|
Hermocrates
Hermocrates (; grc-gre, Ἑρμοκράτης, c. 5th century – 407 BC) was an ancient Syracusan general during the Athenians' Sicilian Expedition in the midst of the Peloponnesian War. He is also remembered as a character in the ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias'' dialogues of Plato. Life The first historical reference to Hermocrates comes from Thucydides, where he appears at the congress of Gela in 424 BC giving a speech demanding the Sicilian Greeks stop their quarrelling and unite against the Athenians, who had been attacking the Sicilian cities for supporting Corinth. When Athens sent an armada to conquer Sicily in 415, Hermocrates called for expanding the anti-Athens coalition, and sent ambassadors to Sparta, Corinth, Carthage, and Italy seeking allies. The Athenians were able to establish a base at Catana, and had defeated the Syracusans at the river Anapus. Hermocrates called for extending his cities fortifications and was able to do away with the traditional fifteen gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens. The expedition was hampered from the outset by uncertainty in its purpose and command structure—political maneuvering in Athens swelled a lightweight force of twenty ships into a massive armada, and the expedition's primary proponent, Alcibiades, was recalled from command to stand trial before the fleet even reached Sicily. Still, the Athenians achieved early successes. Syracuse, the most powerful state in Sicily, responded exceptionally slowly to the Athenian threat and, as a result, was almost completely invested before the arrival of back up in the form of Spartan general, Gylippus, who galvanized its inhabitants into action. From that point forward, however, as the Athe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermocrates (dialogue)
''Hermocrates'' (; el, Ἑρμοκράτης, Hermokrátēs) is a hypothetical dialogue, assumed to be the third part of Plato's late trilogy along with ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias''. No one knows exactly how ''Critias'' ended, as the ending to the book is currently lost, so historians have not been able to say exactly how Hermocrates would begin. In any case, the people that would have appeared are very likely to be the same as in the former dialogues – Timaeus, Critias, Hermocrates, and Socrates – and the unnamed companion mentioned at the beginning of the ''Timaeus'' might have unveiled his identity. The intention of Plato to write this third dialogue becomes evident among others, from the following passage of Critias: Hermocrates had only a small share of the conversation in the previous dialogues. Since the ''Critias'' recounted the story of the ideal state in ancient Athens of nine thousand years ago – and why it was able to repel the invasion by the imperialist naval po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critias (dialogue)
''Critias'' (; el, Κριτίας), one of Plato's late dialogues, recounts the story of the mighty island kingdom Atlantis and its attempt to conquer Athens, which failed due to the ordered society of the Athenians. ''Critias'' is the second of a projected trilogy of dialogues, preceded by ''Timaeus'' and followed by ''Hermocrates''. The latter was possibly never written and the ending to ''Critias'' has been lost. Because of their resemblance (e.g., in terms of persons appearing), modern classicists occasionally combine both ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias'' as ''Timaeus-Critias''. Protagonists *Timaeus Unlike the other speakers of the ''Critias'', it is unclear whether Timaeus is a historical figure or not. While some classicists regard him as definitively historical, others guess that "Plato's picture of him has probably borrowed traits from various quarters". Frank assumes Archytas of Tarentum to be the person which Timaeus is partly based on. On the other hand, F. M. Cornford s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selinunte
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Selīnoûs ; la, Selīnūs , ; scn, Silinunti ) was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modione rivers. It now lies in the ''comune'' Castelvetrano, between the '' frazioni'' of Triscina di Selinunte in the west and Marinella di Selinunte in the east. The archaeological site contains many great temples, the earliest dating from 550 BC, with five centred on an acropolis. At its peak before 409 BC the city may have had 30,000 inhabitants, excluding slaves. It was destroyed and abandoned in 250 BC and never reoccupied. History Selinunte was one of the most important of the Greek colonies in Sicily, situated on the southwest coast of that island, at the mouth of the small river of the same name, and 6.5 km west of the Hypsas river (the modern Belice). It was founded, according to the historian Thucydides, by a colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Peloponnesian War
The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), which was fought between the Peloponnesian League (led by Sparta) and the Delian League (led by Athens). It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian historian who also served as an Athenian general during the war. His account of the conflict is widely considered to be a classic and regarded as one of the earliest scholarly works of history. The ''History'' is divided into eight books. Analyses of the ''History'' generally occur in one of two camps. On the one hand, some scholars such as J. B. Bury view the work as an objective and scientific piece of history. The judgment of Bury reflects this traditional interpretation of the ''History'' as "severe in its detachment, written from a purely intellectual point of view, unencumbered with platitudes and moral judgments, cold and critical." On the other hand, in keeping with more recent interpretations that are associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Gela
The Congress of Gela was a diplomatic meeting between a number of Sicilian cities in 424 BC. It brought a temporary halt to several years of warfare between cities on the island. At the conference, the Sicilian cities agreed to a Syracusan proposal to make peace and agree to a platform of "Sicily for the Sicilians", which has been compared to the Monroe Doctrine. Though the agreement was intended to be perpetual, both war and outside involvement in Sicilian affairs resumed within a few decades. Background A conflict between Syracuse and Leontini led to an appeal for help from Leontini to Athens who sent twenty ships in 427 BC. By 426 BC, it had become a wide-ranging conflict including many Greek cities and native Sicels. Athenian forces, fighting alongside Rhegium, Leontini, Naxos, Kamarina, and various Sicel tribes, won several initial successes. In 426, Athenian forces captured the strategically vital city of Messina and attacked several other towns allied to Syracuse. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timaeus (dialogue)
''Timaeus'' (; grc-gre, Τίμαιος, Timaios, ) is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of long monologues given by Critias and Timaeus, written 360 BC. The work puts forward reasoning on the possible nature of the physical world and human beings and is followed by the dialogue '' Critias''. Participants in the dialogue include Socrates, Timaeus, Hermocrates, and Critias. Some scholars believe that it is not the Critias of the Thirty Tyrants who appears in this dialogue, but his grandfather, who is also named Critias. It has been suggested from some traditions ( Diogenes Laertius (VIII 85) from Hermippus of Smyrna (3rd century BC) and Timon of Phlius ( 320 – 235 BC)) that ''Timaeus'' was influenced by a book about Pythagoras, written by Philolaus, although this assertion is generally considered false. Introduction The dialogue takes place the day after Socrates described his ideal state. In Plato's works, such a discussion occurs in the '' Republic''. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleides (415 BC)
Heracleides ( grc, Ἡρακλείδης), son of Lysimachus, was a Syracusan and one of the three ''strategoi'' (generals) appointed by the Syracusans after their first defeat by the Athenians upon the arrival of the Athenian expedition on Sicily in 415 BC. Heracleides and his colleagues, Hermocrates and Sicanus, were invested with full powers to deal with the Athenian threat. Hermocrates ascribed the Syracusan defeat to the number of the generals, which he deemed too high, and their want of sufficient control over their troops. The Syracusans reduced the number of generals from fifteen to three and invested them with full powers. Heracleides and his colleagues were deposed from their command in the following summer on account of their failure in preventing the progress of the Athenian siege works. Of the three generals appointed in their place, one was also named Heracleides.Thucydides, ''History of the Peloponnesian War The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' is a historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cyzicus
The naval Battle of Cyzicus (Greek: ) took place in May or June 410 BC during the Peloponnesian War. During the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by Alcibiades, Thrasybulus, and Theramenes routed and destroyed a Spartan fleet commanded by Mindarus. The victory allowed Athens to recover control over a number of cities in the Hellespont over the next year. In the wake of their defeat, the Spartans made a peace offer, which the Athenians rejected. Prelude Athens had been debilitated after the Sicilian expedition and its hold on the Hellespont had loosened with Persian support now behind Sparta. Cyzicus revolted from Athens in the summer of 411, but had been recovered by the Athenian fleet after the Battle of Cynossema. In the wake of the Athenian victory at Abydos in November 411 BC, the Spartan admiral Mindarus sent to Sparta for reinforcements and began working with the Persian satrap Pharnabazus to plan for a new offensive. The Athenians, meanwhile, were unable to follow thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilian Wars
The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC. Carthage's economic success and its dependence on seaborne trade led to the creation of a powerful navy to discourage both pirates and rival nations. They had inherited their naval strength and experience from their forebears, the Phoenicians, but had increased it because, unlike the Phoenicians, the Punics did not want to rely on a foreign nation's aid. This, coupled with its success and growing hegemony, brought Carthage into increasing conflict with the Greeks, the other major power contending for control of the central Mediterranean. The Greeks, like the Phoenicians, were expert sailors who had established thriving colonies throughout the Mediterranean. These two rivals fought their wars on the island of Sicily, which lay close to Carthage. From th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
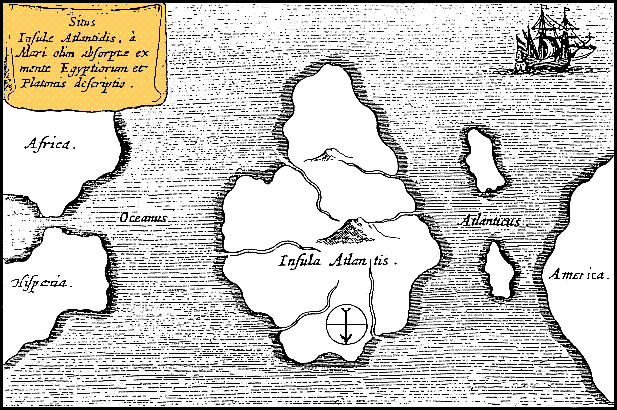
Atlantis
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory on the hubris of nations in Plato's works ''Timaeus'' and ''Critias'', wherein it represents the antagonist naval power that besieges "Ancient Athens", the pseudo-historic embodiment of Plato's ideal state in '' The Republic''. In the story, Athens repels the Atlantean attack unlike any other nation of the known world, supposedly bearing witness to the superiority of Plato's concept of a state. The story concludes with Atlantis falling out of favor with the deities and submerging into the Atlantic Ocean. Despite its minor importance in Plato's work, the Atlantis story has had a considerable impact on literature. The allegorical aspect of Atlantis was taken up in utopian works of several Renaissance writers, such as Francis Bacon's ''New Atlantis'' and Thomas More's ''Utopia''. On the other hand, nineteenth-century amateur scholars misinterpreted Plato's narrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scientific history" by those who accept his claims to have applied strict standards of impartiality and evidence-gathering and analysis of cause and effect, without reference to intervention by the gods, as outlined in his introduction to his work. He also has been called the father of the school of political realism, which views the political behavior of individuals and the subsequent outcomes of relations between states as ultimately mediated by, and constructed upon, fear and self-interest. His text is still studied at universities and military colleges worldwide. The Melian dialogue is regarded as a seminal work of international relations theory, while his version of Pericles' Funeral Oration is widely studied by political theorists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |