Apostolic Prefecture Of Sumatra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sumatra is one of the
 By the year
By the year
File:Minangprocession.jpg, Minangkabau women carrying platters of food to a ceremony
File:House in Nias North Sumatra.jpg, Traditional house in Nias North Sumatra
 The majority of people in Sumatra are Muslims (87.1%), while 10.7% are Christians, and less than 2% are Buddhists and Hindus.
The majority of people in Sumatra are Muslims (87.1%), while 10.7% are Christians, and less than 2% are Buddhists and Hindus.
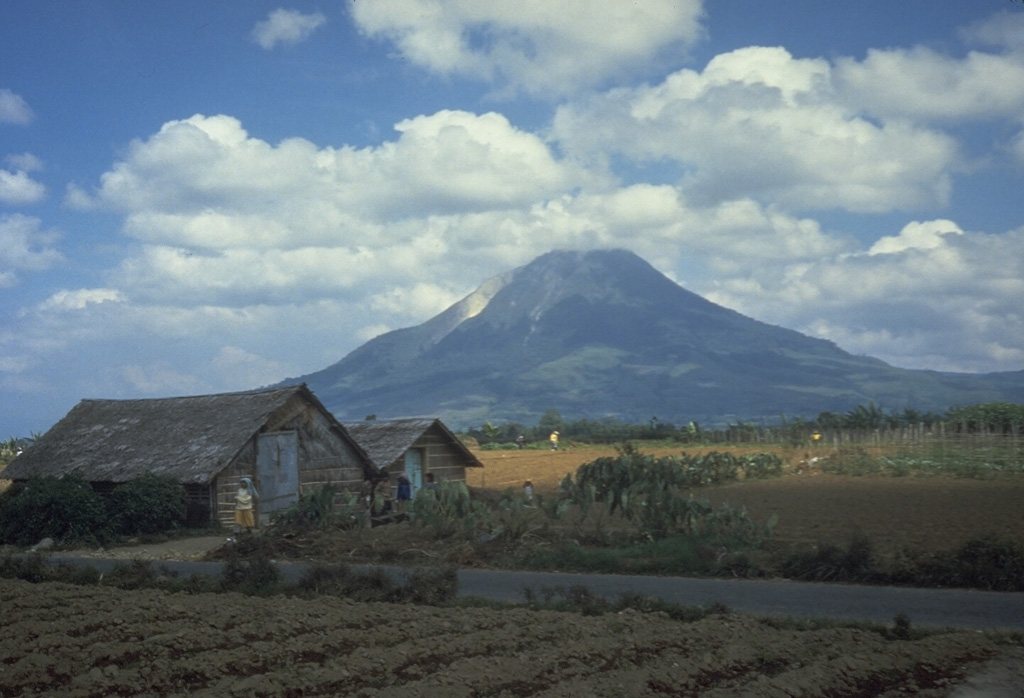
 The longest axis of the island runs approximately northwest–southeast, crossing the equator near the centre. At its widest point, the island spans . The interior of the island is dominated by two geographical regions: the Barisan Mountains in the west and swampy plains in the east. Sumatra is the closest Indonesian island to mainland Asia.
To the southeast is
The longest axis of the island runs approximately northwest–southeast, crossing the equator near the centre. At its widest point, the island spans . The interior of the island is dominated by two geographical regions: the Barisan Mountains in the west and swampy plains in the east. Sumatra is the closest Indonesian island to mainland Asia.
To the southeast is
 By population, Medan is the largest city in Sumatra.Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta. Medan is also the most visited and developed city in Sumatra.
By population, Medan is the largest city in Sumatra.Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta. Medan is also the most visited and developed city in Sumatra.
 Sumatra supports a wide range of vegetation types that are home to a rich variety of species, including 17 endemic genera of plants. Unique species include the
Sumatra supports a wide range of vegetation types that are home to a rich variety of species, including 17 endemic genera of plants. Unique species include the
''The History of Sumatra''
(1783); 3rd ed. (1811) freely available online.
