Bangladesh V Afghanistan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in
,


 The early history of Islam in Bengal is divided into two phases. The first phase is the period of maritime trade with Arabia and Persia between the 8th and 12th centuries. The second phase covers centuries of Muslim dynastic rule after the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The writings of Al-Idrisi,
The early history of Islam in Bengal is divided into two phases. The first phase is the period of maritime trade with Arabia and Persia between the 8th and 12th centuries. The second phase covers centuries of Muslim dynastic rule after the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The writings of Al-Idrisi, 

 The
The
Empire, Mughal
, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017 The Bengal Subah, described as the ''Paradise of the Nations'', was the empire's wealthiest province, and a major global exporter,
''The Mughal Empire'', page 202
Development Centre Studies The World Economy Historical Statistics: Historical Statistics
',
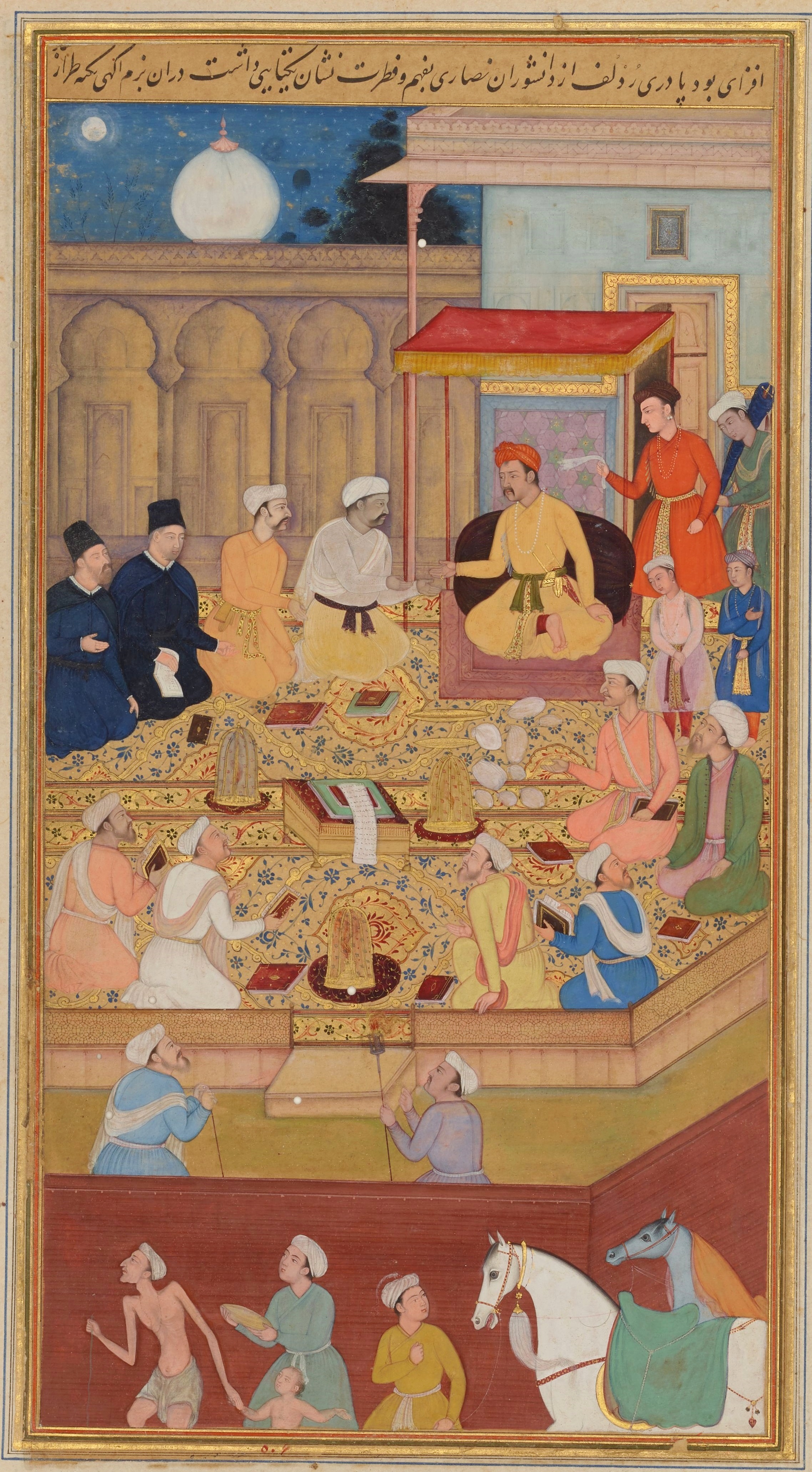 Two decades after
Two decades after  After the 1757
After the 1757
Bengals plunder gifted the British Industrial Revolution
''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', 8 February 2010 Economic mismanagement, alongside drought and a smallpox epidemic, directly led to the Great Bengal famine of 1770, which is estimated to have caused the deaths of between 1 million and 10 million people. Several rebellions broke out during the early 19th century (including one led by Titumir), as Company rule had displaced the Muslim ruling class from power. A conservative Islamic cleric, Haji Shariatullah, sought to overthrow the British by propagating Islamic revivalism. Several towns in Bangladesh participated in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and pledged allegiance to the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, who was later exiled to neighbouring Burma. The challenge posed to company rule by the failed Indian Mutiny led to the creation of the British Indian Empire as a crown colony. The British established several schools, colleges, and a university in Bangladesh. Syed Ahmed Khan and Ram Mohan Roy promoted modern and liberal education in the subcontinent, inspiring the Aligarh movement and the Bengal Renaissance. During the late 19th century, novelists, social reformers and feminists emerged from Muslim Bengali society. Electricity and municipal water systems were introduced in the 1890s; Movie theatre, cinemas opened in many towns during the early 20th century. East Bengal's plantation economy was important to the British Empire, particularly its jute and Tea production in Bangladesh, tea. The British established free port, tax-free river ports, such as the Port of Narayanganj, and large seaports like the Port of Chittagong. Bengal had the highest gross domestic product in British India. Bengal was one of the first regions in Asia to have a railway. The first railway in what is now Bangladesh began operating in 1862. In comparison, Japan saw its first railway in 1872. The main railway companies in the region were the Eastern Bengal Railway and Assam Bengal Railway. Railways competed with waterborne transport to become one of the main mediums of transport. Supported by the Muslim aristocracy, the British government created the province of Although it won most seats in 1937, the Bengal Congress boycotted the legislature. A. K. Fazlul Huq of the Krishak Sramik Party, Krishak Praja Party was elected as the first
Although it won most seats in 1937, the Bengal Congress boycotted the legislature. A. K. Fazlul Huq of the Krishak Sramik Party, Krishak Praja Party was elected as the first
 The
The
"Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900"
. Transaction Publishers, Rutgers University. , Chapter 8
Table 8.2 Pakistan Genocide in Bangladesh Estimates, Sources, and Calculations
Under international pressure, Pakistan released Rahman from imprisonment on 8 January 1972 and he was flown by the British Royal Air Force to a million-strong homecoming in Dacca. Remaining Indian troops were withdrawn by 12 March 1972, three months after the war ended. The cause of Bangladeshi self-determination was recognised around the world. By August 1972, the new state was recognised by 86 countries. Pakistan recognised Bangladesh in 1974 after pressure from most of the Muslim countries.
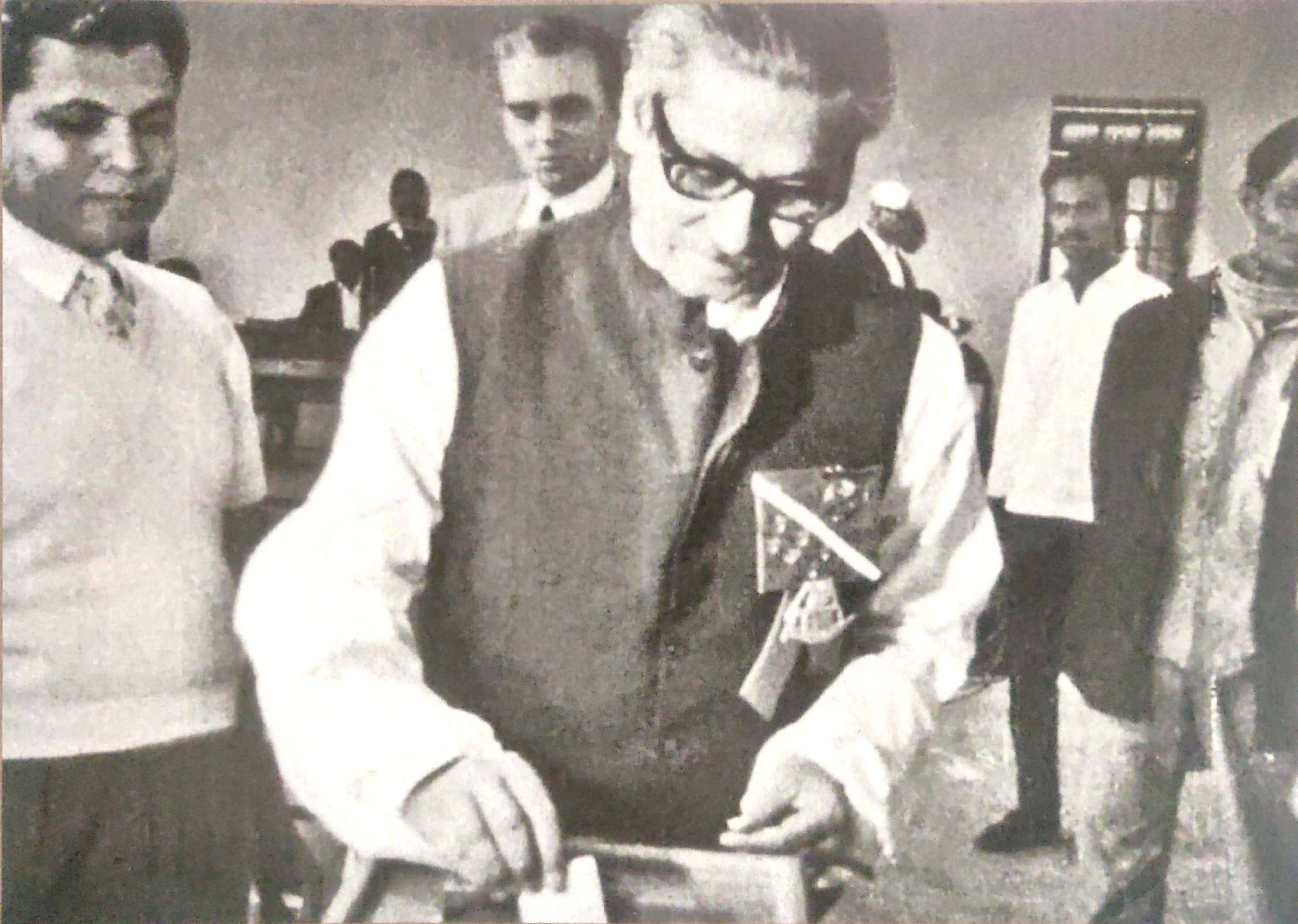 The constituent assembly adopted the constitution of Bangladesh on 4 November 1972, establishing a secular, multiparty parliamentary democracy. The new constitution included references to socialism, and Prime Minister Sheikh Mujibur Rahman nationalised major industries in 1972. A major reconstruction and rehabilitation programme was launched. The Awami League won the country's first general election in 1973, securing a large majority in the "Jatiyo Sangshad", the national parliament. Bangladesh joined the
The constituent assembly adopted the constitution of Bangladesh on 4 November 1972, establishing a secular, multiparty parliamentary democracy. The new constitution included references to socialism, and Prime Minister Sheikh Mujibur Rahman nationalised major industries in 1972. A major reconstruction and rehabilitation programme was launched. The Awami League won the country's first general election in 1973, securing a large majority in the "Jatiyo Sangshad", the national parliament. Bangladesh joined the
 After the 1991 general election, the twelfth amendment to the constitution restored the parliamentary republic and Begum Khaleda Zia became Bangladesh's first female prime minister. Zia, a former first lady, led a BNP government from 1990 to 1996. In 1991, her finance minister, Saifur Rahman (Bangladeshi politician), Saifur Rahman, began a major programme to liberalise the Bangladeshi economy.
In February 1996, February 1996 Bangladeshi general election, a general election was held, which was boycotted by all opposition parties giving a 300 (of 300) seat victory for BNP. This election was deemed illegitimate, so a system of a caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker government was introduced to oversee the transfer of power and a new election was held in June 1996, overseen by Justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman, the first Chief Adviser of Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Awami League, Awami League won the June 1996 Bangladeshi general election, seventh general election, marking its leader Sheikh Hasina, Sheikh Hasina's first term as Prime Minister. Hasina's first term was highlighted by the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord and a
After the 1991 general election, the twelfth amendment to the constitution restored the parliamentary republic and Begum Khaleda Zia became Bangladesh's first female prime minister. Zia, a former first lady, led a BNP government from 1990 to 1996. In 1991, her finance minister, Saifur Rahman (Bangladeshi politician), Saifur Rahman, began a major programme to liberalise the Bangladeshi economy.
In February 1996, February 1996 Bangladeshi general election, a general election was held, which was boycotted by all opposition parties giving a 300 (of 300) seat victory for BNP. This election was deemed illegitimate, so a system of a caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker government was introduced to oversee the transfer of power and a new election was held in June 1996, overseen by Justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman, the first Chief Adviser of Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Awami League, Awami League won the June 1996 Bangladeshi general election, seventh general election, marking its leader Sheikh Hasina, Sheikh Hasina's first term as Prime Minister. Hasina's first term was highlighted by the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord and a
 Bangladesh is a small, lush country in
Bangladesh is a small, lush country in
 Bangladesh is located in the Indomalayan realm, and lies within four terrestrial ecoregions: Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests, Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests, Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests, and Sundarbans mangroves. Its ecology includes a long sea coastline, numerous List of rivers in Bangladesh, rivers and tributaries, lakes, wetlands, evergreen forests, semi evergreen forests, hill forests, moist deciduous forests, freshwater swamp forests and flat land with tall grass. The Bangladesh Plain is famous for its fertile alluvial soil which supports extensive cultivation. The country is dominated by lush vegetation, with villages often buried in groves of mango, jackfruit, bamboo, betel nut, coconut and date palm.Bangladesh , history – geography :: Plant and animal life
Bangladesh is located in the Indomalayan realm, and lies within four terrestrial ecoregions: Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests, Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests, Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests, and Sundarbans mangroves. Its ecology includes a long sea coastline, numerous List of rivers in Bangladesh, rivers and tributaries, lakes, wetlands, evergreen forests, semi evergreen forests, hill forests, moist deciduous forests, freshwater swamp forests and flat land with tall grass. The Bangladesh Plain is famous for its fertile alluvial soil which supports extensive cultivation. The country is dominated by lush vegetation, with villages often buried in groves of mango, jackfruit, bamboo, betel nut, coconut and date palm.Bangladesh , history – geography :: Plant and animal life
. ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. The country has up to 6000 species of plant life, including 5000 flowering plants. Water bodies and wetland systems provide a habitat for many aquatic plants. Nymphaeaceae, Water lilies and Nelumbo nucifera, lotuses grow vividly during the monsoon season. The country has List of protected areas of Bangladesh, 50 wildlife sanctuaries. Bangladesh is home to much of the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest, covering an area of in the southwest littoral region. It is divided into three protected sanctuaries–the Sundarbans South Wildlife Sanctuary, South, Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuary, East and Sundarbans West Wildlife Sanctuary, West zones. The forest is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The northeastern Sylhet region is home to haor wetlands, a unique ecosystem. It also includes tropical and subtropical coniferous forests, a freshwater swamp forest, and mixed deciduous forests. The southeastern Chittagong Division, Chittagong region covers evergreen and semi-evergreen hilly jungles. Central Bangladesh includes the plainland Sal forest running along with the districts of Gazipur, Tangail and Mymensingh. St. Martin's Island is the only coral reef in the country. Bangladesh has an abundance of Wildlife in Bangladesh, wildlife in its forests, marshes, woodlands and hills. The vast majority of animals dwell within a habitat of . The Bengal tiger, clouded leopard, saltwater crocodile, black panther and fishing cat are among the chief predators in the Sundarbans. Northern and eastern Bangladesh is home to the Asian elephant, hoolock gibbon, Asian black bear and oriental pied hornbill. The Chital deer are widely seen in southwestern woodlands. Other animals include the black giant squirrel, capped langur, Bengal fox, sambar deer, jungle cat, king cobra, wild boar, mongooses, pangolins, Python (genus), pythons and Asian water monitor, water monitors. Bangladesh has one of the largest populations of Irrawaddy dolphins and South Asian river dolphin, Ganges dolphins. A 2009 census found 6,000 Irrawaddy dolphins inhabiting the littoral rivers of Bangladesh. The country has numerous species of amphibians (53), reptiles (139), marine reptiles (19) and marine mammals (5). It also has List of birds of Bangladesh, 628 species of birds. Several animals became extinct in Bangladesh during the last century, including the one-horned and two-horned rhinoceros and common peafowl. The human population is concentrated in urban areas, limiting deforestation to a certain extent. Rapid urban growth has threatened natural habitats. Although many areas are protected under law, some Bangladeshi wildlife is threatened by this growth. The Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act was enacted in 1995. The government has designated several regions as Ecologically Critical Areas, including wetlands, forests, and rivers. The Sundarbans tiger project and the Bangladesh Bear Project are among the key initiatives to strengthen conservation. It ratified the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity on 3 May 1994. , the country was set to revise its Biodiversity action plan, National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan.

 Bangladesh is a ''de jure'' representative democracy under its Constitution of Bangladesh, constitution, with a Westminster system, Westminster-style unitary authority, unitary parliamentary republic that has universal suffrage. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is invited to form a government every five years. The President invites the leader of the largest party in parliament to become Prime Minister of the world's fifth-largest democracy. Bangladesh experienced a two party system between 1990 and 2014, when the
Bangladesh is a ''de jure'' representative democracy under its Constitution of Bangladesh, constitution, with a Westminster system, Westminster-style unitary authority, unitary parliamentary republic that has universal suffrage. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is invited to form a government every five years. The President invites the leader of the largest party in parliament to become Prime Minister of the world's fifth-largest democracy. Bangladesh experienced a two party system between 1990 and 2014, when the

 The Bangladesh Armed Forces have inherited the institutional framework of the British military and the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1971 from the military regiments of East Pakistan. In 2022, the active personnel strength of the Bangladesh Army was around 250,000,* excluding the Air Force and the Navy (24,000). In addition to traditional defence roles, the military has supported civil authorities in disaster relief and provided internal security during periods of political unrest. For many years, Bangladesh has been the world's largest contributor to United Nations peacekeeping, UN peacekeeping forces. The military budget of Bangladesh accounts for 1.3% of GDP, amounting to US$4.3 billion in 2021.
The Bangladesh Navy, one of the largest in the Bay of Bengal, includes a List of active ships of the Bangladesh Navy, fleet of frigates, submarines, corvettes and other vessels. The Bangladesh Air Force has a List of active Bangladesh military aircraft, small fleet of multi-role combat aircraft, including the MiG-29 and Chengdu J-7, Chengdu-F7. Most of Bangladesh's military equipment comes from China. In recent years, Bangladesh and India have increased joint military exercises, high level visits of military leaders, counter-terrorism cooperation and intelligence sharing. Bangladesh is vital to ensuring stability and security in northeast India.
Bangladesh's strategic importance in the eastern subcontinent hinges on its proximity to China, its frontier with Burma, the separation of mainland and northeast India, and its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. In 2002, Bangladesh and China signed a Defence Cooperation Agreement (DCA) which the governments of both countries said will "institutionalize the existing accords in defence sector and also to rationalize the existing piecemeal agreements to enhance cooperation in training, maintenance and in some areas of production". The United States has pursued negotiations with Bangladesh on a Status of forces agreement, Status of Forces Agreement, an Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement and a General Security of Military Information Agreement. In 2019, Bangladesh ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Bangladesh Armed Forces have inherited the institutional framework of the British military and the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1971 from the military regiments of East Pakistan. In 2022, the active personnel strength of the Bangladesh Army was around 250,000,* excluding the Air Force and the Navy (24,000). In addition to traditional defence roles, the military has supported civil authorities in disaster relief and provided internal security during periods of political unrest. For many years, Bangladesh has been the world's largest contributor to United Nations peacekeeping, UN peacekeeping forces. The military budget of Bangladesh accounts for 1.3% of GDP, amounting to US$4.3 billion in 2021.
The Bangladesh Navy, one of the largest in the Bay of Bengal, includes a List of active ships of the Bangladesh Navy, fleet of frigates, submarines, corvettes and other vessels. The Bangladesh Air Force has a List of active Bangladesh military aircraft, small fleet of multi-role combat aircraft, including the MiG-29 and Chengdu J-7, Chengdu-F7. Most of Bangladesh's military equipment comes from China. In recent years, Bangladesh and India have increased joint military exercises, high level visits of military leaders, counter-terrorism cooperation and intelligence sharing. Bangladesh is vital to ensuring stability and security in northeast India.
Bangladesh's strategic importance in the eastern subcontinent hinges on its proximity to China, its frontier with Burma, the separation of mainland and northeast India, and its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. In 2002, Bangladesh and China signed a Defence Cooperation Agreement (DCA) which the governments of both countries said will "institutionalize the existing accords in defence sector and also to rationalize the existing piecemeal agreements to enhance cooperation in training, maintenance and in some areas of production". The United States has pursued negotiations with Bangladesh on a Status of forces agreement, Status of Forces Agreement, an Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement and a General Security of Military Information Agreement. In 2019, Bangladesh ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
 Torture is banned by Article 35 (5) of the Constitution of Bangladesh. Despite this constitutional ban, torture is rampantly used by Bangladesh's security forces. Bangladesh joined the Convention against Torture in 1998; but it enacted its first anti-torture law, the Torture and Custodial Death (Prevention) Act, in 2013. The first conviction under this law was announced in 2020. Amnesty International Prisoner of conscience, Prisoners of Conscience from Bangladesh have included Saber Hossain Chowdhury and Shahidul Alam. The Digital Security Act of 2018 has greatly reduced freedom of expression in Bangladesh, particularly on the internet. The Digital Security Act has been used to target critics of the government and bureaucracy. Newspaper editorials have been demanding the repeal of the Digital Security Act.
On International Human Rights Day in December 2021, the United States United States Department of the Treasury, Department of Treasury announced Economic sanctions, sanctions on commanders of the Rapid Action Battalion for extrajudicial killings, torture and other human rights abuses. Freedom House has criticised the ruling party for human rights abuses, crackdown on opposition, mass media, and civil society through politicized enforcement. Bangladesh is ranked "partly free" in Freedom House's ''Freedom in the World'' report, but its press freedom has deteriorated from "free" to "not free" in recent years due to increasing pressure from the authoritarian government. According to the British Economist Intelligence Unit, the country has a hybrid regime: the third of four rankings in its Democracy Index. Bangladesh was ranked 96th among 163 countries in the 2022 Global Peace Index. According to National Human Rights Commission, 70% of alleged human-rights violations are committed by law-enforcement agencies.
LGBT rights in Bangladesh, LGBT rights are heavily suppressed by both government and society, as homosexuality is outlawed by section 377 of the criminal code (a legacy of the colonial period), and is punishable by a maximum of life imprisonment. However, Bangladesh recognises the third gender and accords limited rights for transgender people. According to the 2016 Global Slavery Index, an estimated 1,531,300 people are enslaved in Bangladesh, or roughly 1% of the population. A number of slaves in Bangladesh are forced to work in the fish and shrimp industries.
Torture is banned by Article 35 (5) of the Constitution of Bangladesh. Despite this constitutional ban, torture is rampantly used by Bangladesh's security forces. Bangladesh joined the Convention against Torture in 1998; but it enacted its first anti-torture law, the Torture and Custodial Death (Prevention) Act, in 2013. The first conviction under this law was announced in 2020. Amnesty International Prisoner of conscience, Prisoners of Conscience from Bangladesh have included Saber Hossain Chowdhury and Shahidul Alam. The Digital Security Act of 2018 has greatly reduced freedom of expression in Bangladesh, particularly on the internet. The Digital Security Act has been used to target critics of the government and bureaucracy. Newspaper editorials have been demanding the repeal of the Digital Security Act.
On International Human Rights Day in December 2021, the United States United States Department of the Treasury, Department of Treasury announced Economic sanctions, sanctions on commanders of the Rapid Action Battalion for extrajudicial killings, torture and other human rights abuses. Freedom House has criticised the ruling party for human rights abuses, crackdown on opposition, mass media, and civil society through politicized enforcement. Bangladesh is ranked "partly free" in Freedom House's ''Freedom in the World'' report, but its press freedom has deteriorated from "free" to "not free" in recent years due to increasing pressure from the authoritarian government. According to the British Economist Intelligence Unit, the country has a hybrid regime: the third of four rankings in its Democracy Index. Bangladesh was ranked 96th among 163 countries in the 2022 Global Peace Index. According to National Human Rights Commission, 70% of alleged human-rights violations are committed by law-enforcement agencies.
LGBT rights in Bangladesh, LGBT rights are heavily suppressed by both government and society, as homosexuality is outlawed by section 377 of the criminal code (a legacy of the colonial period), and is punishable by a maximum of life imprisonment. However, Bangladesh recognises the third gender and accords limited rights for transgender people. According to the 2016 Global Slavery Index, an estimated 1,531,300 people are enslaved in Bangladesh, or roughly 1% of the population. A number of slaves in Bangladesh are forced to work in the fish and shrimp industries.
Corruption in Service Sectors: National Household Survey 2015
', Transparency International Bangladesh, Dhaka, 2016, p. 1 Land administration was the sector with the most bribery in 2015, followed by education, police and water supply. The Anti Corruption Commission Bangladesh, Anti Corruption Commission was formed in 2004, and it was active during the 2006–08 Bangladeshi political crisis, indicting many leading politicians, bureaucrats and businessmen for Graft (politics), graft.
 Bangladesh is the second largest economy in South Asia after India. The country has outpaced India (of which it was a part until 1947) and Pakistan (of which it was a part until 1971) in terms of per capita income. According to the World Bank, "When the newly independent country of Bangladesh was born on December 16, 1971, it was the second poorest country in the world—making the country's transformation over the next 50 years one of the great development stories. Since then, poverty has been cut in half at record speed. Enrolment in primary school is now nearly universal. Hundreds of thousands of women have entered the workforce. Steady progress has been made on maternal and child health. And the country is better buttressed against the destructive forces posed by climate change and natural disasters. Bangladesh's success comprises many moving parts—from investing in human capital to establishing macroeconomic stability. Building on this success, the country is now setting the stage for further economic growth and job creation by ramping up investments in energy, inland connectivity, urban projects, and transport infrastructure, as well as prioritizing climate change adaptation and disaster preparedness on its path toward sustainable growth".
Since 2009, Bangladesh has embarked on a series of List of megaprojects in Bangladesh, megaprojects. The 6.15 km long Padma Bridge was built at a cost of US$3.86 billion. The bridge was the first self-financed megaproject in the country's history. Other megaprojects include the Dhaka Metro, Karnaphuli Tunnel, Dhaka Elevated Expressway and Chittagong Elevated Expressway; as well as the Bangladesh Delta Plan to mitigate the impact of climate change. Overseas remittances from expat Bangladeshis and export earnings from the Bangladesh textile industry have allowed the country to have the second largest List of countries by foreign exchange reserves, foreign-exchange reserves in South Asia. The reserves have boosted the government's spending capacity in spite of tax revenues forming only 7.7% of government revenue. A big chunk of investments have gone into the Electric power, power sector. In 2009, Bangladesh was experiencing daily blackouts several times a day. In 2022, the country achieved 100% electrification. One of the major anti-poverty schemes of the Bangladeshi government is the Ashrayan Project which aims to eradicate homelessness by providing free housing.
The private sector accounts for 80% of GDP in comparison to the dwindling role of state-owned companies. Bangladesh's economy is dominated by family-owned List of companies of Bangladesh, conglomerates and small and medium-sized businesses. Some of the largest publicly-traded companies in Bangladesh include Beximco, BRAC Bank, BSRM, GPH Ispat, Grameenphone, Summit Group, and Square Pharmaceuticals. Capital markets include the Dhaka Stock Exchange and the Chittagong Stock Exchange. Its Telecommunications in Bangladesh, telecommunications industry is one of the world's fastest growing, with 171.854 million cellphone subscribers in January 2021. Over 80% of Bangladesh's export earnings come from the garments industry. Other major industries include Shipbuilding in Bangladesh, shipbuilding, pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh, pharmaceuticals, Steel industry in Bangladesh, steel, Electronics industry in Bangladesh, electronics, and Leather industry in Bangladesh, leather goods. Aziz Khan (businessman), Muhammad Aziz Khan became the first person from Bangladesh to be listed as a billionaire by ''Forbes''.
The poverty rate has gone down from 80% in 1971, to 44.2% in 1991, to 12.9% in 2021. The literacy rate stood at 74.66% in 2022. Bangladesh has a labor force of roughly 70 million, which is the world's List of countries by labour force, seventh-largest; with an unemployment rate of 5.2% . The government is setting up 100 special economic zones to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and generate 10 million jobs. The Bangladesh Investment Development Authority (BIDA) and the Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA) have been established to help investors in setting up factories; and to complement the longstanding Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority (BEPZA).
