Ashkenazi Jewish Culture In Sweden on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōųĄūÖ ūÉųĘū®ų░ūüūøų░ų╝ūĀųĘū¢, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, ūÉųĘū®ūøų╝ūĀū¢ūÖū®ūó ūÖūÖų┤ūōū¤, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōųĄūÖ ūÉųĘū®ų░ūüūøų░ų╝ūĀųĘū¢, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, ūÉųĘū®ūøų╝ūĀū¢ūÖū®ūó ūÖūÖų┤ūōū¤, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is
 By the 15th century, the Ashkenazi Jewish communities in Poland were the largest Jewish communities of the
By the 15th century, the Ashkenazi Jewish communities in Poland were the largest Jewish communities of the
 In the first half of the 11th century, Hai Gaon refers to questions that had been addressed to him from Ashkenaz, by which he undoubtedly means Germany. '' Rashi'' in the latter half of the 11th century refers to both the language of Ashkenaz and the country of Ashkenaz. During the 12th century, the word appears quite frequently. In the '' Mahzor Vitry'', the kingdom of Ashkenaz is referred to chiefly in regard to the ritual of the synagogue there, but occasionally also with regard to certain other observances.
In the literature of the 13th century, references to the land and the language of Ashkenaz often occur. Examples include Solomon ben Aderet's Responsa (vol. i., No. 395); the Responsa of Asher ben Jehiel (pp. 4, 6); his ''Halakot'' (Berakot i. 12, ed. Wilna, p. 10); the work of his son Jacob ben Asher, ''Tur Orach Chayim'' (chapter 59); the Responsa of Isaac ben Sheshet (numbers 193, 268, 270).
In the '' Midrash'' compilation, ''Genesis Rabbah'', Rabbi Berechiah mentions Ashkenaz, Riphath, and Togarmah as German tribes or as German lands. It may correspond to a Greek word that may have existed in the Greek dialect of the Jews in
In the first half of the 11th century, Hai Gaon refers to questions that had been addressed to him from Ashkenaz, by which he undoubtedly means Germany. '' Rashi'' in the latter half of the 11th century refers to both the language of Ashkenaz and the country of Ashkenaz. During the 12th century, the word appears quite frequently. In the '' Mahzor Vitry'', the kingdom of Ashkenaz is referred to chiefly in regard to the ritual of the synagogue there, but occasionally also with regard to certain other observances.
In the literature of the 13th century, references to the land and the language of Ashkenaz often occur. Examples include Solomon ben Aderet's Responsa (vol. i., No. 395); the Responsa of Asher ben Jehiel (pp. 4, 6); his ''Halakot'' (Berakot i. 12, ed. Wilna, p. 10); the work of his son Jacob ben Asher, ''Tur Orach Chayim'' (chapter 59); the Responsa of Isaac ben Sheshet (numbers 193, 268, 270).
In the '' Midrash'' compilation, ''Genesis Rabbah'', Rabbi Berechiah mentions Ashkenaz, Riphath, and Togarmah as German tribes or as German lands. It may correspond to a Greek word that may have existed in the Greek dialect of the Jews in
 The ''
The ''
''East and South-East European Jews in the 19th and 20th Centuries''
European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2010, retrieved: 17 December 2012. * Vital, David (1999): ''A People Apart: A History of the Jews in Europe''. Oxford University Press. . *
''The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe''
*
Ćö''European Journal of Human Genetics'', 2007 * ttp://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2156/9/14 "Analysis of genetic variation in Ashkenazi Jews by high density SNP genotyping"
Nusach Ashkenaz, and Discussion Forum
Ashkenaz Heritage
{{Authority control Ashkenazi Jews topics Ethnic groups in Israel Ethnic groups in Russia Jewish ethnic groups Middle Eastern people Semitic-speaking peoples
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
(a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54┬░N, or may be based on other g ...
and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel.
Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science.
The rabbinical term ''Ashkenazi'' refers to diaspora Jews who established communities along the Rhine in western Germany and northern France Northern France may refer to:
*the north of France, especially:
**the region of Hauts-de-France
**the former region of Nord-Pas-de-Calais
**Nord (French department)
Nord (; officially french: d├®partement du Nord; pcd, d├®part├®mint dech Nord ...
during the Middle Ages. Upon their arrival, they adapted traditions carried over from the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
, Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''m─üt Akkad─½'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
, and the western Mediterranean to their new European environment. The Ashkenazi religious rite developed in cities such as Mainz, Worms, and Troyes
Troyes () is a commune and the capital of the department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within the Champagne wine region and is near to ...
. The eminent '' rishon'' from medieval France'','' Rashi, has had a significant influence on the interpretations of Judaism by Ashkenazim.
In the late Middle Ages, due to widespread persecution, the majority of the Ashkenazi population steadily shifted eastward, moving out of the Holy Roman Empire into the areas that later became part of the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth; these areas today comprise parts of present-day Belarus, Estonia, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Le┼Żm┼Ź), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Le┼Żm┼Ź Vab─üm┼Ź, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Moldova, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, and Ukraine.
Over the course of the late-18th and 19th centuries, those Jews who remained in or returned to historical German lands generated a cultural reorientation; under the influence of the Haskalah and the struggle for emancipation as well as the intellectual and cultural ferment in urban centres, they gradually abandoned the use of Yiddish and adopted German while developing new forms of Jewish religious life and cultural identity
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct cultur ...
.
It is estimated that in the 11th century, Ashkenazim comprised 3 percent of the global Jewish population, while an estimate made in 1930 (near the population's peak) listed them as comprising 92 percent of the world's Jewish population. However, the Ashkenazi population was decimated shortly after as a result of the Holocaust that was carried out by Nazi Germany during World War II, which affected almost every Jewish European family. Immediately prior to the Holocaust, the worldwide Jewish population stood at approximately 16.7 million people., based on Statistical figures vary for the contemporary demography of Ashkenazi Jews, ranging from 10 million to 11.2 million. Israeli demographer and statistician Sergio D. Pergola, in a rough calculation of Sephardi Jews and Mizrahi Jews, implies that Ashkenazi Jews made up 65ŌĆō70 percent of Jews worldwide in 2000. Della Pergola does not analyze or mention the Ashkenazi statistics, but the figure is implied by his rough estimate that in 2000, Oriental and Sephardi Jews constituted 26% of the population of world Jewry. Other estimates place the Ashkenazim as comprising upwards of 75 percent of the global Jewish population.''Focus on Genetic Screening Research'', ed. Sandra R. Pupecki, p. 58
Genetic studies on Ashkenazi JewsŌĆöresearching both their paternal and maternal lineages as well as autosomal DNA
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
ŌĆöindicate that they are of mixed Levantine and European (mainly western European and southern European) ancestry. These studies have arrived at diverging conclusions regarding both the degree and the sources of their European admixture, with some focusing on the extent of the European genetic origin observed in Ashkenazi maternal lineages, which is in contrast to the predominant Middle Eastern genetic origin observed in Ashkenazi paternal lineages.
Etymology
The name ''Ashkenazi'' derives from the biblical figure of Ashkenaz, the first son of Gomer, son of Japhet, son ofNoah
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ßŖ¢ßłģ, ''NoßĖź''; ar, ┘å┘Å┘łžŁ '; grc, ╬Øß┐Č╬Ą ''N├┤e'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5ŌĆō ...
, and a Japhetic patriarch in the Table of Nations ( Genesis 10). The name of Gomer has often been linked to the Cimmerians.
The Biblical ''Ashkenaz'' is usually derived from Assyrian ''A┼Īk┼½za'' ( cuneiform ''A┼Īkuzai/I┼Īkuzai''), a people who expelled the Cimmerians from the Armenian area of the Upper Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. TigrisŌĆōEuphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
; the name ''A┼Īk┼½za'' is identified with the Scythians.Vladimir Shneider, ''Traces of the Ten''. Beer-sheva, Israel 2002. p. 237 The intrusive ''n'' in the Biblical name is likely due to a scribal error confusing a ''vav'' with a ''nun'' .
In Jeremiah 51:27, Ashkenaz figures as one of three kingdoms in the far north, the others being Minni and Ararat (corresponding to Urartu), called on by God to resist Babylon. In the Yoma
Yoma (Aramaic: ūÖūĢū×ūÉ, lit. "The Day") is the fifth tractate of ''Seder Moed'' ("Order of Festivals") of the ''Mishnah'' and of the ''Talmud''. It is concerned mainly with the laws of the Jewish holiday Yom Kippur, on which Jews atone for their ...
tractate of the Babylonian Talmud the name Gomer is rendered as ''Germania'', which elsewhere in rabbinical literature was identified with Germanikia in northwestern Syria, but later became associated with ''Germania''. Ashkenaz is linked to Scandza/Scanzia, viewed as the cradle of Germanic tribes, as early as a 6th-century gloss to the Historia Ecclesiastica of Eusebius.
In the 10th-century ''History of Armenia'' of Yovhannes Drasxanakertc'i (1.15), Ashkenaz was associated with Armenia, as it was occasionally in Jewish usage, where its denotation extended at times to Adiabene, Khazaria, Crimea and areas to the east. His contemporary Saadia Gaon identified Ashkenaz with the '' Saquliba'' or Slavic territories, and such usage covered also the lands of tribes neighboring the Slavs, and Eastern and Central Europe. In modern times, Samuel Krauss identified the Biblical "Ashkenaz" with Khazaria.
