Atlantis Kircher Mundus Subterraneus 1678 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of
 The only primary sources for Atlantis are Plato's dialogues ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''; all other mentions of the island are based on them. The dialogues claim to quote
The only primary sources for Atlantis are Plato's dialogues ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''; all other mentions of the island are based on them. The dialogues claim to quote
 Some ancient writers viewed Atlantis as fictional or metaphorical myth; others believed it to be real.
Some ancient writers viewed Atlantis as fictional or metaphorical myth; others believed it to be real.


 Several hypotheses place the sunken island in northern Europe, including Doggerland in the North Sea, and Sweden (by Olof Rudbeck in ''Olaus Rudbeck#Historical linguistics, Atland'', 1672–1702). Doggerland, as well as Viking Bergen Island, is thought to have been flooded by a megatsunami following the Storegga Slide of c. 6100 BC. Some have proposed the Celtic Sea#Seabed, Celtic Shelf as a possible location, and that there is a link to Ireland.
In 2011, a team, working on a documentary for the National Geographic Channel, led by Professor Richard Freund from the University of Hartford, claimed to have found possible evidence of Atlantis in southwestern Andalusia. The team identified its possible location within the marshlands of the Doñana National Park, in Las Marismas, the area that once was the Lacus Ligustinus, between the Huelva Province, Huelva, Cadiz Province, Cádiz, and Seville provinces, and they speculated that Atlantis had been destroyed by a tsunami, extrapolating results from a previous study by Spanish researchers, published four years earlier.
Spanish scientists have dismissed Freund's speculations, claiming that he sensationalised their work. The anthropologist Juan Villarías-Robles, who works with the Spanish National Research Council, said, "Richard Freund was a newcomer to our project and appeared to be involved in his own very controversial issue concerning King Solomon's search for ivory and gold in Tartessos, the well documented settlement in the Doñana area established in the first millennium BC", and described Freund's claims as "fanciful".
A similar theory had previously been put forward by a German researcher, Rainer W. Kühne, that is based only on satellite imagery and places Atlantis in the Marismas de Hinojos, north of the city of Cádiz. Before that, the historian Adolf Schulten had stated in the 1920s that Plato had used Tartessos as the basis for his Atlantis myth.
Several hypotheses place the sunken island in northern Europe, including Doggerland in the North Sea, and Sweden (by Olof Rudbeck in ''Olaus Rudbeck#Historical linguistics, Atland'', 1672–1702). Doggerland, as well as Viking Bergen Island, is thought to have been flooded by a megatsunami following the Storegga Slide of c. 6100 BC. Some have proposed the Celtic Sea#Seabed, Celtic Shelf as a possible location, and that there is a link to Ireland.
In 2011, a team, working on a documentary for the National Geographic Channel, led by Professor Richard Freund from the University of Hartford, claimed to have found possible evidence of Atlantis in southwestern Andalusia. The team identified its possible location within the marshlands of the Doñana National Park, in Las Marismas, the area that once was the Lacus Ligustinus, between the Huelva Province, Huelva, Cadiz Province, Cádiz, and Seville provinces, and they speculated that Atlantis had been destroyed by a tsunami, extrapolating results from a previous study by Spanish researchers, published four years earlier.
Spanish scientists have dismissed Freund's speculations, claiming that he sensationalised their work. The anthropologist Juan Villarías-Robles, who works with the Spanish National Research Council, said, "Richard Freund was a newcomer to our project and appeared to be involved in his own very controversial issue concerning King Solomon's search for ivory and gold in Tartessos, the well documented settlement in the Doñana area established in the first millennium BC", and described Freund's claims as "fanciful".
A similar theory had previously been put forward by a German researcher, Rainer W. Kühne, that is based only on satellite imagery and places Atlantis in the Marismas de Hinojos, north of the city of Cádiz. Before that, the historian Adolf Schulten had stated in the 1920s that Plato had used Tartessos as the basis for his Atlantis myth.
 In order to give his account of Atlantis Verisimilitude (fiction), verisimilitude, Plato mentions that the story was heard by
In order to give his account of Atlantis Verisimilitude (fiction), verisimilitude, Plato mentions that the story was heard by
 The fact that Atlantis is a lost land has made of it a metaphor for something no longer attainable. For the American poet Edith Willis Linn Forbes (1865-1945), "The Lost Atlantis" stands for idealisation of the past; the present moment can only be treasured once that is realised. Ella Wheeler Wilcox finds the location of "The Lost Land" (1910) in one's carefree youthful past. Similarly, for the Irish poet Eavan Boland in "Atlantis, a lost sonnet" (2007), the idea was defined when "the old fable-makers searched hard for a word/ to convey that what is gone is gone forever".
For some male poets too, the idea of Atlantis is constructed from what cannot be obtained. Charles Bewley in his Newdigate Prize poem (1910) thinks it grows from dissatisfaction with one's condition,
in a dream of Atlantis. Similarly for the Australian Gary Catalano in a 1982 prose poem, it is "a vision that sank under the weight of its own perfection". W. H. Auden, however, suggests a way out of such frustration through the metaphor of journeying toward Atlantis in his poem of 1941. While travelling, he advises the one setting out, you will meet with many definitions of the goal in view, only realising at the end that the way has all the time led inward.
The fact that Atlantis is a lost land has made of it a metaphor for something no longer attainable. For the American poet Edith Willis Linn Forbes (1865-1945), "The Lost Atlantis" stands for idealisation of the past; the present moment can only be treasured once that is realised. Ella Wheeler Wilcox finds the location of "The Lost Land" (1910) in one's carefree youthful past. Similarly, for the Irish poet Eavan Boland in "Atlantis, a lost sonnet" (2007), the idea was defined when "the old fable-makers searched hard for a word/ to convey that what is gone is gone forever".
For some male poets too, the idea of Atlantis is constructed from what cannot be obtained. Charles Bewley in his Newdigate Prize poem (1910) thinks it grows from dissatisfaction with one's condition,
in a dream of Atlantis. Similarly for the Australian Gary Catalano in a 1982 prose poem, it is "a vision that sank under the weight of its own perfection". W. H. Auden, however, suggests a way out of such frustration through the metaphor of journeying toward Atlantis in his poem of 1941. While travelling, he advises the one setting out, you will meet with many definitions of the goal in view, only realising at the end that the way has all the time led inward.

 Paintings of the submersion of Atlantis are comparatively rare. In the seventeenth century there was François de Nomé's ''The Fall of Atlantis'', which shows a tidal wave surging toward a Baroque city frontage. The style of architecture apart, it is not very different from Nicholas Roerich's ''The Last of Atlantis'' of 1928.
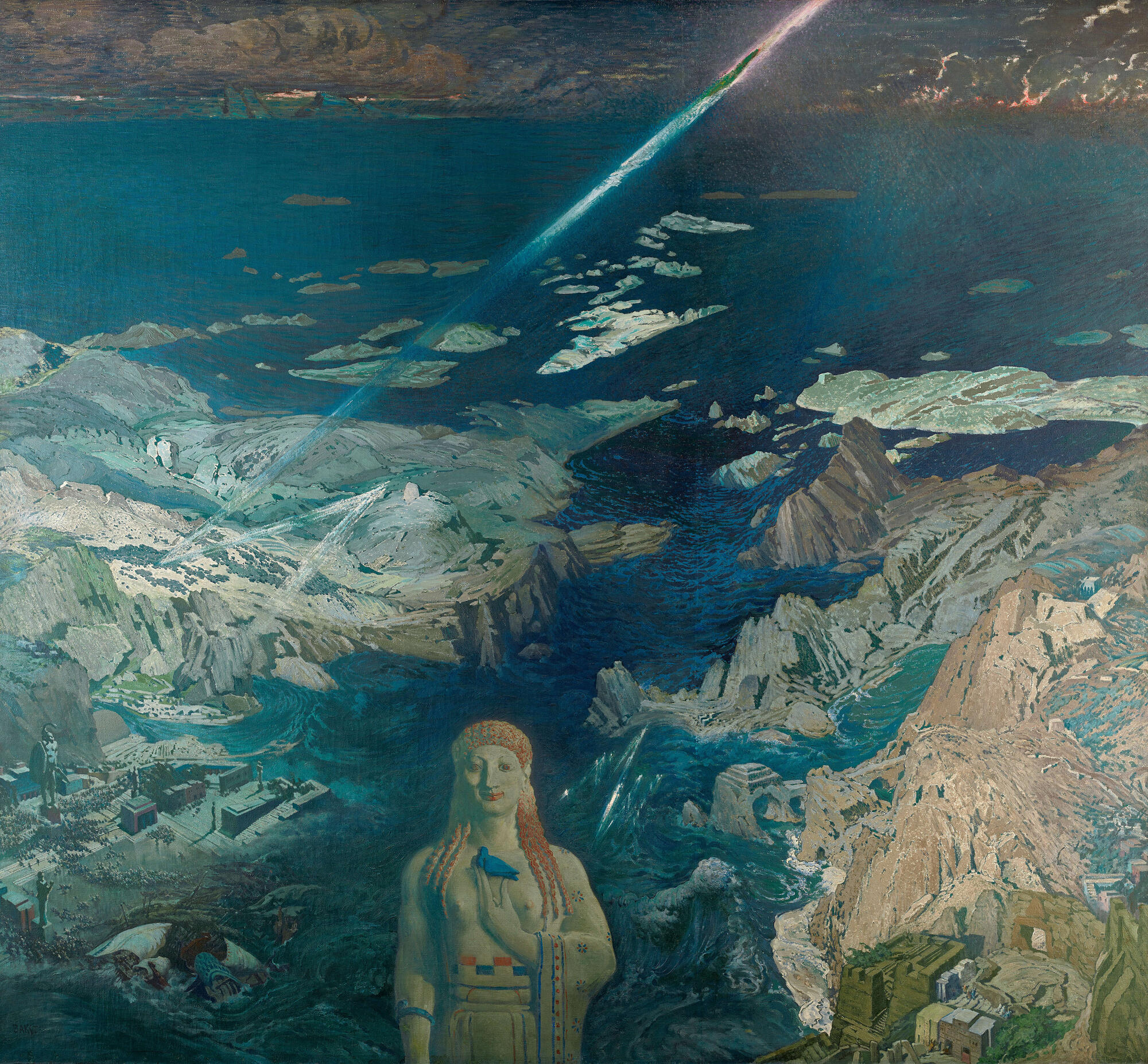
The most dramatic depiction of the catastrophe was Léon Bakst's ''Ancient Terror'' (''Terror Antiquus'', 1908), although it does not name Atlantis directly. It is a mountain-top view of a rocky bay breached by the sea, which is washing inland about the tall structures of an ancient city. A streak of lightning crosses the upper half of the painting, while below it rises the impassive figure of an enigmatic goddess who holds a blue dove between her breasts. Vyacheslav Ivanov (poet), Vyacheslav Ivanov identified the subject as Atlantis in a public lecture on the painting given in 1909, the year it was first exhibited, and he has been followed by other commentators in the years since.
Sculptures referencing Atlantis have often been stylized single figures. One of the earliest was Einar Jónsson's ''The King of Atlantis'' (1919–1922), now in the garden of his museum in Reykjavík. It represents a single figure, clad in a belted skirt and wearing a large triangular helmet, who sits on an ornate throne supported between two young bulls. The walking female entitled ''Atlantis'' (1946) by Ivan Meštrović was from a series inspired by ancient Greek figures with the symbolical meaning of unjustified suffering.
In the case of the Brussels fountain feature known as ''The Man of Atlantis'' (2003) by the Belgian sculptor , the 4-metre tall figure wearing a diving suit steps from a plinth into the spray. It looks light-hearted but the artist's comment on it makes a serious point: "Because habitable land will be scarce, it is no longer improbable that we will return to the water in the long term. As a result, a portion of the population will mutate into fish-like creatures. Global warming and rising water levels are practical problems for the world in general and here in the Netherlands in particular".
Robert Smithson's ''Hypothetical Continent (Map of broken clear glass, Atlantis)'' was first created as a photographical project on Loveladies, New Jersey, Loveladies Island NJ in 1969, and then recreated as a gallery installation of broken glass. On this he commented that he liked "landscapes that suggest prehistory", and this is borne out by the original conceptual drawing of the work that includes an inset map of the continent sited off the coast of Africa and at the straits into the Mediterranean.
Paintings of the submersion of Atlantis are comparatively rare. In the seventeenth century there was François de Nomé's ''The Fall of Atlantis'', which shows a tidal wave surging toward a Baroque city frontage. The style of architecture apart, it is not very different from Nicholas Roerich's ''The Last of Atlantis'' of 1928.
The most dramatic depiction of the catastrophe was Léon Bakst's ''Ancient Terror'' (''Terror Antiquus'', 1908), although it does not name Atlantis directly. It is a mountain-top view of a rocky bay breached by the sea, which is washing inland about the tall structures of an ancient city. A streak of lightning crosses the upper half of the painting, while below it rises the impassive figure of an enigmatic goddess who holds a blue dove between her breasts. Vyacheslav Ivanov (poet), Vyacheslav Ivanov identified the subject as Atlantis in a public lecture on the painting given in 1909, the year it was first exhibited, and he has been followed by other commentators in the years since.
Sculptures referencing Atlantis have often been stylized single figures. One of the earliest was Einar Jónsson's ''The King of Atlantis'' (1919–1922), now in the garden of his museum in Reykjavík. It represents a single figure, clad in a belted skirt and wearing a large triangular helmet, who sits on an ornate throne supported between two young bulls. The walking female entitled ''Atlantis'' (1946) by Ivan Meštrović was from a series inspired by ancient Greek figures with the symbolical meaning of unjustified suffering.
In the case of the Brussels fountain feature known as ''The Man of Atlantis'' (2003) by the Belgian sculptor , the 4-metre tall figure wearing a diving suit steps from a plinth into the spray. It looks light-hearted but the artist's comment on it makes a serious point: "Because habitable land will be scarce, it is no longer improbable that we will return to the water in the long term. As a result, a portion of the population will mutate into fish-like creatures. Global warming and rising water levels are practical problems for the world in general and here in the Netherlands in particular".
Robert Smithson's ''Hypothetical Continent (Map of broken clear glass, Atlantis)'' was first created as a photographical project on Loveladies, New Jersey, Loveladies Island NJ in 1969, and then recreated as a gallery installation of broken glass. On this he commented that he liked "landscapes that suggest prehistory", and this is borne out by the original conceptual drawing of the work that includes an inset map of the continent sited off the coast of Africa and at the straits into the Mediterranean.
Project Gutenbergalternative version
with commentary. *Plato, ''
Project Gutenbergalternative version
with commentary. Modern sources * * * * * * * {{Authority control Atlantis, Allegory Esoteric anthropogenesis Legendary tribes in Greco-Roman historiography Mythological populated places Phantom islands Platonism Theoretical continents Pseudohistory
 Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory
As a literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a hidden meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory th ...
on the hubris of nations in Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
's works ''Timaeus Timaeus (or Timaios) is a Greek name. It may refer to:
* ''Timaeus'' (dialogue), a Socratic dialogue by Plato
*Timaeus of Locri, 5th-century BC Pythagorean philosopher, appearing in Plato's dialogue
*Timaeus (historian) (c. 345 BC-c. 250 BC), Greek ...
'' and ''Critias
Critias (; grc-gre, Κριτίας, ''Kritias''; c. 460 – 403 BC) was an ancient Athenian political figure and author. Born in Athens, Critias was the son of Callaeschrus and a first cousin of Plato's mother Perictione. He became a leading ...
'', wherein it represents the antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, riv ...
naval power that besieges "Ancient Athens", the pseudo-historic embodiment of Plato's ideal state in '' The Republic''. In the story, Athens repels the Atlantean attack unlike any other nation of the known world, supposedly bearing witness to the superiority of Plato's concept of a state. The story concludes with Atlantis falling out of favor with the deities and submerging into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
Despite its minor importance in Plato's work, the Atlantis story has had a considerable impact on literature. The allegorical aspect of Atlantis was taken up in utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', describing a fictional ...
n works of several Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
writers, such as Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
's ''New Atlantis
''New Atlantis'' is an incomplete utopian novel by Sir Francis Bacon, published posthumously in 1626. It appeared unheralded and tucked into the back of a longer work of natural history, ''Sylva Sylvarum'' (forest of materials). In ''New Atlan ...
'' and Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord ...
's ''Utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', describing a fictional ...
''. On the other hand, nineteenth-century amateur scholars misinterpreted Plato's narrative as historical tradition, most famously Ignatius L. Donnelly
Ignatius Loyola Donnelly (November 3, 1831 – January 1, 1901) was an American Congressman, populist writer, and fringe scientist. He is known primarily now for his fringe theories concerning Atlantis, Catastrophism (especially the idea of an a ...
in his '' Atlantis: The Antediluvian World''. Plato's vague indications of the time of the events (more than 9,000 years before his time) and the alleged location of Atlantis ("beyond the Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
") gave rise to much pseudoscientific speculation. As a consequence, Atlantis has become a byword for any and all supposed advanced prehistoric lost civilizations and continues to inspire contemporary fiction, from comic books to films.
While present-day philologists
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics (with especially strong ties to etymology). Philology is also defined ...
and classicists
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
agree on the story's fictional character, there is still debate on what served as its inspiration. Plato is known to have freely borrowed some of his allegories and metaphors from older traditions, as he did, for instance, with the story of Gyges. This led a number of scholars to investigate possible inspiration of Atlantis from Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
records of the Thera eruption
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on near ...
, the Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
invasion, or the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
. Others have rejected this chain of tradition as implausible and insist that Plato created an entirely fictional account, drawing loose inspiration from contemporary events such as the failed Athenian invasion of Sicily in 415–413 BC or the destruction of Helike
Helike (; el, , pronounced , modern ) was an ancient Greek polis (city-state) that was submerged by a tsunami in the winter of 373 BC. It was located in the regional unit of Achaea, northern Peloponnesos, two kilometres (12 stadia) from the ...
in 373 BC.
Plato's dialogues
''Timaeus''
 The only primary sources for Atlantis are Plato's dialogues ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''; all other mentions of the island are based on them. The dialogues claim to quote
The only primary sources for Atlantis are Plato's dialogues ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''; all other mentions of the island are based on them. The dialogues claim to quote Solon
Solon ( grc-gre, Σόλων; BC) was an Athenian statesman, constitutional lawmaker and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in Archaic Athens.Aristotle ''Politics'' ...
, who visited Egypt between 590 and 580 BC; they state that he translated Egyptian records of Atlantis. Plato introduced Atlantis in ''Timaeus'', written in 360 BC:
The four people appearing in those two dialogues are the politicians Critias
Critias (; grc-gre, Κριτίας, ''Kritias''; c. 460 – 403 BC) was an ancient Athenian political figure and author. Born in Athens, Critias was the son of Callaeschrus and a first cousin of Plato's mother Perictione. He became a leading ...
and Hermocrates
Hermocrates (; grc-gre, Ἑρμοκράτης, c. 5th century – 407 BC) was an ancient Syracusan general during the Athenians' Sicilian Expedition in the midst of the Peloponnesian War. He is also remembered as a character in the '' Timaeus'' ...
as well as the philosophers Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
and Timaeus of Locri
Timaeus of Locri (; grc, Τίμαιος ὁ Λοκρός, Tímaios ho Lokrós; la, Timaeus Locrus) is a character in two of Plato's dialogues, ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'' and ''Critias (dialogue), Critias''. In both, he appears as a Ancient G ...
