Antoni Gaudí on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antoni Gaudí i Cornet (; ; 25 June 1852 – 10 June 1926) was a
 Gaudí's exact birthplace is unknown because no supporting documents have been found, leading to a controversy about whether he was born in Reus or Riudoms, two neighbouring municipalities of the
Gaudí's exact birthplace is unknown because no supporting documents have been found, leading to a controversy about whether he was born in Reus or Riudoms, two neighbouring municipalities of the  Young Gaudí suffered from poor health, including
Young Gaudí suffered from poor health, including
 Gaudí's first projects were the lampposts he designed for the
Gaudí's first projects were the lampposts he designed for the 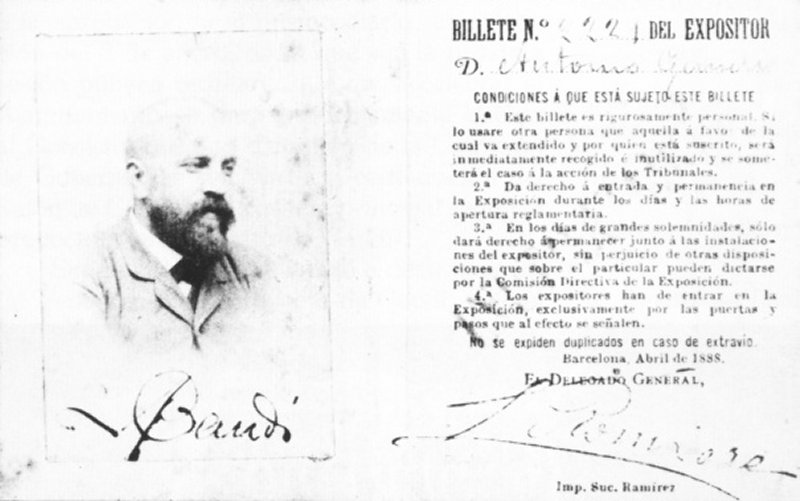 The 1888 World Fair was one of the era's major events in Barcelona and represented a key point in the history of the ''Modernisme'' movement. Leading architects displayed their best works, including Gaudí, who showcased the building he had designed for the Compañía Trasatlántica (Transatlantic Company). Consequently, he received a commission to restructure the Saló de Cent of the Barcelona City Council, but this project was ultimately not carried out. In the early 1890s Gaudí received two commissions from outside of Catalonia, namely the
The 1888 World Fair was one of the era's major events in Barcelona and represented a key point in the history of the ''Modernisme'' movement. Leading architects displayed their best works, including Gaudí, who showcased the building he had designed for the Compañía Trasatlántica (Transatlantic Company). Consequently, he received a commission to restructure the Saló de Cent of the Barcelona City Council, but this project was ultimately not carried out. In the early 1890s Gaudí received two commissions from outside of Catalonia, namely the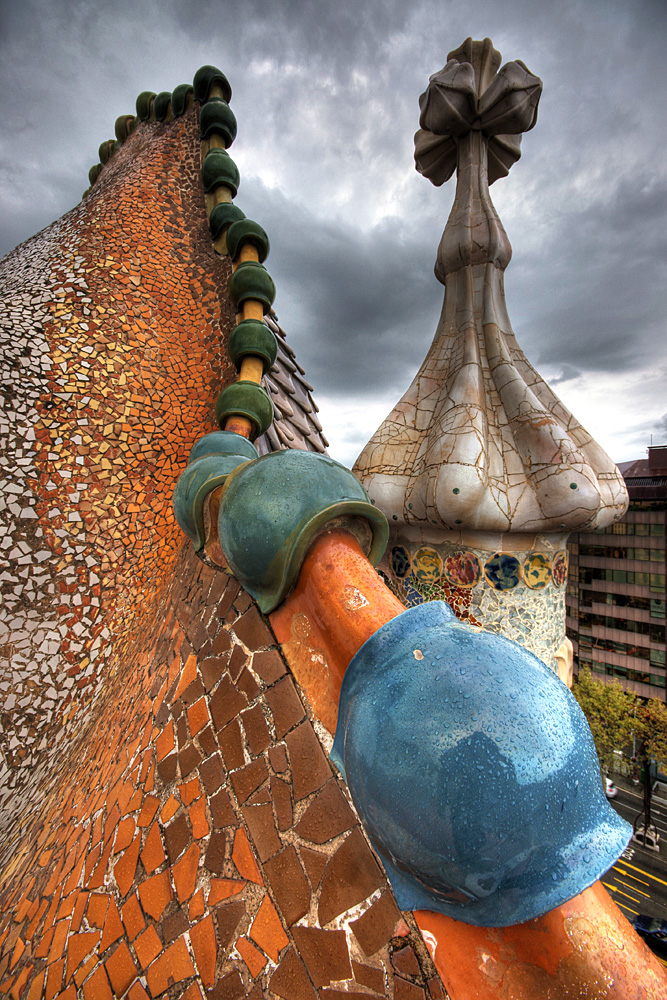  In 1899 Gaudí joined the
In 1899 Gaudí joined the  As a result of Gaudí's increasing fame, in 1902 the painter Joan Llimona chose Gaudí's features to represent
As a result of Gaudí's increasing fame, in 1902 the painter Joan Llimona chose Gaudí's features to represent
 Gaudí's personal appearance—Nordic features, blond hair and blue eyes—changed radically over the course of time. As a young man, he dressed like a
Gaudí's personal appearance—Nordic features, blond hair and blue eyes—changed radically over the course of time. As a young man, he dressed like a
 In 1920 he was beaten by police in a riot during the
In 1920 he was beaten by police in a riot during the
 On 7 June 1926, Gaudí was taking his daily walk to the Sant Felip Neri church for his habitual prayer and confession. While walking along the
On 7 June 1926, Gaudí was taking his daily walk to the Sant Felip Neri church for his habitual prayer and confession. While walking along the
 Gaudí's professional life was distinctive in that he never ceased to investigate mechanical building structures. Early on, Gaudí was inspired by oriental arts (India,
Gaudí's professional life was distinctive in that he never ceased to investigate mechanical building structures. Early on, Gaudí was inspired by oriental arts (India,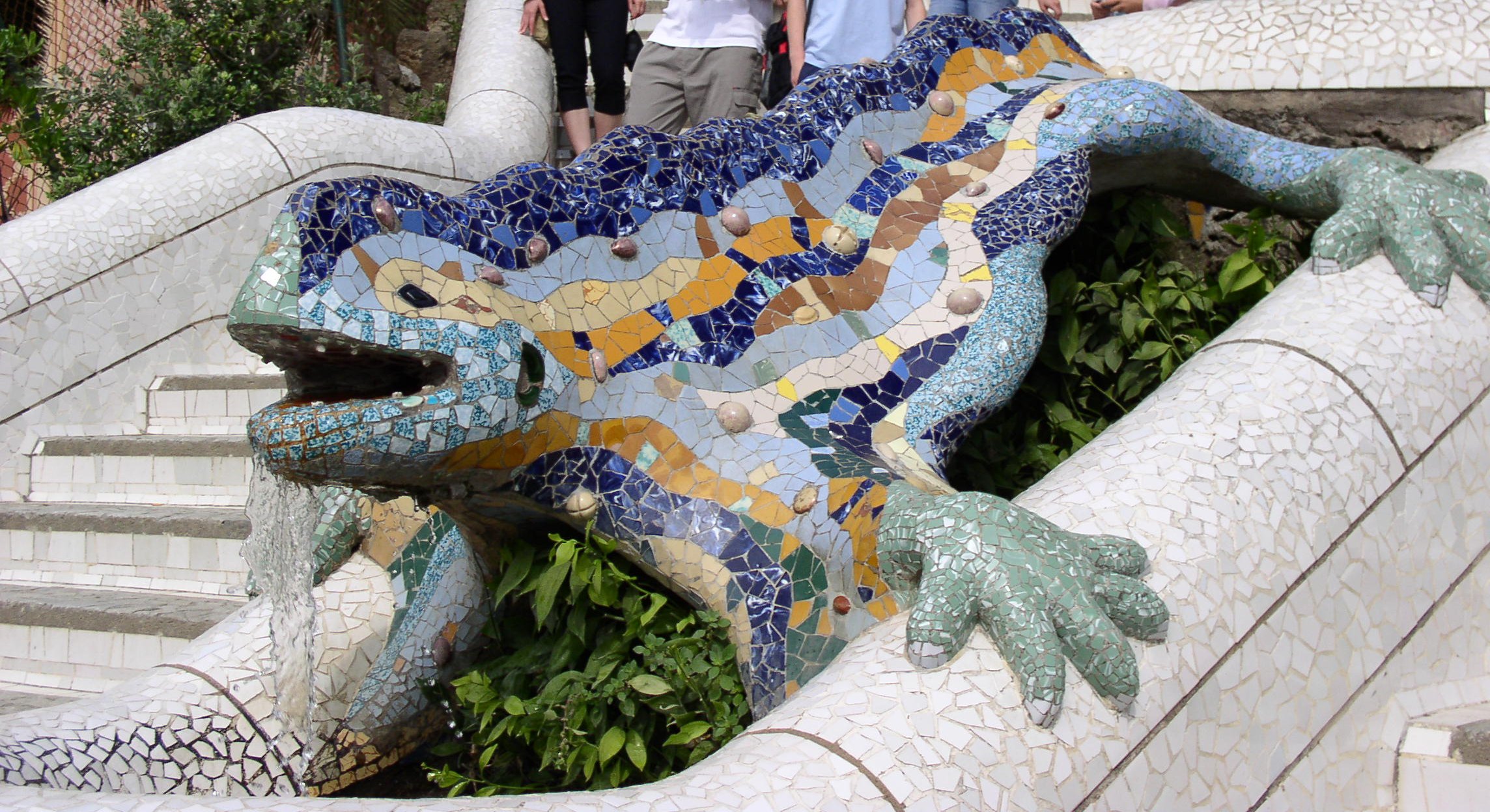  After these initial influences, Gaudí moved towards ''Modernisme'', then in its heyday. ''Modernisme'' in its earlier stages was inspired by historic architecture. Its practitioners saw its return to the past as a response to the industrial forms imposed by the
After these initial influences, Gaudí moved towards ''Modernisme'', then in its heyday. ''Modernisme'' in its earlier stages was inspired by historic architecture. Its practitioners saw its return to the past as a response to the industrial forms imposed by the
 This study of nature translated into his use of ruled geometrical forms such as the
This study of nature translated into his use of ruled geometrical forms such as the
 Another of Gaudí's innovations in the technical realm was the use of a scale model to calculate structures: for the church of the Colònia Güell, he built a 1:10 scale model with a height of in a shed next to the building. There, he set up a model that had strings with small bags full of
Another of Gaudí's innovations in the technical realm was the use of a scale model to calculate structures: for the church of the Colònia Güell, he built a 1:10 scale model with a height of in a shed next to the building. There, he set up a model that had strings with small bags full of
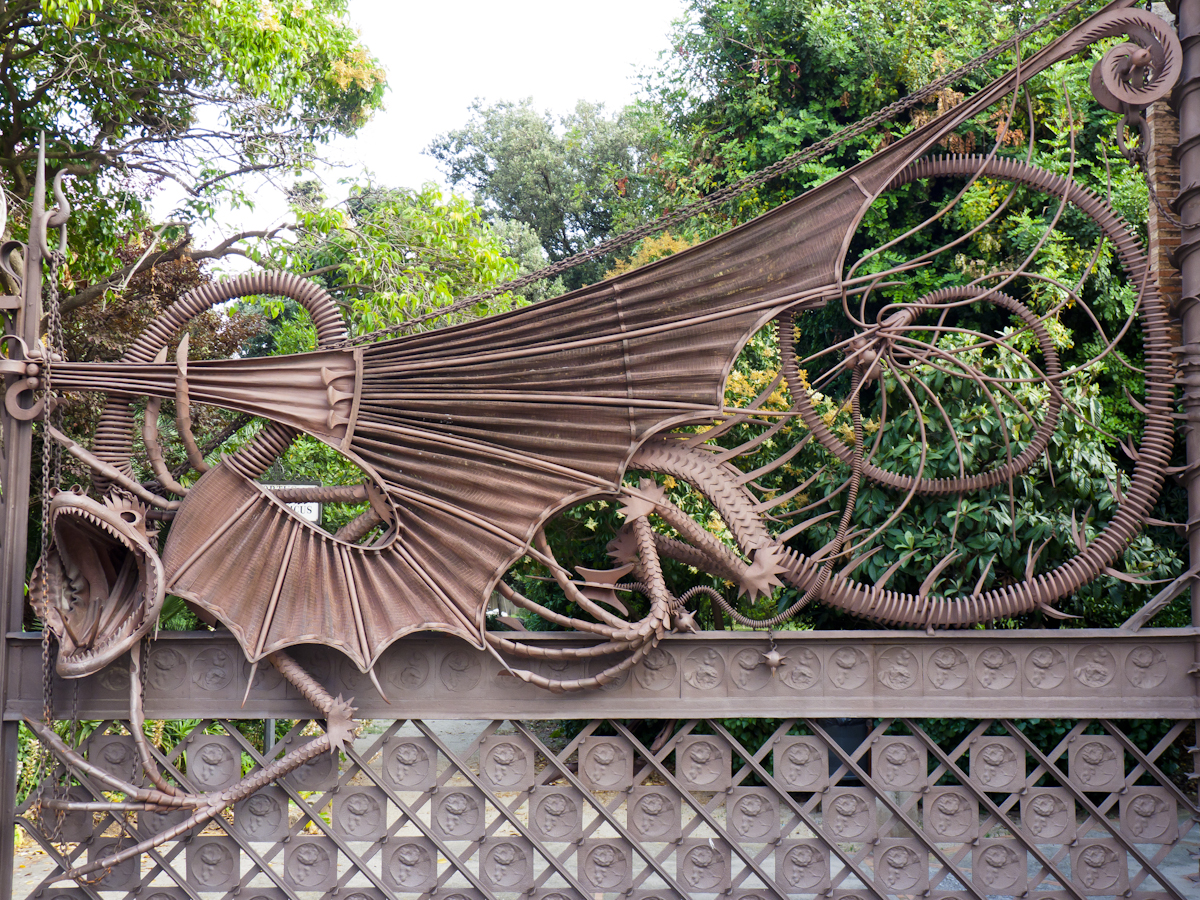 During his student days, Gaudí attended craft workshops, such as those taught by Eudald Puntí, Llorenç Matamala and Joan Oñós, where he learned the basic aspects of techniques relating to architecture, including sculpture, carpentry,
During his student days, Gaudí attended craft workshops, such as those taught by Eudald Puntí, Llorenç Matamala and Joan Oñós, where he learned the basic aspects of techniques relating to architecture, including sculpture, carpentry,  This was how he personally designed many of the Sagrada Família's sculptures. He would thoroughly study the
This was how he personally designed many of the Sagrada Família's sculptures. He would thoroughly study the
 Equally, Gaudí stood out as
Equally, Gaudí stood out as  Another aspect is the intelligent distribution of space, always with the aim of creating a comfortable, intimate, interior atmosphere. For this purpose, Gaudí would divide the space into sections, adapted to their specific use, by means of low walls, dropped ceilings, sliding doors and wall closets. Apart from taking care of every detail of all structural and ornamental elements, he made sure his constructions had good lighting and ventilation. For this purpose, he studied each project's orientation with respect to the cardinal points, as well as the local climate and its place in its surroundings. At that time, there was an increasing demand for more domestic comfort, with piped water and gas and the use of electric light, all of which Gaudí expertly incorporated. For the Sagrada Família, for example, he carried out thorough studies on
Another aspect is the intelligent distribution of space, always with the aim of creating a comfortable, intimate, interior atmosphere. For this purpose, Gaudí would divide the space into sections, adapted to their specific use, by means of low walls, dropped ceilings, sliding doors and wall closets. Apart from taking care of every detail of all structural and ornamental elements, he made sure his constructions had good lighting and ventilation. For this purpose, he studied each project's orientation with respect to the cardinal points, as well as the local climate and its place in its surroundings. At that time, there was an increasing demand for more domestic comfort, with piped water and gas and the use of electric light, all of which Gaudí expertly incorporated. For the Sagrada Família, for example, he carried out thorough studies on
Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
architect from Spain known as the greatest exponent of Catalan Modernism
''Modernisme'' (, Catalan for "modernism"), also known as Catalan modernism and Catalan art nouveau, is the historiographic denomination given to an art and literature movement associated with the search of a new entitlement of Catalan cultu ...
. Gaudí's works have a highly individualized, ''sui generis
''Sui generis'' ( , ) is a Latin phrase that means "of its/their own kind", "in a class by itself", therefore "unique".
A number of disciplines use the term to refer to unique entities. These include:
* Biology, for species that do not fit in ...
'' style. Most are located in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, including his main work, the church of the Sagrada Família
The Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família, shortened as the Sagrada Família, is an unfinished church in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is the largest unfinished Catholic church in the world. Designed by ...
.
Gaudí's work was influenced by his passions in life: architecture, nature, and religion. He considered every detail of his creations and integrated into his architecture such crafts as ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
s, stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
, wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a ...
work forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which i ...
and carpentry. He also introduced new techniques in the treatment of materials, such as ''trencadís
''Trencadís'' (), also known as pique assiette, broken tile mosaics, bits and pieces, memoryware, and shardware, is a type of mosaic made from cemented-together tile shards and broken chinaware. Glazed china tends to be preferred, and glass is so ...
'' which used waste ceramic pieces.
Under the influence of neo-Gothic art and Oriental techniques, Gaudí became part of the ''Modernista'' movement which was reaching its peak in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. His work transcended mainstream ''Modernisme'', culminating in an organic style inspired by natural forms. Gaudí rarely drew detailed plans of his works, instead preferring to create them as three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informal ...
scale model
A scale model is a physical model which is geometrically similar to an object (known as the prototype). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes ...
s and moulding the details as he conceived them.
Gaudí's work enjoys global popularity and continuing admiration and study by architects. His masterpiece, the still-incomplete Sagrada Família, is the most-visited monument in Spain. Between 1984 and 2005, seven of his works were declared World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNES ...
by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
. Gaudí's Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
faith intensified during his life and religious images appear in many of his works. This earned him the nickname "God's Architect" and led to calls for his beatification
Beatification (from Latin ''beatus'', "blessed" and ''facere'', "to make”) is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their nam ...
.
Biography
Birth, childhood, and studies
Gaudí was born on 25 June 1852 inRiudoms
Riudoms is a town in the ''comarca'' of Baix Camp, province of Tarragona, in Catalonia, located about five kilometres from the regional capital Reus.
The main product is the hazelnut, today in recession, and extra virgin olive oil.
History
Ri ...
or Reus
Reus () is the capital of Baix Camp, in the province of Tarragona, in Catalonia, Spain. The area has always been an important producer of wines and spirits, and gained continental importance at the time of the Phylloxera plague. Nowadays it is k ...
to the coppersmith
A coppersmith, also known as a brazier, is a person who makes artifacts from copper and brass. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. The term "redsmith" is used for a tinsmith that uses tinsmithing tools and techniques to make copper items.
Hi ...
Francesc Gaudí i Serra (1813–1906) and Antònia Cornet i Bertran (1819–1876). He was the youngest of five children, of whom three survived to adulthood: Rosa (1844–1879), Francesc (1851–1876) and Antoni. Gaudí's family originated in the Auvergne region in southern France. One of his ancestors, Joan Gaudí, a hawker, moved to Catalonia in the 17th century; possible origins of Gaudí's family name include Gaudy or Gaudin.
 Gaudí's exact birthplace is unknown because no supporting documents have been found, leading to a controversy about whether he was born in Reus or Riudoms, two neighbouring municipalities of the
Gaudí's exact birthplace is unknown because no supporting documents have been found, leading to a controversy about whether he was born in Reus or Riudoms, two neighbouring municipalities of the Baix Camp
Baix Camp () is a comarca of Catalonia. It is one of the three comarques into which Camp de Tarragona was divided in the comarcal division of 1936.
Baix Camp is located on the coast, between Tarragonès to the northeast and Baix Ebre to the sout ...
district. Most of Gaudí's identification documents from both his student and professional years gave Reus as his birthplace. Gaudí stated on various occasions that he was born in Riudoms, his paternal family's village. Gaudí was baptised
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
in the church of Sant Pere Apòstol in Reus the day after his birth under the name "Antoni Plàcid Guillem Gaudí i Cornet".
Gaudí had a deep appreciation for his native land and great pride in his Mediterranean heritage for his art. He believed Mediterranean people to be endowed with creativity, originality and an innate sense for art and design. Gaudí reportedly described this distinction by stating, "We own the image. Fantasy comes from the ghosts. Fantasy is what people in the North own. We are concrete. The image comes from the Mediterranean. Orestes
In Greek mythology, Orestes or Orestis (; grc-gre, Ὀρέστης ) was the son of Clytemnestra and Agamemnon, and the brother of Electra. He is the subject of several Ancient Greek plays and of various myths connected with his madness and ...
knows his way, where Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
is torn apart by his doubts." Time spent outdoors, particularly during summer stays in the Gaudí family home Mas de la Calderera, afforded Gaudí the opportunity to study nature. Gaudí's enjoyment of the natural world led him to join the Centre Excursionista de Catalunya in 1879 at the age of 27. The organisation arranged expeditions to explore Catalonia and southern France, often riding on horseback or walking ten kilometres a day.
 Young Gaudí suffered from poor health, including
Young Gaudí suffered from poor health, including rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including art ...
, which may have contributed to his reticent and reserved character. These health concerns and the hygienist theories of Dr. Kneipp contributed to Gaudí's decision to adopt vegetarianism early in his life. His religious faith and strict vegetarianism led him to undertake several lengthy and severe fasts
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
. These fasts were often unhealthy and occasionally, as in 1894, led to life-threatening illness.
Gaudí attended a nursery school run by Francesc Berenguer, whose son, also called Francesc, was later one of Gaudí's main assistants. He enrolled in the Piarists
The Piarists (), officially named the Order of Poor Clerics Regular of the Mother of God of the Pious Schools ( la, Ordo Clericorum Regularium pauperum Matris Dei Scholarum Piarum), abbreviated SchP, is a religious order of clerics regular of the ...
school in Reus where he displayed his artistic talents via drawings for a seminar called ''El Arlequín'' (the Harlequin). During this time, he worked as an apprentice in the "Vapor Nou" textile mill
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
in Reus. In 1868, he moved to Barcelona to study teaching in the Convent del Carme. In his adolescent years, Gaudí became interested in utopian socialism
Utopian socialism is the term often used to describe the first current of modern socialism and socialist thought as exemplified by the work of Henri de Saint-Simon, Charles Fourier, Étienne Cabet, and Robert Owen. Utopian socialism is often de ...
and, together with his fellow students Eduard Toda i Güell and Josep Ribera i Sans, planned a restoration of the Poblet Monastery
Poblet Abbey, otherwise the Royal Abbey of Santa Maria de Poblet ( ca, Reial Monestir de Santa Maria de Poblet), is a Cistercian monastery, founded in 1151, located at the foot of the Prades Mountains, in the comarca of Conca de Barberà, in Ca ...
that would have transformed it into a Utopian phalanstère
A ''phalanstère'' (or phalanstery) was a type of building designed for a self-contained utopian community, ideally consisting of 500–2000 people working together for mutual benefit, and developed in the early 19th century by Charles Fourier. ...
.
Between 1875 and 1878, Gaudí completed his compulsory military service in the infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine i ...
regiment in Barcelona as a Military Administrator. Most of his service was spent on sick leave, enabling him to continue his studies. His poor health kept him from having to fight in the Third Carlist War
The Third Carlist War ( es, Tercera Guerra Carlista) (1872–1876) was the last Carlist War in Spain. It is sometimes referred to as the "Second Carlist War", as the earlier "Second" War (1847–1849) was smaller in scale and relatively trivial ...
, which lasted from 1872 to 1876. In 1876, Gaudí's mother died at the age of 57, as did his 25-year-old brother Francesc, who had just graduated as a physician. During this time Gaudí studied architecture at the Llotja School and the Barcelona Higher School of Architecture, graduating in 1878. To finance his studies, Gaudí worked as a draughtsman A draughtsman (British spelling) or draftsman (American spelling) may refer to:
* An architectural drafter, who produced architectural drawings until the late 20th century
* An artist who produces drawings that rival or surpass their other types ...
for various architects and constructors such as Leandre Serrallach, Joan Martorell, Emili Sala Cortés, Francisco de Paula del Villar y Lozano and Josep Fontserè. In addition to his architecture classes, he studied French, history, economics, philosophy, and aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed thr ...
. His grades were average and he occasionally failed courses. When handing him his degree, Elies Rogent
Elies Rogent i Amat (Barcelona 18 July 1821 – Barcelona 21 February 1897), was a Catalan architect of Spanish nationality.
Life and work
He studied at the school of Architecture in Madrid, from which he graduated on 20 February 1851. Elies Ro ...
, director of Barcelona Architecture School, said: "We have given this academic title either to a fool or a genius. Time will show." Gaudí, when receiving his degree, reportedly told his friend, the sculptor Llorenç Matamala, with his ironical sense of humour, "Llorenç, they're saying I'm an architect now."
Adulthood and professional work
 Gaudí's first projects were the lampposts he designed for the
Gaudí's first projects were the lampposts he designed for the Plaça Reial
Plaça Reial (In Spanish ''Plaza Real'', meaning "Royal Plaza") is a square in the Barri Gòtic of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is close to La Rambla, and is a popular tourist attraction, especially at night. The plaza hosts many restauran ...
in Barcelona, the unfinished Girossi newsstands, and the Cooperativa Obrera Mataronense (Workers' Cooperative of Mataró
Mataró () is the capital and largest town of the ''comarca'' of the Maresme, in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia Autonomous Community, Spain. It is located on the Costa del Maresme, to the south of Costa Brava, between Cabrera de Mar and Sa ...
) building. He gained wider recognition for his first important commission, the Casa Vicens
Casa Vicens () is a modernist building situated in the Gràcia neighbourhood of Barcelona. It is the work of architect Antoni Gaudí and is considered to be his first major project. It was built between 1883 and 1885, although Gaudí drew up the ...
, and subsequently received more significant proposals. At the Paris World's Fair of 1878 Gaudí displayed a showcase he had produced for the glove manufacturer Comella. Its functional and aesthetic ''modernista'' design impressed Catalan industrialist Eusebi Güell, who then commissioned some of Gaudí's most outstanding work: the Güell wine cellars, the Güell pavilions, the Palau Güell
The Palau Güell (, en, Güell Palace) is a mansion designed by the architect Antoni Gaudí for the industrial tycoon Eusebi Güell, and was built between 1886 and 1888. It is situated on the Carrer Nou de la Rambla, in the El Raval neighbor ...
(Güell palace), the Park Güell
Parc Güell ( ca, Parc Güell ; es, Parque Güell) is a privatized park system composed of gardens and architectural elements located on Carmel Hill, in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. Carmel Hill belongs to the mountain range of Collserola – t ...
(Güell park) and the crypt of the church of the Colònia Güell. Gaudí also became a friend of the marquis of Comillas, the father-in-law of Count Güell, for whom he designed " El Capricho" in Comillas
Comillas is a small township and municipality in the northern reaches of Spain, in the autonomous community of Cantabria. The Marquessate of Comillas, a fiefdom of Spanish nobility, holds ceremonial office in the seat of power at a small castle ...
.
In 1883 Gaudí was put in charge of the recently initiated project to build a Barcelona church called Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família (Basilica and Expiatory Church of the Holy Family, or Sagrada Família). Gaudí completely changed the initial design and imbued it with his own distinctive style. From 1915 until his death he devoted himself entirely to this project. Given the number of commissions he began receiving, he had to rely on his team to work on multiple projects simultaneously. His team consisted of professionals from all fields of construction. Several of the architects who worked under him became prominent in the field later on, such as Josep Maria Jujol
José María Jujol Gibert (16 September 1879 – 1 May 1949) was a Spanish architect. Jujol's wide field of activity ranged from furniture designs and painting, to architecture. He worked with Antoni Gaudí on many of his most famous works. ...
, Joan Rubió
Joan Rubió y Bellver (; 24 April 1870 – 30 November 1952) was a Spanish architect famous for his contributions to the Catalan '' Modernista'' movement.
Biography
Early life, family
Rubió was born in Reus, Province of Tarragona. He was al ...
, Cèsar Martinell, Francesc Folguera and Josep Francesc Ràfols. In 1885, Gaudí moved to rural Sant Feliu de Codines
Sant Feliu de Codines () is a municipality in the comarca of Vallès Oriental, Catalonia, Spain. It is located in the north-west corner of the comarca, on the border with comarca of Moianès to the north, and the comarca of Vallès Occidental to th ...
to escape the cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
epidemic that was ravaging Barcelona. He lived in Francesc Ullar's house, for whom he designed a dinner table as a sign of his gratitude.
 The 1888 World Fair was one of the era's major events in Barcelona and represented a key point in the history of the ''Modernisme'' movement. Leading architects displayed their best works, including Gaudí, who showcased the building he had designed for the Compañía Trasatlántica (Transatlantic Company). Consequently, he received a commission to restructure the Saló de Cent of the Barcelona City Council, but this project was ultimately not carried out. In the early 1890s Gaudí received two commissions from outside of Catalonia, namely the
The 1888 World Fair was one of the era's major events in Barcelona and represented a key point in the history of the ''Modernisme'' movement. Leading architects displayed their best works, including Gaudí, who showcased the building he had designed for the Compañía Trasatlántica (Transatlantic Company). Consequently, he received a commission to restructure the Saló de Cent of the Barcelona City Council, but this project was ultimately not carried out. In the early 1890s Gaudí received two commissions from outside of Catalonia, namely the Episcopal Palace, Astorga
The Episcopal Palace of Astorga (Spanish: ''Palacio Episcopal de Astorga'') is a building by Catalan architect Antoni Gaudí. It was built between 1889 and 1913. Designed in the Catalan Modernisme style, it is one of only three buildings by G ...
, and the Casa Botines
The Casa Botines (built 1891-1892) is a Modernist building in León, Spain designed by Antoni Gaudí. It currently houses a museum dedicated to Gaudi, Spanish art of the 19th and 20th centuries, and the history of the building itself.
After being ...
in León. These works contributed to Gaudí's growing renown across Spain. In 1891, he travelled to Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most pop ...
and Tangiers
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capit ...
to examine the site for a project for the Franciscan Catholic Missions that the 2nd marquis of Comillas had requested him to design.
 In 1899 Gaudí joined the
In 1899 Gaudí joined the Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc
The Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc (, meaning in English "Saint Lluc Artists' Circle") is an arts society which was founded in Barcelona (Catalonia) in 1893 by Joan Llimona, Josep Llimona, Antoni Utrillo, Alexandre de Riquer, the city councillo ...
(Saint Luke artistic circle), a Catholic artistic society founded in 1893 by the bishop Josep Torras i Bages
Josep Torras i Bages (), born at Les Cabanyes, Alt Penedès, on 12 September 1846, died at Vic, Osona, on 7 February 1916, was a Catalan thinker, writer, and bishop. He was one of the main figures in the turn of the 20th century Catholic Cat ...
and the brothers Josep and Joan Llimona. He also joined the Lliga Espiritual de la Mare de Déu de Montserrat (spiritual league of Our lady of Montserrat), another Catholic Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
organisation. The conservative and religious character of his political thought was closely linked to his defence of the cultural identity of the Catalan people.
At the beginning of the century, Gaudí was working on numerous projects simultaneously. They reflected his shift to a more personal style inspired by nature. In 1900, he received an award for the best building of the year from the Barcelona City Council for his Casa Calvet
Casa Calvet () is a building, designed by Antoni Gaudí for a textile manufacturer which served as both a commercial property (in the basement and on the ground floor) and a residence. It is located at Carrer de Casp 48, Eixample district of Ba ...
. During the first decade of the century Gaudí dedicated himself to projects like the Casa Figueras (Figueras house, better known as Bellesguard
Bellesguard (, "Beautiful View"), also known as Casa Figueres, is a modernist manor house designed by Catalan architect Antoni Gaudí, which was constructed between 1900 and 1909.
It is located at the Sarrià-Sant Gervasi district of Barcelona ...
), the Park Güell
Parc Güell ( ca, Parc Güell ; es, Parque Güell) is a privatized park system composed of gardens and architectural elements located on Carmel Hill, in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. Carmel Hill belongs to the mountain range of Collserola – t ...
, an unsuccessful urbanisation project, and the restoration of the Cathedral of Palma de Mallorca, for which he visited Majorca several times. Between 1904 and 1910 he constructed the Casa Batlló
() is a building in the center of Barcelona. It was designed by Antoni Gaudí, and is considered one of his masterpieces. A remodel of a previously built house, it was redesigned in 1904 by Gaudí and has been refurbished several times after th ...
(Batlló house) and the Casa Milà
Casa Milà (, ), popularly known as ''La Pedrera'' (, ; "the stone quarry") in reference to its unconventional rough-hewn appearance, is a '' Modernista'' building in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It was the last private residence designed by arc ...
(Milá house), two of his most emblematic works.
 As a result of Gaudí's increasing fame, in 1902 the painter Joan Llimona chose Gaudí's features to represent
As a result of Gaudí's increasing fame, in 1902 the painter Joan Llimona chose Gaudí's features to represent Saint Philip Neri
Philip Romolo Neri ( ; it, italics=no, Filippo Romolo Neri, ; 22 July 151526 May 1595), known as the "Second Apostle of Rome", after Saint Peter, was an Italian priest noted for founding a society of secular clergy called the Congregation of t ...
in the paintings for the aisle of the Sant Felip Neri church in Barcelona. Together with Joan Santaló, son of his friend the physician Pere Santaló, he unsuccessfully founded a wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a ...
manufacturing company the same year.
After moving to Barcelona, Gaudí frequently changed his address: as a student he lived in residences, generally in the area of the Gothic Quarter; when he started his career he moved around several rented flats in the Eixample
The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and what were once surrounding small towns (Sants, Gràcia, Sant Andreu, etc.), constructed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its population was 262,000 at t ...
area. Finally, in 1906, he settled in a house in the Güell Park that he owned and which had been constructed by his assistant Francesc Berenguer as a showcase property for the estate. It has since been transformed into the Gaudí Museum. There he lived with his father (who died in 1906 at the age of 93) and his niece Rosa Egea Gaudí (who died in 1912 at the age of 36). He lived in the house until 1925, several months before his death, when he began residing inside the workshop of the Sagrada Família.
