Automobile Magazines Published In The United Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A car or automobile is a
 The first working steam-powered vehicle was designed—and quite possibly built—by
The first working steam-powered vehicle was designed—and quite possibly built—by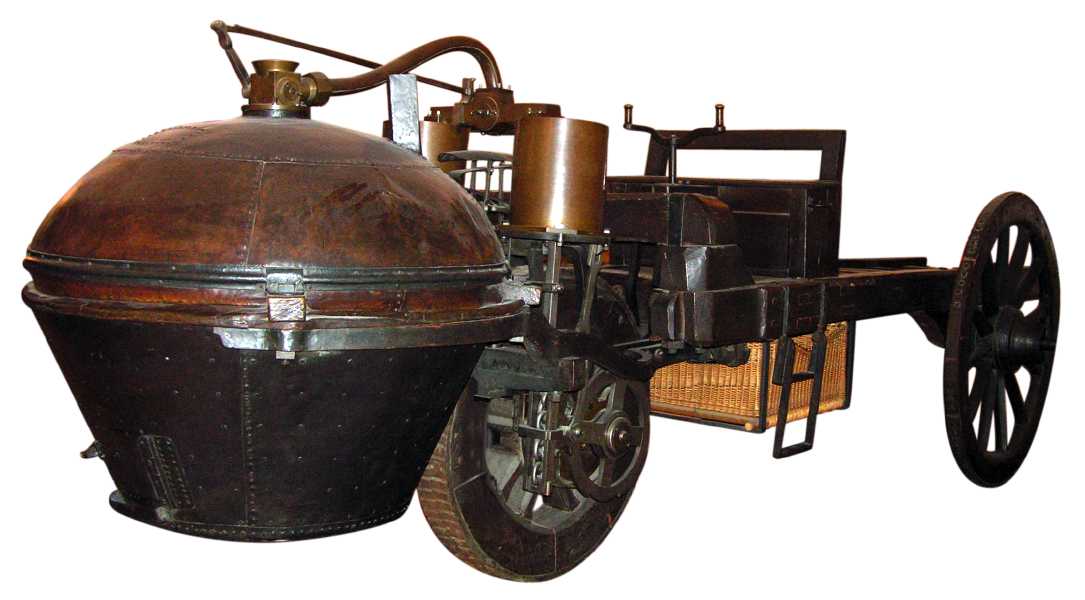 

 In November 1881, French inventor
In November 1881, French inventor  In 1879, Benz was granted a patent for his first engine, which had been designed in 1878. Many of his other inventions made the use of the internal combustion engine feasible for powering a vehicle. His first ''Motorwagen'' was built in 1885 in
In 1879, Benz was granted a patent for his first engine, which had been designed in 1878. Many of his other inventions made the use of the internal combustion engine feasible for powering a vehicle. His first ''Motorwagen'' was built in 1885 in  In 1896, Benz designed and patented the first internal-combustion
In 1896, Benz designed and patented the first internal-combustion 
 In 1890,
In 1890,





 Large-scale,
Large-scale,

 The transport sector is a major contributor to
The transport sector is a major contributor to
 Cars are equipped with controls used for driving, passenger comfort, and safety, normally operated by a combination of the use of feet and hands, and occasionally by voice on 21st-century cars. These controls include a steering wheel, pedals for operating the brakes and controlling the car's speed (and, in a manual transmission car, a clutch pedal), a shift lever or stick for changing gears, and a number of buttons and dials for turning on lights, ventilation, and other functions. Modern cars' controls are now standardized, such as the location for the accelerator and brake, but this was not always the case. Controls are evolving in response to new technologies, for example, the electric car and the integration of mobile communications.
Some of the original controls are no longer required. For example, all cars once had controls for the choke valve, clutch, ignition timing, and a crank instead of an electric Starter (engine), starter. However, new controls have also been added to vehicles, making them more complex. These include
Cars are equipped with controls used for driving, passenger comfort, and safety, normally operated by a combination of the use of feet and hands, and occasionally by voice on 21st-century cars. These controls include a steering wheel, pedals for operating the brakes and controlling the car's speed (and, in a manual transmission car, a clutch pedal), a shift lever or stick for changing gears, and a number of buttons and dials for turning on lights, ventilation, and other functions. Modern cars' controls are now standardized, such as the location for the accelerator and brake, but this was not always the case. Controls are evolving in response to new technologies, for example, the electric car and the integration of mobile communications.
Some of the original controls are no longer required. For example, all cars once had controls for the choke valve, clutch, ignition timing, and a crank instead of an electric Starter (engine), starter. However, new controls have also been added to vehicles, making them more complex. These include
 Cars are typically equipped with interior lighting which can be toggled manually or be set to light up automatically with doors open, an in-car entertainment, entertainment system which originated from car radios, sideways car window, windows which can be lowered or raised electrically (manually on earlier cars), and one or multiple automobile auxiliary power outlet, auxiliary power outlets for supplying portable appliances such as mobile phone charger, mobile phones, portable fridges, power inverters, and electrical air pumps from the on-board electrical system. More costly upper-class and luxury cars are equipped with features earlier such as massage seats and collision avoidance systems.
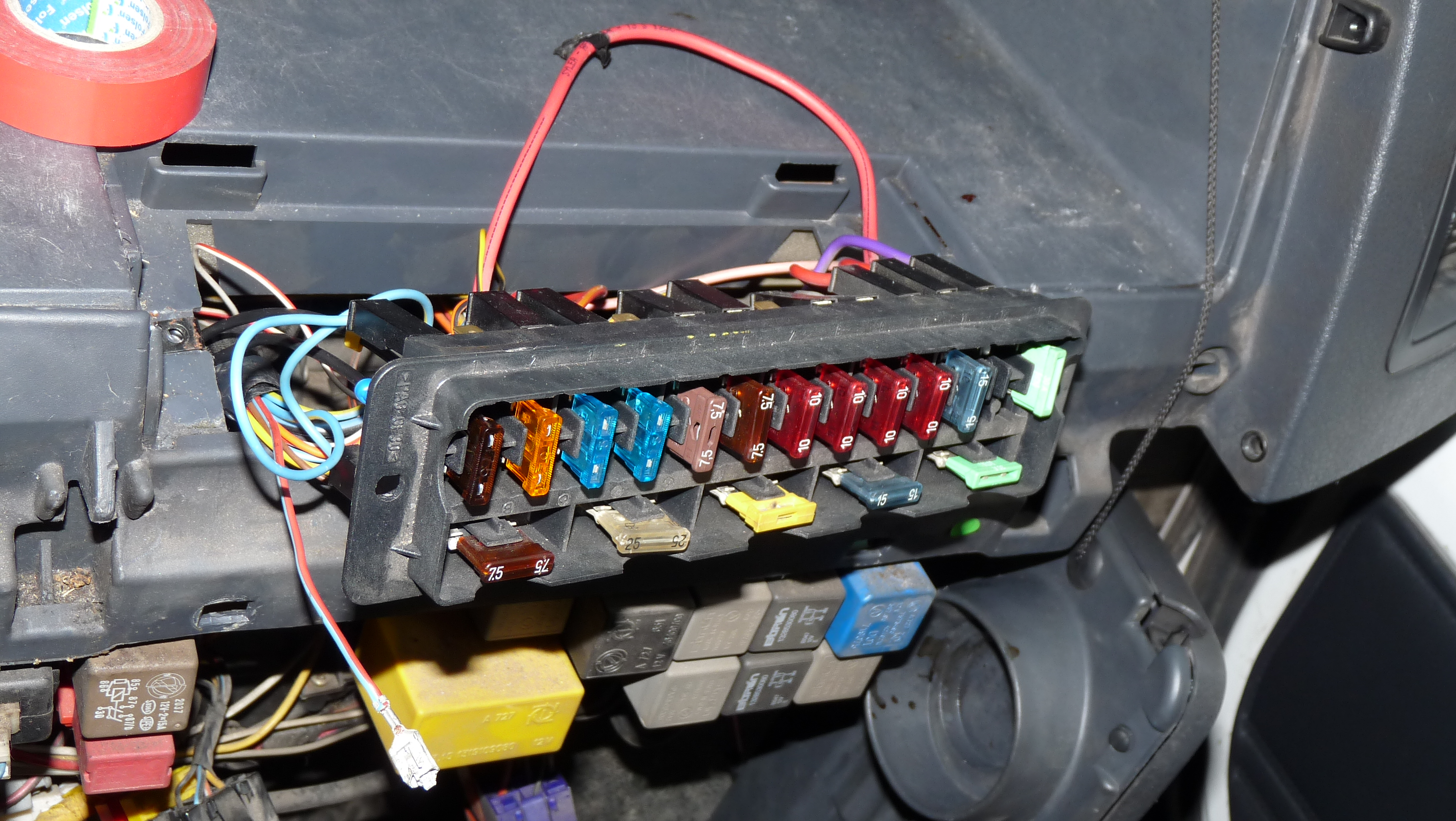
Fuse (automotive), Dedicated automotive fuses and circuit breakers prevent damage from electrical overload.
Cars are typically equipped with interior lighting which can be toggled manually or be set to light up automatically with doors open, an in-car entertainment, entertainment system which originated from car radios, sideways car window, windows which can be lowered or raised electrically (manually on earlier cars), and one or multiple automobile auxiliary power outlet, auxiliary power outlets for supplying portable appliances such as mobile phone charger, mobile phones, portable fridges, power inverters, and electrical air pumps from the on-board electrical system. More costly upper-class and luxury cars are equipped with features earlier such as massage seats and collision avoidance systems.
Fuse (automotive), Dedicated automotive fuses and circuit breakers prevent damage from electrical overload.