, although only Critias speaks of Atlantis. In his works Plato makes extensive use of the Socratic method
The Socratic method (also known as method of Elenchus, elenctic method, or Socratic debate) is a form of cooperative argumentative dialogue between individuals, based on asking and answering questions to stimulate critical thinking and to draw ...
in order to discuss contrary positions within the context of a supposition.
The ''Timaeus'' begins with an introduction, followed by an account of the creations and structure of the universe and ancient civilizations. In the introduction, Socrates muses about the perfect society, described in Plato's ''Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
'' (), and wonders if he and his guests might recollect a story which exemplifies such a society. Critias mentions a tale he considered to be historical, that would make the perfect example, and he then follows by describing Atlantis as is recorded in the ''Critias''. In his account, ancient Athens seems to represent the "perfect society" and Atlantis its opponent, representing the very antithesis of the "perfect" traits described in the ''Republic''.
''Critias''
According to Critias, the Hellenic deities of old divided the land so that each deity might have their own lot;Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a ch ...
was appropriately, and to his liking, bequeathed the island of Atlantis. The island was larger than Ancient Libya
The Latin name ''Libya'' (from Greek Λιβύη: ''Libyē'', which came from Berber: ''Libu'') referred to North Africa during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity. Berbers occupied the area for thousands of years before the recording of histor ...
and Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
combined, but it was later sunk by an earthquake and became an impassable mud shoal, inhibiting travel to any part of the ocean. Plato asserted that the Egyptians described Atlantis as an island consisting mostly of mountains in the northern portions and along the shore and encompassing a great plain in an oblong shape in the south "extending in one direction three thousand ''stadia
Stadia may refer to:
* One of the plurals of stadium, along with "stadiums"
* The plural of stadion, an ancient Greek unit of distance, which equals to 600 Greek feet (''podes'').
* Stadia (Caria), a town of ancient Caria, now in Turkey
* Stadi ...
'' bout 555 km; 345 mi but across the center inland it was two thousand stadia bout 370 km; 230 mi" Fifty stadia km; 6 mifrom the coast was a mountain that was low on all sides ... broke it off all round about ... the central island itself was five stades in diameter bout 0.92 km; 0.57 mi
In Plato's metaphorical tale, Poseidon fell in love with Cleito, the daughter of Evenor
Evenor (Ancient Greek: or Εὐήνορα ''Euenor'' means 'joy of men') is the name of a character from the myth of Atlantis and of several historical figures.
''Mythological''
* Evenor, father of Cleito by Leucippe.
*Evenor, the "brazen-tasl ...
and Leucippe, who bore him five pairs of male twins. The eldest of these, Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
, was made rightful king of the entire island and the ocean (called the Atlantic Ocean in his honor), and was given the mountain of his birth and the surrounding area as his fiefdom
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of f ...
. Atlas's twin Gadeirus, or Eumelus in Greek, was given the extremity of the island toward the pillars of Hercules. The other four pairs of twins—Ampheres and Evaemon, Mneseus and Autochthon, Elasippus and Mestor, and Azaes and Diaprepes—were also given "rule over many men, and a large territory."
Poseidon carved the mountain where his love dwelt into a palace and enclosed it with three circular moats of increasing width, varying from one to three stadia and separated by rings of land proportional in size. The Atlanteans then built bridges northward from the mountain, making a route to the rest of the island. They dug a great canal to the sea, and alongside the bridges carved tunnels into the rings of rock so that ships could pass into the city around the mountain; they carved docks from the rock walls of the moats. Every passage to the city was guarded by gates and towers, and a wall surrounded each ring of the city. The walls were constructed of red, white, and black rock, quarried from the moats, and were covered with brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, and the precious metal orichalcum
Orichalcum or aurichalcum is a metal mentioned in several ancient writings, including the story of Atlantis in the '' Critias'' of Plato. Within the dialogue, Critias (460–403 BC) claims that orichalcum had been considered second only to g ...
, respectively.
According to Critias, 9,000 years before his lifetime a war took place between those outside the Pillars of Hercules at the Strait of Gibraltar and those who dwelt within them. The Atlanteans had conquered the parts of Libya within the Pillars of Hercules, as far as Egypt, and the European continent as far as Tyrrhenia
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscans. Their ...
, and had subjected its people to slavery. The Athenians led an alliance of resistors against the Atlantean empire, and as the alliance disintegrated, prevailed alone against the empire, liberating the occupied lands.
The logographer Hellanicus of Lesbos
Hellanicus (or Hellanikos) of Lesbos (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Lésvios''), also called Hellanicus of Mytilene (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Mutilēnaῖos'') was an ancient Greek logographer who flourished during the latter half of the 5th cen ...
wrote an earlier work entitled ''Atlantis'', of which only a few fragments survive. Hellanicus' work appears to have been a genealogical one concerning the daughters of Atlas (Ἀτλαντὶς in Greek means "of Atlas"), but some authors have suggested a possible connection with Plato's island. John V. Luce notes that when Plato writes about the genealogy of Atlantis's kings, he writes in the same style as Hellanicus, suggesting a similarity between a fragment of Hellanicus's work and an account in the ''Critias''. Rodney Castleden suggests that Plato may have borrowed his title from Hellanicus, who may have based his work on an earlier work about Atlantis.
Castleden has pointed out that Plato wrote of Atlantis in 359 BC, when he returned to Athens from Sicily. He notes a number of parallels between the physical organisation and fortifications of Syracuse and Plato's description of Atlantis. Gunnar Rudberg was the first who elaborated upon the idea that Plato's attempt to realize his political ideas in the city of Syracuse could have heavily inspired the Atlantis account.
Interpretations
Ancient
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
believed that Plato, his teacher, had invented the island to teach philosophy. The philosopher Crantor
Crantor ( el, Κράντωρ, ''gen''.: Κράντορος; died 276/5 BC) was a Greek philosopher and scholarch (leader) of the Old Academy, probably born around the middle of the 4th century BC, at Soli in Cilicia (modern-day Turkey).
Life
C ...
, a student of Plato's student Xenocrates
Xenocrates (; el, Ξενοκράτης; c. 396/5314/3 BC) of Chalcedon was a Greek philosopher, mathematician, and leader (scholarch) of the Platonic Academy from 339/8 to 314/3 BC. His teachings followed those of Plato, which he attempted to d ...
, is cited often as an example of a writer who thought the story to be historical fact. His work, a commentary on ''Timaeus'', is lost, but Proclus, a Neoplatonist
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some id ...
of the fifth century AD, reports on it. The passage in question has been represented in the modern literature either as claiming that Crantor visited Egypt, had conversations with priests, and saw hieroglyphs confirming the story, or, as claiming that he learned about them from other visitors to Egypt. Proclus wrote:
The next sentence is often translated "Crantor adds, that this is testified by the prophets of the Egyptians, who assert that these particulars hich are narrated by Platoare written on pillars which are still preserved." But in the original, the sentence starts not with the name Crantor but with the ambiguous ''He''; whether this referred to Crantor or to Plato is the subject of considerable debate. Proponents of both Atlantis as a metaphorical myth and Atlantis as history have argued that the pronoun refers to Crantor.
Alan Cameron argues that the pronoun should be interpreted as referring to Plato, and that, when Proclus writes that "we must bear in mind concerning this whole feat of the Athenians, that it is neither a mere myth nor unadorned history, although some take it as history and others as myth", he is treating "Crantor's view as mere personal opinion, nothing more; in fact he first quotes and then dismisses it as representing one of the two unacceptable extremes".
Cameron also points out that whether ''he'' refers to Plato or to Crantor, the statement does not support conclusions such as Otto Muck's "Crantor came to Sais and saw there in the temple of Neith
Neith ( grc-koi, Νηΐθ, a borrowing of the Demotic form egy, nt, likely originally to have been nrt "she is the terrifying one"; Coptic: ⲛⲏⲓⲧ; also spelled Nit, Net, or Neit) was an early ancient Egyptian deity. She was said to b ...
the column, completely covered with hieroglyphs, on which the history of Atlantis was recorded. Scholars translated it for him, and he testified that their account fully agreed with Plato's account of Atlantis" or J. V. Luce's suggestion that Crantor sent "a special enquiry to Egypt" and that he may simply be referring to Plato's own claims.
Another passage from the commentary by Proclus on the ''Timaeus'' gives a description of the geography of Atlantis:
Marcellus remains unidentified.
Other ancient historians and philosophers who believed in the existence of Atlantis were Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Posidonius
Posidonius (; grc-gre, Ποσειδώνιος , "of Poseidon") "of Apameia" (ὁ Ἀπαμεύς) or "of Rhodes" (ὁ Ῥόδιος) (), was a Greek politician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, historian, mathematician, and teacher nativ ...
. Some have theorized that, before the sixth century BC, the "Pillars of Hercules" may have applied to mountains on either side of the Gulf of Laconia, and also may have been part of the pillar cult of the Aegean.Davis, J.L. and Cherry, J.F., (1990) "Spatial and temporal uniformitarianism in LCI: Perspectives from Kea and Melos on the prehistory of Akrotiri" in Hardy, D.A and Renfrew, A.C. (Eds)(1990) "Thera and the Aegean World III, Proceedings of the Third International Conference, Santorini, Greece, 3–9 September 1989" (Thera Foundation)Castleden, Rodney (1998), "Atlantis Destroyed" (Routledge), p6 The mountains stood at either side of the southernmost gulf in Greece, the largest in the Peloponnese, and it opens onto the Mediterranean Sea. This would have placed Atlantis in the Mediterranean, lending credence to many details in Plato's discussion.
The fourth-century historian Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae ...
, relying on a lost work by Timagenes
Timagenes ( grc, Τιμαγένης) was a Greek writer, historian and teacher of rhetoric. He came from Alexandria, was captured by Romans in 55 BC and taken to Rome, where he was purchased by Faustus Cornelius Sulla, son of Sulla. It is said th ...
, a historian writing in the first century BC, writes that the Druids
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. Whi ...
of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
said that part of the inhabitants of Gaul had migrated there from distant islands. Some have understood Ammianus's testimony as a claim that at the time of Atlantis's sinking into the sea, its inhabitants fled to western Europe; but Ammianus, in fact, says that "the Drasidae (Druids) recall that a part of the population is indigenous but others also migrated in from islands and lands beyond the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
" (''Res Gestae'' 15.9), an indication that the immigrants came to Gaul from the north (Britain, the Netherlands, or Germany), not from a theorized location in the Atlantic Ocean to the south-west. Instead, the Celts who dwelled along the ocean were reported to venerate twin gods, ( Dioscori), who appeared to them coming from that ocean.
Jewish and Christian
During the early first century, theHellenistic Jewish
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Greek culture. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellenistic Judaism were ...
philosopher Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's de ...
wrote about the destruction of Atlantis in his ''On the Eternity of the World'', xxvi. 141, in a longer passage allegedly citing Aristotle's successor Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routledge ...
:
The theologian Joseph Barber Lightfoot
Joseph Barber Lightfoot (13 April 1828 – 21 December 1889), known as J. B. Lightfoot, was an English theologian and Bishop of Durham.
Life
Lightfoot was born in Liverpool, where his father John Jackson Lightfoot was an accountant. His mo ...
(''Apostolic Fathers'', 1885, II, p. 84) noted on this passage: "Clement may possibly be referring to some known, but hardly accessible land, lying without the pillars of Hercules. But more probably he contemplated some unknown land in the far west beyond the ocean, like the fabled Atlantis of Plato ..."
Other early Christian writers wrote about Atlantis, although they had mixed views on whether it once existed or was an untrustworthy myth of pagan origin. Tertullian
Tertullian (; la, Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus; 155 AD – 220 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of L ...
believed Atlantis was once real and wrote that in the Atlantic Ocean once existed " he islethat was equal in size to Libya or Asia" referring to Plato's geographical description of Atlantis. The early Christian apologist writer Arnobius
Arnobius (died c. 330) was an early Christian apologist of Berber origin during the reign of Diocletian (284–305).
According to Jerome's ''Chronicle,'' Arnobius, before his conversion, was a distinguished Numidian rhetorician at Sicca Ven ...
also believed Atlantis once existed, but blamed its destruction on pagans.
Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
in the sixth century wrote of Atlantis in his '' Christian Topography'' in an attempt to prove his theory that the world was flat and surrounded by water:

Modern
Aside from Plato's original account, modern interpretations regarding Atlantis are an amalgamation of diverse, speculative movements that began in the sixteenth century, when scholars began to identify Atlantis with theNew World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
. Francisco Lopez de Gomara was the first to state that Plato was referring to America, as did Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
and Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, ...
; Janus Joannes Bircherod said in 1663 ''orbe novo non-novo'' ("the New World is not new"). Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fe ...
accepted Plato's account as literally true, describing Atlantis as a small continent in the Atlantic Ocean.
Contemporary perceptions of Atlantis share roots with Mayanism
Mayanism is a non-codified eclectic collection of New Age beliefs, influenced in part by Pre-Columbian Maya mythology and some folk beliefs of the modern Maya peoples.
Contemporary Mayanism places less emphasis on contacts between the ancient ...
, which can be traced to the beginning of the Modern Age, when European imaginations were fueled by their initial encounters with the indigenous peoples of the Americas. From this era sprang apocalyptic and utopian
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia'', describing a fictional island society ...
visions that would inspire many subsequent generations of theorists.
Most of these interpretations are considered pseudohistory
Pseudohistory is a form of pseudoscholarship that attempts to distort or misrepresent the historical record, often by employing methods resembling those used in scholarly historical research. The related term cryptohistory is applied to pseudohi ...
, pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or falsifiability, unfa ...
, or pseudoarchaeology
Pseudoarchaeology—also known as alternative archaeology, fringe archaeology, fantastic archaeology, cult archaeology, and spooky archaeology—is the interpretation of the past from outside the archaeological science community, which rejects ...
, as they have presented their works as academic
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
or scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, but lack the standards or criteria.
The Flemish cartographer and geographer Abraham Ortelius
Abraham Ortelius (; also Ortels, Orthellius, Wortels; 4 or 14 April 152728 June 1598) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the ''Theatrum Orbis Terraru ...
is believed to have been the first person to imagine that the continents were joined before drifting to their present positions. In the 1596 edition of his ''Thesaurus Geographicus'' he wrote: "Unless it be a fable, the island of Gadir or Gades will be the remaining part of the island of Atlantis or America, which was not sunk (as Plato reports in the ''Timaeus'') so much as torn away from Europe and Africa by earthquakes and flood... The traces of the ruptures are shown by the projections of Europe and Africa and the indentations of America in the parts of the coasts of these three said lands that face each other to anyone who, using a map of the world, carefully considered them. So that anyone may say with Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
in Book 2, that what Plato says of the island of Atlantis on the authority of Solon is not a figment."
Early influential literature
The term "utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', describing a fictional ...
" (from "no place") was coined by Sir Thomas More in his sixteenth-century work of fiction ''Utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', describing a fictional ...
''. Inspired by Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
's Atlantis and travelers' accounts of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, More described an imaginary land set in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
. His idealistic vision established a connection between the Americas and utopian societies, a theme that Bacon discussed in '' The New Atlantis'' (). A character in the narrative gives a history of Atlantis that is similar to Plato's and places Atlantis in America. People had begun believing that the Mayan
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
ruins could possibly be the remnants of Atlantis.
Impact of Mayanism
Much speculation began as to the origins of theMaya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
, which led to a variety of narratives and publications that tried to rationalize the discoveries within the context of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
and that had undertones of racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
in their connections between the Old and New World. The Europeans believed the indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
to be inferior and incapable of building that which was now in ruins and by sharing a common history, they insinuate that another race must have been responsible.
In the middle and late nineteenth century, several renowned Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
n scholars, starting with Charles Etienne Brasseur de Bourbourg
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "f ...
, and including Edward Herbert Thompson
Edward Herbert Thompson (September 28, 1857 – May 11, 1935) was an American-born archaeologist and long-time consul to Yucatán, Mexico.
Biography
Edward H. Thompson was born in Worcester, Massachusetts. Thompson devoted much of his career to s ...
and Augustus Le Plongeon
Augustus Henry Julian Le Plongeon (4 May 1825 – 13 December 1908) was a British-American archeologist and photographer who studied the pre-Columbian ruins of America, particularly those of the Maya civilization on the northern Yucatán Penins ...
, formally proposed that Atlantis was somehow related to Mayan and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
culture.
The French scholar Brasseur de Bourbourg traveled extensively through Mesoamerica in the mid-1800s, and was renowned for his translations of Mayan
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
texts, most notably the sacred book Popol Vuh
''Popol Vuh'' (also ''Popol Wuj'' or ''Popul Vuh'' or ''Pop Vuj'') is a text recounting the mythology and history of the Kʼicheʼ people, one of the Maya peoples, who inhabit Guatemala and the Mexican states of Chiapas, Campeche, Yucatan and ...
, as well as a comprehensive history of the region. Soon after these publications, however, Brasseur de Bourbourg lost his academic credibility, due to his claim that the Maya peoples
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people ...
had descended from the Toltecs
The Toltec culture () was a Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula (Mesoamerican site), Tula, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoam ...
, people he believed were the surviving population of the racially superior civilization of Atlantis. His work combined with the skillful, romantic illustrations of Jean Frederic Waldeck, which visually alluded to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and other aspects of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
, created an authoritative fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving Magic (supernatural), magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy ...
that excited much interest in the connections between worlds.
Inspired by Brasseur de Bourbourg's diffusion theories, the pseudoarchaeologist Augustus Le Plongeon traveled to Mesoamerica and performed some of the first excavations
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
of many famous Mayan ruins. Le Plongeon invented narratives, such as the kingdom of Mu saga, which romantically drew connections to him, his wife Alice, and Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
deities Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
and Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
, as well as to Heinrich Schliemann
Johann Ludwig Heinrich Julius Schliemann (; 6 January 1822 – 26 December 1890) was a German businessman and pioneer in the field of archaeology. He was an advocate of the historicity of places mentioned in the works of Homer and an archaeolog ...
, who had just discovered the ancient city of Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in prese ...
from Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's epic poetry
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants.
...
(that had been described as merely mythical). He also believed that he had found connections between the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Mayan languages
The Mayan languagesIn linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and as ...
, which produced a narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional (memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travel literature, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller (ge ...
of the destruction of Atlantis.
Ignatius Donnelly
The 1882 publication of '' Atlantis: the Antediluvian World'' byIgnatius L. Donnelly
Ignatius Loyola Donnelly (November 3, 1831 – January 1, 1901) was an American Congressman, populist writer, and fringe scientist. He is known primarily now for his fringe theories concerning Atlantis, Catastrophism (especially the idea of an a ...
stimulated much popular interest in Atlantis. He was greatly inspired by early works in Mayanism
Mayanism is a non-codified eclectic collection of New Age beliefs, influenced in part by Pre-Columbian Maya mythology and some folk beliefs of the modern Maya peoples.
