Austronesian Expansion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
, Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
that speak Austronesian languages. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands. The nations and territories predominantly populated by Austronesian-speaking peoples are sometimes known collectively as Austronesia.
Based on the current scientific consensus, they originated from a prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion, from pre- Han Taiwan, at around 1500 to 1000 BCE. Austronesians reached the northernmost Philippines, specifically the Batanes Islands, by around 2200 BCE. Austronesians used sails some time before 2000 BCE. In conjunction with their use of other maritime technologies (notably catamarans, outrigger boats, lashed-lug boat building, and the crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Islan ...
), this enabled their dispersal into the islands of the Indo-Pacific, culminating in the settlement of New Zealand . From 2000 BCE they assimilated (or were assimilated by) the earlier Paleolithic Negrito, and Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
Papuan populations. They reached as far as Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its ne ...
to the east, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
to the west, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
to the south. At the furthest extent, they might have also reached the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
.
Aside from language, Austronesian peoples widely share cultural characteristics, including such traditions and technologies as tattooing
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing p ...
, stilt houses, jade carving, wetland agriculture, and various rock art motifs. They also share domesticated plants and animals that were carried along with the migrations, including rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
, bananas
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
, coconuts, breadfruit, '' Dioscorea'' yams, taro, paper mulberry
The paper mulberry (''Broussonetia papyrifera'', syn. ''Morus papyrifera'' L.) is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae. It is native to Asia,chickens,
 The Spanish philologist Lorenzo Hervás later devoted a large part of his ''Idea dell'universo'' (1778–1787) to the establishment of a
The Spanish philologist Lorenzo Hervás later devoted a large part of his ''Idea dell'universo'' (1778–1787) to the establishment of a 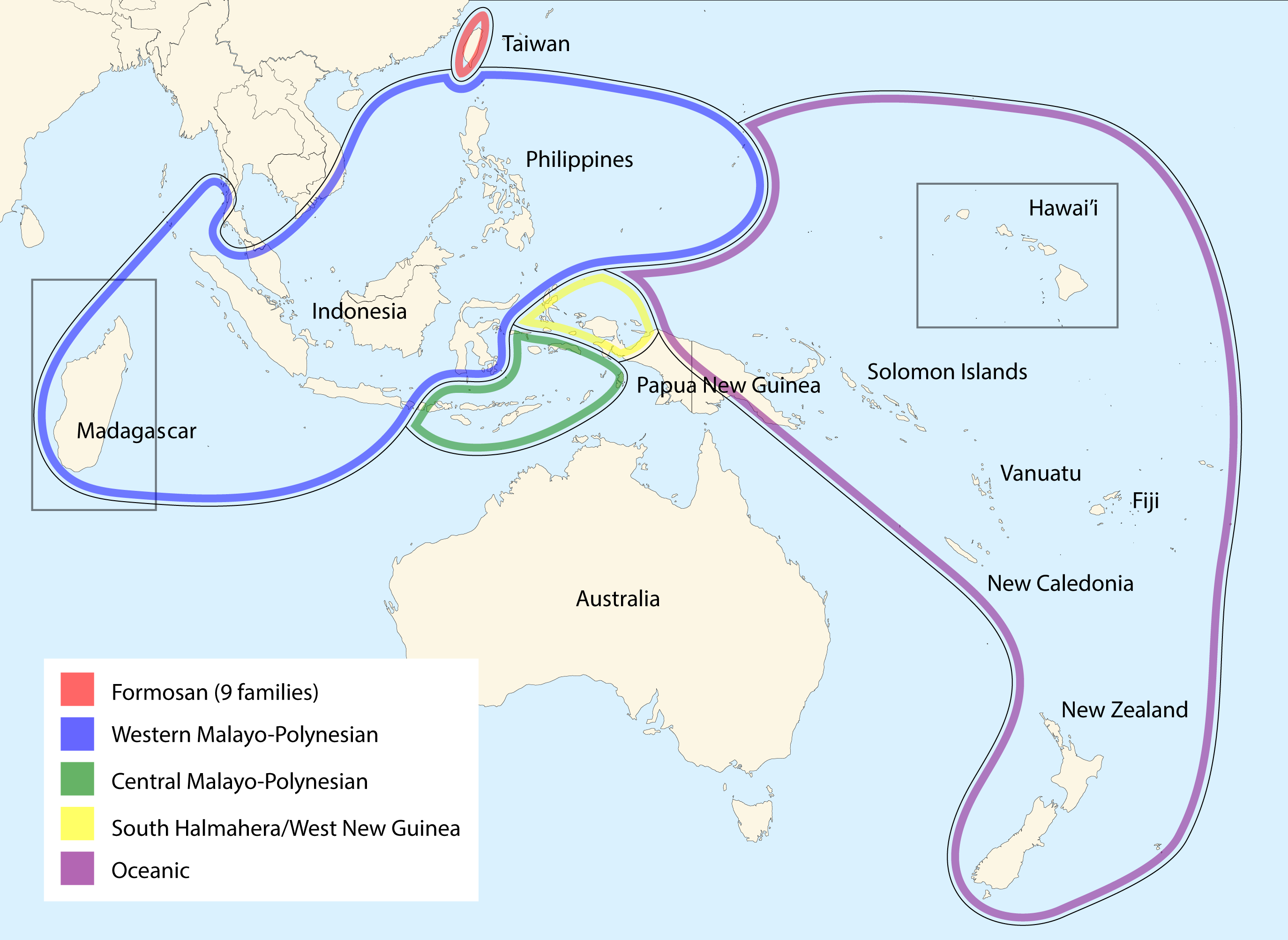 The term "Austronesian", or more accurately "Austronesian-speaking peoples", came to refer the people who speak the languages of the Austronesian
The term "Austronesian", or more accurately "Austronesian-speaking peoples", came to refer the people who speak the languages of the Austronesian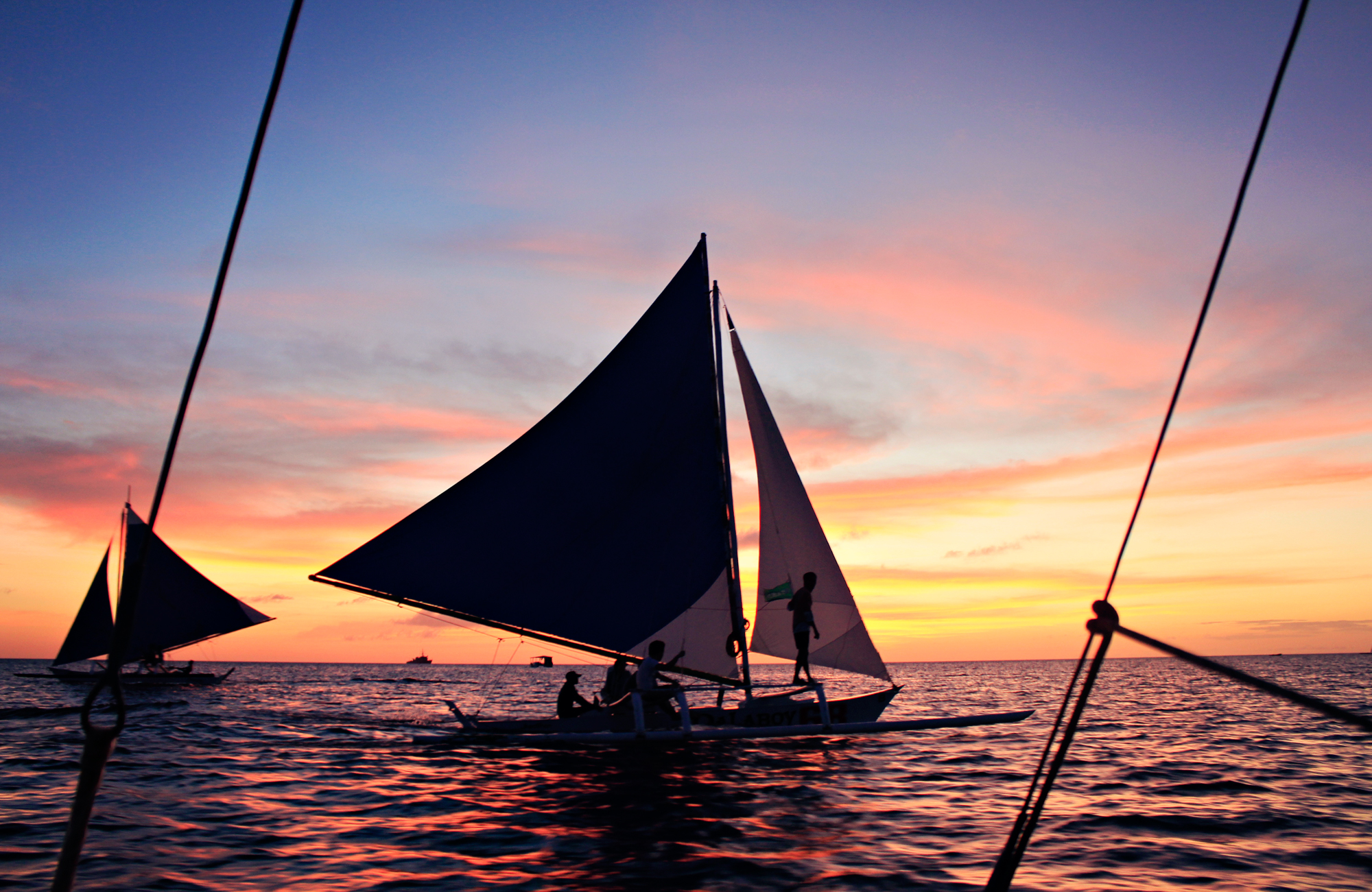  Despite these objections, the general consensus is that the archeological, cultural, genetic, and especially linguistic evidence all separately indicate varying degrees of shared ancestry among Austronesian-speaking peoples that justifies their treatment as a "
Despite these objections, the general consensus is that the archeological, cultural, genetic, and especially linguistic evidence all separately indicate varying degrees of shared ancestry among Austronesian-speaking peoples that justifies their treatment as a "
 It is spoken today by about 386 million people (4.9% of the global population), making it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages with the highest number of speakers are Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, and
It is spoken today by about 386 million people (4.9% of the global population), making it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages with the highest number of speakers are Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, and
 Austronesian peoples include the following groupings by name and geographic location (incomplete):
* Formosan:
Austronesian peoples include the following groupings by name and geographic location (incomplete):
* Formosan:
 These early population groups originally lacked watercraft technology, and thus could only cross narrow interisland seas with primitive floats or rafts (likely bamboo or log rafts) or through accidental means. Especially the deeper waters of the
These early population groups originally lacked watercraft technology, and thus could only cross narrow interisland seas with primitive floats or rafts (likely bamboo or log rafts) or through accidental means. Especially the deeper waters of the  Humans reached the islands in Wallacea as well as the Sahul landmass ( Australia and
Humans reached the islands in Wallacea as well as the Sahul landmass ( Australia and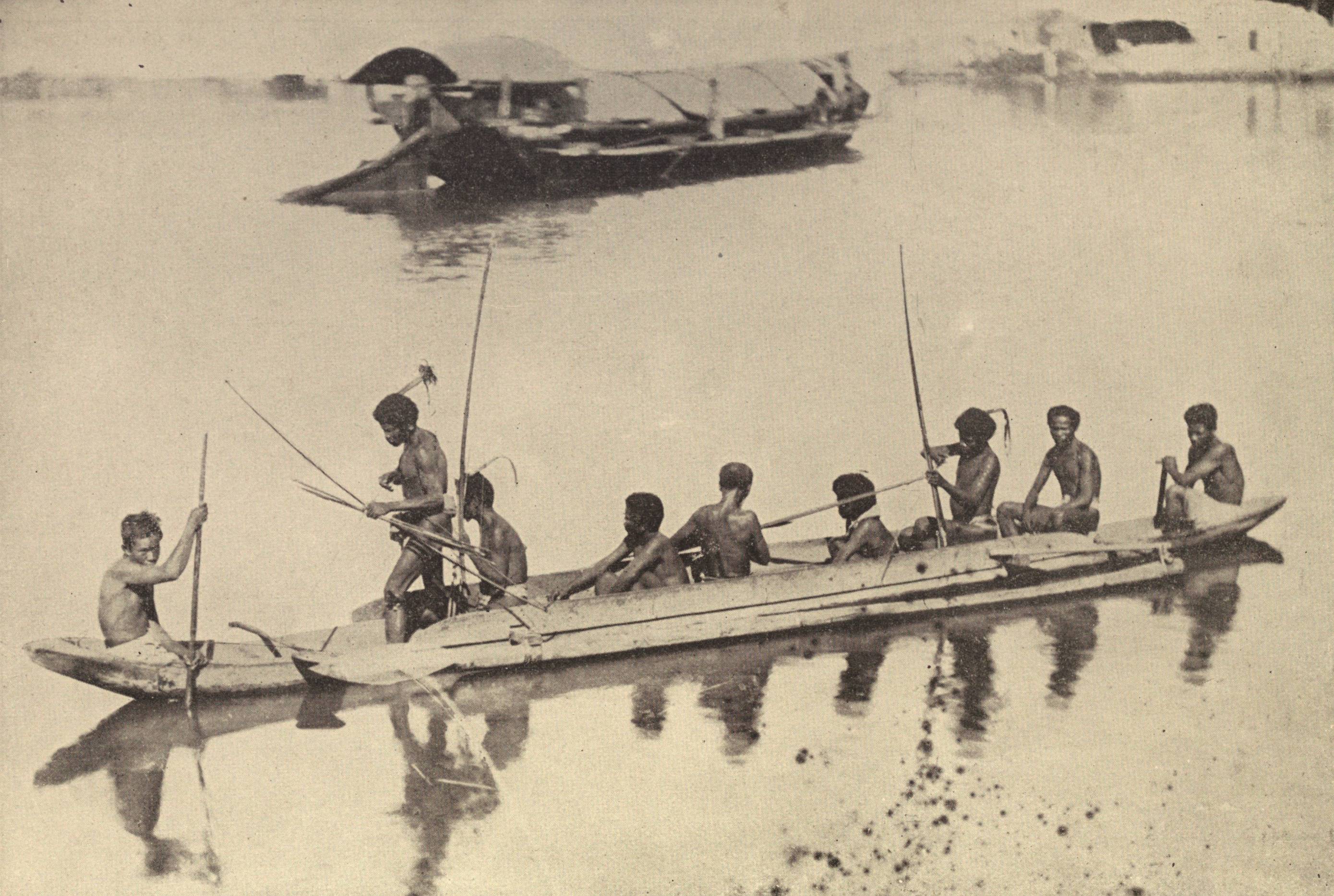  In modern literature, descendants of these groups located in Island Southeast Asia west of Halmahera are usually collectively referred to as " Negritos", while descendants of these groups east of Halmahera (excluding Indigenous Australians) are referred to as "
In modern literature, descendants of these groups located in Island Southeast Asia west of Halmahera are usually collectively referred to as " Negritos", while descendants of these groups east of Halmahera (excluding Indigenous Australians) are referred to as "
 Several authors have also proposed that Kra-Dai speakers may actually be an ancient daughter subgroup of Austronesians that migrated back to the
Several authors have also proposed that Kra-Dai speakers may actually be an ancient daughter subgroup of Austronesians that migrated back to the  The Sino-Austronesian hypothesis, on the other hand, is a relatively new hypothesis by Laurent Sagart, first proposed in 1990. It argues for a north–south linguistic genetic relationship between Chinese and Austronesian. This is based on sound correspondences in the basic vocabulary and morphological parallels. Sagart places special significance in shared vocabulary on cereal crops, citing them as evidence of shared linguistic origin. However, this has largely been rejected by other linguists. The sound correspondences between Old Chinese and Proto-Austronesian can also be explained as a result of the Longshan interaction sphere, when pre-Austronesians from the Yangtze region came into regular contact with Proto-Sinitic speakers in the
The Sino-Austronesian hypothesis, on the other hand, is a relatively new hypothesis by Laurent Sagart, first proposed in 1990. It argues for a north–south linguistic genetic relationship between Chinese and Austronesian. This is based on sound correspondences in the basic vocabulary and morphological parallels. Sagart places special significance in shared vocabulary on cereal crops, citing them as evidence of shared linguistic origin. However, this has largely been rejected by other linguists. The sound correspondences between Old Chinese and Proto-Austronesian can also be explained as a result of the Longshan interaction sphere, when pre-Austronesians from the Yangtze region came into regular contact with Proto-Sinitic speakers in the
Suppose we are wrong about the Austronesian settlement of Taiwan?
'' m.s. Blench considers the Austronesians in Taiwan to have been a melting pot of immigrants from various parts of the coast of Minyue, present-day


 The Austronesian expansion (also called the "Out of Taiwan" model) is a large-scale migration of Austronesians out of Taiwan, occurring around 1500-1000 BCE. Population growth primarily fueled this migration. These first settlers landed in northern Luzon in the archipelago of the Philippines, intermingling with the earlier
The Austronesian expansion (also called the "Out of Taiwan" model) is a large-scale migration of Austronesians out of Taiwan, occurring around 1500-1000 BCE. Population growth primarily fueled this migration. These first settlers landed in northern Luzon in the archipelago of the Philippines, intermingling with the earlier
 By the beginning of the first millennium CE, most of the Austronesian inhabitants in
By the beginning of the first millennium CE, most of the Austronesian inhabitants in
The Austronesian inhabitants of Near Oceania and Remote Oceania were unaffected by this cultural trade and retained their indigenous culture in the Pacific region.
 Sea-going catamaran and outrigger ship technologies were the most important innovations of the Austronesian peoples. They were the first humans with vessels capable of crossing vast distances of water, which enabled them to colonize the Indo-Pacific in prehistoric times. Austronesian groups continue to be the primary users of the outrigger canoes today.
Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamarans evolved from outrigger canoes, but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite.
Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the double-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger, giving way to the single outrigger canoe, then to the reversible single outrigger canoe. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimarans).
This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia tend to favor double outrigger canoes, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking. But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Micronesia,
Sea-going catamaran and outrigger ship technologies were the most important innovations of the Austronesian peoples. They were the first humans with vessels capable of crossing vast distances of water, which enabled them to colonize the Indo-Pacific in prehistoric times. Austronesian groups continue to be the primary users of the outrigger canoes today.
Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamarans evolved from outrigger canoes, but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite.
Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the double-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger, giving way to the single outrigger canoe, then to the reversible single outrigger canoe. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimarans).
This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia tend to favor double outrigger canoes, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking. But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Micronesia,  The ancient Champa of
The ancient Champa of
File:Beinan Taitung Taiwan Aboriginal-Stilt-House-01.jpg, Aboriginal Taiwanese Architecture
File:Philippinen Basilan seezigeuner ph03p42.jpg,
 One branch of the migrations carried pottery to the Marianas Islands at around 1500 BCE, where the earliest archaeological sites have uncovered pottery very similar to those found in the Nagsabaran Site (2000 to 1300 BCE) in Cagayan Valley in the Philippines. This indicates that the northeastern coast of Luzon is the most likely point of origin of the first open-ocean colonizing voyages into the Pacific Islands. Philippine and Marianas red-slipped pottery are both decorated with rows of stamped circles, incised patterns, and tiny delicate punch-marks. While similar red-slipped pottery also exist in the Batanes Islands and
One branch of the migrations carried pottery to the Marianas Islands at around 1500 BCE, where the earliest archaeological sites have uncovered pottery very similar to those found in the Nagsabaran Site (2000 to 1300 BCE) in Cagayan Valley in the Philippines. This indicates that the northeastern coast of Luzon is the most likely point of origin of the first open-ocean colonizing voyages into the Pacific Islands. Philippine and Marianas red-slipped pottery are both decorated with rows of stamped circles, incised patterns, and tiny delicate punch-marks. While similar red-slipped pottery also exist in the Batanes Islands and
File:Jaw harps, flutes, and a slit drum from the Maranao, Molbog, and Sama people (Philippines).jpg, ''Kubing'' jaw harps, flutes, and a ''kagul'' slit drum from the
 The most notable jade products of these regions were the vast amounts of penannular and double-headed earrings and pendants known as ''lingling-o'', primarily produced in the Philippines and the Sa Huỳnh culture of
The most notable jade products of these regions were the vast amounts of penannular and double-headed earrings and pendants known as ''lingling-o'', primarily produced in the Philippines and the Sa Huỳnh culture of
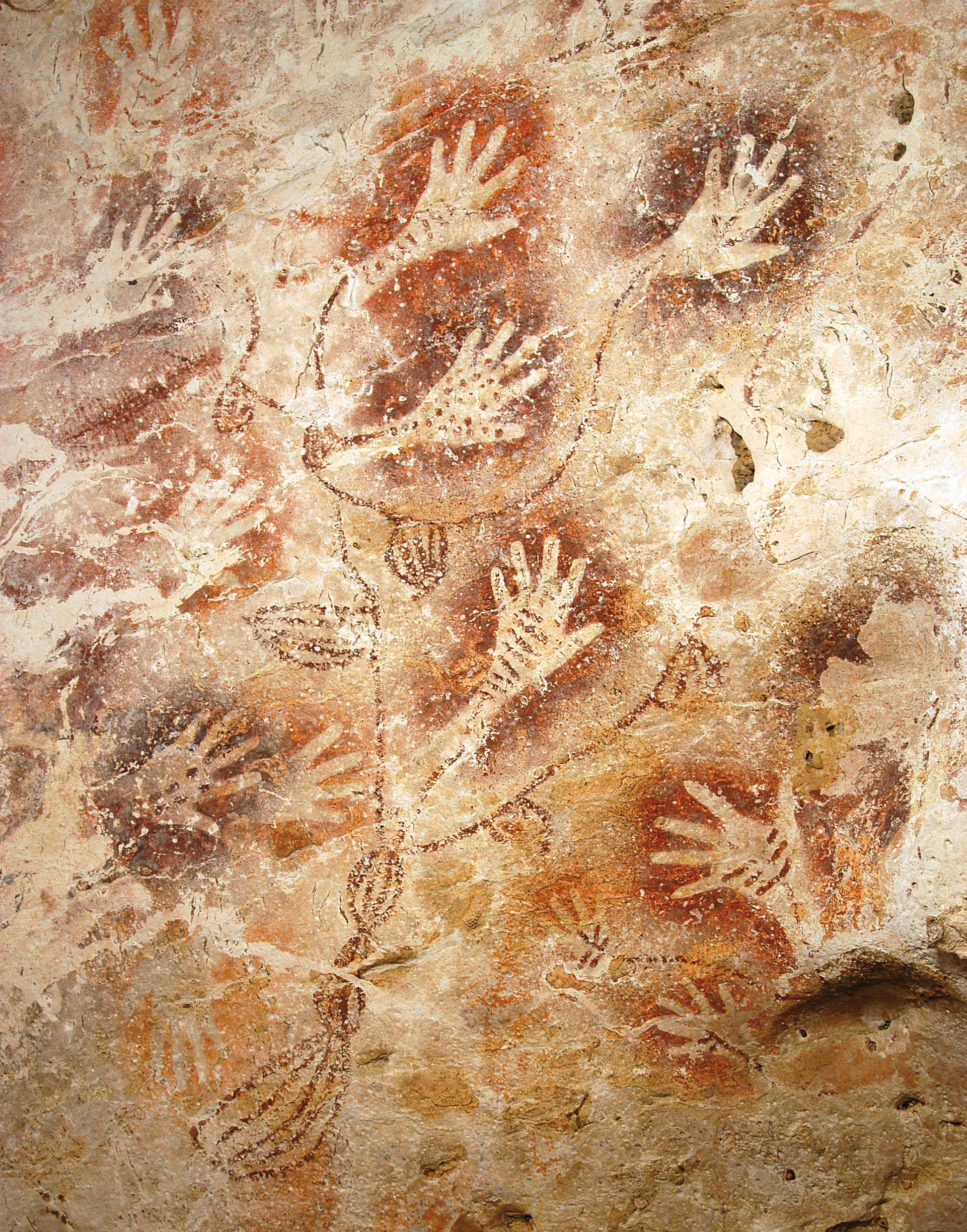 There are around six hundred to seven hundred rock art sites discovered in Southeast Asia and
There are around six hundred to seven hundred rock art sites discovered in Southeast Asia and  Dating rock art is difficult, but some of the sites subjected to Absolute dating, direct dating pre-date Austronesian arrival, like the Lene Hara cave, Lene Hara paintings of
Dating rock art is difficult, but some of the sites subjected to Absolute dating, direct dating pre-date Austronesian arrival, like the Lene Hara cave, Lene Hara paintings of  The Megalithic Culture is mostly limited to western Island Southeast Asia, with the greatest concentration being western Indonesia. While most sites aren't dated, the age ranges of dating sites are between the 2nd to 16th century CE. They are divided into two phases. The first is an older megalithic tradition associated with the Neolithic Austronesian rectangular axe culture (2,500 to 1,500 BCE); while the second is the 3rd or 4th century BCE megalithic tradition associated with the (non-Austronesian) Dong Son culture of
The Megalithic Culture is mostly limited to western Island Southeast Asia, with the greatest concentration being western Indonesia. While most sites aren't dated, the age ranges of dating sites are between the 2nd to 16th century CE. They are divided into two phases. The first is an older megalithic tradition associated with the Neolithic Austronesian rectangular axe culture (2,500 to 1,500 BCE); while the second is the 3rd or 4th century BCE megalithic tradition associated with the (non-Austronesian) Dong Son culture of  The Austronesian Painting Traditions (APT) are the most common types of rock art in Island Southeast Asia. They consist of scenes and pictograms typically found in rock shelters and caves near coastal areas. They are characteristically rendered in red ochre pigments for the earlier forms, later sometimes superseded by paintings done in black charcoal pigments. Their sites are mostly clustered in Eastern Indonesia and
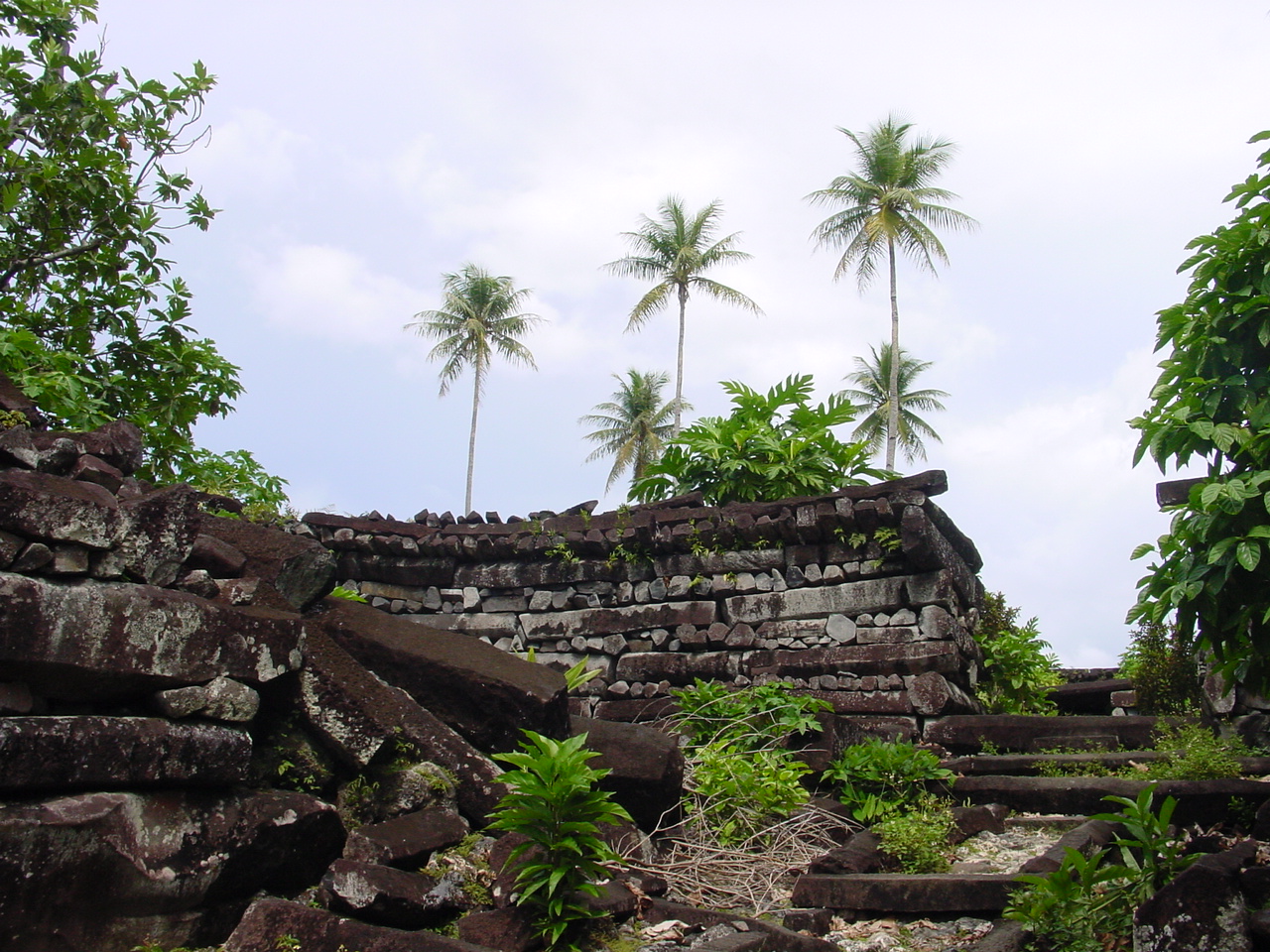
The Austronesian Painting Traditions (APT) are the most common types of rock art in Island Southeast Asia. They consist of scenes and pictograms typically found in rock shelters and caves near coastal areas. They are characteristically rendered in red ochre pigments for the earlier forms, later sometimes superseded by paintings done in black charcoal pigments. Their sites are mostly clustered in Eastern Indonesia and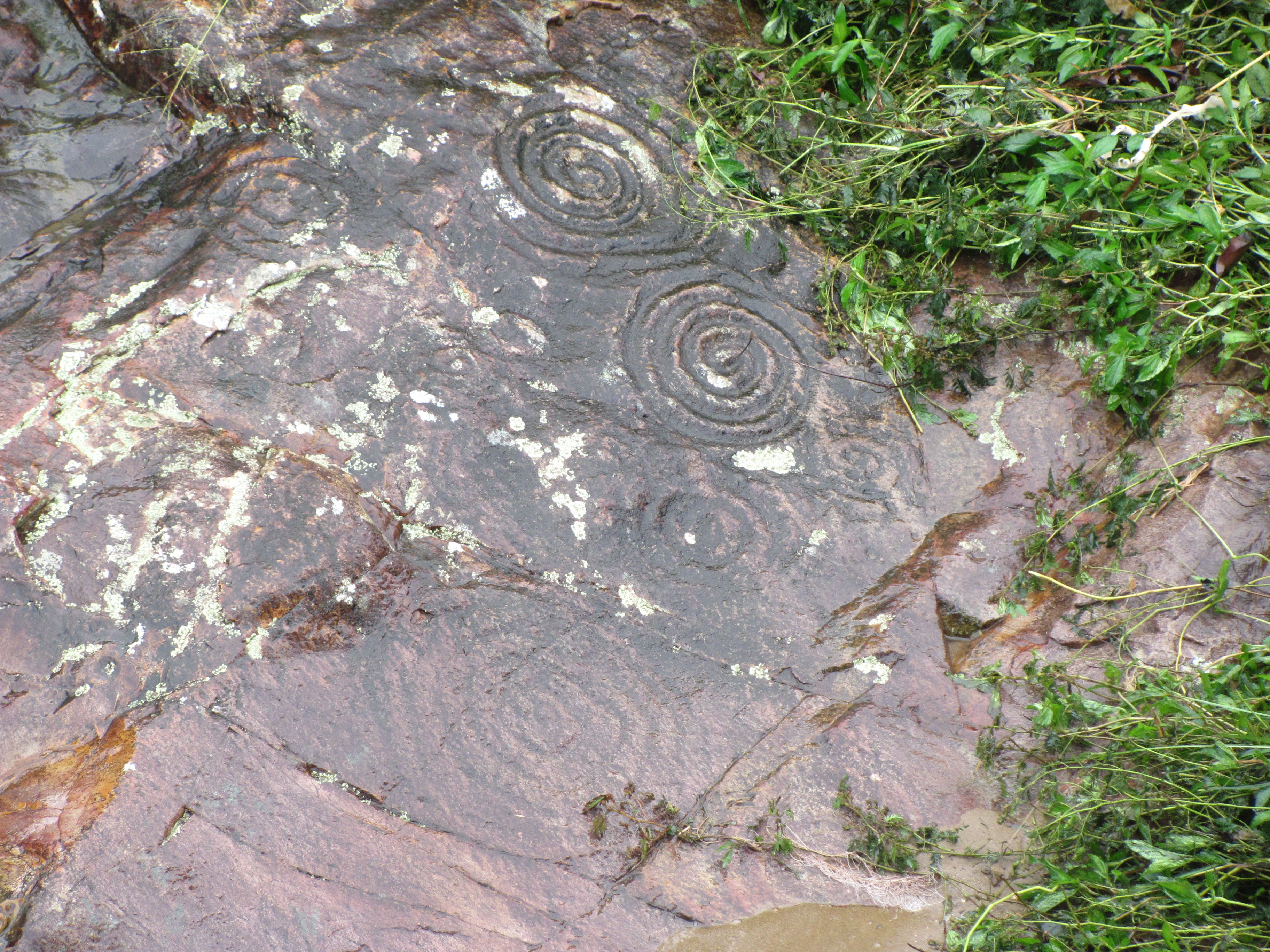  The earliest APT sites dated is from Vanuatu, which was found to be around 3,000 BP, corresponding to the initial migration wave of the Austronesians. These early sites are largely characterized by face motifs and hand stencils. Later sites from 1,500 BP onwards, however, begin to show regional divergence in their art styles. APT can be readily distinguished from older Pleistocene-era Australo-Melanesian cave paintings by their motifs, color, and composition, though they can often be found in the same locality. The most recognizable motifs of APT (like boats) do not occur in cave paintings (or engravings) that definitely pre-date the Austronesian arrival, the sole exception being the stencilled hand motif. Some APT examples are also characteristically found in relatively inaccessible locations like very high up in cliffsides overlooking the sea. No traces of APT has been found in Taiwan or the Philippines, though there is continuity in the motifs of spirals and concentric circles found in ancestral petroglyphs.
The Austronesian Engraving Style (AES), consisting of petroglyphs carved into rock surfaces, is far less common than APT. The majority of these sites are in coastal New Guinea, and
The earliest APT sites dated is from Vanuatu, which was found to be around 3,000 BP, corresponding to the initial migration wave of the Austronesians. These early sites are largely characterized by face motifs and hand stencils. Later sites from 1,500 BP onwards, however, begin to show regional divergence in their art styles. APT can be readily distinguished from older Pleistocene-era Australo-Melanesian cave paintings by their motifs, color, and composition, though they can often be found in the same locality. The most recognizable motifs of APT (like boats) do not occur in cave paintings (or engravings) that definitely pre-date the Austronesian arrival, the sole exception being the stencilled hand motif. Some APT examples are also characteristically found in relatively inaccessible locations like very high up in cliffsides overlooking the sea. No traces of APT has been found in Taiwan or the Philippines, though there is continuity in the motifs of spirals and concentric circles found in ancestral petroglyphs.