The Bangladeshi taka is the national currency. The service sector accounts for about 51.3% of total GDP and employs 39% of the workforce. The industrial sector accounts for 35.1% of GDP and employs 20.4% of the workforce. The Agriculture in Bangladesh, agriculture sector makes up 13.6% of the economy but is the biggest employment sector, with 40.6% of the workforce. In agriculture, the country is a major producer of Rice production in Bangladesh, rice, List of fishes in Bangladesh, fish, Tea production in Bangladesh, tea, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and jute. Lobsters and shrimps are some of Bangladesh's well known exports.
Bangladesh is gradually transitioning to a green economy. Currently, it has the largest off-grid solar power programme in the world, benefiting 20 million people. An electric car called the ''Palki'' is being developed for production in the country. The government has reduced tariffs for the purchase of electric cars. Biogas is being used to produce organic fertilizer.
Bangladesh continues to have huge untapped reserves of natural gas, particularly in its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. The success ratio of finding gas wells in the country stands at 3:5:1, meaning one commercial deposit is found in every three explored zones. The success ratio is well above the global average. A lack of exploration and decreasing proven reserves have forced Bangladesh to import LNG from abroad, despite having substantially untapped gas reserves. Gas shortages were further exasperated by the Russia-Ukraine War.
The Tourism in Bangladesh, tourism industry is expanding, contributing some 3.02% of total GDP. Bangladesh's international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $391 million. The country has List of World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh, three UNESCO World Heritage Sites (Historic Mosque City of Bagerhat, the Mosque City, Ruins of the Buddhist Vihara at Paharpur, the Buddhist Vihara and the Sundarbans) and five World Heritage Site#Nominating process, tentative-list sites. Activities for tourists include angling, water skiing, river cruising, hiking, rowing (sport), rowing, yachting, and sea bathing. The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) reported in 2019 that the travel and tourism industry in Bangladesh directly generated 1,180,500 jobs in 2018 or 1.9% of the country's total employment. According to the same report, Bangladesh experiences around 125,000 international tourist arrivals per year. Domestic spending generated 97.7 percent of direct travel and tourism gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012.
Bangladesh is the second largest economy in South Asia after India. The country has outpaced India (of which it was a part until 1947) and Pakistan (of which it was a part until 1971) in terms of per capita income. According to the World Bank, "When the newly independent country of Bangladesh was born on December 16, 1971, it was the second poorest country in the world—making the country's transformation over the next 50 years one of the great development stories. Since then, poverty has been cut in half at record speed. Enrolment in primary school is now nearly universal. Hundreds of thousands of women have entered the workforce. Steady progress has been made on maternal and child health. And the country is better buttressed against the destructive forces posed by climate change and natural disasters. Bangladesh's success comprises many moving parts—from investing in human capital to establishing macroeconomic stability. Building on this success, the country is now setting the stage for further economic growth and job creation by ramping up investments in energy, inland connectivity, urban projects, and transport infrastructure, as well as prioritizing climate change adaptation and disaster preparedness on its path toward sustainable growth".
Since 2009, Bangladesh has embarked on a series of List of megaprojects in Bangladesh, megaprojects. The 6.15 km long Padma Bridge was built at a cost of US$3.86 billion. The bridge was the first self-financed megaproject in the country's history. Other megaprojects include the Dhaka Metro, Karnaphuli Tunnel, Dhaka Elevated Expressway and Chittagong Elevated Expressway; as well as the Bangladesh Delta Plan to mitigate the impact of climate change. Overseas remittances from expat Bangladeshis and export earnings from the Bangladesh textile industry have allowed the country to have the second largest List of countries by foreign exchange reserves, foreign-exchange reserves in South Asia. The reserves have boosted the government's spending capacity in spite of tax revenues forming only 7.7% of government revenue. A big chunk of investments have gone into the Electric power, power sector. In 2009, Bangladesh was experiencing daily blackouts several times a day. In 2022, the country achieved 100% electrification. One of the major anti-poverty schemes of the Bangladeshi government is the Ashrayan Project which aims to eradicate homelessness by providing free housing.
The private sector accounts for 80% of GDP in comparison to the dwindling role of state-owned companies. Bangladesh's economy is dominated by family-owned List of companies of Bangladesh, conglomerates and small and medium-sized businesses. Some of the largest publicly-traded companies in Bangladesh include Beximco, BRAC Bank, BSRM, GPH Ispat, Grameenphone, Summit Group, and Square Pharmaceuticals. Capital markets include the Dhaka Stock Exchange and the Chittagong Stock Exchange. Its Telecommunications in Bangladesh, telecommunications industry is one of the world's fastest growing, with 171.854 million cellphone subscribers in January 2021. Over 80% of Bangladesh's export earnings come from the garments industry. Other major industries include Shipbuilding in Bangladesh, shipbuilding, pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh, pharmaceuticals, Steel industry in Bangladesh, steel, Electronics industry in Bangladesh, electronics, and Leather industry in Bangladesh, leather goods. Aziz Khan (businessman), Muhammad Aziz Khan became the first person from Bangladesh to be listed as a billionaire by ''Forbes''.
The poverty rate has gone down from 80% in 1971, to 44.2% in 1991, to 12.9% in 2021. The literacy rate stood at 74.66% in 2022. Bangladesh has a labor force of roughly 70 million, which is the world's List of countries by labour force, seventh-largest; with an unemployment rate of 5.2% . The government is setting up 100 special economic zones to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and generate 10 million jobs. The Bangladesh Investment Development Authority (BIDA) and the Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA) have been established to help investors in setting up factories; and to complement the longstanding Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority (BEPZA).
The Bangladeshi taka is the national currency. The service sector accounts for about 51.3% of total GDP and employs 39% of the workforce. The industrial sector accounts for 35.1% of GDP and employs 20.4% of the workforce. The Agriculture in Bangladesh, agriculture sector makes up 13.6% of the economy but is the biggest employment sector, with 40.6% of the workforce. In agriculture, the country is a major producer of Rice production in Bangladesh, rice, List of fishes in Bangladesh, fish, Tea production in Bangladesh, tea, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and jute. Lobsters and shrimps are some of Bangladesh's well known exports.
Bangladesh is gradually transitioning to a green economy. Currently, it has the largest off-grid solar power programme in the world, benefiting 20 million people. An electric car called the ''Palki'' is being developed for production in the country. The government has reduced tariffs for the purchase of electric cars. Biogas is being used to produce organic fertilizer.
Bangladesh continues to have huge untapped reserves of natural gas, particularly in its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. The success ratio of finding gas wells in the country stands at 3:5:1, meaning one commercial deposit is found in every three explored zones. The success ratio is well above the global average. A lack of exploration and decreasing proven reserves have forced Bangladesh to import LNG from abroad, despite having substantially untapped gas reserves. Gas shortages were further exasperated by the Russia-Ukraine War.
The Tourism in Bangladesh, tourism industry is expanding, contributing some 3.02% of total GDP. Bangladesh's international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $391 million. The country has List of World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh, three UNESCO World Heritage Sites (Historic Mosque City of Bagerhat, the Mosque City, Ruins of the Buddhist Vihara at Paharpur, the Buddhist Vihara and the Sundarbans) and five World Heritage Site#Nominating process, tentative-list sites. Activities for tourists include angling, water skiing, river cruising, hiking, rowing (sport), rowing, yachting, and sea bathing. The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) reported in 2019 that the travel and tourism industry in Bangladesh directly generated 1,180,500 jobs in 2018 or 1.9% of the country's total employment. According to the same report, Bangladesh experiences around 125,000 international tourist arrivals per year. Domestic spending generated 97.7 percent of direct travel and tourism gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012.
 The official and predominant language of Bangladesh is
The official and predominant language of Bangladesh is
 Bangladesh was constitutionally proclaimed as the first secular state of South Asia in 1972. It grants freedom of religion and claims to be "secular in practise", while establishing Islam as the state religion. The constitution bans religion-based politics and discrimination, and proclaims equal recognition of people adhering to all faiths. Islam in Bangladesh, Islam is the largest religion across the country, being followed by about 91% of the population. The vast majority of Bangladeshi citizens are Bengali Muslims, adhering to Sunni Islam. The country is the third-most populous Muslim-majority state in the world, and has the fourth-largest overall Muslim population.
Hinduism in Bangladesh, Hinduism is followed by 7.95% of the population, mainly by the Bengali Hindus, who form the country's second-largest religious group and the third-largest Hindu community globally; after those in India and Nepal. Buddhism in Bangladesh, Buddhism is the third-largest religion, at 0.61% of the population. Bangladeshi Buddhists are concentrated among the tribal ethnic groups in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. At the same time, coastal Chittagong is home to many Bengali Buddhists. Christianity is the fourth-largest religion, at 0.3%, followed mainly by a small Bengali Christians, Bengali Christian minority.
Bangladesh was constitutionally proclaimed as the first secular state of South Asia in 1972. It grants freedom of religion and claims to be "secular in practise", while establishing Islam as the state religion. The constitution bans religion-based politics and discrimination, and proclaims equal recognition of people adhering to all faiths. Islam in Bangladesh, Islam is the largest religion across the country, being followed by about 91% of the population. The vast majority of Bangladeshi citizens are Bengali Muslims, adhering to Sunni Islam. The country is the third-most populous Muslim-majority state in the world, and has the fourth-largest overall Muslim population.
Hinduism in Bangladesh, Hinduism is followed by 7.95% of the population, mainly by the Bengali Hindus, who form the country's second-largest religious group and the third-largest Hindu community globally; after those in India and Nepal. Buddhism in Bangladesh, Buddhism is the third-largest religion, at 0.61% of the population. Bangladeshi Buddhists are concentrated among the tribal ethnic groups in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. At the same time, coastal Chittagong is home to many Bengali Buddhists. Christianity is the fourth-largest religion, at 0.3%, followed mainly by a small Bengali Christians, Bengali Christian minority.
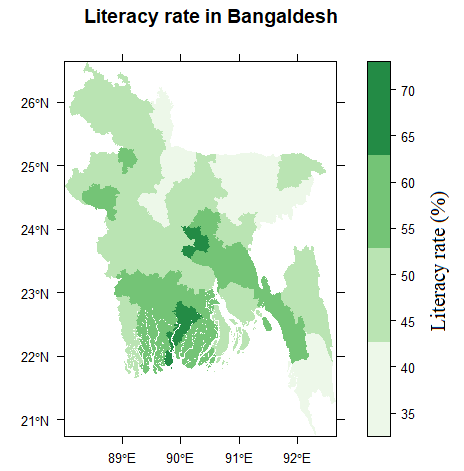 Article (17) of the constitution states that all children shall receive free and compulsory education. Education in Bangladesh is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Bangladesh), Ministry of Education. The Ministry of Primary and Mass Education is responsible for implementing policy for primary education and state-funded schools at a local level. Primary and secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, and is financed by the state and free of charge in public schools. Bangladesh has a literacy rate of 74.7% percent as of 2019: 77.4% for males and 71.9% for females. The country's educational system is three-tiered and heavily subsidised, with the government operating many schools at the primary, secondary and higher secondary levels and subsidising many private schools. In the tertiary education sector, the Bangladeshi government funds over 45 state universities through the University Grants Commission (Bangladesh), University Grants Commission (UGC), created by Presidential Order 10 in 1973.
The education system is divided into five levels: primary (first to fifth grade), junior secondary (sixth to eighth grade), secondary (ninth and tenth grade), higher secondary (11th and 12th grade), and tertiary. Five years of secondary education (including junior secondary) ends with a Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. Since 2009, the Primary Education Closing (PEC) examination has also been introduced. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to secondary or matriculation training, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to three years of junior secondary education, culminating in the Junior School Certificate (JSC) examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of secondary education, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of higher secondary education, culminating in the Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSC) examination.
Universities in Bangladesh are of three general types: public (government-owned and subsidised), private (privately owned universities) and international (operated and funded by international organisations). The country has 47 public, 105 private and two international List of universities in Bangladesh, universities; Bangladesh National University has the largest enrolment, and the University of Dhaka (established in 1921) is the oldest. University of Chittagong, established in 1966, has the largest campus among all universities in Bangladesh. Medical education is provided by 29 government and private List of medical colleges in Bangladesh, medical colleges. All medical colleges are affiliated with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Article (17) of the constitution states that all children shall receive free and compulsory education. Education in Bangladesh is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Bangladesh), Ministry of Education. The Ministry of Primary and Mass Education is responsible for implementing policy for primary education and state-funded schools at a local level. Primary and secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, and is financed by the state and free of charge in public schools. Bangladesh has a literacy rate of 74.7% percent as of 2019: 77.4% for males and 71.9% for females. The country's educational system is three-tiered and heavily subsidised, with the government operating many schools at the primary, secondary and higher secondary levels and subsidising many private schools. In the tertiary education sector, the Bangladeshi government funds over 45 state universities through the University Grants Commission (Bangladesh), University Grants Commission (UGC), created by Presidential Order 10 in 1973.
The education system is divided into five levels: primary (first to fifth grade), junior secondary (sixth to eighth grade), secondary (ninth and tenth grade), higher secondary (11th and 12th grade), and tertiary. Five years of secondary education (including junior secondary) ends with a Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. Since 2009, the Primary Education Closing (PEC) examination has also been introduced. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to secondary or matriculation training, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to three years of junior secondary education, culminating in the Junior School Certificate (JSC) examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of secondary education, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of higher secondary education, culminating in the Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSC) examination.
Universities in Bangladesh are of three general types: public (government-owned and subsidised), private (privately owned universities) and international (operated and funded by international organisations). The country has 47 public, 105 private and two international List of universities in Bangladesh, universities; Bangladesh National University has the largest enrolment, and the University of Dhaka (established in 1921) is the oldest. University of Chittagong, established in 1966, has the largest campus among all universities in Bangladesh. Medical education is provided by 29 government and private List of medical colleges in Bangladesh, medical colleges. All medical colleges are affiliated with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
 Bangladesh, by constitution, guarantees healthcare services as a fundamental right to all of its citizens. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the largest institutional healthcare provider in Bangladesh, and contains two divisions: Health Service Division and Medical Education And Family Welfare Division. However, healthcare facilities in Bangladesh are considered less than adequate, although they have improved as the economy has grown and poverty levels have decreased significantly. Bangladesh faces a severe health workforce crisis, as formally-trained providers make up a short percentage the total health workforce. Significant deficiencies in the treatment practices of village doctors persist, with widespread harmful and inappropriate drug prescribing. Receiving health care from informal providers is encouraged.
Bangladesh's poor healthcare system suffers from severe underfunding from the government. , some 2.48% of total GDP was attributed to healthcare, and domestic general government spending on healthcare was 18.63% of the total budget, while out-of-pocket expenditures made up the vast majority of total budget, totalling 72.68%. Domestic private health expenditure was about 75% of the total healthcare expenditure. , there are only 5.3 doctors per 10,000 people, and about 6 physicians and 3 nurses per 10,000 people, while the number of hospital beds is 8 per 10,000. The overall life expectancy in Bangladesh at birth was 73 years (71 years for males and 75 years for females) , and it has a comparably high infant mortality rate (24 per 1,000 live births) and child mortality rate (29 per 1,000 live births). Maternal death, Maternal mortality remains high, clocking at 173 per 100,000 live births. Bangladesh is a key source market for medical tourism for various countries, mainly Medical tourism in India, India, due to its citizens dissatisfaction and distrust over their own healthcare system.
The main causes of death are coronary artery disease, stroke, and chronic respiratory disease; comprising 62% and 60% of all adult male and female deaths, respectively. Malnutrition is a major and persistent problem in Bangladesh, mainly affecting the rural regions, more than half of the population suffers from it. Severe acute malnutrition affects 450,000 children, while close to 2 million children have moderate acute malnutrition. For children under the age of five, 52% are affected by anaemia, 41% are stunted growth, stunted, 16% are wasting, wasted, and 36% are underweight. A quarter of women are underweight and around 15% have short stature, while over half also suffer from anaemia.
Bangladesh, by constitution, guarantees healthcare services as a fundamental right to all of its citizens. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the largest institutional healthcare provider in Bangladesh, and contains two divisions: Health Service Division and Medical Education And Family Welfare Division. However, healthcare facilities in Bangladesh are considered less than adequate, although they have improved as the economy has grown and poverty levels have decreased significantly. Bangladesh faces a severe health workforce crisis, as formally-trained providers make up a short percentage the total health workforce. Significant deficiencies in the treatment practices of village doctors persist, with widespread harmful and inappropriate drug prescribing. Receiving health care from informal providers is encouraged.
Bangladesh's poor healthcare system suffers from severe underfunding from the government. , some 2.48% of total GDP was attributed to healthcare, and domestic general government spending on healthcare was 18.63% of the total budget, while out-of-pocket expenditures made up the vast majority of total budget, totalling 72.68%. Domestic private health expenditure was about 75% of the total healthcare expenditure. , there are only 5.3 doctors per 10,000 people, and about 6 physicians and 3 nurses per 10,000 people, while the number of hospital beds is 8 per 10,000. The overall life expectancy in Bangladesh at birth was 73 years (71 years for males and 75 years for females) , and it has a comparably high infant mortality rate (24 per 1,000 live births) and child mortality rate (29 per 1,000 live births). Maternal death, Maternal mortality remains high, clocking at 173 per 100,000 live births. Bangladesh is a key source market for medical tourism for various countries, mainly Medical tourism in India, India, due to its citizens dissatisfaction and distrust over their own healthcare system.
The main causes of death are coronary artery disease, stroke, and chronic respiratory disease; comprising 62% and 60% of all adult male and female deaths, respectively. Malnutrition is a major and persistent problem in Bangladesh, mainly affecting the rural regions, more than half of the population suffers from it. Severe acute malnutrition affects 450,000 children, while close to 2 million children have moderate acute malnutrition. For children under the age of five, 52% are affected by anaemia, 41% are stunted growth, stunted, 16% are wasting, wasted, and 36% are underweight. A quarter of women are underweight and around 15% have short stature, while over half also suffer from anaemia.
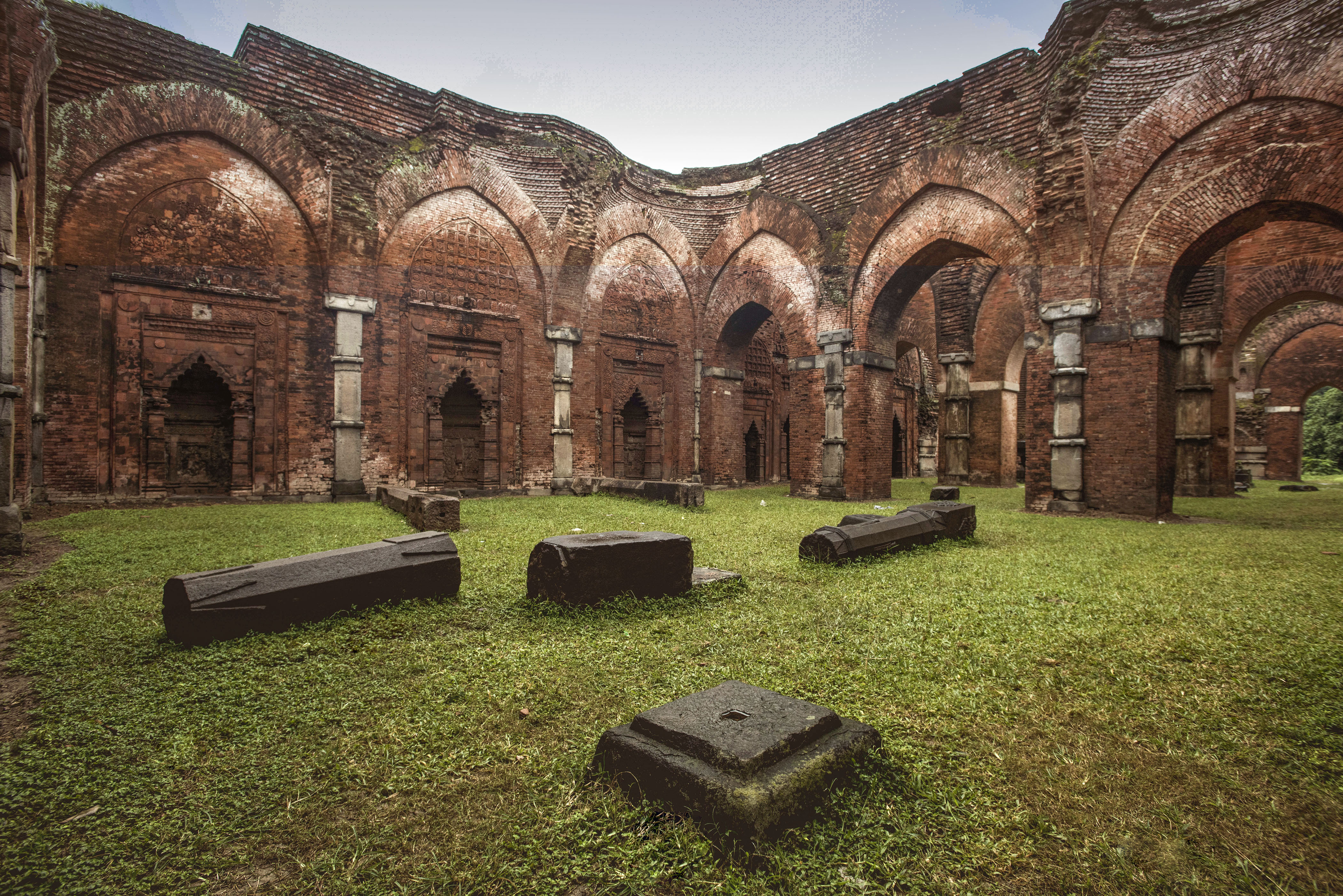
 The recorded history of art in Bangladesh can be traced to the 3rd century BCE, when terracotta sculptures were made in the region. In classical antiquity, a notable sculptural Hindu, Jain and Buddhist art developed in the Pala Empire and the Sena dynasty. Islamic art has evolved since the 14th century. The architecture of the Bengal Sultanate saw a distinct style of domed mosques with complex niche pillars that had no minarets.
The recorded history of art in Bangladesh can be traced to the 3rd century BCE, when terracotta sculptures were made in the region. In classical antiquity, a notable sculptural Hindu, Jain and Buddhist art developed in the Pala Empire and the Sena dynasty. Islamic art has evolved since the 14th century. The architecture of the Bengal Sultanate saw a distinct style of domed mosques with complex niche pillars that had no minarets.
 The oldest evidence of writing in Bangladesh is the Mahasthan Brahmi Inscription, which dates back to the 3rd century BCE. In the Gupta Empire, Sanskrit literature thrived in the region. Bengali developed from Sanskrit and Magadhi Prakrit in the 8th to 10th century. Bengali literature is a millennium-old tradition; the Charyapadas are the earliest examples of Bengali poetry. Sufi spiritualism inspired many
The oldest evidence of writing in Bangladesh is the Mahasthan Brahmi Inscription, which dates back to the 3rd century BCE. In the Gupta Empire, Sanskrit literature thrived in the region. Bengali developed from Sanskrit and Magadhi Prakrit in the 8th to 10th century. Bengali literature is a millennium-old tradition; the Charyapadas are the earliest examples of Bengali poetry. Sufi spiritualism inspired many
 Although , several women occupied major political office in Bangladesh. Its women continue to live under a patriarchal social regime where violence is common.Whispers to Voices: Gender and Social Transformation in Bangladesh
Although , several women occupied major political office in Bangladesh. Its women continue to live under a patriarchal social regime where violence is common.Whispers to Voices: Gender and Social Transformation in Bangladesh
World Bank.org 2008 Whereas in India and Pakistan women participate less in the workforce as their education increases, the reverse is the case in Bangladesh. Bengal has a long history of feminist activism dating back to the 19th century. Begum Rokeya and Nawab Faizunnesa, Faizunnessa Chowdhurani played an important role in emancipating Bengali Muslim women from purdah, before the country's division, as well as promoting girls' education. Several women were elected to the Bengal Legislative Assembly in the British Raj. The first women's magazine, ''Begum (magazine), Begum'', was published in 1948. In 2008, Bangladeshi female workforce participation stood at 26%. Women dominate blue collar jobs in the Bangladeshi garment industry. Agriculture, social services, healthcare and education are also major occupations for Bangladeshi women, while their employment in White-collar worker, white collar positions has steadily increased.
 The architectural traditions of Bangladesh have a 2,500-year-old heritage. Terracotta architecture is a distinct feature of Bengal. Pre-Islamic Bengali architecture reached its pinnacle in the Pala Empire, when the Pala School of Sculptural Art established grand structures such as the Somapura Mahavihara. Islamic architecture began developing under the Bengal Sultanate, when local terracotta styles influenced medieval mosque construction.
The Sixty Dome Mosque was the largest medieval mosque built in Bangladesh and is a fine example of Turkic-Bengali architecture. The Mughal architecture, Mughal style replaced indigenous architecture when Bengal became a province of the Mughal Empire and influenced urban housing development. The Kantajew Temple and Dhakeshwari Temple are excellent examples of late medieval Hindu temple architecture. Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, based on Indo-Islamic styles, flourished during the British period. The zamindar gentry in Bangladesh built numerous Indo-Saracenic palaces and country mansions, such as the Ahsan Manzil, Tajhat Palace, Uttara Gonobhaban, Dighapatia Palace, Puthia Rajbari and Natore Rajbari.
Bengali vernacular architecture is noted for pioneering the bungalow. Bangladeshi villages consist of thatched roofed houses made of natural materials like mud, straw, wood and bamboo. In modern times, village bungalows are increasingly made of tin.
Muzharul Islam was the pioneer of Bangladeshi modern architecture. His varied works set the course of modern architectural practice in the country. Islam brought leading global architects, including Louis Kahn, Richard Neutra, Stanley Tigerman, Paul Rudolph (architect), Paul Rudolph, Robert Boughey and Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis, Konstantinos Doxiadis, to work in erstwhile East Pakistan. Louis Kahn was chosen to design the National Parliament Complex in Sher-e-Bangla Nagar. Kahn's monumental designs, combining regional red brick aesthetics, his own concrete and marble brutalism and the use of lakes to represent Bengali geography, are regarded as one of the masterpieces of the 20th century. In more recent times, award-winning architects like Rafiq Azam have set the course of contemporary architecture by adopting influences from the works of Islam and Kahn.
The architectural traditions of Bangladesh have a 2,500-year-old heritage. Terracotta architecture is a distinct feature of Bengal. Pre-Islamic Bengali architecture reached its pinnacle in the Pala Empire, when the Pala School of Sculptural Art established grand structures such as the Somapura Mahavihara. Islamic architecture began developing under the Bengal Sultanate, when local terracotta styles influenced medieval mosque construction.
The Sixty Dome Mosque was the largest medieval mosque built in Bangladesh and is a fine example of Turkic-Bengali architecture. The Mughal architecture, Mughal style replaced indigenous architecture when Bengal became a province of the Mughal Empire and influenced urban housing development. The Kantajew Temple and Dhakeshwari Temple are excellent examples of late medieval Hindu temple architecture. Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, based on Indo-Islamic styles, flourished during the British period. The zamindar gentry in Bangladesh built numerous Indo-Saracenic palaces and country mansions, such as the Ahsan Manzil, Tajhat Palace, Uttara Gonobhaban, Dighapatia Palace, Puthia Rajbari and Natore Rajbari.
Bengali vernacular architecture is noted for pioneering the bungalow. Bangladeshi villages consist of thatched roofed houses made of natural materials like mud, straw, wood and bamboo. In modern times, village bungalows are increasingly made of tin.
Muzharul Islam was the pioneer of Bangladeshi modern architecture. His varied works set the course of modern architectural practice in the country. Islam brought leading global architects, including Louis Kahn, Richard Neutra, Stanley Tigerman, Paul Rudolph (architect), Paul Rudolph, Robert Boughey and Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis, Konstantinos Doxiadis, to work in erstwhile East Pakistan. Louis Kahn was chosen to design the National Parliament Complex in Sher-e-Bangla Nagar. Kahn's monumental designs, combining regional red brick aesthetics, his own concrete and marble brutalism and the use of lakes to represent Bengali geography, are regarded as one of the masterpieces of the 20th century. In more recent times, award-winning architects like Rafiq Azam have set the course of contemporary architecture by adopting influences from the works of Islam and Kahn.
 Theatre in Bangladesh includes various forms with a history dating back to the 4th century CE. It includes narrative forms, song and dance forms, supra-personae forms, performances with scroll paintings, puppet theatre and processional forms. The Jatra (theatre), Jatra is the most popular form of Bengali folk theatre.
The dance traditions of Bangladesh include indigenous tribal and Bengali dance forms, as well as classical Indian dances, including the Kathak, Odissi and Manipuri dances.
The music of Bangladesh features the
Theatre in Bangladesh includes various forms with a history dating back to the 4th century CE. It includes narrative forms, song and dance forms, supra-personae forms, performances with scroll paintings, puppet theatre and processional forms. The Jatra (theatre), Jatra is the most popular form of Bengali folk theatre.
The dance traditions of Bangladesh include indigenous tribal and Bengali dance forms, as well as classical Indian dances, including the Kathak, Odissi and Manipuri dances.
The music of Bangladesh features the
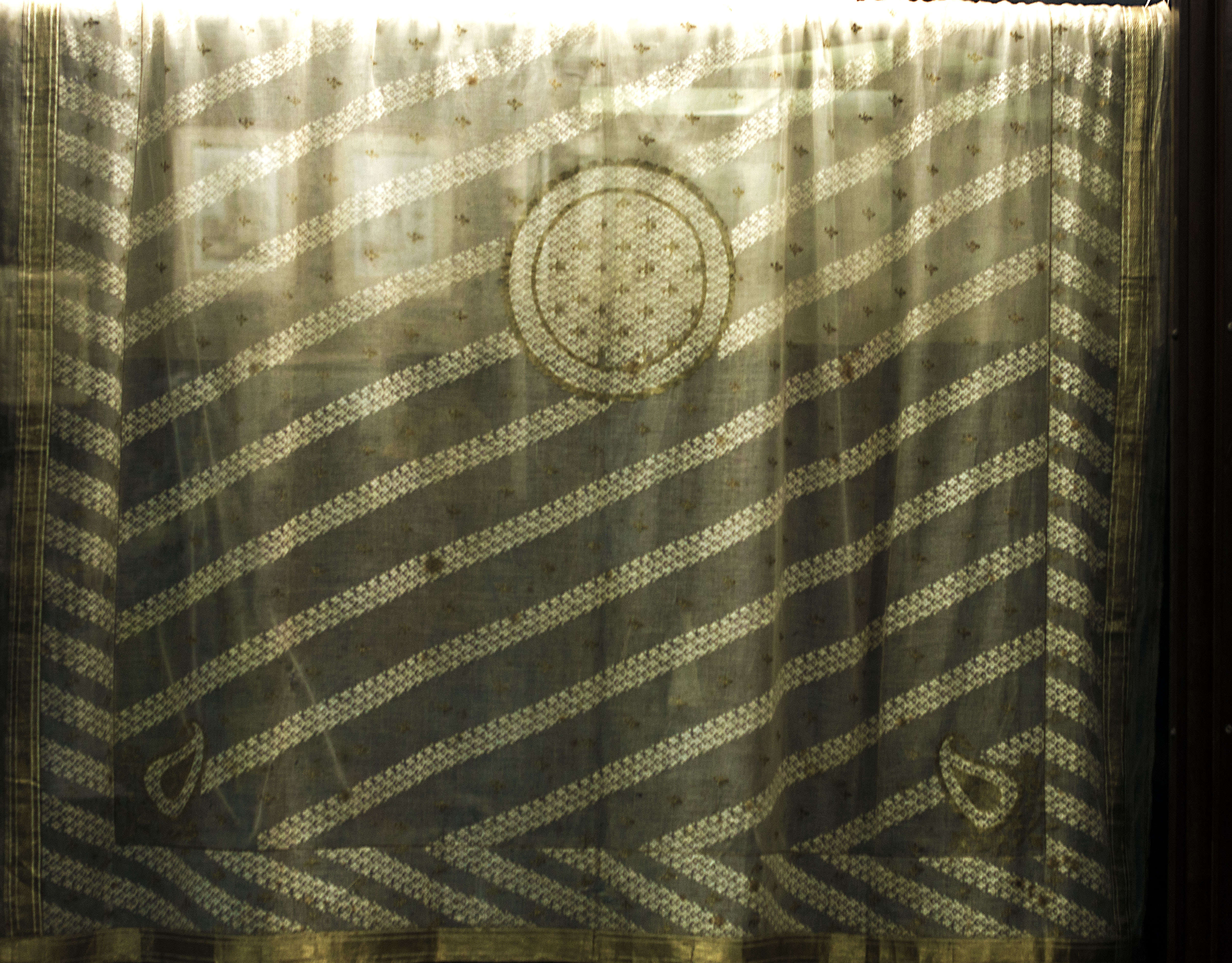
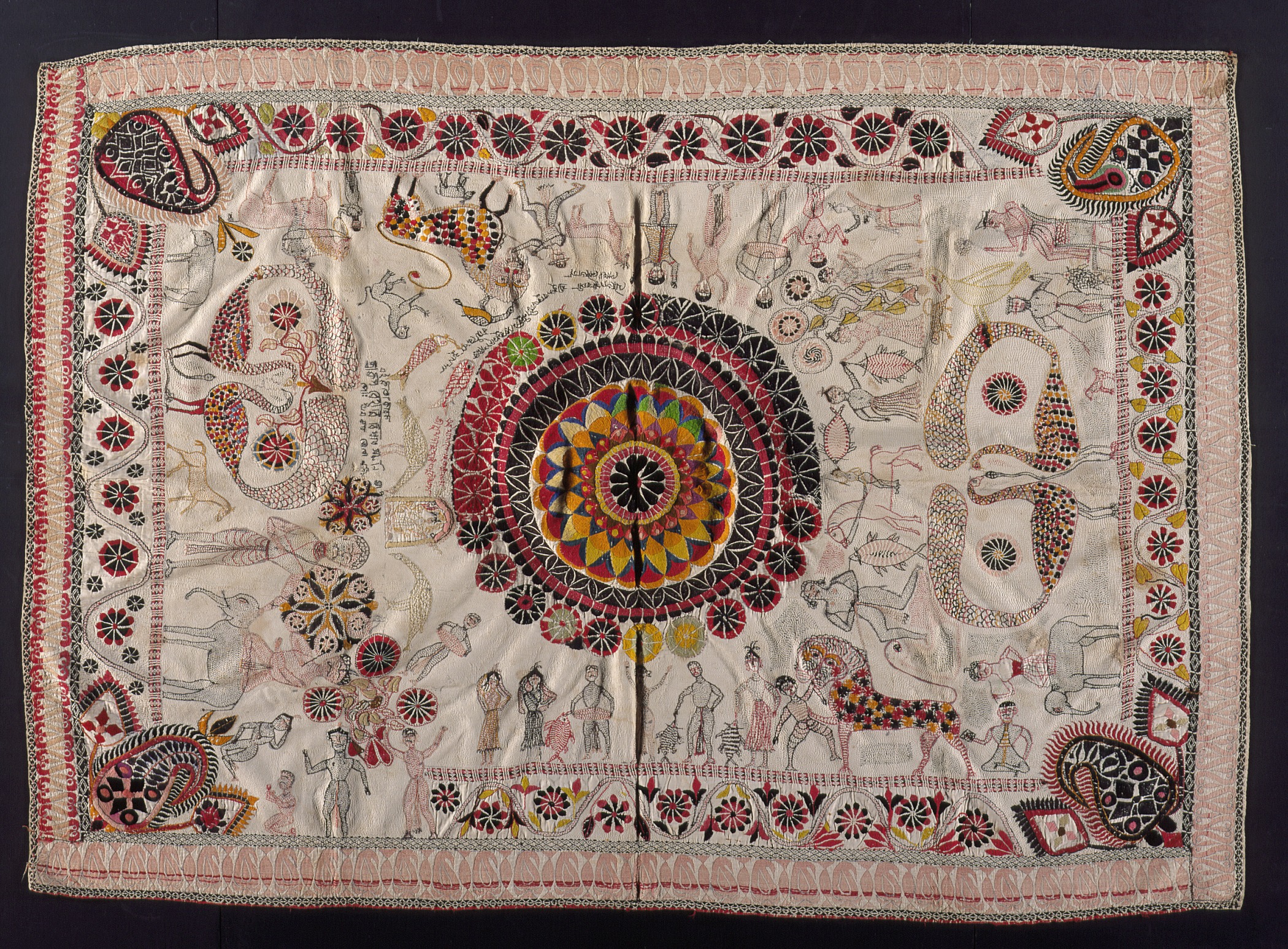 The Nakshi Kantha is a centuries-old embroidery tradition for quilts, said to be indigenous to eastern Bengal (i.e. Bangladesh). The sari is the national dress for Bangladeshi women. Mughal Dhaka was renowned for producing the finest Muslin saris, as well as the famed Dhakai and Jamdani, the weaving of which is listed by UNESCO as one of the masterpieces of humanity's intangible cultural heritage. Bangladesh also produces the Rajshahi silk. The shalwar kameez is also widely worn by Bangladeshi women. In urban areas, some women can be seen in western clothing. The kurta and sherwani are the national dress of Bangladeshi men; the lungi and dhoti are worn by them in informal settings. Aside from ethnic wear, domestically tailored suit (clothing), suits and neckties are customarily worn by the country's men in offices, in schools and at social events.
The handloom industry supplies 60–65% of the country's clothing demand. The Bengali ethnic fashion industry has flourished in the changing environment of the fashion world. The retailer Aarong is one of South Asia's most successful ethnic wear brands. The development of the Bangladesh textile industry, which supplies leading international brands, has promoted the local production and retail of modern Western attire. The country now has a number of expanding local brands like Westecs and Yellow. Bangladesh is the world's second-largest garments exporter. Among Bangladesh's fashion designers, Bibi Russell has received international acclaim for her "Fashion for Development" shows.
The Nakshi Kantha is a centuries-old embroidery tradition for quilts, said to be indigenous to eastern Bengal (i.e. Bangladesh). The sari is the national dress for Bangladeshi women. Mughal Dhaka was renowned for producing the finest Muslin saris, as well as the famed Dhakai and Jamdani, the weaving of which is listed by UNESCO as one of the masterpieces of humanity's intangible cultural heritage. Bangladesh also produces the Rajshahi silk. The shalwar kameez is also widely worn by Bangladeshi women. In urban areas, some women can be seen in western clothing. The kurta and sherwani are the national dress of Bangladeshi men; the lungi and dhoti are worn by them in informal settings. Aside from ethnic wear, domestically tailored suit (clothing), suits and neckties are customarily worn by the country's men in offices, in schools and at social events.
The handloom industry supplies 60–65% of the country's clothing demand. The Bengali ethnic fashion industry has flourished in the changing environment of the fashion world. The retailer Aarong is one of South Asia's most successful ethnic wear brands. The development of the Bangladesh textile industry, which supplies leading international brands, has promoted the local production and retail of modern Western attire. The country now has a number of expanding local brands like Westecs and Yellow. Bangladesh is the world's second-largest garments exporter. Among Bangladesh's fashion designers, Bibi Russell has received international acclaim for her "Fashion for Development" shows.
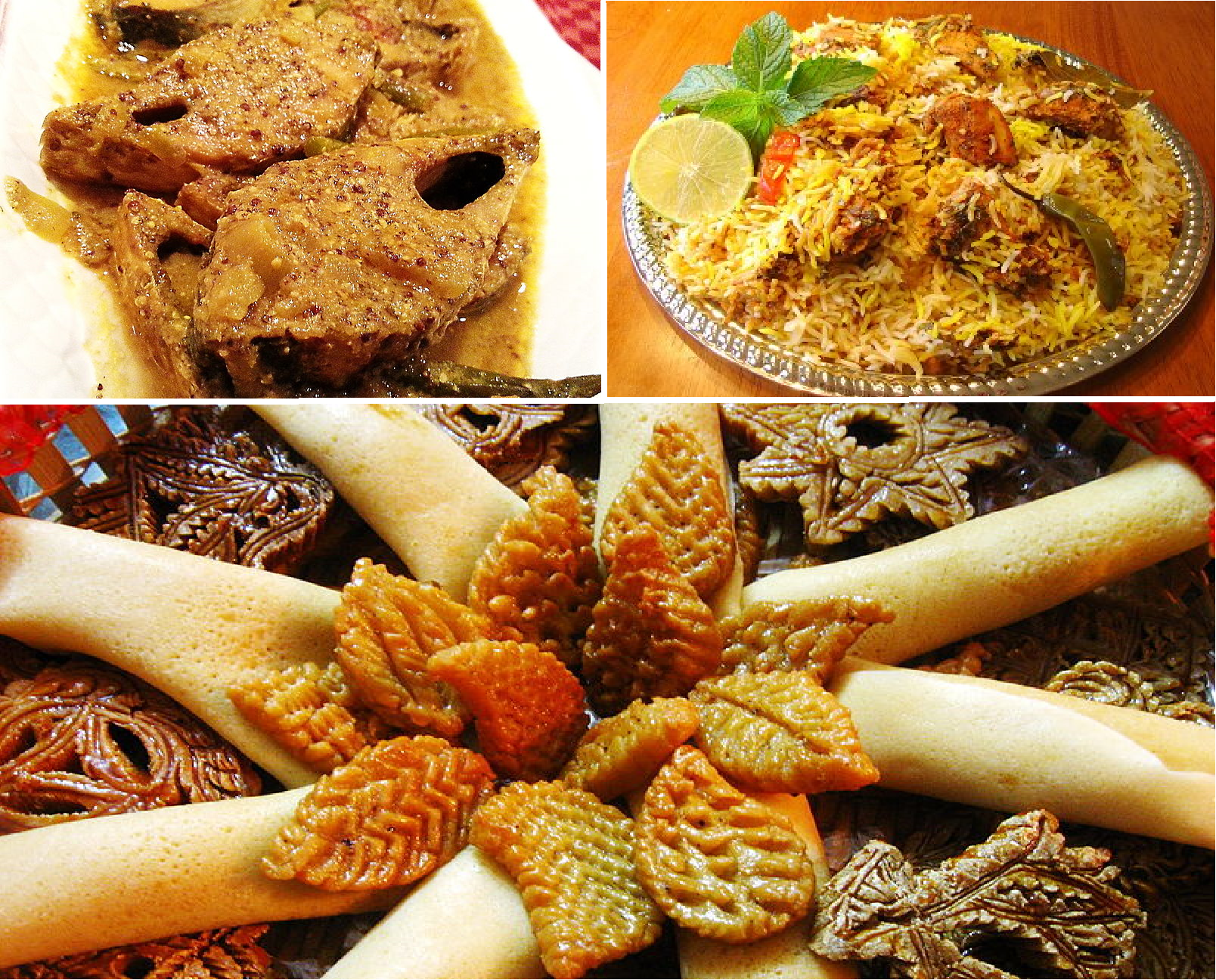 Bangladeshi cuisine, formed by its geographic location and climate, is rich and varied; sharing its culinary heritage with the neighbouring Indian state of West Bengal. White rice is the staple, and along with fish, forms the culinary base. Varieties of leaf vegetables, potatoes, gourds and lentils (dal) also play an important role. Curry, Curries of beef, mutton, chicken and duck are commonly consumed, along with multiple types of Bhurta, bhortas, ''bhajis'' and ''torkaris''. Mughal-influenced dishes include kormas, kalias, biryanis, pilaf, pulaos, Tahri (dish), teharis and khichuris. Among the various spices, turmeric, fenugreek, nigella, coriander, anise, cardamom and chili powder are widely used; a famous spice mix is the panch phoron. Among the condiments and herbs used, red onions, Chili pepper, green chillies, garlic, ginger, cilantro, and Mentha, mint stand out. Coconut milk, Mustard (condiment), mustard paste, mustard seeds, mustard oil, ghee, South Asian pickle, achars and chutneys are also widely used in the cuisine.
Fish is the main source of protein, often enjoyed with its roe. The hilsa is the national fish and immensely popular, a famous dish is shorshe ilish. Rohu, Pangasius pangasius, pangas, and tilapia are also highly consumed. Lobsters, shrimps and dried fish (''shutki'') are also widely consumed, with the chingri malai curry being a famous shrimp dish. In Chittagong, Mezban feasts are a popular tradition, featuring the serving of ''mezbani gosht'', a hot and spicy beef curry. Other famous dishes from the region include kala bhuna. In Sylhet, the ''shatkora'' lemons are used to marinate dishes, a notable one is Beef Hatkhora, beef hatkora. Among the tribal communities in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, cooking with bamboo shoots is popular. Khulna Division, Khulna is renowned for using ''chui jhal'' (piper chaba) in its dishes.
Bangladesh has a vast spread of desserts, including distinctive sweets such as the ''Rasgulla, rôshogolla'', ''Ras malai, roshmalai'', ''chomchom'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sondesh'', ''mishti doi'' and ''Gulab jamun, kalojaam'', and ''Jalebi, jilapi''. Pithas are traditional boiled desserts made with rice or fruits. Halwa is served during religious festivities. Roti, Ruti, naan, paratha, luchi and bakarkhani are the main local breads. Hot milk tea is the most commonly consumed beverage in the country, being the centre of Adda (South Asian), addas. Kebabs are widely popular, particularly seekh kebab, chapli kebab, shami kebab, chicken tikka and shashlik, along with various types of ''chaaps''. Popular street foods include chotpoti, jhal muri and Panipuri, fuchka. The large Bangladeshi diaspora dominate the South Asian restaurant industry in many Western countries, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Bangladeshi cuisine, formed by its geographic location and climate, is rich and varied; sharing its culinary heritage with the neighbouring Indian state of West Bengal. White rice is the staple, and along with fish, forms the culinary base. Varieties of leaf vegetables, potatoes, gourds and lentils (dal) also play an important role. Curry, Curries of beef, mutton, chicken and duck are commonly consumed, along with multiple types of Bhurta, bhortas, ''bhajis'' and ''torkaris''. Mughal-influenced dishes include kormas, kalias, biryanis, pilaf, pulaos, Tahri (dish), teharis and khichuris. Among the various spices, turmeric, fenugreek, nigella, coriander, anise, cardamom and chili powder are widely used; a famous spice mix is the panch phoron. Among the condiments and herbs used, red onions, Chili pepper, green chillies, garlic, ginger, cilantro, and Mentha, mint stand out. Coconut milk, Mustard (condiment), mustard paste, mustard seeds, mustard oil, ghee, South Asian pickle, achars and chutneys are also widely used in the cuisine.
Fish is the main source of protein, often enjoyed with its roe. The hilsa is the national fish and immensely popular, a famous dish is shorshe ilish. Rohu, Pangasius pangasius, pangas, and tilapia are also highly consumed. Lobsters, shrimps and dried fish (''shutki'') are also widely consumed, with the chingri malai curry being a famous shrimp dish. In Chittagong, Mezban feasts are a popular tradition, featuring the serving of ''mezbani gosht'', a hot and spicy beef curry. Other famous dishes from the region include kala bhuna. In Sylhet, the ''shatkora'' lemons are used to marinate dishes, a notable one is Beef Hatkhora, beef hatkora. Among the tribal communities in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, cooking with bamboo shoots is popular. Khulna Division, Khulna is renowned for using ''chui jhal'' (piper chaba) in its dishes.
Bangladesh has a vast spread of desserts, including distinctive sweets such as the ''Rasgulla, rôshogolla'', ''Ras malai, roshmalai'', ''chomchom'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sondesh'', ''mishti doi'' and ''Gulab jamun, kalojaam'', and ''Jalebi, jilapi''. Pithas are traditional boiled desserts made with rice or fruits. Halwa is served during religious festivities. Roti, Ruti, naan, paratha, luchi and bakarkhani are the main local breads. Hot milk tea is the most commonly consumed beverage in the country, being the centre of Adda (South Asian), addas. Kebabs are widely popular, particularly seekh kebab, chapli kebab, shami kebab, chicken tikka and shashlik, along with various types of ''chaaps''. Popular street foods include chotpoti, jhal muri and Panipuri, fuchka. The large Bangladeshi diaspora dominate the South Asian restaurant industry in many Western countries, particularly in the United Kingdom.
 ''Pahela Baishakh'', the Bengali new year, is the major festival of Culture of Bengal, Bengali culture and sees widespread festivities. Of the major holidays celebrated in Bangladesh, only Pahela Baishakh comes without any pre-existing expectations (specific religious identity, culture of gift-giving, etc.) and has become an occasion for celebrating the simpler, rural roots of the Bengal. Other cultural festivals include Nabanna, Nabonno and Poush Parbon, Bengali harvest festivals.
The Muslim festivals of Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, Milad un Nabi, Muharram, Chand Raat, Barat Night, Shab-e-Barat; the Hindu festivals of Durga Puja, Janmashtami and Rath Yatra; the Buddhist festival of Vesak, Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, and the Christian festival of Christmas are Public holidays in Bangladesh, national holidays in Bangladesh and see the most widespread celebrations in the country. The two Eids are celebrated with a long streak of public holidays and give the city-dwellers opportunity to celebrate the festivals with their families outside the city.
Alongside are national days like the remembrance of 21 February 1952 Language Movement Day (declared as International Mother Language Day by UNESCO in 1999), Independence Day (Bangladesh), Independence Day and Victory day of Bangladesh, Victory Day. On Language Movement Day, people congregate at the Shaheed Minar, Dhaka, Shaheed Minar in Dhaka to remember the national heroes of the Bengali Language Movement. Similar gatherings are observed at the National Martyrs' Memorial on Independence Day and Victory Day to remember the national heroes of the
''Pahela Baishakh'', the Bengali new year, is the major festival of Culture of Bengal, Bengali culture and sees widespread festivities. Of the major holidays celebrated in Bangladesh, only Pahela Baishakh comes without any pre-existing expectations (specific religious identity, culture of gift-giving, etc.) and has become an occasion for celebrating the simpler, rural roots of the Bengal. Other cultural festivals include Nabanna, Nabonno and Poush Parbon, Bengali harvest festivals.
The Muslim festivals of Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, Milad un Nabi, Muharram, Chand Raat, Barat Night, Shab-e-Barat; the Hindu festivals of Durga Puja, Janmashtami and Rath Yatra; the Buddhist festival of Vesak, Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, and the Christian festival of Christmas are Public holidays in Bangladesh, national holidays in Bangladesh and see the most widespread celebrations in the country. The two Eids are celebrated with a long streak of public holidays and give the city-dwellers opportunity to celebrate the festivals with their families outside the city.
Alongside are national days like the remembrance of 21 February 1952 Language Movement Day (declared as International Mother Language Day by UNESCO in 1999), Independence Day (Bangladesh), Independence Day and Victory day of Bangladesh, Victory Day. On Language Movement Day, people congregate at the Shaheed Minar, Dhaka, Shaheed Minar in Dhaka to remember the national heroes of the Bengali Language Movement. Similar gatherings are observed at the National Martyrs' Memorial on Independence Day and Victory Day to remember the national heroes of the
 The Bangladeshi press is diverse, outspoken and privately owned. Over 200 newspapers are published in the country. Bangladesh Betar is the state-run radio service. The British Broadcasting Corporation operates the popular BBC Bangla news and current affairs service. Bengali broadcasts from Voice of America are also very popular. Bangladesh Television (BTV) is a state-owned television network. More than 20 privately owned television networks, including several news channels. Freedom of the media remains a major concern due to government attempts at censorship and the harassment of journalists.
The cinema of Bangladesh dates back to 1898 when films began screening at the Crown Theatre in Dhaka. The first bioscope on the subcontinent was established in Dhaka that year. The Dhaka Nawab Family patronised the production of several silent films in the 1920s and 30s. In 1931, the East Bengal Cinematograph Society released the first full-length feature film in Bangladesh, titled the ''Last Kiss''. The first feature film in East Pakistan, ''Mukh O Mukhosh'', was released in 1956. During the 1960s, 25–30 films were produced annually in Dhaka. By the 2000s, Bangladesh produced 80–100 films a year. While the Bangladeshi film industry has achieved limited commercial success, the country has produced notable independent filmmakers. Zahir Raihan was a prominent documentary-maker assassinated in 1971. The late Tareque Masud is regarded as one of Bangladesh's outstanding directors for his critically acclaimed films on social issues. Masud was honoured by FIPRESCI at the 2002 Cannes Film Festival for his film ''Matir Moina, The Clay Bird''. Tanvir Mokammel, Mostofa Sarwar Farooki, Humayun Ahmed, Alamgir Kabir (filmmaker), Alamgir Kabir, and Chashi Nazrul Islam are some of the prominent directors of Bangladeshi cinema. Bangladesh has a very active film society culture. It started in 1963 in Dhaka. Now around 40 Film Societies are active all over Bangladesh. Federation of Film Societies of Bangladesh is the parent organisation of the film society movement of Bangladesh. Active film societies include the Rainbow Film Society, Children's Film Society, Moviyana Film Society and Dhaka University Film Society.
The Bangladeshi press is diverse, outspoken and privately owned. Over 200 newspapers are published in the country. Bangladesh Betar is the state-run radio service. The British Broadcasting Corporation operates the popular BBC Bangla news and current affairs service. Bengali broadcasts from Voice of America are also very popular. Bangladesh Television (BTV) is a state-owned television network. More than 20 privately owned television networks, including several news channels. Freedom of the media remains a major concern due to government attempts at censorship and the harassment of journalists.
The cinema of Bangladesh dates back to 1898 when films began screening at the Crown Theatre in Dhaka. The first bioscope on the subcontinent was established in Dhaka that year. The Dhaka Nawab Family patronised the production of several silent films in the 1920s and 30s. In 1931, the East Bengal Cinematograph Society released the first full-length feature film in Bangladesh, titled the ''Last Kiss''. The first feature film in East Pakistan, ''Mukh O Mukhosh'', was released in 1956. During the 1960s, 25–30 films were produced annually in Dhaka. By the 2000s, Bangladesh produced 80–100 films a year. While the Bangladeshi film industry has achieved limited commercial success, the country has produced notable independent filmmakers. Zahir Raihan was a prominent documentary-maker assassinated in 1971. The late Tareque Masud is regarded as one of Bangladesh's outstanding directors for his critically acclaimed films on social issues. Masud was honoured by FIPRESCI at the 2002 Cannes Film Festival for his film ''Matir Moina, The Clay Bird''. Tanvir Mokammel, Mostofa Sarwar Farooki, Humayun Ahmed, Alamgir Kabir (filmmaker), Alamgir Kabir, and Chashi Nazrul Islam are some of the prominent directors of Bangladeshi cinema. Bangladesh has a very active film society culture. It started in 1963 in Dhaka. Now around 40 Film Societies are active all over Bangladesh. Federation of Film Societies of Bangladesh is the parent organisation of the film society movement of Bangladesh. Active film societies include the Rainbow Film Society, Children's Film Society, Moviyana Film Society and Dhaka University Film Society.
online
* Iftekhar Iqbal (2010) ''The Bengal Delta: Ecology, State and Social Change, 1840–1943'' (Palgrave Macmillan) * Islam, Saiful, and Md Ziaur Rahman Khan. "A review of the energy sector of Bangladesh." ''Energy Procedia'' 110 (2017): 611–618
online
* Jannuzi, F. Tomasson, and James T. Peach. ''The agrarian structure of Bangladesh: An impediment to development'' (Routledge, 2019). * * * M. Mufakharul Islam (edited) (2004) Socio-Economic History of Bangladesh: essays in memory of Professor Shafiqur Rahman, 1st Edition, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * M. Mufakharul Islam (2007) ''Bengal Agriculture 1920–1946: A Quantitative Study'' (Cambridge University Press), * Prodhan, Mohit. "The educational system in Bangladesh and scope for improvement." ''Journal of International Social Issues'' 4.1 (2016): 11–23
online
* * * Riaz, Ali. ''Bangladesh: A political history since independence'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2016). * * * * Shelley, Israt J., et al. "Rice cultivation in Bangladesh: present scenario, problems, and prospects." ''Journal of International Cooperation for Agricultural Development'' 14.4 (2016): 20–29
online
* Sirajul Islam (edited) (1997) History of Bangladesh 1704–1971(Three Volumes: Vol 1: Political History, Vol 2: Economic History Vol 3: Social and Cultural History), 2nd Edition (Revised New Edition), The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * Sirajul Islam (Chief Editor) (2003) Banglapedia: A National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh.(10 Vols. Set), (written by 1300 scholars & 22 editors) The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * * * * Van Schendel, Willem. ''A history of Bangladesh'' (Cambridge University Press, 2020). * *
Official Site of Bangladesh Investment Development Authority
General information
Bangladesh
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. *
Bangladesh
from the BBC News
Bangladesh
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * *
Key Development Forecasts for Bangladesh
from International Futures {{Authority control Bangladesh, Bengal Bengali-speaking countries and territories Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Developing 8 Countries member states Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia Least developed countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation Member states of the United Nations South Asian countries States and territories established in 1971 1971 establishments in Asia Countries in Asia Geographical articles missing image alternative text
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the most densely populated countries in the world, and shares land borders with India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
to the southeast; to the south it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
. It is narrowly separated from Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
and Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
by the Siliguri Corridor
The Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken's Neck, is a stretch of land around the city of Siliguri in West Bengal, India. at the narrowest section, this geo-political and geo-economical corridor connects the eight states of northeast I ...
; and from China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
by the Indian state of Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siligur ...
in the north. Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
, the capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
, is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
, the second-largest city, is the busiest port on the Bay of Bengal. The official language is Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, one of the easternmost branches of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
.
Bangladesh forms the sovereign part of the historic and ethnolinguistic
Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language and the nonlinguistic cultural behavior of the people who speak that language.
__NOTOC__
Examples ...
region of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, which was divided during the Partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
in 1947. The country has a Bengali Muslim
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
majority. Ancient Bengal was an important cultural centre in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
as the home of the states of Vanga
The family Vangidae (from ''vanga'', Malagasy for the hook-billed vanga, ''Vanga curvirostris'') comprises a group of often shrike-like medium-sized birds distributed from Asia to Africa, including the vangas of Madagascar to which the family o ...