Contemporary Mayanism places less emphasis on contacts between the ancient ...
, and like them, attempted to establish that all known ancient civilizations
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Civi ...
were descended from Atlantis, which he saw as a technologically sophisticated, more advanced culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
. Donnelly drew parallels between creation stories in the Old and New Worlds, attributing the connections to Atlantis, where he believed the Biblical Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
existed. As implied by the title of his book, he also believed that Atlantis was destroyed by the Great Flood
A flood myth or a deluge myth is a myth in which a great flood, usually sent by a deity or deities, destroys civilization, often in an act of divine retribution. Parallels are often drawn between the flood waters of these myths and the primaeval ...
mentioned in the Bible.
Donnelly is credited as the "father of the nineteenth century Atlantis revival" and is the reason the myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
endures today. He unintentionally promoted an alternative method of inquiry to history and science, and the idea that myths contain hidden information that opens them to "ingenious" interpretation by people who believe they have new or special insight.
Madame Blavatsky and the Theosophists

Helena Petrovna Blavatsky
Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, uk, Олена Петрівна Блаватська, Olena Petrivna Blavatska (; – 8 May 1891), often known as Madame Blavatsky, was a Russian mystic and author who co-founded the Theosophical Society in 1875 ...
, the founder of the Theosophists
Theosophy is a religion established in the United States during the late 19th century. It was founded primarily by the Russian Helena Blavatsky and draws its teachings predominantly from Blavatsky's writings. Categorized by scholars of religion ...
, took up Donnelly's interpretations when she wrote ''The Secret Doctrine
''The Secret Doctrine, the Synthesis of Science, Religion and Philosophy'', is a pseudo-scientific esoteric book originally published as two volumes in 1888 written by Helena Blavatsky. The first volume is named ''Cosmogenesis'', the second ''An ...
'' (1888), which she claimed was originally dictated in Atlantis. She maintained that the Atlanteans were cultural heroes (contrary to Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, who describes them mainly as a military threat). She believed in a form of racial evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
(as opposed to primate evolution). In her process of evolution the Atlanteans were the fourth "root race
Root races are stages in human evolution in the esoteric cosmology of theosophist Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, as described in her book ''The Secret Doctrine'' (1888). These races existed mainly on now-lost continents. Blavatsky's model was develop ...
", which were succeeded by the fifth, the "Aryan race
The Aryan race is an obsolete historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people of Proto-Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern I ...
", which she identified with the modern human race.
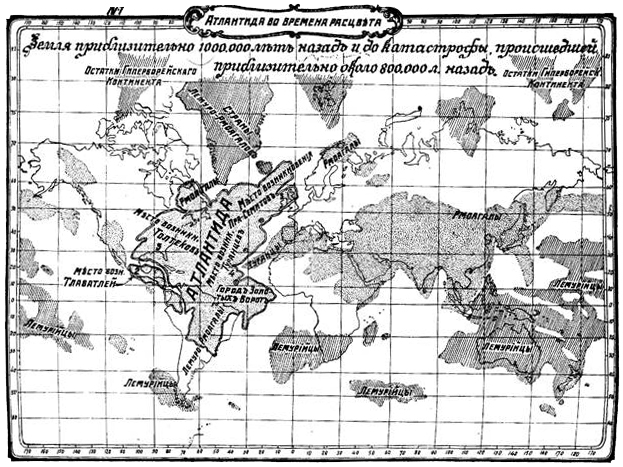
In her book, Blavatsky reported that the civilization of Atlantis reached its peak between 1,000,000 and 900,000 years ago, but destroyed itself through internal warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
brought about by the dangerous use of psychic
A psychic is a person who claims to use extrasensory perception (ESP) to identify information hidden from the normal senses, particularly involving telepathy or clairvoyance, or who performs acts that are apparently inexplicable by natural laws, ...
and supernatural powers of the inhabitants. Rudolf Steiner
Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner (27 or 25 February 1861 – 30 March 1925) was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century as ...
, the founder of anthroposophy
Anthroposophy is a spiritualist movement founded in the early 20th century by the esotericist Rudolf Steiner that postulates the existence of an objective, intellectually comprehensible spiritual world, accessible to human experience. Follower ...
and Waldorf Schools
Waldorf education, also known as Steiner education, is based on the educational philosophy of Rudolf Steiner, the founder of anthroposophy. Its educational style is Holistic education, holistic, intended to develop pupils' intellectual, artisti ...
, along with other well known Theosophists, such as Annie Besant, also wrote of cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
evolution in much the same vein. Other occultists followed the same lead, at least to the point of tracing the lineage of occult practices back to Atlantis. Among the most famous is Dion Fortune
Dion Fortune (born Violet Mary Firth, 6 December 1890 – 6 January 1946) was a British occultist, ceremonial magician, novelist and author. She was a co-founder of the Fraternity of the Inner Light, an occult organisation that promoted ph ...
in her ''Esoteric Orders and Their Work''.
Drawing on the ideas of Rudolf Steiner and Hanns Hörbiger
Johannes "Hanns" Evangelist Hörbiger (29 November 1860, in Atzgersdorf – 11 October 1931, in Mauer), better known as Hanns Hörbiger, was an Austrian engineer from Vienna with roots in Tyrol. He took part in the construction of the Budapes ...
, Egon Friedell
Egon Friedell (born ''Egon Friedmann''; 21 January 1878, in Vienna – 16 March 1938, in Vienna) was a prominent Austrian cultural historian, playwright, actor and Kabarett performer, journalist and theatre critic. Friedell has been described a ...
started his book ', and thus his historical analysis of antiquity, with the ancient culture of Atlantis. The book was published in 1940.
Nazism and occultism
Blavatsky
Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, uk, Олена Петрівна Блаватська, Olena Petrivna Blavatska (; – 8 May 1891), often known as Madame Blavatsky, was a Russian mystic and author who co-founded the Theosophical Society in 1875 ...
was also inspired by the work of the 18th-century astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, g ...
Jean-Sylvain Bailly
Jean Sylvain Bailly (; 15 September 1736 – 12 November 1793) was a French astronomer, mathematician, freemason, and political leader of the early part of the French Revolution. He presided over the Tennis Court Oath, served as the mayor of Pa ...
, who had "Orientalized" the Atlantis myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
in his mythical continent of Hyperborea
In Greek mythology, the Hyperboreans ( grc, Ὑπερβόρε(ι)οι, ; la, Hyperborei) were a mythical people who lived in the far northern part of the known world. Their name appears to derive from the Greek , "beyond Boreas" (the God of ...
, a reference to Greek myths featuring a Northern European region of the same name, home to a giant, godlike race. Dan Edelstein claims that her reshaping of this theory in ''The Secret Doctrine
''The Secret Doctrine, the Synthesis of Science, Religion and Philosophy'', is a pseudo-scientific esoteric book originally published as two volumes in 1888 written by Helena Blavatsky. The first volume is named ''Cosmogenesis'', the second ''An ...
'' provided the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
with a mythological precedent and a pretext for their ideological platform and their subsequent genocide. However, Blavatsky's writings mention that the Atlantean were in fact olive-skinned peoples with Mongoloid traits who were the ancestors of modern Native Americans, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
ns, and Malayans
Malays ( ms, Orang Melayu, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: أورڠ ملايو) are an Austronesian peoples, Austronesian ethnic group native to eastern Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula and coastal Borneo, as well as the smaller islands that lie between the ...
.Powell, ''The Solar System'', pp. 25–26. (Ch. 36. "The second Atlantean sub-race: the Tlavatli".)Powell, ''The Solar System'', pp. 252–263. (Ch. 39. "Ancient Peru: A Toltec remnant".)
The idea that the Atlanteans were Hyperborean
In Greek mythology, the Hyperboreans ( grc, Ὑπερβόρε(ι)οι, ; la, Hyperborei) were a mythical people who lived in the far northern part of the known world. Their name appears to derive from the Greek , "beyond Boreas" (the God of ...
, Nordic supermen who originated in the Northern Atlantic or even in the far North, was popular in the German ariosophic movement around 1900, propagated by Guido von List
Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List (5 October 1848 – 17 May 1919), was an Austrian occultist, journalist, playwright, and novelist. He expounded a modern Pagan new religious movement known as Wotanism, which he claimed was ...
and others. It gave its name to the ''Thule Gesellschaft'', an antisemite Münich lodge, which preceded the German Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that crea ...
(see Thule
Thule ( grc-gre, Θούλη, Thoúlē; la, Thūlē) is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Modern interpretations have included Orkney, Shetland, northern Scotland, the island of Saar ...
). The scholars (1920) and Herman Wirth
Herman may refer to:
People
* Herman (name), list of people with this name
* Saint Herman (disambiguation)
* Peter Noone (born 1947), known by the mononym Herman
Places in the United States
* Herman, Arkansas
* Herman, Michigan
* Herman, Min ...
(1928) were the first to speak of a "Nordic-Atlantean" or "Aryan-Nordic" master race that spread from Atlantis over the Northern Hemisphere and beyond. The Hyperboreans were contrasted with the Jewish people. Party ideologist Alfred Rosenberg
Alfred Ernst Rosenberg ( – 16 October 1946) was a Baltic German Nazi theorist and ideologue. Rosenberg was first introduced to Adolf Hitler by Dietrich Eckart and he held several important posts in the Nazi government. He was the head o ...
(in ''The Myth of the Twentieth Century
''The Myth of the Twentieth Century'' (german: Der Mythus des zwanzigsten Jahrhunderts) is a 1930 book by Alfred Rosenberg, one of the principal ideologues of the Nazi Party and editor of the Nazi paper '' Völkischer Beobachter''. The titular ...
'', 1930) and SS-leader Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
made it part of the official doctrine. The idea was followed up by the adherents of Esoteric Nazism such as Julius Evola
Giulio Cesare Andrea "Julius" Evola (; 19 May 1898 – 11 June 1974) was an Italian philosopher, poet, painter, esotericist, and radical-right ideologue. Evola regarded his values as aristocratic, masculine, traditionalist, heroic, and defiant ...
(1934) and, more recently, Miguel Serrano
Miguel Joaquín Diego del Carmen Serrano Fernández, known as Miguel Serrano (10 September 1917 – 28 February 2009), was a Chilean diplomat, writer, occultist, and fascist activist. A Nazi sympathiser in the late 1930s and early 1940s, he lat ...
(1978).
The idea of Atlantis as the homeland of the Caucasian race would contradict the beliefs of older Esoteric and Theosophic groups, which taught that the Atlanteans were non-Caucasian brown-skinned peoples. Modern Esoteric groups, including the Theosophic Society, do not consider Atlantean society to have been superior or Utopian—they rather consider it a lower stage of evolution.
Edgar Cayce
The clairvoyantEdgar Cayce
Edgar Cayce (; 18 March 1877 – 3 January 1945) was an American clairvoyant who claimed to channel his higher self while in a trance-like state. His words were recorded by his friend, Al Layne; his wife, Gertrude Evans, and later by his s ...
spoke frequently of Atlantis. During his "life readings", he claimed that many of his subjects were reincarnations
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the philosophical or religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new life in a different physical form or body after biological death. Resurrection is a ...
of people who had lived there. By tapping into their collective consciousness, the "Akashic Records
In the religion of theosophy and the philosophical school called anthroposophy, the Akashic records are a compendium of all universal events, thoughts, words, emotions and intent ever to have occurred in the past, present, or future in terms of ...
" (a term borrowed from Theosophy
Theosophy is a religion established in the United States during the late 19th century. It was founded primarily by the Russian Helena Blavatsky and draws its teachings predominantly from Blavatsky's writings. Categorized by scholars of religion ...
), Cayce declared that he was able to give detailed descriptions of the lost continent. He also asserted that Atlantis would "rise" again in the 1960s (sparking much popularity of the myth in that decade) and that there is a "Hall of Records
The Hall of Records is a purported ancient library claimed to lie under the Great Sphinx of Giza. There is no evidence to indicate that it ever existed.
Overview
The story of the Hall of Records is popular among those who hold alternative theo ...
" beneath the Egyptian Sphinx
The Great Sphinx of Giza is a limestone statue of a reclining sphinx, a mythical creature with the head of a human, and the body of a lion. Facing directly from west to east, it stands on the Giza Plateau on the west bank of the Nile in Giza, E ...
which holds the historical texts of Atlantis.
Recent times
Ascontinental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pla ...
became widely accepted during the 1960s, and the increased understanding of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
demonstrated the impossibility of a lost continent in the geologically recent past, most "Lost Continent" theories of Atlantis began to wane in popularity.
Plato scholar Julia Annas
Julia Elizabeth Annas (born 1946) is a British philosopher who has taught in the United States for the last quarter-century. She is Regents Professor of Philosophy Emerita at the University of Arizona.
Education and career
Annas graduated from ...
, Regents Professor
Distinguished Professor is an academic title given to some top tenured professors in a university, school, or department. Some distinguished professors may have endowed chairs.
In the United States
Often specific to one institution, titles such ...
of Philosophy at the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory.
T ...
, had this to say on the matter:
One of the proposed explanations for the historical context of the Atlantis story is a warning of Plato to his contemporary fourth-century fellow-citizens against their striving for naval power.
Kenneth Feder
Kenneth L. "Kenny" Feder (born August 1, 1952) is a professor of archaeology at Central Connecticut State University and the author of several books on archaeology and criticism of pseudoarchaeology such as '' Frauds, Myths, and Mysteries: Scien ...
points out that Critias's story in the ''Timaeus'' provides a major clue. In the dialogue, Critias says, referring to Socrates' hypothetical society:
Feder quotes A. E. Taylor, who wrote, "We could not be told much more plainly that the whole narrative of Solon's conversation with the priests and his intention of writing the poem about Atlantis are an invention of Plato's fancy."
Location hypotheses
Since Donnelly's day, there have been dozens of locations proposed for Atlantis, to the point where the name has become a generic concept, divorced from the specifics of Plato's account. This is reflected in the fact that many proposed sites are not within the Atlantic at all. Few today are scholarly or archaeological hypotheses, while others have been made bypsychic
A psychic is a person who claims to use extrasensory perception (ESP) to identify information hidden from the normal senses, particularly involving telepathy or clairvoyance, or who performs acts that are apparently inexplicable by natural laws, ...
(e.g., Edgar Cayce
Edgar Cayce (; 18 March 1877 – 3 January 1945) was an American clairvoyant who claimed to channel his higher self while in a trance-like state. His words were recorded by his friend, Al Layne; his wife, Gertrude Evans, and later by his s ...
) or other pseudoscientific means. (The Atlantis researchers Jacques Collina-Girard and Georgeos Díaz-Montexano, for instance, each claim the other's hypothesis is pseudoscience.) Many of the proposed sites share some of the characteristics of the Atlantis story (water, catastrophic end, relevant time period), but none has been demonstrated to be a true historical Atlantis.

In or near the Mediterranean Sea
Most of the historically proposed locations are in or near the Mediterranean Sea: islands such asSardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
, Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
, Santorini (Thera), Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, and Malta; land-based cities or states such as Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in prese ...
, Tartessos, and Tantalis (in the province of Manisa, Turkey); Israel-Sinai peninsula, Sinai or Canaan; and northwestern Africa, including the Richat Structure in Mauritania.
The Thera eruption
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on near ...
, dated to the seventeenth or sixteenth century BC, caused a large tsunami that some experts hypothesize devastated the Minoan civilization on the nearby island of Crete, further leading some to believe that this may have been the catastrophe that inspired the story. In the area of the Black Sea the following locations have been proposed: Bosporus and Ancomah (a legendary place near Trabzon).
Others have noted that, before the sixth century BC, the mountains on either side of the Laconian Gulf were called the "Pillars of Hercules", and they could be the geographical location being described in ancient reports upon which Plato was basing his story. The mountains stood at either side of the southernmost gulf in Greece, the largest in the Peloponnese, and that gulf opens onto the Mediterranean Sea. If from the beginning of discussions, misinterpretation of Gibraltar as the location rather than being at the Gulf of Laconia, would lend itself to many erroneous concepts regarding the location of Atlantis. Plato may have not been aware of the difference. The Laconian pillars open to the south toward Crete and beyond which is Egypt. The Thera eruption
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on near ...
and the Late Bronze Age collapse affected that area and might have been the devastation to which the sources used by Plato referred. Significant events such as these would have been likely material for tales passed from one generation to another for almost a thousand years.
In the Atlantic Ocean
The location of Atlantis in the Atlantic Ocean has a certain appeal given the closely related names. Popular culture often places Atlantis there, perpetuating the original Platonic setting as they understand it. The Canary Islands and Madeira Islands have been identified as a possible location, west of the Straits of Gibraltar, but in relative proximity to the Mediterranean Sea. Detailed studies of their geomorphology and geology have demonstrated, however, that they have been steadily uplifted, without any significant periods of subsidence, over the last four million years, by geologic processes such as erosional unloading, gravitational unloading, lithospheric flexure induced by adjacent islands, and volcanic underplating.Menendez, I., P.G. Silva, M. Martín-Betancor, F.J. Perez-Torrado, H. Guillou, and S. Scaillet, 2009, ''Fluvial dissection, isostatic uplift, and geomorphological evolution of volcanic islands (Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, Spain)'' Geomorphology. v. 102, no.1, pp. 189–202.Meco J., S. Scaillet, H. Guillou, A. Lomoschitz, J.C. Carracedo, J. Ballester, J.-F. Betancort, and A. Cilleros, 2007, ''Evidence for long-term uplift on the Canary Islands from emergent Mio–Pliocene littoral deposits.'' Global and Planetary Change. v. 57, no. 3-4, pp. 222–234. Various islands or island groups in the Atlantic were also identified as possible locations, notably the Azores. Similarly, cores of sediment covering the ocean bottom surrounding the Azores and other evidence demonstrate that it has been an undersea plateau for millions of years.Huang, T.C., N.D. Watkins, and L. Wilson, 1979, ''Deep-sea tephra from the Azores during the past 300,000 years: eruptive cloud height and ash volume estimates.'' Geological Society of America Bulletin. vol. 90, no. 2, pp. 131–133.Dennielou, B. G.A. Auffret, A. Boelaert, T. Richter, T. Garlan, and R. Kerbrat, 1999, ''Control of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Gulf Stream over Quaternary sedimentation on the Azores Plateau.'' Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série II. Sciences de la Terre et des Planètes. v. 328, no. 12, pp. 831–837., The area is known for its volcanism however, which is associated with rifting along the Azores Triple Junction. The spread of the crust along the existing faults and fractures has produced many volcanic and seismic events.Ferreira, 2005, p. 4 The area is supported by a buoyant upwelling in the deeper mantle, which some associate with an Azores hotspot. Most of the volcanic activity has occurred primarily along the Terceira Rift. From the beginning of the islands' settlement, around the 15th century, there have been about 30 volcanic eruptions (terrestrial and submarine) as well as numerous, powerful earthquakes. The island of São Miguel Island, São Miguel in the Azores is the site of the Sete Cidades Massif, Sete Cidades volcano and caldera, which are the byproducts of historical volcanic activity in the Azores. The submerged island of Spartel near the Strait of Gibraltar has also been suggested.Ireland
In 2004, Swedish Physical geography, physiographist Ulf Erlingsson proposed that the legend of Atlantis was based on Stone Age Ireland. He later stated that he does not believe that Atlantis ever existed but maintained that his hypothesis that its description matches Ireland's geography has a 99.8% probability. The director of the National Museum of Ireland commented that there was no archaeology supporting this.In Europe
Other locations
Several writers, such as Flavio Barbiero as early as 1974, have speculated that Antarctica is the site of Atlantis. A number of claims involve the Caribbean Sea, Caribbean, such as an alleged Cuban underwater formation, underwater formation off the Guanahacabibes Peninsula in Cuba. The adjacent Bahamas or the folkloric Bermuda Triangle have been proposed as well. Areas in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans have also been proposed, including Indonesia (i.e. Sundaland). The stories of a lost continent off the coast of India, named "Kumari Kandam", have inspired some to draw parallels to Atlantis.Literary interpretations
Ancient versions
 In order to give his account of Atlantis Verisimilitude (fiction), verisimilitude, Plato mentions that the story was heard by
In order to give his account of Atlantis Verisimilitude (fiction), verisimilitude, Plato mentions that the story was heard by Solon
Solon ( grc-gre, Σόλων; BC) was an Athenian statesman, constitutional lawmaker and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in Archaic Athens.Aristotle ''Politics'' ...