The Austronesian Engraving Style (AES), consisting of petroglyphs carved into rock surfaces, is far less common than APT. The majority of these sites are in coastal New Guinea, and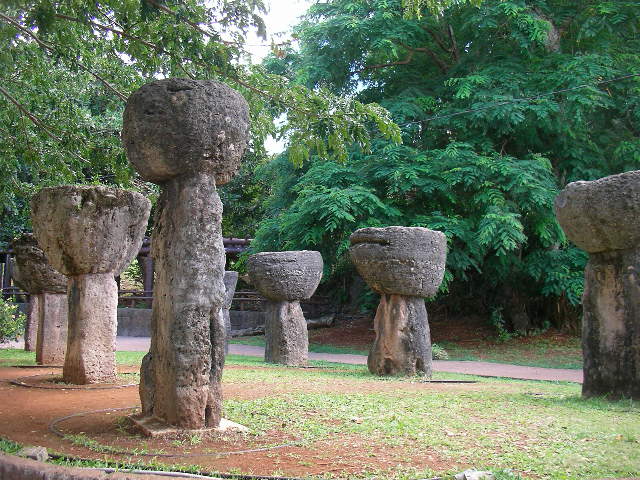  O'Connor ''et al.'' (2015) proposes that APT developed during the initial rapid southward Austronesian expansion, and not before, possibly as a response to the communication challenges brought about by the new maritime mode of living. Along with AES, these material symbols and associated rituals and technologies may been the manifestations of "powerful ideologies" spread by Austronesian settlers that were central to the "Neolithization" and rapid assimilation of the various non-Austronesian indigenous populations of ISEA and Melanesia.
O'Connor ''et al.'' (2015) proposes that APT developed during the initial rapid southward Austronesian expansion, and not before, possibly as a response to the communication challenges brought about by the new maritime mode of living. Along with AES, these material symbols and associated rituals and technologies may been the manifestations of "powerful ideologies" spread by Austronesian settlers that were central to the "Neolithization" and rapid assimilation of the various non-Austronesian indigenous populations of ISEA and Melanesia.
 The easternmost islands of Island Melanesia (Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia) are considered part of Remote Oceania as they are beyond the interisland visibility threshold. These island groups begin to show divergence from the APT and AES traditions of Near Oceania. While their art traditions show a clear continuation of the APT and AES traditions, they also feature innovations unique to each island group, like the increasing use of black charcoal, rectilinear motifs, and being found more inside sacred caves rather than in open cliffsides.
The easternmost islands of Island Melanesia (Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia) are considered part of Remote Oceania as they are beyond the interisland visibility threshold. These island groups begin to show divergence from the APT and AES traditions of Near Oceania. While their art traditions show a clear continuation of the APT and AES traditions, they also feature innovations unique to each island group, like the increasing use of black charcoal, rectilinear motifs, and being found more inside sacred caves rather than in open cliffsides.
 In Micronesia, the rock art traditions can be divided into three general regions: western, central, and eastern Micronesia. The divisions reflect the various major migration waves from the Philippines into the Mariana Islands and
In Micronesia, the rock art traditions can be divided into three general regions: western, central, and eastern Micronesia. The divisions reflect the various major migration waves from the Philippines into the Mariana Islands and 
 In
In
 Among the Indigenous Taiwanese, tattoos were present for both men and women. Among the Tayal people, facial tattoos are dominant. They indicated maturity and skill in weaving and farming for women, and skill in hunting and battle for men. Like in most of Austronesia, tattooing traditions in Taiwan have largely disappeared due to the Sinicization of native peoples after the Taiwan under Qing rule, Chinese colonization of
Among the Indigenous Taiwanese, tattoos were present for both men and women. Among the Tayal people, facial tattoos are dominant. They indicated maturity and skill in weaving and farming for women, and skill in hunting and battle for men. Like in most of Austronesia, tattooing traditions in Taiwan have largely disappeared due to the Sinicization of native peoples after the Taiwan under Qing rule, Chinese colonization of
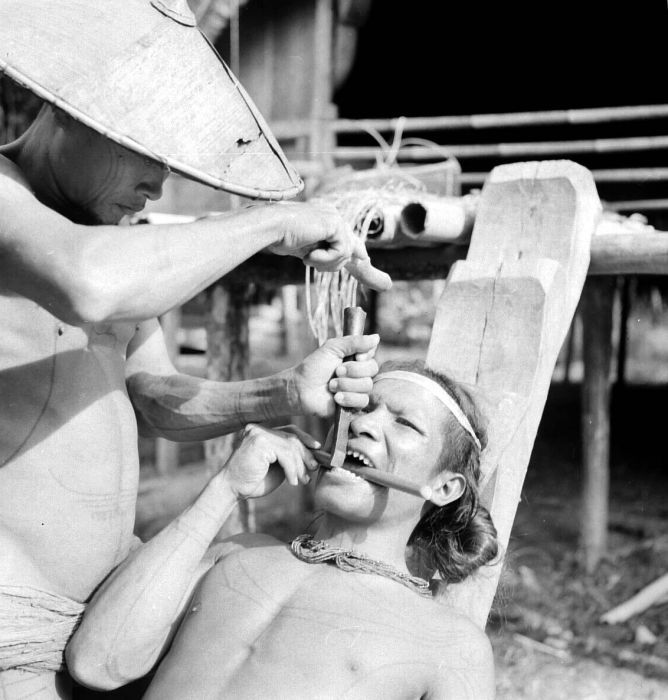 Teeth blackening was the custom of dyeing one's teeth black with various tannin-rich plant dyes. It was practiced throughout almost the entire range of Austronesia, including Island Southeast Asia, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Island Melanesia, reaching as far east as Malaita. However, it was absent in Polynesia. It also existed in non-Austronesian populations in Mainland Southeast Asia and Japan. The practice was primarily preventative, as it reduced the chances of developing tooth decay similar to modern dental sealants. It also had cultural significance and was seen as beautiful. A common sentiment was that blackened teeth separated humans from animals.
Teeth blackening was often done in conjunction with other modifications to the teeth associated with beauty standards, including dental evulsion and teeth filing.
Teeth blackening was the custom of dyeing one's teeth black with various tannin-rich plant dyes. It was practiced throughout almost the entire range of Austronesia, including Island Southeast Asia, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Island Melanesia, reaching as far east as Malaita. However, it was absent in Polynesia. It also existed in non-Austronesian populations in Mainland Southeast Asia and Japan. The practice was primarily preventative, as it reduced the chances of developing tooth decay similar to modern dental sealants. It also had cultural significance and was seen as beautiful. A common sentiment was that blackened teeth separated humans from animals.
Teeth blackening was often done in conjunction with other modifications to the teeth associated with beauty standards, including dental evulsion and teeth filing.
File:Poteau funéraire, aloalo, détail, Musée du quai Branly.jpg, ''Aloalo'' funerary pole of the Sakalava people of
File:Rongorongo B-v Aruku-Kurenga (color) edit1.jpg, Tablet B of rongorongo, an undeciphered system of glyphs from With the possible exception of rongorongo on
Books, some online, on Austronesian subjects by the Australian National University
Encyclopædia Britannica: Austronesian Languages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Austronesian Peoples Austronesian peoples, Austronesian culture Indigenous peoples of Asia Indigenous peoples of Oceania Indigenous peoples of Africa Ethnic groups in Southeast Asia Ethnic groups in Oceania Ethnic groups in East Africa Prehistoric migrations
pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
, and dogs.
History of research
The linguistic connections betweenMadagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, particularly the remarkable similarities between Malagasy, Malay, and Polynesian numerals
A numeral is a figure, symbol, or group of figures or symbols denoting a number. It may refer to:
* Numeral system used in mathematics
* Numeral (linguistics), a part of speech denoting numbers (e.g. ''one'' and ''first'' in English)
* Numerical d ...
, were recognized early in the colonial era by European authors. The first formal publication on these relationships was in 1708 by Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
Orientalist Adriaan Reland
Adriaan Reland (also known as ''Adriaen Reeland/Reelant'', ''Hadrianus Relandus'') (17 July 1676, De Rijp, North Holland5 February 1718, UtrechtJohn Gorton, ''A General Biographical Dictionary'', 1838, Whittaker & Co.) was a noted Dutch Oriental ...
, who recognized a "common language" from Madagascar to western Polynesia, although Dutch explorer Cornelis de Houtman
Cornelis de Houtman (2 April 1565 – 1 September 1599) was a Dutch merchant seaman who commanded the first Dutch expedition to the East Indies. Although the voyage was difficult and yielded only a modest profit, Houtman showed that the Po ...
observed linguistic links between Madagascar and the Malay Archipelago a century earlier in 1603. German naturalist Johann Reinhold Forster
Johann Reinhold Forster (22 October 1729 – 9 December 1798) was a German Reformed (Calvinist) pastor and naturalist of partially Scottish descent who made contributions to the early ornithology of Europe and North America. He is best known ...
, who traveled with James Cook on his second voyage, also recognized the similarities of Polynesian languages to those of Island Southeast Asia. In his book '' Observations Made during a Voyage round the World'' (1778), he posited that the ultimate origins of the Polynesians might have been the lowland regions of the Philippines and proposed that they arrived to the islands via long-distance voyaging. But, Johann Reinhold's ''Observations Made During a Voyage Round the World'' (1778) and Georg's ''A Voyage Round the World
''A Voyage Round the World'' (complete title ''A Voyage Round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop, Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, During the Years 1772, 3, 4, and 5'') is Georg Forster's report on the second voyage of the B ...
'' (1777), mark a key moment in the beginnings of modern racism. "Employing the English word "race" as a synonym for human variety, they interpret the multiplicity of Polynesian culture
Polynesian culture is the culture of the indigenous peoples of Polynesia who share common traits in language, customs and society. The development of Polynesian culture is typically divided into four different historical eras:
*Exploration and se ...
in terms of a linear hierarchy that naturally ascends towards the white European ideal."
language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
linking the Malay Peninsula, the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
( Sunda Islands and Moluccas
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
), the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and the Pacific Islands eastward to Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its ne ...
. Multiple other authors corroborated this classification (except for the erroneous inclusion of Maldivian), and the language family came to be known as "Malayo-Polynesian," first coined by the German linguist Franz Bopp
Franz Bopp (; 14 September 1791 – 23 October 1867) was a German linguist known for extensive and pioneering comparative work on Indo-European languages.
Early life
Bopp was born in Mainz, but the political disarray in the Republic of Mai ...
in 1841 ( German: ''malayisch-polynesisch''). The connections between Southeast Asia, Madagascar, and the Pacific Islands were also noted by other European explorers, including the orientalist William Marsden and the naturalist Johann Reinhold Forster
Johann Reinhold Forster (22 October 1729 – 9 December 1798) was a German Reformed (Calvinist) pastor and naturalist of partially Scottish descent who made contributions to the early ornithology of Europe and North America. He is best known ...
.
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840) was a German physician, naturalist, physiologist, and anthropologist. He is considered to be a main founder of zoology and anthropology as comparative, scientific disciplines. He ...
added Austronesians as the fifth category to his "varieties" of humans in the second edition of ''De Generis Humani Varietate Nativa'' (1781). He initially grouped them by geography and thus called Austronesians the "people from the southern world." In the third edition published in 1795, he named Austronesians the "Malay race
The concept of a Malay race was originally proposed by the German physician Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840), and classified as a brown race. ''Malay'' is a loose term used in the late 19th century and early 20th century to describe the ...
" or the " brown race," after correspondence with Joseph Banks who was part of the first voyage of James Cook
The first voyage of James Cook was a combined Royal Navy and Royal Society expedition to the south Pacific Ocean aboard HMS ''Endeavour'', from 1768 to 1771. It was the first of three Pacific voyages of which James Cook was the commander. The ...
. Blumenbach used the term "Malay" due to his belief that most Austronesians spoke the "Malay idiom" (i.e. the Austronesian languages), though he inadvertently caused the later confusion of his racial category with the Malay (ethnic group). The other varieties Blumenbach identified were the "Caucasians" (white), "Mongolians" (yellow), "Ethiopians" (black), and "Americans" (red). Blumenbach's definition of the Malay race is largely identical to the modern distribution of the Austronesian peoples, including not only Islander Southeast Asians, but also the people of Madagascar and the Pacific Islands. Although Blumenbach's work was later used in scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
, Blumenbach was a monogenist and did not believe the human "varieties" were inherently inferior to each other.
By the 19th century, however, scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
was favoring a classification of Austronesians as being a subset of the "Mongolian" race, as well as polygenism
Polygenism is a theory of human origins which posits the view that the human races are of different origins (''polygenesis''). This view is opposite to the idea of monogenism, which posits a single origin of humanity. Modern scientific views no ...
. The Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
populations of Southeast Asia and Melanesia (whom Blumenbach initially classified as a "subrace" of the "Malay" race) were also now being treated as a separate "Ethiopian" race by authors like Georges Cuvier, Conrad Malte-Brun
Conrad Malte-Brun (12 August 177514 December 1826), born Malthe Conrad Bruun, and sometimes referred to simply as Malte-Brun, was a Dano-French geographer and journalist. His second son, Victor Adolphe Malte-Brun, was also a geographer. Today he ...
(who first coined the term "Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
" as ''Océanique''), Julien-Joseph Virey
Julien-Joseph Virey (21 December 1775, Langres – 9 March 1846) was a French naturalist and anthropologist.
Biography
Julien-Joseph Virey grew up in Hortes village in southern Haute-Marne, where he had access to a library. He educated himself a ...
, and René Lesson.
The British naturalist James Cowles Prichard
James Cowles Prichard, FRS (11 February 1786 – 23 December 1848) was a British physician and ethnologist with broad interests in physical anthropology and psychiatry. His influential ''Researches into the Physical History of Mankind'' touched ...
originally followed Blumenbach by treating Papuans and Native Australians as being descendants of the same stock as Austronesians. But by his third edition of ''Researches into the Physical History of Man'' (1836–1847), his work had become more racialized due to the influence of polygenism. He classified the peoples of Austronesia into two groups: the "Malayo-Polynesians" (roughly equivalent to the Austronesian peoples) and the "Kelænonesians" (roughly equivalent to the Australo-Melanesians). He further subdivided the latter into the "Alfourous" (also "Haraforas" or "Alfoërs", the Native Australians), and the "Pelagian or Oceanic Negroes" (the Melanesians and western Polynesians). Despite this, he acknowledges that "Malayo-Polynesians" and "Pelagian Negroes" had "remarkable characters in common", particularly in terms of language and craniometry
Craniometry is measurement of the cranium (the main part of the skull), usually the human cranium. It is a subset of cephalometry, measurement of the head, which in humans is a subset of anthropometry, measurement of the human body. It is dis ...
.
In linguistics, the Malayo-Polynesian language family also initially excluded Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
and Micronesia, due to what they perceived were marked physical differences between the inhabitants of these regions from the Malayo-Polynesian speakers. However, there was growing evidence of their linguistic relationship to Malayo-Polynesian languages, notably from studies on the Melanesian languages In linguistics, Melanesian is an obsolete term referring to the Austronesian languages of Melanesia: that is, the Oceanic, Eastern Malayo-Polynesian, or Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages apart from Polynesian and Micronesian. A typ ...
by Georg von der Gabelentz
Hans Georg Conon von der Gabelentz (16 March 1840 – 11 December 1893) was a German general linguist and sinologist. His (1881), according to a critic, "remains until today recognized as probably the finest overall grammatical survey of the Clas ...
, Robert Henry Codrington and Sidney Herbert Ray. Codrington coined and used the term "Ocean" language family rather than "Malayo-Polynesian" in 1891, in opposition to the exclusion of Melanesian and Micronesian languages. This was adopted by Ray who defined the "Oceanic" language family as encompassing the languages of Southeast Asia and Madagascar, Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.
In 1899, the Austrian linguist and ethnologist Wilhelm Schmidt coined the term "Austronesian" (German: ''austronesisch'', from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''auster
Auster Aircraft Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer from 1938 to 1961.Willis, issue 122, p.55
History
The company began in 1938 at the Britannia Works, Thurmaston near Leicester, England, as Taylorcraft Aeroplanes (England) Limited, ma ...
'', "south wind"; and Greek '' νῆσος'', "island") to refer to the language family. Schmidt had the same motivations as Codrington. He proposed the term as a replacement to "Malayo-Polynesian", because he also opposed the implied exclusion of the languages of Melanesia and Micronesia in the latter name. It became the accepted name for the language family, with Oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
and Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
being retained as names for subgroups.
 The term "Austronesian", or more accurately "Austronesian-speaking peoples", came to refer the people who speak the languages of the Austronesian
The term "Austronesian", or more accurately "Austronesian-speaking peoples", came to refer the people who speak the languages of the Austronesian language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
. Some authors, however, object to the use of the term to refer to people, as they question whether there really is any biological or cultural shared ancestry between all Austronesian-speaking groups.According to the anthropologist Wilhelm Solheim II: "I emphasize again, as I have done in many other articles, that 'Austronesian' is a linguistic term and is the name of a super language family. It should never be used as a name for a people, genetically speaking, or a culture. To refer to people who speak an Austronesian language the phrase 'Austronesian-speaking people' should be used." ''Origins of the Filipinos and Their Languages'' (January 2006) This is especially true for authors who reject the prevailing "Out of Taiwan" hypothesis and instead offer scenarios where the Austronesian languages spread among preexisting static populations through borrowing or convergence, with little or no population movements.
 Despite these objections, the general consensus is that the archeological, cultural, genetic, and especially linguistic evidence all separately indicate varying degrees of shared ancestry among Austronesian-speaking peoples that justifies their treatment as a "
Despite these objections, the general consensus is that the archeological, cultural, genetic, and especially linguistic evidence all separately indicate varying degrees of shared ancestry among Austronesian-speaking peoples that justifies their treatment as a "phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
unit." This has led to the use of the term "Austronesian" in academic literature to refer not only to the Austronesian languages, but also the Austronesian-speaking peoples, their societies, and the geographic area of Austronesia.
