|
Rubia
''Rubia'' is the type genus of the Rubiaceae family of flowering plants, which also contains coffee. It contains around 80 species of perennial scrambling or climbing herbs and subshrubs native to the Old World. The genus and its best-known species are commonly known as madder, e.g. ''Rubia tinctorum'' (common madder), ''Rubia peregrina'' (wild madder), and ''Rubia cordifolia'' (Indian madder). Uses ''Rubia'' was an economically important source of a red pigment in many regions of Asia, Europe and Africa. The genus name ''Rubia'' derives from the Latin ' meaning "red". The plant's roots contain an anthracene compound called alizarin that gives its red colour to a textile dye known as Rose madder. It was also used as a colourant, especially for paint, that is referred to as Madder lake. The synthesis of alizarin greatly reduced demand for the natural compound. In Georgia, Rubia is used for dying Easter eggs in red. History Several species, such as ''Rubia tinctorum'' in Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubiaceae
The Rubiaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with interpetiolar stipules and sympetalous actinomorphic flowers. The family contains about 13,500 species in about 620 genera, which makes it the fourth-largest angiosperm family. Rubiaceae has a cosmopolitan distribution; however, the largest species diversity is concentrated in the tropics and subtropics. Economically important genera include '' Coffea'', the source of coffee, '' Cinchona'', the source of the antimalarial alkaloid quinine, ornamental cultivars (''e.g.'', '' Gardenia'', '' Ixora'', '' Pentas''), and historically some dye plants (''e.g.'', '' Rubia''). Description The Rubiaceae are morphologically easily recognizable as a coherent group by a combination of characters: opposite or whorled leaves that are simple and entire, interpetiolar sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
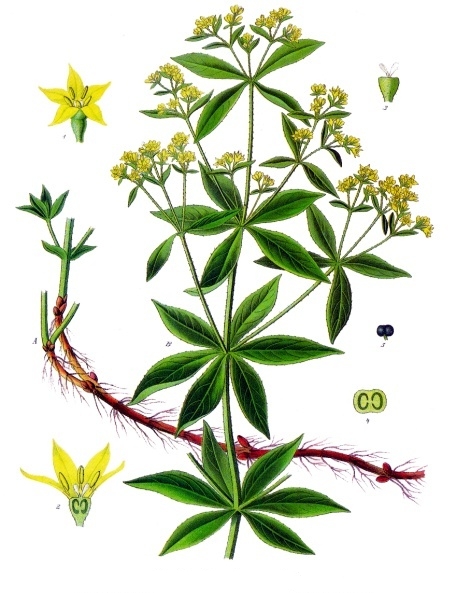
Rubia Peregrina
''Rubia peregrina'', the common wild madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae. Etymology The genus name ''Rubia'' derives from the Latin ' meaning "red", as the roots of some species (mainly ''Rubia tinctorum'') have been used since ancient times as a vegetable red dye. The specific epithet is the Latin adjective ' meaning "foreign, alien, exotic, strange." Description The stem is woody, hairless, square and climbing and reaches on average long.Pignatti S. - Flora d'Italia – Edagricole – 1982. Vol. II, pag. 379 The evergreen leaves are sessile, glossy, leathery, oval-lanceolate and toothed on the margins. They are arranged in whorls, usually with five or more leaves radiating from a single node. The small flowers have five petals and are pale green-yellowish, about 5–7 mm in diameter, arranged at the top of long stalks. The flowering period extends from April through June. The hermaphroditic flowers are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubia Cordifolia
''Rubia cordifolia'', often known as common madder or Indian madder, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee family, Rubiaceae. It has been cultivated for a red pigment derived from roots. Common names of this plant include manjistha in Sanskrit, Marathi, Kannada and Bengali, majith in Hindi and Gujarati, བཙོད་ in Tibetan, tamaralli in Telugu, manditti in Tamil. Description It can grow to 1.5 m in height. The evergreen leaves are 5–10 cm long and 2–3 cm broad, produced in whorls of 4-7 starlike around the central stem. It climbs with tiny hooks at the leaves and stems. The flowers are small (3–5 mm across), with five pale yellow petals, in dense racemes, and appear from June to August, followed by small (4–6 mm diameter) red to black berries. The roots can be over 1 m long, up to 12 mm thick. It prefers loamy soils with a constant level of moisture. Madders are used as food plants for the larvae of some Lepidoptera species incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubia Tinctorum
