Arc-welding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arc welding is a
 To supply the electrical energy necessary for arc welding processes, a number of different power supplies can be used. The most common classification is constant
To supply the electrical energy necessary for arc welding processes, a number of different power supplies can be used. The most common classification is constant
 Exposure to the brightness of the weld area leads to a condition called
Exposure to the brightness of the weld area leads to a condition called
 While examples of
While examples of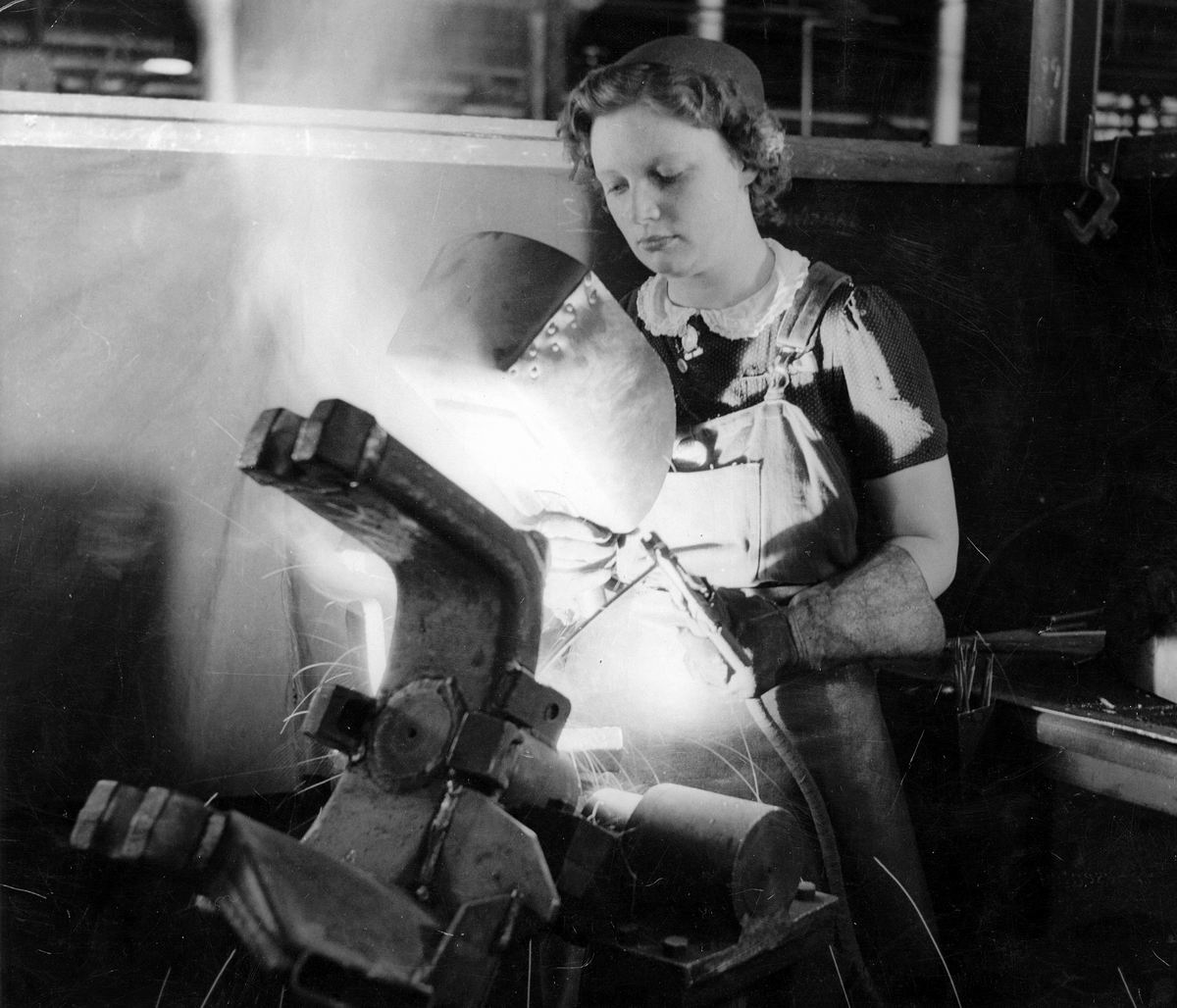  During
During
Arc Flash Awareness
video (25:39) from U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health {{DEFAULTSORT:Arc Welding Electric arcs Russian inventions Articles containing video clips
welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Welding is distinct from lower ...