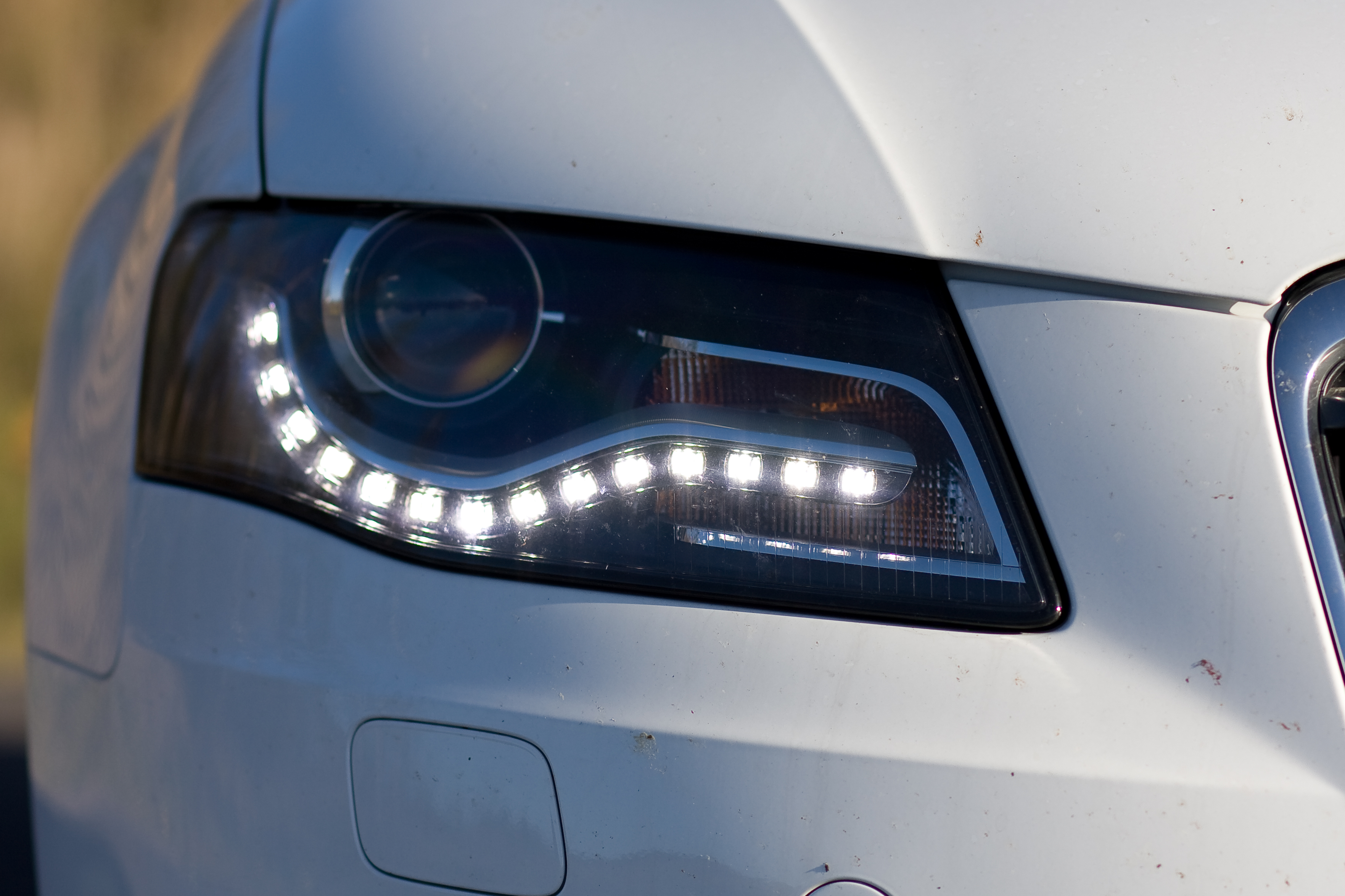 Cars are typically fitted with multiple types of lights. These include headlights, which are used to illuminate the way ahead and make the car visible to other users, so that the vehicle can be used at night; in some jurisdictions, daytime running lights; red brake lights to indicate when the brakes are applied; amber turn signal lights to indicate the turn intentions of the driver; white-colored reverse lights to illuminate the area behind the car (and indicate that the driver will be or is reversing); and on some vehicles, additional lights (e.g., side marker lights) to increase the visibility of the car. Interior lights on the ceiling of the car are usually fitted for the driver and passengers. Some vehicles also have a boot light and, more rarely, an engine compartment light.
Cars are typically fitted with multiple types of lights. These include headlights, which are used to illuminate the way ahead and make the car visible to other users, so that the vehicle can be used at night; in some jurisdictions, daytime running lights; red brake lights to indicate when the brakes are applied; amber turn signal lights to indicate the turn intentions of the driver; white-colored reverse lights to illuminate the area behind the car (and indicate that the driver will be or is reversing); and on some vehicles, additional lights (e.g., side marker lights) to increase the visibility of the car. Interior lights on the ceiling of the car are usually fitted for the driver and passengers. Some vehicles also have a boot light and, more rarely, an engine compartment light.
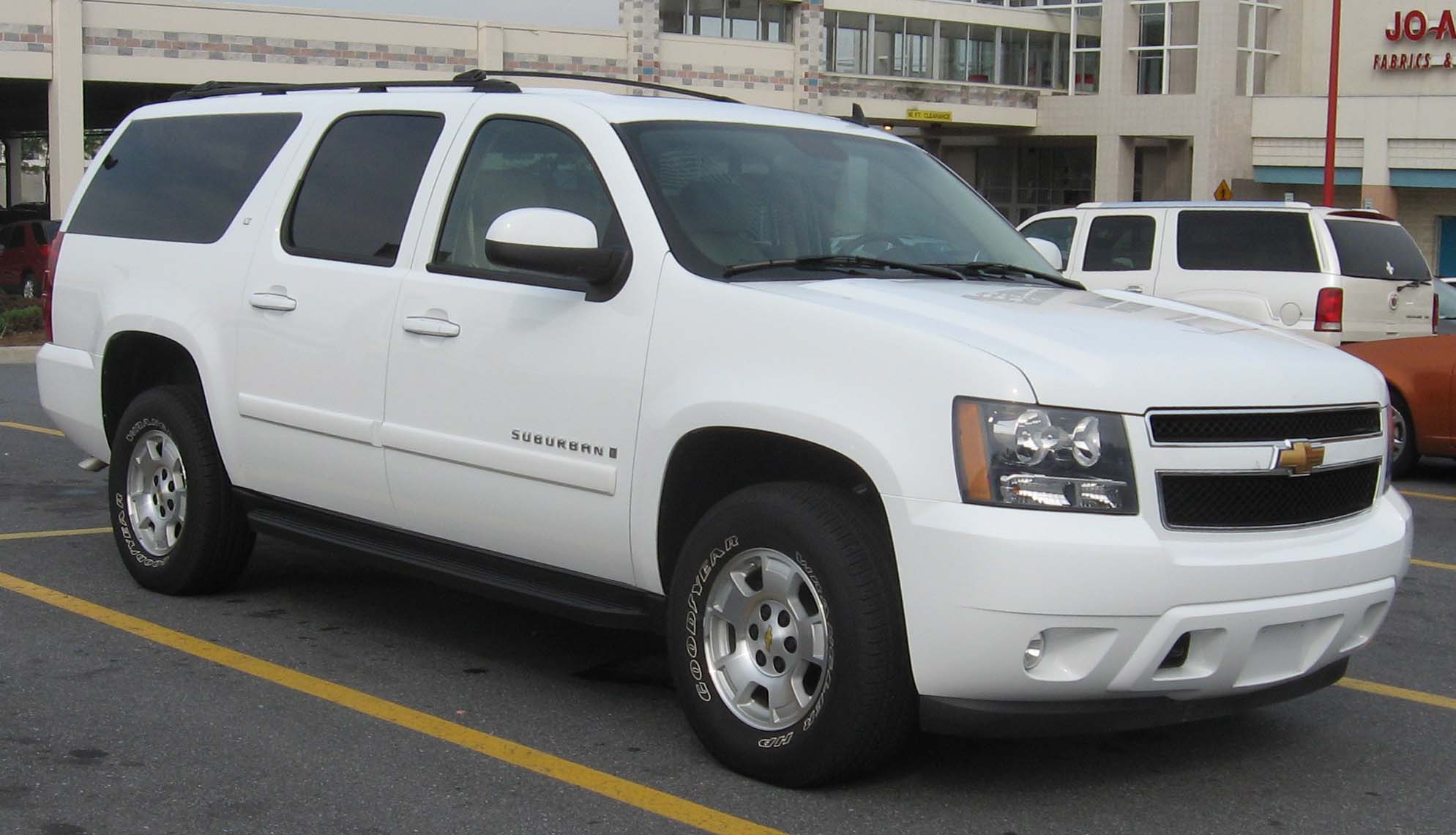 During the late 20th and early 21st century, cars increased in weight due to batteries, modern steel safety cages, anti-lock brakes, airbags, and "more-powerful—if more efficient—engines" and, , typically weigh between . Heavier cars are safer for the driver from a crash perspective, but more dangerous for other vehicles and road users. The weight of a car influences fuel consumption and performance, with more weight resulting in increased fuel consumption and decreased performance. The Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, a typical city car, weighs about . Heavier cars include SUVs and extended-length SUVs like the Chevrolet Suburban, Suburban.
Some places tax heavier cars more: as well as improving pedestrian safety this can encourage manufacturers to use materials such as recycled aluminium instead of steel. It has been suggested that one benefit of subsidizing Electric vehicle charging network, charging infrastructure is that cars can use lighter batteries.
During the late 20th and early 21st century, cars increased in weight due to batteries, modern steel safety cages, anti-lock brakes, airbags, and "more-powerful—if more efficient—engines" and, , typically weigh between . Heavier cars are safer for the driver from a crash perspective, but more dangerous for other vehicles and road users. The weight of a car influences fuel consumption and performance, with more weight resulting in increased fuel consumption and decreased performance. The Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, a typical city car, weighs about . Heavier cars include SUVs and extended-length SUVs like the Chevrolet Suburban, Suburban.
Some places tax heavier cars more: as well as improving pedestrian safety this can encourage manufacturers to use materials such as recycled aluminium instead of steel. It has been suggested that one benefit of subsidizing Electric vehicle charging network, charging infrastructure is that cars can use lighter batteries.
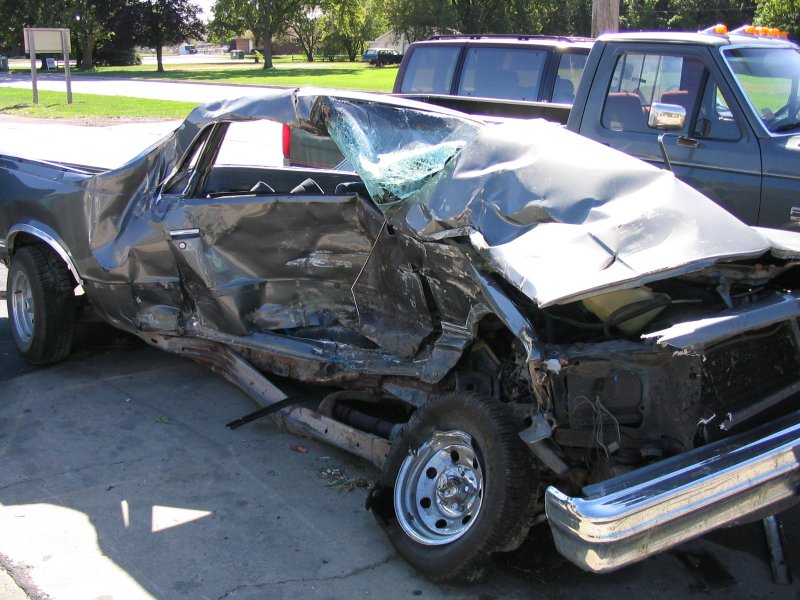 Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide. Mary Ward (scientist), Mary Ward became one of the first documented car fatalities in 1869 in Birr, County Offaly, Parsonstown, Ireland, and Henry Bliss (road accident victim), Henry Bliss one of the US's first pedestrian car casualties in 1899 in New York City. There are now standard tests for safety in new cars, such as the Euro NCAP, Euro and US NCAP, US NCAP tests, and insurance-industry-backed tests by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide. Mary Ward (scientist), Mary Ward became one of the first documented car fatalities in 1869 in Birr, County Offaly, Parsonstown, Ireland, and Henry Bliss (road accident victim), Henry Bliss one of the US's first pedestrian car casualties in 1899 in New York City. There are now standard tests for safety in new cars, such as the Euro NCAP, Euro and US NCAP, US NCAP tests, and insurance-industry-backed tests by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
 The costs of car usage, which may include the cost of: acquiring the vehicle, repairs and auto maintenance, fuel,
The costs of car usage, which may include the cost of: acquiring the vehicle, repairs and auto maintenance, fuel,
 Cars are a major cause of urban
Cars are a major cause of urban
 Fully autonomous vehicles, also known as driverless cars, already exist as Robotaxi, robotaxis but have a long way to go before they are in general use.
Fully autonomous vehicles, also known as driverless cars, already exist as Robotaxi, robotaxis but have a long way to go before they are in general use.
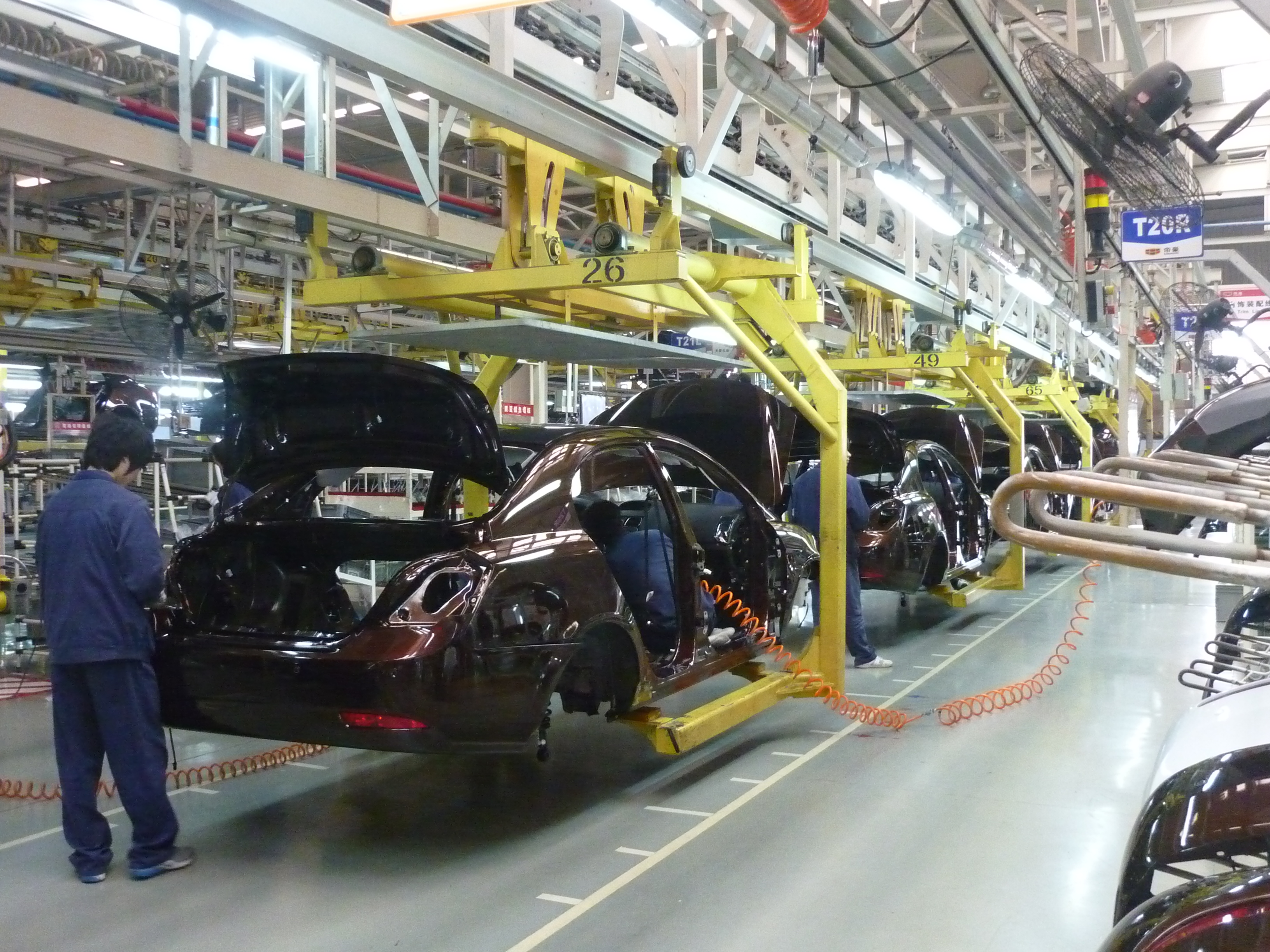 The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells the world's
The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells the world's
Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
Forum for the Automobile and Society
{{Authority control Cars, Private transport Vehicles by type Wheeled vehicles German inventions 19th-century inventions Motor vehicles
motor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on Track (rail transport), rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of pe ...
with wheels
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be ...
. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
s, seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
one to eight people, have four wheels
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be ...
, and mainly transport people
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of pr ...
instead of goods
In economics, goods are items that satisfy human wants
and provide utility, for example, to a consumer making a purchase of a satisfying product. A common distinction is made between goods which are transferable, and services, which are not tran ...
.
The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the car, when German inventor Carl Benz
Carl Friedrich Benz (; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929), sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and fir ...
patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen
The Benz Patent-Motorwagen ("patent motorcar"), built in 1885 by the German Carl Benz, is widely regarded as the world's first practical modern automobile and was the first car put into series production. It was patented and unveiled in 1886. T ...
. Cars became widely available during the 20th century. One of the first cars affordable by the masses was the 1908 Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relati ...
, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobi ...
. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
s and carts. In Europe and other parts of the world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The car is considered an essential part of the developed economy
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and o ...
.
Cars have controls for driving
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a vehicle, including cars, motorcycles, trucks, buses, and bicycles. Permission to drive on public highways is granted based on a set of conditions being met and drivers are required to fol ...
, parking
Parking is the act of stopping and disengaging a vehicle and leaving it unoccupied. Parking on one or both sides of a road is often permitted, though sometimes with restrictions. Some buildings have parking facilities for use of the buildings' ...
, passenger
A passenger (also abbreviated as pax) is a person who travels in a vehicle, but does not bear any responsibility for the tasks required for that vehicle to arrive at its destination or otherwise operate the vehicle, and is not a steward. The ...
comfort, and a variety of lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls have been added to vehicles, making them progressively more complex. These include rear-reversing cameras, air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
, navigation systems, and in-car entertainment
In-car entertainment (ICE), or in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), is a collection of hardware and software in automobiles that provides audio or video entertainment. In car entertainment originated with car audio systems that consisted of radios and ...
. Most cars in use in the early 2020s are propelled by an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
, fuelled by the combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combusti ...
of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s. Electric car
An electric car, battery electric car, or all-electric car is an automobile that is propelled by one or more electric motors, using only energy stored in batteries. Compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric cars are quie ...
s, which were invented early in the history of the car
Development of the automobile started in 1672 with the invention of the first steam-powered vehicle, which led to the creation of the first steam-powered automobile capable of human transportation, built by Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot in 1769. Invento ...
, became commercially available in the 2000s and are predicted to cost less to buy than gasoline cars before 2025. The transition from fossil fuels to electric cars features prominently in most climate change mitigation scenarios
Climate change scenarios or socioeconomic scenarios are projections of future greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions used by analysts to assess future vulnerability to climate change. Scenarios and pathways are created by scientists to survey any long ...
, such as Project Drawdown
Climate drawdown refers to the future point in time when levels of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere stop climbing and start to steadily decline. Drawdown is a milestone in reversing climate change and eventually reducing global ave ...
's 100 actionable solutions for climate change.
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs to the individual include acquiring the vehicle, interest payments (if the car is financed), repairs and maintenance
Maintenance may refer to:
Biological science
* Maintenance of an organism
* Maintenance respiration
Non-technical maintenance
* Alimony, also called ''maintenance'' in British English
* Champerty and maintenance, two related legal doctrine ...
, fuel, depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation is a term that refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, the actual decrease of fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wear, and second, the a ...
, driving time, parking fees, taxes, and insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge ...
. The costs to society include maintaining roads, land use
Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as settlements and semi-natural habitats such as arable fields, pastures, and managed woods. Land use by humans has a long h ...
, road congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
, air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
, healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
, and disposing of the vehicle at the end of its life. Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide.
Personal benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility, independence, and convenience. Societal benefits include economic benefits, such as job and wealth creation from the automotive industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of company, companies and organizations involved in the design, Business development, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industry ...
, transportation provision, societal well-being from leisure and travel opportunities, and revenue generation from taxes
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or ...
. People's ability to move flexibly from place to place has far-reaching implications for the nature of societies. There are around one billion cars in use worldwide. Car usage is increasing rapidly, especially in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and other newly industrialized countries
The category of newly industrialized country (NIC), newly industrialized economy (NIE) or middle income country is a socioeconomic classification applied to several countries around the world by political scientists and economists. They represent ...
.
Etymology
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
word ''car'' is believed to originate from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
/ "wheeled vehicle" or (via Old North French) Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
''carre'' "two-wheeled cart", both of which in turn derive from Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium ...
''karros'' "chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nbs ...
". It originally referred to any wheeled horse-drawn vehicle
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have m ...
, such as a cart
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people.
It is different from the flatbed tr ...
, carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
, or wagon
A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.
Wagons are immediately distinguished from ...
.
"Motor car", attested from 1895, is the usual formal term in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
. "Autocar", a variant likewise attested from 1895 and literally meaning " self-propelled car", is now considered archaic. "Horseless carriage
Horseless carriage is an early name for the car, motor car or automobile. Prior to the invention of the motor car, carriages were usually pulled by animals, typically horses. The term can be compared to other transitional terms, such as mobile ph ...
" is attested from 1895.
"Automobile", a classical compound
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms (which act as affixes or stems) derived from classical Latin or ancient Greek roots. New Latin comprises many such words and is a substantial component of the technical and ...
derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
''autós'' (αὐτός) "self" and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''mobilis'' "movable", entered English from French and was first adopted by the Automobile Club of Great Britain
The Royal Automobile Club is a British private social and athletic club. It has two clubhouses: one in London at 89 Pall Mall, and the other in the countryside at Woodcote Park, near Epsom in Surrey. Both provide accommodation and a rang ...
in 1897. It fell out of favour in Britain and is now used chiefly in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, where the abbreviated form "auto" commonly appears as an adjective in compound formations like "auto industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % such ...
" and "auto mechanic
An auto mechanic (automotive technician in most of North America, light vehicle technician in British English, and motor mechanic in Australian English) is a mechanic who services and repairs automobiles, sometimes specializing in one or more ...
".
History
 The first working steam-powered vehicle was designed—and quite possibly built—by
The first working steam-powered vehicle was designed—and quite possibly built—by Ferdinand Verbiest
Father Ferdinand Verbiest (9 October 1623 – 28 January 1688) was a Flemish Jesuit missionary in China during the Qing dynasty. He was born in Pittem near Tielt in the County of Flanders (now part of Belgium). He is known as Nan Huairen () in Chi ...
, a Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
member of a Jesuit mission in China around 1672. It was a scale-model toy for the Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
that was unable to carry a driver or a passenger. – Note that the vehicle pictured is the 20th century diecast model made by Brumm, of a later vehicle, not a model based on Verbiest's plans. It is not known with certainty if Verbiest's model was successfully built or run.

Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot (26 February 1725 – 2 October 1804) was a French inventor who built the world's first full-size and working self-propelled mechanical land-vehicle, the "Fardier à vapeur" – effectively the world's first automobile.
B ...
is widely credited with building the first full-scale, self-propelled mechanical vehicle or car in about 1769; he created a steam-powered tricycle. He also constructed two steam tractors for the French Army, one of which is preserved in the French National Conservatory of Arts and Crafts. His inventions were, however, limited by problems with water supply and maintaining steam pressure. In 1801, Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
built and demonstrated his Puffing Devil
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
road locomotive, believed by many to be the first demonstration of a steam-powered road vehicle. It was unable to maintain sufficient steam pressure for long periods and was of little practical use.
The development of external combustion engines is detailed as part of the history of the car
Development of the automobile started in 1672 with the invention of the first steam-powered vehicle, which led to the creation of the first steam-powered automobile capable of human transportation, built by Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot in 1769. Invento ...
but often treated separately from the development of true cars. A variety of steam-powered road vehicles were used during the first part of the 19th century, including steam car
A steam car is a car (automobile) propelled by a steam engine. A steam engine is an external combustion engine (ECE) in which the fuel is combusted outside of the engine, unlike an internal combustion engine (ICE) in which fuel is combusted ins ...
s, steam bus
A steam bus is a bus powered by a steam engine. Early steam-powered vehicles designed for carrying passengers were more usually known as steam carriages, although this term was sometimes used to describe other early experimental vehicles too.
H ...
es, phaetons, and steam roller
A steamroller (or steam roller) is a form of road roller – a type of heavy construction machinery used for leveling surfaces, such as roads or airfields – that is powered by a steam engine. The leveling/flattening action is achieved through ...
s. In the UK, sentiment against them led to the Locomotive Acts
The Locomotive Acts (or Red Flag Acts) were a series of Acts of Parliament in the United Kingdom regulating the use of mechanically propelled vehicles on British public highways during the latter part of the 19th century.
The first three, the Lo ...
of 1865.
In 1807, Nicéphore Niépce
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (; 7 March 1765 – 5 July 1833), commonly known or referred to simply as Nicéphore Niépce, was a French inventor, usually credited with the invention of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he use ...
and his brother Claude created what was probably the world's first internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
(which they called a Pyréolophore
The Pyréolophore () was probably the world's first internal combustion engine. It was invented in the early 19th century in Chalon-sur-Saône, France, by the Niépce brothers: Nicéphore (who went on to invent photography) and Claude. In 180 ...
), but they chose to install it in a boat on the river Saone in France. Coincidentally, in 1807 the Swiss inventor François Isaac de Rivaz
François Isaac de Rivaz (Paris, December 19, 1752 – Sion, July 30, 1828) was a French-born Swiss inventor and a politician. He invented a hydrogen-powered internal combustion engine with electric ignition and described it in a French paten ...
designed his own ' de Rivaz internal combustion engine' and used it to develop the world's first vehicle to be powered by such an engine. The Niépces' Pyréolophore was fuelled by a mixture of Lycopodium powder
Lycopodium powder is a yellow-tan dust-like powder, consisting of the dry spores of clubmoss plants, or various fern relatives. When it is mixed with air, the spores are highly flammable and are used to create dust explosions as theatrical spec ...
(dried spores of the Lycopodium
''Lycopodium'' (from Greek ''lykos'', wolf and ''podion'', diminutive of ''pous'', foot) is a genus of clubmosses, also known as ground pines or creeping cedars, in the family Lycopodiaceae. Two very different circumscriptions of the genus are i ...
plant), finely crushed coal dust and resin that were mixed with oil, whereas de Rivaz used a mixture of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. Neither design was very successful, as was the case with others, such as Samuel Brown Samuel Brown may refer to:
* Samuel Brown (Royal Navy officer) (1776–1852), English pioneer suspension bridge engineer and inventor
* Samuel Brown (engineer) (died 1849), English inventor of early internal combustion engine
* Samuel Brown (Wisco ...
, Samuel Morey
Samuel Morey (October 23, 1762 – April 17, 1843) was an American inventor, who worked on early internal combustion engines and was a pioneer in steamships who accumulated a total of 20 patents.
Early life
The son of a Revolutionary War Officer ...
, and Etienne Lenoir with his hippomobile
The Hippomobile is an automobile invented by Étienne Lenoir in 1863 which carried its own internal combustion engine. It was based on his 1860 invention, the Lenoir gas engine.
History
In 1863 the Hippomobile, powered by one cylinder internal ...
, who each produced vehicles (usually adapted carriages or carts) powered by internal combustion engines.

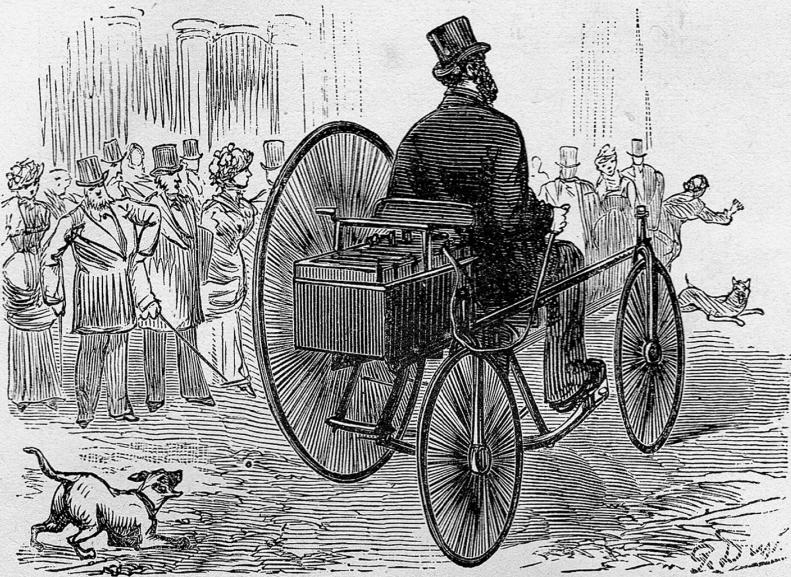
 In November 1881, French inventor
In November 1881, French inventor Gustave Trouvé
Gustave Pierre Trouvé (2 January 1839 – 27 July 1902) was a French electrical engineer and inventor in the 19th century.
Trouvé was born on 2 January 1839 in La Haye-Descartes (Indre-et-Loire, France) and died on 27 July 1902 in Paris. A pol ...
demonstrated the first working (three-wheeled) car powered by electricity at the International Exposition of Electricity, Paris
The first International Exposition of Electricity in Paris ran from August 15, 1881 through to November 15, 1881 at the Palais de l'Industrie on the Champs-Élysées. It served to display the advances in electrical technology since the small elect ...
. Although several other German engineers (including Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf (Kingdom of Württemberg, a federal state of the German Confederation), in what is now Germany. He was a ...
, Wilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 – 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
, and Siegfried Marcus
Siegfried Samuel Marcus (; 18 September 1831 – 1 July 1898) was a German inventor. Marcus was born of Jewish descent in Malchin, in the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. He made the first petrol-powered vehicle in 1864, while living ...
) were working on the problem at about the same time, the year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the car when the German Carl Benz
Carl Friedrich Benz (; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929), sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and fir ...
patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen
The Benz Patent-Motorwagen ("patent motorcar"), built in 1885 by the German Carl Benz, is widely regarded as the world's first practical modern automobile and was the first car put into series production. It was patented and unveiled in 1886. T ...
