated and uncoated forms. Z-Cote i ...
). The most important customers for this segment are the pharmaceutical, construction, textile, and automotive industries.
Plastics
BASF's plastic products include high-performance materials inthermoplastics
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
, foams, and urethanes.
Engineering PlasticsBASF's Engineering Plastics consists of the "4 Ultras" – Ultramid
polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made through ...
(PA) nylon-based resins, Ultradur, polybutylene terephthalate
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT resists solvents, s ...
(PBT), Ultraform, polyacetal
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, polyacetal, and polyformaldehyde, is an engineering thermoplastic used in precision parts requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. As with many other synthetic pol ...
(POM), and Ultrason, polysulfone
Polysulfones are a family of high performance thermoplastics. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. Technically used polysulfones contain an aryl- SO2-aryl subunit. Due to the high cost of raw material ...
(PSU) and polyethersulfone
Polysulfones are a family of high performance thermoplastics. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. Technically used polysulfones contain an aryl- SO2-aryl subunit. Due to the high cost of raw material ...
(PES).
StyrenicsBASF Styrenics consists of the Foams and Copolymers. BASF's styrenic copolymers have applications in electronics, building and construction, and automotive components. In 2011 BASF and
INEOS
INEOS Group Limited is a British multinational chemicals company headquartered and registered in London. , it is the fourth largest chemical company in the world.
Ineos is organised into about 20 standalone business units, each with its own ...
blended their global business activities in the fields of styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
monomers (SM), polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
(PS), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
A ...
(ABS), styrene butadiene copolymers (SBC) and other styrene-based copolymers
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are some ...
(SAN, AMSAN, ASA, MABS) into a joint venture named Styrolution.
PolyurethanesBASF's
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethan ...
s business consists of diverse technologies and finished products. Urethane chemicals are raw materials used in rigid and flexible foams commonly used for insulation in the construction and appliance industries, furniture, packaging, and transportation.
FoamsFoams like Styropor are generally used as insulating materials. They are eco-efficient and offer advantages over other materials in terms of cost-effectiveness, preservation of resources and environmental protection. Investments made for insulating materials usually pay for themselves within a short time and contribute to retaining and even enhancing the value of buildings. Polyamides and Intermediates
BASF manufactures polyamide precursors and
polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made through ...
.
Biodegradable plasticsBASF developed a
biodegradable plastic
Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually microbes, into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Biodegradable plastics are commonly produced with renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, ...
with a high content of polylactic acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula or , formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by rin ...
.
Performance products
BASF produces a range of performance chemicals,coatings
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Powder ...
and functional polymers. These include raw materials for detergents, textile and leather chemicals, pigments and raw materials for adhesives, paper chemicals
Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing it ...
. Customers are the automotive, oil, paper, packaging, textile, sanitary products, detergents, construction materials, coatings, printing, and leather industries.
Functional Solutions

 BASF's Functional Solutions segment consists of the Catalysts, Construction Chemicals and Coatings divisions. These divisions develop customer-specific products, in particular for the automotive and construction industries.
BASF's Functional Solutions segment consists of the Catalysts, Construction Chemicals and Coatings divisions. These divisions develop customer-specific products, in particular for the automotive and construction industries.
Agricultural
BASF supplies agricultural products and chemicals includingfungicides
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
, herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
, insecticides
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
and seed treatment products. The company also researches nutrigenomics
Nutritional genomics, also known as nutrigenomics, is a science studying the relationship between human genome, human nutrition and health. People in the field work toward developing an understanding of how the whole body responds to a food via s ...
. BASF opened a new crop protection technology center in Limburgerhof, Germany in 2016.
Biotechnology
BASF was cooperating withMonsanto Company
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best known product is Roundup (herbicide), Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbic ...
in research, development and marketing of biotechnology. In correlation to this work, BASF has licensed many gene editing tools including CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacte ...
Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic e ...
and CRISPR Cas12a (Cpf1).