process that is used to join metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
to metal by using electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a binding of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply
A welding power supply is a device that provides or modulates an electric current to perform arc welding.- - There are multiple arc welding processes in common use ranging from relatively simple Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) to more complicat ...
to create an electric arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The electric current, current through a normally Electrical conductance, nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma (p ...
between a metal stick ("electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials de ...
") and the base material to melt the metals at the point of contact. Arc welders can use either direct
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), a ...
(DC) or alternating (AC) current, and consumable or non-consumable electrodes.
The welding area is usually protected by some type of shielding gas
Shielding gases are inert or semi-inert gases that are commonly used in several welding processes, most notably gas metal arc welding and gas tungsten arc welding (GMAW and GTAW, more popularly known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Iner ...
(e.g. an inert gas), vapor, or slag. Arc welding processes may be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated. First developed in the late part of the 19th century, arc welding became commercially important in shipbuilding during the Second World War. Today it remains an important process for the fabrication of steel structures and vehicles.
Power supplies
 To supply the electrical energy necessary for arc welding processes, a number of different power supplies can be used. The most common classification is constant
To supply the electrical energy necessary for arc welding processes, a number of different power supplies can be used. The most common classification is constant current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
power supplies and constant voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
power supplies. In arc welding, the voltage is directly related to the length of the arc, and the current is related to the amount of heat input. Constant current power supplies are most often used for manual welding processes such as gas tungsten arc welding and shielded metal arc welding, because they maintain a relatively constant current even as the voltage varies. This is important because in manual welding, it can be difficult to hold the electrode perfectly steady, and as a result, the arc length and thus voltage tend to fluctuate. Constant voltage power supplies hold the voltage constant and vary the current, and as a result, are most often used for automated welding processes such as gas metal arc welding, flux cored arc welding, and submerged arc welding. In these processes, arc length is kept constant, since any fluctuation in the distance between the wire and the base material is quickly rectified by a large change in current. For example, if the wire and the base material get too close, the current will rapidly increase, which in turn causes the heat to increase and the tip of the wire to melt, returning it to its original separation distance. Under normal arc length conditions, a constant current power supply with a stick electrode operates at about 20 volts.
The direction of current used in arc welding also plays an important role in welding. Consumable electrode processes such as shielded metal arc welding and gas metal arc welding generally use direct current, but the electrode can be charged either positively or negatively. In general, the positively charged anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
will have a greater heat concentration (around 60%). "Note that for stick welding in general, DC+ polarity is most commonly used. It produces a good bead profile with a higher level of penetration. DC- polarity results in less penetration and a higher electrode melt-off rate. It is sometimes used, for example, on thin sheet metal in an attempt to prevent burn-through." "With few exceptions, electrode-positive (reversed polarity) results in deeper penetration. Electrode-negative (straight polarity) results in faster melt-off of the electrode and, therefore, faster deposition rate." Non-consumable electrode processes, such as gas tungsten arc welding, can use either type of direct current (DC), as well as alternating current (AC). With direct current however, because the electrode only creates the arc and does not provide filler material, a positively charged electrode causes shallow welds, while a negatively charged electrode makes deeper welds. Alternating current rapidly moves between these two, resulting in medium-penetration welds. One disadvantage of AC, the fact that the arc must be re-ignited after every zero crossing, has been addressed with the invention of special power units that produce a square wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
pattern instead of the normal sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a curve, mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph of a function, graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a Smoothness, smooth p ...
, eliminating low-voltage time after the zero crossings and minimizing the effects of the problem.
Duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formu ...
is a welding equipment specification which defines the number of minutes, within a 10-minute period, during which a given arc welder can safely be used. For example, an 80 A welder with a 60% duty cycle must be "rested" for at least 4 minutes after 6 minutes of continuous welding. Failure to observe duty cycle limitations could damage the welder. Commercial- or professional-grade welders typically have a 100% duty cycle.
Consumable electrode methods
One of the most common types of arc welding isshielded metal arc welding
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), also known as manual metal arc welding (MMA or MMAW), flux shielded arc welding or informally as stick welding, is a manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the wel ...
(SMAW), which is also known as manual metal arc welding (MMAW) or stick welding. An electric current is used to strike an arc between the base material and a consumable electrode rod or ''stick''. The electrode rod is made of a material that is compatible with the base material being welded and is covered with a flux that gives off vapors that serve as a shielding gas and provide a layer of slag, both of which protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. The electrode core itself acts as filler material, making a separate filler unnecessary. The process is very versatile, requiring little operator training and inexpensive equipment. However, weld times are rather slow, since the consumable electrodes must be frequently replaced and because slag, the residue from the flux, must be chipped away after welding. Furthermore, the process is generally limited to welding ferrous materials, though specialty electrodes have made possible the welding of cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
, aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and other metals. The versatility of the method makes it popular in a number of applications including repair work and construction.
Gas metal arc welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), sometimes referred to by its subtypes metal inert gas (MIG) and metal active gas (MAG) is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the workpiece metal(s), which hea ...
(GMAW), commonly called ''MIG'' (for ''metal/inert-gas''), is a semi-automatic or automatic welding process with a continuously fed consumable wire acting as both electrode and filler metal, along with an inert or semi-inert shielding gas flowed around the wire to protect the weld site from contamination. Constant voltage, direct current power source is most commonly used with GMAW, but constant current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
alternating current are used as well. With continuously fed filler electrodes, GMAW offers relatively high welding speeds; however the more complicated equipment reduces convenience and versatility in comparison to the SMAW process. Originally developed for welding aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
and other non-ferrous materials in the 1940s, GMAW was soon economically applied to steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
s. Today, GMAW is commonly used in industries such as the automobile industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % such ...
for its quality, versatility and speed. Because of the need to maintain a stable shroud of shielding gas around the weld site, it can be problematic to use the GMAW process in areas of high air movement such as outdoors.
Flux-cored arc welding Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW or FCA) is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process. FCAW requires a continuously-fed consumable tubular electrode containing a flux and a constant-voltage or, less commonly, a constant-current welding power s ...
(FCAW) is a variation of the GMAW technique. FCAW wire is actually a fine metal tube filled with powdered flux materials. An externally supplied shielding gas is sometimes used, but often the flux itself is relied upon to generate the necessary protection from the atmosphere. The process is widely used in construction because of its high welding speed and portability.
Submerged arc welding
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a common arc welding process. The first SAW patent was taken out in 1935. The process requires a continuously fed consumable solid or tubular (metal cored) electrode. The molten weld and the arc zone are protect ...
(SAW) is a high-productivity welding process in which the arc is struck beneath a covering layer of granular flux. This increases arc quality, since contaminants in the atmosphere are blocked by the flux. The slag that forms on the weld generally comes off by itself and, combined with the use of a continuous wire feed, the weld deposition rate is high. Working conditions are much improved over other arc welding processes since the flux hides the arc and no smoke is produced. The process is commonly used in industry, especially for large products. As the arc is not visible, it is typically automated. SAW is only possible in the 1F (flat fillet), 2F (horizontal fillet), and 1G (flat groove) positions.
Non-consumable electrode methods
Gas tungsten arc welding
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode are protected from oxidation or other atmo ...
(GTAW), or ''tungsten/inert-gas'' (TIG) welding, is a manual welding process that uses a non-consumable electrode made of tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
, an inert or semi-inert gas mixture, and a separate filler material. Especially useful for welding thin materials, this method is characterized by a stable arc and high quality welds, but it requires significant operator skill and can only be accomplished at relatively low speeds. It can be used on nearly all weldable metals, though it is most often applied to stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
and light metals. It is often used when quality welds are extremely important, such as in bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
, aircraft and marine applications.
A related process, plasma arc welding
Plasma arc welding (PAW) is an arc welding process similar to gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). The electric arc is formed between an electrode (which is usually but not always made of sintered tungsten) and the workpiece. The key difference from ...