Sometime in the Early Medieval period, the Jews of central and eastern Europe came to be called by this term. Conforming to the custom of designating areas of Jewish settlement with biblical names, Spain was denominated ''Sefarad'' ( Obadiah 20), France was called ''Tsarefat'' ( 1 Kings 17:9), and Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, ─īechy ; ; hsb, ─ī─øska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
was called the '' Land of Canaan''. By the high medieval
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500 ...
period, Talmudic commentators like Rashi began to use ''Ashkenaz/Eretz Ashkenaz'' to designate Germany, earlier known as '' Loter'', where, especially in the Rhineland communities of Speyer, Worms and Mainz, the most important Jewish communities arose. Rashi uses ''leshon Ashkenaz'' (Ashkenazi language) to describe Yiddish, and Byzantium and Syrian Jewish letters referred to the Crusaders as Ashkenazim. Given the close links between the Jewish communities of France and Germany following the Carolingian unification, the term Ashkenazi came to refer to the Jews of both medieval Germany and France.
History
Like other Jewish ethnic groups, the Ashkenazi Jews originate from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical Israel and Judah. Ashkenazi Jews share a significant amount of ancestry with other Jewish populations and derive their ancestry mostly from populations in the Middle East and Southern Europe. Other than their origins in ancient Israel, the question of how Ashkenazi Jews came to exist as a distinct community is shrouded in mystery, and has given rise to several theories.Early Jewish communities in Europe
Beginning in the fourth century BCE, Jewish colonies sprung up in southern Europe, including the Aegean Islands, Greece, and Italy. Jews left ancient Israel for a number of causes, including a number of push and pull factors. More Jews moved into these communities as a result of wars, persecution, unrest, and for opportunities in trade and commerce. Jews migrated to southern Europe from the Middle East voluntarily for opportunities in trade and commerce. Following Alexander the Great's conquests, Jews migrated to Greek settlements in the Eastern Mediterranean, spurred on by economic opportunities. Jewish economic migration to southern Europe is also believed to have occurred during the Roman period. In 63 BCE, the Siege of Jerusalem saw the Roman Republic conquer Judea, and thousands of Jewish prisoners of war were brought to Rome as slaves. After gaining their freedom, they settled permanently in Rome as traders. It is likely that there was an additional influx of Jewish slaves taken to southern Europe by Roman forces after the capture of Jerusalem by the forces of Herod the Great with assistance from Roman forces in 37 BCE. It is known that Jewish war captives were sold into slavery after the suppression of a minor Jewish revolt in 53 BCE, and some were probably taken to southern Europe. Regarding Jewish settlements founded in southern Europe during the Roman era,E. Mary Smallwood
Edith Mary Smallwood (born 8 December 1919) was a historian and a professor of Romano-Jewish History at the Queen's University, Belfast.
Early life
Smallwood was born in Wandsworth, Surrey (now London) in December 1919. She received her education ...
wrote that "no date or origin can be assigned to the numerous settlements eventually known in the west, and some may have been founded as a result of the dispersal of Palestinian Jews after the revolts of AD 66ŌĆō70 and 132ŌĆō135, but it is reasonable to conjecture that many, such as the settlement in Puteoli attested in 4 BC, went back to the late republic or early empire and originated in voluntary emigration and the lure of trade and commerce."
Jewish-Roman Wars
The first and second centuries CE saw a series of unsuccessful large-scale Jewish revolts against Rome. The Roman suppression of these revolts led to wide-scale destruction, a very high toll of life and enslavement. The First Jewish-Roman War (66ŌĆō73 CE) resulted in the destruction of Jerusalem and the Second Temple. Two generations later, theBar Kokhba Revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''MereßĖÅ Bar K┼ŹßĖĄßĖć─ü╩ŠŌĆÄ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Judea (Roman province), Roman province of Judea, led b ...
(132ŌĆō136 CE) erupted. Judea's countryside was devastated, and many were killed, displaced or sold into slavery. Jerusalem was rebuilt as a Roman colony under the name of Aelia Capitolina, and the province of Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina (literally, "Palestinian Syria";Trevor Bryce, 2009, ''The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia''Roland de Vaux, 1978, ''The Early History of Israel'', Page 2: "After the revolt of Bar Cochba in 135 ...
.H.H. Ben-Sasson, ''A History of the Jewish People'', Harvard University Press, 1976, , page 334: "In an effort to wipe out all memory of the bond between the Jews and the land, Hadrian changed the name of the province from Judaea to Syria-Palestina, a name that became common in non-Jewish literature."Ariel Lewin. ''The archaeology of Ancient Judea and Palestine''. Getty Publications, 2005 p. 33. "It seems clear that by choosing a seemingly neutral name ŌĆō one juxtaposing that of a neighboring province with the revived name of an ancient geographical entity (Palestine), already known from the writings of Herodotus ŌĆō Hadrian was intending to suppress any connection between the Jewish people and that land." Jews were prohibited from entering the city on pain of death. Jewish presence in the region significantly dwindled after the failure of the Bar Kokhba revolt.
With their national aspirations crushed and widespread devastation in Judea, despondent Jews migrated out of Judea in the aftermath of both revolts, and many settled in southern Europe. In contrast to the earlier Assyrian and Babylonian captivities, the movement was by no means a singular, centralized event, and a Jewish diaspora had already been established before.
During both of these rebellions, many Jews were captured and sold into slavery by the Romans. According to the Jewish historian Josephus, 97,000 Jews were sold as slaves in the aftermath of the first revolt. In one occasion, Vespasian reportedly ordered 6,000 Jewish prisoners of war from Galilee
Galilee (; he, ūöųĘūÆųĖų╝ū£ų┤ūÖū£, hagG─ül─½l; ar, ž¦┘äž¼┘ä┘Ŗ┘ä, al-jal─½l) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galil ...
to work on the Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth (Greek: ╬ÖŽā╬Ė╬╝ŽīŽé Žä╬ĘŽé ╬Ü╬┐Žü╬»╬Į╬Ė╬┐Žģ) is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancien ...
in Greece. Jewish slaves and their children eventually gained their freedom and joined local free Jewish communities.
Late Antiquity
Many Jews were denied full Roman citizenship until Emperor Caracalla granted all free peoples this privilege in 212 CE. Jews were required to pay apoll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
until the reign of Emperor Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331ŌĆō363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
in 363 CE. In the late Roman Empire, Jews were free to form networks of cultural and religious ties and enter into various local occupations. But, after Christianity became the official religion of Rome and Constantinople in 380 CE, Jews were increasingly marginalized.
The Synagogue in the Agora of Athens The Synagogue in the Agora of Athens is an ancient synagogue located in the Ancient Agora of Athens.
During an excavation in the summer of 1977, a piece of Pentelic marble apparently once part of a curvilinear frieze over a doorway or niche was d ...
is dated to the period between 267 and 396 CE. The Stobi Synagogue in Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
was built on the ruins of a more ancient synagogue in the 4th century, while later in the 5th century, the synagogue was transformed into a Christian basilica. Hellenistic Judaism thrived in Antioch and Alexandria, and many of these Greek-speaking Jews would convert to Christianity.
Sporadic epigraphic evidence in gravesite excavations, particularly in Brigetio ( Sz┼æny), Aquincum ( ├ōbuda), Intercisa ( Duna├║jv├Īros), Triccinae ( S├Īrv├Īr), Savaria ( Szombathely), Sopianae ( P├®cs) in Hungary, and Mursa (Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja ...
) in Croatia, attest to the presence of Jews after the 2nd and 3rd centuries where Roman garrisons were established. There was a sufficient number of Jews in Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
to form communities and build a synagogue. Jewish troops were among the Syrian soldiers transferred there, and replenished from the Middle East. After 175 CE Jews and especially Syrians came from Antioch, Tarsus, and Cappadocia. Others came from Italy and the Hellenized parts of the Roman Empire. The excavations suggest they first lived in isolated enclaves attached to Roman legion camps and intermarried with other similar oriental families within the military orders of the region.
Raphael Patai states that later Roman writers remarked that they differed little in either customs, manner of writing, or names from the people among whom they dwelt; and it was especially difficult to differentiate Jews from the Syrians. After Pannonia was ceded to the Huns in 433, the garrison populations were withdrawn to Italy, and only a few, enigmatic traces remain of a possible Jewish presence in the area some centuries later. No evidence has yet been found of a Jewish presence in antiquity in Germany beyond its Roman border, nor in Eastern Europe. In Gaul and Germany itself, with the possible exception of Trier and Cologne, the archeological evidence suggests at most a fleeting presence of very few Jews, primarily itinerant traders or artisans.
Estimating the number of Jews in antiquity is a task fraught with peril due to the nature of and lack of accurate documentation. The number of Jews in the Roman Empire for a long time was based on the accounts of Syrian Orthodox bishop Bar Hebraeus who lived between 1226 and 1286 CE, who stated by the time of the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, as many as six million Jews were already living in the Roman Empire, a conclusion which has been contested as highly exaggerated. The 13th-century author Bar Hebraeus gave a figure of 6,944,000 Jews in the Roman world. Salo Wittmayer Baron considered the figure convincing. The figure of seven million within and one million outside the Roman world in the mid-first century became widely accepted, including by Louis Feldman. However, contemporary scholars now accept that Bar Hebraeus based his figure on a census of total Roman citizens and thus included non-Jews, the figure of 6,944,000 being recorded in Eusebius' ''Chronicon''. Louis Feldman, previously an active supporter of the figure, now states that he and Baron were mistaken. Philo gives a figure of one million Jews living in Egypt. Brian McGing rejects Baron's figures entirely, arguing that we have no clue as to the size of the Jewish demographic in the ancient world. Sometimes the scholars who accepted the high number of Jews in Rome had explained it by Jews having been active in proselytising. The idea of ancient Jews trying to convert Gentiles to Judaism is nowadays rejected by several scholars. The Romans did not distinguish between Jews inside and outside of the land of Israel/Judaea. They collected an annual temple tax from Jews both in and outside of Israel. The revolts in and suppression of diaspora communities in Egypt, Libya and Crete during the Kitos War of 115ŌĆō117 CE had a severe impact on the Jewish diaspora.
