|
Lydekker Line
Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 – 16 April 1915) was an English naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history. Biography Richard Lydekker was born at Tavistock Square in London. His father was Gerard Wolfe Lydekker, a barrister-at-law with Dutch ancestry. The family moved to Harpenden Lodge soon after Richard's birth. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he took a first-class in the Natural Science tripos (1872). In 1874 he joined the Geological Survey of India and made studies of the vertebrate palaeontology of northern India (especially Kashmir). He remained in this post until the death of his father in 1881. His main work in India was on the Siwalik palaeofauna; it was published in ''Palaeontologia Indica''. He was responsible for the cataloguing of the fossil mammals, reptiles, and birds in the Natural History Museum (10 vols., 1891). He named a variety of taxa including the golden-bellied mangabey; as a taxon authority he is nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpenden
Harpenden () is a town and civil parish in the City and District of St Albans in the county of Hertfordshire, England. The population of the built-up area was 30,240 in the 2011 census, whilst the population of the civil parish was 29,448. Harpenden is a commuter town, with a direct rail connection through Central London and property prices well over triple the national average. History There is evidence of pre-Roman Belgic farmers in the area. In 1867 several items were found including a bronze escutcheon, rams-head shaped mounts, and a bronze bowl. There are Roman remains in land around Harpenden, for instance the site of a mausoleum in the park at Rothamsted. A tumulus near the river Lea was opened in the 1820s and it contained a stone sarcophagus of Romano-Celtic origin. Five objects dating from around 150 AD, were inside including a glass jug with a Mediterranean stamp and samian ware dishes used for libations. Up to the 13th century the area of the parish cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Flower
Sir William Henry Flower (30 November 18311 July 1899) was an English surgeon, museum curator and comparative anatomist, who became a leading authority on mammals and especially on the primate brain. He supported Thomas Henry Huxley in an important controversy with Richard Owen about the human brain and eventually succeeded Owen as Director of the Natural History Museum in London. Origins Born on 30 November 1831 in his father's house at Stratford-upon-Avon in Warwickshire, he was the second son of Selina née Greaves (d. 1884), eldest daughter of Mary Whitehead and John Greaves, and Edward Fordham Flower, founder of the town brewery. His grandfather Richard Flower had married Elizabeth Fordham and settled at Albion, Illinois, where his father grew up. His uncles included the slate entrepreneur John Whitehead Greaves and William Pickering, Governor of Washington. His elder brother Charles Edward Flower ran the family brewery with the third brother Edgar Flower, while he ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Alleyne Nicholson
Henry Alleyne Nicholson FRS FRSE FGS FLS (11 September 1844 – 19 January 1899) was a British palaeontologist and zoologist. Life The son of John Nicholson (1809–1886), a biblical scholar, and his wife Annie Elizabeth Waring, he was born at Penrith, Cumberland on 11 September 1844. His younger sister was the writer Annie Elizabeth Nicholson Ireland, and one of his brothers was John Henry Nicholson, author and poet. He was educated at Appleby Grammar School and then studied Sciences at the universities of Göttingen (Ph.D., 1866) and Edinburgh (D.Sc., 1867; M.D., 1869). Geology had early attracted his attention, and his first publication was a thesis for his D.Sc. degree titled ''On the Geology of Cumberland and Westmoreland'' (1868). In 1869 he began lecturing in Natural History at the extramural classes linked to Edinburgh University. In 1871 he was appointed professor of natural history in the University of Toronto; in 1874 professor of biology in the Durham College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Society Of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows. Fellows are entitled to the postnominal FGS (Fellow of the Geological Society), over 2,000 of whom are Chartered Geologists (CGeol). The Society is a Registered Charity, No. 210161. It is also a member of the Science Council, and is licensed to award Chartered Scientist to qualifying members. The mission of the society is: "Making geologists acquainted with each other, stimulating their zeal, inducing them to adopt one nomenclature, facilitating the communication of new facts and ascertaining what is known in their science and what remains to be discovered". History The Society was founded on 13 November 1807 at the Freemasons' Tavern, Great Queen Street, in the Covent Garden district of London. It was partly the outcome of a previous cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of British Birds (1843)
William Yarrell's ''A History of British Birds'' was first published as a whole in three volumes in 1843, having been serialized, three sheets (=48 pages) every two months, over the previous six years. It is not a history of ornithology but a natural history, a handbook or field guide systematically describing every species of bird known to occur in Britain. A separate article of about six pages, containing an image, a description, and an account of worldwide distribution, together with reports of behaviour, is provided for each species. It quickly became the standard reference work for a generation of British ornithologists, replacing Thomas Bewick's book of the same name through its increased scientific accuracy, but following Bewick in its mixture of scientific data, accurate illustrations, detailed descriptions and varied anecdotes, as well as in the use of small 'tail-piece' engravings at the ends of articles. This made the book attractive to the public as well as to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Yarrell
William Yarrell (3 June 1784 – 1 September 1856) was an English zoologist, prolific writer, bookseller and naturalist admired by his contemporaries for his precise scientific work. Yarrell is best known as the author of ''The History of British Fishes'' (2 vols., 1836) and ''A History of British Birds'' featuring 564 original engravings (in 3 vols., first ed. 1843, second ed. 1845, third ed. 1856). The latter went into several editions and was the standard reference work for a generation of British ornithologists. He described Bewick's swan in 1830, distinguishing it from the larger whooper swan. Early life Yarrell was born in Duke Street, St James's in London, to Francis Yarrell and his wife Sarah (née Blane). His father and uncle ran a newspaper agency and bookshop. He studied at Dr Nicholson's school in Ealing. His father died in 1794 and the Yarrells moved the short distance to Great Ryder Street, where William lived the rest of his life. In 1802 he became a clerk with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Cuckoo
The common cuckoo (''Cuculus canorus'') is a member of the cuckoo order of birds, Cuculiformes, which includes the roadrunners, the anis and the coucals. This species is a widespread summer migrant to Europe and Asia, and winters in Africa. It is a brood parasite, which means it lays eggs in the nests of other bird species, particularly of dunnocks, meadow pipits, and reed warblers. Although its eggs are larger than those of its hosts, the eggs in each type of host nest resemble the host's eggs. The adult too is a mimic, in its case of the sparrowhawk; since that species is a predator, the mimicry gives the female time to lay her eggs without being attacked. Taxonomy The species' binomial name is derived from the Latin ''cuculus'' (the cuckoo) and ''canorus'' (melodious; from ''canere'', meaning to sing). The cuckoo family gets its common name and genus name by onomatopoeia for the call of the male common cuckoo. The English word "cuckoo" comes from the Old French ''cucu'', an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821) are published by Times Newspapers, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', which do not share editorial staff, were founded independently and have only had common ownership since 1966. In general, the political position of ''The Times'' is considered to be centre-right. ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, such as ''The Times of India'', ''The New York Times'', and more recently, digital-first publications such as TheTimesBlog.com (Since 2017). In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as , or as , although the newspaper is of nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
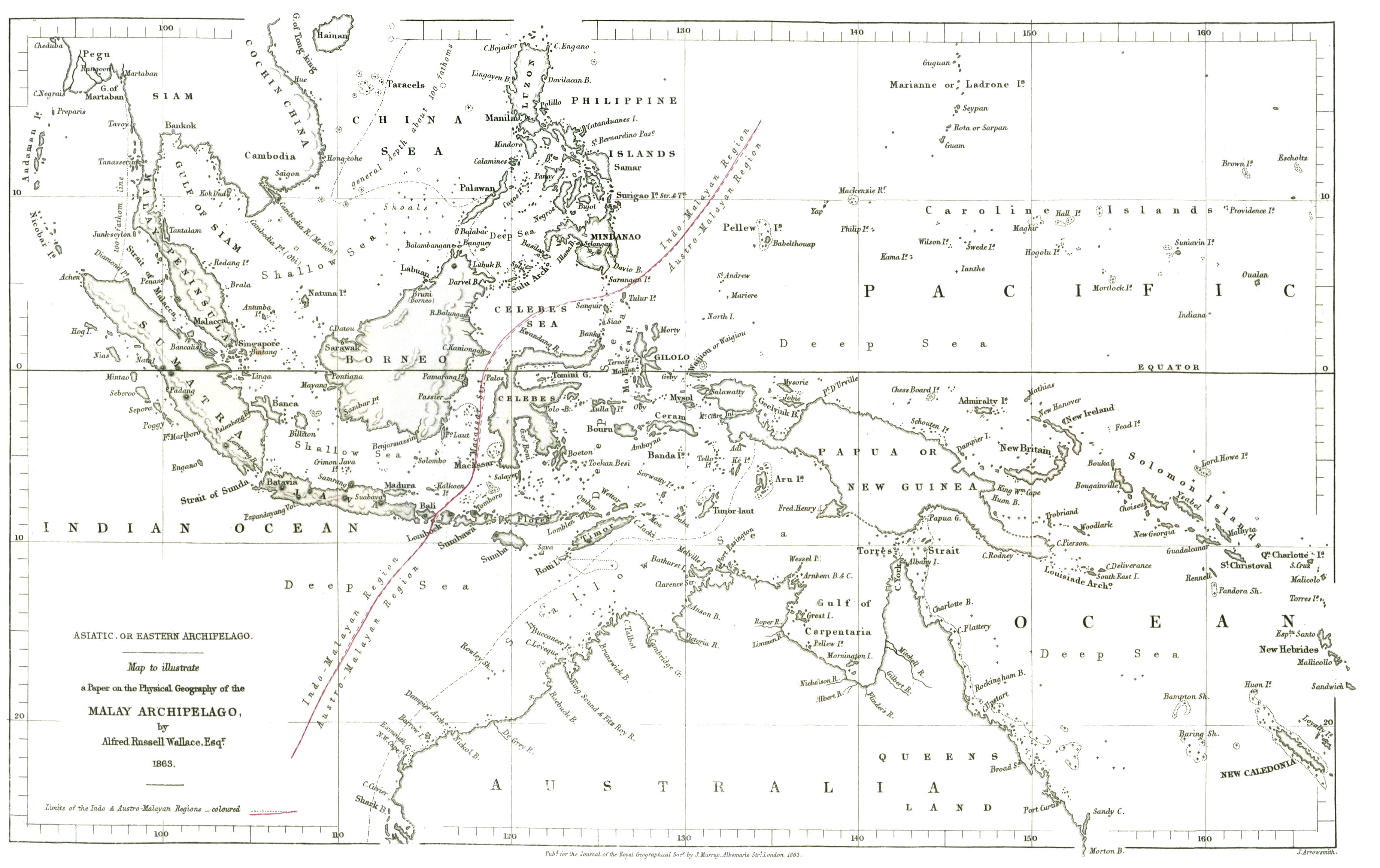
Wallace's Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present. Wallace noticed this clear division during his travels through the East Indies in the 19th century. The line runs through Indonesia, between Borneo and Sulawesi (Celebes), and through the Lombok Strait between Bali and Lombok. The distance between Bali and Lombok is small, about . The distributions of many bird species observe the line, since many birds do not cross even the shortest stretches of open ocean water. Some bats have distributions that cross the line, but larger terrestrial mammals are generally limited to one side or the other; exceptions include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aru Islands
The Aru Islands Regency ( id, Kabupaten Kepulauan Aru) is a group of about 95 low-lying islands in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia. It also forms a regency of Maluku Province, with a land area of . At the 2011 Census the Regency had a population of 84,138;Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. the 2020 Census produced a total of 102,237. Some sources regard the archipelago as part of Asia, while others regard it as part of Melanesia. Administration At the time of the 2010 Census, the regency was divided into seven districts (''kecamatan''), but subsequently an additional three districts have been created by the splitting of existing districts. The districts are tabulated below with their areas (in km2) and their populations at the 2010 Census and 2020 Census. The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of villages (''desa'') in each district, and its postal code. Notes: (a) the 2010 population of Aru Utara Timur Batuley and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)