The BASF Plant Science
BASF Plant Science is a subsidiary of BASF in which all plant biotechnology activities are consolidated. The company was founded in 1998 and employs approximately 700 people at 6 different locations worldwide. The headquarters of BASF Plant Scienc ...
subsidiary produces the Amflora
Amflora (also known as EH92-527-1) is a genetically modified potato cultivar developed by BASF Plant Science. "Amflora" potato plants produce pure amylopectin starch that is processed to waxy potato starch. It was approved for industrial applica ...
and Starch Potato genetically modified potato
A genetically modified potato is a potato that has had its genes modified, using genetic engineering. Goals of modification include introducing pest resistance, tweaking the amounts of certain chemicals produced by the plant, and to prevent br ...
with reduced amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose ...
. In 2010 BASF conducted Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs approved trials of genetically modified potatoes in the United Kingdom. Starch Potato was authorised for use in the USA in 2014.
Other GM crops are Phytaseed Canola varieties with phytase
A phytase (''myo''-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolase) is any type of phosphatase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phytic acid (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate) – an indigestible, organic form of phosphorus that is found in many pl ...
, sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta ...
herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
tolerant soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu an ...
and drought tolerant corn (with cold shock protein B) developed with Monsanto.
Oil and gas
BASF explores for and produces oil and gas through its subsidiaryWintershall Dea
Wintershall Dea GmbH is a German gas and oil producer. The joint venture was created in May 2019 by the merger between Wintershall Holding GmbH and DEA Deutsche Erdoel AG. BASF SE has a 67% stake in it, with the other 33% being held by LetterO ...
. In Central and Eastern Europe, Wintershall works with its Russian partner Gazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the larges ...
.
Investors
75% of the BASF shares are held byinstitutional investor
An institutional investor is an entity which pools money to purchase securities, real property, and other investment assets or originate loans. Institutional investors include commercial banks, central banks, credit unions, government-linked co ...
s (BlackRock
BlackRock, Inc. is an American Multinational corporation, multi-national investment company based in New York City. Founded in 1988, initially as a Enterprise risk management, risk management and fixed income institutional asset manager, BlackR ...
more than 5%). 36% of the shares are held in Germany, 11% in the UK and 17% in the U.S.
Production
 BASF's recent success is characterized by a focus on creating resource efficient product lines after completely abandoning consumer products. This strategy was reflected in production by a re-focus towards integrated production sites. The largest such integrated production site is located in
BASF's recent success is characterized by a focus on creating resource efficient product lines after completely abandoning consumer products. This strategy was reflected in production by a re-focus towards integrated production sites. The largest such integrated production site is located in Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it form ...
employing 33,000 people.
Integrated production sites are characterized by co-location of many individual production lines (producing a specific chemical), which share an interconnected material flow. Piping is used ubiquitously for volume materials. All production lines use common raw material sourcing and feed back waste resources, which can be used elsewhere (e.g. steam of various temperatures, sulfuric acid, carbon monoxide). The economic incentive for this approach is high resource and energy efficiency of the overall process, reduced shipping cost and associated reduced risk of accidents. Due to the high cost of such an integrated production site, it establishes a high entry barrier for competitors trying to enter the market for volume chemicals.
BASF built a new chemical complex in Dahej
Dahej is a cargo port situated on the South-west coast of Gujarat, India in Bharuch district. There is 17.5 million tonnes per year capacity LNG terminal operated by Petronet in Dahej.
Port Information
General
The Port of Dahej is located in t ...
, Gujarat at a cost of $100 million. This facility has South Asia's first methylene diphenyl diisocyanate
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is an aromatic diisocyanate. Three isomers are common, varying by the positions of the isocyanate groups around the rings: 2,2′-MDI, 2,4′-MDI, and 4,4′-MDI. The 4,4′ isomer is most widely used, and i ...
(MDI) splitter for processing crude MDI. BASF has 8 production facilities in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.
BASF SE has succeeded in developing a semi-crystalline polyamide that allows light to pass through largely unhindered. Ultramid Vision combines very high light transmission with low light scattering. This makes it the world's first semi-crystalline polyamide for semi-transparent or transparent components in chemically challenging environments. Additionally, the unique polyamide is UV and temperature resistant, scratch-proof as well as suitable for flame-retardant requirements. Ultramid Vision can be used in various application fields: It recommends itself especially for parts for visual check, illumination or light design. Ultramid Vision presents a versatile alternative to commonly used materials such as amorphous aliphatic polyamides, polycarbonate or styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers.
Environmental record
According to the 2020 “Top 100 Polluters Indexes” published by theUniversity of Massachusetts, Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst, UMass) is a public research university in Amherst, Massachusetts and the sole public land-grant university in Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded in 1863 as an agricultural college, i ...
’s “Political Economy Research Institute” (PERI), among US corporations, BASF was ranked the #2 largest polluter of water and #4 largest polluter of air in 2018, the most recent year for which data is available from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
.
In 2006 BASF was included in the Climate Leadership Index for their efforts in relation to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
and greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
emissions.
BASF has created filters for wastewater treatment plants
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environmen ...
that help to reduce emissions.
The BASF Company and Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
formed a partnership to further research "environmentally benign and sustainable energy
Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". Most definitions of sustainable energy include considerations of environmental aspects such as greenh ...
sources". The company has recently reported their emissions in 2006 to be "1.50 million metric tons of waste," which is a decrease from previous years. The amount of waste BASF produces has continued to fall.
While BASF publishes its environmental information in the US and Europe, Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe, immigrant environmental activists from the United States. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth t ...
has expressed deep concerns at BASF's refusal to release environmental information on its operations in China.
In May 2009, a BASF Plant in Hannibal, Missouri
Hannibal is a city along the Mississippi River in Marion and Ralls counties in the U.S. state of Missouri. According to the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 17,312, making it the largest city in Marion County. The bulk of the city is in Mario ...
, United States, accidentally discharged chromium into the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. The local Department of Natural Resources performed tests in December 2009 showing the chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
levels did not exceed regulatory safety limits. BASF worked with the Missouri Department of Natural Resources
The Missouri Department of Natural Resources (MoDNR) of the government of the U.S. state of Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied fo ...
(MoDNR) to resolve questions regarding the elevated level of hexavalent chromium
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is chromium in any chemical compound that contains the element in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the ...
that was detected in the effluent
Effluent is wastewater from sewers or industrial outfalls that flows directly into surface waters either untreated or after being treated at a facility. The term has slightly different meanings in certain contexts, and may contain various pollut ...
from one of its permitted outfalls into the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. The state department of health reviewed the test results and determined that the amounts found were well below recommended public health screening levels.
In 2013, BASF reported a spill of several hundred kilogrammes of the chelating agent
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
Trilon-B (tetrasodium Edta
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula H2N(CH2CO2H)2sub>2. This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes eve ...
) into the river Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
from BASF's headquarters in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
See also
*Dow Chemical Company
The Dow Chemical Company, officially Dow Inc., is an American multinational chemical corporation headquartered in Midland, Michigan, United States. The company is among the three largest chemical producers in the world.
Dow manufactures plastic ...
* Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befor ...
* Sculpteo
Sculpteo is a French company specialized in 3D printing in the cloud. Sculpteo offers an online 3D printing service, using rapid prototyping and a manufacturing process involving laser sintering or stereo lithography. The company was founded in ...
References
Further reading
* * Beer, John J. ''The Emergence of the German Dye Industry'' (1959).External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Basf Chemical companies of Germany Chemical companies established in 1865 IG Farben German brands The Holocaust Companies based in Rhineland-Palatinate Paint manufacturers Multinational companies headquartered in Germany Electronics companies of Germany Companies in the Euro Stoxx 50 Companies listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange Companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange Companies involved in the Holocaust Engelhorn family