|
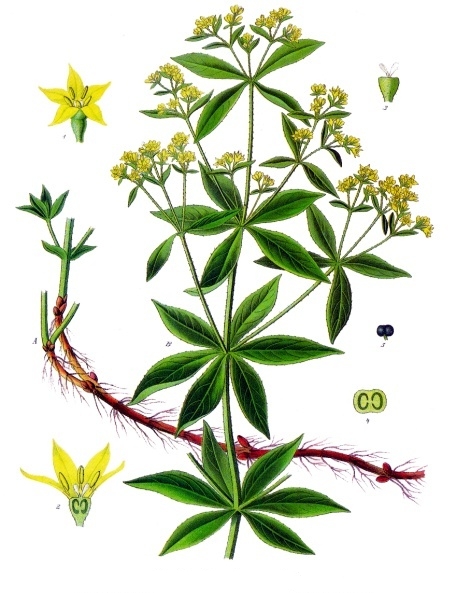
Rubia Tinctorum
''Rubia tinctorum'', the rose madder or common madder or dyer's madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the Galium, bedstraw and Coffea, coffee family Rubiaceae. Description The common madder can grow up to 1.5 m in height. The evergreen leaf, leaves are approximately 5–10 cm long and 2–3 cm broad, produced in whorls of 4–7 starlike around the central stem. It climbs with tiny hooks at the leaves and stems. The flowers are small (3–5 mm across), with five pale yellow petals, in dense racemes, and appear from June to August, followed by small (4–6 mm diameter) red to black berry (botany), berries. The roots can be over a metre long, up to 12 mm thick and the source of red dyes known as rose madder and Turkey red. It prefers loamy soils (sand and clay soil) with a constant level of moisture. Madder is used as a food plant by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the Macroglossum stellatarum, hummingbird hawk moth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroglossum Stellatarum
The hummingbird hawk-moth (''Macroglossum stellatarum'') is a species of hawk moth found across temperate regions of Eurasia. The species is named for its similarity to hummingbirds, as they feed on the nectar of tube-shaped flowers using their long proboscis while hovering in the air; this resemblance is an example of convergent evolution. The hummingbird hawk-moth was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. As of 2018, its entire genome and mitogenome have been sequenced. Distribution The hummingbird hawk-moth is distributed throughout the northern Old World from Portugal to Japan, but it breeds mainly in warmer climates (southern Europe, North Africa, and points east). Three generations are produced in a year in Spain. It is a strong flier, dispersing widely in the summer. However it rarely survives the winter in northern latitudes (e.g. north of the Alps in Europe, north of the Caucasus in Russia). Moths in the genus ''Hemari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French ( Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the ''Organisation internationale de la Francophonie'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garance (born 1998), French actress
{{given name ...
Garance is a given name that is derived from , which is the French name of the plant ''Rubia tinctorum.'' Notable people with the name include: * Garance Doré (born 1975), French photographer * Garance Genicot (born 1974), Belgian-American economist * Garance Le Guillermic (born 1997), French actress * Garance Marillier Garance Marillier (born 11 February 1998) is a French actress. She is known for her lead role in '' Raw'' released in 2016. Early life Prior to becoming an actress she learned the trombone and classical percussion at the Conservatoire of the 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released may boi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madder Lake
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia is both caust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Jean Robiquet
Pierre Jean Robiquet (13 January 1780 – 29 April 1840) was a French chemist. He laid founding work in identifying amino acids, the fundamental building blocks of proteins. He did this through recognizing the first of them, asparagine, in 1806, in the industry's adoption of industrial dyes, with the identification of alizarin in 1826, and in the emergence of modern medications, through the identification of codeine in 1832, a opiate alkaloid substance of widespread use with analgesic and antidiarrheal properties. Robiquet was born in Rennes. He was at first a pharmacist in the French armies during the French Revolution years and became a professor at the École de pharmacie in Paris, where he died. Notable scientific achievements were among other things his isolation and characterization of properties of asparagine (the first amino acid to be identified, from asparagus, achieved. In 1806, with Louis Nicolas Vauquelin), cantharidin (1810), the sigma-1 receptor agonist noscapi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2,4-Trihydroxyanthraquinone
1,2,4-Trihydroxyanthraquinone, commonly called purpurin, is an anthraquinone. It is a naturally occurring red/yellow dye. It is formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacement of three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. Purpurin is also called verantin, smoke Brown G, hydroxylizaric acid, and C.I. 58205. It is a minor component of the classical lake pigment "madder lake" or Rose Madder. History Madder root has been used for dying cloth at least since 1500 BC.Madder Root'' catalog entry at Natural Pigments website. Accessed on 2010-01-22. Purpurin and alizarin were isolated from the root by Pierre Robiquet and Colin, two French chemists, in 1826. They were identified as anthracene derivatives by Gräbe and Liebermann in 1868. They also synthesized alizarin from bromoanthraquinone, which, together with the conversion of alizarin into purpurin published previously by M. F. De Lalande, provided the first synthetic route to purpurin. The positions of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alizarin
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-3D-balls.png)