, Pundra
Pundravardhana or Pundra Kingdom ( sa, Puṇḍravardhana), was an ancient kingdom during the Iron Age period in India with a territory that included parts of present-day Rajshahi and Rangpur Divisions of Bangladesh as well as the West Dina ...
, Gangaridai
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writ ...
, Gauda, Samatata
Samataṭa (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-ṭa'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of ''Sounagoura'' is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much ...
, and Harikela
Harikela () was an ancient empire located in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, it was a neighboring independent and independent township of ancient East Bengal, which had a continuous existence of about 500 years. The st ...
. The Mauryan
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until ...
, Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
, Pala Pala may refer to:
Places
Chad
*Pala, Chad, the capital of the region of Mayo-Kebbi Ouest
Estonia
* Pala, Kose Parish, village in Kose Parish, Harju County
* Pala, Kuusalu Parish, village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County
*Pala, Järva County, vi ...
, Sena
Sena may refer to:
Places
* Sanandaj or Sena, city in northwestern Iran
* Sena (state constituency), represented in the Perlis State Legislative Assembly
* Sena, Dashtestan, village in Bushehr Province, Iran
* Sena, Huesca, municipality in Huesc ...
, Chandra
Chandra ( sa, चन्द्र, Candra, shining' or 'moon), also known as Soma ( sa, सोम), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and ...
and Deva
Deva may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Deva'' (1989 film), a 1989 Kannada film
* ''Deva'' (1995 film), a 1995 Tamil film
* ''Deva'' (2002 film), a 2002 Bengali film
* Deva (2007 Telugu film)
* ''Deva'' (2017 film), a 2017 Marathi film
* Deva ...
dynasties were the last pre-Islamic rulers of Bengal. The Muslim conquest of Bengal began in 1204 when Bakhtiar Khalji overran northern Bengal and invaded Tibet. Becoming part of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
, three city-states emerged in the 14th century with much of eastern Bengal being ruled from Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is one ...
. Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
missionary leaders like Sultan Balkhi
Shah Sultan Balkhi ( bn, শাহ সুলতান বলখী, fa, ), also known by his sobriquet, Mahisawar ( bn, মাহিসওয়ার, fa, , Mâhi-Savâr, Fish-rider), was a 14th-century Muslim saint. His name is associated wi ...
, Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions bet ...
and Shah Makhdum Rupos
‘Abd al-Quddūs Jalāl ad-Dīn ( ar, عبد القدوس جلال الدين), best known as Shah Makhdum ( bn, শাহ মখদুম), and also known as Rupos, was a Sufi Muslim figure in Bangladesh. He is associated with the spread of Is ...
helped in spreading Muslim rule. The region was unified into an independent, unitary Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominan ...
. Under Mughal rule
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, eastern Bengal continued to prosper as the melting pot of Muslims in the eastern subcontinent and attracted traders from around the world. The Bengali elite were among the richest people in the world due to strong trade networks like the muslin trade which supplied textiles, such as 40% of Dutch imports from Asia.Om Prakash, "Empire, Mughal", History of World Trade Since 1450, edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference US, 2006, pp. 237–240, World History in Context. Retrieved 3 August 2017 Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
became increasingly assertive and independent under the Nawabs of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
in the 18th century. In 1757, the betrayal of Mir Jafar
Sayyid Mīr Jaʿfar ʿAlī Khān Bahādur ( – 5 February 1765) was a military general who became the first dependent Nawab of Bengal of the British East India Company. His reign has been considered by many historians as the start of the expan ...
resulted in the defeat of Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Be ...
to the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
and eventual British dominance across South Asia. The Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
grew into the largest administrative unit in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. The creation of Eastern Bengal and Assam
Eastern Bengal and Assam was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.
Hist ...
in 1905 set a precedent for the emergence of Bangladesh. In 1940, the first Prime Minister of Bengal
The Prime Minister of Bengal was the head of government of Bengal Presidency, Bengal Province and the Leader of the House in the Bengal Legislative Assembly in British India. The position was dissolved upon the Partition of Bengal (1947), Partitio ...
supported the Lahore Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
with the hope of creating a state in the eastern subcontinent. Prior to the partition of Bengal, the Prime Minister of Bengal proposed a Bengali sovereign state. A referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
and the announcement of the Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab Province and Bengal Presidency of British India. It was named after Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissi ...
established the present-day territorial boundary of Bangladesh.
In 1947, East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = East ...
became the most populous province in the Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of I ...
. It was renamed as East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
with Dhaka becoming the country's legislative capital. The Bengali Language Movement in 1952; the East Bengali legislative election, 1954
Legislative elections were held in East Bengal between 8 and 12 March 1954, the first since Pakistan became an independent country in 1947. The opposition United Front led by the Awami League and Krishak Sramik Party won a landslide victory with ...
; the 1958 Pakistani coup d'état
The 1958 Pakistani coup d'état began on October 7, when the first President of Pakistan Iskander Mirza abrogated the Constitution of Pakistan and declared martial law, and lasted until October 27, when Mirza himself was deposed by Gen. Ayub Kha ...
; the Six point movement
The six point movement was a movement in East Pakistan, spearheaded by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, which called for greater autonomy for East Pakistan. The movement's main agenda was to realize the six demands put forward by a coalition of Bengali na ...
of 1966; and the 1970 Pakistani general election
General elections were held in Pakistan on 7 December 1970 to elect members of the National Assembly. They were the first general elections since the independence of Pakistan and ultimately the only ones held prior to the independence of Bang ...
resulted in the rise of Bengali nationalism
Bengalism or Bengali nationalism () was a form of nationalism that focused on Bengalis as a singular nation. The people of Bengali ethnicity speak Bengali language. Bengalis mostly live across Bangladesh and the Indian states of Tripura and ...
and pro-democracy
Democratization, or democratisation, is the transition to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction. It may be a hybrid regime in transition from an authoritarian regime to a full ...
movements in East Pakistan. The refusal of the Pakistani military junta to transfer power to the Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengalis, Beng ...
led to the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
in 1971, in which the Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
aided by India waged a successful armed revolution
This is a list of revolutions, rebellions, insurrections, and uprisings.
BC
:
:
:
:
1–999 AD
1000–1499
1500–1699
* 1501–1504: The Knut Alvsson, Alvsson's Dano-Swedish War (1501–12), rebellion against King John, ...
. The conflict saw the 1971 Bangladesh genocide
The genocide in Bangladesh began on 25 March 1971 with the launch of Operation Searchlight, as the government of Pakistan, dominated by West Pakistan, began a military crackdown on East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) to suppress Bengali peopl ...
and the massacre of pro-independence Bengali civilians, including intellectuals
An intellectual is a person who engages in critical thinking
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments to form a judgement. The subject is complex; several different definitions exist, ...
. The new state of Bangladesh became the first constitutionally secular state
A secular state is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a State (polity), state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens ...
in South Asia in 1972. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was declared the state religion in 1988. In 2010, the Bangladesh Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Bangladesh ( bn, বাংলাদেশ সুপ্রীম কোর্ট) is the highest court of law in Bangladesh. It is composed of the High Court Division and the Appellate Division, and was created by Part VI C ...
reaffirmed secular principles in the constitution.
A middle power
In international relations, a middle power is a sovereign state that is not a great power nor a superpower, but still has large or moderate influence and international recognition.
The concept of the "middle power" dates back to the origins of ...
in the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth.
In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
, Bangladesh is the second largest economy in South Asia. It maintains the third-largest military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
in the region and is a major contributor to UN peacekeeping
Peacekeeping by the United Nations is a role held by the Department of Peace Operations as an "instrument developed by the organization as a way to help countries torn by conflict to create the conditions for lasting peace". It is distinguished ...
operations. The large Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
population of Bangladesh makes it the third-largest Muslim-majority country. Bangladesh is a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
constitutional republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
based on the Westminster system. Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the ...
make up 99% of the total population of Bangladesh. The country consists of eight divisions, 64 districts and 495 subdistricts. It hosts one of the largest refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
populations in the world due to the Rohingya genocide
The Rohingya genocide is a series of ongoing persecutions and killings of the Muslim Rohingya people by the Burmese military. The genocide has consisted of two phases to date: the first was a military crackdown that occurred from October 2016 ...
. Bangladesh faces many challenges, particularly effects of climate change
The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the water cycle, oceans, sea and land ice (glaciers), sea level ...
. Bangladesh has been a leader within the Climate Vulnerable Forum
The Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) is a global partnership of countries that are disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. The forum addresses the negative effects of climate change as a result of heightened socioeconomic ...
. It hosts the headquarters of BIMSTEC
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations, housing 1.73 billion people and having a combined gross domestic pro ...
. It is a founding member of SAARC
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, ...
, as well as a member of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
and the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
.
Etymology
The etymology of ''Bangladesh'' ("Bengali Country") can be traced to the early 20th century, when Bengali patriotic songs, such as ''Namo Namo Namo Bangladesh Momo'' byKazi Nazrul Islam
Kazi Nazrul Islam ( bn, কাজী নজরুল ইসলাম, ; 24 May 1899 – 29 August 1976) was a Bengali poet, Bengali literature, writer, Bangladeshi music, musician, and is the national poet of Bangladesh. Nazrul is regarded as one ...
and ''Aaji Bangladesher Hridoy'' by Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (; bn, রবীন্দ্রনাথ ঠাকুর; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer and painter. He resh ...
, used the term. The term ''Bangladesh'' was often written as two words, ''Bangla Desh'', in the past. Starting in the 1950s, Bengali nationalists used the term in political rallies in East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
. The term ''Bangla'' is a major name for both the Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
region and the Bengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second m ...
. The origins of the term ''Bangla'' are unclear, with theories pointing to a Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
proto-Dravidian
Proto-Dravidian is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Dravidian languages. It is thought to have differentiated into Proto-North Dravidian, Proto-Central Dravidian, and Proto-South Dravidian, although the date of diversi ...
tribe, the Austric
The Austric languages are a proposed language family that includes the Austronesian languages spoken in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Madagascar, as well as the Austroasiatic languages spoken in Mainland Southeast As ...
word "Bonga" (Sun god), and the Iron Age Vanga Kingdom
Vanga was an ancient kingdom and geopolitical division within the Ganges delta in the Indian subcontinent. The kingdom is one of the namesakes of the Bengal region. It was located in southern Bengal, with the core region including present-day ...
. The earliest known usage of the term is the Nesari plate in 805 AD. The term ''Vangaladesa'' is found in 11th-century South Indian records. The term gained official status during the Sultanate of Bengal
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominan ...
in the 14th century. Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah
Haji Ilyas, better known as Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah ( bn, শামসুদ্দীন ইলিয়াস শাহ, fa, ), was the founder of the Sultanate of Bengal and its inaugural Ilyas Shahi dynasty which ruled the region for 150 year ...
proclaimed himself as the first "Shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
of Bangala" in 1342. The word ''Bangāl'' became the most common name for the region during the Islamic period. 16th-century historian Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak
Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak, also known as Abul sharma, Abu'l Fadl and Abu'l-Fadl 'Allami (14 January 1551 – 22 August 1602), was the grand vizier of the Mughal emperor Akbar, from his appointment in 1579 until his death in 1602. He was the au ...
mentions in his ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' ( fa, ) or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language. It for ...
'' that the addition of the suffix ''"al"'' came from the fact that the ancient rajahs of the land raised mounds of earth 10 feet high and 20 in breadth in lowlands at the foot of the hills which were called "al". This is also mentioned in Ghulam Husain Salim
Ğulām Husayn "Salīm" Zaydpūrī was a historian who migrated to Bengal and was employed there as a postmaster to the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded ...
's Riyaz-us-Salatin
Riyaz-us-Salatin ( fa, ) is the first British-era historic book on the Muslim rule in Bengal that was published in Bengal in 1788. It was written by Ghulam Husain Salim Zaidpuri.
Content
The books starts with the arrival of Muhammad bin Bakhti ...
.RIYAZU-S-SALĀTĪN: A History of Bengal,
Ghulam Husain Salim
Ğulām Husayn "Salīm" Zaydpūrī was a historian who migrated to Bengal and was employed there as a postmaster to the English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded ...
, The Asiatic Society, Calcutta, 1902. The Indo-Aryan suffix ''Desh'' is derived from the Sanskrit word ''deśha'', which means "land" or "country". Hence, the name ''Bangladesh'' means "Land of Bengal" or "Country of Bengal".
History
Ancient Bengal


Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
tools found in Bangladesh indicate human habitation for over 20,000 years, and remnants of Copper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
settlements date back 4,000 years. Ancient Bengal was settled by Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The te ...
s, Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ...
s, Dravidians
The Dravidian peoples, or Dravidians, are an ethnolinguistic and cultural group living in South Asia who predominantly speak any of the Dravidian languages. There are around 250 million native speakers of Dravidian languages. Dravidian spe ...
and Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and intr ...
in consecutive waves of migration. Archaeological evidence confirms that by the second millennium BCE, rice-cultivating communities inhabited the region. By the 11th century people lived in systemically aligned housing, buried their dead, and manufactured copper ornaments and black and red pottery. The Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
, Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
and Meghna
The Meghna River ( bn, মেঘনা নদী) is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, ...
rivers were natural arteries for communication and transportation, and estuaries on the Bay of Bengal permitted maritime trade. The early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
saw the development of metal weaponry, coinage, agriculture and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
. Major urban settlements formed during the late Iron Age, in the mid-first millennium BCE
The 1st millennium BC, also known as the last millennium BC, was the period of time lasting from the years 1000 BC to 1 BC (10th to 1st centuries BC; in astronomy: JD – ). It encompasses the Iron Age in the Old World and sees the transit ...
, when the Northern Black Polished Ware
The Northern Black Polished Ware culture (abbreviated NBPW or NBP) is an urban Iron Age Indian culture of the Indian Subcontinent, lasting c. 700–200 BCE (proto NBPW between 1200 and 700 BCE), succeeding the Painted Grey Ware culture and Blac ...
culture developed. In 1879, Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Engineer Group who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly ...
identified Mahasthangarh
Mahasthangarh ( bn, মহাস্থানগড়, ''Môhasthangôṛ'') is one of the earliest urban archaeological sites so far discovered in Bangladesh. The village Mahasthan in Shibganj upazila of Bogra District contains the remain ...
as the capital of the Pundra Kingdom
Pundravardhana or Pundra Kingdom ( sa, Puṇḍravardhana), was an ancient kingdom during the Iron Age period in India with a territory that included parts of present-day Rajshahi and Rangpur Divisions of Bangladesh as well as the West Dinaj ...
mentioned in the ''Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
''. The oldest inscription in Bangladesh was found in Mahasthangarh and dates from the 3rd century BCE. It is written in the Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
.
Greek and Roman records of the ancient Gangaridai
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writ ...
Kingdom, which (according to legend) deterred the invasion of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, are linked to the fort city in Wari-Bateshwar
The Wari-Bateshwar (Bengali: উয়ারী-বটেশ্বর,''Uari-Bôṭeshshor'') ruins in Narsingdi, Dhaka Division, Bangladesh is one of the earliest urban archaeological sites in Bangladesh. Excavation in the site unearthed a ...
. The site is also identified with the prosperous trading centre of Souanagoura listed on Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book ''Geography'', written . Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manusc ...
. Roman geographers noted a large seaport in southeastern Bengal, corresponding to the present-day Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
region.
Ancient Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
states which ruled Bangladesh included the Vanga
The family Vangidae (from ''vanga'', Malagasy for the hook-billed vanga, ''Vanga curvirostris'') comprises a group of often shrike-like medium-sized birds distributed from Asia to Africa, including the vangas of Madagascar to which the family o ...
, Samatata
Samataṭa (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-ṭa'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of ''Sounagoura'' is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much ...
and Pundra kingdoms, the Mauryan and Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
s, the Varman dynasty
The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Gup ...
, Shashanka
Shashanka (IAST: Śaśāṃka) was the first independent king of a unified polity in the Bengal region, called the Gauda Kingdom and is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in the 7th century, some historians place his rule between circ ...
's kingdom, the Khadga
The Khadga dynasty ( bn, খড়্গ বংশ) was a dynasty which ruled the areas of Vanga and Samatata in Bengal from the mid 7th to early 8th Century CE. Chronologically, the dynasty emerged as a powerful kingdom between the fall of Gauda ...
and Candra dynasties, the Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffi ...
, the Sena dynasty
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcont ...
, the Harikela
Harikela () was an ancient empire located in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, it was a neighboring independent and independent township of ancient East Bengal, which had a continuous existence of about 500 years. The st ...
kingdom and the Deva dynasty. These states had well-developed currencies, banking, shipping, architecture, and art, and the ancient universities of Bikrampur
Bikrampur ("City of Courage") was a pargana situated south of Dhaka, the modern capital city of Bangladesh. In the present day, it is known as Munshiganj District of Bangladesh. It is a historic region in Bengal and was a part of the Bhawal Est ...
and Mainamati
Moinamoti (''Môynamoti'') is an isolated low, dimpled range of hills, dotted with more than 50 ancient Buddhist settlements dating between the 8th and 12th century CE. It was part of the ancient Tripura division of Bengal. It extends through the ...
hosted scholars and students from other parts of Asia. Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
of China was a noted scholar who resided at the Somapura Mahavihara
Somapura Mahavihara ( bn, সোমপুর মহাবিহার, Shompur Môhabihar) in Paharpur, Badalgachhi Upazila, Badalgachhi, Naogaon District, Naogaon, Bangladesh is among the best known Buddhist viharas or monasteries in the Indi ...
(the largest monastery in ancient India), and Atisa travelled from Bengal to Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
to preach Buddhism. The earliest form of the Bengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second m ...
emerged during the eighth century. Seafarers in the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
where modern Bangladesh is now located, have also been sailing and trading with Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
and exported Buddhist and Hindu cultures to the region since the early Christian era.
Islamic Bengal

 The early history of Islam in Bengal is divided into two phases. The first phase is the period of maritime trade with Arabia and Persia between the 8th and 12th centuries. The second phase covers centuries of Muslim dynastic rule after the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The writings of Al-Idrisi,
The early history of Islam in Bengal is divided into two phases. The first phase is the period of maritime trade with Arabia and Persia between the 8th and 12th centuries. The second phase covers centuries of Muslim dynastic rule after the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The writings of Al-Idrisi, Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
, Al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
, Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh ( ar, ابوالقاسم عبیدالله ابن خرداذبه; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking Persian bureaucrat and ...
and Sulaiman Sulaiman is an English transliteration of the Arabic name that means "peaceful" and corresponds to the Jewish name Hebrew: שְׁלֹמֹה, Shlomoh) and the English Solomon (/ˈsɒləmən/) . Solomon was the scriptural figure who was king of ...
record the maritime links between Arabia, Persia and Bengal. Muslim trade with Bengal flourished after the fall of the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
and the Arab takeover of Persian trade routes. Much of this trade occurred with southeastern Bengal in areas east of the Meghna River
The Meghna River ( bn, মেঘনা নদী) is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, ...
. There is speculation regarding the presence of a Muslim community in Bangladesh as early as 690 CE; this is based on the discovery of one of South Asia's oldest mosques in northern Bangladesh. Bengal was possibly used as a transit route to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
by the earliest Muslims. Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
coins have been discovered in the archaeological ruins of Paharpur and Mainamati
Moinamoti (''Môynamoti'') is an isolated low, dimpled range of hills, dotted with more than 50 ancient Buddhist settlements dating between the 8th and 12th century CE. It was part of the ancient Tripura division of Bengal. It extends through the ...
. A collection of Sasanian, Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and Abbasid coins are preserved in the Bangladesh National Museum
The Bangladesh National Museum ( bn, বাংলাদেশ জাতীয় জাদুঘর), is the national museum of Bangladesh. The museum is well organized and displays have been housed chronologically in several departments like dep ...
.
The Muslim conquest of Bengal began with the 1204 Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the ...
expeditions led by Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bakhtiyār Khaljī, (Pashto :اختيار الدين محمد بختيار غلزۍ, fa, اختیارالدین محمد بختیار خلجی, bn, ইখতিয়ারউদ্দীন মুহম্মদ � ...
, who overran the Sena capital in Gauda and led the first Muslim army into Tibet. The conquest of Bengal was inscribed in gold coins of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
. Bengal was ruled by the Sultans of Delhi for a century under the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
, Balban, and Tughluq dynasties. In the 14th century, three city-states emerged in Bengal, including Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is one ...
led by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah
Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah ( bn, ফখরুদ্দীন মুবারক শাহ, fa, ; reigned: 1338–1349), also known simply as Fakhra, was the founder of an independent sultanate comprising modern-day eastern and southeastern Banglad ...
, Satgaon
Saptagram (Bengali: সপ্তগ্রাম; colloquially called ''Satgaon'') was a major port, the chief city and sometimes capital of southern Bengal, in ancient and medieval times, the location presently being in the Hooghly district in t ...
led by Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah
Haji Ilyas, better known as Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah ( bn, শামসুদ্দীন ইলিয়াস শাহ, fa, ), was the founder of the Sultanate of Bengal and its inaugural Ilyas Shahi dynasty which ruled the region for 150 year ...
and Lakhnauti led by Alauddin Ali Shah
Alī Mubārak ( fa, علی مبارک), better known by his regnal title `Alā ad-Dīn `Alī Shāh ( bn, আলাউদ্দীন আলী শাহ, fa, علاء الدین علی شاه; r. 1338–1342) was an independent Sultan of Lakh ...
. These city-states were led by former governors who declared independence from Delhi. The Moroccan traveler Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
visited eastern Bengal during the reign of Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah. Ibn Battuta also visited the Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
leader Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions bet ...
in Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of the Sylhet Division. Located on the north bank of the Surma River at the eastern tip of Bengal, Sylhet has a subtropical climate an ...
. Sufis played an important role in spreading Islam in Bengal through both peaceful conversion and militarily overthrowing pre-Islamic rulers. In 1352, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah united the three city-states into a single, unitary and independent Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominan ...
. The new Sultan of Bengal led the first Muslim army into Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
and forced the Sultan of Delhi to retreat during an invasion. The army of Ilyas Shah reached as far as Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
in the northwest, Kathmandu
, pushpin_map = Nepal Bagmati Province#Nepal#Asia
, coordinates =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 = Bagmati Prov ...
in the north, Kamarupa
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam.
Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to 11 ...
in the east and Orissa
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of Sch ...
in the south. Ilyas Shah raided many of these areas and returned to Bengal with treasures. During the reign of Sikandar Shah
Abul Mujāhid Sikandar Shāh ( bn, আবুল মুজাহিদ সিকান্দর শাহ, fa, ), commonly known as Sikandar Shah; was the second Sultan of Bengal and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty. He was the son of Shamsuddin Ilyas Sha ...
, Delhi recognised Bengal's independence. The Bengal Sultanate established a network of mint towns which acted as a provincial capitals where the Sultan's currency was minted. Bengal became the eastern frontier of the Islamic world, which stretched from Muslim Spain
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
in the west to Bengal in the east. The Bengali language crystallized as an official court language during the Bengal Sultanate, with prominent writers like Nur Qutb Alam, Usman Serajuddin
ʿUthmān Sirāj ad-Dīn al-Bangālī ( ar, عثمان سراج الدين البنغالي; 1258-1357), known affectionately by followers as Akhi Siraj ( bn, আখি সিরাজ), was a 14th-century Bengali Muslim Islamic scholar, scholar. ...
, Alaul Haq
ʿAlā ul-Ḥaq wa ad-Dīn ʿUmar ibn As`ad al-Khālidī al-Bangālī ( ar, علاء الحق والدين عمر بن أسعد الخالدي البنغالي), commonly known as Alaul Haq ( bn, আলাউল হক) or reverentially by the sob ...
, Alaol
Syed Alaol ( bn, সৈয়দ আলাওল; 1607 – 1680) was a 17th century poet of Bengal. His most well known work is ''Padmavati'', which depicts the story of Padmavati, the Sinhalese princess. He is considered to be one of the most prol ...
, Shah Muhammad Sagir
Shah Muhammad Sagir ( bn, শাহ মুহম্মদ সগীর) was one of the earliest Bengali Muslim poets, if not the first.
Life
Shah Muhammad Sagir was a poet of the 14/15th century, during the reign of the Sultan of Bengal Ghiyasuddi ...
, Abdul Hakim
Abdul Hakim ( ar, عبد الحكيم, translit=ʻAbd al-Ḥakīm) is a Muslim male given name, and in modern usage, first name or surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' Abd'', ''al-'' and ''Hakim''. The name means "servant of the All-wise" ...
and Syed Sultan
Syed Sultan ( bn, সৈয়দ সুলতান) was a medieval Bengali Muslim writer and epic poet. He is best known for his magnum opus, the ''Nabibangsha'', which was one of the first translations of the Qisas Al-Anbiya into the Bengali la ...
; and the emergence of ''Dobhashi
Dobhashi ( bn, দোভাষী, Dobhāṣī, bilingual) is a neologism used to refer to a historical Register (sociolinguistics), register of the Bengali language which borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian. It became ...
'' to write Muslim epics in Bengali literature.
The Bengal Sultanate was a melting pot of Muslim political, mercantile and military elites. Muslims from other parts of the world migrated to Bengal for military, bureaucratic and household services. Immigrants included Persians who were lawyers, teachers, clerics, and scholars; Turks from upper India who were originally recruited in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
; and Abyssinians who came via East Africa and arrived in the Bengali port of Chittagong. A highly commercialized and monetized economy evolved.
The two most prominent dynasties of the Bengal Sultanate were the Ilyas Shahi and Hussain Shahi dynasties. The reign of Sultan Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah
Ghiyasuddin A'zam Shah ( bn, গিয়াসউদ্দীন আজম শাহ, fa, ) was the third Sultan of Bengal and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty. He was one of the most prominent medieval Bengali sultans. He established diplomatic relatio ...
saw the opening of diplomatic relations with Ming China
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
. Ghiyasuddin was also a friend of the Persian poet Hafez
Khwāje Shams-od-Dīn Moḥammad Ḥāfeẓ-e Shīrāzī ( fa, خواجه شمسالدین محمّد حافظ شیرازی), known by his pen name Hafez (, ''Ḥāfeẓ'', 'the memorizer; the (safe) keeper'; 1325–1390) and as "Hafiz", ...
. The reign of the Sultan Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah
Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah ( bn, জালালউদ্দীন মুহম্মদ শাহ; born as Yadu or Jadu) was a 15th-century Sultan of Bengal and an important figure in medieval Bengali history. Born a Hindu to his aristocratic fat ...
saw the development of Bengali architecture
The architecture of Bengal, which comprises the modern country of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley, has a long and rich history, blending indigenous elements from the Indian subcontinent, with influ ...
. During the early 15th century, the Restoration of Min Saw Mon
The restoration of Min Saw Mon was a military campaign led by the Bengal Sultanate to help Min Saw Mon regain control of his Launggyet Dynasty. The campaign was successful. Min Saw Mon was restored to the Launggyet throne, and northern Arakan becam ...
in Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
was aided by the army of the Bengal Sultanate. As a result, Arakan became a tributary state of Bengal. Even though Arakan later became independent, Bengali Muslim influence in Arakan persisted for 300 years due to the settlement of Bengali bureaucrats, poets, military personnel, farmers, artisans, and sailors. The kings of Arakan fashioned themselves after Bengali Sultans and adopted Muslim titles. During the reign of Sultan Alauddin Hussain Shah
Ala-ud-din Husain Shah ( bn, আলাউদ্দিন হোসেন শাহ (1494–1519)Majumdar, R.C. (ed.) (2006). ''The Delhi Sultanate'', Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, pp.215-20 was an independent late medieval Sultan of Bengal, who ...
, the Bengal Sultanate dispatched a naval flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' (fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same class ...
and an army of 24,000 soldiers led by Shah Ismail Ghazi
Shah Ismail Ghazi ( bn, শাহ ইসমাঈল গাজী) was a 15th-century Sufi Muslim preacher based in Bengal. He came to Bengal in the mid-fifteenth century during the reign of Rukunuddin Barbak Shah, settling in the country's capit ...
to conquer Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
.Majumdar, R.C. (ed.) (2006). ''The Delhi Sultanate'', Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, pp.215–20 Bengali forces penetrated deep into the Brahmaputra Valley
The Brahmaputra Valley is a region situated between hill ranges of the eastern and northeastern Himalayan range in Eastern India.
The valley consists of the Western Brahmaputra Valley covering the regions of Goalpara and Kamrup; the Central ...
. Hussain Shah's forces also conquered Jajnagar in Orissa. In Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east a ...
, Bengal helped Ratna Manikya I
Ratna Manikya I (d. 1487), also known as Ratna Fa, was the Maharaja of Tripura from 1462 to the late 1480s. Though he had gained the throne by overthrowing his predecessor, Ratna's reign was notable for the peace and prosperity it had entailed in ...
to assume the throne. The Jaunpur Sultanate
The Jaunpur Sultanate ( fa, ) was an independent Islamic state in northern India between 1394 and 1479, ruled by the Sharqi dynasty. It was founded in 1394 by Khwajah-i-Jahan Malik Sarwar, a former wazir of Sultan Nasiruddin Muhammad Shah IV ...
, Pratapgarh Kingdom
The Pratapgarh Kingdom ( bn, প্রতাপগড় রাজ্য) was a Medieval India, medieval state in the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. Composed of the present-day Indian district of Karimganj district, Karimganj, as well ...
and the island of Chandradwip
Chandradwip or Chandradvipa is a small region in Barisal District, Bangladesh. It was once the ancient and medieval name of Barishal.
History
The history of Chandradwip goes back to the Pre-Pala Period.
Chandradwip was successively ruled by the ...
also came under Bengali control. By 1500, Gaur became the fifth-most populous city in the world with a population of 200,000. The river port of Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is one ...
was used as a base by the Sultans of Bengal during campaigns against Assam, Tripura and Arakan. The Sultans launched many naval raids from Sonargaon. João de Barros
João de Barros () (1496 – 20 October 1570), called the ''Portuguese Livy'', is one of the first great Portuguese historians, most famous for his ''Décadas da Ásia'' ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India, Asia, and southea ...
described the seaport of Chittagong as "the most famous and wealthy city of the Kingdom of Bengal". Maritime trade linked Bengal with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
, East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
, Arabia, Persia, Mesopotamia, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
. Bengali ships were among the biggest vessels plying the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
, Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
and Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. A royal vessel from Bengal accommodated three embassies from Bengal, Brunei and Sumatra while en route to China and was the only vessel capable of transporting three embassies. Many wealthy Bengali shipowners and merchants lived in Malacca. The Sultans permitted the opening of the Portuguese settlement in Chittagong
Chittagong, the second largest city and main port of Bangladesh, was home to a thriving trading post of the Portuguese Empire in the East in the 16th and 17th centuries. The Portuguese first arrived in Chittagong around 1528 and left in 1666 af ...
. The disintegration of the Bengal Sultanate began with the intervention of the Suri Empire
The Sur Empire ( ps, د سرو امپراتورۍ, dë sru amparāturəi; fa, امپراطوری سور, emperâturi sur) was an Afghan dynasty which ruled a large territory in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent for nearly 16 year ...
. Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
began invading Bengal after creating the Mughal Empire. The Bengal Sultanate collapsed with the overthrow of the Karrani dynasty
The Karrani dynasty ( ps, کرلاڼي, Karlāṇī, bn, কররাণী, Korrāṇī) was founded in 1564 by Taj Khan Karrani, an ethnic Pashtun from the Karlani tribe, hailing from Bangash district. It was the last dynasty to rule the Sultan ...
during the reign of Akbar. However, the Bhati
Bhati is a clan of Rajputs
History
The Bhatis reportedly originated in Mathura through a common ancestor named Bhati, who was a descendant of Pradyumn. According to the seventeenth-century Nainsi ri Khyat, the Bhatis after losing Mathura ...
region of eastern Bengal continued to be ruled by aristocrats of the former Bengal Sultanate led by Isa Khan
Isa Khan (c. 1529 – September 1599) was a Muslim Rajput zamindar who was one of the Baro Bhuiyans (twelve landlords) and a Zamindar of Khizirpur in 16th-century Bengal. Throughout his reign he resisted the Mughal empire invasion. It was on ...
. They formed an independent federation called the Twelve Bhuiyans, with their capital in Sonargaon. They defeated the Mughals in several naval battles. The Bhuiyans ultimately succumbed to the Mughals after Musa Khan was defeated.


 The
The Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
controlled Bengal by the 17th century. During the reign of Emperor Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
, the Bengali agrarian calendar was reformed to facilitate tax collection. The Mughals established Dhaka as a fort city and commercial metropolis, and it was the capital of Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Ben ...
for 75 years. In 1666, the Mughals expelled the Arakanese from Chittagong. Mughal Bengal attracted foreign traders for its muslin
Muslin () is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq, where it was first manufactured.
Muslin of uncommonly delicate handsp ...
and silk goods, and the Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
were a notable merchant community. A Portuguese settlement in Chittagong
Chittagong, the second largest city and main port of Bangladesh, was home to a thriving trading post of the Portuguese Empire in the East in the 16th and 17th centuries. The Portuguese first arrived in Chittagong around 1528 and left in 1666 af ...
flourished in the southeast, and a Dutch settlement in Rajshahi
A trading post of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) existed in Rajshahi, Bengal, during the 18th century. The Dutch were the first Europeans to arrive in this area. The trading station was located on the banks of the Padma River. It included fa ...
existed in the north. Bengal accounted for 40% of overall Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
imports from Asia; including more than 50% of textiles and around 80% of silks.Om Prakash
Om Prakash (born Om Prakash Chibber 19 December 1919 – 21 February 1998) was an Indian film actor. He was born in Jammu as Om Prakash Chibber and went on to become a well-known character actor of Bollywood. His most well-known movies are Nam ...
,Empire, Mughal
, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017 The Bengal Subah, described as the ''Paradise of the Nations'', was the empire's wealthiest province, and a major global exporter,
John F. Richards
John F. Richards (November 3, 1938 – August 23, 2007) was a historian of South Asia and in particular of the Mughal Empire. He was Professor of History at Duke University, North Carolina, and a recipient in 2007 of the Distinguished Contributio ...
(1995)''The Mughal Empire'', page 202
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
a notable centre of worldwide industries such as muslin
Muslin () is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq, where it was first manufactured.
Muslin of uncommonly delicate handsp ...
, cotton textiles, silk, and shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
. Its citizens also enjoyed one of the world's most superior living standards
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
.
During the 18th century, the Nawabs of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
became the region's ''de facto'' rulers. The ruler's title is popularly known as the ''Nawab of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa'', given that the Bengali Nawab's realm encompassed much of the eastern subcontinent. The Nawabs forged alliances with European colonial companies, making the region relatively prosperous early in the century. Bengal accounted for 50% of the gross domestic product of the empire. The Bengali economy relied on textile manufacturing
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
, shipbuilding, saltpetre
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitra ...
production, craftsmanship, and agricultural produce. Bengal was a major hub for international trade – silk and cotton textiles from Bengal were worn in Europe, Japan, Indonesia, and Central Asia. Annual Bengali shipbuilding output was 223,250tons, compared to an output of 23,061tons in the nineteen colonies of North America. Bengali shipbuilding proved to be more advanced than European shipbuilding before the Industrial Revolution. The flush deck
Flush deck is a term in naval architecture. It can refer to any deck of a ship which is continuous from stem to stern.
History
The flush deck design originated with rice ships built in Bengal Subah, Mughal India (modern Bangladesh), resulting i ...
of Bengali rice ships was later replicated in European shipbuilding to replace the stepped deck design for ship hulls. Maddison, Angus (2003): Development Centre Studies The World Economy Historical Statistics: Historical Statistics
',
OECD Publishing
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
, , pages 259–261
Eastern Bengal was a thriving melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
with strong trade and cultural networks. It was a relatively prosperous part of the subcontinent and the center of the Muslim population in the eastern subcontinent. The Muslims of eastern Bengal included people of diverse origins from different parts of the world.
The Bengali Muslim
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
population was a product of conversion and religious evolution, and their pre-Islamic beliefs included elements of Buddhism and Hinduism. The construction of mosques, Islamic academies (madrasas) and Sufi monasteries (khanqah
A khanqah ( fa, خانقاه) or khangah ( fa, خانگاه; also transliterated as ''khankah'', ''khaneqa'', ''khanegah'' or ''khaneqah''; also Arabized ''hanegah'', ''hanikah'', ''hanekah'', ''khankan''), also known as a ribat (), is a buildin ...
s) facilitated conversion, and Islamic cosmology
Islamic cosmology is the cosmology of Islamic societies. It is mainly derived from the Qur'an, Hadith, Sunnah, and current Islamic as well as other pre-Islamic sources. The Qur'an itself mentions seven heavens.Qur'an 2:29
Metaphysical principl ...
played a significant role in developing Bengali Muslim society. Scholars have theorised that Bengalis were attracted to Islam by its egalitarian social order, which contrasted with the Hindu caste system. By the 15th century, Muslim poets were widely writing in the Bengali language. Syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
cults, such as the Baul
The Baul ( bn, বাউল) are a group of mystic minstrels of mixed elements of Sufism, Vaishnavism and Tantra from Bangladesh and the neighboring Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley and Meghalaya. Bauls constitut ...
movement, emerged on the fringes of Bengali Muslim society. The Persianate
A Persianate society is a society that is based on or strongly influenced by the Persian language, culture, literature, art and/or identity.
The term "Persianate" is a neologism credited to Marshall Hodgson. In his 1974 book, ''The Venture of Is ...
culture was significant in Bengal, where cities like Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is one ...
became the easternmost centres of Persian influence.
In 1756, nawab Siraj ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Beng ...
sought to rein in the rising power of the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
by revoking their free trade rights and demanding the dismantling of their fortification in Calcutta. A military conflict ensued which culminated in the Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, ...
on 22 June 1757. Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
exploited rivalries within the nawab's family, bribing Mir Jafar
Sayyid Mīr Jaʿfar ʿAlī Khān Bahādur ( – 5 February 1765) was a military general who became the first dependent Nawab of Bengal of the British East India Company. His reign has been considered by many historians as the start of the expan ...
, the nawab's uncle and commander in chief, to ensure Siraj-ud-Daula's defeat. Clive rewarded Mir Jafar by making him nawab in place of Siraj-ud-Daula, but henceforth the position was a figurehead appointed and controlled by the company. After Plassey, the Mughal emperor ruled Bengal in name only. Effective power rested with the company. Historians often describe the battle as "the beginning of British colonial rule in South Asia". Historian Willem van Schendel describes it as "The beginning of empire" for Britain.
The Company replaced Mir Jafar with his son-in-law, Mir Kasim, in 1760. Mir Kasim challenged British control by allying with Mughal emperor Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
and the Nawab of Awadh, Shuja ud-Daulah, but the company decisively defeated the three at the Battle of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, led by Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, Nawab of Bengal till 1764; the Nawab of Awadh, Sh ...
on 23 October 1764. The resulting treaty made the Mughal emperor a puppet of the British and gave the company the right to collect taxes (''diwani
Diwani is a calligraphic variety of Arabic script, a cursive style developed during the reign of the early Ottoman Turks (16th century - early 17th century). It reached its height of popularity under Süleyman I the Magnificent (1520–1566) ...
'') in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa, giving them de facto control of the region. The Company used Bengal's tax revenue to conquer the rest of India. By 1857, the Company controlled over 60% of the subcontinent directly, and exercised indirect rule over the remainder.
Colonial period
 Two decades after
Two decades after Vasco Da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link E ...
's landing in Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second la ...
, the Bengal Sultanate permitted the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
settlement in Chittagong to be established in 1528. It became the first European colonial enclave in Bengal. The Bengal Sultanate lost control of Chittagong in 1531 after Arakan declared independence and the established Kingdom of Mrauk U.
Portuguese ships from Goa and Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
began frequenting the port city in the 16th century. The ''cartaz
The Cartaz (plural cartazes, in Portuguese) was a naval trade license or pass issued by the Portuguese empire in the Indian ocean during the sixteenth century (circa 1502–1750). Its name derives from the Portuguese term 'cartas', meaning letters. ...
'' system was introduced and required all ships in the area to purchase naval trading licenses from the Portuguese settlement. Slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and piracy flourished. The nearby island of Sandwip
Sandwip ( bn, সন্দ্বীপ, Shondip) is an island located along the southeastern coast of Bangladesh in the Chattogram District. Along with the island of Urir Char, it is a part of the Sandwip Upazila.
Description
Sandwip is locate ...
was conquered in 1602. In 1615, the Portuguese Navy
The Portuguese Navy ( pt, Marinha Portuguesa, also known as ''Marinha de Guerra Portuguesa'' or as ''Armada Portuguesa'') is the naval branch of the Portuguese Armed Forces which, in cooperation and integrated with the other branches of the Port ...
defeated a joint Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and Arakanese fleet near the coast of Chittagong.
The Bengal Sultan after 1534 allowed the Portuguese to create several settlements at Chitagoong, Satgaon, Hughli, Bandel, and Dhaka. In 1535, the Portuguese allied with the Bengal sultan and held the Teliagarhi pass from Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
helping to avoid the invasion by the Mughals. By then several of the products came from Patna and the Portuguese send in traders, establishing a factory there since 1580.
By the time the Portuguese assured military help against Sher Shah, the Mughals already had started to conquer the Sultanate of Ghiyasuddin Mahmud.
The region has been described as the "Paradise of Nations", and its inhabitants's living standards
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
and real wages
Real wages are wages adjusted for inflation, or, equivalently, wages in terms of the amount of goods and services that can be bought. This term is used in contrast to nominal wages or unadjusted wages.
Because it has been adjusted to account f ...
were among the highest in the world. It alone accounted for 40% of Dutch imports outside the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an continent. The eastern part of Bengal was globally prominent in industries such as textile manufacturing
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
and shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
, and it was a major exporter of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
and cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
s, steel, saltpeter, and agricultural and industrial produce in the world.
In 1666, the Mughal government of Bengal led by viceroy Shaista Khan moved to retake Chittagong from Portuguese and Arakanese control. The Anglo-Mughal War was witnessed in 1686.
 After the 1757
After the 1757 Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, ...
, Bengal was the first region of the Indian subcontinent conquered by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
. The company formed the Bengal Presidency, Presidency of Fort William, which administered the region until 1858. A notable aspect of Company rule in India, Company rule was the Permanent Settlement, which established the feudal zamindari system; in addition, Company policies led to the deindustrialisation of Bengal's textile industry. The capital amassed by the East India Company in Bengal was invested in the emerging Industrial Revolution in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain, in industries such as Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution, textile manufacturing.Shombit SenguptaBengals plunder gifted the British Industrial Revolution
''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', 8 February 2010 Economic mismanagement, alongside drought and a smallpox epidemic, directly led to the Great Bengal famine of 1770, which is estimated to have caused the deaths of between 1 million and 10 million people. Several rebellions broke out during the early 19th century (including one led by Titumir), as Company rule had displaced the Muslim ruling class from power. A conservative Islamic cleric, Haji Shariatullah, sought to overthrow the British by propagating Islamic revivalism. Several towns in Bangladesh participated in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and pledged allegiance to the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, who was later exiled to neighbouring Burma. The challenge posed to company rule by the failed Indian Mutiny led to the creation of the British Indian Empire as a crown colony. The British established several schools, colleges, and a university in Bangladesh. Syed Ahmed Khan and Ram Mohan Roy promoted modern and liberal education in the subcontinent, inspiring the Aligarh movement and the Bengal Renaissance. During the late 19th century, novelists, social reformers and feminists emerged from Muslim Bengali society. Electricity and municipal water systems were introduced in the 1890s; Movie theatre, cinemas opened in many towns during the early 20th century. East Bengal's plantation economy was important to the British Empire, particularly its jute and Tea production in Bangladesh, tea. The British established free port, tax-free river ports, such as the Port of Narayanganj, and large seaports like the Port of Chittagong. Bengal had the highest gross domestic product in British India. Bengal was one of the first regions in Asia to have a railway. The first railway in what is now Bangladesh began operating in 1862. In comparison, Japan saw its first railway in 1872. The main railway companies in the region were the Eastern Bengal Railway and Assam Bengal Railway. Railways competed with waterborne transport to become one of the main mediums of transport. Supported by the Muslim aristocracy, the British government created the province of
Eastern Bengal and Assam
Eastern Bengal and Assam was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.
Hist ...
in 1905; the new province received increased investment in education, transport, and industry. However, the Partition of Bengal (1905), first partition of Bengal created an uproar in Kolkata, Calcutta and the Indian National Congress. In response to growing Hindu nationalism, the All India Muslim League was formed in Dhaka during the 1906 All India Muhammadan Educational Conference. The British government reorganised the provinces in 1912, reuniting East and West Bengal and making Assam Province, Assam a second province.
The Raj was slow to allow self-rule in the colonial subcontinent. It established the Bengal Legislative Council in 1862, and the council's native Bengali representation increased during the early 20th century. The Bengal Provincial Muslim League was formed in 1913 to advocate civil rights for Bengali Muslims within a constitutional framework. During the 1920s, the league was divided into factions supporting the Khilafat movement and favouring co-operation with the British to achieve self-rule. Segments of the Bengali elite supported Mustafa Kemal Atatürk's Secularism in Turkey, secularist forces. In 1929, the Praja Party, All Bengal Tenants Association was formed in the Bengal Legislative Council to counter the influence of the Hindu landed gentry, and the Indian Independence Movement, Indian Independence and Pakistan Movements strengthened during the early 20th century. After the Morley-Minto Reforms and the Government of India Act 1919, diarchy era in the legislatures of British India, the British government promised Government of India Act 1935, limited provincial autonomy in 1935. The Bengal Legislative Assembly, British India's largest legislature, was established in 1937.
 Although it won most seats in 1937, the Bengal Congress boycotted the legislature. A. K. Fazlul Huq of the Krishak Sramik Party, Krishak Praja Party was elected as the first
Although it won most seats in 1937, the Bengal Congress boycotted the legislature. A. K. Fazlul Huq of the Krishak Sramik Party, Krishak Praja Party was elected as the first Prime Minister of Bengal
The Prime Minister of Bengal was the head of government of Bengal Presidency, Bengal Province and the Leader of the House in the Bengal Legislative Assembly in British India. The position was dissolved upon the Partition of Bengal (1947), Partitio ...
. In 1940 Huq supported the Lahore Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
, which envisaged independent states in the subcontinent's northwestern and eastern Muslim-majority regions. The first Huq ministry, a coalition with the Bengal Provincial Muslim League, lasted until 1941; it was followed by a Huq coalition with the Hindu Mahasabha which lasted until 1943. Huq was succeeded by Khawaja Nazimuddin, who grappled with the effects of the Burma Campaign, the Bengal famine of 1943, which killed up to 3 million people, and the Quit India movement. In 1946, the Bengal Provincial Muslim League won the provincial election, taking 113 of the 250-seat assembly (the largest Muslim League mandate in British India). H. S. Suhrawardy, who made a final futile effort for a United Bengal in 1946, was the last premier of Bengal.
Partition of Bengal (1947)
On 3 June 1947, the Mountbatten Plan outlined the partition of British India. On 20 June, the Bengal Legislative Assembly met to decide on the partition of Bengal. At the preliminary joint meeting, it was decided (120 votes to 90) that if the province remained united, it should join the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan. At a separate meeting of legislators from West Bengal, it was decided (58 votes to 21) that the province should be partitioned and West Bengal should join the Constituent Assembly of India. At another meeting of legislators fromEast Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = East ...
, it was decided (106 votes to 35) that the province should not be partitioned and (107 votes to 34) that East Bengal should join the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan if Bengal was partitioned. On 6 July, the Sylhet Division, Sylhet region of Assam voted in a 1947 Sylhet referendum, referendum to join East Bengal.
Cyril Radcliffe was tasked with drawing the borders of Pakistan and India, and the Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab Province and Bengal Presidency of British India. It was named after Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissi ...
established the borders of present-day Bangladesh. The Radcliffe Line awarded two-thirds of Bengal as the eastern wing of Pakistan, although the medieval and early modern Bengali capitals of Gauda (city), Gaur, Pandua, Malda, Pandua and Murshidabad fell on the Indian side close to the border with Pakistan.
Union with Pakistan
 The
The Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of I ...
was created on 14 August 1947. East Bengal, with Dhaka as its capital, was the most populous province of the 1947 State of Pakistan, Pakistani federation (led by Governor General of Pakistan, Governor General Muhammad Ali Jinnah, who promised freedom of religion and secular democracy in the new state).
Khawaja Nazimuddin was East Bengal's first Chief Minister of East Bengal, chief minister with Frederick Chalmers Bourne its governor. The All Pakistan Awami Muslim League was formed in 1949. In 1950, the East Bengal Legislative Assembly enacted land reform, abolishing the Permanent Settlement and the zamindari system. The 1952 Bengali Language Movement was the first sign of friction between the country's geographically separated wings. The Awami Muslim League was renamed the more-secular Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
in 1953."ts present name in December 1953" The first constituent assembly was dissolved in 1954; this was challenged by its East Bengali speaker, Maulvi Tamizuddin Khan. The United Front (East Pakistan), United Front coalition swept aside the Muslim League in a landslide victory in the 1954 East Bengali legislative election. The following year, East Bengal was renamed East Pakistan as part of the One Unit programme, and the province became a vital part of the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization.
Pakistan adopted a new constitution in 1956. Three Bengalis were its Prime Minister until 1957: Nazimuddin, Mohammad Ali of Bogra and Suhrawardy. None of the three completed their terms and resigned from office. The Pakistan Army imposed 1958 Pakistani coup d'état, military rule in 1958, and Ayub Khan (general), Ayub Khan was the country's strongman for 11 years. Political repression increased after the coup. Khan introduced a new constitution in 1962, replacing Pakistan's parliamentary system with a presidential and gubernatorial system (based on electoral college selection) known as Basic Democracy. In 1962 Dhaka became the seat of the National Assembly of Pakistan, a move seen as appeasing increased Bengali nationalism. The Pakistani government built the controversial Kaptai Dam, displacing the Chakma people from their indigenous homeland in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. During the 1965 Pakistani presidential election, 1965 presidential election, Fatima Jinnah lost to Ayub Khan despite support from the Combined Opposition alliance (which included the Awami League). The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 blocked cross-border transport links with neighbouring India in what is described as a second partition. In 1966, Awami League leader Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengalis, Beng ...
announced a six point movement, six-point movement for a federal parliamentary democracy.
According to senior World Bank officials, the Pakistani government practised extensive economic discrimination against East Pakistan: greater government spending on West Pakistan, financial transfers from East to West Pakistan, the use of East Pakistan's foreign-exchange surpluses to finance West Pakistani imports, and refusal by the central government to release funds allocated to East Pakistan because the previous spending had been under budget; though East Pakistan generated 70 percent of Pakistan's export revenue with its jute and tea. Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was arrested for treason in the Agartala Conspiracy Case and was released during the 1969 uprising in East Pakistan which resulted in Ayub Khan's resignation. General Yahya Khan assumed power, reintroducing martial law.
Ethnic and linguistic discrimination was common in Pakistan's civil and military services, in which Bengalis were under-represented. Fifteen percent of Pakistani central-government offices were occupied by East Pakistanis, who formed 10 percent of the military. Cultural discrimination also prevailed, making East Pakistan forge a distinct political identity. Authorities banned Bengali literature and music in state media, including the works of Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore. A 1970 Bhola cyclone, cyclone devastated the coast of East Pakistan in 1970, killing an estimated 500,000 people, and the central government was criticised for its poor response. After the December 1970 elections, calls for the independence of East Bengal became louder; the Bengali-nationalist Awami League won 167 of 169 East Pakistani seats in the National Assembly. The League claimed the right to form a government and develop a new constitution but was strongly opposed by the Pakistani military and the Pakistan Peoples Party (led by Zulfikar Ali Bhutto).
War of Independence
The Bengali population was angered when Prime Minister-electSheikh Mujibur Rahman
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman ( bn, শেখ মুজিবুর রহমান; 17 March 1920 – 15 August 1975), often shortened as Sheikh Mujib or Mujib and widely known as Bangabandhu (meaning ''Friend of Bengal''), was a Bengalis, Beng ...
was prevented from taking the office. Non-cooperation movement (1971), Civil disobedience erupted across East Pakistan, with calls for independence. Mujib addressed a 7 March Speech of Bangabandhu, pro-independence rally of nearly 2 million people in Dacca (as Dhaka used to be spelled in English) on 7 March 1971, where he said, "This time the struggle is for our freedom. This time the struggle is for our independence." The flag of Bangladesh was raised for the first time on 23 March, Pakistan's Republic Day. Later, on 25 March late evening, the Pakistani military junta led by Yahya Khan launched a sustained military assault on East Pakistan under the code name of Operation Searchlight. The Pakistan Army arrested Sheikh Mujibur Rahman and flew him to Karachi. However, before his arrest Mujib proclaimed the Proclamation of Bangladeshi Independence, Independence of Bangladesh at midnight on 26 March which led the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
to break out within hours. The Pakistan Army and its local supporters continued to massacre Bengalis, in particular 1971 Dhaka University massacre, students, intellectuals
An intellectual is a person who engages in critical thinking
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments to form a judgement. The subject is complex; several different definitions exist, ...
, political figures, and Hindus in the 1971 Bangladesh genocide
The genocide in Bangladesh began on 25 March 1971 with the launch of Operation Searchlight, as the government of Pakistan, dominated by West Pakistan, began a military crackdown on East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) to suppress Bengali peopl ...
. The Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary ...
, a guerrilla resistance force, also violated human rights during the conflict. During the war, an estimated 0.3 to 3.0 million people were killed and several million people took shelter in neighbouring India.
Global public opinion turned against Pakistan as news of the atrocities spread; the Bangladesh movement was supported by prominent political and cultural figures in the West, including Ted Kennedy, George Harrison, Bob Dylan, Joan Baez, Victoria Ocampo and André Malraux. The Concert for Bangladesh was held at Madison Square Garden in New York City to raise funds for Bangladeshi refugees. The first major benefit concert in history, it was organised by Harrison and Indian Bengali sitarist Ravi Shankar.
During the Bangladesh Liberation War, Bengali nationalists declared independence and formed the Mukti Bahini (the Bangladeshi National Liberation Army). The Provisional Government of Bangladesh was established on 17 April 1971, converting the 469 elected members of the Pakistani national assembly and East Pakistani provincial assembly into the Constituent Assembly of Bangladesh. The provisional government issued a Proclamation of Bangladeshi Independence, proclamation that became the country's interim constitution and declared "equality, human dignity, and social justice" as its fundamental principles. Due to Mujib's detention, Syed Nazrul Islam took over the role of Acting President, while Tajuddin Ahmad was named Bangladesh's first Prime Minister. The Mukti Bahini and other Bengali guerrilla forces formed the Bangladesh Forces, which became the military wing of the provisional government. Led by General M. A. G. Osmani and eleven List of sectors in Bangladesh Liberation War, sector commanders, the forces held the countryside during the war. They conducted wide-ranging guerrilla operations against Pakistani forces. As a result, almost the entire country except for the capital Dacca was liberated by Bangladesh Forces by late November.
This led the Pakistan Army to attack neighbouring India's western front on 2 December 1971. India retaliated in both the western and eastern fronts. With a joint ground advance by Bangladeshi and Indian forces, coupled with air strikes by both India and the small Bangladeshi air contingent, the capital Dacca was liberated from Pakistani occupation in mid-December. During the last phase of the war, both the Soviet Union and the United States dispatched naval forces to the Bay of Bengal in a Cold War standoff. The nine month long war ended with the Surrender of Pakistan, surrender of Pakistani armed forces to the Bangladesh-India Allied Forces on 16 December 1971.Rummel, Rudolph J. (1997"Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900"
. Transaction Publishers, Rutgers University. , Chapter 8
Table 8.2 Pakistan Genocide in Bangladesh Estimates, Sources, and Calculations
Under international pressure, Pakistan released Rahman from imprisonment on 8 January 1972 and he was flown by the British Royal Air Force to a million-strong homecoming in Dacca. Remaining Indian troops were withdrawn by 12 March 1972, three months after the war ended. The cause of Bangladeshi self-determination was recognised around the world. By August 1972, the new state was recognised by 86 countries. Pakistan recognised Bangladesh in 1974 after pressure from most of the Muslim countries.
Modern Bangladesh
First parliamentary era
 The constituent assembly adopted the constitution of Bangladesh on 4 November 1972, establishing a secular, multiparty parliamentary democracy. The new constitution included references to socialism, and Prime Minister Sheikh Mujibur Rahman nationalised major industries in 1972. A major reconstruction and rehabilitation programme was launched. The Awami League won the country's first general election in 1973, securing a large majority in the "Jatiyo Sangshad", the national parliament. Bangladesh joined the
The constituent assembly adopted the constitution of Bangladesh on 4 November 1972, establishing a secular, multiparty parliamentary democracy. The new constitution included references to socialism, and Prime Minister Sheikh Mujibur Rahman nationalised major industries in 1972. A major reconstruction and rehabilitation programme was launched. The Awami League won the country's first general election in 1973, securing a large majority in the "Jatiyo Sangshad", the national parliament. Bangladesh joined the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
, the UN, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, OIC and the Non-Aligned Movement, and Rahman strengthened ties with India. Amid growing agitation by the opposition National Awami Party and Jashod, he became increasingly authoritarian. Rahman amended the constitution, giving himself more emergency powers (including the suspension of fundamental rights). The Bangladesh famine of 1974 also worsened the political situation.