A substantial Jewish population emerged in northern Gaul by the Middle Ages, but Jewish communities existed in 465 CE in Brittany, in 524 CE in Valence
Valence or valency may refer to:
Science
* Valence (chemistry), a measure of an element's combining power with other atoms
* Degree (graph theory), also called the valency of a vertex in graph theory
* Valency (linguistics), aspect of verbs rel ...
, and in 533 CE in Orl├®ans. Throughout this period and into the early Middle Ages, some Jews assimilated into the dominant Greek and Latin cultures, mostly through conversion to Christianity. King Dagobert I of the Franks expelled the Jews from his Merovingian kingdom in 629. Jews in former Roman territories faced new challenges as harsher anti-Jewish Church rulings were enforced.
Early Middle Ages
Charlemagne's expansion of the Frankish empire around 800, including northern Italy and Rome, brought on a brief period of stability and unity in Francia. This created opportunities for Jewish merchants to settle again north of the Alps. Charlemagne granted the Jews freedoms similar to those once enjoyed under the Roman Empire. In addition, Jews from southern Italy, fleeing religious persecution, began to move into Central Europe. Returning to Frankish lands, many Jewish merchants took up occupations in finance and commerce, including money lending, or usury. (Church legislation banned Christians from lending money in exchange for interest.) From Charlemagne's time to the present, Jewish life in northern Europe is well documented. By the 11th century, when Rashi ofTroyes
Troyes () is a commune and the capital of the department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within the Champagne wine region and is near to ...
wrote his commentaries, Jews in what came to be known as "Ashkenaz" were known for their halakhic learning, and Talmudic studies. They were criticized by Sephardim and other Jewish scholars in Islamic lands for their lack of expertise in Jewish jurisprudence and general ignorance of Hebrew linguistics and literature. Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
emerged as a result of Judeo-Latin language contact with various High German vernaculars in the medieval period. It is a Germanic language written in Hebrew letters, and heavily influenced by Hebrew and Aramaic, with some elements of Romance and later Slavic languages.
High and Late Middle Ages migrations
Historical records show evidence of Jewish communities north of the Alps and Pyrenees as early as the 8th and 9th centuries. By the 11th century, Jewish settlers moving from southern European and Middle Eastern centers (such asBabylonian Jews
The history of the Jews in Iraq ( he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōų┤ūÖūØ ūæųĖų╝ūæų░ū£ų┤ūÖūØ, ', ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ┘ć┘łž» ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, ) is documented from the time of the Babylonian captivity c. 586 BC. Iraqi Jews constitute one of the world's oldest and mo ...
and Persian Jews) and Maghrebi Jewish traders from North Africa who had contacts with their Ashkenazi brethren and had visited each other from time to time in each's domain appear to have begun to settle in the north, especially along the Rhine, often in response to new economic opportunities and at the invitation of local Christian rulers. Thus Baldwin V, Count of Flanders
Baldwin V ( 1012 ŌĆō 1 September 1067) was Count of Flanders from 1035 until his death. He secured the personal union between the counties of Flanders and Hainaut and maintained close links to the Anglo-Saxon monarchy, which was overthrown by hi ...
, invited Jacob ben Yekutiel and his fellow Jews to settle in his lands; and soon after the Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, Duchy of Brittany, Breton, County of Flanders, Flemish, and Kingdom of France, French troops, ...
, William the Conqueror likewise extended a welcome to continental Jews to take up residence there. Bishop R├╝diger Huzmann called on the Jews of Mainz to relocate to Speyer. In all of these decisions, the idea that Jews had the know-how and capacity to jump-start the economy, improve revenues, and enlarge trade seems to have played a prominent role. Typically, Jews relocated close to the markets and churches in town centres, where, though they came under the authority of both royal and ecclesiastical powers, they were accorded administrative autonomy.
In the 11th century, both Rabbinic Judaism and the culture of the Babylonian Talmud that underlies it became established in southern Italy and then spread north to Ashkenaz.
Numerous massacres of Jews occurred throughout Europe during the Christian Crusades. Inspired by the preaching of a First Crusade, crusader mobs in France and Germany perpetrated the Rhineland massacres of 1096, devastating Jewish communities along the Rhine River, including the SHuM cities
The history of the Jews in Germany goes back at least to the year 321, and continued through the Early Middle Ages (5th to 10th centuries CE) and High Middle Ages (''circa'' 1000ŌĆō1299 CE) when Jewish immigrants founded the Ashkenazi Jewish ...
of Speyer, Worms, and Mainz. The cluster of cities contain the earliest Jewish settlements north of the Alps, and played a major role in the formation of Ashkenazi Jewish religious tradition, along with Troyes and Sens in France. Nonetheless, Jewish life in Germany persisted, while some Ashkenazi Jews joined Sephardic Jewry in Spain. Expulsions from England (1290), France (1394), and parts of Germany (15th century), gradually pushed Ashkenazi Jewry eastward, to Poland (10th century), Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
(10th century), and Russia (12th century). Over this period of several hundred years, some have suggested, Jewish economic activity was focused on trade, business management, and financial services, due to several presumed factors: Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christ├│s'' (╬¦Žü╬╣ ...
European prohibitions restricting certain activities by Jews, preventing certain financial activities (such as " usurious" loans) between Christians, high rates of literacy, near-universal male education, and ability of merchants to rely upon and trust family members living in different regions and countries.
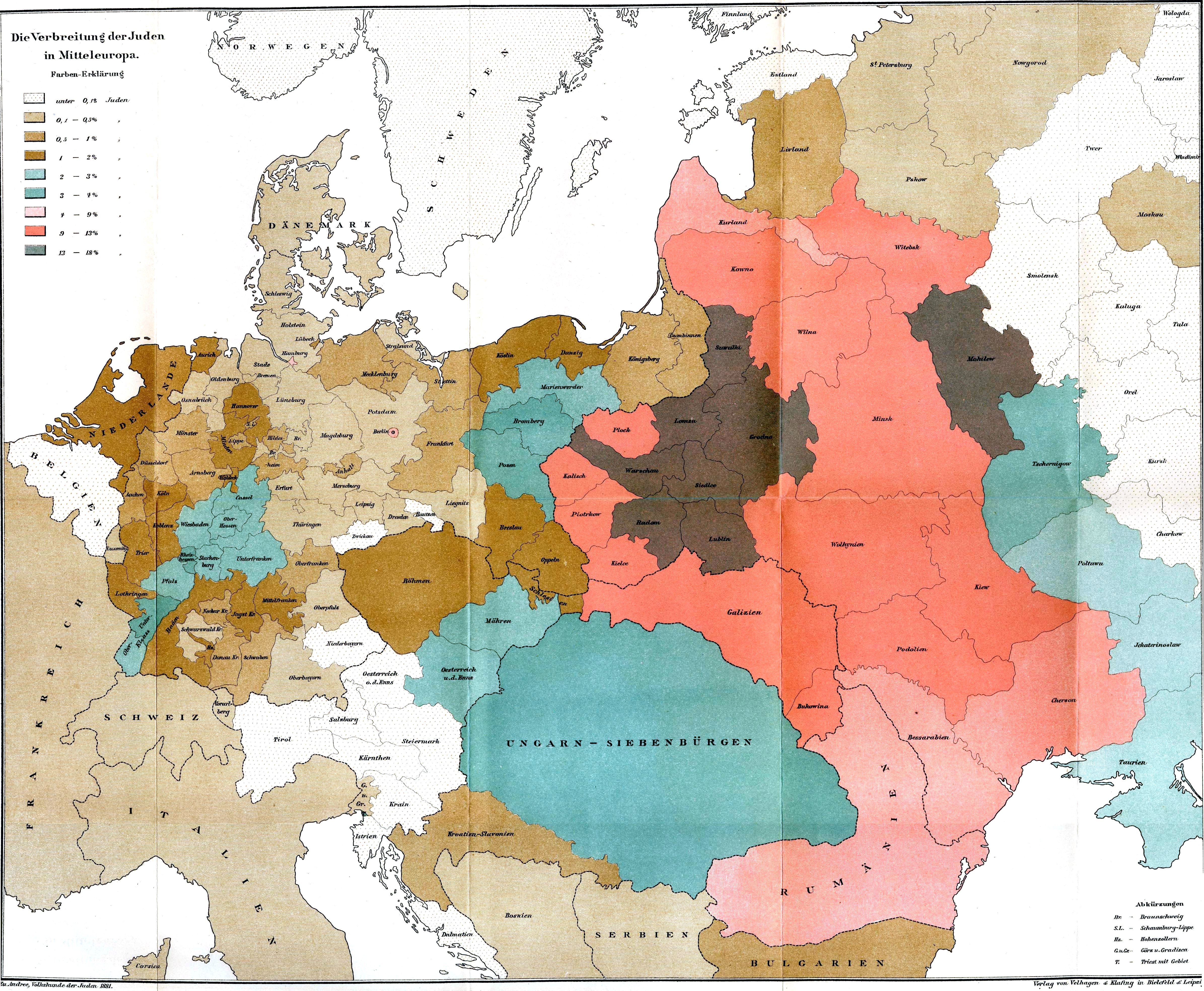
 By the 15th century, the Ashkenazi Jewish communities in Poland were the largest Jewish communities of the
By the 15th century, the Ashkenazi Jewish communities in Poland were the largest Jewish communities of the Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
. This area, which eventually fell under the domination of Russia, Austria, and Prussia (Germany), would remain the main center of Ashkenazi Jewry until the Holocaust.
The answer to why there was so little assimilation of Jews in central and eastern Europe for so long would seem to lie in part in the probability that the alien surroundings in central and eastern Europe were not conducive, though there was some assimilation. Furthermore, Jews lived almost exclusively in shtetls, maintained a strong system of education for males, heeded rabbinic leadership, and had a very different lifestyle to that of their neighbours; all of these tendencies increased with every outbreak of antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
.