Sunda Islands
The Sunda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Sunda) are a group of islands in the Malay Archipelago.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sunda Islands" . ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 26 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. They consist of the Greater Sunda ...
of western Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 475,807.63 km2 (182,812 mi.2), including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias
Nias ( id, Pulau Nias, Nias language: ''Tanö Niha'') (sometimes called Little Sumatra in English) is an island located off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago () of which the island is the centre, ...
, Mentawai, Enggano
Enggano Island is about 100 km (60 mi) southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia, though it can also be considered a barrier island of Sumatra.
Enggano is about long from e ...
, Riau Islands
The Riau Islands ( id, Kepulauan Riau) is a province of Indonesia. It comprises a total of 1,796 islands scattered between Sumatra, Malay Peninsula, and Borneo including the Riau Archipelago. Situated on one of the world's busiest shipping la ...
, Bangka Belitung
The Bangka Belitung Islands ( id, Kepulauan Bangka Belitung) is a province of Indonesia. Situated off the southeastern coast of Sumatra, the province comprises two main landmasses— Bangka and Belitung—and numerous smaller islands. Bangka Beli ...
and Krakatoa archipelago.
Sumatra is an elongated landmass spanning a diagonal northwest–southeast axis. The Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
borders the northwest, west, and southwest coasts of Sumatra, with the island chain of Simeulue, Nias
Nias ( id, Pulau Nias, Nias language: ''Tanö Niha'') (sometimes called Little Sumatra in English) is an island located off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago () of which the island is the centre, ...
, Mentawai, and Enggano
Enggano Island is about 100 km (60 mi) southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia, though it can also be considered a barrier island of Sumatra.
Enggano is about long from e ...
off the western coast. In the northeast, the narrow Strait of Malacca separates the island from the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
, which is an extension of the Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
n continent. In the southeast, the narrow Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java island, Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean.
Etymology
The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the weste ...
, containing the Krakatoa Archipelago, separates Sumatra from Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
. The northern tip of Sumatra is near the Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between th ...
, while off the southeastern coast lie the islands of Bangka and Belitung, Karimata Strait and the Java Sea
The Java Sea ( id, Laut Jawa, jv, Segara Jawa) is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its nort ...
. The Bukit Barisan mountains, which contain several active volcanoes, form the backbone of the island, while the northeastern area contains large plains and lowlands with swamps, mangrove forest
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangroves cannot withstand fr ...
and complex river systems. The equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
crosses the island at its centre in West Sumatra
West Sumatra ( id, Sumatra Barat) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the west coast of the island of Sumatra and includes the Mentawai Islands off that coast. The province has an area of , with a population of 5, ...
and Riau
Riau is a province of Indonesia. It is located on the central eastern coast of Sumatra along the Strait of Malacca. The province shares land borders with North Sumatra to the northwest, West Sumatra to the west, and Jambi to the south. Accord ...
provinces. The climate of the island is tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
, hot, and humid. Lush tropical rain forest once dominated the landscape.
Sumatra has a wide range of plant and animal species but has lost almost 50% of its tropical rainforest in the last 35 years. Many species are now critically endangered, such as the Sumatran ground cuckoo
The Sumatran ground cuckoo (''Carpococcyx viridis'') is a large, terrestrial species of cuckoo. It was introduced to Western science in 1879 and was formerly considered conspecific with the Bornean ground cuckoo but was given status as a unique s ...
, the Sumatran tiger
The Sumatran tiger is a population of ''Panthera tigris sondaica'' on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. It is the only surviving tiger population in the Sunda Islands, where the Bali and Javan tigers are extinct.
Sequences from complete mitochon ...
, the Sumatran elephant, the Sumatran rhinoceros, and the Sumatran orangutan
The Sumatran orangutan (''Pongo abelii'') is one of the three species of orangutans. Critically Endangered, and found only in the north of the Indonesian island of Sumatra, it is rarer than the Bornean orangutan but more common than the recent ...
. Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
on the island has also resulted in serious seasonal smoke haze over neighbouring countries, such as the 2013 Southeast Asian haze
The 2013 Southeast Asian haze was a haze crisis that affected several countries in Southeast Asia, including Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and Southern Thailand, mainly during June and July 2013. The haze period was caused by large- ...
which caused considerable tensions between Indonesia and affected countries Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
.
Etymology
Sumatra was known in ancient times by theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
names of ('Island of Gold') and ('Land of Gold'), because of the gold deposits in the island's highlands. The earliest known mention of the current form "Sumatra" was in 1017, when the local king Haji Sumatrabhumi Haji Sumatrabhumi (meaning "King of the land of Sumatra") was a king of the Srivijaya Kingdom who sent envoys to the Chinese Song dynasty in 1017. His name is recorded in Li Tao's '' Xu Zizhi Tongjian Changbian'' as Xiachi Suwuzhapumi (霞遲蘇� ...
("king of the land of Sumatra") sent an envoy to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
geographers referred to the island as (''Lamuri
Lamuri or Lambri was a kingdom in northern Sumatra, Indonesia from the Srivijaya period until the early 16th century. The area was inhabited by Hindu population around the seventh century. There is also evidence of Buddhism. The region is also ...
'', ''Lambri'' or ''Ramni'') in the tenth through thirteenth centuries, in reference to a kingdom near modern-day Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh ( Acehnese: ''Banda Acèh'', Jawoë: كوتا بند اچيه) is the capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra and has an elevation of . The city covers an area of and had ...
which was the first landfall for traders. The island has also been known by other names, including ''Andalas'' or ''Percha Island''.
In the late 13th century, Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
referred to the kingdom as , while his contemporary fellow Italian traveller Odoric of Pordenone used the form . Later in the 14th century the local form "Sumatra" became popular abroad due to the rising power of the kingdom of Samudera Pasai
The Samudera Pasai Sultanate (), also known as Samudera or Pasai or Samudera Darussalam or Pacem, was a Muslim harbour kingdom on the north coast of Sumatra from the 13th to the 16th centuries CE. The kingdom was believed to have been founded ...
and the subsequent Sultanate of Aceh.
From then on, subsequent European writers mostly used ''Sumatra'' or similar forms of the name for the entire island.
History
 By the year
By the year 692
__NOTOC__
Year 692 ( DCXCII) was a leap year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 692 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era be ...
, the Melayu Kingdom was absorbed by Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
.
Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
influence waned in the 11th century year 1025 after being defeated by the Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamils, Tamil thalassocratic Tamil Dynasties, empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated ...
Empire in southern India. By the end of the 12th century Srivijaya had been reduced to a small kingdom, and its dominant role in South Sumatra with the last king ratu Sekekhummong. At the same time, the spread of Islam in Indonesia occurred gradually and indirectly, starting from the western regions of Indonesia such as the Sumatra area which became the first place for the spread of Islam in the archipelago then Java to the eastern regions of Indonesia, Sulawesi and Maluku. The island of Sumatra is also an area in the archipelago that received the spread of Islam first compared to other islands or other areas. The island of Sumatra became the first area to receive the spread of Islam because of the position of the island of Sumatra which is close to the Malacca strait. The initial process of Islamization related to trade and also the formation of the kingdom. Islam entered Sumatra through pious Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
traders in the 6th and 7th centuries AD. At the beginning and end of the 13th century the formation of the kingdom, the king of the Samudra kingdom had converted to Islam. Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
visited the island in 1292, and his fellow Italian Odoric of Pordenone in 1321.
Moroccan scholar Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
visited with the sultan for 15 days, noting the city of Samudra was "a fine, big city with wooden walls and towers", and another two months on his return journey. Samudra was succeeded by the powerful Aceh Sultanate
The Sultanate of Aceh, officially the Kingdom of Aceh Darussalam ( ace, Keurajeuën Acèh Darussalam; Jawoë: كاورجاون اچيه دارالسلام), was a sultanate centered in the modern-day Indonesian province of Aceh. It was a major ...
, which survived to the 20th century. With the coming of the Dutch, the many Sumatran princely states gradually fell under their control. Aceh, in the north, was the major obstacle, as the Dutch were involved in the long and costly Aceh War (1873–1903).
The Free Aceh Movement
The Free Aceh Movement ( id, Gerakan Aceh Merdeka, GAM; ace, Geurakan Acèh Meurdèka / Gěrakan Aceh Měrdeka) was a separatist group seeking independence for the Aceh region of Sumatra, Indonesia. GAM fought against Indonesian government f ...
fought against Indonesian government forces in the Aceh Insurgency from 1976 to 2005. Security crackdowns in 2001 and 2002 resulted in several thousand civilian deaths.
The island was heavily impacted by both the 1883 Krakatoa eruption and the 2004 Boxing Day Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Suma ...
.
Demographics
Sumatra is not particularly densely populated, with an average of about 126 people per km2 – about 59,977,300 people in total (according to official estimates as at mid 2022). Because of its size, it is nonetheless the fifth most populous island in the world.Ethnic groups
The largest indigenous ethnic groups in Sumatra are Malays, Minangkabaus, Bataks, Acehnese, and Lampungs. Other major non-indigenous ethnic groups are Javanese, Sundanese, andChinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
.
Below are 11 largest ethnic groups in Sumatra based on the 2010 census (including Riau Islands
The Riau Islands ( id, Kepulauan Riau) is a province of Indonesia. It comprises a total of 1,796 islands scattered between Sumatra, Malay Peninsula, and Borneo including the Riau Archipelago. Situated on one of the world's busiest shipping la ...
, Bangka Belitung
The Bangka Belitung Islands ( id, Kepulauan Bangka Belitung) is a province of Indonesia. Situated off the southeastern coast of Sumatra, the province comprises two main landmasses— Bangka and Belitung—and numerous smaller islands. Bangka Beli ...
, Nias
Nias ( id, Pulau Nias, Nias language: ''Tanö Niha'') (sometimes called Little Sumatra in English) is an island located off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago () of which the island is the centre, ...
, Mentawai, Simeulue and islands around it)
Languages
There are over 52languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
spoken, all of which (except Chinese and Tamil) belong to the Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast ...
branch of the Austronesian language family. Within Malayo-Polynesian, they are divided into several sub-branches: Chamic
The Chamic languages, also known as Aceh–Chamic and Achinese–Chamic, are a group of ten languages spoken in Aceh (Sumatra, Indonesia) and in parts of Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam and Hainan, China. The Chamic languages are a subgroup of Malay ...
(which are represented by Acehnese in which its closest relatives are languages spoken by Ethnic Chams in Cambodia and Vietnam), Malayic
The Malayic languages are a branch of the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The most prominent member is Malay, which is the national language of Brunei, Singapore and Malaysia; it further serves as basis for Indon ...
(Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, Minangkabau and other closely related languages), Northwest Sumatra–Barrier Islands ( Batak languages, Gayo and others), Lampungic (includes Proper Lampung and Komering) and Bornean (represented by Rejang in which its closest linguistic relatives are Bukar Sadong and Land Dayak
The Land Dayak languages are a group of dozen or so languages spoken by the Bidayuh Land Dayaks of Borneo.
Languages ''Glottolog''
''Glottolog'' classifies the Land Dayak languages as follows.
*Benyadu-Bekati: Bekati (Bekatiq), Sara, Lara (Rar ...
spoken in West Kalimantan and Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the M ...
(Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
)). Northwest Sumatra–Barrier Islands and Lampungic branches are endemic to the island. Like all parts of Indonesia, Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
(which was based on Riau Malay) is the official language and the main lingua franca. Although Sumatra has its own local lingua franca, variants of Malay like Medan Malay and Palembang Malay
Palembang, also known as Palembang Malay (), or Musi, is a Malayic languages, Malayic language primarily spoken in about two thirds of South Sumatra Province in Indonesia, especially along the Musi River (Indonesia), Musi River. It consists of ...
are popular in North and South Sumatra, especially in urban areas. Minangkabau (Padang dialect) is popular in West Sumatra, some parts of North Sumatra, Bengkulu, Jambi and Riau (especially in Pekanbaru
Pekanbaru is the capital of Indonesian province of Riau, and a major economic center on the eastern part of Sumatra, Sumatra Island. Its name is derived from the Malay language, Malay words for 'new market' ('pekan' is market and 'baru' is new). ...
and areas bordered with West Sumatra
West Sumatra ( id, Sumatra Barat) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the west coast of the island of Sumatra and includes the Mentawai Islands off that coast. The province has an area of , with a population of 5, ...
) while Acehnese is also used as an inter-ethnic means of communication in some parts of Aceh province.
Religion
 The majority of people in Sumatra are Muslims (87.1%), while 10.7% are Christians, and less than 2% are Buddhists and Hindus.
The majority of people in Sumatra are Muslims (87.1%), while 10.7% are Christians, and less than 2% are Buddhists and Hindus.
Administration
Sumatra is one of seven geographicalregions of Indonesia
This is a list of some of the regions of Indonesia. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the central government. At different times of Indonesia's history, the nation has been designated as having regions that do not necessarily corr ...
which includes its adjacent smaller islands. Sumatra was one of the eight original provinces of Indonesia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
between 1945 and 1948. Including adjacent archipelagoes normally included with Sumatra (such as the Riau Islands, Nias and the Bangka-Belitung group), it now covers ten of Indonesia's 37 provinces, which are set out below with their areas and populations.
Geography

 The longest axis of the island runs approximately northwest–southeast, crossing the equator near the centre. At its widest point, the island spans . The interior of the island is dominated by two geographical regions: the Barisan Mountains in the west and swampy plains in the east. Sumatra is the closest Indonesian island to mainland Asia.
To the southeast is
The longest axis of the island runs approximately northwest–southeast, crossing the equator near the centre. At its widest point, the island spans . The interior of the island is dominated by two geographical regions: the Barisan Mountains in the west and swampy plains in the east. Sumatra is the closest Indonesian island to mainland Asia.
To the southeast is Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
, separated by the Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java island, Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean.
Etymology
The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the weste ...
. To the north is the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
(located on the Asian mainland), separated by the Strait of Malacca. To the east is Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
, across the Karimata Strait. West of the island is the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
.
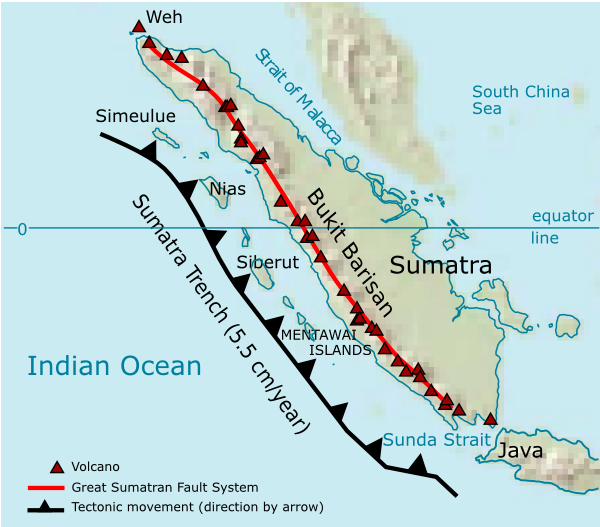
The Great Sumatran fault
The Indonesian island of Sumatra is located in a highly seismic area of the world. In addition to the subduction, subduction zone off the west coast of the island, Sumatra also has a large Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, strike-slip fault, th ...
(a strike-slip
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
fault), and the Sunda megathrust
The Sunda megathrust is a fault (geology), fault that extends approximately 5,500 km (3300 mi) from Burma, Myanmar (Burma) in the north, running along the southwestern side of Sumatra, to the south of Java and Bali before terminating ne ...
(a subduction zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
), run the entire length of the island along its west coast. On 26 December 2004, the western coast and islands of Sumatra, particularly Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
province, were struck by a tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
following the Indian Ocean earthquake
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sum ...
. This was the longest earthquake recorded, lasting between 500 and 600 seconds. More than 170,000 Indonesians were killed, primarily in Aceh. Other recent earthquakes to strike Sumatra include the 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake
The 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake occurred on 28 March off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. At least 915 people were killed, mostly on the island of Nias. The event caused panic in the region, which had already been devastated by ...
and the 2010 Mentawai earthquake and tsunami
The 2010 Mentawai earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 7.8 on 25 October off the western coast of Sumatra at 21:42 local time (14:42 UTC). The earthquake occurred on the same fault that produced the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. It was ...
.
Lake Toba
Lake Toba ( id, Danau Toba) ( Toba Batak: ᯖᯀᯬ ᯖᯬᯅ; romanized: ''Tao Toba'') is a large natural lake in North Sumatra, Indonesia, occupying the caldera of a supervolcano. The lake is located in the middle of the northern part of the ...
is the site of a supervolcanic eruption that occurred around 74,000 years ago, representing a climate-changing event.
The most important rivers in Sumatra belong to the catchment area of the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
. Heading north to south, the Rokan, Siak, Kampar Kampar may refer to:
Indonesia
*Kampar Regency, Riau Province, eastern Sumatra
*Kampar River, a river in the same province
Malaysia
*Kampar District, Perak
*Kampar, Perak, a town in Kampar District
*Kampar River, Malaysia Kampar may refer to:
Ind ...
, Indragiri, Batanghari
The Batang Hari (Indonesian: ''Sungai Batanghari'') is the longest river in Jambi province, Sumatra island, Indonesia, about northwest of the capital Jakarta.
Hydrology
The river originates in the Minangkabau Highlands, home of the Minangkaba ...
flow into the Malacca Strait
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, 500 mi (800 km) long and from 40 to 155 mi (65–250 km) wide, between the Malay Peninsula (Peninsular Malaysia) to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, conne ...
, while the island's largest river, the Musi, flows into the sea at Bangka Strait
Bangka Strait is the strait that separates the island of Sumatra from Bangka Island ( id, Pulau Bangka) in the Java Sea, Indonesia. The strait is about long, with a width varying from about to .
See also
* Japanese cruiser Ashigara
* List of st ...
in the south.
To the east, big rivers carry silt from the mountains, forming the vast lowland interspersed by swamps. Even if mostly unsuitable for farming, the area is currently of great economic importance for Indonesia. It produces oil from both above and below the soil – palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from ...
and petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
.
Sumatra is the largest producer of Indonesian coffee
Indonesia was the fourth-largest producer of coffee in the world in 2014.http://www.ico.org/prices/po-production.pdf Coffee cultivation in Indonesia began in the late 1600s and early 1700s, in the early Dutch colonial period, and has played an ...
. Small-holders grow Arabica coffee (''Coffea arabica
''Coffea arabica'' (), also known as the Arabic coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is believed to be the first species of coffee to have been cultivated and is currently the dominant cultivar, r ...
'') in the highlands, while Robusta ('' Coffea canephora'') is found in the lowlands. Arabica coffee from the regions of Gayo, Lintong and Sidikilang is typically processed using the Giling Basah
Giling Basah is a term used by Indonesian coffee processors to describe the method they use to remove the hulls of '' Coffea arabica''. Literally translated from Indonesian, the term means "wet grinding".
The Arabica coffee industry also ...
(wet hulling) technique, which gives it a heavy body and low acidity.
Sumatra is a highly seismic island, huge earthquakes have been recorded throughout history, in 1797 an 8.9 earthquake shook Western Sumatra, in 1833 a 9.2 earthquake shook Bengkulu and Western Sumatra both events caused large tsunamis. They are very common throughout the coastal area of the west and center of the island, tsunamis are common due to the high seismicity in the area.
Largest cities
 By population, Medan is the largest city in Sumatra.Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta. Medan is also the most visited and developed city in Sumatra.
By population, Medan is the largest city in Sumatra.Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta. Medan is also the most visited and developed city in Sumatra.
Flora and fauna

 Sumatra supports a wide range of vegetation types that are home to a rich variety of species, including 17 endemic genera of plants. Unique species include the
Sumatra supports a wide range of vegetation types that are home to a rich variety of species, including 17 endemic genera of plants. Unique species include the Sumatran pine
''Pinus merkusii'', the Merkus pine or Sumatran pine, is a pine native to the Malesia region of southeast Asia, and the only one that occurs naturally south of the equator.
Description
''Pinus merkusii'' is a medium-sized to large tree, reachin ...
which dominates the Sumatran tropical pine forests
The Sumatran tropical pine forests is a tropical coniferous forest ecoregion on the island of Sumatra in Indonesia.
Location and description
These pine forests are found on the higher slopes of Sumatra, especially in the north of the island ne ...
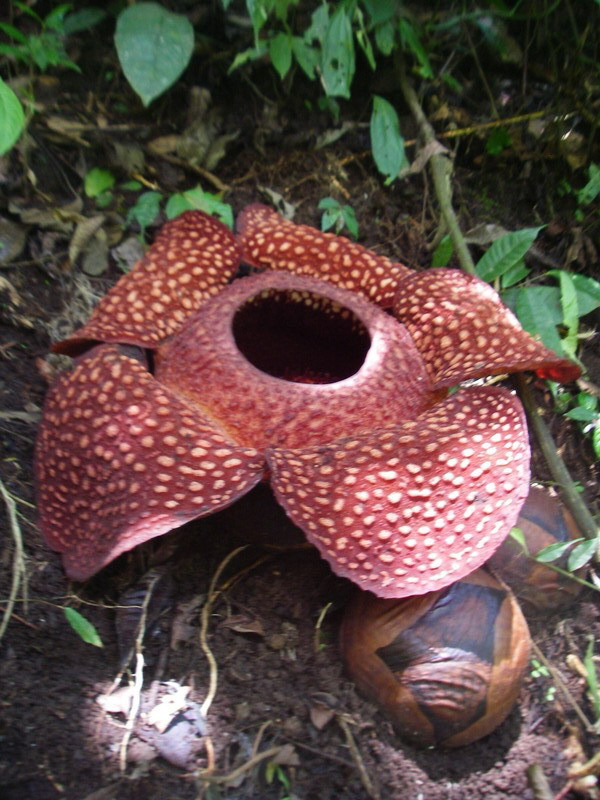
of the higher mountainsides in the north of the island and rainforest plants such as ''Rafflesia arnoldii
''Rafflesia arnoldii'', the corpse flower or giant padma, is a species of flowering plant in the parasitic genus ''Rafflesia''. It is noted for producing the largest individual flower on Earth. It has a strong and unpleasant odor of decaying f ...
'' (the world's largest individual flower), and the titan arum (the world's largest unbranched inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed o ...
).
The island is home to 201 mammal species and 580 bird species. There are nine endemic mammal species on mainland Sumatra and 14 more endemic to the nearby Mentawai Islands Mentawai may refer to:
* Mentawai Islands
* Mentawai Strait
* Mentawai people
* Mentawai language
The Mentawai language is an Austronesian language, spoken by the Mentawai people of the Mentawai Islands, West Sumatra, Indonesia.
Dialects
Acco ...
. There are about 300 freshwater fish species in Sumatra. There are 93 amphibian species in Sumatra, 21 of which are endemic to Sumatra.
The Sumatran tiger
The Sumatran tiger is a population of ''Panthera tigris sondaica'' on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. It is the only surviving tiger population in the Sunda Islands, where the Bali and Javan tigers are extinct.
Sequences from complete mitochon ...
, Sumatran rhinoceros, Sumatran elephant, Sumatran ground cuckoo
The Sumatran ground cuckoo (''Carpococcyx viridis'') is a large, terrestrial species of cuckoo. It was introduced to Western science in 1879 and was formerly considered conspecific with the Bornean ground cuckoo but was given status as a unique s ...
, Sumatran orangutan
The Sumatran orangutan (''Pongo abelii'') is one of the three species of orangutans. Critically Endangered, and found only in the north of the Indonesian island of Sumatra, it is rarer than the Bornean orangutan but more common than the recent ...
and Tapanuli orangutan
The Tapanuli orangutan (''Pongo tapanuliensis'') is a species of orangutan restricted to South Tapanuli in the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. It is one of three known species of orangutan, alongside the Sumatran orangutan (''P. abelii''), found ...
are all critically endangered, indicating the highest level of threat to their survival. In October 2008, the Indonesian government announced a plan to protect Sumatra's remaining forests.
The island includes more than 10 national parks, including three which are listed as the Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
– Gunung Leuser National Park
Gunung Leuser National Park is a national park covering 7,927 km2 in northern Sumatra, Indonesia, straddling the border of North Sumatra and Aceh provinces, a fourth portion and three-fourths portion, respectively. The national park, settled ...
, Kerinci Seblat National Park
Kerinci Seblat National Park is the largest national park on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia. It has a total area of 13,791 km2, and spans four provinces: West Sumatra, Jambi, Bengkulu, and South Sumatra.
Geography
It is located between 1 ...
and Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park
Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park is a national park in Sumatra, Indonesia. The park located along the Bukit Barisan mountain range, has a total area of 3,568 km2, and spans three provinces: Lampung, Bengkulu, and South Sumatra. Together ...
. The Berbak National Park
The Berbak National Park in Sumatra island, Jambi province of Indonesia, forms part of the largest undisturbed swamp forest in southeastern Asia,Indonesian Ministry of Forestry"Berbak National Park", retrieved 04-12-2009 and the peat swamp fores ...
is one of three national parks in Indonesia listed as a wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
of international importance under the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It i ...
.
Rail transport
Several unconnected railway networks built duringNetherlands East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
exist in Sumatra, such as the ones connecting Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh ( Acehnese: ''Banda Acèh'', Jawoë: كوتا بند اچيه) is the capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra and has an elevation of . The city covers an area of and had ...
- Lhokseumawe- Besitang-Medan
Medan (; English: ) is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of North Sumatra, as well as a regional hub and financial centre of Sumatra. According to the National Development Planning Agency, Medan is one of the four main ...
-Tebingtinggi- Pematang Siantar-Rantau Prapat in Northern Sumatra (the Banda Aceh-Besitang section was closed in 1971, but is currently being rebuilt). Padang-Solok
(BERAS)(Clean, Elegant, Neat, Safe and Prosperous)
, image_shield = Logo Kota Solok.png
, image_map = Lokasi Sumatra Barat Kota Solok.svg
, map_caption = Location within West Sumatra
, pushpin_map =Indon ...
- Bukittinggi in West Sumatra
West Sumatra ( id, Sumatra Barat) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the west coast of the island of Sumatra and includes the Mentawai Islands off that coast. The province has an area of , with a population of 5, ...
, and Bandar Lampung
Bandar Lampung (Lampung: , ''Kutak Bandarlampung'', formerly Dutch: ''Oosthaven'', lit. "Eastern Harbor") is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Lampung. Located on the southern tip of Sumatra, Bandar Lampung was original ...
-Palembang
Palembang () is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River on the eastern lowland of southern Sumatra. It had a population of 1,668,848 at the 2020 Census. Palembang ...
-Lahat-Lubuk Linggau in Southern Sumatra.
See also
*Architecture of Sumatra
The Indonesian island of Sumatra is the sixth largest island in the world. The rich ethnic diversity and historical heritage in Sumatra is reflected in the range of architectural styles in the island. The vernacular style is the native Sumatran e ...
* Bukit Seguntang
* Communism in Sumatra
Communism in Sumatra has historically had an influence in the politics and society of Sumatra.
Padang, Pariaman, Silungkang, Sawah Lunto, Alahan Panjang, and Suliki of West Sumatra have been cited as an area which was particular active in comm ...
* Music of Sumatra
The Music of Sumatra, Sumatra is a part of Indonesia; its best-known musical output is probably dangdut, a rabab/ saluang instrumental style.
The Sumatran Toba people are distinctive in their use of tuned drums to carry the melody in their mu ...
References
Further reading
* * William Marsden''The History of Sumatra''
(1783); 3rd ed. (1811) freely available online.
External links
* {{Authority control Greater Sunda Islands Maritime Southeast Asia Islands of the Indian Ocean Populated places in Indonesia Islands of Indonesia