Some Austronesian-speaking groups are not direct descendants of Austronesians and acquired their languages through language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer or language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are percei ...
, but this is believed to have happened only in a few instances since the Austronesian expansion was too rapid for language shifts to have occurred fast enough. In parts of Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, migrations and paternal admixture from Papuan groups after the Austronesian expansion (estimated to have started at around 500 BCE) also resulted in gradual population turnover. These secondary migrations were incremental, and happened gradually enough that the culture and language of these groups remained Austronesian, even though in modern times they are genetically more Papuan. In the vast majority of cases, the language and material culture of Austronesian-speaking groups descend directly through generational continuity, especially in islands that were previously uninhabited.
Serious research into the Austronesian languages and its speakers has been ongoing since the 19th century. Modern scholarship on Austronesian dispersion models is generally credited to two influential papers in the late 20th century: ''The Colonisation of the Pacific: A Genetic Trail'' (Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not a ...
& Serjeantson, eds., 1989), and ''The Austronesian Dispersal and the Origin of Languages'' ( Bellwood, 1991). The topic is particularly interesting to scientists for the remarkably unique characteristics of the Austronesian speakers: their extent, diversity, and rapid dispersal.
Regardless certain disagreements still exist among researchers with regards to chronology, origin, dispersal, adaptations to the island environments, interactions with preexisting populations in areas they settled, and cultural developments over time. The mainstream accepted hypothesis is the "Out of Taiwan" model first proposed by Peter Bellwood
Peter Stafford Bellwood (born Leicester, England, 1943) is Emeritus Professor of Archaeology in the School of Archaeology and Anthropology at the Australian National University (ANU) in Canberra. He is well known for his Out of Taiwan model rega ...
. But there are multiple rival models that create a sort of "pseudo-competition" among their supporters due to narrow focus on data from limited geographic areas or disciplines. The most notable of which is the "Out of Sundaland" (or "Out of Island Southeast Asia") model. As a generalization, authors that are based in Indonesia and Malaysia tend to favor the "Out of Sundaland" model, while authors based in Taiwan and the Pacific Islands tend to favor the "Out of Taiwan" model.
Geographical distribution
Prior to the 16th century Colonial Era, the Austronesian language family was the most widespread language family in the world, spanning half the planet fromEaster Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its ne ...
in the eastern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
to Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
in the western Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
.
 It is spoken today by about 386 million people (4.9% of the global population), making it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages with the highest number of speakers are Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, and
It is spoken today by about 386 million people (4.9% of the global population), making it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages with the highest number of speakers are Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, and Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
( Tagalog). The family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family.
The geographic region that encompasses native Austronesian-speaking populations is sometimes referred to as Austronesia. Other geographic names for various subregions include Malay Peninsula, Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands ( Indonesian and Malay: ''Kepulauan Sunda Besar'') are four tropical islands situated within Indonesian Archipelago, in the Pacific Ocean. The islands, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi and Sumatra, are internationally recognised ...
, Lesser Sunda Islands, Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, Island Southeast Asia (ISEA), Malay Archipelago, Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
(MSEA), Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
, Micronesia, Near Oceania, Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, Pacific Islands, Remote Oceania, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, and Wallacea. In Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, the nationalistic term Nusantara from the Old Javanese
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the island ...
is also popularly used for their islands.
Historically, Austronesians uniquely live in an "island world". Austronesian regions are almost exclusively islands in the Pacific and Indian oceans, with predominantly tropical or subtropical climates with considerable seasonal rainfall. They had limited penetration into the interiors of large islands or mainlands.
They include Taiwanese indigenous peoples
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 5 ...
, the majority of ethnic groups in Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by t ...
, East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Micronesia, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
. Also included are the Malays of Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
; the Polynesians of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
, and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
; the Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders () are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often groupe ...
of Australia; the non- Papuan peoples of Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
and coastal New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
; the Shibushi-speakers of Comoros, and the Malagasy and Shibushi-speakers of Réunion. They are also found in the regions of Southern Thailand
Southern Thailand, Southern Siam or Tambralinga is a southernmost cultural region of Thailand, separated from Central Thailand region by the Kra Isthmus.
Geography
Southern Thailand is on the Malay Peninsula, with an area of around , bounde ...
; the Cham
Cham or CHAM may refer to:
Ethnicities and languages
*Chams, people in Vietnam and Cambodia
**Cham language, the language of the Cham people
***Cham script
*** Cham (Unicode block), a block of Unicode characters of the Cham script
*Cham Albania ...
areas in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, and Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
; and the Mergui Archipelago of Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
.
Additionally, modern-era migration brought Austronesian-speaking people to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, Australia, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, mainland Europe, Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
, Sri Lanka, Suriname, Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
, Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
, and West Asian countries.
Some authors also propose further settlements and contacts in the past in areas that are not inhabited by Austronesian speakers today. These range from likely hypotheses to very controversial claims with minimal evidence. In 2009, Roger Blench compiled an expanded map of Austronesia that encompass these claims based on various evidence like historical accounts, loanwords, introduced plants and animals, genetics, archeological sites, and material culture. They include areas like the Pacific coast of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, Japan, the Yaeyama Islands, the Australian coast, Sri Lanka and coastal South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
, some of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
islands, East Africa, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
, and West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
.
List of Austronesian peoples
 Austronesian peoples include the following groupings by name and geographic location (incomplete):
* Formosan:
Austronesian peoples include the following groupings by name and geographic location (incomplete):
* Formosan: Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
(e.g., Amis, Atayal, Bunun, Paiwan, collectively known as Taiwanese indigenous peoples
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 5 ...
).
* Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
:
** Borneo groups (e.g., Kadazan-Dusun
Kadazan-Dusun (also written as Kadazandusun or Mamasok Kadazan-Dusun) also less-known as "Mamasok Sabah" are two indigenous peoples of Sabah, Malaysia—the ethnic groups Kadazan and Dusun. The Kadazandusun is the largest native group of Bu ...
, Murut, Iban, Bidayuh, Dayak, Lun Bawang/Lundayeh)
** Chamic group: Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, Cham areas of Vietnam (remnants of the Champa kingdom which covered central and southern Vietnam) as well as Aceh in northern Sumatra (e.g., Acehnese, Chams
The Cham ( Cham: ''Čaṃ'') or Champa people ( Cham: , ''Urang Campa''; vi, Người Chăm or ; km, ជនជាតិចាម, ) are an Austronesian ethnic group. From the 2nd century to 1832 the Cham populated Champa, a contiguous territ ...
, Jarai, Utsuls).
** Central Luzon group: (e.g., Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Sambal
Sambal is an Indonesian chilli sauce or paste, typically made from a mixture of a variety of chilli peppers with secondary ingredients, such as shrimp paste, garlic, ginger, shallot, scallion, palm sugar, and lime juice. ''Sambal'' is an ...
.)
** Igorot (Cordillerans): Cordilleras (e.g., Balangao, Ibaloi
The Ibaloi (also spelled Ibaloy; Ibaloi: ''ivadoy'', ) are an indigenous ethnic group found in Benguet Province of the northern Philippines.
''Ibaloi'' is derived from ''i-'', a prefix signifying "pertaining to" and ''badoy'' or house, together ...
, Ifugao, Itneg
The Itneg (exonym "Tinguian" or "Tingguian") are an Austronesian ethnic group from the upland province of Abra in northwestern Luzon, in the Philippines.
Overview
The Itneg live in the mountainous area of Abra in northwestern Luzon who descen ...
, Kankanaey).
**Lumad
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopte ...
: Mindanao (e.g., Kamayo, Mandaya, Mansaka, Kalagan, Manobo, Tasaday, T'boli
The Tboli people () are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Philippines, indigenous peoples of South Cotabato in southern Mindanao. In the body of ethnographic and linguistic literature on Mindanao, their name is variously spelt Tboli, T'boli, ...
).
** Malagasy: Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
(e.g., Betsileo
The Betsileo are a highland ethnic group of Madagascar, the third largest in terms of population. They chose their name, meaning "The Many Invincible Ones", after a failed invasion by King Ramitraho of the Menabe kingdom in the early 19th centu ...
, Merina
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina ...
, Sihanaka, Bezanozano).
** Melanesians: Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
(e.g., Fijians, Kanak
The Kanak (French spelling until 1984: Canaque) are the indigenous Melanesian inhabitants of New Caledonia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southwest Pacific. According to the 2019 census, the Kanak make up 41.2% of New Caledonia' ...
, Ni-Vanuatu, Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
).
** Micronesians: Micronesia (e.g., Carolinian, Chamorro, Palauans).
** Moken: Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
.
** Moro: Bangsamoro
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsamoro Hymn
, image_skyline ...
( Mindanao & Sulu Archipelago, e.g., Maguindanao, Iranun, Maranao
The Maranao people (Maranao: mәranaw Filipino: ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranao, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is the term used by the Philippine government to refer to the southern indigenous people who are the "people of the lake", a predomi ...
, Tausug, Yakan, Sama-Bajau
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exo ...
).
** Northern Luzon lowlanders (e.g., Ilocano, Ibanag, Itawes).
** Polynesians: Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
(e.g., Māori, Native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
s, Samoans, Tongans
Tongans, a Polynesians, Polynesian group, represent more than 98% of the inhabitants of Tonga. The rest are European (the majority are British people, British), mixed European, and other Pacific Islanders. There also are several hundred Chinese i ...
).
** Southern Luzon lowlanders (e.g., Tagalog, Bicolano)
** Sunda– Sulawesi language and ethnic groups including Malay, Sundanese, Javanese, Balinese, Batak (geographically includes Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by t ...
, Pattani, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
, parts of Sri Lanka, southern Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, and much of western and central Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
).
** Visayans
Visayans ( Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group ...
: Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
and neighbouring islands (e.g., Aklanon, Boholano, Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Masbateño, Waray).
Prehistory
The broad consensus on Austronesian origins is the "two-layer model" where an original Paleolithic indigenous population in Island Southeast Asia were assimilated to varying degrees by incoming migrations ofNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Austronesian-speaking peoples from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, in southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
from around 4,000 BP. Austronesians also mixed with other preexisting populations as well as later migrant populations among the islands they settled, resulting in further genetic input. The most notable are the Austroasiatic-speaking peoples in western Island Southeast Asia ( peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo, and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
); the Bantu peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Souther ...
in Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and the Comoros; as well as Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Indian, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, and Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
traders and migrants in the more recent centuries.
Paleolithic
Island Southeast Asia was settled by modern humans in the Paleolithic following coastal migration routes, presumably starting before 70,000 BP, long before the development of Austronesian cultures. These populations are typified by having dark skin, curly hair, and short statures, leading Europeans to believe they were related toAfrican Pygmies
The African Pygmies (or Congo Pygmies, variously also Central African foragers, "African rainforest hunter-gatherers" (RHG) or "Forest People of Central Africa") are a group of ethnicities native to Central Africa, mostly the Congo Basin, tra ...
in the scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
of the 19th century. However, despite these physical differences, genetic studies have shown that they are more closely related to other Eurasian populations than to Africans.
 These early population groups originally lacked watercraft technology, and thus could only cross narrow interisland seas with primitive floats or rafts (likely bamboo or log rafts) or through accidental means. Especially the deeper waters of the
These early population groups originally lacked watercraft technology, and thus could only cross narrow interisland seas with primitive floats or rafts (likely bamboo or log rafts) or through accidental means. Especially the deeper waters of the Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a trans ...
, Weber Line, and Lydekker Line with islands disconnected from mainland Asia even in the lower sea levels of the last glacial period. They settled in what are now islands mostly through land migrations into the coastal lowland plains of Sundaland and Sahul, most of which are now underwater.Some authors that support an ISEA origin of Austronesians, however, have proposed that they may have later been the original developers of the maritime culture that later characterized Austronesians, during several rapid sea-level rise events that took place near the end of the last glacial period that flooded the landmasses in Southeast Asia. Developing the catamaran originally from lashing two canoes, which eventually became the prototype for the numerous types of water vessels of the Austronesians, as well as the Chinese '' chuán'', after northward migrations of Negrito populations in the Neolithic (Mahdi, 2017).
 Humans reached the islands in Wallacea as well as the Sahul landmass ( Australia and
Humans reached the islands in Wallacea as well as the Sahul landmass ( Australia and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
) by around 53,000 BP (some give even older dates up to 65,000 BP). By 45,400 years ago, humans had reached the Bismarck Archipelago in Near Oceania. They were once also present in Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, but their populations are now extinct or assimilated. The oldest confirmed human fossils in the Philippines is from the Tabon Caves of Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in t ...
, dated to around 47,000 BP.
Previously, it was believed that the earliest putative record of modern humans in Southeast Asia is from the Callao Cave of northern Luzon in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
dated to around 67,000 BP. However, in 2019, the remains were identified as belonging to a new species of archaic humans, ''Homo luzonensis
''Homo luzonensis'', also locally called "Ubag" after a mythical caveman, is an extinct, possibly pygmy peoples, pygmy, species of archaic human from the Late Pleistocene of Luzon, the Philippines. Their remains, teeth and phalanges, are known on ...
''.
These people are generally historically referred to as " Australo-Melanesians", though the terminology is problematic as they are genetically diverse and most groups within Austronesia have significant Austronesian admixture and culture. The unmixed descendants of these groups today include the interior Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
and Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
.
 In modern literature, descendants of these groups located in Island Southeast Asia west of Halmahera are usually collectively referred to as " Negritos", while descendants of these groups east of Halmahera (excluding Indigenous Australians) are referred to as "
In modern literature, descendants of these groups located in Island Southeast Asia west of Halmahera are usually collectively referred to as " Negritos", while descendants of these groups east of Halmahera (excluding Indigenous Australians) are referred to as "Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
". They can also be divided into two broad groups based on Denisovan admixture. Philippine Negritos, Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
, Melanesians, and Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
display Denisovan admixture; while Malaysian and western Indonesian Negritos ( Orang Asli) and Andamanese islanders do not.The absence of Denisovan admixture in western Southeast Asian populations seem to indicate that interbreeding between modern humans and Denisovans happened within Southeast Asia itself, possibly east of the Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a trans ...
, and not in mainland Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
(Reich ''et al.'', 2011; Cooper & Stringer, 2013)
Mahdi (2017) also uses the term "Qata" (from Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *qata) to distinguish the indigenous populations of Southeast Asia, versus "Tau" (from Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
*Cau) for the later settlers from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
; both are based on proto-forms for the word "person" in Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
that referred to darker-skinned and lighter-skinned groups respectively. Jinam ''et al.'' (2017) also proposed the term "First Sundaland People" in place of "Negrito", as a more accurate name for the original population of Southeast Asia.
These populations are genetically distinct from later Austronesians, but through fairly extensive population admixture, most modern Austronesians have varying levels of ancestry from these groups. The same is true for some populations historically considered "non-Austronesians" due to physical differences; like Philippine Negritos, Orang Asli, and Austronesian-speaking Melanesians, all of whom have Austronesian admixture. In Polynesians in Remote Oceania, for example, the admixture is around 20 to 30% Papuan, and 70 to 80% Austronesian. The Melanesians in Near Oceania are roughly around 20% Austronesian and 80% Papuan, while in the natives of the Lesser Sunda Islands, the admixture is around 50% Austronesian and 50% Papuan. Similarly, in the Philippines, the groups traditionally considered to be "Negrito" vary between 30 and 50% Austronesian.
The high degree of assimilation among Austronesian, Negrito, and Papuan groups indicate that the Austronesian expansion was largely peaceful. Rather than violent displacement, the settlers and the indigenous groups absorbed each other. It is believed that in some cases, like in the Toalean culture
The Toalean (or Toalian or ''Toala'' in Indonesian) people were hunter-gatherers who inhabited the Indonesian island of Sulawesi during the Mid- to Late-Holocene period prior to the spread of Austronesian Neolithic farmers some 3,500 years ago fro ...
of Sulawesi (c. 8,000–1,500 BP), it is even more accurate to say that the densely-populated indigenous hunter-gatherer groups absorbed the incoming Austronesian farmers, rather than the other way around. Mahdi (2016) further asserts that Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *tau-mata ("person") Cognates include Sangir ''taumata'', Molima ''tomotau'', Kola ''tamata'', Fijian ''tamata'', Samoan ''tangata'', and Hawaiian ''kanaka'' is derived from a composite protoform *Cau ma-qata, combining "Tau" and "Qata" and indicative of the mixing the two ancestral population types in these regions.
Neolithic China
The broad consensus on theUrheimat
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ''Urheimat'' (, from German '' ur-'' "original" and ''Heimat'', home) of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the r ...
(homeland) of Austronesian languages as well as the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
early Austronesian peoples is accepted to be Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, as well as the Penghu Islands
The Penghu (, Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, located approximately west from the main island of Taiwan, covering an are ...
. They are believed to have descended from ancestral populations in coastal Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, in mainland southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
, which are generally referred to as the "preAustronesians".Sometimes confusingly also as "early Austronesians" or "proto-Austronesians". The latter should not be confused with the reconstructed Proto-Austronesian language
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
(PAN), which the pre-Austronesians did not speak. (Bellwood, 1988) Through these pre-Austronesians, Austronesians may also share a common ancestry with neighboring groups in Neolithic Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
.
These Neolithic pre-Austronesians from the coast of Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
are believed to have migrated to Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
between approximately 10,000–6000 BCE. Other research has suggested that, according to radiocarbon dates, Austronesians may have migrated from Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
to Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
as late as 4000 BCE ( Dapenkeng culture). They continued to maintain regular contact with the mainland until 1500 BCE.
The identity of the Neolithic pre-Austronesian cultures in Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
is contentious. Tracing Austronesian prehistory in Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
has been difficult due to the southward expansion of the Han dynasty
The southward expansion of the Han dynasty was a series of Chinese military campaigns and expeditions in what is now modern Southern China and Northern Vietnam. Military expansion to the south began under the previous Qin dynasty and continued ...