In parts of Eastern Europe, before the arrival of the Ashkenazi Jews from Central Europe, some non-Ashkenazi Jews were present who spoke Leshon Knaan and held various other Non-Ashkenazi traditions and customs. In 1966, the historian Cecil Roth questioned the inclusion of all Yiddish speaking Jews as Ashkenazim in descent, suggesting that upon the arrival of Ashkenazi Jews from central Europe to Eastern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the 16th century, there were a substantial number of non-Ashkenazim Jews already there who later abandoned their original Eastern European Jewish culture in favor of the Ashkenazi one. However, according to more recent research, mass migrations of Yiddish-speaking Ashkenazi Jews occurred to Eastern Europe, from Central Europe in the west, who due to high birth rates absorbed and largely replaced the preceding non-Ashkenazi Jewish groups of Eastern Europe (whose numbers the demographer Sergio Della Pergola considers to have been small). Genetic evidence also indicates that Yiddish-speaking Eastern European Jews largely descend from Ashkenazi Jews who migrated from central to eastern Europe and subsequently experienced high birthrates and genetic isolation.
Some Jewish immigration from southern Europe to Eastern Europe continued into the early modern period. During the 16th century, as conditions for Italian Jews worsened, many Jews from Venice and the surrounding area migrated to Poland and Lithuania. During the 16th and 17th centuries, some Sephardi Jews and Romaniote Jews from throughout the Ottoman Empire migrated to Eastern Europe, as did Arabic-speaking Mizrahi Jews and Persian Jews.
Medieval references
 In the first half of the 11th century, Hai Gaon refers to questions that had been addressed to him from Ashkenaz, by which he undoubtedly means Germany. '' Rashi'' in the latter half of the 11th century refers to both the language of Ashkenaz and the country of Ashkenaz. During the 12th century, the word appears quite frequently. In the '' Mahzor Vitry'', the kingdom of Ashkenaz is referred to chiefly in regard to the ritual of the synagogue there, but occasionally also with regard to certain other observances.
In the literature of the 13th century, references to the land and the language of Ashkenaz often occur. Examples include Solomon ben Aderet's Responsa (vol. i., No. 395); the Responsa of Asher ben Jehiel (pp. 4, 6); his ''Halakot'' (Berakot i. 12, ed. Wilna, p. 10); the work of his son Jacob ben Asher, ''Tur Orach Chayim'' (chapter 59); the Responsa of Isaac ben Sheshet (numbers 193, 268, 270).
In the '' Midrash'' compilation, ''Genesis Rabbah'', Rabbi Berechiah mentions Ashkenaz, Riphath, and Togarmah as German tribes or as German lands. It may correspond to a Greek word that may have existed in the Greek dialect of the Jews in
In the first half of the 11th century, Hai Gaon refers to questions that had been addressed to him from Ashkenaz, by which he undoubtedly means Germany. '' Rashi'' in the latter half of the 11th century refers to both the language of Ashkenaz and the country of Ashkenaz. During the 12th century, the word appears quite frequently. In the '' Mahzor Vitry'', the kingdom of Ashkenaz is referred to chiefly in regard to the ritual of the synagogue there, but occasionally also with regard to certain other observances.
In the literature of the 13th century, references to the land and the language of Ashkenaz often occur. Examples include Solomon ben Aderet's Responsa (vol. i., No. 395); the Responsa of Asher ben Jehiel (pp. 4, 6); his ''Halakot'' (Berakot i. 12, ed. Wilna, p. 10); the work of his son Jacob ben Asher, ''Tur Orach Chayim'' (chapter 59); the Responsa of Isaac ben Sheshet (numbers 193, 268, 270).
In the '' Midrash'' compilation, ''Genesis Rabbah'', Rabbi Berechiah mentions Ashkenaz, Riphath, and Togarmah as German tribes or as German lands. It may correspond to a Greek word that may have existed in the Greek dialect of the Jews in Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina (literally, "Palestinian Syria";Trevor Bryce, 2009, ''The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia''Roland de Vaux, 1978, ''The Early History of Israel'', Page 2: "After the revolt of Bar Cochba in 135 ...
, or the text is corrupted from "Germanica". This view of Berechiah is based on the Talmud (Yoma 10a; Jerusalem Talmud Megillah 71b), where Gomer, the father of Ashkenaz, is translated by ''Germamia'', which evidently stands for Germany, and which was suggested by the similarity of the sound.
In later times, the word Ashkenaz is used to designate southern and western Germany, the ritual of which sections differs somewhat from that of eastern Germany and Poland. Thus the prayer-book of Isaiah Horowitz, and many others, give the piyyutim according to the Minhag
''Minhag'' ( he, ū×ūĀūöūÆ "custom", classical pl. ū×ūĀūöūÆūĢū¬, modern pl. , ''minhagim'') is an accepted tradition or group of traditions in Judaism. A related concept, ''Nusach (Jewish custom), Nusach'' (), refers to the traditional order and fo ...
of Ashkenaz and Poland.
According to 16th-century mystic Rabbi Elijah of Chelm, Ashkenazi Jews lived in Jerusalem during the 11th century. The story is told that a German-speaking Jew saved the life of a young German man surnamed Dolberger. So when the knights of the First Crusade came to siege Jerusalem, one of Dolberger's family members who was among them rescued Jews in Palestine and carried them back to Worms to repay the favor. Further evidence of German communities in the holy city comes in the form of halakhic
''Halakha'' (; he, ūöų▓ū£ųĖūøųĖūö, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
questions sent from Germany to Jerusalem during the second half of the 11th century.
Modern history
Material relating to the history of German Jews has been preserved in the communal accounts of certain communities on the Rhine, a '' Memorbuch'', and a ''Liebesbrief'', documents that are now part of the Sassoon Collection. Heinrich Graetz also added to the history of German Jewry in modern times in the abstract of his seminal work, ''History of the Jews'', which he entitled "Volksth├╝mliche Geschichte der Juden." In an essay on Sephardi Jewry,Daniel Elazar
Daniel Judah Elazar (August 25, 1934 ŌĆō December 2, 1999) was a political scientist known for his seminal studies of political culture of the US states. He was professor of political science at Bar-Ilan University in Israel and Temple University ...
at the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs
The Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs (JCPA) is an Israeli research institute specializing in public diplomacy and foreign policy founded in 1976. Currently, the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs's research portfolio consists of five primar ...
summarized the demographic history of Ashkenazi Jews in the last thousand years. He noted that at the end of the 11th century, 97% of world Jewry was Sephardic and 3% Ashkenazi; in the mid-17th century, "Sephardim still outnumbered Ashkenazim three to two"; by the end of the 18th century, "Ashkenazim outnumbered Sephardim three to two, the result of improved living conditions in Christian Europe versus the Ottoman Muslim world." By 1930, Arthur Ruppin estimated that Ashkenazi Jews accounted for nearly 92% of world Jewry. These factors are sheer demography showing the migration patterns of Jews from Southern and Western Europe to Central and Eastern Europe.
In 1740, a family from Lithuania became the first Ashkenazi Jews to settle in the Jewish Quarter of Jerusalem.
In the generations after emigration from the west, Jewish communities in places like Poland, Russia, and Belarus enjoyed a comparatively stable socio-political environment. A thriving publishing industry and the printing of hundreds of biblical commentaries precipitated the development of the Hasidic
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: ūŚūĪūÖūōūĢū¬ ''ßĖż─ās─½dus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contem ...
movement as well as major Jewish academic centers. After two centuries of comparative tolerance in the new nations, massive westward emigration occurred in the 19th and 20th centuries in response to pogroms in the east and the economic opportunities offered in other parts of the world. Ashkenazi Jews have made up the majority of the American Jew
American Jews or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by religion, ethnicity, culture, or nationality. Today the Jewish community in the United States consists primarily of Ashkenazi Jews, who descend from diasp ...
ish community since 1750.
In the context of the European Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
, Jewish emancipation began in 18th century France and spread throughout Western and Central Europe. Disabilities
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, se ...
that had limited the rights of Jews since the Middle Ages were abolished, including the requirements to wear distinctive clothing, pay special taxes, and live in ghettos isolated from non-Jewish communities and the prohibitions on certain professions. Laws were passed to integrate Jews into their host countries, forcing Ashkenazi Jews to adopt family names (they had formerly used patronymics). Newfound inclusion into public life led to cultural growth in the '' Haskalah'', or Jewish Enlightenment, with its goal of integrating modern European values into Jewish life. As a reaction to increasing antisemitism and assimilation following the emancipation, Zionism developed in central Europe. Other Jews, particularly those in the Pale of Settlement, turned to socialism. These tendencies would be united in Labor Zionism
Labor Zionism ( he, ū”ų┤ūÖų╝ūĢų╣ūĀūĢų╝ū¬ ūĪūĢų╣ū”ų░ūÖųĖūÉū£ų┤ūÖūĪų░ūśų┤ūÖū¬, ) or socialist Zionism ( he, ū¬ų░ų╝ūĀūĢų╝ūóųĖū¬ ūöųĖūóųĘūæūĢų╣ūōųĖūö, label=none, translit=Tnu╩Įat ha╩Įavoda) refers to the left-wing, socialist variation of Zionism. ...
, the founding ideology of the State of Israel.