in Egypt, and transmitted orally over several generations through the family of Dropides, until it reached Critias, a dialogue speaker in ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''. Solon had supposedly tried to adapt the Atlantis oral tradition into a poem (that if published, was to be greater than the works of Hesiod and Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
). While it was never completed, Solon passed on the story to Dropides. Modern classicists deny the existence of Solon's Atlantis poem and the story as an oral tradition. Instead, Plato is thought to be the sole inventor or fabricator.
Hellanicus of Lesbos
Hellanicus (or Hellanikos) of Lesbos (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Lésvios''), also called Hellanicus of Mytilene (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Mutilēnaῖos'') was an ancient Greek logographer who flourished during the latter half of the 5th cen ...
used the word "Atlantis" as the title for a poem published before Plato, a fragment of which may be Oxyrhynchus Papyrus 11, 1359. This work only describes the Atlantides (the daughters of Atlas), however, and has no relation to Plato's Atlantis account.
In the new era, the third century AD Neoplatonism, Neoplatonist Zoticus wrote an epic poem based on Plato's account of Atlantis. Plato's work may already have inspired parody, parodic imitation, however. Writing only a few decades after the ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias'', the historian Theopompus of Chios wrote of a land beyond the ocean known as Meropis. This description was included in Book 8 of his ''Philippica'', which contains a dialogue between Silenus and King Midas. Silenus describes the Meropids, a race of men who grow to twice normal size, and inhabit two cities on the island of Meropis: ''Eusebes'' (, "Pious-town") and ''Machimos'' (, "Fighting-town"). He also reports that an army of ten million soldiers crossed the ocean to conquer Hyperborea
In Greek mythology, the Hyperboreans ( grc, Ὑπερβόρε(ι)οι, ; la, Hyperborei) were a mythical people who lived in the far northern part of the known world. Their name appears to derive from the Greek , "beyond Boreas" (the God of ...
, but abandoned this proposal when they realized that the Hyperboreans were the luckiest people on earth. Heinz-Günther Nesselrath has argued that these and other details of Silenus' story are meant as imitation and exaggeration of the Atlantis story, by parody, for the purpose of exposing Plato's ideas to ridicule.
Utopias and dystopias
The creation of Utopian and dystopian fictions was renewed after the Renaissance, most notably in Francis Bacon's ''New Atlantis
''New Atlantis'' is an incomplete utopian novel by Sir Francis Bacon, published posthumously in 1626. It appeared unheralded and tucked into the back of a longer work of natural history, ''Sylva Sylvarum'' (forest of materials). In ''New Atlan ...
'' (1627), the description of an ideal society that he located off the western coast of America. Thomas Heyrick (1649-1694) followed him with "The New Atlantis" (1687), a satirical poem in three parts. His new continent of uncertain location, perhaps even a floating island either in the sea or the sky, serves as background for his exposure of what he described in a second edition as "A True Character of Popery and Jesuitism".
The title of ''The New Atalantis'' by Delarivier Manley (1709), distinguished from the two others by the single letter, is an equally dystopian work but set this time on a fictional Mediterranean island. In it sexual violence and exploitation is made a metaphor for the hypocritical behaviour of politicians in their dealings with the general public. In Manley's case, the target of satire was the Whigs (British political party), Whig Party, while in David Maclean Parry's ''The Scarlet Empire'' (1906) it is Socialism as practised in foundered Atlantis. It was followed in Russia by Velimir Khlebnikov's poem ''The Fall of Atlantis'' (''Gibel' Atlantidy'', 1912), which is set in a future rationalist dystopia that has discovered the secret of immortality and is so dedicated to progress that it has lost touch with the past. When the high priest of this ideology is tempted by a slave girl into an act of irrationality, he murders her and precipitates a second flood, above which her severed head floats vengefully among the stars.
A slightly later work, ''The Ancient of Atlantis'' (Boston, 1915) by Albert Armstrong Manship, expounds the Atlantean wisdom that is to redeem the earth. Its three parts consist of a verse narrative of the life and training of an Atlantean wise one, followed by his Utopian moral teachings and then a psychic drama set in modern times in which a reincarnated child embodying the lost wisdom is reborn on earth.
In Hispanic eyes, Atlantis had a more intimate interpretation. The land had been a colonial power which, although it had brought civilization to ancient Europe, had also enslaved its peoples. Its tyrannical fall from grace had contributed to the fate that had overtaken it, but now its disappearance had unbalanced the world. This was the point of view of Jacint Verdaguer's vast mythological epic ''L'Atlantida'' (1877). After the sinking of the former continent, Hercules travels east across the Atlantic to found the city of Barcelona and then departs westward again to the Hesperides. The story is told by a hermit to a shipwrecked mariner, who is inspired to follow in his tracks and so "call the New World into existence to redress the balance of the Old". This mariner, of course, was Christopher Columbus.
Verdaguer's poem was written in Catalan language, Catalan, but was widely translated in both Europe and Hispano-America. One response was the similarly entitled Argentinian ''Atlantida'' of Olegario Víctor Andrade (1881), which sees in "Enchanted Atlantis that Plato foresaw, a golden promise to the fruitful race" of Latins. The bad example of the colonising world remains, however. José Juan Tablada characterises its threat in his "De Atlántida" (1894) through the beguiling picture of the lost world populated by the underwater creatures of Classical myth, among whom is the Siren (mythology), Siren of its final stanza with
There is a similar ambivalence in Janus Djurhuus' six-stanza "Atlantis" (1917), where a celebration of the Faroese language conflict, Faroese linguistic revival grants it an ancient pedigree by linking Greek to Norse legend. In the poem a female figure rising from the sea against a background of Classical palaces is recognised as a priestess of Atlantis. The poet recalls "that the Faroes lie there in the north Atlantic Ocean/ where before lay the poet-dreamt lands," but also that in Norse belief, such a figure only appears to those about to drown.
A land lost in the distance
 The fact that Atlantis is a lost land has made of it a metaphor for something no longer attainable. For the American poet Edith Willis Linn Forbes (1865-1945), "The Lost Atlantis" stands for idealisation of the past; the present moment can only be treasured once that is realised. Ella Wheeler Wilcox finds the location of "The Lost Land" (1910) in one's carefree youthful past. Similarly, for the Irish poet Eavan Boland in "Atlantis, a lost sonnet" (2007), the idea was defined when "the old fable-makers searched hard for a word/ to convey that what is gone is gone forever".
For some male poets too, the idea of Atlantis is constructed from what cannot be obtained. Charles Bewley in his Newdigate Prize poem (1910) thinks it grows from dissatisfaction with one's condition,
in a dream of Atlantis. Similarly for the Australian Gary Catalano in a 1982 prose poem, it is "a vision that sank under the weight of its own perfection". W. H. Auden, however, suggests a way out of such frustration through the metaphor of journeying toward Atlantis in his poem of 1941. While travelling, he advises the one setting out, you will meet with many definitions of the goal in view, only realising at the end that the way has all the time led inward.
The fact that Atlantis is a lost land has made of it a metaphor for something no longer attainable. For the American poet Edith Willis Linn Forbes (1865-1945), "The Lost Atlantis" stands for idealisation of the past; the present moment can only be treasured once that is realised. Ella Wheeler Wilcox finds the location of "The Lost Land" (1910) in one's carefree youthful past. Similarly, for the Irish poet Eavan Boland in "Atlantis, a lost sonnet" (2007), the idea was defined when "the old fable-makers searched hard for a word/ to convey that what is gone is gone forever".
For some male poets too, the idea of Atlantis is constructed from what cannot be obtained. Charles Bewley in his Newdigate Prize poem (1910) thinks it grows from dissatisfaction with one's condition,
in a dream of Atlantis. Similarly for the Australian Gary Catalano in a 1982 prose poem, it is "a vision that sank under the weight of its own perfection". W. H. Auden, however, suggests a way out of such frustration through the metaphor of journeying toward Atlantis in his poem of 1941. While travelling, he advises the one setting out, you will meet with many definitions of the goal in view, only realising at the end that the way has all the time led inward.