Presidential era (1975–1991)
In January 1975, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman introduced One-party state, one-party socialist rule under Bangladesh Krishak Sramik Awami League, BAKSAL. Rahman banned all newspapers except four state-owned publications and amended the constitution to increase his power. He was Assassination of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, assassinated during a coup on 15 August 1975. Martial law was declared, and the presidency passed to the usurper Khondaker Mostaq Ahmad for four months. Ahmad is widely regarded as a traitor by Bangladeshis. Tajuddin Ahmad, the nation's first prime minister, and four other independence leaders were assassinated on 4 November 1975. Chief Justice Abu Sadat Mohammad Sayem was installed as president by the military on 6 November 1975. Bangladesh was governed by a military junta led by the Chief Martial Law Administrator for three years. In 1977, the army chief Ziaur Rahman became president. Rahman reinstated multiparty politics, privatised industries and newspapers, established Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority, BEPZA and held the country's second general election in 1979. A semi-presidential system evolved, with the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) governing until 1982. Rahman was assassinated in 1981 and was succeeded by Vice-president Abdus Sattar (president), Abdus Sattar. Sattar received 65.5 per cent of the vote in the 1981 Bangladeshi presidential election, 1981 presidential election. After a year in office, Sattar was overthrown in the 1982 Bangladesh coup d'état. Chief Justice A. F. M. Ahsanuddin Chowdhury was installed as president, but army chief Hussain Muhammad Ershad became the country's ''de facto'' leader and assumed the presidency in 1983. Ershad lifted martial law in 1986. He governed with four successive prime ministers (Ataur Rahman Khan, Mizanur Rahman Chowdhury, Moudud Ahmed and Kazi Zafar Ahmed) and a parliament dominated by his Jatiya Party (Ershad), Jatiyo Party. General elections were held in 1986 and 1988, although the opposition BNP and Awami League boycotted the latter. Ershad pursued administrative decentralisation, dividing the country into 64 districts, and pushed Parliament to make Islam the state religion in 1988. A 1990 Mass Uprising in Bangladesh, 1990 mass uprising forced him to resign, and Chief Justice Shahabuddin Ahmed led the country's first caretaker government as part of the transition to parliamentary rule.Parliamentary era (1991–present)
 After the 1991 general election, the twelfth amendment to the constitution restored the parliamentary republic and Begum Khaleda Zia became Bangladesh's first female prime minister. Zia, a former first lady, led a BNP government from 1990 to 1996. In 1991, her finance minister, Saifur Rahman (Bangladeshi politician), Saifur Rahman, began a major programme to liberalise the Bangladeshi economy.
In February 1996, February 1996 Bangladeshi general election, a general election was held, which was boycotted by all opposition parties giving a 300 (of 300) seat victory for BNP. This election was deemed illegitimate, so a system of a caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker government was introduced to oversee the transfer of power and a new election was held in June 1996, overseen by Justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman, the first Chief Adviser of Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Awami League, Awami League won the June 1996 Bangladeshi general election, seventh general election, marking its leader Sheikh Hasina, Sheikh Hasina's first term as Prime Minister. Hasina's first term was highlighted by the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord and a
After the 1991 general election, the twelfth amendment to the constitution restored the parliamentary republic and Begum Khaleda Zia became Bangladesh's first female prime minister. Zia, a former first lady, led a BNP government from 1990 to 1996. In 1991, her finance minister, Saifur Rahman (Bangladeshi politician), Saifur Rahman, began a major programme to liberalise the Bangladeshi economy.
In February 1996, February 1996 Bangladeshi general election, a general election was held, which was boycotted by all opposition parties giving a 300 (of 300) seat victory for BNP. This election was deemed illegitimate, so a system of a caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker government was introduced to oversee the transfer of power and a new election was held in June 1996, overseen by Justice Muhammad Habibur Rahman, the first Chief Adviser of Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Awami League, Awami League won the June 1996 Bangladeshi general election, seventh general election, marking its leader Sheikh Hasina, Sheikh Hasina's first term as Prime Minister. Hasina's first term was highlighted by the Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord and a Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
water-sharing treaty with India. The second caretaker government, led by Chief Adviser Justice Latifur Rahman, oversaw the 2001 Bangladeshi general election which returned Begum Zia and the BNP to power.
The second Zia administration saw improved economic growth, but political turmoil gripped the country between 2004 and 2006. A radical Islamist militant group, the Jamaat-ul-Mujahideen Bangladesh, JMB, carried out a series of terror attacks. The evidence of staging these attacks by these extremist groups have been found in the investigation. Hundreds of suspected members were detained in numerous security operations in 2006, including the two chiefs of the JMB, Shaykh Abdur Rahman and Bangla Bhai, who was executed with other top leaders in March 2007, bringing the militant group to an end.
In 2006, at the end of the term of the BNP administration, there was widespread political unrest related to the handover of power to a caretaker government. As such, the Bangladeshi military urged President Iajuddin Ahmed to impose a state of emergency and a caretaker government, led by technocrat Fakhruddin Ahmed, was installed. Emergency rule lasted for two years, during which time investigations into members of both Awami League and BNP were conducted, including their leaders Sheikh Hasina and Khaleda Zia. In 2008, the 2008 Bangladeshi general election, ninth general election saw a return to power for Sheikh Hasina and the Bangladesh Awami League, Awami League led Grand Alliance (Bangladesh), Grand Alliance in a landslide victory. In 2010, the Supreme Court of Bangladesh, Supreme Court ruled martial law illegal and affirmed Secularism, secular principles in the constitution. The following year, the Awami League abolished the caretaker government system.
Citing the lack of caretaker government, the 2014 Bangladeshi general election, 2014 general election was boycotted by the BNP and other opposition parties, giving the Awami League a decisive victory. The election was controversial with reports of violence and an alleged crackdown on the opposition in the run-up to the election, and 153 seats (of 300) went uncontested in the election. Despite the controversy, Hasina went on to form a government that saw her return for a third term as Prime Minister. Due to strong domestic demand, Bangladesh emerged as one of the List of countries by real GDP growth rate, fastest-growing economies in the world. However, human rights abuses increased under the Hasina administration, particularly Forced disappearance in Bangladesh, enforced disappearances. Between 2016 and 2017, an estimated 1 million Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh, Rohingya refugees took shelter in Cox's Bazar District, southeastern Bangladesh amid a military crackdown in neighbouring Rakhine State, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
.
In 2018, the country saw major movements for 2018 Bangladesh quota reform movement, government quota reforms and 2018 Bangladesh road-safety protests, road-safety. The 2018 Bangladeshi general election was marred by allegations of widespread vote rigging. The Awami League won 259 out of 300 seats and the main opposition alliance Jatiya Oikya Front secured only 8 seats, with Sheikh Hasina becoming the longest-serving prime minister in Bangladeshi history. Pro-democracy leader Dr. Kamal Hossain called for an annulment of the election result and for a new election to be held in a free and fair manner. The election was also observed by European Union observers.
Geography
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
, located on the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
. It is surrounded almost entirely by neighbouring India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
—and shares a small border with Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
to its southeast, though it lies very close to Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The country is divided into three regions. Most of the country is dominated by the fertile Ganges Delta, the largest river delta in the world. The northwest and central parts of the country are formed by the Madhupur tract, Madhupur and the Barind Tract, Barind plateaus. The northeast and southeast are home to evergreen hill ranges.
The Ganges delta is formed by the confluence of the Ganges (local name Padma River, Padma or ''Pôdda''), Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra (Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna or ''Jomuna''), and Meghna River, Meghna rivers and their respective tributaries. The Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna, finally flowing into the Bay of Bengal. Bangladesh is called the "Land of Rivers"; as it is home to over 57 trans-boundary rivers. However, this resolves water issues politically complicated, in most cases, as the country is a lower riparian zone, riparian state to India.
Bangladesh is predominantly rich fertile flat land. Most of it is less than above sea level, and it is estimated that about 10% of its land would be flooded if the sea level were to rise by . 17% of the country is covered by forests and 12% is covered by hill systems. The country's haor wetlands are of significance to global environmental science. The List of mountains of Bangladesh, highest point in Bangladesh is the Saka Haphong, located near the border with Myanmar, with an elevation of . Previously, either Keokradong or Tazing Dong were considered the highest.
Administrative geography
Bangladesh is divided into eight administrative divisions, each named after their respective divisional headquarters: Barisal Division, Barisal (officially ''Barishal''), Chittagong Division, Chittagong (officially ''Chattogram''), Dhaka Division, Dhaka, Khulna Division, Khulna, Mymensingh Division, Mymensingh, Rajshahi, Rangpur, and Sylhet. Divisions are subdivided into districts (''zila''). There are 64 districts in Bangladesh, each further subdivided into ''upazila'' (subdistricts) or ''thana''. The area within each police station, except for those in metropolitan areas, is divided into several ''Union Councils of Bangladesh, unions'', with each union consisting of multiple villages. In the metropolitan areas, police stations are divided into wards, further divided into ''mahallas''. There are no elected officials at the divisional or district levels, and the administration is composed only of government officials. Direct elections are held in each union (or ward) for a chairperson and a number of members. In 1997, a parliamentary act was passed to reserve three seats (out of 12) in every union for female candidates.Climate
Straddling the Tropic of Cancer, Bangladesh's climate is tropical, with a mild winter from October to March and a hot, humid summer from March to June. The country has never recorded an air temperature below , with a record low of in the northwest city of Dinajpur on 3 February 1905. A warm and humid monsoon season lasts from June to October and supplies most of the country's rainfall. Natural calamities, such as Floods in Bangladesh, floods, tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and tidal bores occur almost every year, combined with the effects of deforestation, Soils retrogression and degradation, soil degradation and erosion. The List of Bangladesh tropical cyclones, cyclones of 1970 and 1991 were particularly devastating, the 1991 Bangladesh cyclone, latter killing approximately 140,000 people. In September 1998, Bangladesh saw the 1998 Bangladesh floods, most severe flooding in modern history, after which two-thirds of the country went underwater, along with a death toll of 1,000. As a result of various international and national level initiatives in disaster risk reduction, human toll and economic damage from floods and cyclones have come down over the years. The 2007 South Asian floods ravaged areas across the country, leaving five million people displaced, had a death toll around 500. Bangladesh is recognised to be one of the countries most Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change. Over the course of a century, 508 cyclones have affected the Bay of Bengal region, 17 percent of which are believed to have caused landfall in Bangladesh. Natural hazards that come from increased rainfall, rising sea levels, and tropical cyclones are expected to increase as the climate changes, each seriously affecting agriculture, water and food security, human health, and shelter. It is estimated that by 2050, a 3 feet rise in sea levels will inundate some 20 percent of the land and displace more than 30 million people. To address the sea level rise threat in Bangladesh, the Bangladesh Delta Plan 2100 has been launched.Biodiversity
 Bangladesh is located in the Indomalayan realm, and lies within four terrestrial ecoregions: Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests, Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests, Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests, and Sundarbans mangroves. Its ecology includes a long sea coastline, numerous List of rivers in Bangladesh, rivers and tributaries, lakes, wetlands, evergreen forests, semi evergreen forests, hill forests, moist deciduous forests, freshwater swamp forests and flat land with tall grass. The Bangladesh Plain is famous for its fertile alluvial soil which supports extensive cultivation. The country is dominated by lush vegetation, with villages often buried in groves of mango, jackfruit, bamboo, betel nut, coconut and date palm.Bangladesh , history – geography :: Plant and animal life
Bangladesh is located in the Indomalayan realm, and lies within four terrestrial ecoregions: Lower Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests, Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests, Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests, and Sundarbans mangroves. Its ecology includes a long sea coastline, numerous List of rivers in Bangladesh, rivers and tributaries, lakes, wetlands, evergreen forests, semi evergreen forests, hill forests, moist deciduous forests, freshwater swamp forests and flat land with tall grass. The Bangladesh Plain is famous for its fertile alluvial soil which supports extensive cultivation. The country is dominated by lush vegetation, with villages often buried in groves of mango, jackfruit, bamboo, betel nut, coconut and date palm.Bangladesh , history – geography :: Plant and animal life. ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. The country has up to 6000 species of plant life, including 5000 flowering plants. Water bodies and wetland systems provide a habitat for many aquatic plants. Nymphaeaceae, Water lilies and Nelumbo nucifera, lotuses grow vividly during the monsoon season. The country has List of protected areas of Bangladesh, 50 wildlife sanctuaries. Bangladesh is home to much of the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest, covering an area of in the southwest littoral region. It is divided into three protected sanctuaries–the Sundarbans South Wildlife Sanctuary, South, Sundarbans East Wildlife Sanctuary, East and Sundarbans West Wildlife Sanctuary, West zones. The forest is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The northeastern Sylhet region is home to haor wetlands, a unique ecosystem. It also includes tropical and subtropical coniferous forests, a freshwater swamp forest, and mixed deciduous forests. The southeastern Chittagong Division, Chittagong region covers evergreen and semi-evergreen hilly jungles. Central Bangladesh includes the plainland Sal forest running along with the districts of Gazipur, Tangail and Mymensingh. St. Martin's Island is the only coral reef in the country. Bangladesh has an abundance of Wildlife in Bangladesh, wildlife in its forests, marshes, woodlands and hills. The vast majority of animals dwell within a habitat of . The Bengal tiger, clouded leopard, saltwater crocodile, black panther and fishing cat are among the chief predators in the Sundarbans. Northern and eastern Bangladesh is home to the Asian elephant, hoolock gibbon, Asian black bear and oriental pied hornbill. The Chital deer are widely seen in southwestern woodlands. Other animals include the black giant squirrel, capped langur, Bengal fox, sambar deer, jungle cat, king cobra, wild boar, mongooses, pangolins, Python (genus), pythons and Asian water monitor, water monitors. Bangladesh has one of the largest populations of Irrawaddy dolphins and South Asian river dolphin, Ganges dolphins. A 2009 census found 6,000 Irrawaddy dolphins inhabiting the littoral rivers of Bangladesh. The country has numerous species of amphibians (53), reptiles (139), marine reptiles (19) and marine mammals (5). It also has List of birds of Bangladesh, 628 species of birds. Several animals became extinct in Bangladesh during the last century, including the one-horned and two-horned rhinoceros and common peafowl. The human population is concentrated in urban areas, limiting deforestation to a certain extent. Rapid urban growth has threatened natural habitats. Although many areas are protected under law, some Bangladeshi wildlife is threatened by this growth. The Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act was enacted in 1995. The government has designated several regions as Ecologically Critical Areas, including wetlands, forests, and rivers. The Sundarbans tiger project and the Bangladesh Bear Project are among the key initiatives to strengthen conservation. It ratified the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity on 3 May 1994. , the country was set to revise its Biodiversity action plan, National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan.
Politics and government

 Bangladesh is a ''de jure'' representative democracy under its Constitution of Bangladesh, constitution, with a Westminster system, Westminster-style unitary authority, unitary parliamentary republic that has universal suffrage. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is invited to form a government every five years. The President invites the leader of the largest party in parliament to become Prime Minister of the world's fifth-largest democracy. Bangladesh experienced a two party system between 1990 and 2014, when the
Bangladesh is a ''de jure'' representative democracy under its Constitution of Bangladesh, constitution, with a Westminster system, Westminster-style unitary authority, unitary parliamentary republic that has universal suffrage. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is invited to form a government every five years. The President invites the leader of the largest party in parliament to become Prime Minister of the world's fifth-largest democracy. Bangladesh experienced a two party system between 1990 and 2014, when the Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) alternated in power. During this period, elections were managed by a neutral Caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker government. But the caretaker government was abolished by the Awami League government in 2011.
One of the key aspects of Bangladeshi politics is the "spirit of the liberation war", which refers to the ideals of the liberation movement during the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
. The Proclamation of Independence enunciated the values of "equality, human dignity and social justice". In 1972, the constitution included a bill of rights and declared "nationalism, socialism, democracy and secularity" as the principles of government policy. Socialism was later de-emphasised and neglected by successive governments. Bangladesh has a market-based economy. To many Bangladeshis, especially in the younger generation, the spirit of the liberation war is a vision for a society based on civil liberties, human rights, the rule of law and good governance.
*Legislature, Legislative: The Jatiya Sangshad (National Parliament) is the unicameral parliament. It has 350 Member of parliament, Members of Parliament (MPs), including 300 MPs elected on the first past the post system and 50 MPs appointed to reserved seats for women's empowerment. Article 70 of the Constitution of Bangladesh forbids MPs from voting against their party. However, several laws proposed independently by MPs have been transformed into legislation, including the anti-torture law. The parliament is presided over by the Speaker of the Jatiya Sangsad, who is second in line to the president as per the constitution. There is also a Deputy Speaker. When a president is incapable of performing duties (i.e. due to illness), the Speaker steps in as Acting President and the Deputy Speaker becomes Acting Speaker. A recurring proposal suggests that the Deputy Speaker should be an opposition member.
*Executive (government), Executive: The Government of Bangladesh is overseen by a Cabinet of Bangladesh, cabinet headed by the Prime Minister of Bangladesh. The tenure of a parliamentary government is five years. The Bangladesh Civil Service assists the cabinet in running the government. Recruitment for the civil service is based on a public examination. In theory, the civil service should be a meritocracy. But a disputed quota system coupled with politicisation and preference for seniority have allegedly affected the civil service's meritocracy. The President of Bangladesh is the ceremonial head of state whose powers include signing bills passed by parliament into law. The President is elected by the parliament and has a five-year term. Under the constitution, the president acts on the prime minister's advice. The President is the Supreme Commander of the Bangladesh Armed Forces and the chancellor of all universities.
*Laws in Bangladesh, Judiciary: The Supreme Court of Bangladesh is the highest court of the land, followed by the High Court Division, High Court and Appellate Divisions. The head of the judiciary is the Chief Justice of Bangladesh, who sits on the Supreme Court. The courts have wide latitude in judicial review in Bangladesh, judicial review, and judicial precedent is supported by Article 111 of the constitution. The Judiciary of Bangladesh, judiciary includes district and metropolitan courts divided into civil and criminal courts. Due to a shortage of judges, the judiciary has a large backlog. The Bangladesh Judicial Service Commission is responsible for judicial appointments, salaries, and discipline.
Military

 The Bangladesh Armed Forces have inherited the institutional framework of the British military and the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1971 from the military regiments of East Pakistan. In 2022, the active personnel strength of the Bangladesh Army was around 250,000,* excluding the Air Force and the Navy (24,000). In addition to traditional defence roles, the military has supported civil authorities in disaster relief and provided internal security during periods of political unrest. For many years, Bangladesh has been the world's largest contributor to United Nations peacekeeping, UN peacekeeping forces. The military budget of Bangladesh accounts for 1.3% of GDP, amounting to US$4.3 billion in 2021.
The Bangladesh Navy, one of the largest in the Bay of Bengal, includes a List of active ships of the Bangladesh Navy, fleet of frigates, submarines, corvettes and other vessels. The Bangladesh Air Force has a List of active Bangladesh military aircraft, small fleet of multi-role combat aircraft, including the MiG-29 and Chengdu J-7, Chengdu-F7. Most of Bangladesh's military equipment comes from China. In recent years, Bangladesh and India have increased joint military exercises, high level visits of military leaders, counter-terrorism cooperation and intelligence sharing. Bangladesh is vital to ensuring stability and security in northeast India.
Bangladesh's strategic importance in the eastern subcontinent hinges on its proximity to China, its frontier with Burma, the separation of mainland and northeast India, and its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. In 2002, Bangladesh and China signed a Defence Cooperation Agreement (DCA) which the governments of both countries said will "institutionalize the existing accords in defence sector and also to rationalize the existing piecemeal agreements to enhance cooperation in training, maintenance and in some areas of production". The United States has pursued negotiations with Bangladesh on a Status of forces agreement, Status of Forces Agreement, an Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement and a General Security of Military Information Agreement. In 2019, Bangladesh ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Bangladesh Armed Forces have inherited the institutional framework of the British military and the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1971 from the military regiments of East Pakistan. In 2022, the active personnel strength of the Bangladesh Army was around 250,000,* excluding the Air Force and the Navy (24,000). In addition to traditional defence roles, the military has supported civil authorities in disaster relief and provided internal security during periods of political unrest. For many years, Bangladesh has been the world's largest contributor to United Nations peacekeeping, UN peacekeeping forces. The military budget of Bangladesh accounts for 1.3% of GDP, amounting to US$4.3 billion in 2021.
The Bangladesh Navy, one of the largest in the Bay of Bengal, includes a List of active ships of the Bangladesh Navy, fleet of frigates, submarines, corvettes and other vessels. The Bangladesh Air Force has a List of active Bangladesh military aircraft, small fleet of multi-role combat aircraft, including the MiG-29 and Chengdu J-7, Chengdu-F7. Most of Bangladesh's military equipment comes from China. In recent years, Bangladesh and India have increased joint military exercises, high level visits of military leaders, counter-terrorism cooperation and intelligence sharing. Bangladesh is vital to ensuring stability and security in northeast India.
Bangladesh's strategic importance in the eastern subcontinent hinges on its proximity to China, its frontier with Burma, the separation of mainland and northeast India, and its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. In 2002, Bangladesh and China signed a Defence Cooperation Agreement (DCA) which the governments of both countries said will "institutionalize the existing accords in defence sector and also to rationalize the existing piecemeal agreements to enhance cooperation in training, maintenance and in some areas of production". The United States has pursued negotiations with Bangladesh on a Status of forces agreement, Status of Forces Agreement, an Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement and a General Security of Military Information Agreement. In 2019, Bangladesh ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Foreign relations
Bangladesh is considered amiddle power
In international relations, a middle power is a sovereign state that is not a great power nor a superpower, but still has large or moderate influence and international recognition.
The concept of the "middle power" dates back to the origins of ...
in global politics. It plays an important role in the geopolitical affairs of the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth.
In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
, due to its strategic location between South and Southeast Asia. Bangladesh joined the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
in 1972 and the United Nations in 1974. It relies on multilateralism, multilateral diplomacy on issues like climate change, nuclear nonproliferation, trade policy and non-traditional security issues. At the World Trade Organization, WTO, Bangladesh has used the dispute resolution mechanism to settle trade disputes with India and other countries. Bangladesh pioneered the creation of South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, SAARC, which has been the preeminent forum for regional diplomacy among the countries of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. It joined the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, OIC, an intergovernmental organisation of the Muslim world in 1974, and is a founding member of the Developing 8 Countries. In recent years, Bangladesh has focused on promoting regional trade and transport links with support from the World Bank. Dhaka hosts the headquarters of BIMSTEC
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations, housing 1.73 billion people and having a combined gross domestic pro ...
, an organisation that brings together countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal.
Bangladesh–Myanmar relations, Relations with neighbouring Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
have been severely strained since 2016–2017, after over 700,000 Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh, Rohingya refugees illegally entered Bangladesh fleeing persecution, ethnic cleansing, genocide, and other atrocities in their native state. The parliament, government, and civil society of Bangladesh have been at the forefront of International reaction to the 2016–17 Rohingya exodus, international criticism against Myanmar for military operations against the Rohingya, and have demanded their right of return to Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
. In 2021, Bangladesh provided a US$200 million loan to Sri Lanka and a US$7.7 million donation to Sudan as economic assistance.
Bangladesh shares an important Bangladesh–India relations, bilateral and economic relationship with its largest neighbour India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, which is often strained by Water politics in India, water politics of the Ganges water dispute, Ganges and the Teesta River#Water sharing challenge, Teesta, and the Deaths along the Bangladesh–India border, border killings of Bangladeshi civilians. Post-independent Bangladesh has continued to have a problematic relationship with Pakistan, mainly due to its denial of the 1971 Bangladesh genocide
The genocide in Bangladesh began on 25 March 1971 with the launch of Operation Searchlight, as the government of Pakistan, dominated by West Pakistan, began a military crackdown on East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) to suppress Bengali peopl ...
. It maintains a Bangladesh-China relations, warm relationship with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, which is its largest trading partner, and the largest arms supplier. Japan is Bangladesh's largest economic aid provider, and the two maintain a Bangladesh–Japan relations, strategic and economic partnership. Political relations with Middle Eastern countries are robust. Bangladesh receives 59% of its remittances from the Middle East, despite poor working conditions affecting over 4 million Bangladeshis in the Middle East, Bangladeshi workers. Bangladesh plays a major role in Climate change, global climate diplomacy as a leader of the Climate Vulnerable Forum
The Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) is a global partnership of countries that are disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. The forum addresses the negative effects of climate change as a result of heightened socioeconomic ...
.
Civil society
Since the colonial period, Bangladesh has had a prominent civil society. There are various special interest groups, including non-governmental organisations, human rights organisations, professional associations, chamber of commerce, chambers of commerce, employers' associations and trade unions. The National Human Rights Commission of Bangladesh was set up in 2007. Notable human rights organisations and initiatives include the Centre for Law and Mediation (Bangladesh), Centre for Law and Mediation, Odhikar, the Alliance for Bangladesh Worker Safety, the Bangladesh Environmental Lawyers Association, the Bangladesh Hindu Buddhist Christian Unity Council and the War Crimes Fact Finding Committee. The world's largest international NGO BRAC (organisation), BRAC is based in Bangladesh. There have been concerns regarding the shrinking space for independent civil society in recent years, with commentators labelling the civil society movement dead under the authoritarianism of the Awami League.Human rights
 Torture is banned by Article 35 (5) of the Constitution of Bangladesh. Despite this constitutional ban, torture is rampantly used by Bangladesh's security forces. Bangladesh joined the Convention against Torture in 1998; but it enacted its first anti-torture law, the Torture and Custodial Death (Prevention) Act, in 2013. The first conviction under this law was announced in 2020. Amnesty International Prisoner of conscience, Prisoners of Conscience from Bangladesh have included Saber Hossain Chowdhury and Shahidul Alam. The Digital Security Act of 2018 has greatly reduced freedom of expression in Bangladesh, particularly on the internet. The Digital Security Act has been used to target critics of the government and bureaucracy. Newspaper editorials have been demanding the repeal of the Digital Security Act.
On International Human Rights Day in December 2021, the United States United States Department of the Treasury, Department of Treasury announced Economic sanctions, sanctions on commanders of the Rapid Action Battalion for extrajudicial killings, torture and other human rights abuses. Freedom House has criticised the ruling party for human rights abuses, crackdown on opposition, mass media, and civil society through politicized enforcement. Bangladesh is ranked "partly free" in Freedom House's ''Freedom in the World'' report, but its press freedom has deteriorated from "free" to "not free" in recent years due to increasing pressure from the authoritarian government. According to the British Economist Intelligence Unit, the country has a hybrid regime: the third of four rankings in its Democracy Index. Bangladesh was ranked 96th among 163 countries in the 2022 Global Peace Index. According to National Human Rights Commission, 70% of alleged human-rights violations are committed by law-enforcement agencies.
LGBT rights in Bangladesh, LGBT rights are heavily suppressed by both government and society, as homosexuality is outlawed by section 377 of the criminal code (a legacy of the colonial period), and is punishable by a maximum of life imprisonment. However, Bangladesh recognises the third gender and accords limited rights for transgender people. According to the 2016 Global Slavery Index, an estimated 1,531,300 people are enslaved in Bangladesh, or roughly 1% of the population. A number of slaves in Bangladesh are forced to work in the fish and shrimp industries.
Torture is banned by Article 35 (5) of the Constitution of Bangladesh. Despite this constitutional ban, torture is rampantly used by Bangladesh's security forces. Bangladesh joined the Convention against Torture in 1998; but it enacted its first anti-torture law, the Torture and Custodial Death (Prevention) Act, in 2013. The first conviction under this law was announced in 2020. Amnesty International Prisoner of conscience, Prisoners of Conscience from Bangladesh have included Saber Hossain Chowdhury and Shahidul Alam. The Digital Security Act of 2018 has greatly reduced freedom of expression in Bangladesh, particularly on the internet. The Digital Security Act has been used to target critics of the government and bureaucracy. Newspaper editorials have been demanding the repeal of the Digital Security Act.
On International Human Rights Day in December 2021, the United States United States Department of the Treasury, Department of Treasury announced Economic sanctions, sanctions on commanders of the Rapid Action Battalion for extrajudicial killings, torture and other human rights abuses. Freedom House has criticised the ruling party for human rights abuses, crackdown on opposition, mass media, and civil society through politicized enforcement. Bangladesh is ranked "partly free" in Freedom House's ''Freedom in the World'' report, but its press freedom has deteriorated from "free" to "not free" in recent years due to increasing pressure from the authoritarian government. According to the British Economist Intelligence Unit, the country has a hybrid regime: the third of four rankings in its Democracy Index. Bangladesh was ranked 96th among 163 countries in the 2022 Global Peace Index. According to National Human Rights Commission, 70% of alleged human-rights violations are committed by law-enforcement agencies.
LGBT rights in Bangladesh, LGBT rights are heavily suppressed by both government and society, as homosexuality is outlawed by section 377 of the criminal code (a legacy of the colonial period), and is punishable by a maximum of life imprisonment. However, Bangladesh recognises the third gender and accords limited rights for transgender people. According to the 2016 Global Slavery Index, an estimated 1,531,300 people are enslaved in Bangladesh, or roughly 1% of the population. A number of slaves in Bangladesh are forced to work in the fish and shrimp industries.
Corruption
Like for many developing countries, institutional corruption is a serious concern for Bangladesh. Bangladesh was ranked 146th among 180 countries on Transparency International's 2018 Corruption Perceptions Index. According to a survey conducted by the Bangladesh chapter of TI, in 2015, the level of bribery was equivalent to 3.7 percent of the national budget.Corruption in Service Sectors: National Household Survey 2015
', Transparency International Bangladesh, Dhaka, 2016, p. 1 Land administration was the sector with the most bribery in 2015, followed by education, police and water supply. The Anti Corruption Commission Bangladesh, Anti Corruption Commission was formed in 2004, and it was active during the 2006–08 Bangladeshi political crisis, indicting many leading politicians, bureaucrats and businessmen for Graft (politics), graft.