; he is generally acknowledged as the inventor of the car.
 In 1879, Benz was granted a patent for his first engine, which had been designed in 1878. Many of his other inventions made the use of the internal combustion engine feasible for powering a vehicle. His first ''Motorwagen'' was built in 1885 in
In 1879, Benz was granted a patent for his first engine, which had been designed in 1878. Many of his other inventions made the use of the internal combustion engine feasible for powering a vehicle. His first ''Motorwagen'' was built in 1885 in Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 2 ...
, Germany. He was awarded the patent for its invention as of his application on 29 January 1886 (under the auspices of his major company, Benz & Cie., which was founded in 1883). Benz began promotion of the vehicle on 3 July 1886, and about 25 Benz vehicles were sold between 1888 and 1893, when his first four-wheeler was introduced along with a cheaper model. They also were powered with four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directio ...
engines of his own design. Emile Roger of France, already producing Benz engines under license, now added the Benz car to his line of products. Because France was more open to the early cars, initially more were built and sold in France through Roger than Benz sold in Germany. In August 1888, Bertha Benz
Bertha Benz (; ; 3 May 1849 – 5 May 1944) was a German automotive pioneer and inventor. She was the business partner and wife of automobile inventor Carl Benz. On 5 August 1888, she was the first person to drive an internal-combustion-engined a ...
, the wife of Carl Benz, undertook the first road trip
A road trip, sometimes spelled roadtrip, is a long-distance journey on the road. Typically, road trips are long distances travelled by automobile.
History
First road trips by automobile
The world's first recorded long-distance road trip by t ...
by car, to prove the road-worthiness of her husband's invention.
 In 1896, Benz designed and patented the first internal-combustion
In 1896, Benz designed and patented the first internal-combustion flat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, ...
, called ''boxermotor''. During the last years of the 19th century, Benz was the largest car company in the world with 572 units produced in 1899 and, because of its size, Benz & Cie., became a joint-stock company
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's capital stock, stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their share (finance), shares (certificates ...
. The first motor car in central Europe and one of the first factory-made cars in the world, was produced by Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
company Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau (later renamed to Tatra) in 1897, the Präsident
The Präsident was an automobile manufactured by Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriks-Gesellschaft A.G. (Nesselsdorf or NW, now known as Tatra) in 1897. It was the first actually drivable factory made petrol-engined automobile produced in Austria-Hu ...
automobil.
Daimler and Maybach founded Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft
Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (abbreviated as DMG, also known as ''Daimler Motors Corporation'') was a German engineering company and later automobile manufacturer, in operation from 1890 until 1926. Founded by Gottlieb Daimler (1834–1900) and ...
(DMG) in Cannstatt
Bad Cannstatt, also called Cannstatt (until July 23, 1933) or Kannstadt (until 1900), is one of the outer stadtbezirke, or city boroughs, of Stuttgart in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Bad Cannstatt is the oldest and most populous of Stuttgart's ...
in 1890, and sold their first car in 1892 under the brand name ''Daimler''. It was a horse-drawn stagecoach built by another manufacturer, which they retrofitted with an engine of their design. By 1895, about 30 vehicles had been built by Daimler and Maybach, either at the Daimler works or in the Hotel Hermann, where they set up shop after disputes with their backers. Benz, Maybach, and the Daimler team seem to have been unaware of each other's early work. They never worked together; by the time of the merger of the two companies, Daimler and Maybach were no longer part of DMG. Daimler died in 1900 and later that year, Maybach designed an engine named ''Daimler-Mercedes'' that was placed in a specially ordered model built to specifications set by Emil Jellinek
Emil Jellinek, known after 1903 as Emil Jellinek-Mercedes (6 April 1853 – 21 January 1918) was a wealthy European automobile entrepreneur with Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft (DMG), responsible in 1900 for commissioning the first modern automobile ...
. This was a production of a small number of vehicles for Jellinek to race and market in his country. Two years later, in 1902, a new model DMG car was produced and the model was named Mercedes after the Maybach engine, which generated 35 hp. Maybach quit DMG shortly thereafter and opened a business of his own. Rights to the ''Daimler'' brand name were sold to other manufacturers.
Carl Benz proposed co-operation between DMG and Benz & Cie. when economic conditions began to deteriorate in Germany following World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, but the directors of DMG refused to consider it initially. Negotiations between the two companies resumed several years later when these conditions worsened, and in 1924, they signed an Agreement of Mutual Interest, valid until the year 2000. Both enterprises standardized design, production, purchasing, and sales and they advertised or marketed their car models jointly, although keeping their respective brands. On 28 June 1926, Benz & Cie. and DMG finally merged as the Daimler-Benz company, baptizing all of its cars Mercedes Benz, as a brand honoring the most important model of the DMG cars, the Maybach design later referred to as the 1902 Mercedes-35 hp, along with the Benz name. Carl Benz remained a member of the board of directors of Daimler-Benz until his death in 1929, and at times, his two sons also participated in the management of the company.

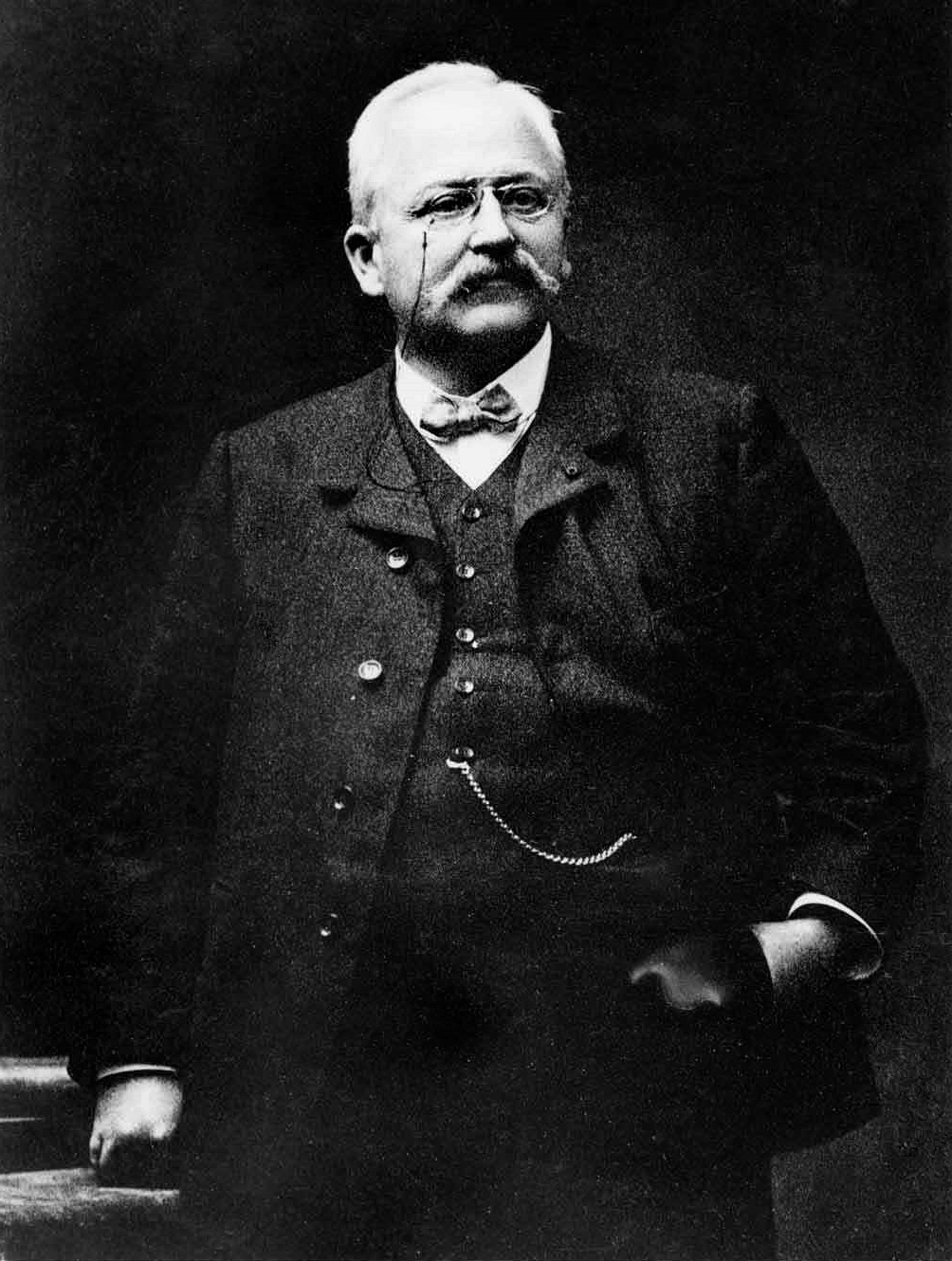
 In 1890,
In 1890, Émile Levassor
Émile Constant Levassor (21 January 1843 – 14 April 1897) was a French engineer and a pioneer of the automobile industry and car racing in France.
Biography
Levassor was born in Marolles-en-Hurepoix. After studying engineering and graduatin ...
and Armand Peugeot
Armand Peugeot (; 18 February 1849 – 4 February 1915) was an industrialist in France, pioneer of the automobile industry and the man who transformed Peugeot into a manufacturer of bicycles and, later, of automobiles. He was accepted into the Au ...
of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
began producing vehicles with Daimler engines, and so laid the foundation of the automotive industry in France
France was a pioneer in the automotive industry and is the 11th-largest automobile manufacturer in the world by 2015 unit production and the third-largest in Europe (after Germany and Spain). It had consistently been the 4th-largest from the end ...
. In 1891, Auguste Doriot
Auguste Frédéric Doriot (24 October 1863 – 1955) was a French motoring pioneer who developed, built and raced cars for Peugeot before founding his own manufacturing company D.F.P. in combination with Ludovic Flandrin and the Parant brothers. ...
and his Peugeot colleague Louis Rigoulot completed the longest trip by a gasoline-powered vehicle when their self-designed and built Daimler powered Peugeot Type 3
Background
The earliest Peugeot models from 1889 were steam-powered tricycles, built in collaboration with Léon Serpollet. In 1890, Armand Peugeot met with car technology innovators Gottlieb Daimler and Émile Levassor and became convinced t ...
completed from Valentigney
Valentigney () is a commune in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France.
Valentigney is best known as the place where Peugeot began operations; several members of the Peugeot family still live in the area.