The Holocaust
Of the estimated 8.8 million Jews living in Europe at the beginning of World War II, the majority of whom were Ashkenazi, about 6 million ŌĆō more than two-thirds ŌĆō were systematically murdered in the Holocaust. These included 3 million of 3.3 million Polish Jews (91%); 900,000 of 1.5 million in Ukraine (60%); and 50ŌĆō90% of the Jews of other Slavic nations, Germany, Hungary, and the Baltic states, and over 25% of the Jews in France. Sephardi communities suffered similar devastation in a few countries, including Greece, the Netherlands and the former Yugoslavia. As the large majority of the victims were Ashkenazi Jews, their percentage dropped from an estimate of 92% of world Jewry in 1930 to nearly 80% of world Jewry today. The Holocaust also effectively put an end to the dynamic development of the Yiddish language in the previous decades, as the vast majority of the Jewish victims of the Holocaust, around 5 million, were Yiddish speakers. Many of the surviving Ashkenazi Jews emigrated to countries such as Israel, Canada, Argentina,Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, and the United States after the war.
Following the Holocaust, some sources place Ashkenazim today as making up approximately 83ŌĆō85 percent of Jews worldwide, while Sergio DellaPergola in a rough calculation of Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djud├Łos Sefard├Łes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: S╔Öp╠ä─üradd├«m, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Jud├Łos sefard├Łes (or ), ...
and Mizrahi Jews, implies that Ashkenazi make up a notably lower figure, less than 74%. Other estimates place Ashkenazi Jews as making up about 75% of Jews worldwide.
Israel
In Israel, the term ''Ashkenazi'' is now used in a manner unrelated to its original meaning, often applied to all Jews who settled in Europe and sometimes including those whose ethnic background is actually Sephardic. Jews of any non-Ashkenazi background, including Mizrahi, Yemenite, Kurdish and others who have no connection with the Iberian Peninsula, have similarly come to be lumped together as Sephardic. Jews of mixed background are increasingly common, partly because of intermarriage between Ashkenazi and non-Ashkenazi, and partly because many do not see such historic markers as relevant to their life experiences as Jews. Religious Ashkenazi Jews living in Israel are obliged to follow the authority of the chief Ashkenazi rabbi inhalakhic
''Halakha'' (; he, ūöų▓ū£ųĖūøųĖūö, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
matters. In this respect, a religiously Ashkenazi Jew is an Israeli who is more likely to support certain religious interests in Israel, including certain political parties. These political parties result from the fact that a portion of the Israeli electorate votes for Jewish religious parties; although the electoral map changes from one election to another, there are generally several small parties associated with the interests of religious Ashkenazi Jews. The role of religious parties, including small religious parties that play important roles as coalition members, results in turn from Israel's composition as a complex society in which competing social, economic, and religious interests stand for election to the Knesset, a unicameral legislature with 120 seats.
Ashkenazi Jews have played a prominent role in the economy, media, and politics of Israel since its founding. During the first decades of Israel as a state, strong cultural conflict occurred between Sephardic and Ashkenazi Jews (mainly east European Ashkenazim). The roots of this conflict, which still exists to a much smaller extent in present-day Israeli society, are chiefly attributed to the concept of the "melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
". That is to say, all Jewish immigrants who arrived in Israel were strongly encouraged to "meltdown" their own particular exilic identities within the general social "pot" in order to become Israeli.
Definition
By religion
Religious Jews haveminhag
''Minhag'' ( he, ū×ūĀūöūÆ "custom", classical pl. ū×ūĀūöūÆūĢū¬, modern pl. , ''minhagim'') is an accepted tradition or group of traditions in Judaism. A related concept, ''Nusach (Jewish custom), Nusach'' (), refers to the traditional order and fo ...
im, customs, in addition to halakha, or religious law, and different interpretations of the law. Different groups of religious Jews in different geographic areas historically adopted different customs and interpretations. On certain issues, Orthodox Jews are required to follow the customs of their ancestors and do not believe they have the option of picking and choosing. For this reason, observant Jews at times find it important for religious reasons to ascertain who their household's religious ancestors are in order to know what customs their household should follow. These times include, for example, when two Jews of different ethnic background marry, when a non-Jew converts to Judaism and determines what customs to follow for the first time, or when a lapsed or less observant Jew returns to traditional Judaism and must determine what was done in his or her family's past. In this sense, "Ashkenazic" refers both to a family ancestry and to a body of customs binding on Jews of that ancestry. Reform Judaism, which does not necessarily follow those minhagim, did nonetheless originate among Ashkenazi Jews.
In a religious sense, an Ashkenazi Jew is any Jew whose family tradition and ritual follow Ashkenazi practice. Until the Ashkenazi community first began to develop in the Early Middle Ages, the centers of Jewish religious authority were in the Islamic world, at Baghdad and in Islamic Spain. Ashkenaz (Germany) was so distant geographically that it developed a ''minhag
''Minhag'' ( he, ū×ūĀūöūÆ "custom", classical pl. ū×ūĀūöūÆūĢū¬, modern pl. , ''minhagim'') is an accepted tradition or group of traditions in Judaism. A related concept, ''Nusach (Jewish custom), Nusach'' (), refers to the traditional order and fo ...
'' of its own. Ashkenazi Hebrew came to be pronounced in ways distinct from other forms of Hebrew.
In this respect, the counterpart of Ashkenazi is Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djud├Łos Sefard├Łes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: S╔Öp╠ä─üradd├«m, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Jud├Łos sefard├Łes (or ), ...
, since most non-Ashkenazi Orthodox Jews follow Sephardic rabbinical authorities, whether or not they are ethnically Sephardic. By tradition, a Sephardic or Mizrahi woman who marries into an Orthodox or Haredi Ashkenazi Jewish family raises her children to be Ashkenazi Jews; conversely an Ashkenazi woman who marries a Sephardi or Mizrahi man is expected to take on Sephardic practice and the children inherit a Sephardic identity, though in practice many families compromise. A convert generally follows the practice of the beth din that converted him or her. With the integration of Jews from around the world in Israel, North America, and other places, the religious definition of an Ashkenazi Jew is blurring, especially outside Orthodox Judaism.
New developments in Judaism often transcend differences in religious practice between Ashkenazi and Sephardic Jews. In North American cities, social trends such as the chavurah movement, and the emergence of "post-denominational Judaism" often bring together younger Jews of diverse ethnic backgrounds. In recent years, there has been increased interest in '' Kabbalah'', which many Ashkenazi Jews study outside of the Yeshiva framework. Another trend is the new popularity of ecstatic worship in the Jewish Renewal
Jewish Renewal () is a recent movement in Judaism which endeavors to reinvigorate modern Judaism with Kabbalistic, Hasidic, and musical practices. Specifically, it seeks to reintroduce the "ancient Judaic traditions of mysticism and meditation, ...
movement and the Carlebach style minyan
In Judaism, a ''minyan'' ( he, ū×ūĀūÖūÖū¤ \ ū×ų┤ūĀų░ūÖųĖū¤ ''m─½ny─ün'' , lit. (noun) ''count, number''; pl. ''m─½ny─ün─½m'' ) is the quorum of ten Jewish adults required for certain religious obligations. In more traditional streams of Jud ...
, both of which are nominally of Ashkenazi origin. Outside of Haredi communities, the traditional Ashkenazi pronunciation of Hebrew has also drastically declined in favor of the Sephardi-based pronunciation of Modern Hebrew.
By culture
Culturally, an Ashkenazi Jew can be identified by the concept of '' Yiddishkeit'', which means "Jewishness" in theYiddish language
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
. ''Yiddishkeit'' is specifically the Jewishness of Ashkenazi Jews. Before the Haskalah and the emancipation of Jews in Europe, this meant the study of Torah and Talmud for men, and a family and communal life governed by the observance of Jewish Law for men and women. From the Rhineland to Riga
Riga (; lv, R─½ga , liv, R─½g├Ą) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
to Romania, most Jews prayed in liturgical Ashkenazi Hebrew, and spoke Yiddish in their secular lives. But with modernization, ''Yiddishkeit'' now encompasses not just Orthodoxy and Hasidism, but a broad range of movements, ideologies, practices, and traditions in which Ashkenazi Jews have participated and somehow retained a sense of Jewishness. Although a far smaller number of Jews still speak Yiddish, ''Yiddishkeit'' can be identified in manners of speech, in styles of humor, in patterns of association. Broadly speaking, a Jew is one who associates culturally with Jews, supports Jewish institutions, reads Jewish books and periodicals, attends Jewish movies and theater, travels to Israel, visits historical synagogues, and so forth. It is a definition that applies to Jewish culture in general, and to Ashkenazi Yiddishkeit in particular.
As Ashkenazi Jews moved away from Europe, mostly in the form of aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, ūóų▓ū£ų┤ūÖųĖų╝ūö ''╩┐─āl─½yy─ü'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel ...
to Israel, or immigration to North America, and other English-speaking areas such as South Africa; and Europe (particularly France) and Latin America, the geographic isolation that gave rise to Ashkenazim have given way to mixing with other cultures, and with non-Ashkenazi Jews who, similarly, are no longer isolated in distinct geographic locales. Hebrew has replaced Yiddish as the primary Jewish language for many Ashkenazi Jews, although many Hasidic
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: ūŚūĪūÖūōūĢū¬ ''ßĖż─ās─½dus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contem ...
and Hareidi groups continue to use Yiddish in daily life. (There are numerous Ashkenazi Jewish anglophones and Russian-speakers as well, although English and Russian are not originally Jewish languages.)
France's blended Jewish community is typical of the cultural recombination that is going on among Jews throughout the world. Although France expelled its original Jewish population in the Middle Ages, by the time of the French Revolution, there were two distinct Jewish populations. One consisted of Sephardic Jews, originally refugees from the Inquisition and concentrated in the southwest, while the other community was Ashkenazi, concentrated in formerly German Alsace, and mainly speaking a German dialect similar to Yiddish. (The third community of Proven├¦al Jews living in Comtat Venaissin were technically outside France, and were later absorbed into the Sephardim.) The two communities were so separate and different that the National Assembly emancipated them separately in 1790 and 1791.
But after emancipation, a sense of a unified French Jewry emerged, especially when France was wracked by the Dreyfus affair in the 1890s. In the 1920s and 1930s, Ashkenazi Jews from Europe arrived in large numbers as refugees from antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
, the Russian revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
, and the economic turmoil of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. By the 1930s, Paris had a vibrant Yiddish culture, and many Jews were involved in diverse political movements. After the Vichy years and the Holocaust, the French Jewish population was augmented once again, first by Ashkenazi refugees from Central Europe, and later by Sephardi immigrants and refugees from North Africa, many of them francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
.
Ashkenazi Jews did not record their traditions or achievements by text, instead these traditions were passed down orally from one generation to the next. The desire to maintain pre- Holocaust traditions relating to Ashkenazi culture has often been met with criticism by Jews in Eastern Europe. Reasoning for this could be related to the development of a new style of Jewish arts and culture developed by the Jews of Palestine during the 1930s and 1940s, which in conjunction with the decimation of European Ashkenazi Jews and their culture by the Nazi regime made it easier to assimilate to the new style of ritual rather than try to repair the older traditions. This new style of tradition was referred to as the ''Mediterranean Style'', and was noted for its simplicity and metaphorical rejuvenation of Jews abroad. This was intended to replace the Galut traditions, which were more sorrowful in practice.
Then, in the 1990s, yet another Ashkenazi Jewish wave began to arrive from countries of the former Soviet Union and Central Europe. The result is a pluralistic Jewish community that still has some distinct elements of both Ashkenazi and Sephardic culture. But in France, it is becoming much more difficult to sort out the two, and a distinctly French Jewishness has emerged.
By ethnicity
In an ethnic sense, an Ashkenazi Jew is one whose ancestry can be traced to the Jews who settled in Central Europe. For roughly a thousand years, the Ashkenazim were a reproductively isolated population in Europe, despite living in many countries, with little inflow or outflow from migration, conversion, or intermarriage with other groups, including other Jews. Human geneticists have argued that genetic variations have been identified that show high frequencies among Ashkenazi Jews, but not in the general European population, be they for patrilineal markers ( Y-chromosomehaplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA or ...
s) and for matrilineal markers ( mitotypes). Since the middle of the 20th century, many Ashkenazi Jews have intermarried, both with members of other Jewish communities and with people of region
Customs, laws and traditions
 The ''
The ''Halakhic
''Halakha'' (; he, ūöų▓ū£ųĖūøųĖūö, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
'' practices of ( Orthodox) Ashkenazi Jews may differ from those of Sephardi Jews, particularly in matters of custom. Differences are noted in the '' Shulkhan Arukh'' itself, in the gloss of Moses Isserles. Well known differences in practice include:
* Observance of '' Pesach'' (Passover): Ashkenazi Jews traditionally refrain from eating legumes
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ...
, grain, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
, and rice ( quinoa, however, has become accepted as foodgrain in the North American communities), whereas Sephardi Jews typically do not prohibit these foods.
* Ashkenazi Jews freely mix and eat fish and milk products; some Sephardic Jews refrain from doing so.
* Ashkenazim are more permissive toward the usage of wigs as a hair covering for married and widowed women.
* In the case of ''kashrut
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, ūøų╝ū®ū©), fro ...
'' for meat, conversely, Sephardi Jews have stricter requirements ŌĆō this level is commonly referred to as ''Beth Yosef
Beth may refer to:
Letter and number
*Bet (letter)
Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician B─ōt , Hebrew B─ōt , Aramaic B─ōth , Syriac B─ōß╣» , and Arabic . Its sound value is the voiced bi ...
''. Meat products that are acceptable to Ashkenazi Jews as kosher may therefore be rejected by Sephardi Jews. Notwithstanding stricter requirements for the actual slaughter, Sephardi Jews permit the rear portions of an animal after proper Halakhic
''Halakha'' (; he, ūöų▓ū£ųĖūøųĖūö, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
removal of the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest si ...
, while many Ashkenazi Jews do not. This is not because of different interpretations of the law; rather, slaughterhouses could not find adequate skills for correct removal of the sciatic nerve and found it more economical to separate the hindquarters and sell them as non-kosher meat.
* Ashkenazi Jews often name newborn children after deceased family members, but not after living relatives. Sephardi Jews, in contrast, often name their children after the children's grandparents, even if those grandparents are still living. A notable exception to this generally reliable rule is among Dutch Jews, where Ashkenazim for centuries used the naming conventions otherwise attributed exclusively to Sephardim such as Chuts
Chuts is the name applied to Jews who immigrated to London from the Netherlands during the latter part of the 19th century. They typically came from Amsterdam and practised trades they had already learned there, most notably cigar-, cap- and sl ...
.
* Ashkenazi tefillin bear some differences from Sephardic tefillin. In the traditional Ashkenazic rite, the tefillin are wound towards the body, not away from it. Ashkenazim traditionally don tefillin while standing, whereas other Jews generally do so while sitting down.
* Ashkenazic traditional pronunciations of Hebrew differ from those of other groups. The most prominent consonantal difference from Sephardic and Mizrahic Hebrew dialects is the pronunciation of the Hebrew letter tav in certain Hebrew words (historically, in postvocalic undoubled context) as an /s/ and not a /t/ or /╬Ė/ sound.
* The prayer shawl, or tallit (or tallis in Ashkenazi Hebrew), is worn by the majority of Ashkenazi men after marriage, but western European Ashkenazi men wear it from Bar Mitzvah. In Sephardi or Mizrahi Judaism, the prayer shawl is commonly worn from early childhood.
Ashkenazic liturgy
The term ''Ashkenazi'' also refers to the '' nusach Ashkenaz'' ( Hebrew, "liturgical tradition", or rite) used by Ashkenazi Jews in their '' Siddur'' (prayer book). A ''nusach'' is defined by a liturgical tradition's choice of prayers, the order of prayers, the text of prayers, and melodies used in the singing of prayers. Two other major forms of nusach among Ashkenazic Jews are Nusach Sefard (not to be confused with the Sephardic ritual), which is the general Polish Hasidic nusach, and Nusach Ari, as used by Lubavitch Hasidim.Ashkenazi as a surname
Several famous people have Ashkenazi as a surname, such as Vladimir Ashkenazy. However, most people with this surname hail from within Sephardic communities, particularly from theSyrian Jew
Syrian Jews ( he, ūÖūöūĢūōūÖ ūĪūĢū©ūÖūö ''Yehudey Surya'', ar, ž¦┘ä┘Æ┘Ŗ┘Ä┘ć┘Å┘łž» ž¦┘äž│┘Å┘æ┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Å┘æ┘ł┘å ''al-Yah┼½d as-S┼½riyy┼½n'', colloquially called SYs in the United States) are Jews who lived in the region of the modern state of Syr ...
ish community. The Sephardic carriers of the surname would have some Ashkenazi ancestors since the surname was adopted by families who were initially of Ashkenazic origins who moved to countries with Sephardi communities and joined those communities. Ashkenazi would be formally adopted as the family surname having started off as a nickname imposed by their adopted communities. Some have shortened the name to Ash.
Relations with Sephardim
Relations between Ashkenazim and Sephardim have at times been tense and clouded by arrogance, snobbery and claims of racial superiority with both sides claiming the inferiority of the other, based upon such features as physical traits and culture. North African Sephardim and Berber Jews were often looked down upon by Ashkenazim as second-class citizens during the first decade after the creation of Israel. This has led to protest movements such as the IsraeliBlack Panthers
The Black Panther Party (BPP), originally the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense, was a Marxism-Leninism, Marxist-Leninist and Black Power movement, black power political organization founded by college students Bobby Seale and Huey P. New ...
led by Saadia Marciano, a Moroccan Jew. Nowadays, relations are getting warmer. In some instances, Ashkenazi communities have accepted significant numbers of Sephardi newcomers, sometimes resulting in intermarriage and the possible merging between the two communities.
Notable Ashkenazim
Ashkenazi Jews have a notable history of achievement in Western societies in the fields of natural and social sciences, mathematics, literature, finance, politics, media, and others. In those societies where they have been free to enter any profession, they have a record of high occupational achievement, entering professions and fields of commerce where higher education is required. Ashkenazi Jews have won a large number of the Nobel awards. According to the 2000 book '' From Chance to Choice: Genetics and Justice'' published by Cambridge University, 21% of Ivy League students, 25% of the Turing Award winners, 23% of the wealthiest Americans, 38% of the Oscar-winning film directors, and 29% of Oslo awardees are Ashkenazi Jews. The achievements of so many Ashkenazi Jews, have led some to the view that Ashkenazi Jews have higher than average intelligence. However many of these studies which show superior intelligence have been discredited, and other studies note that one should not "confuse racial categories with scientific ones."Genetics
Genetic origins
Efforts to identify the origins of Ashkenazi Jews through DNA analysis began in the 1990s. Currently, there are three types of genetic origin testing, autosomal DNA (atDNA),mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
(mtDNA), and Y-chromosomal DNA ( Y-DNA). Autosomal DNA is a mixture from an individual's entire ancestry, Y-DNA shows a male's lineage only along his strict paternal line, mtDNA shows any person's lineage only along the strict maternal line. Genome-wide association studies have also been employed to yield findings relevant to genetic origins.
Like most DNA studies of human migration patterns, the earliest studies on Ashkenazi Jews focused on the Y-DNA and mtDNA segments of the human genome. Both segments are unaffected by recombination (except for the ends of the Y chromosome ŌĆō the pseudoautosomal regions known as PAR1 and PAR2), thus allowing tracing of direct maternal and paternal lineages.
These studies revealed that Ashkenazi Jews originate from an ancient (2000ŌĆō700 BCE) population of the Middle East who had spread to Europe. Ashkenazic Jews display the homogeneity of a genetic bottleneck, meaning they descend from a larger population whose numbers were greatly reduced but recovered through a few founding individuals. Although the Jewish people, in general, were present across a wide geographical area as described, genetic research done by Gil Atzmon of the Longevity Genes Project at Albert Einstein College of Medicine suggests "that Ashkenazim branched off from other Jews around the time of the destruction of the First Temple, 2,500 years ago ... flourished during the Roman Empire but then went through a 'severe bottleneck' as they dispersed, reducing a population of several million to just 400 families who left Northern Italy around the year 1000 for Central and eventually Eastern Europe."
Various studies have arrived at diverging conclusions regarding both the degree and the sources of the non-Levantine admixture
Admixture may refer to:
* Genetic admixture, the result of interbreeding between two or more previously isolated populations within a species
* Racial admixture, admixture between humans, also referred to as miscegenation
* Hybrid
* Mixture, the ch ...
in Ashkenazim, particularly with respect to the extent of the non-Levantine genetic origin observed in Ashkenazi maternal lineages, which is in contrast to the predominant Levantine genetic origin observed in Ashkenazi paternal lineages. All studies nevertheless agree that genetic overlap with the Fertile Crescent exists in both lineages, albeit at differing rates. Collectively, Ashkenazi Jews are less genetically diverse than other Jewish ethnic divisions
Jewish ethnic divisions refer to many distinctive communities within the world's ethnically Jewish population. Although considered a self-identifying ethnicity, there are distinct ethnic subdivisions among Jews, most of which are primarily the ...
, due to their genetic bottleneck.
Male lineages: Y-chromosomal DNA
The majority of genetic findings to date concerning Ashkenazi Jews conclude that the male lines were founded by ancestors from the Middle East. A study of haplotypes of the Y-chromosome, published in 2000, addressed the paternal origins of Ashkenazi Jews. Hammer ''et al.'' found that the Y-chromosome of Ashkenazi and Sephardic Jews contained mutations that are also common among other Middle Eastern peoples, but uncommon in the autochthonous European population. This suggested that the male ancestors of the Ashkenazi Jews could be traced mostly to the Middle East. The proportion of male genetic admixture in Ashkenazi Jews amounts to less than 0.5% per generation over an estimated 80 generations, with "relatively minor contribution of European Y chromosomes to the Ashkenazim," and a total admixture estimate "very similar to Motulsky's average estimate of 12.5%." This supported the finding that "Diaspora Jews from Europe, Northwest Africa, and theNear East
The ''Near East''; he, ūöū×ū¢ū©ūŚ ūöū¦ū©ūĢūæ; arc, ▄Ģ▄ó▄Ü▄É ▄®▄¬▄Æ; fa, ž«ž¦┘łž▒ ┘åž▓ž»█ī┌®, X─üvar-e nazdik; tr, Yak─▒n Do─¤u is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
resemble each other more closely than they resemble their non-Jewish neighbors." "Past research found that 50ŌĆō80 percent of DNA from the Ashkenazi Y chromosome, which is used to trace the male lineage, originated in the Near East," Richards said. The population has subsequently spread out.
A 2001 study by Nebel ''et al.'' showed that both Ashkenazi and Sephardic Jewish populations share the same overall paternal Near Eastern ancestries. In comparison with data available from other relevant populations in the region, Jews were found to be more closely related to groups in the north of the Fertile Crescent. The authors also report on Eu 19 ( R1a) chromosomes, which are very frequent in Central and Eastern Europeans (54ŌĆō60%) at elevated frequency (13%) in Ashkenazi Jews. They hypothesized that the differences among Ashkenazim Jews could reflect low-level gene flow from surrounding European populations or genetic drift during isolation. A later 2005 study by Nebel ''et al.'', found a similar level of 11.5% of male Ashkenazim belonging to R1a1a (M17+), the dominant Y-chromosome haplogroup in Central and Eastern Europeans. However, a 2017 study, concentrating on the Ashkenazi Levites where the proportion reaches 50%, while signalling that there's a "rich variation of haplogroup R1a outside of Europe which is phylogenetically separate from the typically European R1a branches", precises that the particular R1a-Y2619 sub-clade testifies for a local origin, and that the "Middle Eastern origin of the Ashkenazi Levite lineage based on what was previously a relatively limited number of reported samples, can now be considered firmly validated."
Female lineages: Mitochondrial DNA
Before 2006, geneticists had largely attributed the ethnogenesis of most of the world's Jewish populations, including Ashkenazi Jews, to Israelite Jewish male migrants from the Middle East and "the women from each local population whom they took as wives and converted to Judaism." Thus, in 2002, in line with this model of origin, David Goldstein, now of Duke University, reported that unlike male Ashkenazi lineages, the female lineages in Ashkenazi Jewish communities "did not seem to be Middle Eastern", and that each community had its own genetic pattern and even that "in some cases the mitochondrial DNA was closely related to that of the host community." In his view, this suggested, "that Jewish men had arrived from the Middle East, taken wives from the host population and converted them to Judaism, after which there was no further intermarriage with non-Jews." In 2006, a study by Behar ''et al.'', based on what was at that time high-resolution analysis of haplogroup K (mtDNA), suggested that about 40% of the current Ashkenazi population is descended matrilineally from just four women, or "founder lineages", that were "likely from a Hebrew/ Levantine mtDNA pool" originating in the Middle East in the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. Additionally, Behar ''et al.'' suggested that the rest of Ashkenazi mtDNA is originated from ~150 women, and that most of those were also likely of Middle Eastern origin. In reference specifically to Haplogroup K, they suggested that although it is common throughout western Eurasia, "the observed global pattern of distribution renders very unlikely the possibility that the four aforementioned founder lineages entered the Ashkenazi mtDNA pool via gene flow from a European host population". In 2013, a study of Ashkenazi mitochondrial DNA by a team led by Martin B. Richards of the University of Huddersfield in England reached different conclusions, in line with the pre-2006 origin hypothesis. Testing was performed on the full 16,600 DNA units composing mitochondrial DNA (the 2006 Behar study had only tested 1,000 units) in all their subjects, and the study found that the four main female Ashkenazi founders had descent lines that were established in Europe 10,000 to 20,000 years in the past while most of the remaining minor founders also have a deep European ancestry. The study argued that the great majority of Ashkenazi maternal lineages were not brought from the Near East or the Caucasus, but instead assimilated within Europe, primarily of Italian and Old French origins. The Richards study estimated that more than 80 percent of Ashkenazi maternal ancestry comes from women indigenous to (mainly prehistoric Western) Europe, and only 8 percent from the Near East, while the origin of the remainder is undetermined. According to the study these findings "point to a significant role for the conversion of women in the formation of Ashkenazi communities." Karl Skorecki criticized the study for perceived flaws in phylogenetic analysis. "While Costa et al have re-opened the question of the maternal origins of Ashkenazi Jewry, the phylogenetic analysis in the manuscript does not 'settle' the question." A 2014 study by Fern├Īndez et al. found that Ashkenazi Jews display a frequency of haplogroup K in their maternal DNA, suggesting an ancient Near Eastern matrilineal origin, similar to the results of the Behar study in 2006. Fern├Īndez noted that this observation clearly contradicts the results of the 2013 study led by Richards that suggested a European source for 3 exclusively Ashkenazi K lineages.Association and linkage studies (autosomal dna)
Ingenetic epidemiology
Genetic epidemiology is the study of the role of genetic factors in determining health and disease in families and in populations, and the interplay of such genetic factors with environmental factors. Genetic epidemiology seeks to derive a statist ...
, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS) is an examination of all or most of the genes (the genome) of different individuals of a particular species to see how much the genes vary from individual to individual. These techniques were originally designed for epidemiological uses, to identify genetic associations with observable traits.
A 2006 study by Seldin et al. used over five thousand autosomal SNPs to demonstrate European genetic substructure. The results showed "a consistent and reproducible distinction between 'northern' and 'southern' European population groups". Most northern, central, and eastern Europeans (Finns, Swedes, English, Irish, Germans, and Ukrainians) showed >90% in the "northern" population group, while most individual participants with southern European ancestry (Italians, Greeks, Portuguese, Spaniards) showed >85% in the "southern" group. Both Ashkenazi Jews as well as Sephardic Jews showed >85% membership in the "southern" group. Referring to the Jews clustering with southern Europeans, the authors state the results were "consistent with a later Mediterranean origin of these ethnic groups".
A 2007 study by Bauchet et al. found that Ashkenazi Jews were most closely clustered with Arabic North African populations when compared to Global population, and in the European structure analysis, they share similarities only with Greeks and Southern Italians, reflecting their east Mediterranean origins.
A 2010 study on Jewish ancestry by Atzmon-Ostrer et al. stated "Two major groups were identified by principal component, phylogenetic, and identity by descent (IBD) analysis: Middle Eastern Jews and European/Syrian Jews. The IBD segment sharing and the proximity of European Jews to each other and to southern European populations suggested similar origins for European Jewry and refuted large-scale genetic contributions of Central and Eastern European and Slavic populations to the formation of Ashkenazi Jewry", as both groups ŌĆō the Middle Eastern Jews and European/Syrian Jews ŌĆō shared common ancestors in the Middle East about 2500 years ago. The study examines genetic markers spread across the entire genome and shows that the Jewish groups (Ashkenazi and non-Ashkenazi) share large swaths of DNA, indicating close relationships and that each of the Jewish groups in the study (Iranian, Iraqi, Syrian, Italian, Turkish, Greek and Ashkenazi) has its own genetic signature but is more closely related to the other Jewish groups than to their fellow non-Jewish countrymen. Atzmon's team found that the SNP markers in genetic segments of 3 million DNA letters or longer were 10 times more likely to be identical among Jews than non-Jews. Results of the analysis also tally with biblical accounts of the fate of the Jews. The study also found that with respect to non-Jewish European groups, the population most closely related to Ashkenazi Jews are modern-day Italians. The study speculated that the genetic-similarity between Ashkenazi Jews and Italians may be due to inter-marriage and conversions in the time of the Roman Empire. It was also found that any two Ashkenazi Jewish participants in the study shared about as much DNA as fourth or fifth cousins.
A 2010 study by Bray et al., using SNP microarray
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrateŌĆöusually a glass slide or silicon t ...
techniques and linkage analysis found that when assuming Druze
The Druze (; ar, ž»┘Äž▒┘Æž▓┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
and Palestinian Arab populations to represent the reference to world Jewry ancestor genome, between 35 and 55 percent of the modern Ashkenazi genome can possibly be of European origin, and that European "admixture is considerably higher than previous estimates by studies that used the Y chromosome" with this reference point. Assuming this reference point the linkage disequilibrium in the Ashkenazi Jewish population was interpreted as "matches signs of interbreeding or 'admixture' between Middle Eastern and European populations". On the Bray et al. tree, Ashkenazi Jews were found to be a genetically more divergent population than Russians, Orcadians, French, Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
, Sardinians, Italians and Tuscans
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
. The study also observed that Ashkenazim are more diverse than their Middle Eastern relatives, which was counterintuitive because Ashkenazim are supposed to be a subset, not a superset, of their assumed geographical source population. Bray et al. therefore postulate that these results reflect not the population antiquity but a history of mixing between genetically distinct populations in Europe. However, it is possible that the relaxation of marriage prescription in the ancestors of Ashkenazim drove their heterozygosity up, while the maintenance of the FBD rule in native Middle Easterners has been keeping their heterozygosity values in check. Ashkenazim distinctiveness as found in the Bray et al. study, therefore, may come from their ethnic endogamy (ethnic inbreeding), which allowed them to "mine" their ancestral gene pool in the context of relative reproductive isolation from European neighbors, and not from clan endogamy (clan inbreeding). Consequently, their higher diversity compared to Middle Easterners stems from the latter's marriage practices, not necessarily from the former's admixture with Europeans.
The genome-wide genetic study carried out in 2010 by Behar et al. examined the genetic relationships among all major Jewish groups, including Ashkenazim, as well as the genetic relationship between these Jewish groups and non-Jewish ethnic populations. The study found that contemporary Jews (excluding Indian and Ethiopian Jews) have a close genetic relationship with people from the Levant. The authors explained that "the most parsimonious explanation for these observations is a common genetic origin, which is consistent with an historical formulation of the Jewish people as descending from ancient Hebrew and Israelite residents of the Levant".
A study by Behar et al. (2013) found evidence in Ashkenazim of mixed European and Levantine origins. The authors found the greatest affinity and shared ancestry of Ashkenazi Jews to be firstly with other Jewish groups from southern Europe, Syria, and North Africa, and secondly with both southern Europeans (such as Italians) and modern Levantines (such as the Druze
The Druze (; ar, ž»┘Äž▒┘Æž▓┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
, Cypriots, Lebanese and Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; he, ū®ūĢū×ū©ūĢūĀūÖūØ, translit=┼Ā┼Źmr┼Źn─½m, lit=; ar, ž¦┘äž│ž¦┘ģž▒┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, translit=as-S─ümiriyy┼½n) are an ethnoreligious group who originate from the ancient Israelites. They are native to the Levant and adhere to Samarit ...
). In addition to finding no affinity in Ashkenazim with northern Caucasus populations, the authors found no more affinity in Ashkenazi Jews to modern south Caucasus and eastern Anatolian populations (such as Armenians, Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most numer ...
, Georgians
The Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ßāźßāÉßāĀßāŚßāĢßāößāÜßāößāæßāś, tr, ), are a nation and indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus. Georgian diaspora communities are also present throughout Russia, Turkey, G ...
, and Turks) than found in non-Ashkenazi Jews or non-Jewish Middle Easterners (such as the Kurds, Iranians, Druze and Lebanese). Final version at http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/humbiol/vol85/iss6/9/
A 2017 autosomal study by Xue, Shai Carmi et al. found an admixture of Middle-Eastern and European ancestry in Ashkenazi Jews: with the European component comprising Ōēł50%-70% (estimated at "possibly 60%") and largely being of a Southern European source with a minority being Eastern European, and the remainder (estimated at possibly Ōēł40%) being Middle Eastern ancestry showing the strongest affinity to Levantine populations such as the Druze and Lebanese.
A 2018 study, referencing the popular theory of Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) origins in "an initial settlement in Western Europe (Northern France and Germany), followed by migration to Poland and an expansion there and in the rest of Eastern Europe", tested "whether Ashkenazi Jews with recent origins in Eastern Europe are genetically distinct from Western European Ashkenazi". The study concluded that "Western AJ consist of two slightly distinct groups: one that descends from a subset of the original founders ho remained in Western Europe and another that migrated there back from Eastern Europe, possibly after absorbing a limited degree of gene flow".
The Khazar hypothesis
In the late 19th century, it was proposed that the core of today's Ashkenazi Jewry are genetically descended from a hypothetical Khazarian Jewish diaspora who had migrated westward from modern Russia and Ukraine into modern France and Germany (as opposed to the currently held theory that Jews migrated from France and Germany into Eastern Europe). The hypothesis is not corroborated by historical sources, and is unsubstantiated by genetics, but it is still occasionally supported by scholars who have had some success in keeping the theory in the academic consciousness. The theory has sometimes been used by Jewish authors such as Arthur Koestler as part of an argument against traditional forms of antisemitism (for example the claim that "the Jews killed Christ"), just as similar arguments have been advanced on behalf of the Crimean Karaites. Today, however, the theory is more often associated withantisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
and anti-Zionism
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestin ...
.
A 2013 trans-genome study carried out by 30 geneticists, from 13 universities and academies, from nine countries, assembling the largest data set available to date, for assessment of Ashkenazi Jewish genetic origins found no evidence of Khazar origin among Ashkenazi Jews. The authors concluded:
The authors found no affinity in Ashkenazim with north Caucasus populations, as well as no greater affinity in Ashkenazim to south Caucasus or Anatolian populations than that found in non-Ashkenazi Jews and non-Jewish Middle Easterners (such as the Kurds, Iranians, Druze and Lebanese). The greatest affinity and shared ancestry of Ashkenazi Jews were found to be (after those with other Jewish groups from southern Europe, Syria, and North Africa) with both southern Europeans and Levantines such as Druze, Cypriot, Lebanese and Samaritan groups.
Medical genetics
There are many references to Ashkenazi Jews in the literature of medical and population genetics. Indeed, much awareness of "Ashkenazi Jews" as an ethnic group or category stems from the large number of genetic studies of disease, including many that are well reported in the media, that have been conducted among Jews. Jewish populations have been studied more thoroughly than most other human populations, for a variety of reasons: * Jewish populations, and particularly the large Ashkenazi Jewish population, are ideal for such research studies, because they exhibit a high degree of endogamy, yet they are sizable. * Jewish communities are comparatively well informed about genetics research, and have been supportive of community efforts to study and prevent genetic diseases. The result is a form of ascertainment bias. This has sometimes created an impression that Jews are more susceptible to genetic disease than other populations. Healthcare professionals are often taught to consider those of Ashkenazi descent to be at increased risk forcolon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel mo ...
. People of Ashkenazi descent are at much higher risk of being a carrier for Tay-Sachs disease, which is fatal in its homozygous form.
Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; t ...
and genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
are often undertaken by couples where both partners are of Ashkenazi ancestry. Some organizations, most notably Dor Yeshorim, organize screening programs to prevent homozygosity for the genes that cause related diseases.
See also
*Jewish ethnic divisions
Jewish ethnic divisions refer to many distinctive communities within the world's ethnically Jewish population. Although considered a self-identifying ethnicity, there are distinct ethnic subdivisions among Jews, most of which are primarily the ...
* List of Israeli Ashkenazi Jews
This is a list of notable Israeli Ashkenazi Jews, including both original immigrants who obtained Israeli citizenship and their Israeli descendants.
Although traditionally the term "Ashkenazi Jews" was used as an all-encompassing term referring t ...
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
Sources
* *References for "Who is an Ashkenazi Jew?"
* * * *Other references
* Beider, Alexander (2001): ''A Dictionary of Ashkenazic Given Names: Their Origins, Structure, Pronunciations, and Migrations''. Avotaynu. . * Biale, David (2002): ''Cultures of the Jews: A New History''. Schoken Books. . * * Brook, Kevin Alan (2003): "The Origins of East European Jews" in ''Russian History/Histoire Russe'' vol. 30, nos. 1ŌĆō2, pp. 1ŌĆō22. * Gross, N. (1975): ''Economic History of the Jews''. Schocken Books, New York. * Haumann, Heiko (2001): ''A History of East European Jews''.Central European University Press
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center (disambiguation), center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa ...
. .
* Kriwaczek, Paul (2005): ''Yiddish Civilization: The Rise and Fall of a Forgotten Nation''. Alfred A. Knopf, New York. .
* Lewis, Bernard (1984): ''The Jews of Islam''. Princeton University Press. .
* Bukovec, Predrag''East and South-East European Jews in the 19th and 20th Centuries''
European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2010, retrieved: 17 December 2012. * Vital, David (1999): ''A People Apart: A History of the Jews in Europe''. Oxford University Press. . *
External links
''The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe''
*
Ćö''European Journal of Human Genetics'', 2007 * ttp://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2156/9/14 "Analysis of genetic variation in Ashkenazi Jews by high density SNP genotyping"
Nusach Ashkenaz, and Discussion Forum
Ashkenaz Heritage
{{Authority control Ashkenazi Jews topics Ethnic groups in Israel Ethnic groups in Russia Jewish ethnic groups Middle Eastern people Semitic-speaking peoples