Economy
 Bangladesh is the second largest economy in South Asia after India. The country has outpaced India (of which it was a part until 1947) and Pakistan (of which it was a part until 1971) in terms of per capita income. According to the World Bank, "When the newly independent country of Bangladesh was born on December 16, 1971, it was the second poorest country in the world—making the country's transformation over the next 50 years one of the great development stories. Since then, poverty has been cut in half at record speed. Enrolment in primary school is now nearly universal. Hundreds of thousands of women have entered the workforce. Steady progress has been made on maternal and child health. And the country is better buttressed against the destructive forces posed by climate change and natural disasters. Bangladesh's success comprises many moving parts—from investing in human capital to establishing macroeconomic stability. Building on this success, the country is now setting the stage for further economic growth and job creation by ramping up investments in energy, inland connectivity, urban projects, and transport infrastructure, as well as prioritizing climate change adaptation and disaster preparedness on its path toward sustainable growth".
Since 2009, Bangladesh has embarked on a series of List of megaprojects in Bangladesh, megaprojects. The 6.15 km long Padma Bridge was built at a cost of US$3.86 billion. The bridge was the first self-financed megaproject in the country's history. Other megaprojects include the Dhaka Metro, Karnaphuli Tunnel, Dhaka Elevated Expressway and Chittagong Elevated Expressway; as well as the Bangladesh Delta Plan to mitigate the impact of climate change. Overseas remittances from expat Bangladeshis and export earnings from the Bangladesh textile industry have allowed the country to have the second largest List of countries by foreign exchange reserves, foreign-exchange reserves in South Asia. The reserves have boosted the government's spending capacity in spite of tax revenues forming only 7.7% of government revenue. A big chunk of investments have gone into the Electric power, power sector. In 2009, Bangladesh was experiencing daily blackouts several times a day. In 2022, the country achieved 100% electrification. One of the major anti-poverty schemes of the Bangladeshi government is the Ashrayan Project which aims to eradicate homelessness by providing free housing.
The private sector accounts for 80% of GDP in comparison to the dwindling role of state-owned companies. Bangladesh's economy is dominated by family-owned List of companies of Bangladesh, conglomerates and small and medium-sized businesses. Some of the largest publicly-traded companies in Bangladesh include Beximco, BRAC Bank, BSRM, GPH Ispat, Grameenphone, Summit Group, and Square Pharmaceuticals. Capital markets include the Dhaka Stock Exchange and the Chittagong Stock Exchange. Its Telecommunications in Bangladesh, telecommunications industry is one of the world's fastest growing, with 171.854 million cellphone subscribers in January 2021. Over 80% of Bangladesh's export earnings come from the garments industry. Other major industries include Shipbuilding in Bangladesh, shipbuilding, pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh, pharmaceuticals, Steel industry in Bangladesh, steel, Electronics industry in Bangladesh, electronics, and Leather industry in Bangladesh, leather goods. Aziz Khan (businessman), Muhammad Aziz Khan became the first person from Bangladesh to be listed as a billionaire by ''Forbes''.
The poverty rate has gone down from 80% in 1971, to 44.2% in 1991, to 12.9% in 2021. The literacy rate stood at 74.66% in 2022. Bangladesh has a labor force of roughly 70 million, which is the world's List of countries by labour force, seventh-largest; with an unemployment rate of 5.2% . The government is setting up 100 special economic zones to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and generate 10 million jobs. The Bangladesh Investment Development Authority (BIDA) and the Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA) have been established to help investors in setting up factories; and to complement the longstanding Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority (BEPZA).
The Bangladeshi taka is the national currency. The service sector accounts for about 51.3% of total GDP and employs 39% of the workforce. The industrial sector accounts for 35.1% of GDP and employs 20.4% of the workforce. The Agriculture in Bangladesh, agriculture sector makes up 13.6% of the economy but is the biggest employment sector, with 40.6% of the workforce. In agriculture, the country is a major producer of Rice production in Bangladesh, rice, List of fishes in Bangladesh, fish, Tea production in Bangladesh, tea, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and jute. Lobsters and shrimps are some of Bangladesh's well known exports.
Bangladesh is gradually transitioning to a green economy. Currently, it has the largest off-grid solar power programme in the world, benefiting 20 million people. An electric car called the ''Palki'' is being developed for production in the country. The government has reduced tariffs for the purchase of electric cars. Biogas is being used to produce organic fertilizer.
Bangladesh continues to have huge untapped reserves of natural gas, particularly in its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. The success ratio of finding gas wells in the country stands at 3:5:1, meaning one commercial deposit is found in every three explored zones. The success ratio is well above the global average. A lack of exploration and decreasing proven reserves have forced Bangladesh to import LNG from abroad, despite having substantially untapped gas reserves. Gas shortages were further exasperated by the Russia-Ukraine War.
The Tourism in Bangladesh, tourism industry is expanding, contributing some 3.02% of total GDP. Bangladesh's international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $391 million. The country has List of World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh, three UNESCO World Heritage Sites (Historic Mosque City of Bagerhat, the Mosque City, Ruins of the Buddhist Vihara at Paharpur, the Buddhist Vihara and the Sundarbans) and five World Heritage Site#Nominating process, tentative-list sites. Activities for tourists include angling, water skiing, river cruising, hiking, rowing (sport), rowing, yachting, and sea bathing. The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) reported in 2019 that the travel and tourism industry in Bangladesh directly generated 1,180,500 jobs in 2018 or 1.9% of the country's total employment. According to the same report, Bangladesh experiences around 125,000 international tourist arrivals per year. Domestic spending generated 97.7 percent of direct travel and tourism gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012.
Bangladesh is the second largest economy in South Asia after India. The country has outpaced India (of which it was a part until 1947) and Pakistan (of which it was a part until 1971) in terms of per capita income. According to the World Bank, "When the newly independent country of Bangladesh was born on December 16, 1971, it was the second poorest country in the world—making the country's transformation over the next 50 years one of the great development stories. Since then, poverty has been cut in half at record speed. Enrolment in primary school is now nearly universal. Hundreds of thousands of women have entered the workforce. Steady progress has been made on maternal and child health. And the country is better buttressed against the destructive forces posed by climate change and natural disasters. Bangladesh's success comprises many moving parts—from investing in human capital to establishing macroeconomic stability. Building on this success, the country is now setting the stage for further economic growth and job creation by ramping up investments in energy, inland connectivity, urban projects, and transport infrastructure, as well as prioritizing climate change adaptation and disaster preparedness on its path toward sustainable growth".
Since 2009, Bangladesh has embarked on a series of List of megaprojects in Bangladesh, megaprojects. The 6.15 km long Padma Bridge was built at a cost of US$3.86 billion. The bridge was the first self-financed megaproject in the country's history. Other megaprojects include the Dhaka Metro, Karnaphuli Tunnel, Dhaka Elevated Expressway and Chittagong Elevated Expressway; as well as the Bangladesh Delta Plan to mitigate the impact of climate change. Overseas remittances from expat Bangladeshis and export earnings from the Bangladesh textile industry have allowed the country to have the second largest List of countries by foreign exchange reserves, foreign-exchange reserves in South Asia. The reserves have boosted the government's spending capacity in spite of tax revenues forming only 7.7% of government revenue. A big chunk of investments have gone into the Electric power, power sector. In 2009, Bangladesh was experiencing daily blackouts several times a day. In 2022, the country achieved 100% electrification. One of the major anti-poverty schemes of the Bangladeshi government is the Ashrayan Project which aims to eradicate homelessness by providing free housing.
The private sector accounts for 80% of GDP in comparison to the dwindling role of state-owned companies. Bangladesh's economy is dominated by family-owned List of companies of Bangladesh, conglomerates and small and medium-sized businesses. Some of the largest publicly-traded companies in Bangladesh include Beximco, BRAC Bank, BSRM, GPH Ispat, Grameenphone, Summit Group, and Square Pharmaceuticals. Capital markets include the Dhaka Stock Exchange and the Chittagong Stock Exchange. Its Telecommunications in Bangladesh, telecommunications industry is one of the world's fastest growing, with 171.854 million cellphone subscribers in January 2021. Over 80% of Bangladesh's export earnings come from the garments industry. Other major industries include Shipbuilding in Bangladesh, shipbuilding, pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh, pharmaceuticals, Steel industry in Bangladesh, steel, Electronics industry in Bangladesh, electronics, and Leather industry in Bangladesh, leather goods. Aziz Khan (businessman), Muhammad Aziz Khan became the first person from Bangladesh to be listed as a billionaire by ''Forbes''.
The poverty rate has gone down from 80% in 1971, to 44.2% in 1991, to 12.9% in 2021. The literacy rate stood at 74.66% in 2022. Bangladesh has a labor force of roughly 70 million, which is the world's List of countries by labour force, seventh-largest; with an unemployment rate of 5.2% . The government is setting up 100 special economic zones to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and generate 10 million jobs. The Bangladesh Investment Development Authority (BIDA) and the Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA) have been established to help investors in setting up factories; and to complement the longstanding Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority (BEPZA).
The Bangladeshi taka is the national currency. The service sector accounts for about 51.3% of total GDP and employs 39% of the workforce. The industrial sector accounts for 35.1% of GDP and employs 20.4% of the workforce. The Agriculture in Bangladesh, agriculture sector makes up 13.6% of the economy but is the biggest employment sector, with 40.6% of the workforce. In agriculture, the country is a major producer of Rice production in Bangladesh, rice, List of fishes in Bangladesh, fish, Tea production in Bangladesh, tea, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and jute. Lobsters and shrimps are some of Bangladesh's well known exports.
Bangladesh is gradually transitioning to a green economy. Currently, it has the largest off-grid solar power programme in the world, benefiting 20 million people. An electric car called the ''Palki'' is being developed for production in the country. The government has reduced tariffs for the purchase of electric cars. Biogas is being used to produce organic fertilizer.
Bangladesh continues to have huge untapped reserves of natural gas, particularly in its maritime territory in the Bay of Bengal. The success ratio of finding gas wells in the country stands at 3:5:1, meaning one commercial deposit is found in every three explored zones. The success ratio is well above the global average. A lack of exploration and decreasing proven reserves have forced Bangladesh to import LNG from abroad, despite having substantially untapped gas reserves. Gas shortages were further exasperated by the Russia-Ukraine War.
The Tourism in Bangladesh, tourism industry is expanding, contributing some 3.02% of total GDP. Bangladesh's international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $391 million. The country has List of World Heritage Sites in Bangladesh, three UNESCO World Heritage Sites (Historic Mosque City of Bagerhat, the Mosque City, Ruins of the Buddhist Vihara at Paharpur, the Buddhist Vihara and the Sundarbans) and five World Heritage Site#Nominating process, tentative-list sites. Activities for tourists include angling, water skiing, river cruising, hiking, rowing (sport), rowing, yachting, and sea bathing. The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) reported in 2019 that the travel and tourism industry in Bangladesh directly generated 1,180,500 jobs in 2018 or 1.9% of the country's total employment. According to the same report, Bangladesh experiences around 125,000 international tourist arrivals per year. Domestic spending generated 97.7 percent of direct travel and tourism gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012.
Electricity sector
While List of government-owned companies of Bangladesh, government-owned companies in Bangladesh generate nearly half of Bangladesh's electricity, privately-owned companies like the Summit Group and Orion Group are playing an increasingly important role in both generating electricity, and supplying machinery, reactors, and equipment. Bangladesh increased electricity production from 5 gigawatts in 2009 to 25.5 gigawatts in 2022. It plans to produce 50 gigawatts by 2041. U.S. companies like Chevron Corporation, Chevron and General Electric supply around 55% of Bangladesh's domestic natural gas production and are among the largest investors in power projects. 80% of Bangladesh's installed gas-fired power generation capacity comes from turbines manufactured in the United States. On 4 October 2022, the national grid collapsed and plunged the whole country into a nationwide blackout. The grid resumed operations after eight hours. The government's investigation focused on technical failure, negligence, and possible sabotage. The investigation found that grid capacity has not kept up with the expansion of electricity generation and the opening of new power plants. Gas shortages were also to blame, including the lack of new gas sources and insufficient gas pipeline infrastructure. There was a shortage of natural gas because of the 2021–present global energy crisis as 77 natural gas power plants had insufficient fuel to meet demand. The electricity sector in Bangladesh is heavily reliant on natural gas. Gas shortages forced the government to import Liquified natural gas, LNG from abroad. As a result, Texas-based Excelerate Energy opened Bangladesh's first floating LNG terminal in 2018 off the coast of Maheshkhali Island. The Summit LNG Terminal was opened in 2019. The Government of Bangladesh has subsidized LNG imports worth several billion dollars. Since October 2021, Bangladesh imported LNG for US$30-37 per million British thermal unit, Btu which is 10 times the price it paid in May 2020. The government stopped buying spot price LNG in June 2022. The country's forex reserves declined due to surging fuel imports. Bangladesh imported 30% of its LNG on the spot price market in 2022, down from 40% in 2021. Bangladesh continues to trade in LNG on the futures exchange markets.Demographics
According to the 2022 Census of Bangladesh, 2022 Census, Bangladesh has a population of 165.1 million, and is the List of countries by population, eighth-most-populous country in the world, the List of Asian countries by population, fifth-most populous country in Asia, and the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated large country in the world, with a headline population density of 1,265 people/km2 . Its total fertility rate (TFR), once among the highest in the world, has experienced a dramatic decline, from 5.5 in 1985, to 3.7 in 1995, all the way down to 2.0 in 2020, which is below the sub-replacement fertility of 2.1; due to the government promoting birth control since the 1980s and increased education attainment of females. The vast majority of Bangladeshis live in rural areas, with only 39% of the population living in urban areas . It has a median age of roughly 28 years, and its population is relatively young, with 26% of the total population aged 14 or younger, and merely 5% aged 65 and above. Bangladesh is an List of countries ranked by ethnic and cultural diversity level, ethnically and culturally homogeneous society, as Bengali people, Bengalis form 99% of the population. The Adivasi population includes the Chakma people, Chakmas, Marma people, Marmas, Santhal people, Santhals, Mru people (Mrucha), Mros, Tanchangya people, Tanchangyas, Bawm people, Bawms, Tripuri people, Tripuris, Khasi people, Khasis, Khumi people, Khumis, Kuki people, Kukis, Garo people, Garos, and Bisnupriya Manipuri people, Bisnupriya Manipuris. The Chittagong Hill Tracts region experienced unrest and an Chittagong Hill Tracts conflict, insurgency from 1975 to 1997 in an autonomy movement by its indigenous people. Although a peace accord was signed in 1997, the region remains militarised. Urdu-speaking stranded Pakistanis were given citizenship by the Supreme Court in 2008. Bangladesh also hosts over 700,000 Rohingya refugees since 2017, giving it one of the largest refugee populations in the world.Urban centres
Dhaka is Bangladesh's capital and largest city and is overseen by two city corporations who manage between them the northern and southern part of the city. There are 12 List of City Corporations of Bangladesh, city corporations which hold mayoral elections: Dhaka South, Dhaka North, Chittagong, Comilla, Khulna, Mymensingh,Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of the Sylhet Division. Located on the north bank of the Surma River at the eastern tip of Bengal, Sylhet has a subtropical climate an ...
, Rajshahi, Barisal, Rangpur, Bangladesh, Rangpur, Gazipur, Dhaka Division, Gazipur and Narayanganj. Mayors are elected for five-year terms. Altogether there are 506 urban centres in Bangladesh among which 43 cities have a population of more than 100,000.
Language
 The official and predominant language of Bangladesh is
The official and predominant language of Bangladesh is Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, which is spoken by more than 98% of the population as their first language, native language. It is among the easternmost branches of the Indo-European language family, and is a part of the Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, which developed between the 10th and 13th centuries. Bengali is described as a dialect continuum where there are various Bengali dialects, dialects spoken throughout the country. There is a diglossia in which much of the population are able to understand or speak Standard Colloquial Bengali and in their regional dialect, such as Chittagonian language, Chittagonian, Sylheti language, Sylheti and which some linguists consider as separate languages; noted for their Arabic, Arab-Persian language, Persian influences.
English language, English plays an important role in Bangladesh's judicial and educational affairs, due to the country's history as part of the British Empire. It is widely spoken and commonly understood, and is taught as a compulsory subject in all List of schools in Bangladesh, schools, List of colleges in Bangladesh, colleges and List of universities in Bangladesh, universities; while the English-medium educational system is widely attended. Tribal languages, although increasingly endangered, include the Chakma language, another native Eastern Indo-Aryan language, spoken by the Chakma people. Others include Garo language, Garo, Meitei language, Meitei, Kokborok and Rakhine language, Rakhine. Among the Austroasiatic languages, the most spoken is the Santali language, native to the Santal people. The Stranded Pakistanis in Bangladesh, stranded Pakistanis and some sections of the Dhakaiyas, Old Dhakaites often use Urdu as their native tongue, although the usage of the latter remains highly reproached.
Religion
 Bangladesh was constitutionally proclaimed as the first secular state of South Asia in 1972. It grants freedom of religion and claims to be "secular in practise", while establishing Islam as the state religion. The constitution bans religion-based politics and discrimination, and proclaims equal recognition of people adhering to all faiths. Islam in Bangladesh, Islam is the largest religion across the country, being followed by about 91% of the population. The vast majority of Bangladeshi citizens are Bengali Muslims, adhering to Sunni Islam. The country is the third-most populous Muslim-majority state in the world, and has the fourth-largest overall Muslim population.
Hinduism in Bangladesh, Hinduism is followed by 7.95% of the population, mainly by the Bengali Hindus, who form the country's second-largest religious group and the third-largest Hindu community globally; after those in India and Nepal. Buddhism in Bangladesh, Buddhism is the third-largest religion, at 0.61% of the population. Bangladeshi Buddhists are concentrated among the tribal ethnic groups in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. At the same time, coastal Chittagong is home to many Bengali Buddhists. Christianity is the fourth-largest religion, at 0.3%, followed mainly by a small Bengali Christians, Bengali Christian minority.
Bangladesh was constitutionally proclaimed as the first secular state of South Asia in 1972. It grants freedom of religion and claims to be "secular in practise", while establishing Islam as the state religion. The constitution bans religion-based politics and discrimination, and proclaims equal recognition of people adhering to all faiths. Islam in Bangladesh, Islam is the largest religion across the country, being followed by about 91% of the population. The vast majority of Bangladeshi citizens are Bengali Muslims, adhering to Sunni Islam. The country is the third-most populous Muslim-majority state in the world, and has the fourth-largest overall Muslim population.
Hinduism in Bangladesh, Hinduism is followed by 7.95% of the population, mainly by the Bengali Hindus, who form the country's second-largest religious group and the third-largest Hindu community globally; after those in India and Nepal. Buddhism in Bangladesh, Buddhism is the third-largest religion, at 0.61% of the population. Bangladeshi Buddhists are concentrated among the tribal ethnic groups in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. At the same time, coastal Chittagong is home to many Bengali Buddhists. Christianity is the fourth-largest religion, at 0.3%, followed mainly by a small Bengali Christians, Bengali Christian minority.
Education
 Article (17) of the constitution states that all children shall receive free and compulsory education. Education in Bangladesh is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Bangladesh), Ministry of Education. The Ministry of Primary and Mass Education is responsible for implementing policy for primary education and state-funded schools at a local level. Primary and secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, and is financed by the state and free of charge in public schools. Bangladesh has a literacy rate of 74.7% percent as of 2019: 77.4% for males and 71.9% for females. The country's educational system is three-tiered and heavily subsidised, with the government operating many schools at the primary, secondary and higher secondary levels and subsidising many private schools. In the tertiary education sector, the Bangladeshi government funds over 45 state universities through the University Grants Commission (Bangladesh), University Grants Commission (UGC), created by Presidential Order 10 in 1973.
The education system is divided into five levels: primary (first to fifth grade), junior secondary (sixth to eighth grade), secondary (ninth and tenth grade), higher secondary (11th and 12th grade), and tertiary. Five years of secondary education (including junior secondary) ends with a Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. Since 2009, the Primary Education Closing (PEC) examination has also been introduced. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to secondary or matriculation training, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to three years of junior secondary education, culminating in the Junior School Certificate (JSC) examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of secondary education, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of higher secondary education, culminating in the Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSC) examination.
Universities in Bangladesh are of three general types: public (government-owned and subsidised), private (privately owned universities) and international (operated and funded by international organisations). The country has 47 public, 105 private and two international List of universities in Bangladesh, universities; Bangladesh National University has the largest enrolment, and the University of Dhaka (established in 1921) is the oldest. University of Chittagong, established in 1966, has the largest campus among all universities in Bangladesh. Medical education is provided by 29 government and private List of medical colleges in Bangladesh, medical colleges. All medical colleges are affiliated with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Article (17) of the constitution states that all children shall receive free and compulsory education. Education in Bangladesh is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Bangladesh), Ministry of Education. The Ministry of Primary and Mass Education is responsible for implementing policy for primary education and state-funded schools at a local level. Primary and secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, and is financed by the state and free of charge in public schools. Bangladesh has a literacy rate of 74.7% percent as of 2019: 77.4% for males and 71.9% for females. The country's educational system is three-tiered and heavily subsidised, with the government operating many schools at the primary, secondary and higher secondary levels and subsidising many private schools. In the tertiary education sector, the Bangladeshi government funds over 45 state universities through the University Grants Commission (Bangladesh), University Grants Commission (UGC), created by Presidential Order 10 in 1973.
The education system is divided into five levels: primary (first to fifth grade), junior secondary (sixth to eighth grade), secondary (ninth and tenth grade), higher secondary (11th and 12th grade), and tertiary. Five years of secondary education (including junior secondary) ends with a Secondary School Certificate (SSC) examination. Since 2009, the Primary Education Closing (PEC) examination has also been introduced. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to secondary or matriculation training, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass the PEC examination proceed to three years of junior secondary education, culminating in the Junior School Certificate (JSC) examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of secondary education, culminating in the SSC examination. Students who pass this examination proceed to two years of higher secondary education, culminating in the Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSC) examination.
Universities in Bangladesh are of three general types: public (government-owned and subsidised), private (privately owned universities) and international (operated and funded by international organisations). The country has 47 public, 105 private and two international List of universities in Bangladesh, universities; Bangladesh National University has the largest enrolment, and the University of Dhaka (established in 1921) is the oldest. University of Chittagong, established in 1966, has the largest campus among all universities in Bangladesh. Medical education is provided by 29 government and private List of medical colleges in Bangladesh, medical colleges. All medical colleges are affiliated with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Health
Culture
Visual arts
 The recorded history of art in Bangladesh can be traced to the 3rd century BCE, when terracotta sculptures were made in the region. In classical antiquity, a notable sculptural Hindu, Jain and Buddhist art developed in the Pala Empire and the Sena dynasty. Islamic art has evolved since the 14th century. The architecture of the Bengal Sultanate saw a distinct style of domed mosques with complex niche pillars that had no minarets.
The recorded history of art in Bangladesh can be traced to the 3rd century BCE, when terracotta sculptures were made in the region. In classical antiquity, a notable sculptural Hindu, Jain and Buddhist art developed in the Pala Empire and the Sena dynasty. Islamic art has evolved since the 14th century. The architecture of the Bengal Sultanate saw a distinct style of domed mosques with complex niche pillars that had no minarets. Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
's most celebrated artistic tradition was the weaving of Jamdani Motif (textile arts), motifs on fine muslin, which is now classified by UNESCO as an intangible cultural heritage. Jamdani motifs were similar to Iranian textile art (buta motifs) and Western textile art (Paisley (design), paisley). The Jamdani weavers in Dhaka received imperial patronage. Ivory and brass were also widely used in Mughal art. Pottery is widely used in Bengali culture.
The modern art movement in Bangladesh took shape during the 1950s, particularly with the pioneering works of Zainul Abedin. East Bengal developed its own modernist painting and sculpture traditions, which were distinct from the art movements in West Bengal. The Art Institute Dhaka has been an important centre for visual art in the region. Its annual Mangal Shobhajatra, Bengali New Year parade was enlisted as an intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO in 2016.
Modern Bangladesh has produced many of South Asia's leading painters, including SM Sultan, Mohammad Kibria, Shahabuddin Ahmed (artist), Shahabuddin Ahmed, Kanak Chanpa Chakma, Kafil Ahmed, Saifuddin Ahmed, Qayyum Chowdhury, Rashid Choudhury, Quamrul Hassan, Rafiqun Nabi and Syed Jahangir, among others. Novera Ahmed and Nitun Kundu were the country's pioneers of modernist sculpture.
In recent times, photography as a medium of art has become popular. Biennial Chobi Mela is considered the largest photography festival in Asia.
Literature
 The oldest evidence of writing in Bangladesh is the Mahasthan Brahmi Inscription, which dates back to the 3rd century BCE. In the Gupta Empire, Sanskrit literature thrived in the region. Bengali developed from Sanskrit and Magadhi Prakrit in the 8th to 10th century. Bengali literature is a millennium-old tradition; the Charyapadas are the earliest examples of Bengali poetry. Sufi spiritualism inspired many
The oldest evidence of writing in Bangladesh is the Mahasthan Brahmi Inscription, which dates back to the 3rd century BCE. In the Gupta Empire, Sanskrit literature thrived in the region. Bengali developed from Sanskrit and Magadhi Prakrit in the 8th to 10th century. Bengali literature is a millennium-old tradition; the Charyapadas are the earliest examples of Bengali poetry. Sufi spiritualism inspired many Bengali Muslim
Bengali Muslims ( bn, বাঙালি মুসলমান; ) are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the sec ...
writers. During the Bengal Sultanate, medieval Bengali writers were influenced by Arabic literature, Arabic and Persian literature, Persian works. Sultans of Bengal patronized Bengali literature. Examples include the writings of Maladhar Basu, Bipradas Pipilai, Vijay Gupta (poet), Vijay Gupta and Yasoraj Khan. The Chandidas are the notable lyric poets from the early Medieval Age. Alaol, Syed Alaol was the bard of middle Bengali literature. The Bengal Renaissance shaped modern Bengali literature, including novels, short stories and Bengali science fiction, science fiction. Rabindranath Tagore was the first non-European laureate of the Nobel Prize in Literature and is described as the Bengali Shakespeare. Kazi Nazrul Islam
Kazi Nazrul Islam ( bn, কাজী নজরুল ইসলাম, ; 24 May 1899 – 29 August 1976) was a Bengali poet, Bengali literature, writer, Bangladeshi music, musician, and is the national poet of Bangladesh. Nazrul is regarded as one ...
was a revolutionary poet who espoused political rebellion against colonialism and fascism. Begum Rokeya is regarded as the pioneer feminist writer of Bangladesh. Other renaissance icons included Michael Madhusudan Dutt and Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay.
The writer Syed Mujtaba Ali is noted for his cosmopolitan Bengali worldview. Jasimuddin was a renowned pastoral poet. Shamsur Rahman (poet), Shamsur Rahman and Al Mahmud are considered two of the greatest Bengali poets to have emerged in the 20th century. Farrukh Ahmad, Sufia Kamal, Syed Ali Ahsan, Ahsan Habib, Abul Hussain, Shahid Qadri, Fazal Shahabuddin, Abu Zafar Obaidullah, Omar Ali (poet), Omar Ali, Al Mujahidi, Syed Shamsul Huq, Nirmalendu Goon, Abid Azad, Hasan Hafizur Rahman and Abdul Hye Sikder are important figures of modern Bangladeshi poetry. Ahmed Sofa is regarded as the most important Bangladeshi intellectual in the post-independence era. Humayun Ahmed was a popular writer of modern Bangladeshi magical realism and science fiction. Notable writers of Bangladeshi fictions include Mir Mosharraf Hossain, Akhteruzzaman Elias, Alauddin Al Azad, Shahidul Zahir, Rashid Karim, Mahmudul Haque, Syed Waliullah, Shahidullah Kaiser, Shawkat Osman, Selina Hossain, Shahed Ali, Razia Khan, Anisul Hoque, and Abdul Mannan Syed.
The annual Ekushey Book Fair and Hay Festival Dhaka, Dhaka Literature Festival, organised by the Bangla Academy, are among the largest literary festivals in South Asia.
Women
 Although , several women occupied major political office in Bangladesh. Its women continue to live under a patriarchal social regime where violence is common.Whispers to Voices: Gender and Social Transformation in Bangladesh
Although , several women occupied major political office in Bangladesh. Its women continue to live under a patriarchal social regime where violence is common.Whispers to Voices: Gender and Social Transformation in BangladeshWorld Bank.org 2008 Whereas in India and Pakistan women participate less in the workforce as their education increases, the reverse is the case in Bangladesh. Bengal has a long history of feminist activism dating back to the 19th century. Begum Rokeya and Nawab Faizunnesa, Faizunnessa Chowdhurani played an important role in emancipating Bengali Muslim women from purdah, before the country's division, as well as promoting girls' education. Several women were elected to the Bengal Legislative Assembly in the British Raj. The first women's magazine, ''Begum (magazine), Begum'', was published in 1948. In 2008, Bangladeshi female workforce participation stood at 26%. Women dominate blue collar jobs in the Bangladeshi garment industry. Agriculture, social services, healthcare and education are also major occupations for Bangladeshi women, while their employment in White-collar worker, white collar positions has steadily increased.
Architecture
 The architectural traditions of Bangladesh have a 2,500-year-old heritage. Terracotta architecture is a distinct feature of Bengal. Pre-Islamic Bengali architecture reached its pinnacle in the Pala Empire, when the Pala School of Sculptural Art established grand structures such as the Somapura Mahavihara. Islamic architecture began developing under the Bengal Sultanate, when local terracotta styles influenced medieval mosque construction.
The Sixty Dome Mosque was the largest medieval mosque built in Bangladesh and is a fine example of Turkic-Bengali architecture. The Mughal architecture, Mughal style replaced indigenous architecture when Bengal became a province of the Mughal Empire and influenced urban housing development. The Kantajew Temple and Dhakeshwari Temple are excellent examples of late medieval Hindu temple architecture. Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, based on Indo-Islamic styles, flourished during the British period. The zamindar gentry in Bangladesh built numerous Indo-Saracenic palaces and country mansions, such as the Ahsan Manzil, Tajhat Palace, Uttara Gonobhaban, Dighapatia Palace, Puthia Rajbari and Natore Rajbari.
Bengali vernacular architecture is noted for pioneering the bungalow. Bangladeshi villages consist of thatched roofed houses made of natural materials like mud, straw, wood and bamboo. In modern times, village bungalows are increasingly made of tin.
Muzharul Islam was the pioneer of Bangladeshi modern architecture. His varied works set the course of modern architectural practice in the country. Islam brought leading global architects, including Louis Kahn, Richard Neutra, Stanley Tigerman, Paul Rudolph (architect), Paul Rudolph, Robert Boughey and Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis, Konstantinos Doxiadis, to work in erstwhile East Pakistan. Louis Kahn was chosen to design the National Parliament Complex in Sher-e-Bangla Nagar. Kahn's monumental designs, combining regional red brick aesthetics, his own concrete and marble brutalism and the use of lakes to represent Bengali geography, are regarded as one of the masterpieces of the 20th century. In more recent times, award-winning architects like Rafiq Azam have set the course of contemporary architecture by adopting influences from the works of Islam and Kahn.
The architectural traditions of Bangladesh have a 2,500-year-old heritage. Terracotta architecture is a distinct feature of Bengal. Pre-Islamic Bengali architecture reached its pinnacle in the Pala Empire, when the Pala School of Sculptural Art established grand structures such as the Somapura Mahavihara. Islamic architecture began developing under the Bengal Sultanate, when local terracotta styles influenced medieval mosque construction.
The Sixty Dome Mosque was the largest medieval mosque built in Bangladesh and is a fine example of Turkic-Bengali architecture. The Mughal architecture, Mughal style replaced indigenous architecture when Bengal became a province of the Mughal Empire and influenced urban housing development. The Kantajew Temple and Dhakeshwari Temple are excellent examples of late medieval Hindu temple architecture. Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, based on Indo-Islamic styles, flourished during the British period. The zamindar gentry in Bangladesh built numerous Indo-Saracenic palaces and country mansions, such as the Ahsan Manzil, Tajhat Palace, Uttara Gonobhaban, Dighapatia Palace, Puthia Rajbari and Natore Rajbari.
Bengali vernacular architecture is noted for pioneering the bungalow. Bangladeshi villages consist of thatched roofed houses made of natural materials like mud, straw, wood and bamboo. In modern times, village bungalows are increasingly made of tin.
Muzharul Islam was the pioneer of Bangladeshi modern architecture. His varied works set the course of modern architectural practice in the country. Islam brought leading global architects, including Louis Kahn, Richard Neutra, Stanley Tigerman, Paul Rudolph (architect), Paul Rudolph, Robert Boughey and Konstantinos Apostolos Doxiadis, Konstantinos Doxiadis, to work in erstwhile East Pakistan. Louis Kahn was chosen to design the National Parliament Complex in Sher-e-Bangla Nagar. Kahn's monumental designs, combining regional red brick aesthetics, his own concrete and marble brutalism and the use of lakes to represent Bengali geography, are regarded as one of the masterpieces of the 20th century. In more recent times, award-winning architects like Rafiq Azam have set the course of contemporary architecture by adopting influences from the works of Islam and Kahn.
Performing arts
 Theatre in Bangladesh includes various forms with a history dating back to the 4th century CE. It includes narrative forms, song and dance forms, supra-personae forms, performances with scroll paintings, puppet theatre and processional forms. The Jatra (theatre), Jatra is the most popular form of Bengali folk theatre.
The dance traditions of Bangladesh include indigenous tribal and Bengali dance forms, as well as classical Indian dances, including the Kathak, Odissi and Manipuri dances.
The music of Bangladesh features the
Theatre in Bangladesh includes various forms with a history dating back to the 4th century CE. It includes narrative forms, song and dance forms, supra-personae forms, performances with scroll paintings, puppet theatre and processional forms. The Jatra (theatre), Jatra is the most popular form of Bengali folk theatre.
The dance traditions of Bangladesh include indigenous tribal and Bengali dance forms, as well as classical Indian dances, including the Kathak, Odissi and Manipuri dances.
The music of Bangladesh features the Baul
The Baul ( bn, বাউল) are a group of mystic minstrels of mixed elements of Sufism, Vaishnavism and Tantra from Bangladesh and the neighboring Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley and Meghalaya. Bauls constitut ...
Mysticism, mystical tradition, listed by UNESCO as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Lalon, Fakir Lalon Shah popularised Baul
The Baul ( bn, বাউল) are a group of mystic minstrels of mixed elements of Sufism, Vaishnavism and Tantra from Bangladesh and the neighboring Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley and Meghalaya. Bauls constitut ...
music in the country in the 18th century and it has since been one of the most popular music genera in the country since then. Most modern Bauls are devoted to Lalon Shah. Numerous lyric-based musical traditions, varying from one region to the next, exist, including Gombhira, Bhatiali and Bhawaiya. Folk music is accompanied by a one-stringed instrument known as the ektara. Other instruments include the dotara, dhol, flute, and tabla. Bengali classical music includes Tagore songs and Nazrul geeti, Nazrul Sangeet. Bangladesh has a rich tradition of Indian classical music, which uses instruments like the sitar, tabla, sarod and santoor. Sabina Yasmin and Runa Laila are considered the leading playback singers in the modern time, while musicians such as Ayub Bachchu and James (musician), James are credited with popularising rock music in Bangladesh.
Textiles
 The Nakshi Kantha is a centuries-old embroidery tradition for quilts, said to be indigenous to eastern Bengal (i.e. Bangladesh). The sari is the national dress for Bangladeshi women. Mughal Dhaka was renowned for producing the finest Muslin saris, as well as the famed Dhakai and Jamdani, the weaving of which is listed by UNESCO as one of the masterpieces of humanity's intangible cultural heritage. Bangladesh also produces the Rajshahi silk. The shalwar kameez is also widely worn by Bangladeshi women. In urban areas, some women can be seen in western clothing. The kurta and sherwani are the national dress of Bangladeshi men; the lungi and dhoti are worn by them in informal settings. Aside from ethnic wear, domestically tailored suit (clothing), suits and neckties are customarily worn by the country's men in offices, in schools and at social events.
The handloom industry supplies 60–65% of the country's clothing demand. The Bengali ethnic fashion industry has flourished in the changing environment of the fashion world. The retailer Aarong is one of South Asia's most successful ethnic wear brands. The development of the Bangladesh textile industry, which supplies leading international brands, has promoted the local production and retail of modern Western attire. The country now has a number of expanding local brands like Westecs and Yellow. Bangladesh is the world's second-largest garments exporter. Among Bangladesh's fashion designers, Bibi Russell has received international acclaim for her "Fashion for Development" shows.
The Nakshi Kantha is a centuries-old embroidery tradition for quilts, said to be indigenous to eastern Bengal (i.e. Bangladesh). The sari is the national dress for Bangladeshi women. Mughal Dhaka was renowned for producing the finest Muslin saris, as well as the famed Dhakai and Jamdani, the weaving of which is listed by UNESCO as one of the masterpieces of humanity's intangible cultural heritage. Bangladesh also produces the Rajshahi silk. The shalwar kameez is also widely worn by Bangladeshi women. In urban areas, some women can be seen in western clothing. The kurta and sherwani are the national dress of Bangladeshi men; the lungi and dhoti are worn by them in informal settings. Aside from ethnic wear, domestically tailored suit (clothing), suits and neckties are customarily worn by the country's men in offices, in schools and at social events.
The handloom industry supplies 60–65% of the country's clothing demand. The Bengali ethnic fashion industry has flourished in the changing environment of the fashion world. The retailer Aarong is one of South Asia's most successful ethnic wear brands. The development of the Bangladesh textile industry, which supplies leading international brands, has promoted the local production and retail of modern Western attire. The country now has a number of expanding local brands like Westecs and Yellow. Bangladesh is the world's second-largest garments exporter. Among Bangladesh's fashion designers, Bibi Russell has received international acclaim for her "Fashion for Development" shows.
Cuisine
 Bangladeshi cuisine, formed by its geographic location and climate, is rich and varied; sharing its culinary heritage with the neighbouring Indian state of West Bengal. White rice is the staple, and along with fish, forms the culinary base. Varieties of leaf vegetables, potatoes, gourds and lentils (dal) also play an important role. Curry, Curries of beef, mutton, chicken and duck are commonly consumed, along with multiple types of Bhurta, bhortas, ''bhajis'' and ''torkaris''. Mughal-influenced dishes include kormas, kalias, biryanis, pilaf, pulaos, Tahri (dish), teharis and khichuris. Among the various spices, turmeric, fenugreek, nigella, coriander, anise, cardamom and chili powder are widely used; a famous spice mix is the panch phoron. Among the condiments and herbs used, red onions, Chili pepper, green chillies, garlic, ginger, cilantro, and Mentha, mint stand out. Coconut milk, Mustard (condiment), mustard paste, mustard seeds, mustard oil, ghee, South Asian pickle, achars and chutneys are also widely used in the cuisine.
Fish is the main source of protein, often enjoyed with its roe. The hilsa is the national fish and immensely popular, a famous dish is shorshe ilish. Rohu, Pangasius pangasius, pangas, and tilapia are also highly consumed. Lobsters, shrimps and dried fish (''shutki'') are also widely consumed, with the chingri malai curry being a famous shrimp dish. In Chittagong, Mezban feasts are a popular tradition, featuring the serving of ''mezbani gosht'', a hot and spicy beef curry. Other famous dishes from the region include kala bhuna. In Sylhet, the ''shatkora'' lemons are used to marinate dishes, a notable one is Beef Hatkhora, beef hatkora. Among the tribal communities in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, cooking with bamboo shoots is popular. Khulna Division, Khulna is renowned for using ''chui jhal'' (piper chaba) in its dishes.
Bangladesh has a vast spread of desserts, including distinctive sweets such as the ''Rasgulla, rôshogolla'', ''Ras malai, roshmalai'', ''chomchom'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sondesh'', ''mishti doi'' and ''Gulab jamun, kalojaam'', and ''Jalebi, jilapi''. Pithas are traditional boiled desserts made with rice or fruits. Halwa is served during religious festivities. Roti, Ruti, naan, paratha, luchi and bakarkhani are the main local breads. Hot milk tea is the most commonly consumed beverage in the country, being the centre of Adda (South Asian), addas. Kebabs are widely popular, particularly seekh kebab, chapli kebab, shami kebab, chicken tikka and shashlik, along with various types of ''chaaps''. Popular street foods include chotpoti, jhal muri and Panipuri, fuchka. The large Bangladeshi diaspora dominate the South Asian restaurant industry in many Western countries, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Bangladeshi cuisine, formed by its geographic location and climate, is rich and varied; sharing its culinary heritage with the neighbouring Indian state of West Bengal. White rice is the staple, and along with fish, forms the culinary base. Varieties of leaf vegetables, potatoes, gourds and lentils (dal) also play an important role. Curry, Curries of beef, mutton, chicken and duck are commonly consumed, along with multiple types of Bhurta, bhortas, ''bhajis'' and ''torkaris''. Mughal-influenced dishes include kormas, kalias, biryanis, pilaf, pulaos, Tahri (dish), teharis and khichuris. Among the various spices, turmeric, fenugreek, nigella, coriander, anise, cardamom and chili powder are widely used; a famous spice mix is the panch phoron. Among the condiments and herbs used, red onions, Chili pepper, green chillies, garlic, ginger, cilantro, and Mentha, mint stand out. Coconut milk, Mustard (condiment), mustard paste, mustard seeds, mustard oil, ghee, South Asian pickle, achars and chutneys are also widely used in the cuisine.
Fish is the main source of protein, often enjoyed with its roe. The hilsa is the national fish and immensely popular, a famous dish is shorshe ilish. Rohu, Pangasius pangasius, pangas, and tilapia are also highly consumed. Lobsters, shrimps and dried fish (''shutki'') are also widely consumed, with the chingri malai curry being a famous shrimp dish. In Chittagong, Mezban feasts are a popular tradition, featuring the serving of ''mezbani gosht'', a hot and spicy beef curry. Other famous dishes from the region include kala bhuna. In Sylhet, the ''shatkora'' lemons are used to marinate dishes, a notable one is Beef Hatkhora, beef hatkora. Among the tribal communities in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, cooking with bamboo shoots is popular. Khulna Division, Khulna is renowned for using ''chui jhal'' (piper chaba) in its dishes.
Bangladesh has a vast spread of desserts, including distinctive sweets such as the ''Rasgulla, rôshogolla'', ''Ras malai, roshmalai'', ''chomchom'', ''Sandesh (confectionery), sondesh'', ''mishti doi'' and ''Gulab jamun, kalojaam'', and ''Jalebi, jilapi''. Pithas are traditional boiled desserts made with rice or fruits. Halwa is served during religious festivities. Roti, Ruti, naan, paratha, luchi and bakarkhani are the main local breads. Hot milk tea is the most commonly consumed beverage in the country, being the centre of Adda (South Asian), addas. Kebabs are widely popular, particularly seekh kebab, chapli kebab, shami kebab, chicken tikka and shashlik, along with various types of ''chaaps''. Popular street foods include chotpoti, jhal muri and Panipuri, fuchka. The large Bangladeshi diaspora dominate the South Asian restaurant industry in many Western countries, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Festivals
 ''Pahela Baishakh'', the Bengali new year, is the major festival of Culture of Bengal, Bengali culture and sees widespread festivities. Of the major holidays celebrated in Bangladesh, only Pahela Baishakh comes without any pre-existing expectations (specific religious identity, culture of gift-giving, etc.) and has become an occasion for celebrating the simpler, rural roots of the Bengal. Other cultural festivals include Nabanna, Nabonno and Poush Parbon, Bengali harvest festivals.
The Muslim festivals of Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, Milad un Nabi, Muharram, Chand Raat, Barat Night, Shab-e-Barat; the Hindu festivals of Durga Puja, Janmashtami and Rath Yatra; the Buddhist festival of Vesak, Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, and the Christian festival of Christmas are Public holidays in Bangladesh, national holidays in Bangladesh and see the most widespread celebrations in the country. The two Eids are celebrated with a long streak of public holidays and give the city-dwellers opportunity to celebrate the festivals with their families outside the city.
Alongside are national days like the remembrance of 21 February 1952 Language Movement Day (declared as International Mother Language Day by UNESCO in 1999), Independence Day (Bangladesh), Independence Day and Victory day of Bangladesh, Victory Day. On Language Movement Day, people congregate at the Shaheed Minar, Dhaka, Shaheed Minar in Dhaka to remember the national heroes of the Bengali Language Movement. Similar gatherings are observed at the National Martyrs' Memorial on Independence Day and Victory Day to remember the national heroes of the
''Pahela Baishakh'', the Bengali new year, is the major festival of Culture of Bengal, Bengali culture and sees widespread festivities. Of the major holidays celebrated in Bangladesh, only Pahela Baishakh comes without any pre-existing expectations (specific religious identity, culture of gift-giving, etc.) and has become an occasion for celebrating the simpler, rural roots of the Bengal. Other cultural festivals include Nabanna, Nabonno and Poush Parbon, Bengali harvest festivals.
The Muslim festivals of Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, Milad un Nabi, Muharram, Chand Raat, Barat Night, Shab-e-Barat; the Hindu festivals of Durga Puja, Janmashtami and Rath Yatra; the Buddhist festival of Vesak, Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, and the Christian festival of Christmas are Public holidays in Bangladesh, national holidays in Bangladesh and see the most widespread celebrations in the country. The two Eids are celebrated with a long streak of public holidays and give the city-dwellers opportunity to celebrate the festivals with their families outside the city.
Alongside are national days like the remembrance of 21 February 1952 Language Movement Day (declared as International Mother Language Day by UNESCO in 1999), Independence Day (Bangladesh), Independence Day and Victory day of Bangladesh, Victory Day. On Language Movement Day, people congregate at the Shaheed Minar, Dhaka, Shaheed Minar in Dhaka to remember the national heroes of the Bengali Language Movement. Similar gatherings are observed at the National Martyrs' Memorial on Independence Day and Victory Day to remember the national heroes of the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
. These occasions are celebrated with public ceremonies, parades, rallies by citizens, political speeches, fairs, concerts, and various other public and private events, celebrating the history and traditions of Bangladesh. TV and radio stations broadcast special programmes and patriotic songs. Many schools and colleges organise fairs, festivals, and concerts that draw the participation of citizens from all levels of Bangladeshi society.
Sports
In rural Bangladesh, several Traditional games of Bangladesh, traditional indigenous sports such as Kabaddi, Boli Khela, Lathi Khela and Nouka Baich remain fairly popular. While Kabaddi is the national sport, cricket is the most popular sport in the country. The Bangladesh national cricket team, national cricket team participated in their first Cricket World Cup in 1999 and the following year was granted Test cricket status. Bangladesh reached the quarter-final of the 2015 Cricket World Cup, the semi-final of the 2017 ICC Champions Trophy and they reached the final of the Asia Cup 3 times – in 2012, 2016 and 2018. In February 2020, the Bangladesh youth national cricket team won the men's 2020 Under-19 Cricket World Cup, Under-19 Cricket World Cup, held in South Africa. This was Bangladesh's first World Cup victory. Women's sports saw significant progress in the 2010s decade in Bangladesh. In 2018, the Bangladesh women's national cricket team won the 2018 Women's Twenty20 Asia Cup defeating India women's national cricket team in the final. Football is a major sport in Bangladesh, and is governed by the Bangladesh Football Federation (BFF). Although football was seen as the most popular sport in the country before the 21st century, success in cricket has overshadowed its past popularity. The first instance of a Bangladesh national football team was the emergence of the Shadhin Bangla Football Team that toured throughoutIndia
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
playing a total of 16 friendly matches to raise international awareness about the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Benga ...
, in 1971. After independence, the national team also participated in the 1980 AFC Asian Cup, becoming only the second South Asian team to do so. Bangladesh's most notable achievements in football include the 2003 South Asian Football Federation Gold Cup, 2003 SAFF Championship and Football at the 1999 South Asian Games, 1999 South Asian Games. The Bangladesh women's national football team has also registered some success at regional level, especially the Under-15 and Under-18 teams. In 2022, the women's team created history by winning the 2022 SAFF Women's Championship.
Bangladesh archers Ety Khatun and Roman Sana won several gold medals winning all the 10 archery events (both individual, and team events) in the 2019 South Asian Games. The National Sports Council regulates 42 sporting federations. Athletics, swimming, archery, boxing, volleyball, weight-lifting and wrestling and different forms of martial arts remain popular. Chess is very popular in Bangladesh. Bangladesh has five grandmasters in chess. Among them, Niaz Murshed was the first grandmaster in South Asia. In 2010, mountain climber Musa Ibrahim became the first Bangladeshi climber to conquer Mount Everest. Wasfia Nazreen is the first Bangladeshi climber to climb the Seven Summits.
Bangladesh hosts a number of international tournaments. Bangabandhu Cup is an international football tournament hosted in the country. Bangladesh hosted the South Asian Games several times. In 2011, Bangladesh co-hosted the ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 with India and Sri Lanka. Bangladesh solely hosted the 2014 ICC World Twenty20 championship. Bangladesh hosted the Asia Cup Cricket Tournament in 2000, 2012, 2014 and 2016.
Media and cinema
 The Bangladeshi press is diverse, outspoken and privately owned. Over 200 newspapers are published in the country. Bangladesh Betar is the state-run radio service. The British Broadcasting Corporation operates the popular BBC Bangla news and current affairs service. Bengali broadcasts from Voice of America are also very popular. Bangladesh Television (BTV) is a state-owned television network. More than 20 privately owned television networks, including several news channels. Freedom of the media remains a major concern due to government attempts at censorship and the harassment of journalists.
The cinema of Bangladesh dates back to 1898 when films began screening at the Crown Theatre in Dhaka. The first bioscope on the subcontinent was established in Dhaka that year. The Dhaka Nawab Family patronised the production of several silent films in the 1920s and 30s. In 1931, the East Bengal Cinematograph Society released the first full-length feature film in Bangladesh, titled the ''Last Kiss''. The first feature film in East Pakistan, ''Mukh O Mukhosh'', was released in 1956. During the 1960s, 25–30 films were produced annually in Dhaka. By the 2000s, Bangladesh produced 80–100 films a year. While the Bangladeshi film industry has achieved limited commercial success, the country has produced notable independent filmmakers. Zahir Raihan was a prominent documentary-maker assassinated in 1971. The late Tareque Masud is regarded as one of Bangladesh's outstanding directors for his critically acclaimed films on social issues. Masud was honoured by FIPRESCI at the 2002 Cannes Film Festival for his film ''Matir Moina, The Clay Bird''. Tanvir Mokammel, Mostofa Sarwar Farooki, Humayun Ahmed, Alamgir Kabir (filmmaker), Alamgir Kabir, and Chashi Nazrul Islam are some of the prominent directors of Bangladeshi cinema. Bangladesh has a very active film society culture. It started in 1963 in Dhaka. Now around 40 Film Societies are active all over Bangladesh. Federation of Film Societies of Bangladesh is the parent organisation of the film society movement of Bangladesh. Active film societies include the Rainbow Film Society, Children's Film Society, Moviyana Film Society and Dhaka University Film Society.
The Bangladeshi press is diverse, outspoken and privately owned. Over 200 newspapers are published in the country. Bangladesh Betar is the state-run radio service. The British Broadcasting Corporation operates the popular BBC Bangla news and current affairs service. Bengali broadcasts from Voice of America are also very popular. Bangladesh Television (BTV) is a state-owned television network. More than 20 privately owned television networks, including several news channels. Freedom of the media remains a major concern due to government attempts at censorship and the harassment of journalists.
The cinema of Bangladesh dates back to 1898 when films began screening at the Crown Theatre in Dhaka. The first bioscope on the subcontinent was established in Dhaka that year. The Dhaka Nawab Family patronised the production of several silent films in the 1920s and 30s. In 1931, the East Bengal Cinematograph Society released the first full-length feature film in Bangladesh, titled the ''Last Kiss''. The first feature film in East Pakistan, ''Mukh O Mukhosh'', was released in 1956. During the 1960s, 25–30 films were produced annually in Dhaka. By the 2000s, Bangladesh produced 80–100 films a year. While the Bangladeshi film industry has achieved limited commercial success, the country has produced notable independent filmmakers. Zahir Raihan was a prominent documentary-maker assassinated in 1971. The late Tareque Masud is regarded as one of Bangladesh's outstanding directors for his critically acclaimed films on social issues. Masud was honoured by FIPRESCI at the 2002 Cannes Film Festival for his film ''Matir Moina, The Clay Bird''. Tanvir Mokammel, Mostofa Sarwar Farooki, Humayun Ahmed, Alamgir Kabir (filmmaker), Alamgir Kabir, and Chashi Nazrul Islam are some of the prominent directors of Bangladeshi cinema. Bangladesh has a very active film society culture. It started in 1963 in Dhaka. Now around 40 Film Societies are active all over Bangladesh. Federation of Film Societies of Bangladesh is the parent organisation of the film society movement of Bangladesh. Active film societies include the Rainbow Film Society, Children's Film Society, Moviyana Film Society and Dhaka University Film Society.
Museums and libraries
The Varendra Research Museum is the oldest museum in Bangladesh. It houses important collections from both the pre-Islamic and Islamic periods, including the sculptures of the Pala-Sena School of Art and the Indus Valley civilisation, and Sanskrit, Arabic, and Persian manuscripts and inscriptions. The Ahsan Manzil, the former residence of the Nawab of Dhaka, is a national museum housing collections from the British Raj. It was the site of the founding conference of the All India Muslim League and hosted many British Viceroys in Dhaka. The Tajhat Palace Museum preserves artefacts of the rich cultural heritage of North Bengal, including Hindu-Buddhist sculptures and Islamic manuscripts. The Mymensingh Museum houses the personal antique collections of Bengali aristocrats in central Bengal. The Ethnological Museum of Chittagong showcases the lifestyle of various tribes in Bangladesh. TheBangladesh National Museum
The Bangladesh National Museum ( bn, বাংলাদেশ জাতীয় জাদুঘর), is the national museum of Bangladesh. The museum is well organized and displays have been housed chronologically in several departments like dep ...
is located in Ramna, Dhaka and has a rich collection of antiquities. The Liberation War Museum documents the Bangladeshi struggle for independence and the 1971 genocide.
In ancient times, manuscripts were written on palm leaves, tree barks, parchment vellum and terracotta plates and preserved at monasteries known as ''viharas''. The Hussain Shahi dynasty established royal libraries during the Bengal Sultanate. Libraries were established in each district of Bengal by the zamindar gentry during the Bengal Renaissance in the 19th century. The trend of establishing libraries continued until the beginning of World War II. In 1854, four major public libraries were opened, including the Bogra Woodburn Library, the Rangpur Public Library, the Jessore Institute Public Library and the Barisal Public Library.
The Northbrook Hall, Northbrook Hall Public Library was established in Dhaka in 1882 in honour of Lord Northbrook, the Governor-General. Other libraries established in the British period included the Victoria Public Library, Natore (1901), the Sirajganj Public Library (1882), the Rajshahi Public Library (1884), the Comilla Birchandra Library (1885), the Shah Makhdum Institute Public Library, Rajshahi (1891), the Noakhali Town Hall Public Library (1896), the Prize Memorial Library, Sylhet (1897), the Chittagong Municipality Public Library (1904) and the Varendra Research Library (1910). The Great Bengal Library Association was formed in 1925. The Central Public Library (Dhaka), Central Public Library of Dhaka was established in 1959. The National Library of Bangladesh was established in 1972. The Bishwo Shahitto Kendro, World Literature Centre, founded by Ramon Magsaysay Award winner Abdullah Abu Sayeed, is noted for operating numerous mobile library, mobile libraries across Bangladesh and was awarded the UNESCO Jon, Amos Comenius Medal.
See also
* Index of Bangladesh-related articles * Outline of BangladeshReferences
Cited sources
* * *Further reading
* Ahmed, Nizam. ''The Parliament of Bangladesh'' (Routledge, 2018). * * * Baxter, Craig. ''Bangladesh: From a nation to a state'' (Routledge, 2018). * * * * * Hasnat, GN Tanjina, Md Alamgir Kabir, and Md Akhter Hossain. "Major environmental issues and problems of South Asia, particularly Bangladesh." ''Handbook of environmental materials management'' (2018): 1-40online
* Iftekhar Iqbal (2010) ''The Bengal Delta: Ecology, State and Social Change, 1840–1943'' (Palgrave Macmillan) * Islam, Saiful, and Md Ziaur Rahman Khan. "A review of the energy sector of Bangladesh." ''Energy Procedia'' 110 (2017): 611–618
online
* Jannuzi, F. Tomasson, and James T. Peach. ''The agrarian structure of Bangladesh: An impediment to development'' (Routledge, 2019). * * * M. Mufakharul Islam (edited) (2004) Socio-Economic History of Bangladesh: essays in memory of Professor Shafiqur Rahman, 1st Edition, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * M. Mufakharul Islam (2007) ''Bengal Agriculture 1920–1946: A Quantitative Study'' (Cambridge University Press), * Prodhan, Mohit. "The educational system in Bangladesh and scope for improvement." ''Journal of International Social Issues'' 4.1 (2016): 11–23
online
* * * Riaz, Ali. ''Bangladesh: A political history since independence'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2016). * * * * Shelley, Israt J., et al. "Rice cultivation in Bangladesh: present scenario, problems, and prospects." ''Journal of International Cooperation for Agricultural Development'' 14.4 (2016): 20–29
online
* Sirajul Islam (edited) (1997) History of Bangladesh 1704–1971(Three Volumes: Vol 1: Political History, Vol 2: Economic History Vol 3: Social and Cultural History), 2nd Edition (Revised New Edition), The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * Sirajul Islam (Chief Editor) (2003) Banglapedia: A National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh.(10 Vols. Set), (written by 1300 scholars & 22 editors) The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, * * * * Van Schendel, Willem. ''A history of Bangladesh'' (Cambridge University Press, 2020). * *
External links
Government *Official Site of Bangladesh Investment Development Authority
General information
Bangladesh
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. *
Bangladesh
from the BBC News
Bangladesh
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * *
Key Development Forecasts for Bangladesh
from International Futures {{Authority control Bangladesh, Bengal Bengali-speaking countries and territories Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Developing 8 Countries member states Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia Least developed countries Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation Member states of the United Nations South Asian countries States and territories established in 1971 1971 establishments in Asia Countries in Asia Geographical articles missing image alternative text