, also uses a tungsten electrode but uses plasma gas to make the arc. The arc is more concentrated than the GTAW arc, making transverse control more critical and thus generally restricting the technique to a mechanized process. Because of its stable current, the method can be used on a wider range of material thicknesses than can the GTAW process and is much faster. It can be applied to all of the same materials as GTAW except magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
; automated welding of stainless steel is one important application of the process. A variation of the process is plasma cutting
Plasma cutting is a process that cuts through electrically conductive materials by means of an accelerated jet of hot plasma. Typical materials cut with a plasma torch include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass and copper, although other con ...
, an efficient steel cutting process.
Other arc welding processes include atomic hydrogen welding
Atomic hydrogen welding (AHW) is an arc welding process that uses an arc between two tungsten electrodes in a shielding atmosphere of hydrogen. The process was invented by Irving Langmuir in the course of his studies of atomic hydrogen. The elec ...
, carbon arc welding Carbon arc welding (CAW) is a process which produces coalescence of metals by heating them with an arc between a non-consumable carbon (graphite) electrode and the work-piece. It was the first arc-welding process developed but is not used for many ...
, electroslag welding
Electroslag welding (ESW) is a highly productive, single pass welding process for thick (greater than 25 mm up to about 300 mm) materials in a vertical or close to vertical position. (ESW) is similar to electrogas welding, but the main ...
, electrogas welding Electrogas welding (EGW) is a continuous vertical position arc welding process developed in 1961, in which an arc is struck between a consumable electrode and the workpiece. A shielding gas is sometimes used, but pressure is not applied. A major dif ...
, and stud arc welding
Stud welding is a technique similar to flash welding where a fastener or specially formed nut is welded onto another metal part, typically a base metal or substrate. The fastener can take different forms, but typically fall under threaded, unthre ...
.
Corrosion issues
Some materials, notably high-strength steels, aluminum, and titanium alloys, are susceptible tohydrogen embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can permeate solid metals. Once absorbed ...
. If the electrodes used for welding contain traces of moisture, the water decomposes in the heat of the arc and the liberated hydrogen enters the lattice of the material, causing its brittleness. Stick electrodes for such materials, with special low-hydrogen coating, are delivered in sealed moisture-proof packaging. New electrodes can be used straight from the can, but when moisture absorption may be suspected, they have to be dried by baking (usually at ) in a drying oven. Flux used has to be kept dry as well.
Some austenitic
Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron with an alloying element. In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1000 K ...
stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
s and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
-based alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
s are prone to intergranular corrosion
In materials science, intergranular corrosion (IGC), also known as intergranular attack (IGA), is a form of corrosion where the boundaries of crystallites of the material are more susceptible to corrosion than their insides. (''Cf.'' transgranu ...
. When subjected to temperatures around for too long a time, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
reacts with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
in the material, forming chromium carbide
Chromium(II) carbide is a ceramic compound that exists in several chemical compositions: Cr3C2, Cr7C3, and Cr23C6. At standard conditions it exists as a gray solid. It is extremely hard and corrosion resistant. It is also a refractory compound, ...
and depleting the crystal edges of chromium, impairing their corrosion resistance in a process called sensitization
Sensitization is a non-associative learning process in which repeated administration of a stimulus results in the progressive amplification of a response. Sensitization often is characterized by an enhancement of response to a whole class of stim ...
. Such sensitized steel undergoes corrosion in the areas near the welds where the temperature-time was favorable for forming the carbide. This kind of corrosion is often termed weld decay.
Knifeline attack (KLA) is another kind of corrosion affecting welds, impacting steels stabilized by niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
. Niobium and niobium carbide
Niobium carbide ( Nb C and Nb2C) is an extremely hard refractory ceramic material, commercially used in tool bits for cutting tools. It is usually processed by sintering and is a frequent additive as grain growth inhibitor in cemented carbides. It ...
dissolves in steel at very high temperatures. At some cooling regimes, niobium carbide does not precipitate, and the steel then behaves like unstabilized steel, forming chromium carbide instead. This affects only a thin zone several millimeters wide in the very vicinity of the weld, making it difficult to spot and increasing the corrosion speed. Structures made of such steels have to be heated in a whole to about , when the chromium carbide dissolves and niobium carbide forms. The cooling rate after this treatment is not important.
Filler metal (electrode material) improperly chosen for the environmental conditions can make them corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
-sensitive as well. There are also issues of galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. A sim ...
if the electrode composition is sufficiently dissimilar to the materials welded, or the materials are dissimilar themselves. Even between different grades of nickel-based stainless steels, corrosion of welded joints can be severe, despite that they rarely undergo galvanic corrosion when mechanically joined.
Safety issues
Welding can be a dangerous and unhealthy practice without the proper precautions; however, with the use of new technology and proper protection the risks of injury or death associated with welding can be greatly reduced.Heat, fire, and explosion hazard
Because many common welding procedures involve an open electric arc or flame, the risk of burns from heat andsparks
Sparks may refer to:
Places
*Sparks, Georgia
* Sparks, Kansas
*Sparks, Kentucky
*Sparks, Maryland
* Sparks, Nebraska
*Sparks, Nevada
*Sparks, Oklahoma
*Sparks, Texas
* Sparks, Bell County, Texas
* Sparks, West Virginia
Books
* ''Sparks'' (Raffi ...
is significant. To prevent them, welder
In a broad sense, a welder is anyone, amateur or professional, who uses welding equipment, perhaps especially one who uses such equipment fairly often. In a narrower sense, a welder is a tradesperson who specializes in fusing materials together ...
s wear protective clothing
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, ele ...
in the form of heavy leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
glove
A glove is a garment covering the hand. Gloves usually have separate sheaths or openings for each finger and the thumb.
If there is an opening but no (or a short) covering sheath for each finger they are called fingerless gloves. Fingerless glov ...
s and protective long sleeve jackets to avoid exposure to extreme heat, flames, and sparks. The use of compressed gases and flames in many welding processes also pose an explosion and fire risk; some common precautions include limiting the amount of oxygen in the air and keeping combustible materials away from the workplace.
Eye damage
 Exposure to the brightness of the weld area leads to a condition called
Exposure to the brightness of the weld area leads to a condition called arc eye
Photokeratitis or ultraviolet keratitis is a painful eye condition caused by exposure of insufficiently protected eyes to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from either natural (e.g. intense sunlight) or artificial (e.g. the electric arc during welding) ...
in which ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
causes inflammation of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power ...
and can burn the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
s of the eyes. Welding goggles
Welding goggles provide a degree of eye protection while some forms of welding and cutting are being done. They are intended to protect the eyes not only from the heat and optical radiation produced by the welding, such as the intense ultraviolet ...
and helmets
A helmet is a form of protective gear worn to protect the head. More specifically, a helmet complements the skull in protecting the human brain. Ceremonial or symbolic helmets (e.g., a policeman's helmet in the United Kingdom) without protect ...
with dark face plates—much darker than those in sunglass
Sunglasses or sun glasses (informally called shades or sunnies; more names below) are a form of protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damaging or discomforting the eyes. They can s ...
es or oxy-fuel goggles—are worn to prevent this exposure. In recent years, new helmet models have been produced featuring a face plate which automatically self-darkens electronically. To protect bystanders, transparent welding curtains often surround the welding area. These curtains, made of a polyvinyl chloride plastic film, shield nearby workers from exposure to the UV light from the electric arc.
Inhaled matter
Welders are also often exposed to dangerous gases andparticulate
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
matter. Processes like flux-cored arc welding and shielded metal arc welding produce smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product ...
containing particles of various types of oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
s. The size of the particles in question tends to influence the toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
ity of the fumes, with smaller particles presenting a greater danger. Additionally, many processes produce various gases (most commonly carbon dioxide and ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
, but others as well) that can prove dangerous if ventilation is inadequate.
Electrical safety
While the open-circuit voltage of an arc welding machine may be only a few tens of volts up to about 120 volts, even these low voltages can present a hazard of electric shock for the operators. Locations such as ship's hulls, storage tanks, metal structural steel, or in wet areas are usually at earth ground potential and operators may be standing or resting on these surfaces during operating of the electric arc. Welding machines operating off AC power distribution systems must isolate the arc circuit from earth ground to prevent insulation faults in the machine from exposing operators to high voltage. The return clamp of the welding machine is located near to the work area, to reduce the risk of stray current traveling a long way to create heating hazards or electric shock exposure, or to cause damage to sensitive electronic devices. Welding operators are careful to install return clamps so that welding current cannot pass through the bearings of electric motors, conveyor rollers, or other rotating components, which would cause damage to bearings. Welding on electrical buswork connected totransformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s presents a danger of the low welding voltage being "stepped up" to much higher voltages, so extra grounding cables may be required.
Interference with pacemakers
Certain welding machines which use a high frequency alternating current component have been found to affect pacemaker operation when within 2 meters of the power unit and 1 meter of the weld site.History
 While examples of
While examples of forge welding
Forge welding (FOW), also called fire welding, is a solid-state welding process that joins two pieces of metal by heating them to a high temperature and then hammering them together. It may also consist of heating and forcing the metals together ...
go back to the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, arc welding did not come into practice until much later.
In 1800 Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
discovered the short pulsed electric arcs. Independently a Russian physicist Vasily Petrov
Vasili, Vasily, Vasilii or Vasiliy (Russian language, Russian: wikt:Василий, Василий) is a Russian masculine given name of Greek language, Greek origin and corresponds to ''Basil (name)#Given name, Basil''. It may refer to:
*Vasili ...
discovered the continuous electric arc in 1802 and subsequently proposed its possible practical applications, including welding. Arc welding was first developed when Nikolai Benardos
Nikolay Nikolayevich Benardos (russian: Никола́й Никола́евич Бенардо́с) (1842–1905) was a Russian inventor of Greek origin who in 1881 introduced carbon arc welding, which was the first practical arc welding method.
...
presented arc welding of metals using a carbon electrode at the International Exposition of Electricity, Paris
The first International Exposition of Electricity in Paris ran from August 15, 1881 through to November 15, 1881 at the Palais de l'Industrie on the Champs-Élysées. It served to display the advances in electrical technology since the small elect ...
in 1881, which was patented together with Stanisław Olszewski
Stanisław Olszewski (1852–1898) was a Polish engineer and inventor. He is best known as the co-creator of the technology of arc welding (along with Nikolay Benardos).
Biography
He studied in Belgium at the University of Liège. Upon his ret ...
in 1887. In the same year, French electrical inventor Auguste de Méritens
Baron Auguste de Méritens was a French electrical engineer of the 19th century.
He was born in 1834.
He is best known his work on magneto generators, particularly those used for arc lighting and lighthouses. Similar magneto generators had been ...
also invented a carbon arc welding method, patented in 1881, which was successfully used for welding lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
in the manufacture of lead–acid batteries. The advances in arc welding continued with the invention of metal electrodes in the late 19th century by a Russian, Nikolai Slavyanov (1888), and an American, C. L. Coffin
Charles L. Coffin of Detroit was awarded for an arc welding process using a metal electrode. This was the first time that metal melted from the electrode carried across the arc to deposit filler metal in the joint to make a weld. Two years earli ...
. Around 1900, A. P. Strohmenger released in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
a coated metal electrode which gave a more stable arc. In 1905 Russian scientist Vladimir Mitkevich
Vladimir Fedorovich Mitkevich (1872–1951) was a scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a mod ...
proposed the usage of three-phase electric arc for welding. In 1919, alternating current welding was invented by C. J. Holslag but did not become popular for another decade.
Competing welding processes such as resistance welding
Electric resistance welding (ERW) is a welding process where metal parts in contact are permanently joined by heating them with an electric current, melting the metal at the joint. Electric resistance welding is widely used, for example, in manufa ...
and oxyfuel welding
Principle of burn cutting
Oxy-fuel welding (commonly called oxyacetylene welding, oxy welding, or gas welding in the United States) and oxy-fuel cutting are processes that use fuel gases (or liquid fuels such as gasoline or petrol, diesel, ...
were developed during this time as well; but both, especially the latter, faced stiff competition from arc welding especially after metal coverings (known as flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications to physics. For transport ph ...
) for the electrode, to stabilize the arc and shield the base material from impurities, continued to be developed.