Epic narratives
A few late-19th century verse narratives complement the Atlantis in popular culture#Fiction, genre fiction that was beginning to be written at the same period. Two of them report the disaster that overtook the continent as related by long-lived survivors. In Frederick Tennyson's ''Atlantis'' (1888), an ancient Greek mariner sails west and discovers an inhabited island which is all that remains of the former kingdom. He learns of its end and views the shattered remnant of its former glory, from which a few had escaped to set up the Mediterranean civilisations. In the second, ''Mona, Queen of Lost Atlantis: An Idyllic Re-embodiment of Long Forgotten History'' (Los Angeles CA 1925) by James Logue Dryden (1840–1925), the story is told in a series of visions. A Seer is taken to Mona's burial chamber in the ruins of Atlantis, where she revives and describes the catastrophe. There follows a survey of the lost civilisations of Hyperborea and Lemuria as well as Atlantis, accompanied by much spiritualist lore. William Walton Hoskins (1856–1919) admits to the readers of his ''Atlantis and other poems'' (Cleveland OH, 1881), that he is only 24. Its melodramatic plot concerns the poisoning of the descendant of god-born kings. The usurping poisoner is poisoned in his turn, following which the continent is swallowed in the waves. Asian gods people the landscape of ''The Lost Island'' (Ottawa 1889) by Edward Taylor Fletcher (1816–97). An angel foresees impending catastrophe and that the people will be allowed to escape if their semi-divine rulers will sacrifice themselves. A final example, Edward N. Beecher's ''The Lost Atlantis or The Great Deluge of All'' (Cleveland OH, 1898) is just a doggerel vehicle for its author's opinions: that the continent was the location of the Garden of Eden; that Darwin's theory of evolution is correct, as are Donnelly's views. Atlantis was to become a theme in Russia following the 1890s, taken up in unfinished poems by Valery Bryusov and Konstantin Balmont, as well as in a drama by the schoolgirl Larissa Reissner, Larissa Reisner. One other long narrative poem was published in New York by George V. Golokhvastoff. His 250-page ''The Fall of Atlantis'' (1938) records how a high priest, distressed by the prevailing degeneracy of the ruling classes, seeks to create an androgynous being from royal twins as a means to overcome this polarity. When he is unable to control the forces unleashed by his occult ceremony, the continent is destroyed.Artistic representations
Music
The Spanish composer Manuel de Falla worked on a dramatic cantata based on Verdaguer's ''L'Atlántida'', during the last 20 years of his life. The name has been affixed to symphonies by Jānis Ivanovs (1941), Richard Nanes, and Vaclav Buzek (2009). There was also the symphonic celebration of Alan Hovhaness: "Fanfare for the New Atlantis" (Op. 281, 1975). The Bohemian-American composer and arranger Vincent Frank Safranek wrote ''Atlantis (The Lost Continent) Suite in Four Parts''; I. Nocturne and Morning Hymn of Praise, II. A Court Function, III. "I Love Thee" (The Prince and Aana), IV. The Destruction of Atlantis, for military (concert) band in 1913. The opera ''Der Kaiser von Atlantis'' (''The Emperor of Atlantis'') was written in 1943 by Viktor Ullmann with a libretto by Petr Kien, while they were both inmates at the Nazi concentration camp of Theresienstadt Ghetto, Theresienstadt. The Nazis did not allow it to be performed, assuming the opera's reference to an Emperor of Atlantis to be a satire on Adolf Hitler, Hitler. Though Ullmann and Kiel were murdered in Auschwitz, the manuscript survived and was performed for the first time in 1975 in Amsterdam.Painting and sculpture


 Paintings of the submersion of Atlantis are comparatively rare. In the seventeenth century there was François de Nomé's ''The Fall of Atlantis'', which shows a tidal wave surging toward a Baroque city frontage. The style of architecture apart, it is not very different from Nicholas Roerich's ''The Last of Atlantis'' of 1928.
The most dramatic depiction of the catastrophe was Léon Bakst's ''Ancient Terror'' (''Terror Antiquus'', 1908), although it does not name Atlantis directly. It is a mountain-top view of a rocky bay breached by the sea, which is washing inland about the tall structures of an ancient city. A streak of lightning crosses the upper half of the painting, while below it rises the impassive figure of an enigmatic goddess who holds a blue dove between her breasts. Vyacheslav Ivanov (poet), Vyacheslav Ivanov identified the subject as Atlantis in a public lecture on the painting given in 1909, the year it was first exhibited, and he has been followed by other commentators in the years since.
Sculptures referencing Atlantis have often been stylized single figures. One of the earliest was Einar Jónsson's ''The King of Atlantis'' (1919–1922), now in the garden of his museum in Reykjavík. It represents a single figure, clad in a belted skirt and wearing a large triangular helmet, who sits on an ornate throne supported between two young bulls. The walking female entitled ''Atlantis'' (1946) by Ivan Meštrović was from a series inspired by ancient Greek figures with the symbolical meaning of unjustified suffering.
In the case of the Brussels fountain feature known as ''The Man of Atlantis'' (2003) by the Belgian sculptor , the 4-metre tall figure wearing a diving suit steps from a plinth into the spray. It looks light-hearted but the artist's comment on it makes a serious point: "Because habitable land will be scarce, it is no longer improbable that we will return to the water in the long term. As a result, a portion of the population will mutate into fish-like creatures. Global warming and rising water levels are practical problems for the world in general and here in the Netherlands in particular".
Robert Smithson's ''Hypothetical Continent (Map of broken clear glass, Atlantis)'' was first created as a photographical project on Loveladies, New Jersey, Loveladies Island NJ in 1969, and then recreated as a gallery installation of broken glass. On this he commented that he liked "landscapes that suggest prehistory", and this is borne out by the original conceptual drawing of the work that includes an inset map of the continent sited off the coast of Africa and at the straits into the Mediterranean.
Paintings of the submersion of Atlantis are comparatively rare. In the seventeenth century there was François de Nomé's ''The Fall of Atlantis'', which shows a tidal wave surging toward a Baroque city frontage. The style of architecture apart, it is not very different from Nicholas Roerich's ''The Last of Atlantis'' of 1928.
The most dramatic depiction of the catastrophe was Léon Bakst's ''Ancient Terror'' (''Terror Antiquus'', 1908), although it does not name Atlantis directly. It is a mountain-top view of a rocky bay breached by the sea, which is washing inland about the tall structures of an ancient city. A streak of lightning crosses the upper half of the painting, while below it rises the impassive figure of an enigmatic goddess who holds a blue dove between her breasts. Vyacheslav Ivanov (poet), Vyacheslav Ivanov identified the subject as Atlantis in a public lecture on the painting given in 1909, the year it was first exhibited, and he has been followed by other commentators in the years since.
Sculptures referencing Atlantis have often been stylized single figures. One of the earliest was Einar Jónsson's ''The King of Atlantis'' (1919–1922), now in the garden of his museum in Reykjavík. It represents a single figure, clad in a belted skirt and wearing a large triangular helmet, who sits on an ornate throne supported between two young bulls. The walking female entitled ''Atlantis'' (1946) by Ivan Meštrović was from a series inspired by ancient Greek figures with the symbolical meaning of unjustified suffering.
In the case of the Brussels fountain feature known as ''The Man of Atlantis'' (2003) by the Belgian sculptor , the 4-metre tall figure wearing a diving suit steps from a plinth into the spray. It looks light-hearted but the artist's comment on it makes a serious point: "Because habitable land will be scarce, it is no longer improbable that we will return to the water in the long term. As a result, a portion of the population will mutate into fish-like creatures. Global warming and rising water levels are practical problems for the world in general and here in the Netherlands in particular".
Robert Smithson's ''Hypothetical Continent (Map of broken clear glass, Atlantis)'' was first created as a photographical project on Loveladies, New Jersey, Loveladies Island NJ in 1969, and then recreated as a gallery installation of broken glass. On this he commented that he liked "landscapes that suggest prehistory", and this is borne out by the original conceptual drawing of the work that includes an inset map of the continent sited off the coast of Africa and at the straits into the Mediterranean.
See also
*Atlantis in comics * List of mythological places *Antillia *Avalon *Brasil (mythical island) *Brittia *Cantre'r Gwaelod *Iram of the Pillars *Lemuria (continent) *Mayda *Mu (lost continent) *Mythical place *Numenor *Saint Brendan's Island *Sandy Island, New Caledonia *Thule
Thule ( grc-gre, Θούλη, Thoúlē; la, Thūlē) is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Modern interpretations have included Orkney, Shetland, northern Scotland, the island of Saar ...
*Ys
Underwater geography:
*Yonaguni Monument
*Bimini Road
General:
* Doggerland
* Lost lands
* Kumari Kandam
* Minoan eruption
Notes
Further reading
* * Ancient sources *Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, ''Timaeus Timaeus (or Timaios) is a Greek name. It may refer to:
* ''Timaeus'' (dialogue), a Socratic dialogue by Plato
*Timaeus of Locri, 5th-century BC Pythagorean philosopher, appearing in Plato's dialogue
*Timaeus (historian) (c. 345 BC-c. 250 BC), Greek ...
'', translated by Benjamin Jowett aProject Gutenberg
with commentary. *Plato, ''
Critias
Critias (; grc-gre, Κριτίας, ''Kritias''; c. 460 – 403 BC) was an ancient Athenian political figure and author. Born in Athens, Critias was the son of Callaeschrus and a first cousin of Plato's mother Perictione. He became a leading ...
'', translated by Benjamin Jowett aProject Gutenberg
with commentary. Modern sources * * * * * * * {{Authority control Atlantis, Allegory Esoteric anthropogenesis Legendary tribes in Greco-Roman historiography Mythological populated places Phantom islands Platonism Theoretical continents Pseudohistory