(2nd century BCE), and the recent Qing dynasty annexation of Taiwan (1683 CE). Today, the only Austronesian language in southern China is Tsat language
Tsat, also known as Utsat, Utset, Hainan Cham, or Huíhuī (), is a tonal language spoken by 4,500 Utsul people in Yanglan () and Huixin () villages near Sanya, Hainan, China. Tsat is a member of the Malayo-Polynesian group within the Austron ...
in Hainan. The politicization of archaeology is also problematic, particularly erroneous reconstructions among some Chinese archaeologists of non-Sinitic sites as Han. Some authors, favoring the "Out of Sundaland" model like William Meacham, reject the southern Chinese mainland origin of pre-Austronesians entirely.
Nevertheless, based on linguistic, archaeological, and genetic evidence, Austronesians are most strongly associated with the early farming cultures
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylo ...
of the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
basin that domesticated rice from around 13,500 to 8,200 BP. They display typical Austronesian technological hallmarks, including tooth removal, teeth blackening
Teeth blackening or teeth lacquering is a custom of dyeing one's teeth black. It was most predominantly practiced in Southeast Asian and Oceanic cultures, particularly among Austronesian, Austroasiatic, and Kra–Dai-speaking peoples. It was al ...
, jade carving, tattooing, stilt houses, advanced boat-building, aquaculture, wetland agriculture, and the domestication of dogs, pigs, and chickens. These include the Kuahuqiao, Hemudu
The Hemudu culture (5500 BC to 3300 BC) was a Neolithic culture that flourished just south of the Hangzhou Bay in Jiangnan in modern Yuyao, Zhejiang, China. The culture may be divided into early and late phases, before and after 4000 BC respecti ...
, Majiabang, Songze, Liangzhu, and Dapenkeng cultures
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylo ...
which occupied the coastal regions between the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
delta to the Min River delta.
Relations with other groups
Based on linguistic evidence, there have been proposals linking Austronesians with other linguistic families into linguistic macrofamilies that are relevant to the identity of the pre-Austronesian populations. The most notable are the connections of Austronesians to the neighboring Austroasiatic, Kra-Dai, andSinitic
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is ...
peoples (as Austric
The Austric languages are a proposed language family that includes the Austronesian languages spoken in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Madagascar, as well as the Austroasiatic languages spoken in Mainland Southeast ...
, Austro-Tai, and Sino-Austronesian, respectively). But they are still not widely accepted as evidence of these relationships are still tenuous and the methods used are highly contentious.
In support of both the Austric
The Austric languages are a proposed language family that includes the Austronesian languages spoken in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Madagascar, as well as the Austroasiatic languages spoken in Mainland Southeast ...
and Austro-Tai hypothesis, Robert Blust connects the lower Yangtze Neolithic Austro-Tai entity with the rice-cultivating Austroasiatic cultures; assuming the center of East Asian rice domestication, and putative Austric
The Austric languages are a proposed language family that includes the Austronesian languages spoken in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Madagascar, as well as the Austroasiatic languages spoken in Mainland Southeast ...
homeland, to be located in the Yunnan/Burma border area, instead of the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
basin as is currently accepted. Under that view, there was an east–west genetic alignment, resulting from a rice-based population expansion, in the southern part of East Asia: Austroasiatic- Kra-Dai- Austronesian, with unrelated Sino-Tibetan occupying a more northerly tier. Depending on the author, other hypotheses have also included other language families like Hmong-Mien and even Japanese-Ryukyuan into the larger Austric hypothesis.
While the Austric hypothesis remains contentious, there is genetic evidence that at least in western Island Southeast Asia there had been earlier Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
overland migrations (pre-4,000 BP) by Austroasiatic-speaking peoples into what is now the Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands ( Indonesian and Malay: ''Kepulauan Sunda Besar'') are four tropical islands situated within Indonesian Archipelago, in the Pacific Ocean. The islands, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi and Sumatra, are internationally recognised ...
when the sea levels were lower in the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
. These peoples were assimilated linguistically and culturally by incoming Austronesian peoples in what is now modern-day Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
.
 Several authors have also proposed that Kra-Dai speakers may actually be an ancient daughter subgroup of Austronesians that migrated back to the
Several authors have also proposed that Kra-Dai speakers may actually be an ancient daughter subgroup of Austronesians that migrated back to the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
delta from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and/or Luzon shortly after the Austronesian expansion. Later migrating further westwards to Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, Mainland Southeast Asia and Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
. They propose that the distinctiveness of Kra-Dai (it is tonal and monosyllabic In linguistics, a monosyllable is a word or utterance of only one syllable. It is most commonly studied in the fields of phonology and morphology and it has no semantic content. The word has originated from the Greek language.
"Yes", "no", "jump", ...
) was the result of linguistic restructuring due to contact with Hmong-Mien and Sinitic
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is ...
cultures. Aside from linguistic evidence, Roger Blench has also noted cultural similarities between the two groups, like facial tattooing, tooth removal or ablation, teeth blackening
Teeth blackening or teeth lacquering is a custom of dyeing one's teeth black. It was most predominantly practiced in Southeast Asian and Oceanic cultures, particularly among Austronesian, Austroasiatic, and Kra–Dai-speaking peoples. It was al ...
, snake (or dragon) cults, and the multiple-tongued jaw harps shared by the Indigenous Taiwanese and Kra-Dai-speakers. However archaeological evidence for this is still sparse. This is believed to be similar to what happened to the Cham people
The Cham (Cham: ''Čaṃ'') or Champa people (Cham: , ''Urang Campa''; vi, Người Chăm or ; km, ជនជាតិចាម, ) are an Austronesian ethnic group. From the 2nd century to 1832 the Cham populated Champa, a contiguous territor ...
, who were originally Austronesian settlers (likely from Borneo) to southern Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
at around 2,100 to 1,900 BP, and had languages similar to Malay. Their languages underwent several restructuring events to syntax and phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
due to contact with the nearby tonal languages of Mainland Southeast Asia and Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
. Although the Malaysian are diverse in genetic information. There are many studies that supported the indication of Malaysian belonging to the Austronesian speaking groups, instead of Austroasiatic groups that being proposed in Simanjutak studies in 2017. The Austronesian expansion did occur in the Malay Peninsula at roughly 3000 years ago with the supports of fossil indication. Concluding that Malaysian are Austroasiatic due to linguistic difference aren't sufficient, Malaysian underwent heavy linguistic chances due to islamization in the early 7th centuries and incorporation of tonal chances of previous migration of Austroasiatic speakers in the region.
According to Juha Janhunen
Juha Janhunen (born 12 February 1952 in Pori, Finland) is a Finnish linguist whose wide interests include Uralic and Mongolic languages. Since 1994 he has been Professor in East Asian studies at the University of Helsinki. He has done fieldwork on ...
and Ann Kumar, Austronesians may have also settled parts of southern Japan, especially on the islands of Kyushu and Shikoku
is the smallest of the four main islands of Japan. It is long and between wide. It has a population of 3.8 million (, 3.1%). It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include ''Iyo-no-futana-shima'' (), '' ...
, and influenced or created the ''"Japanese-hierarchical society"''. It is suggested that Japanese tribes like the Hayato people, the Kumaso
The were a mythical people of ancient Japan mentioned in the ''Kojiki'', believed to have lived in the south of Kyūshū until at least the Nara period. The last leader of the Kumaso, Torishi-Kaya was killed by Yamato Takeru in 397. The name of K ...
and the Azumi people
The were a warrior clan and tribe during the Jōmon period in Japan, whose cultures and beliefs are considered to be one of Japan’s earliest sea religions. Their existence dates back to the early 3rd – 7th centuries, when their extensive k ...
were of Austronesian origin. Until today, local traditions and festivals show similarities to the Malayo-Polynesian culture.
 The Sino-Austronesian hypothesis, on the other hand, is a relatively new hypothesis by Laurent Sagart, first proposed in 1990. It argues for a north–south linguistic genetic relationship between Chinese and Austronesian. This is based on sound correspondences in the basic vocabulary and morphological parallels. Sagart places special significance in shared vocabulary on cereal crops, citing them as evidence of shared linguistic origin. However, this has largely been rejected by other linguists. The sound correspondences between Old Chinese and Proto-Austronesian can also be explained as a result of the Longshan interaction sphere, when pre-Austronesians from the Yangtze region came into regular contact with Proto-Sinitic speakers in the
The Sino-Austronesian hypothesis, on the other hand, is a relatively new hypothesis by Laurent Sagart, first proposed in 1990. It argues for a north–south linguistic genetic relationship between Chinese and Austronesian. This is based on sound correspondences in the basic vocabulary and morphological parallels. Sagart places special significance in shared vocabulary on cereal crops, citing them as evidence of shared linguistic origin. However, this has largely been rejected by other linguists. The sound correspondences between Old Chinese and Proto-Austronesian can also be explained as a result of the Longshan interaction sphere, when pre-Austronesians from the Yangtze region came into regular contact with Proto-Sinitic speakers in the Shandong Peninsula
The Shandong (Shantung) Peninsula or Jiaodong (Chiaotung) Peninsula is a peninsula in Shandong Province in eastern China, between the Bohai Sea to the north and the Yellow Sea to the south. The latter name refers to the east and Jiaozhou.
Geo ...
at around the 4th to 3rd millennia BCE. This corresponded with the widespread introduction of rice cultivation
The history of rice cultivation is an interdisciplinary subject that studies archaeological and documentary evidence to explain how rice was first domesticated and cultivated by humans, the spread of cultivation to different regions of the planet, ...
to Proto-Sinitic speakers and conversely, millet cultivation to Pre-Austronesians. An Austronesian substratum in formerly Austronesian territories that have been Sinicized
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies come under the influence of Chinese culture, particularly the language, societal norms, cul ...
after the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Han expansion
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
is also another explanation for the correspondences that do not require a genetic relationship.
In relation to Sino-Austronesian models and the Longshan interaction sphere, Roger Blench (2014) suggests that the single migration model for the spread of the Neolithic into Taiwan is problematic, pointing out the genetic and linguistic inconsistencies between different Taiwanese Austronesian groups. The surviving Austronesian populations on Taiwan should rather be considered as the result of various Neolithic migration waves from the mainland and back migration from the Philippines. These incoming migrants almost certainly spoke languages related to Austronesian or pre-Austronesian, although their phonology and grammar would have been quite diverse.Blench, Roger. 2014. Suppose we are wrong about the Austronesian settlement of Taiwan?
'' m.s. Blench considers the Austronesians in Taiwan to have been a melting pot of immigrants from various parts of the coast of Minyue, present-day
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, eastern China that had been migrating to Taiwan by 4,000 BP These immigrants included people from the foxtail millet-cultivating Longshan culture
The Longshan (or Lung-shan) culture, also sometimes referred to as the Black Pottery Culture, was a late Neolithic culture in the middle and lower Yellow River valley areas of northern China from about 3000 to 1900 BC. The first archaeological fi ...
of Shandong (with Longshan-type cultures found in southern Taiwan), the fishing-based Dapenkeng culture of coastal Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, and the Yuanshan culture of northernmost Taiwan which Blench suggests may have originated from the coast of Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ...
. Based on geography and cultural vocabulary, Blench believes that the Yuanshan people may have spoken Northeast Formosan languages. Thus, Blench believes that there is in fact no "apical" ancestor of Austronesian in the sense that there was no true single Proto-Austronesian language
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
that gave rise to present-day Austronesian languages. Instead, multiple migrations of various pre-Austronesian peoples and languages from the Chinese mainland that were related but distinct came together to form what we now know as Austronesian in Taiwan. Hence, Blench considers the single-migration model into Taiwan by pre-Austronesians to be inconsistent with both the archaeological and linguistic (lexical) evidence.
Austronesian expansion

 The Austronesian expansion (also called the "Out of Taiwan" model) is a large-scale migration of Austronesians out of Taiwan, occurring around 1500-1000 BCE. Population growth primarily fueled this migration. These first settlers landed in northern Luzon in the archipelago of the Philippines, intermingling with the earlier
The Austronesian expansion (also called the "Out of Taiwan" model) is a large-scale migration of Austronesians out of Taiwan, occurring around 1500-1000 BCE. Population growth primarily fueled this migration. These first settlers landed in northern Luzon in the archipelago of the Philippines, intermingling with the earlier Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
population who had inhabited the islands since about 23,000 years earlier. Over the next thousand years, Austronesian peoples migrated southeast to the rest of the Philippines, and into the islands of the Celebes Sea
The Celebes Sea, (; ms, Laut Sulawesi, id, Laut Sulawesi, fil, Dagat Selebes) or Sulawesi Sea, of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east b ...
, Borneo, and Indonesia. The Austronesians that spread westward through Maritime Southeast Asia also colonized parts of mainland Southeast Asia.
Soon after reaching the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Austronesians colonized the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
by 1500 BCE and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
and Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
by 1000 BCE, becoming the first humans to reach Remote Oceania. Another important migration branch was by the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
, which rapidly spread into the islands off the coast of northern New Guinea and into the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
and other parts of Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
by 1200 BCE. They reached the islands of Fiji, Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
and Tonga by around 900 to 800 BCE. This remained the furthest extent of the Austronesian expansion into Polynesia until around 700 CE when there was another surge of island colonization. They reached the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
, Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austra ...
, and the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
by 700 CE; Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
by 900 CE; Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
by 1000 CE; and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
by 1200 CE. There is also putative evidence, based in the spread of the sweet potato, that Austronesians may have reached South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
from Polynesia where they traded with American Indians.
In the Indian Ocean, they sailed west from Maritime Southeast Asia; the Austronesian peoples reached Madagascar by ca. 50–500 CE. As for their route, one possibility is that the Indonesian Austronesian came directly across the Indian Ocean from Java to Madagascar. It is likely that they went through the Maldives where evidence of old Indonesian boat design and fishing technology persists until the present.
Alternative views
A competing hypothesis to the "Out of Taiwan" model is the "Out of Sundaland" hypothesis, favored by a minority of authors. Notable proponents include William Meacham,Stephen Oppenheimer
Stephen Oppenheimer (born 1947) is a British paediatrician, geneticist, and writer. He is a graduate of Balliol College, Oxford and an honorary fellow of the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. In addition to his work in medicine and tropi ...
, and Wilhelm Solheim. For various reasons, they proposed that the homelands of Austronesians were within Island Southeast Asia (ISEA), particularly in the Sundaland landmass drowned during the end of the last glacial period by rising sea levels. Proponents of these hypotheses point to the ancient origins of mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
in Southeast Asian populations, pre-dating the Austronesian expansion, as proof that Austronesians originated from within Island Southeast Asia.
However, these have been repudiated by studies using whole genome sequencing which has found that all ISEA populations had genes originating from the aboriginal Taiwanese. Contrary to the claim of a south-to-north migration in the "Out of Sundaland" hypothesis, the new whole genome analysis strongly confirms the north-to-south dispersal of the Austronesian peoples in the prevailing "Out of Taiwan" hypothesis. The researchers further pointed out that while humans have been living in Sundaland for at least 40,000 years, the Austronesian people were recent arrivals. The results of the previous studies failed to take into account admixture with the more ancient but unrelated Negrito and Papuan populations.
Historical period
 By the beginning of the first millennium CE, most of the Austronesian inhabitants in
By the beginning of the first millennium CE, most of the Austronesian inhabitants in Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
began trading with India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and China. The adoption of Hindu statecraft model allowed the creation of Indianized kingdoms such as Tarumanagara
Tarumanagara or Taruma Kingdom or just Taruma is an early Sundanese Indianised kingdom, located in western Java, whose 5th-century ruler, Purnawarman, produced the earliest known inscriptions in Java, which are estimated to date from arou ...
, Champa, Butuan
Butuan (pronounced ), officially the City of Butuan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Butuan; Butuanon: ''Dakbayan hong Butuan''; fil, Lungsod ng Butuan), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Caraga, Philippines. It is the ''de facto'' c ...
, Langkasuka
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of ''langkha'' for "resplendent land" -'' sukkha'' for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old K ...
, Melayu, Srivijaya, Mataram, Majapahit, and Bali. Between the 5th to 15th century Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
were established as the main religion in the region.
Muslim traders from the Arabian peninsula were thought to have brought Islam by the 10th century. Islam was established as the dominant religion in the Malay archipelago by the 16th centuThe Austronesian inhabitants of Near Oceania and Remote Oceania were unaffected by this cultural trade and retained their indigenous culture in the Pacific region.
Kingdom of Larantuka
The Kingdom of Larantuka was a historical monarchy in present-day East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It was the one of the few, if not the only, indigenous Catholic polities in the territory of modern Indonesia. Acting as a tributary state of the ...
in Flores, East Nusa Tenggara
East Nusa Tenggara ( id, Nusa Tenggara Timur – NTT; pt, Sonda Oriental) is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It comprises the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the nor ...
was the only Christian (Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
) indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
kingdom in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, with the first king named Lorenzo.
Western Europeans in search of spices and gold later colonized most of the Austronesian-speaking countries of the Asia-Pacific region, beginning from the 16th century with the Portuguese and Spanish colonization of the Philippines, Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
, Guam, the Mariana Islands, and some parts of Indonesia (present-day East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
); the Dutch colonization of the Indonesian archipelago; the British colonization of Malaysia and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
; the French colonization of French Polynesia; and later, the American governance of the Pacific.
Meanwhile, the British, Germans, French, Americans, and Japanese began establishing spheres of influence within the Pacific Islands during the 19th and early 20th centuries. The Japanese later invaded most of Southeast Asia and some parts of the Pacific during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The latter half of the 20th century initiated independence of modern-day Indonesia, Malaysia, East Timor and many of the Pacific Island nations, as well as the re-independence of the Philippines.
Culture
The native culture of Austronesia varies from region to region. The early Austronesian peoples considered the sea as the basic feature of their life. Following their diaspora toSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, they migrated by boat to other islands. Boats of different sizes and shapes have been found in every Austronesian culture, from Madagascar, Maritime Southeast Asia, to Polynesia, and have different names.
In Southeast Asia, head-hunting was restricted to the highlands as a result of warfare. Mummification is only found among the highland Austronesian Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
, and in some Indonesian groups in Celebes and Borneo.
Ships and sailing
 Sea-going catamaran and outrigger ship technologies were the most important innovations of the Austronesian peoples. They were the first humans with vessels capable of crossing vast distances of water, which enabled them to colonize the Indo-Pacific in prehistoric times. Austronesian groups continue to be the primary users of the outrigger canoes today.
Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamarans evolved from outrigger canoes, but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite.
Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the double-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger, giving way to the single outrigger canoe, then to the reversible single outrigger canoe. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimarans).
This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia tend to favor double outrigger canoes, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking. But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Micronesia,
Sea-going catamaran and outrigger ship technologies were the most important innovations of the Austronesian peoples. They were the first humans with vessels capable of crossing vast distances of water, which enabled them to colonize the Indo-Pacific in prehistoric times. Austronesian groups continue to be the primary users of the outrigger canoes today.
Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamarans evolved from outrigger canoes, but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite.
Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the double-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger, giving way to the single outrigger canoe, then to the reversible single outrigger canoe. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimarans).
This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia tend to favor double outrigger canoes, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking. But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Micronesia, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, and the Comoros retained the double-hull and the single outrigger canoe types, but the technology for double outriggers never reached them (although it exists in western Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
). To deal with the problem of the instability of the boat when the outrigger faces leeward when tacking, they instead developed the shunting technique in sailing, in conjunction with reversibleThe boat is symmetrical front and back, and the prow alternately becomes the stern and vice versa when sailing against the wind single-outriggers.
The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of a single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the prow and stern. These were fitted tightly together edge-to-edge with dowels inserted into holes in between, and then lashed to each other with ropes (made from rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan, is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the closed- canopy old-growth tropical fores ...
or fibre) wrapped around protruding lugs on the planks. This characteristic and ancient Austronesian boat-building practice is known as the " lashed-lug" technique. They were commonly caulked with pastes made from various plants as well as Paper mulberry, tapa bark and fibres which would expand when wet, further tightening joints and making the hull watertight. They formed the shell of the boat, which was then reinforced by horizontal ribs. Shipwrecks of Austronesian ships can be identified from this construction, as well as the absence of metal nails. Austronesian ships traditionally had no central rudders but were instead steered using an oar on one side.
The ancestral rig was the mastless triangular crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Islan ...
which had two booms that could be tilted to the wind. These were built in the double-canoe configuration or had a single outrigger on the windward side. In Island Southeast Asia, these developed into double outriggers on each side that provided greater stability. The triangular crab claw sails also later developed into square or rectangular tanja sails, which like crab claw sails, had distinctive booms spanning the upper and lower edges. Fixed masts also developed later in both Southeast Asia (usually as bipod or tripod masts) and Oceania. Austronesians traditionally made their sails from woven mats of the resilient and salt-resistant pandanus leaves. These sails allowed Austronesians to embark on long-distance voyaging. In some cases, however, they were one-way voyages. The failure of pandanus to establish populations in Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
is believed to have isolated their settlements from the rest of Polynesia.
 The ancient Champa of
The ancient Champa of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
also uniquely developed basket-hulled boats whose hulls were composed of woven and resin-caulked bamboo, either entirely or in conjunction with plank strakes. They range from small coracles (the ''o thúng'') to large ocean-going trading ships like the ''ghe mành''.
The acquisition of the catamaran and outrigger technology by the non-Austronesian peoples in Sri Lanka and southern India is due to the result of very early Austronesian contact with the region, including the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
and the Laccadive Islands, estimated to have occurred around 1000 to 600 BCE and onwards. This may have possibly included limited colonization that have since been assimilated. This is still evident in Sri Lankan and South Indian languages. For example, Tamil language, Tamil ''paṭavu'', Telugu language, Telugu ''paḍava'', and Kannada language, Kannada ''paḍahu'', all meaning "ship", are all derived from Proto-Hesperonesian *padaw, "sailboat", with Austronesian cognates like Javanese ''perahu'', Kadazan language, Kadazan ''padau'', Maranao language, Maranao ''padaw'', Cebuano language, Cebuano ''paráw'', Samoan ''folau'', Hawaiian ''halau'', and Māori language, Māori ''wharau''.
Early contact with Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
ships in the Indian Ocean during Austronesian voyages is also believed to have resulted in the development of the triangular lateen sail.
Architecture
Austronesian architecture is a vernacular highly diverse, often with striking designs; but they all share certain characteristics that indicate a common origin. The Comparative method, reconstructedProto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
and Proto-Malayo-Polynesian forms of various terms for "house", "building", or "granary" among the different linguistic subgroups of Austronesians include *Rumaq ("house");Cognate, Cognates include Paiwan language, Paiwan ''umaq'', Tboli language, T'boli ''lumak'', Malay ''rumah'', Acehnese language, Acehnese ''rumòh'', Sawai language, Sawai ''um'', Rotinese language, Rotinese ''uma'', Torau language, Torau ''ruma'', and Chuukese language, Chuukese ''iimw''. *balay ("public building", "community house", or "guest house");Cognates include Tagalog ''Bahay kubo, báhay'', Cebuano language, Cebuano ''baláy'', Malay ''balai'', Balinese language, Balinese ''bale'', Fijian ''vale'', Hawaiian ''hale'', and Māori language, Māori ''whare''. *lepaw ("hut", "field hut", or "granary");Cognates include Kavalan language, Kavalan ''repaw'', Kenyah language, Kenyah ''lepaw'', Malay ''lepau'', and Sika language, Sika ''lepo''. *kamaliR ("bachelor's house" or "men's house");Cognates include Yami language, Yami ''kamalig'', Tagalog ''kamálig'', Old Javanese
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the island ...
''kamalir'', Hawu language, Hawu ''kemali'', and Papitalai language, Papitalai ''kamal''. and *banua ("inhabited land" or "community territory").Cognates include Cebuano language, Cebuano ''banwá'', Iban language, Iban ''menoa'', Banggai language, Banggai ''bonua'', Selaru language, Selaru ''hnua'', Sawai language, Sawai ''pnu'', Fijian ''vanua'', Samoan ''fanua'', Hawaiian ''honua'', and Māori language, Māori ''whenua''.
The most ubiquitous common feature of Austronesian structures is the raised floor. The structures are raised on Stilt house, piles, usually with space underneath also utilized for storage or Domesticated animals of Austronesia, domestic animals. The raised design had multiple advantages, they mitigate damage during flooding and (in very tall examples) can act as defensive structures during conflicts. The house posts are also distinctively capped with larger-diameter discs at the top, to prevent vermin and pests from entering the structures by climbing them. Austronesian houses and other structures are usually built in wetlands and alongside bodies of water, but can also be built in the highlands or even directly on shallow water.
Building structures on pilings is believed to be derived from the design of raised granaries and storehouses, which are highly important status symbols among the ancestrally rice-cultivating Austronesians. The rice granary shrine was also the archetypal religious building among Austronesian cultures and was used to store carvings of ancestor spirits and local deities.
Another common feature are Pitched roof, pitched roofs with ornamented Gable, gables. The most notable of which are the saddlebacked roofs, a design common for Longhouse, longhouses used for village meetings or ceremonies. The overall effect of which is reminiscent of boats, underlining the strong maritime connections of Austronesian cultures. The boat motif is common throughout, particularly in eastern Indonesia. In some ethnic groups, the houses are built on platforms that resemble Catamaran, catamarans. Among the Nage people, a woven representation of a boat is added to the ridge of the roof; among the Manggarai people, the roofs of houses are shaped like an upside-down boat; while among the people of Tanimbar and eastern Flores, the ridge itself is carved into a representation of a boat. Furthermore, elements of Austronesian structures (as well as society in general) are often referred to in terminologies used for boats and sailing. These include calling elements of structures as "masts", "sails", or "rudders" or calling the village leaders as "captains" or "steersmen". In the case of the Philippines, the villages themselves are referred to as ''barangay'', from an alternate form of ''balangay'', a type of sailboat used for trading and colonization.
Austronesian buildings have spiritual significance, often containing what is coined by anthropologist James J. Fox as a "ritual attractor." These are specific posts, beams, platforms, altars, and so on that embody the house as a whole, usually consecrated at the time of building.
The Austronesian house itself also often symbolizes various aspects of indigenous Austronesian cosmology and animism. In the majority of cases, the loft of the house (usually placed above the hearth), is considered to be the domain of deities and spirits. It is essentially a raised granary built into the structure of the house itself and functioned as a second floor. It is usually used to store sacred objects (like effigies of granary idols or deceased ancestors), heirlooms, and other important objects. These areas are usually not part of the regular living space, and may only be accessible to certain members of the family or after performing a specific ritual. Other parts of the house may also be associated with certain deities, and thus certain activities like receiving guests or conducting marriage ceremonies can only be performed in specific areas.
While rice cultivation wasn't among the technologies carried into Remote Oceania, raised storehouses still survived. The ''pataka'' of the Māori people is an example. The largest ''pataka'' are elaborately adorned with carvings and are often the tallest buildings in the Māori ''pā''. These were used to store implements, weapons, ships, and other valuables; while smaller ''pataka''s were used to store provisions. A special type of ''pataka'' supported by a single tall post also had ritual importance and were used to isolate high-born children during their training for leadership.
The majority of Austronesian structures are not permanent. They are made from perishable materials like wood, bamboo, plant fibre, and leaves. Similar to traditional Austronesian boats, they do not use nails but are traditionally constructed solely by joints, weaving, ties, and Dowel, dowels. Elements of the structures are repaired and replaced regularly or as they get damaged. Because of this, archaeological records of prehistoric Austronesian structures are usually limited to traces of house posts, with no way of determining the original building plans.
Indirect evidence of traditional Austronesian architecture, however, can be gleaned from their contemporary representations in art, like in friezes on the walls of later Indian religions, Hindu-Buddhist stone temples (like in reliefs in Borobudur and Prambanan). But these are limited to the recent centuries. They can also be reconstructed linguistically from shared terms for architectural elements, like ridge-poles, thatch, rafters, house posts, hearth, notched log ladders, storage racks, public buildings, and so on. Linguistic evidence also makes it clear that Stilt house, stilt houses were already present among Austronesian groups since at least the Late Neolithic.
In modern Indonesia, varying styles are collectively known as Rumah adat.
Arbi ''et al.'' (2013) have also noted the striking similarities between Austronesian architecture and Japanese traditional raised architecture (''shinmei-zukuri''). Particularly the buildings of the Ise Grand Shrine, which contrast with the pit-houses typical of the Neolithic Yayoi period. They propose significant Neolithic contact between the people of southern Japan and Austronesians or pre-Austronesians that occurred prior to the spread of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
cultural influence to the islands. Rice cultivation is also believed to have been introduced to Japan from a para-Austronesian group from coastal eastern China. Waterson (2009) has also argued that the architectural tradition of Stilt house, stilt houses is originally Austronesian, and that similar building traditions in Japan and mainland Asia (notably among Kra-Dai and Austroasiatic-speaking groups) correspond to contacts with a prehistoric Austronesian network.
Sama-Bajau
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exo ...
villages are typically built directly on shallow water
File:Traditional stilt houses in Bangaan of the Ifugao people.jpg, The raised ''bale'' houses of the Ifugao people with capped house posts are believed to be derived from the designs of traditional granaries
File:Toraja house.jpg, ''Tongkonan'' houses of the Toraja people with the distinctive saddleback roofs reminiscent of boats
File:Details on a bai at the National Museum in Palau.jpg, ''Bai'' meeting house of the Palauan people with colourfully decorated gables
File:Besakana traditional Merina andriana house Rova Antananarivo Madagascar.jpg, ''Besakana'' of the Merina people
File:House in suburbs of Manila, 1899.jpg, ''Bahay kubo'' of the Filipinos. Also known as ''Payag'' in Bisayan languages, Visayan.
File:Maori pataka.jpg, Māori culture, Māori ''pataka'' storehouses
File:Fijian chiefs cottage.jpg, ''Bure (Fiji), Bure'' of the Fijian people
File:Houses bondokodi sumba.JPG, ''Uma mbatangu'' of the Sumba people
File:Batak Toba House.jpg, ''Batak architecture, Jabu'' of the Toba Batak people
File:TMII Aceh House.jpg, ''Rumoh Aceh, Rumoh'' of the Acehnese people
File:Rumah Gadang Minangkabau.jpg, ''Rumah gadang'' of the Minangkabau people
File:Model of Torogan Marano.jpg, ''Torogan'' of the Maranao people
Pottery
Outside of Taiwan, assemblages of red-slipped pottery, plainware, and incised and stamped pottery associated with the Austronesian migrations are first documented from around 2000 to 1800 BCE in the northernPhilippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, from sites in the Batanes Islands and the Cagayan Valley of Northern Luzon. From there pottery technology rapidly spread to the east, south, and southwest.
 One branch of the migrations carried pottery to the Marianas Islands at around 1500 BCE, where the earliest archaeological sites have uncovered pottery very similar to those found in the Nagsabaran Site (2000 to 1300 BCE) in Cagayan Valley in the Philippines. This indicates that the northeastern coast of Luzon is the most likely point of origin of the first open-ocean colonizing voyages into the Pacific Islands. Philippine and Marianas red-slipped pottery are both decorated with rows of stamped circles, incised patterns, and tiny delicate punch-marks. While similar red-slipped pottery also exist in the Batanes Islands and
One branch of the migrations carried pottery to the Marianas Islands at around 1500 BCE, where the earliest archaeological sites have uncovered pottery very similar to those found in the Nagsabaran Site (2000 to 1300 BCE) in Cagayan Valley in the Philippines. This indicates that the northeastern coast of Luzon is the most likely point of origin of the first open-ocean colonizing voyages into the Pacific Islands. Philippine and Marianas red-slipped pottery are both decorated with rows of stamped circles, incised patterns, and tiny delicate punch-marks. While similar red-slipped pottery also exist in the Batanes Islands and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, they lack the characteristic circle and punctate-stamped decorations. Other migrations, meanwhile, dispersed south and southwest to the rest of Island Southeast Asia. The eastward and the southward branches of the migrations converged in Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
resulting in what is now known as the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
centered around the Bismarck Archipelago.
The Lapita culture made distinctive dentate-stamped pottery. It also retained elements also found in the Nagsabaran pottery in the Philippines, including stamped circles as well as the cross-in-circle motif. They carried pottery technology as far as Tonga in Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
. Pottery technology in Tonga, however, became reduced to undecorated plainware within only two centuries before abruptly disappearing completely by around 400 BCE. The reasons for this are still unknown. Pottery was absent in subsequent migrations to the rest of Remote Oceania, being replaced instead with carved wooden or bamboo containers, bottle gourds, and baskets. However, the geometric designs and stylized figures used in the pottery are still present in other surviving artforms like in tattooing, weaving, and barkcloth patterns.
A common practice among Austronesians in a large area of Island Southeast Asia is the use of burial jars which emerged during the Late Neolithic and flourished in the first millennium CE. They are characteristic of a region bordered by the Philippines to the north, southern Sumatra in the southwest, and Sumba and the Maluku Islands in the southeast. However, these didn't comprise a single tradition, but can be grouped into at least fourteen different traditions scattered across the islands. In most cases, the earliest burial jars used were large indigenous earthenware jars, followed by indigenous or imported stoneware jars (''martaban jar, martaban''), and finally imported porcelain jars acquired from the burgeoning maritime trade with China and Mainland Southeast Asia at around the 14th century CE.
Music and dance
Slit drums are indigenous Austronesian musical instrument that were invented and used by the Southeast Asian-Austronesian, and Oceanic-Austronesian ethnic groups. Gong ensembles are also a common musical heritage of Island Southeast Asia. The casting of gong instruments are believed to have originated from the Bronze Age cultures of Mainland Southeast Asia. It spread to Austronesian islands initially through trade as prestige goods. However, Mainland Asian gongs were never used in ensembles. The innovation of using gong sets is uniquely Austronesian. Gong ensembles are found in western Malayo-Polynesian groups, though they never penetrated much further east. There are roughly two gong ensemble traditions among Austronesians, which also produced gongs in ancient times. In western Island Southeast Asia, these traditions are collectively known as Gamelan, being centred on the island ofJava
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mos ...
in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. It includes the Celempung of the Malay Peninsula, Talempung of northern Sumatra, Caklempung of central Sumatra, Chalempung of southern Sumatra, Bonang of Java, Kromong of western Kalimantan, Engkromong of Sarawak, and Trompong of western Nusa Tenggara.
In eastern Island Southeast Asia, these traditions are known as Kulintang and are centred in Mindanao and the Sulu archipelago of the southern Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. It includes the Kulintangan of Sabah and Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in t ...
, Kolintang of northern Sulawesi, Kulintang of Halmahera and Timor, and the Totobuang of the southern Maluku Islands.
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
File:Karinding-West Javan je'ws harp.JPG, ''Karinding'' jaw harps of the Sundanese people, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:YanAriefSapeh.jpg, ''Sapeh'', traditional lutes of the Orang Ulu people of Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
File:Wooden slit drums from Vanuatu, Bernice P. Bishop Museum.JPG, ''Atingting kon'', wooden slit drums from Vanuatu
File:Traditional indonesian instruments02.jpg, An Indonesian ''gamelan'' ensemble
File:Hula Kahiko Hawaii Volcanoes National Park 01.jpg, A Native Hawaiians, ''kanaka maoli'' (native) from Hawaii performing the ''Hula Dance, hula''
File:Young Maori man dancing.jpg, ''Kapa haka'' of the Māori people
File:Traditional song and dance Tana Toraja.jpg, Traditional song and dance at a funeral in Tana Toraja, Sulawesi, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:Ramawijaya dan Shinta pada Sendratari Ramayana Prambanan.jpg, Ramayana Ballet, traditional theatre dance from Javanese dance, Java, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:Gadispalembang.jpg, Gending Sriwijaya, traditional dance from Palembang, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:KABASARAN.jpg, A Minahasan Kabasaran war dancer from Tomohon, North Sulawesi, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:Kecak dancers cliffside Uluwatu.jpg, Kecak, Kecak dancers from Bali, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:The Hudoq Dancers.jpg, Hudoq, traditional dance from Kalimantan, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
Jade carving
The ancestral pre-Austronesian Liangzhu culture (3400–2250 BCE) of theYangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
delta was one of the ancient centres of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
jade carving. Jade was spread to Taiwan by around 3,000 BCE, then further into the Philippines at 2,000 BCE and Vietnam at 1,800–1,500 BCE. All of them began to produce various tools and ornaments in indigenous jade workshops, including adzes, bracelets, beads, and rings.
 The most notable jade products of these regions were the vast amounts of penannular and double-headed earrings and pendants known as ''lingling-o'', primarily produced in the Philippines and the Sa Huỳnh culture of
The most notable jade products of these regions were the vast amounts of penannular and double-headed earrings and pendants known as ''lingling-o'', primarily produced in the Philippines and the Sa Huỳnh culture of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, though remarkably mostly with the raw jade material sourced from eastern Taiwan. These typically depict two-headed animals or were ring-shaped with side projections. They were indicative of a very active ancient maritime trading region that imported and exported raw jade and finished jade ornaments known as the Sa Huynh-Kalanay Interaction Sphere. They were produced during a period between 500 BCE to as late as 1000 CE, although later examples were replaced with metal, wood, bone, clay, green mica, black nephrite, or shell materials, rather than green jade.
Polished and ground stone adzes, Chisel, gouges, and other implements, some of which are made from jade-like stone, have also been recorded in areas of Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
and eastern New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
associated with the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
. These were considered valuable currency and were primarily used to trade for goods. In 2012, a Lapita culture jadeite gouge used for wood carving was found in Emirau Island in the Bismarck Archipelago. It was dated to around 3,300 BP, but the origin of the jade material is unknown. Similar prestige stone tools have also been found in New Caledonia.
Jade was absent in most of Remote Oceania, due to the lack of jade deposits. However, there is putative evidence that Polynesians may have remained familiar with jade and may have acquired them through prehistoric trade contacts with New Caledonia, Island Melanesia, and/or New Zealand.
Jade carving traditions reappeared among the Māori people of New Zealand. These were produced from locally sourced (greenstone) and were used to produce (treasure). They include various tools and weapons like adzes, scrapers, fishing hooks, and , as well as ornaments like the and . Certain ornaments like the (double-headed animal pendant) and the (bird leg ring) bear remarkably strong resemblances to the double-headed and ring-type ''linglingo''. Bellwood ''et al.'' (2011) has suggested that the reappearance of these motifs might be evidence of a preserved tradition of Southeast Asian jade motifs (perhaps carved in perishable wood, bone, or shell by Polynesians prior to the reacquisition of a jade source), or they might even be the result of a later Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
contact between eastern Polynesia and the Philippines.
Rock art
 There are around six hundred to seven hundred rock art sites discovered in Southeast Asia and
There are around six hundred to seven hundred rock art sites discovered in Southeast Asia and Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, as well as over eight hundred megalithic sites. The sites specifically associated with the Austronesian expansion contain examples of indigenous pictograms and petroglyphs. Within Southeast Asia, the sites associated with Austronesians can be divided into three general rock art traditions: the Megalithic Culture of Borneo, Sulawesi, and the Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands ( Indonesian and Malay: ''Kepulauan Sunda Besar'') are four tropical islands situated within Indonesian Archipelago, in the Pacific Ocean. The islands, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi and Sumatra, are internationally recognised ...
; the Austronesian Painting Tradition of the Lesser Sunda Islands, coastal New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
, and Island Melanesia; and the Austronesian Engraving Style of Papua New Guinea and Island Melanesia. Despite proximity, these traditions can be distinguished readily from the Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
rock art traditions of Australia (except the Torres Strait Islands) as well as the interior highlands of New Guinea, indicating the borders of the extent of the Austronesian expansion.
 Dating rock art is difficult, but some of the sites subjected to Absolute dating, direct dating pre-date Austronesian arrival, like the Lene Hara cave, Lene Hara paintings of
Dating rock art is difficult, but some of the sites subjected to Absolute dating, direct dating pre-date Austronesian arrival, like the Lene Hara cave, Lene Hara paintings of East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
which has an age range of 6,300 to 26,000 BP. Conversely, others are more recent and can be dated indirectly by their subjects. The depictions of pottery, ships, and metal objects, for example, put certain rock art sites at a range of 2,000 to 4,000 BP. Some hunter-gatherer groups have also continued to produce rock art well into the present period, as evidenced by their modern subjects.
 The Megalithic Culture is mostly limited to western Island Southeast Asia, with the greatest concentration being western Indonesia. While most sites aren't dated, the age ranges of dating sites are between the 2nd to 16th century CE. They are divided into two phases. The first is an older megalithic tradition associated with the Neolithic Austronesian rectangular axe culture (2,500 to 1,500 BCE); while the second is the 3rd or 4th century BCE megalithic tradition associated with the (non-Austronesian) Dong Son culture of
The Megalithic Culture is mostly limited to western Island Southeast Asia, with the greatest concentration being western Indonesia. While most sites aren't dated, the age ranges of dating sites are between the 2nd to 16th century CE. They are divided into two phases. The first is an older megalithic tradition associated with the Neolithic Austronesian rectangular axe culture (2,500 to 1,500 BCE); while the second is the 3rd or 4th century BCE megalithic tradition associated with the (non-Austronesian) Dong Son culture of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. Prasetyo (2006) suggests that the megalithic traditions are not originally Austronesian, but rather innovations acquired through trade with India and China, but this has little to no evidence in the intervening regions in Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
 The Austronesian Painting Traditions (APT) are the most common types of rock art in Island Southeast Asia. They consist of scenes and pictograms typically found in rock shelters and caves near coastal areas. They are characteristically rendered in red ochre pigments for the earlier forms, later sometimes superseded by paintings done in black charcoal pigments. Their sites are mostly clustered in Eastern Indonesia and
The Austronesian Painting Traditions (APT) are the most common types of rock art in Island Southeast Asia. They consist of scenes and pictograms typically found in rock shelters and caves near coastal areas. They are characteristically rendered in red ochre pigments for the earlier forms, later sometimes superseded by paintings done in black charcoal pigments. Their sites are mostly clustered in Eastern Indonesia and Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, although a few examples can be found in the rest of Island Southeast Asia. Their occurrence has a high correlation to Austronesian-speaking areas, further evidenced by the appearance of metal (bronze) artifacts in the paintings. They are mostly found near the coastlines. Their common motifs include hand stencils, "sun-ray" designs, boats, and active human figures with headdresses or weapons and other paraphernalia. They also feature geometric motifs similar to the motifs of the Austronesian Engraving Style. Some paintings are also associated with traces of human burials and funerary rites, including ship burials. The representations of boats themselves are believed to be connected to the widespread "ship of the dead" Austronesian funerary practices.
 The earliest APT sites dated is from Vanuatu, which was found to be around 3,000 BP, corresponding to the initial migration wave of the Austronesians. These early sites are largely characterized by face motifs and hand stencils. Later sites from 1,500 BP onwards, however, begin to show regional divergence in their art styles. APT can be readily distinguished from older Pleistocene-era Australo-Melanesian cave paintings by their motifs, color, and composition, though they can often be found in the same locality. The most recognizable motifs of APT (like boats) do not occur in cave paintings (or engravings) that definitely pre-date the Austronesian arrival, the sole exception being the stencilled hand motif. Some APT examples are also characteristically found in relatively inaccessible locations like very high up in cliffsides overlooking the sea. No traces of APT has been found in Taiwan or the Philippines, though there is continuity in the motifs of spirals and concentric circles found in ancestral petroglyphs.
The Austronesian Engraving Style (AES), consisting of petroglyphs carved into rock surfaces, is far less common than APT. The majority of these sites are in coastal New Guinea, and
The earliest APT sites dated is from Vanuatu, which was found to be around 3,000 BP, corresponding to the initial migration wave of the Austronesians. These early sites are largely characterized by face motifs and hand stencils. Later sites from 1,500 BP onwards, however, begin to show regional divergence in their art styles. APT can be readily distinguished from older Pleistocene-era Australo-Melanesian cave paintings by their motifs, color, and composition, though they can often be found in the same locality. The most recognizable motifs of APT (like boats) do not occur in cave paintings (or engravings) that definitely pre-date the Austronesian arrival, the sole exception being the stencilled hand motif. Some APT examples are also characteristically found in relatively inaccessible locations like very high up in cliffsides overlooking the sea. No traces of APT has been found in Taiwan or the Philippines, though there is continuity in the motifs of spirals and concentric circles found in ancestral petroglyphs.
The Austronesian Engraving Style (AES), consisting of petroglyphs carved into rock surfaces, is far less common than APT. The majority of these sites are in coastal New Guinea, and Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
. AES sites, which can be tentatively traced back to the similar Wanshan Rock Carvings Archeological Site, Wanshan petroglyphs of Taiwan, are believed to be largely correlated to the prehistoric extent of the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
. The common motif of this tradition is curvilinear geometric engravings like spirals, concentric circles, and face-like forms. These resemble the geometric motifs in APT, though they are considered to be two separate artistic traditions. AES is particularly dominant in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
and New Caledonia, where engravings are far more abundant than painted sites.
 O'Connor ''et al.'' (2015) proposes that APT developed during the initial rapid southward Austronesian expansion, and not before, possibly as a response to the communication challenges brought about by the new maritime mode of living. Along with AES, these material symbols and associated rituals and technologies may been the manifestations of "powerful ideologies" spread by Austronesian settlers that were central to the "Neolithization" and rapid assimilation of the various non-Austronesian indigenous populations of ISEA and Melanesia.
O'Connor ''et al.'' (2015) proposes that APT developed during the initial rapid southward Austronesian expansion, and not before, possibly as a response to the communication challenges brought about by the new maritime mode of living. Along with AES, these material symbols and associated rituals and technologies may been the manifestations of "powerful ideologies" spread by Austronesian settlers that were central to the "Neolithization" and rapid assimilation of the various non-Austronesian indigenous populations of ISEA and Melanesia.
 The easternmost islands of Island Melanesia (Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia) are considered part of Remote Oceania as they are beyond the interisland visibility threshold. These island groups begin to show divergence from the APT and AES traditions of Near Oceania. While their art traditions show a clear continuation of the APT and AES traditions, they also feature innovations unique to each island group, like the increasing use of black charcoal, rectilinear motifs, and being found more inside sacred caves rather than in open cliffsides.
The easternmost islands of Island Melanesia (Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia) are considered part of Remote Oceania as they are beyond the interisland visibility threshold. These island groups begin to show divergence from the APT and AES traditions of Near Oceania. While their art traditions show a clear continuation of the APT and AES traditions, they also feature innovations unique to each island group, like the increasing use of black charcoal, rectilinear motifs, and being found more inside sacred caves rather than in open cliffsides.
 In Micronesia, the rock art traditions can be divided into three general regions: western, central, and eastern Micronesia. The divisions reflect the various major migration waves from the Philippines into the Mariana Islands and
In Micronesia, the rock art traditions can be divided into three general regions: western, central, and eastern Micronesia. The divisions reflect the various major migration waves from the Philippines into the Mariana Islands and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
at 3,500 BP; a Lapita culture back-migration from Island Melanesia into central and eastern Micronesia at around 2,200 BP; and finally a back-migration from western Polynesia into eastern Micronesia at around 1,000 BP.
In western Micronesia (Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
, Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
), rock art primarily consist of paintings on high cave ceilings and sea-facing cliffs. They are very similar to APT in terms of their motifs as well as their relatively inaccessible locations. Common motifs include hand stencils, faces, turtles and fish, concentric circles, and characteristic four-pointed stars. Petroglyphs are rare, but mainly consist of human forms with triangular bodies without heads or arms. This is believed to be connected to the funerary rite of removing the heads from the bodies of deceased relatives. A notable megalithic tradition in western Micronesia are the ''Latte stone, haligi'' stone pillars of the Chamorro people. These are capped stone pillars which are believed to have served as supports for raised buildings. They are associated with the Latte period (900 to 1700 CE), when a new wave of migrants from Southeast Asia reintroduced rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
Rice#History of domestication and cultivation, cultivation into the islands. Another megalithic tradition is also that of the rai stones, massive doughnut-shaped discs of rock which were used as currency in Yap.
Rock art in central Micronesia (Chuuk State, Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae), in contrast, are dominated by rock engravings with motifs tying it to the rock art traditions of Island Melanesia. They include curvilinear shapes like spirals and concentric circles, tree-like shapes, and the distinctive "enveloped cross" motif. The Pohnpaid petroglyphs are the largest assemblage of rock engravings in the region, with motifs dominated by footprints, enveloped crosses, and outlined "sword-paddles". Central Micronesia also hosts the ruins of the stone cities of Nan Madol (1,180–1,200 CE) and Leluh archaeological site, Leluh (1,200–1,800 CE), in the islands of Pohnpei and Kosrae, respectively.
In the low-lying atolls of eastern Micronesia, rock art is rare to nonexistent, due to the absence of suitable rock surfaces for painting or engraving.

 In
In Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, rock art is dominated by petroglyphs, rather than paintings, and they show less variation than the rock art of Near Oceania and ISEA. In the western Polynesian islands nearest to Island Melanesia, rock art is rare (like in Tonga and Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
) or are absent entirely (like in the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
). However, petroglyphs are abundant in the islands in the further reaches of the Polynesian triangle, particularly in Hawaii, the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
, and Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
. Rapa Nui has the densest concentration of engravings in Polynesia as a whole; while the Puuloa petroglyphs site in Hawaii has the largest number of petroglyphs in a single site at over 21,000 engravings. Polynesia also features megalithic sacred ceremonial centres generally known as ''marae''.
In Tonga and Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
, the existing rock art sites consist mostly of engravings with motifs including curvilinear shapes, human figures, "jellyfish", turtles, birds, and footprints. These are typically carved in natural rock formations or ''marae'' sites.
In the central-eastern Polynesian islands, which include the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
and the Society Islands, petroglyphs are more numerous. They show the archetypal Polynesian motifs of turtles, faces, cup-like depressions (cupules), stick-like human figures, boats, fish, curvilinear shapes, and concentric circles. Like in western Polynesia, they are typically carved into ''marae'' sites or in rocks beside streams. The existing rock paintings also display the same motifs but are rendered in different styles.
In the Hawaiian islands, the abundant petroglyphs are remarkably all similar in execution. Their common subjects include stick-like human figures, dogs, boats, sails, paddles, footprints, and ceremonial headdresses. Depictions of marine life, however, is rare, unlike the rest of Polynesia. They are typically carved into boulders, lava rock formations, and cliffsides. Red paintings of dogs in cliffsides and caves can also be found in Kauai, Kauai and Maui. The megalithic traditions of Hawaii can be exemplified by the ''heiau'' sacred sites, which can range from simple earth terraces to standing stones.
In Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
, the engravings are distinctive but still show similarities to the techniques and motifs of the Marquesas. Their motifs commonly include disembodied parts of the human body (Vagina and vulva in art, vulvae in particular), animals, plants, ceremonial objects, and boats. A prominent motif is also that of the "birdman" figure which is associated with the ''tangata manu'' cult of Makemake (deity), Makemake. The most well-known rock art assemblage of Rapa Nui, however, are the ''moai'' megaliths. A few paintings mostly of birds and boats have also been discovered which are associated with the engravings, rather than being separate artforms.
The rock art in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
can be divided into two regions. North Island features more engravings than paintings, while South Island is unique in that it is the only Polynesian island where there are more paintings than engravings. New Zealand rock paintings are done in red and black pigments and can sometimes be found in inaccessible heights. They typically depict human figures (particularly a front-facing human figure with flexed arms), birds, lizards, dogs, fish, and what has been identified as "birdmen". Engravings in open spaces like cliffsides are generally of spirals and curvilinear shapes, while engravings in enclosed caves and shelters depict faces and boats. The same motifs can also be seen in dendroglyphs on living trees.
Body art
Body art among Austronesian peoples is common, especially elaborate tattooing which is one of the most well-known pan-Austronesian traditions.Tattooing
In modern times, tattoos are usually associated with Polynesian people, Polynesian culture, due to the highly influential accounts of James Cook in his explorations of the Pacific in the 18th century. Cook introduced the word "tattoo" (archaic: "tattaow", "tattow") into the English language, English vocabulary, from Tahitian language, Tahitian and Samoan ''tātau'' ("to tap"). However, tattoos exist prominently in various other Austronesian groups prior to contacts with other cultures. Tattoos had various functions among Austronesian societies. Among men, they were strongly linked to the widespread practice of head-hunting raids. In head-hunting societies, tattoos were records of how many heads the warriors had taken in battle, and was part of the initiation rites into adulthood. The number and location of tattoos, therefore, were indicative of a warrior's status and prowess. Among the Indigenous Taiwanese, tattoos were present for both men and women. Among the Tayal people, facial tattoos are dominant. They indicated maturity and skill in weaving and farming for women, and skill in hunting and battle for men. Like in most of Austronesia, tattooing traditions in Taiwan have largely disappeared due to the Sinicization of native peoples after the Taiwan under Qing rule, Chinese colonization of
Among the Indigenous Taiwanese, tattoos were present for both men and women. Among the Tayal people, facial tattoos are dominant. They indicated maturity and skill in weaving and farming for women, and skill in hunting and battle for men. Like in most of Austronesia, tattooing traditions in Taiwan have largely disappeared due to the Sinicization of native peoples after the Taiwan under Qing rule, Chinese colonization of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
in the 17th century, as well as conversion to Christianity. Most of the remaining tattoos are only found among elders.
One of the earliest descriptions of Austronesian tattoos by Europeans was during the 16th century History of the Philippines (1521–1898), Spanish expeditions to the Philippines, beginning with the Magellan expedition, first voyage of circumnavigation by Ferdinand Magellan. The Spanish encountered the heavily tattooed Visayan people in the Visayas, Visayas Islands, whom they named the "''Pintados''" (Spanish language, Spanish for "the painted ones"). However, Philippine tattooing traditions (''batok'') have mostly been lost as the natives of the islands converted to Christianity and Islam, though they are still practiced in isolated groups in the highlands of Luzon and Mindanao. Philippine tattoos were usually geometric patterns or stylized depictions of animals, plants, and human figures. Some of the few remaining traditional tattoos in the Philippines are from elders of the Igorot peoples. Most of these were records of war exploits against the Japanese during Military history of the Philippines during World War II, World War II.
Among the Māori of New Zealand, tattoos (''Tā moko, moko'') were originally carved into the skin using bone chisels (''uhi'') rather than through puncturing as in usual practice. In addition to being pigmented, the skin was also left raised into ridges of swirling patterns.
Dental modification
 Teeth blackening was the custom of dyeing one's teeth black with various tannin-rich plant dyes. It was practiced throughout almost the entire range of Austronesia, including Island Southeast Asia, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Island Melanesia, reaching as far east as Malaita. However, it was absent in Polynesia. It also existed in non-Austronesian populations in Mainland Southeast Asia and Japan. The practice was primarily preventative, as it reduced the chances of developing tooth decay similar to modern dental sealants. It also had cultural significance and was seen as beautiful. A common sentiment was that blackened teeth separated humans from animals.
Teeth blackening was often done in conjunction with other modifications to the teeth associated with beauty standards, including dental evulsion and teeth filing.
Teeth blackening was the custom of dyeing one's teeth black with various tannin-rich plant dyes. It was practiced throughout almost the entire range of Austronesia, including Island Southeast Asia, Madagascar, Micronesia, and Island Melanesia, reaching as far east as Malaita. However, it was absent in Polynesia. It also existed in non-Austronesian populations in Mainland Southeast Asia and Japan. The practice was primarily preventative, as it reduced the chances of developing tooth decay similar to modern dental sealants. It also had cultural significance and was seen as beautiful. A common sentiment was that blackened teeth separated humans from animals.
Teeth blackening was often done in conjunction with other modifications to the teeth associated with beauty standards, including dental evulsion and teeth filing.
Religion
The religious traditions of the Austronesian people focus mostly on ancestral spirits, nature spirits and gods. It is basically a complex Animism, animistic religion. Mythologies vary by culture and geographical location but share common basic aspects such as ancestor worship, animism, shamanism and the belief in a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world and powerful deities. There is also a great amount of shared mythology and a common belief in Mana. Currently, many of these beliefs have gradually been replaced. Examples of native religions include: Indigenous Philippine folk religions (including beliefs on the Anito), Sunda Wiwitan, Kejawen, Kaharingan or the Māori religion. Many Austronesian religious beliefs were incorporated into foreign religions introduced unto them, such asHinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, Christianity and Islam.
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
File:Nias Ahnenfiguren Museum Rietberg RIN 403.jpg, ''Adu zatua'' ancestor carvings of the Nias people of western Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:Anitos of Northern tribes (c. 1900, Philippines).jpg, ''Anito, Taotao'' carvings of ''anito'' ancestor spirits from the Ifugao people, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
File:Tikimarquesas.jpg, Stone ''tiki'' from Hiva Oa, Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
File:Kii at Puuhonua O Honaunau 01.jpg, ''Ki'i'' carving at Puʻuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park, Puʻuhonua o Hōnaunau, Hawaii
File:Maori wooden carvings in the Rotorua Museum-2.jpg, Māori ''Poupou (architecture), poupou'' from the Ruato tomb of Rotorua
File:AhuTongariki.JPG, ''Moai'' in Ahu Tongariki, Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
File:Tana Toraja, Tampangallo, coffins and tau taus (6823243058).jpg, Toraja ''tau tau'' (wooden statue of the deceased) in South Sulawesi, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
File:Balinese Traditional House Shrines 1452.jpg, Balinese small familial house shrines to Veneration of the dead, honor the households' ancestors in Bali, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
Writing
Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
File:Petroglifos en Orongo I.jpg, An example of the abundant petroglyphs in Orongo, Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
associated with the ''tangata manu'' cult of Makemake (deity), Makemake. Rongorongo does not appear in any of these petroglyphs.
File:Talang Tuo Inscription.jpg, The Talang Tuo inscription, a 7th-century Srivijaya stele featuring Old Malay written in a derivative of the Pallava script
File:DoctrinaChristianaEspanolaYTagala8-9.jpg, Page from ''Doctrina Christiana, Doctrina Cristiana Española Y Tagala'' (1593) featuring the Baybayin script alongside the Latin alphabet
Rapa Nui
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
, Austronesians did not have an indigenous writing system but rather adopted or developed writing systems after contact with various non-Austronesian cultures. There are various forms of symbolic communication by #Rock art, pictograms and petroglyphs, but these did not encode language.
Rongorongo, said to have originally been called ''kohau motu mo rongorongo'' ("lines of inscriptions for chanting out"), is the only pre-contact indigenous Austronesian system of glyphs that appear to be true writing or at least proto-writing. They consist of around 120 glyphs, ranging from representations of plants to animals, celestial objects, and geometric shapes. They were inscribed into wooden tablets about long using shark teeth and obsidian flakes. The wood allegedly came from Sophora toromiro, toromiro and Thespesia populnea, makoi trees, which is notable given that Rapa Nui was completely deforested at the History of Easter Island, time of European contact. Although of the surviving two dozen tablets, a few were made from trees introduced after European contact, as well as wood originating from European ships and driftwood. Rapa Nui also has a very rich assemblage of petroglyphs largely associated with the ''tangata manu'' ("birdman") cult of Makemake (deity), Makemake. Although some rongorongo glyphs may have been derived from these petroglyphs, rongorongo does not appear in any of the abundant rock carvings in Rapa Nui and seems to be restricted to the wooden tablets.
The tablets were first described by an outsider in 1864 by the Catholic Church, Catholic missionary Eugène Eyraud who said they were found "in all the houses." However, he paid them little attention and they remained unnoticed by the outside world. It wasn't until 1869 that one of the tablets came into the possession of Florentin-Étienne Jaussen, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Papeete, Bishop of Tahiti. He brought the tablets to the world's attention and instructed the Rapa Nui mission to gather more information about them. But by then, most of the tablets were allegedly already destroyed, presumed to have been used as fuel by the natives in the deforested island.
At the time of discovery of the tablets, Rapa Nui had undergone severe depopulation. This was largely due to the loss of the island's last trees and the Peruvian and Chilean Blackbirding, slave raids in the early 1860s. The literate ruling classes of the Rapa Nui people (including the royal family and the religious caste) and the majority of the island's population were kidnapped or killed in the slave raids. Most of those taken died after only one or two years in captivity from the harsh working conditions and European diseases. Succeeding epidemics of smallpox and tuberculosis further decimated the island's population to the point that there were not enough people to bury the dead. The last remnants of the Rapa Nui people were assimilated by the Tahitian people, Tahitians who were later brought to the island in an effort to repopulate it, further resulting in the loss of most of the Old Rapa Nui language.
Oral tradition holds that the ruling classes were the only ones who could read the tablets, and the ability to decipher the tablets was lost along with them. Numerous attempts have been made to read the tablets, starting from a few years after their discovery. But to this day, none have proven successful. Some authors have proposed that rongorongo may have been an attempt to imitate European script after the idea of writing was introduced during the "signing" of the History of Easter Island#European contacts, 1770 Spanish Treaty of Annexation or through knowledge of European writing acquired elsewhere. They cite various reasons including the lack of attestation of rongorongo prior to the 1860s, the clearly more recent provenance of some of the tablets, the lack of antecedents, and the lack of additional archaeological evidence since its discovery. Others argue that it was merely a mnemonic list of symbols meant to guide incantations. Whether rongorongo is merely an example of trans-cultural diffusion, or a true indigenous Austronesian writing system (and one of the few Invention of writing, independent inventions of writing in human history) remains unknown and may never be known.
In Southeast Asia, the first true writing systems of pre-modern Austronesian cultures were all derived from the Grantha script, Grantha and Pallava script, Pallava Brahmic scripts, all of which are abugidas from South India. Various forms of abugidas spread throughout Austronesian cultures in Southeast Asia as kingdoms became Greater India#Indianization, Indianized through early maritime trading. The oldest use of abugida scripts in Austronesian cultures are 4th century stone inscriptions written in Cham script from Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. There are numerous other Brahmic-derived writing systems among Southeast Asian Austronesians, usually specific to a certain ethnic group. Notable examples include Balinese script, Balinese, Batak script, Batak, Baybayin, Buhid script, Buhid, Hanunuo script, Hanunó'o, Javanese script, Javanese, Kulitan alphabet, Kulitan, Lontara script, Lontara, Old Kawi, Rejang script, Rejang, Rencong script, Rencong, Sundanese script, Sundanese, and Tagbanwa script, Tagbanwa. They vary from having letters with rounded shapes to letters with sharp cuneiform-like angles; a result of the difference in writing mediums, with the former being ideal for writing on soft leaves and the latter ideal for writing on bamboo panels. The use of the scripts ranged from mundane records to encoding esoteric knowledge on magico-religious rituals and folk medicine.
In regions which converted to Islam, abjads derived from the Arabic script started replacing the earlier abugidas at around the 13th century in Southeast Asia. Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, as well, adopted the Arabic script in the 14th century. Abjads, however, have an even greater inherent problem with encoding Austronesian languages than abugidas, because Austronesian languages have more varied and salient vowels which the Arabic script can not usually encode. As a result, the Austronesian adaptations such as the Jawi alphabet, Jawi and the Pegon scripts have been modified with a system of diacritics that encode sounds, both vowels and consonants, native to Austronesian languages but absent in Semitic languages. With the advent of the Colonial Era, almost all of these writing systems have been replaced with alphabets adapted from the Latin alphabet, as in the Hawaiian alphabet, Filipino alphabet, and Malay alphabet; however, several Formosan languages had been written in zhuyin, and Cia-Cia language, Cia-Cia off Sulawesi has experimented with hangul.
On Woleai and surrounding islands, a Woleai script, script was developed for the Woleaian language in the early 20th century. Approximately 20% of the script's letterforms were borrowed from Latin letters; the remaining characters seem to have been derived from indigenous iconography. Despite this heavy Latin influence, the script was a syllabary.
Vanuatu has a unique tradition of Sand drawing#Vanuatu (Sandroings), sand drawing, by which images are created by a single continuous line drawn in the sand. It is believed to have functioned as a means of symbolic communication in pre-contact Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, especially between travelers and ethnic groups that do not speak the same language. The sand drawings consist of around 300 different designs, and seem to be shared across language groups. In the 1990s, elements of the drawings were adapted into a modern constructed script called Avoiuli by the Turaga nation, Turaga indigenous movement on Pentecost Island.
Genetic studies
Genetic studies have been done on the people and related groups. The Haplogroup O1 (Y-DNA)a-M119 genetic marker is frequently detected in Native Taiwanese, northern Philippines and Polynesians, as well as some people in Indonesia, Malaysia and non-Austronesian populations insouthern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
.
A 2007 analysis of the DNA recovered from human remains in archaeological sites of prehistoric peoples along the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
in China also shows high frequencies of Haplogroup O1 in the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Liangzhu culture, linking them to Austronesian and Tai–Kadai languages, Tai-Kadai peoples. The Liangzhu culture existed in coastal areas around the Yangtze River Delta, mouth of the Yangtze. Haplogroup O1 was absent in other archaeological sites inland. The authors of the study suggest that this may be evidence of two different human migration routes during the peopling of Eastern Asia; one coastal and the other inland, with little gene flow between them.
An important breakthrough in studies in Austronesian genetics was the identification of the "Polynesian motif" (Haplogroup B4a1a1) in 1989, a specific nine-base-pair deletion mutation in mtDNA. Several studies have shown that it is shared by Polynesians and Island Southeast Asians, with a sub-branch also identified in Madagascar, indicating shared maternal ancestry of Austronesians. Austronesian-speaking regions also have high to moderate frequencies of Haplogroup O1 of the Y-DNA (including Madagascar) indicating shared paternal ancestry, with the exception of Polynesia where the Papuan-derived Haplogroup C2a1 predominates (although lower frequencies of Austronesian Haplogroup O-M122 also exist). This indicates that the Lapita people, the direct ancestors of Polynesians, were likely matrilocal, assimilating Papuan men from outside the community by marriage in Near Oceania, prior to the Polynesian expansion into Remote Oceania.
Moodley ''et al.'' (2009) identified two distinct populations of the gut bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' that accompanied human migrations into Island Southeast Asia and Oceania, called hpSahul and hspMāori. The study sampled Native Australians, Native Taiwanese, highlanders in New Guinea, and Melanesians and Polynesians in New Caledonia, which were then compared with other ''H. pylori'' haplotypes from Europeans, Asians, Pacific Islanders, and others. They found that hpSahul diverged from mainland Asian ''H. pylori'' populations approximately 31,000 to 37,000 years ago and have remained isolated for 23,000 to 32,000 years confirming the Australo-Melanesian
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
substratum in Island Southeast Asia and New Guinea. hspMāori, on the other hand, is a subpopulation of hpEastAsia, previously isolated from Polynesians (Māori, Tongans, and Samoans) in New Zealand, and three individuals from the Philippines and Japan. The study found hspMāori from Native Taiwanese, Melanesians, Polynesians, and two inhabitants from the Torres Strait Islands, all of which are Austronesian sources. As expected, hspMāori showed greatest genetic diversity in Taiwan, while all non-Taiwanese hspMāori populations belonged to a single lineage they called the "Pacific clade." They also calculated the isolation-with-migration model (IMa), which showed that the divergence of the Pacific clade of hspMāori were unidirectional from Taiwan to the Pacific. This is consistent with the Out-of-Taiwan model of the Austronesian expansion.
On 16 January 2020, the personal genomics company 23andMe added the category "Filipino & Austronesian" after customers with no known Filipino ancestors were getting false positives for 5% or more "Filipino" ancestry in their Ancestry Composition report (the proportion was as high as 75% in Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
, 71% in Tonga, 68% in Guam, 18% in Hawaii, and 34% in Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
). The company's scientists surmised that this was due to the shared Austronesian genetic heritage being incorrectly identified as Filipino ancestry.
A recent study from 2021 found that an ancient preboreal holocene hunter-gatherer from South Sulawesi had ancestry from both a distinct lineage related to modern Papuans and Aboriginal Australians and from an East-Eurasian lineage (represented by modern East Asians). The hunter-gatherer individual had approximately ~50% "Basal-East Asian" ancestry, and was positioned in between modern East Asians and Papuans of Oceania. The authors concluded that East Asian-related ancestry expanded much earlier into Maritime Southeast Asia than previously suggested, long before the expansion of Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic and Austronesian groups.
Another study about the ancestral composition of modern ethnic groups in the Philippines from 2021 similarly suggests that distinctive East Asian people, Basal-East Asian (East-Eurasian) ancestry originated in Mainland Southeast Asia at ~50,000BC, and expanded through multiple migration waves southwards and northwards respectively. Basal-East Asian ancestry, as well as later Austroasiatic ancestry, from Mainland Southeast Asia, arrived into the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
prior to the Austronesian expansion. Austronesian-speakers themself are suggested to have arrived on Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan and the northern Philippines between 10,000BC to 7,000BC from coastal Minyue, present-day Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
. The authors concluded that the Austronesian expansion into Insular Southeast Asia and Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
was outgoing from the Philippines rather than Taiwan, and that modern Austronesian-speaking people have largely ancestry from the earliest Basal-East Asians, Austroasiatic migrants from Mainland Southeast Asia, and Austronesian-speaking seafarers from the Philippines.
Evidence from agriculture
Genomic analysis of cultivated coconut (''Coconut, Cocos nucifera'') has shed light on the movements of Austronesian peoples. By examining 10 microsatellite loci, researchers found that there are 2 genetically distinct subpopulations of coconut – one originating in the Indian Ocean, the other in the Pacific Ocean. However, there is evidence of Genetic admixture, admixture, the transfer of genetic material, between the two populations. Given that coconuts are ideally suited for ocean dispersal, it seems possible that individuals from one population could have floated to the other. However, the locations of the admixture events are limited toMadagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and coastal east Africa and exclude the Seychelles and Mauritius. Sailing west from Maritime Southeast Asia in the Indian Ocean, the Austronesian peoples reached Madagascar by ca. 50–500 CE, and reached other parts thereafter. This forms a pattern that coincides with the known trade routes of Austronesian sailors. Additionally, there is a genetically distinct sub-population of coconuts on the eastern coast of South America which has undergone a genetic bottleneck resulting from a founder effect; however, its ancestral population is the pacific coconut, which suggests that Austronesian peoples may have sailed as far east as the Americas.
Pre-Columbian contact with the Americas
A genome analysis in 2020 showed Austronesian contact toSouth America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
around 1150–1200 CE, the earliest one between Fatu Hiva from the Marquesas Islands, and Colombia.
See also
* Ancient maritime history * Domesticated plants and animals of Austronesia *Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
* Maritime Silk Road
Notes
References
Books
* * * * * *External links
* *Books, some online, on Austronesian subjects by the Australian National University
Encyclopædia Britannica: Austronesian Languages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Austronesian Peoples Austronesian peoples, Austronesian culture Indigenous peoples of Asia Indigenous peoples of Oceania Indigenous peoples of Africa Ethnic groups in Southeast Asia Ethnic groups in Oceania Ethnic groups in East Africa Prehistoric migrations