D ...
to Paris and Brest and back again. They were attached to the first Paris–Brest–Paris
Paris–Brest–Paris (PBP) is a long-distance cycling event. It was originally a 1,200 km () bicycle race from Paris to Brest and back to Paris in 1891. The last time it was run as a race was 1951. The most recent edition of PBP was held on 18� ...
bicycle race, but finished six days after the winning cyclist, Charles Terront
Charles Terront (9 April 1857 – 31 October 1932) was the first major French cycling star. He won sprint, middle distance and endurance events in Europe and the United States. In September 1891 he won the first Paris–Brest–Paris cycle ra ...
.
The first design for an American car with a gasoline internal combustion engine was made in 1877 by George Selden of Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a City (New York), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, the county seat, seat of Monroe County, New York, Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, ...
. Selden applied for a patent for a car in 1879, but the patent application expired because the vehicle was never built. After a delay of 16 years and a series of attachments to his application, on 5 November 1895, Selden was granted a US patent () for a two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a Thermodynamic power cycle, power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being comple ...
car engine, which hindered, more than encouraged, development of cars in the US. His patent was challenged by Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of mass production. By creating the first automobile that mi ...
and others, and overturned in 1911.
In 1893, the first running, gasoline-powered American car was built and road-tested by the Duryea brothers
Charles Edgar Duryea (December 15, 1861 – September 28, 1938) was an American engineer. He was the engineer of the first-ever working American gasoline-powered car and co-founder of Duryea Motor Wagon Company. He was born near Canton, I ...
of Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is a city in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, United States, and the seat of Hampden County. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers: the western Westfield River, the ...
. The first public run of the Duryea Motor Wagon
The Duryea Motor Wagon was among the first standardized automobiles and among the first powered by gasoline. Fifteen examples were built by the Duryea Motor Wagon Company of Chicopee, Massachusetts, between 1893 and 1896. Their enterprise follo ...
took place on 21 September 1893, on Taylor Street in Metro Center Springfield. Studebaker
Studebaker was an American wagon and automobile manufacturer based in South Bend, Indiana, with a building at 1600 Broadway, Times Square, Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1852 and incorporated in 1868 as the Studebaker Brothers M ...
, subsidiary of a long-established wagon and coach manufacturer, started to build cars in 1897 and commenced sales of electric vehicles in 1902 and gasoline vehicles in 1904.
In Britain, there had been several attempts to build steam cars with varying degrees of success, with Thomas Rickett even attempting a production run in 1860. Santler from Malvern is recognized by the Veteran Car Club of Great Britain as having made the first gasoline-powered car in the country in 1894, followed by Frederick William Lanchester
Frederick William Lanchester LLD, Hon FRAeS, FRS (23 October 1868 – 8 March 1946), was an English polymath and engineer who made important contributions to automotive engineering and to aerodynamics, and co-invented the topic of operation ...
in 1895, but these were both one-offs. The first production vehicles in Great Britain came from the Daimler Company
The Daimler Company Limited ( ), prior to 1910 The Daimler Motor Company Limited, was an independent British motor vehicle manufacturer founded in London by H. J. Lawson in 1896, which set up its manufacturing base in Coventry. The compan ...
, a company founded by Harry J. Lawson
Henry John Lawson, also known as Harry Lawson, (23 February 1852–12 July 1925) was a British bicycle designer, racing cyclist, motor industry pioneer, and fraudster. As part of his attempt to create and control a British motor industry Lawson ...
in 1896, after purchasing the right to use the name of the engines. Lawson's company made its first car in 1897, and they bore the name ''Daimler''.
In 1892, German engineer Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the diesel engine, which burns diesel fuel; both are named after him.
...
was granted a patent for a "New Rational Combustion Engine". In 1897, he built the first diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-call ...
. Steam-, electric-, and gasoline-powered vehicles competed for decades, with gasoline internal combustion engines achieving dominance in the 1910s. Although various pistonless rotary engine
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons. Although many different ...
designs have attempted to compete with the conventional piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
and crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
design, only Mazda
, commonly referred to as simply Mazda, is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Fuchū, Hiroshima, Japan.
In 2015, Mazda produced 1.5 million vehicles for global sales, the majority of which (nearly one m ...
's version of the Wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and desi ...
has had more than very limited success.
All in all, it is estimated that over 100,000 patents created the modern automobile and motorcycle.
Mass production




 Large-scale,
Large-scale, production-line
A production line is a set of sequential operations established in a factory where components are assembled to make a finished article or where materials are put through a refining process to produce an end-product that is suitable for onward co ...
manufacturing of affordable cars was started by Ransom Olds in 1901 at his Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile or formally the Oldsmobile Division of General Motors was a brand of American automobiles, produced for most of its existence by General Motors. Originally established as "Olds Motor Vehicle Company" by Ransom E. Olds in 1897, it produ ...
factory in Lansing, Michigan
Lansing () is the capital of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is mostly in Ingham County, although portions of the city extend west into Eaton County and north into Clinton County. The 2020 census placed the city's population at 112,644, making ...
and based upon stationary assembly line
An assembly line is a manufacturing process (often called a ''progressive assembly'') in which parts (usually interchangeable parts) are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from workstation to workstation where the parts are added in seq ...
techniques pioneered by Marc Isambard Brunel
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the Thames Tunnel and was the father of Isambard Kingdom Brunel.
Born in Franc ...
at the Portsmouth Block Mills
The Portsmouth Block Mills form part of the Portsmouth Dockyard at Portsmouth, Hampshire, England, and were built during the Napoleonic Wars to supply the British Royal Navy with pulley blocks. They started the age of mass-production using all- ...
, England, in 1802. The assembly line style of mass production and interchangeable parts had been pioneered in the US by Thomas Blanchard in 1821, at the Springfield Armory
The Springfield Armory, more formally known as the United States Armory and Arsenal at Springfield located in the city of Springfield, Massachusetts, was the primary center for the manufacture of United States military firearms from 1777 until ...
in Springfield, Massachusetts
Springfield is a city in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, United States, and the seat of Hampden County. Springfield sits on the eastern bank of the Connecticut River near its confluence with three rivers: the western Westfield River, the ...
. This concept was greatly expanded by Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of mass production. By creating the first automobile that mi ...
, beginning in 1913 with the world's first ''moving'' assembly line for cars at the Highland Park Ford Plant
The Highland Park Ford Plant is a former Ford Motor Company factory located at 91 Manchester Avenue (at Woodward Avenue) in Highland Park, Michigan. It was the second American production facility for the Model T automobile and the first facto ...
.
As a result, Ford's cars came off the line in 15-minute intervals, much faster than previous methods, increasing productivity eightfold, while using less manpower (from 12.5 manhours to 1 hour 33 minutes). It was so successful, paint
Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many ...
became a bottleneck. Only Japan black
Japan black (also called black japan) is a lacquer or varnish suitable for many substrates but known especially for its use on iron and steel. It is so named due to the history of black lacquer being associated in the West with products from Japan. ...
would dry fast enough, forcing the company to drop the variety of colors available before 1913, until fast-drying Duco
Duco was a trade name assigned to a product line of automotive lacquer developed by the DuPont Company in the 1920s. Under the Duco brand, DuPont introduced the first quick drying multi-color line of nitrocellulose lacquers made especially for t ...
lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be ca ...
was developed in 1926. This is the source of Ford's apocryphal
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
remark, "any color as long as it's black". In 1914, an assembly line worker could buy a Model T with four months' pay.
Ford's complex safety procedures—especially assigning each worker to a specific location instead of allowing them to roam about—dramatically reduced the rate of injury. The combination of high wages and high efficiency is called "Fordism
Fordism is a manufacturing technology that serves as the basis of modern economic and social systems in industrialized, standardized mass production and mass consumption. The concept is named after Henry Ford. It is used in social, economic, and ...
" and was copied by most major industries. The efficiency gains from the assembly line also coincided with the economic rise of the US. The assembly line forced workers to work at a certain pace with very repetitive motions which led to more output per worker while other countries were using less productive methods.
In the automotive industry, its success was dominating, and quickly spread worldwide seeing the founding of Ford France and Ford Britain in 1911, Ford Denmark 1923, Ford Germany 1925; in 1921, Citroën
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired ...
was the first native European manufacturer to adopt the production method. Soon, companies had to have assembly lines, or risk going broke; by 1930, 250 companies which did not, had disappeared.
Development of automotive technology was rapid, due in part to the hundreds of small manufacturers competing to gain the world's attention. Key developments included electric ignition
Ignition may refer to:
Science and technology
* Firelighting, the human act of creating a fire for warmth, cooking and other uses
* Combustion, an exothermic chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant
* Fusion ignition, the point at which a ...
and the electric self-starter (both by Charles Kettering
Charles Franklin Kettering (August 29, 1876 – November 25, 1958) sometimes known as Charles Fredrick Kettering was an American inventor, engineer, businessman, and the holder of 186 patents.
For the list of patents issued to Kettering, see, Le ...
, for the Cadillac
The Cadillac Motor Car Division () is a division of the American automobile manufacturer General Motors (GM) that designs and builds luxury vehicles. Its major markets are the United States, Canada, and China. Cadillac models are distributed i ...
Motor Company in 1910–1911), independent suspension
Suspension or suspended may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Suspension (topology), in mathematics
* Suspension (dynamical systems), in mathematics
* Suspension of a ring, in mathematics
* Suspension (chemistry), small solid particles suspend ...
, and four-wheel brakes.
Since the 1920s, nearly all cars have been mass-produced to meet market needs, so marketing plans often have heavily influenced car design. It was Alfred P. Sloan who established the idea of different makes of cars produced by one company, called the General Motors Companion Make Program, so that buyers could "move up" as their fortunes improved.
Reflecting the rapid pace of change, makes shared parts with one another so larger production volume resulted in lower costs for each price range. For example, in the 1930s, LaSalles, sold by Cadillac
The Cadillac Motor Car Division () is a division of the American automobile manufacturer General Motors (GM) that designs and builds luxury vehicles. Its major markets are the United States, Canada, and China. Cadillac models are distributed i ...
, used cheaper mechanical parts made by Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile or formally the Oldsmobile Division of General Motors was a brand of American automobiles, produced for most of its existence by General Motors. Originally established as "Olds Motor Vehicle Company" by Ransom E. Olds in 1897, it produ ...