''Rubia tinctorum'', the rose madder or common madder or dyer's madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae. Description The common madder can grow up to 1.5 m in height. The evergreen leaves are approximately 5–10 cm long and 2–3 cm broad, produced in whorls of 4–7 starlike around the central stem. It climbs with tiny hooks at the leaves and stems. The flowers are small (3–5 mm across), with five pale yellow petals, in dense racemes, and appear from June to August, followed by small (4–6 mm diameter) red to black berries. The roots can be over a metre long, up to 12 mm thick and the source of red dyes known as rose madder and Turkey red. It prefers loamy soils (sand and clay soil) with a constant level of moisture. Madder is used as a food plant by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the hummingbird hawk moth. Uses It has been used since ancient times as a vegetab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubia Argyi
''Rubia argyi'' is a species of flowering plant of the family Rubiaceae. Its common name In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contra ...s may include "East Asian madder". References argyi {{Improve categories, date=January 2022 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
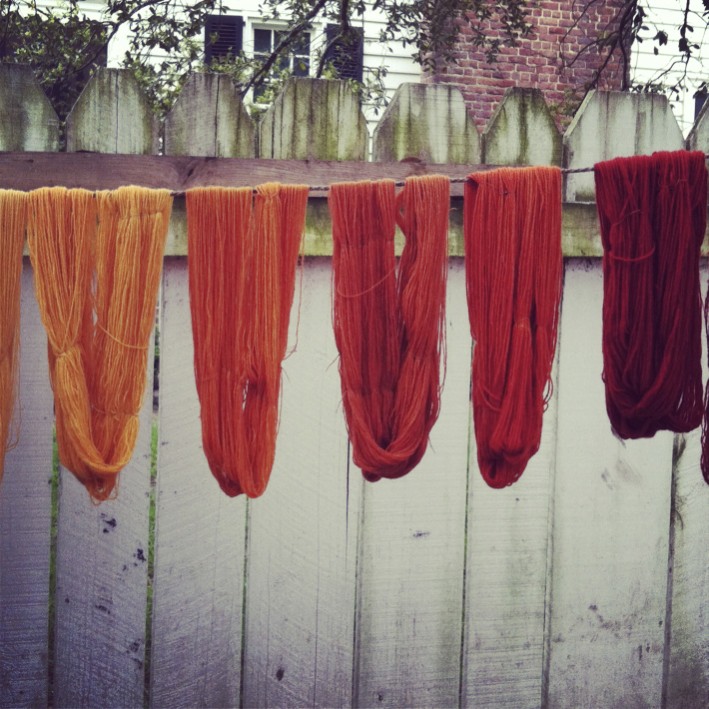
Alizarin
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose Madder
Rose madder (also known as madder) is a red paint made from the pigment madder lake, a traditional lake pigment extracted from the common madder plant ''Rubia tinctorum''. Madder lake contains two organic red dyes: alizarin and purpurin. As a paint, it has been described as a fugitive, transparent, nonstaining, mid valued, moderately dull violet red pigment in tints and medium solutions, darkening to an impermanent, dull magenta red in masstone. History Madder has been cultivated as a dyestuff since antiquity in Central Asia, South Asia, and Egypt, where it was grown as early as 1500 BC. Cloth dyed with madder root dye was found in the tomb of the Pharaoh Tutankhamun and on an Egyptian tomb painting from the Graeco-Roman period, diluted with gypsum to produce a pink color. It was also found in ancient Greece (in Corinth), and in Italy in the Baths of Titus and the ruins of Pompeii. It is referred to in the Talmud as well as mentioned in writings by Dioscoride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madder Lake
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ἀγγεῖον / ('container, vessel') and σπέρμα / ('seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Angiosperms are distinguished from the other seed-producing plants, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, or the formulation of humoral theory. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated ( theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners of Hippocratic medicine, and the actions of Hippocrates himself were often conflated; thus very little is known about what Hippocrates actual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |