Arm Slave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The
The
 The musculocutaneous nerve, from C5, C6, C7, is the main supplier of muscles of the anterior compartment. It originates from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus of nerves. It pierces the coracobrachialis muscle and gives off branches to the muscle, as well as to
The musculocutaneous nerve, from C5, C6, C7, is the main supplier of muscles of the anterior compartment. It originates from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus of nerves. It pierces the coracobrachialis muscle and gives off branches to the muscle, as well as to
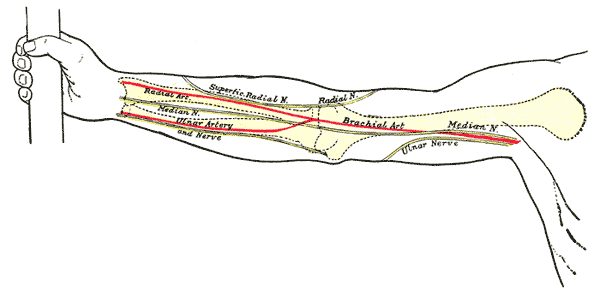 The main artery in the arm is the
The main artery in the arm is the
File:Arm Bones.png, Gross anatomy of the upper arm and elbow.
human anatomy
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a he ...
, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint ( wrist joint) is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
.
By anatomical definitions, the bones, ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal li ...
s and skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
s of the shoulder girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of t ...
, as well as the axilla between them, is considered parts of the upper limb, and thus also components of the arm. The Latin term ''brachium'', which serves as a root word
A root (or root word) is the core of a word that is irreducible into more meaningful elements. In morphology, a root is a morphologically simple unit which can be left bare or to which a prefix or a suffix can attach. The root word is the prima ...
for naming many anatomical structures, may refer to either the upper limb as a whole or to the upper arm on its own.
Anatomy
Bones
humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
is one of the three long bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, Short bone, short, Flat bone, flat, Irregular bone, irregular and Sesamoid bone, sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subj ...
s of the arm. It joins with the scapula at the shoulder joint and with the other long bones of the arm, the ulna and radius at the elbow joint. The elbow is a complex hinge joint
A hinge joint (ginglymus or ginglymoid) is a bone joint in which the articular surfaces are molded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane. According to one classification system they are said to be uniaxial (having ...
between the end of the humerus and the ends of the radius and ulna.
Muscles
The arm is divided by afascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. ...
l layer (known as lateral and medial intermuscular septa) separating the muscles into two ''osteofascial compartments'': the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
and the posterior compartments of the arm. The fascia merges with the periosteum (outer bone layer) of the humerus.
The anterior compartment contains three muscles: biceps brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join t ...
, brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus), also known as the Teichmann muscle, is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies deeper than the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pi ...
and coracobrachialis muscles. They are all innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. The posterior compartment contains only the triceps brachii muscle
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsibl ...
, supplied by the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial comp ...
.
Nerve supply
brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus), also known as the Teichmann muscle, is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies deeper than the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pi ...
and biceps brachii. It terminates as the anterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm
The lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve (or lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm) (branch of musculocutaneous nerve, also sometimes spelled "antebrachial") passes behind the cephalic vein, and divides, opposite the elbow-joint, into a volar and a ...
.
The radial nerve, which is from the fifth cervical spinal nerve to the first thoracic spinal nerve, originates as the continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. This nerve enters the lower triangular space
The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: ...
(an imaginary space bounded by, amongst others, the shaft of the humerus and the triceps brachii) of the arm and lies deep to the triceps brachii. Here it travels with the deep artery of the arm, which sits in the radial groove
The radial groove (also known as the musculospiral groove, radial sulcus, or spiral groove) is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery. It is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus b ...
of the humerus. This fact is very important clinically as a fracture of the shaft of the bone here can cause lesions or even transections in the nerve.
Other nerves passing through give no supply to the arm. These include:
* The median nerve, nerve origin C5-T1, which is a branch of the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus. This nerve continues in the arm, travelling in a plane between the biceps and triceps muscles. At the cubital fossa, this nerve is deep to the pronator teres
The pronator teres is a muscle (located mainly in the forearm) that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm (turning it so that the palm faces posteriorly when from the anatomical position). It has two attachments, to t ...
muscle and is the most medial structure in the fossa. The nerve passes into the forearm.
* The ulnar nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is ...
, origin C8-T1, is a continuation of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. This nerve passes in the same plane as the median nerve, between the biceps and triceps muscles. At the elbow, this nerve travels posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. This means that condylar
A condyle (;Entry "condyle"
in
fracture Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
s can cause lesion to this nerve.
in
fracture Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
Blood supply
 The main artery in the arm is the
The main artery in the arm is the brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa ...
. This artery is a continuation of the axillary artery. The point at which the axillary becomes the brachial is distal to the lower border of teres major. The brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa ...
gives off an unimportant branch, the deep artery of arm. This branching occurs just below the lower border of teres major.
The brachial artery continues to the cubital fossa in the anterior compartment of the arm. It travels in a plane between the biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join ...
and triceps muscles, the same as the median nerve and basilic vein. It is accompanied by venae comitantes (accompanying veins). It gives branches to the muscles of the anterior compartment. The artery is in between the median nerve and the tendon of the biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join ...
muscle in the cubital fossa. It then continues into the forearm.
The deep artery of the arm travels through the lower triangular space
The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: ...
with the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial comp ...
. From here onwards it has an intimate relationship with the radial nerve. They are both found deep to the triceps muscle and are located on the spiral groove of the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
. Therefore, fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
of the bone may not only lead to lesion of the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial comp ...
, but also haematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is b ...
of the internal structures of the arm. The artery then continues on to anastamose with the recurrent radial
The radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery immediately below the elbow.
It ascends between the branches of the radial nerve, lying on the supinator muscle and then between the brachioradialis muscle and the brachialis muscle, suppl ...
branch of the brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa ...
, providing a diffuse blood supply for the elbow joint.
Veins
The veins of the arm carry blood from the extremities of the limb, as well as drain the arm itself. The two main veins are the basilic and the cephalic veins. There is a connecting vein between the two, the median cubital vein, which passes through the cubital fossa and is clinically important forvenepuncture
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical labor ...
(withdrawing blood).
The basilic vein travels on the medial side of the arm and terminates at the level of the seventh rib.
The cephalic vein travels on the lateral side of the arm and terminates as the axillary vein. It passes through the deltopectoral triangle, a space between the deltoid and the pectoralis major muscles.
Society and culture
In Hindu, Buddhist and Egyptian iconography the symbol of the arm is used to illustrate the power of the sovereign. In Hindu tradition gods are depicted with several arms which carry specific symbols of their powers. It is believed that several arms depict omnipotence of gods. In popular culture Thakur did not have arms in the movie Sholay. In West Africa, the Bambara use forearm to symbolize the spirit, which is a link between God and man. Symbolic gestures of raising both hands signal surrender, appeals for mercy, and justice.Clinical significance
The cubital fossa is clinically important forvenepuncture
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical labor ...
and for blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
measurement.
When the arm is fractured this may refer to a fracture of the humerus bone.
Veins on the arm may be taken when a coronary artery bypass graft is needed.
Other animals
In other animals, the term ''arm'' can also be used for homologous or analogous structures (such as one of the pairedforelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. ...
s of a four-legged animal or the arms of cephalopods, respectively). In anatomical usage, the term ''arm'' may sometimes refer specifically to the segment between the shoulder and the elbow, while the segment between the elbow and wrist is the forearm. However, in common, literary, and historical usage, ''arm'' refers to the entire upper limb from shoulder to wrist. This article uses the former definition; see upper limb for the wider definition.
In primates the arm is adapted for precise positioning of the hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
and thus assist in the hand's manipulative tasks. The ball and socket shoulder joint allows for movement of the arms in a wide circular plane, while the structure of the two forearm bones which can rotate around each other allows for additional range of motion at that level.
Additional images
See also
* Axilla – also known as armpit, underarm or oxter *Common flexor tendon
The common flexor tendon is a tendon that attaches to the medial epicondyle of the humerus (lower part of the bone of the upper arm that is near the elbow joint).
It serves as the upper attachment point for the superficial muscles of the fro ...
References
{{Authority control Upper limb anatomy