; in the 1950s, Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ), colloquially referred to as Chevy and formally the Chevrolet Motor Division of General Motors Company, is an American automobile division of the American manufacturer General Motors (GM). Louis Chevrolet (1878–1941) and ous ...
shared bonnet, doors, roof, and windows with Pontiac Pontiac may refer to:
*Pontiac (automobile), a car brand
*Pontiac (Ottawa leader) ( – 1769), a Native American war chief
Places and jurisdictions Canada
*Pontiac, Quebec, a municipality
** Apostolic Vicariate of Pontiac, now the Roman Catholic D ...
; by the 1990s, corporate powertrain
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components o ...
s and shared platforms (with interchangeable brake
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Background ...
s, suspension, and other parts) were common. Even so, only major makers could afford high costs, and even companies with decades of production, such as Apperson
The Apperson was a brand of American automobile manufactured from 1901 to 1926 in Kokomo, Indiana.
Company history
The company was founded by the brothers Edgar and Elmer Apperson shortly after they left Haynes-Apperson; for a time they con ...
, Cole
Cole may refer to:
Plants
* Cole crops of the genus ''Brassica'', especially cabbage, kale, or rape (rapeseed).
People
* Cole (given name), people with the given name Cole
* Cole (surname), people with the surname Cole
Companies
*Cole Motor C ...
, Dorris, Haynes Haynes may refer to:
People
*Haynes (surname)
Places
In Australia:
* Haynes, Western Australia
In Canada:
* Haynes, Alberta
In the United Kingdom:
*Haynes, Bedfordshire
** Haynes Church End
In the United States:
*Haynes, Arkansas
* Haynes, Nort ...
, or Premier, could not manage: of some two hundred American car makers in existence in 1920, only 43 survived in 1930, and with the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, by 1940, only 17 of those were left.
In Europe, much the same would happen. Morris
Morris may refer to:
Places
Australia
*St Morris, South Australia, place in South Australia
Canada
* Morris Township, Ontario, now part of the municipality of Morris-Turnberry
* Rural Municipality of Morris, Manitoba
** Morris, Manitob ...
set up its production line at Cowley in 1924, and soon outsold Ford, while beginning in 1923 to follow Ford's practice of vertical integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration is a term that describes the arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the suppl ...
, buying Hotchkiss (engines), Wrigley (gearboxes), and Osberton (radiators), for instance, as well as competitors, such as Wolseley: in 1925, Morris had 41 per cent of total British car production. Most British small-car assemblers, from Abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns.
The conce ...
to Xtra
Extra or Xtra may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Film
* ''The Extra'' (1962 film), a Mexican film
* ''The Extra'' (2005 film), an Australian film
Literature
* ''Extra'' (newspaper), a Brazilian newspaper
* '' Extra!'', an American m ...
, had gone under. Citroën did the same in France, coming to cars in 1919; between them and other cheap cars in reply such as Renault
Groupe Renault ( , , , also known as the Renault Group in English; legally Renault S.A.) is a French multinational automobile manufacturer established in 1899. The company produces a range of cars and vans, and in the past has manufactured ...
's 10CV and Peugeot's Peugeot 5CV, 5CV, they produced 550,000 cars in 1925, and Mors (automobile), Mors, Hurtu, and others could not compete. Germany's first mass-manufactured car, the Opel Opel Laubfrosch, 4PS ''Laubfrosch'' (Tree Frog), came off the line at Rüsselsheim in 1924, soon making Opel the top car builder in Germany, with 37.5 per cent of the market.
In Japan, car production was very limited before World War II. Only a handful of companies were producing vehicles in limited numbers, and these were small, three-wheeled for commercial uses, like Daihatsu, or were the result of partnering with European companies, like Isuzu Motors, Isuzu building the Wolseley Motors, Wolseley A-9 in 1922. Mitsubishi was also partnered with Fiat S.p.A., Fiat and built the Mitsubishi Model A based on a Fiat vehicle. Toyota, Nissan, Suzuki, Mazda, and Honda began as companies producing non-automotive products before the war, switching to car production during the 1950s. Kiichiro Toyoda's decision to take Toyoda Loom Works into automobile manufacturing would create what would eventually become Toyota Motor Corporation, the largest automobile manufacturer in the world. Subaru, meanwhile, was formed from a conglomerate of six companies who banded together as Fuji Heavy Industries, as a result of having been broken up under ''keiretsu'' legislation.
Fuel and propulsion technologies

air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, noise pollution and climate change.
Most cars in use in the early 2020s run on gasoline burnt in an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
(ICE). The Organisation Internationale des Constructeurs d'Automobiles, International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers says that, in countries that mandate low sulfur gasoline, gasoline-fuelled cars built to late 2010s standards (such as Euro-6) emit very little local air pollution. Some cities ban older gasoline-fuelled cars and some countries plan to ban sales in future. However, some environmental groups say this phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles must be brought forwards to limit climate change. Production of gasoline-fuelled cars peaked in 2017.
Other hydrocarbon fossil fuels also burnt by deflagration (rather than detonation) in ICE cars include Diesel fuel, diesel, autogas, and Compressed natural gas, CNG. Removal of fossil fuel subsidies, concerns about energy security, oil dependence, tightening environmental laws and restrictions on greenhouse gas emissions are propelling work on alternative power systems for cars. This includes hybrid vehicles, plug-in electric vehicles and hydrogen vehicles. Out of all cars sold in 2021, nine per cent were electric, and by the end of that year there were more than 16 million plug-in electric car, electric cars on the world's roads. Despite rapid growth, less than two per cent of cars on the world's roads were Battery electric vehicle, fully electric and plug-in hybrid cars by the end of 2021. Cars for racing or land speed record, speed records have sometimes employed jet car, jet or rocket car, rocket engines, but these are impractical for common use.
Oil consumption has increased rapidly in the 20th and 21st centuries because there are more cars; the 1980s oil glut even fuelled the sales of low-economy vehicles in OECD countries. The BRIC countries are adding to this consumption.
User interface
 Cars are equipped with controls used for driving, passenger comfort, and safety, normally operated by a combination of the use of feet and hands, and occasionally by voice on 21st-century cars. These controls include a steering wheel, pedals for operating the brakes and controlling the car's speed (and, in a manual transmission car, a clutch pedal), a shift lever or stick for changing gears, and a number of buttons and dials for turning on lights, ventilation, and other functions. Modern cars' controls are now standardized, such as the location for the accelerator and brake, but this was not always the case. Controls are evolving in response to new technologies, for example, the electric car and the integration of mobile communications.
Some of the original controls are no longer required. For example, all cars once had controls for the choke valve, clutch, ignition timing, and a crank instead of an electric Starter (engine), starter. However, new controls have also been added to vehicles, making them more complex. These include
Cars are equipped with controls used for driving, passenger comfort, and safety, normally operated by a combination of the use of feet and hands, and occasionally by voice on 21st-century cars. These controls include a steering wheel, pedals for operating the brakes and controlling the car's speed (and, in a manual transmission car, a clutch pedal), a shift lever or stick for changing gears, and a number of buttons and dials for turning on lights, ventilation, and other functions. Modern cars' controls are now standardized, such as the location for the accelerator and brake, but this was not always the case. Controls are evolving in response to new technologies, for example, the electric car and the integration of mobile communications.
Some of the original controls are no longer required. For example, all cars once had controls for the choke valve, clutch, ignition timing, and a crank instead of an electric Starter (engine), starter. However, new controls have also been added to vehicles, making them more complex. These include air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
, navigation systems, and in-car entertainment
In-car entertainment (ICE), or in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), is a collection of hardware and software in automobiles that provides audio or video entertainment. In car entertainment originated with car audio systems that consisted of radios and ...
. Another trend is the replacement of physical knobs and switches by secondary controls with touchscreen controls such as BMW's ''iDrive'' and Ford Motor Company, Ford's ''MyFord Touch''. Another change is that while early cars' pedals were physically linked to the brake mechanism and throttle, in the early 2020s, cars have increasingly replaced these physical linkages with electronic controls.
Electronics and interior
Lighting
 Cars are typically fitted with multiple types of lights. These include headlights, which are used to illuminate the way ahead and make the car visible to other users, so that the vehicle can be used at night; in some jurisdictions, daytime running lights; red brake lights to indicate when the brakes are applied; amber turn signal lights to indicate the turn intentions of the driver; white-colored reverse lights to illuminate the area behind the car (and indicate that the driver will be or is reversing); and on some vehicles, additional lights (e.g., side marker lights) to increase the visibility of the car. Interior lights on the ceiling of the car are usually fitted for the driver and passengers. Some vehicles also have a boot light and, more rarely, an engine compartment light.
Cars are typically fitted with multiple types of lights. These include headlights, which are used to illuminate the way ahead and make the car visible to other users, so that the vehicle can be used at night; in some jurisdictions, daytime running lights; red brake lights to indicate when the brakes are applied; amber turn signal lights to indicate the turn intentions of the driver; white-colored reverse lights to illuminate the area behind the car (and indicate that the driver will be or is reversing); and on some vehicles, additional lights (e.g., side marker lights) to increase the visibility of the car. Interior lights on the ceiling of the car are usually fitted for the driver and passengers. Some vehicles also have a boot light and, more rarely, an engine compartment light.
Weight
 During the late 20th and early 21st century, cars increased in weight due to batteries, modern steel safety cages, anti-lock brakes, airbags, and "more-powerful—if more efficient—engines" and, , typically weigh between . Heavier cars are safer for the driver from a crash perspective, but more dangerous for other vehicles and road users. The weight of a car influences fuel consumption and performance, with more weight resulting in increased fuel consumption and decreased performance. The Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, a typical city car, weighs about . Heavier cars include SUVs and extended-length SUVs like the Chevrolet Suburban, Suburban.
Some places tax heavier cars more: as well as improving pedestrian safety this can encourage manufacturers to use materials such as recycled aluminium instead of steel. It has been suggested that one benefit of subsidizing Electric vehicle charging network, charging infrastructure is that cars can use lighter batteries.
During the late 20th and early 21st century, cars increased in weight due to batteries, modern steel safety cages, anti-lock brakes, airbags, and "more-powerful—if more efficient—engines" and, , typically weigh between . Heavier cars are safer for the driver from a crash perspective, but more dangerous for other vehicles and road users. The weight of a car influences fuel consumption and performance, with more weight resulting in increased fuel consumption and decreased performance. The Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, a typical city car, weighs about . Heavier cars include SUVs and extended-length SUVs like the Chevrolet Suburban, Suburban.