 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
welding started to be used in shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
in Great Britain in place of rivet
A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite to the head is called the ''tail''. On installation, the rivet is placed in a punched ...
ed steel plates. The Americans also became more accepting of the new technology when the process allowed them to repair their ships quickly after a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
attack in the New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
at the beginning of the war. Arc welding was first applied to aircraft during the war as well, and some German airplane fuselages were constructed using this process. In 1919, the British shipbuilder Cammell Laird
Cammell Laird is a British shipbuilding company. It was formed from the merger of Laird Brothers of Birkenhead and Johnson Cammell & Co of Sheffield at the turn of the twentieth century. The company also built railway rolling stock until 1929, ...
started construction of a merchant ship, the ''Fullagar'', with an entirely welded hull; she was launched in 1921.
During the 1920s, major advances were made in welding technology, including the 1920 introduction of automatic welding in which electrode wire was continuously fed. Shielding gas became a subject receiving much attention as scientists attempted to protect welds from the effects of oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere. Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
and brittleness
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Bre ...
were the primary problems and the solutions that developed included the use of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
, and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
as welding atmospheres. During the following decade, further advances allowed for the welding of reactive metals such as aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
. This, in conjunction with developments in automatic welding, alternating current, and fluxes fed a major expansion of arc welding during the 1930s and then during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
During the middle of the century, many new welding methods were invented. Submerged arc welding
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a common arc welding process. The first SAW patent was taken out in 1935. The process requires a continuously fed consumable solid or tubular (metal cored) electrode. The molten weld and the arc zone are protect ...
was invented in 1930 and continues to be popular today. In 1932 a Russian, Konstantin Khrenov
Konstantin Konstantinovich Khrenov (russian: Константин Константинович Хренов; 13 February 1894 – 12 October 1984) was a Soviet engineer and inventor who in 1932 introduced underwater welding and cutting of metals ...
successfully implemented the first underwater electric arc welding. Gas tungsten arc welding
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode are protected from oxidation or other atmo ...
, after decades of development, was finally perfected in 1941 and gas metal arc welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), sometimes referred to by its subtypes metal inert gas (MIG) and metal active gas (MAG) is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the workpiece metal(s), which hea ...
followed in 1948, allowing for fast welding of non-ferrous
In chemistry, the adjective Ferrous indicates a compound that contains iron(II), meaning iron in its +2 oxidation state, possibly as the divalent cation Fe2+. It is opposed to "ferric" or iron(III), meaning iron in its +3 oxidation state, such a ...
materials but requiring expensive shielding gases. Using a consumable electrode and a carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
atmosphere as a shielding gas, it quickly became the most popular metal arc welding process. In 1957, the flux-cored arc welding Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW or FCA) is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process. FCAW requires a continuously-fed consumable tubular electrode containing a flux and a constant-voltage or, less commonly, a constant-current welding power s ...
process debuted in which the self-shielded wire electrode could be used with automatic equipment, resulting in greatly increased welding speeds. In that same year, plasma arc welding
Plasma arc welding (PAW) is an arc welding process similar to gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). The electric arc is formed between an electrode (which is usually but not always made of sintered tungsten) and the workpiece. The key difference from ...
was invented. Electroslag welding
Electroslag welding (ESW) is a highly productive, single pass welding process for thick (greater than 25 mm up to about 300 mm) materials in a vertical or close to vertical position. (ESW) is similar to electrogas welding, but the main ...
was released in 1958 and was followed by its cousin, electrogas welding Electrogas welding (EGW) is a continuous vertical position arc welding process developed in 1961, in which an arc is struck between a consumable electrode and the workpiece. A shielding gas is sometimes used, but pressure is not applied. A major dif ...
, in 1961.
See also
* * *References
Notes
Sources
* * * *Further reading
*ASM International
ASM International is a Dutch headquartered multinational corporation that specializes in design, manufacturing, sales and service of semiconductor wafer processing equipment for the fabrication of semiconductor devices. ASM's products are use ...
(2003). ''Trends in Welding Research''. Materials Park, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
: ASM International.
*Blunt, Jane and Nigel C. Balchin (2002). ''Health and Safety in Welding and Allied Processes''. Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
: Woodhead. .
*Hicks, John (1999). ''Welded Joint Design''. New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
: Industrial Press. .
External links
Arc Flash Awareness
video (25:39) from U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health {{DEFAULTSORT:Arc Welding Electric arcs Russian inventions Articles containing video clips