Some places tax heavier cars more: as well as improving pedestrian safety this can encourage manufacturers to use materials such as recycled aluminium instead of steel. It has been suggested that one benefit of subsidizing Electric vehicle charging network, charging infrastructure is that cars can use lighter batteries.
Seating and body style
Most cars are designed to carry multiple occupants, often with four or five seats. Cars with five seats typically seat two passengers in the front and three in the rear. Full-size cars and large sport utility vehicles can often carry six, seven, or more occupants depending on the arrangement of the seats. On the other hand, sports cars are most often designed with only two seats. The differing needs for passenger capacity and their luggage or cargo space has resulted in the availability of a large variety of body styles to meet individual consumer requirements that include, among others, the Sedan (automobile), sedan/saloon, hatchback, station wagon/estate, and minivan.Safety
 Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide. Mary Ward (scientist), Mary Ward became one of the first documented car fatalities in 1869 in Birr, County Offaly, Parsonstown, Ireland, and Henry Bliss (road accident victim), Henry Bliss one of the US's first pedestrian car casualties in 1899 in New York City. There are now standard tests for safety in new cars, such as the Euro NCAP, Euro and US NCAP, US NCAP tests, and insurance-industry-backed tests by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
Traffic collisions are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide. Mary Ward (scientist), Mary Ward became one of the first documented car fatalities in 1869 in Birr, County Offaly, Parsonstown, Ireland, and Henry Bliss (road accident victim), Henry Bliss one of the US's first pedestrian car casualties in 1899 in New York City. There are now standard tests for safety in new cars, such as the Euro NCAP, Euro and US NCAP, US NCAP tests, and insurance-industry-backed tests by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
Costs and benefits
 The costs of car usage, which may include the cost of: acquiring the vehicle, repairs and auto maintenance, fuel,
The costs of car usage, which may include the cost of: acquiring the vehicle, repairs and auto maintenance, fuel, depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation is a term that refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, the actual decrease of fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wear, and second, the a ...
, driving time, parking fees, taxes, and insurance, are weighed against the cost of the alternatives, and the value of the benefits—perceived and real—of vehicle usage. The benefits may include on-demand transportation, mobility, independence, and convenience, and Emergency power system, emergency power. During the 1920s, cars had another benefit: "[c]ouples finally had a way to head off on unchaperoned dates, plus they had a private space to snuggle up close at the end of the night."
Similarly the costs to society of car use may include; maintaining roads, land use
Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as settlements and semi-natural habitats such as arable fields, pastures, and managed woods. Land use by humans has a long h ...
, air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, road congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
, public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
, health care, and of disposing of the vehicle at the end of its life; and can be balanced against the value of the benefits to society that car use generates. Societal benefits may include: economy benefits, such as job and wealth creation, of car production and maintenance, transportation provision, society wellbeing derived from leisure and travel opportunities, and revenue generation from the :Vehicle taxes, tax opportunities. The ability of humans to move flexibly from place to place has far-reaching implications for the nature of societies.
Environmental effects
 Cars are a major cause of urban
Cars are a major cause of urban air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, with all types of cars producing Non-exhaust emissions, dust from brakes, tyres, and road wear, although these may be limited by Vehicle emission standard, vehicle emission standards. While there are different ways to power cars most rely on gasoline or diesel fuel, diesel, and they consume almost a quarter of world oil production . Both gasoline and diesel cars pollute more than electric cars. Cars and vans caused 8% of direct carbon dioxide emissions in 2021. , due to greenhouse gases emitted during battery production, electric cars must be driven tens of thousands of kilometers before their lifecycle carbon emissions are less than fossil fuel cars; however this varies considerably and is expected to improve in future due to Low-carbon power, lower carbon electricity, and longer lasting batteries produced in larger factories. Many governments use fiscal policies, such as road tax, to discourage the purchase and use of more polluting cars; and many cities are doing the same with low-emission zones. Fuel taxes may act as an incentive for the production of more efficient, hence less polluting, car designs (e.g., hybrid vehicles) and the development of alternative fuels. High fuel taxes or cultural change may provide a strong incentive for consumers to purchase lighter, smaller, more fuel-efficient cars, or to Car-free movement, not drive.
The Car longevity, lifetime of a car built in the 2020s is expected to be about 16 years, or about if driven a lot. According to the International Energy Agency fuel economy improved 0.7 per cent in 2017, but an annual improvement of 3.7 per cent is needed to meet the Global Fuel Economy Initiative 2030 target. The increase in sales of SUVs is bad for fuel economy. Many cities in Europe, have Low-emission zone, banned older fossil fuel cars and all fossil fuel vehicles will be banned in Amsterdam from 2030. Many Chinese cities limit licensing of fossil fuel cars, and Phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles, many countries plan to stop selling them between 2025 and 2050.
The manufacture of vehicles is resource intensive, and many manufacturers now report on the environmental performance of their factories, including energy usage, waste and water consumption. Manufacturing each kWh of battery emits a similar amount of carbon as burning through one full tank of gasoline. The growth in popularity of the car allowed cities to Urban sprawl, sprawl, therefore encouraging more travel by car resulting in inactivity and obesity, which in turn can lead to increased risk of a variety of diseases.
Animals and plants are often negatively affected by cars via habitat destruction and pollution. Over the lifetime of the average car, the "loss of habitat potential" may be over based on primary production correlations. Animals are also killed every year on roads by cars, referred to as roadkill. More recent road developments are including significant environmental mitigation in their designs, such as green bridges (designed to allow wildlife crossings) and creating wildlife corridors.
Growth in the popularity of cars and commuting has led to traffic congestion. Moscow, Istanbul, Bogota, Mexico City and Sao Paulo were the world's most congested cities in 2018 according to INRIX, a data analytics company.
Social issues
Mass production of personal motor vehicles in the United States and other developed countries with extensive territories such as Australia, Argentina, and France vastly increased individual and group mobility and greatly increased and expanded economic development in urban, suburban, exurban and rural areas. In the United States, the transport divide and car dependency resulting from domination of Automotive city, car-based transport systems presents barriers to employment in low-income neighbourhoods, with many low-income individuals and families forced to run cars they cannot afford in order to maintain their income. The historic commitment to a car-based transport system continued during the presidency of Joe Biden. Dependency on automobiles by African Americans may result in exposure to the hazards of driving while black and other types of racial discrimination related to buying, financing and insuring them.Emerging car technologies
Although intensive development of conventional battery electric vehicles is continuing into the 2020s, other car propulsion technologies that are under development include wheel hub motors, Inductive charging#Electric vehicles, wireless charging, hydrogen cars, and hydrogen/electric hybrids. Research into alternative forms of power includes using ammonia instead of hydrogen in fuel cells. New materials which may replace steel car bodies include aluminium, fiberglass, carbon fiber, biocomposites, and carbon nanotubes. Telematics technology is allowing more and more people to share cars, on a City Car Club, pay-as-you-go basis, through car share and carpool schemes. Communication is also evolving due to connected car systems.Autonomous car
 Fully autonomous vehicles, also known as driverless cars, already exist as Robotaxi, robotaxis but have a long way to go before they are in general use.
Fully autonomous vehicles, also known as driverless cars, already exist as Robotaxi, robotaxis but have a long way to go before they are in general use.
Open source development
There have been several projects aiming to develop a car on the principles of open design, an approach to designing in which the plans for the machinery and systems are publicly shared, often without monetary compensation. None of the projects have succeeded in developing a car as a whole including both hardware and software, and no mass production ready open-source based designs have been introduced. Some car Hacker (programmer subculture), hacking through on-board diagnostics (OBD) has been done so far.Car sharing
Carsharing, Car-share arrangements and carpooling are also increasingly popular, in the US and Europe. For example, in the US, some car-sharing services have experienced double-digit growth in revenue and membership growth between 2006 and 2007. Services like car sharing offer residents to "share" a vehicle rather than own a car in already congested neighbourhoods.Industry
motor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on Track (rail transport), rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of pe ...
s, more than three-quarters of which are cars. In 2020, there were 56 million cars manufactured worldwide, down from 67 million the previous year.
The automotive industry in China produces by far the most (20 million in 2020), followed by Japan (seven million), then Germany, South Korea and India. The largest market is China, followed by the US.
Around the world, there are about a billion cars on the road; they burn over of gasoline and diesel fuel yearly, consuming about of energy. The numbers of cars are increasing rapidly in China and India. In the opinion of some, urban transport systems based around the car have proved unsustainable, consuming excessive energy, affecting the health of populations, and delivering a declining level of service despite increasing investment. Many of these negative effects fall disproportionately on those social groups who are also least likely to own and drive cars. The sustainable transport movement focuses on solutions to these problems. The car industry is also facing increasing competition from the public transport sector, as some people re-evaluate their private vehicle usage.
Alternatives
Established alternatives for some aspects of car use include public transport such as busses, trolleybusses, trains, Rapid transit, subways, tram system, tramways, light rail, cycling, and walking. Bicycle sharing systems have been established in China and many European cities, including Copenhagen and Amsterdam. Similar programs have been developed in large US cities. Additional individual modes of transport, such as personal rapid transit could serve as an alternative to cars if they prove to be socially accepted.Other meanings
The term ''motorcar'' was formerly also used in the context of electrified rail systems to denote a car which functions as a small locomotive but also provides space for passengers and baggage. These locomotive cars were often used on suburban routes by both interurban and intercity railroad systems.See also
General: *Automotive safety *Car classification *Car costs *Green vehicle *Jaywalking *Motor vehicle fatality rate in U.S. by year *Motor vehicle theft *Peak car *Steering *Traffic collision Effects: *Car dependency *Effects of the car on societies *Environmental effects of transport *Externalities of automobiles *Fenceline community *Mobile source air pollution *Noise pollution *Roadway noise *Traffic congestion *Urban decay *Urban sprawl Mitigation: *Car-free movement *Carfree city *Congestion pricing *Highway revolt *New Urbanism *Smart growth *Transit-oriented developmentNotes
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
*Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
Forum for the Automobile and Society
{{Authority control Cars, Private transport Vehicles by type Wheeled vehicles German inventions 19th-century inventions Motor vehicles