An event that had a profound impact on Gaudí's personality was Tragic Week in 1909. Gaudí remained in his house in Güell Park during this turbulent period. The anticlerical atmosphere and attacks on churches and convents caused Gaudí to worry for the safety of the Sagrada Família, but the building escaped damage.
In 1910, an exhibition in the Grand Palais
The Grand Palais des Champs-Élysées ( en, Great Palace of the Elysian Fields), commonly known as the Grand Palais (English: Great Palace), is a historic site, exhibition hall and museum complex located at the Champs-Élysées in the 8th arro ...
of Paris was devoted to his work, during the annual salon of the Société des Beaux-Arts (Fine Arts Society) of France. Gaudí participated on the invitation of count Güell, displaying a series of pictures, plans and plaster scale models of several of his works. Although he participated ''hors concours'', he received good reviews from the French press. A large part of this exposition could be seen the following year at the I Salón Nacional de Arquitectura that took place in the municipal exhibition hall of El Buen Retiro in Madrid.
During the Paris exposition in May 1910, Gaudí spent a holiday in Vic
Vic (; es, Vic or Pancracio Celdrán (2004). Diccionario de topónimos españoles y sus gentilicios (5ª edición). Madrid: Espasa Calpe. p. 843. ISBN 978-84-670-3054-9. «Vic o Vich (viquense, vigitano, vigatán, ausense, ausetano, ausonense): ...
, where he designed two basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
lampposts and wrought iron for the Plaça Major of Vic in honor of Jaume Balmes
Jaime Luciano Balmes y Urpiá ( ca, Jaume Llucià Antoni Balmes i Urpià; August 28, 1810July 9, 1848) was a Spanish philosopher, theologian, Catholic apologist, sociologist and political writer. Familiar with the doctrine of Saint Thomas Aqui ...
's centenary. The following year he resided as a convalescent in Puigcerdà
Puigcerdà (; es, Puigcerdá) is the capital of the '' Catalan comarca'' of Cerdanya, in the province of Girona, Catalonia, northern Spain, near the Segre River and on the border with France (it abuts directly onto the French town of Bourg-Ma ...
while suffering from tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
. During this time he conceived the idea for the façade of the Passion of the Sagrada Família. Due to ill health he prepared a will
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
at the office of the notary Ramon Cantó i Figueres on 9 June, but later completely recovered.
The decade from 1910 was a hard one for Gaudí. During this decade, the architect experienced the deaths of his niece Rosa in 1912 and his main collaborator Francesc Berenguer in 1914; a severe economic crisis which paralysed work on the Sagrada Família in 1915; the 1916 death of his friend Josep Torras i Bages, bishop of Vic; the 1917 disruption of work at the Colonia Güell; and the 1918 death of his friend and patron Eusebi Güell. Perhaps because of these tragedies he devoted himself entirely to the Sagrada Família from 1915, taking refuge in his work. Gaudí confessed to his collaborators:
Gaudí dedicated the last years of his life entirely to the "Cathedral of the Poor", as it was commonly known, for which he took alms
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of virtue or Charity (practice), charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving, and it is a widespread p ...
in order to continue. Apart from his dedication to this cause, he participated in few other activities, the majority of which were related to his Catholic faith: in 1916 he participated in a course about Gregorian chant
Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin (and occasionally Greek) of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe durin ...
at the Palau de la Música Catalana
Palau de la Música Catalana (, en, Palace of Catalan Music) is a concert hall in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. Designed in the Catalan '' modernista'' style by the architect Lluís Domènech i Montaner, it was built between 1905 and 1908 for O ...
taught by the Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monk Gregori M. Sunyol.
In 1936, during the course of the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
, Gaudí's workshop in the Sagrada Familia Sagrada is a Spanish word meaning "sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. T ...
was assaulted, destroying a large number of documents, plans and models of the modernist architect.
Personal life
Gaudí devoted his life entirely to his profession, remaining single. He is known to have been attracted to only one woman—Josefa Moreu, teacher at the Mataró Cooperative, in 1884—but this was not reciprocated. Thereafter Gaudí took refuge in the profound spiritual peace his Catholic faith offered him. Gaudí is often depicted as unsociable and unpleasant, a man of gruff reactions and arrogant gestures. However, those who were close to him described him as friendly and polite, pleasant to talk to and faithful to friends. Among these, his patrons Eusebi Güell and the bishop of Vic, Josep Torras i Bages, stand out, as well as the writersJoan Maragall
Joan Maragall i Gorina (; 10 October 1860 in Barcelona – 20 December 1911) was a Spanish poet, journalist and translator, the foremost member of the ''modernisme'' movement in literature. His manuscripts are preserved in the Joan Maragall ...
and Jacint Verdaguer
Jacint Verdaguer i Santaló (; 17 May 1845 – 10 June 1902) was a Catalan / Spanish writer, regarded as one of the greatest poets of Catalan literature and a prominent literary figure of the Renaixença, a cultural revival movement of the ...
, the physician Pere Santaló and some of his most faithful collaborators, such as Francesc Berenguer and Llorenç Matamala.
 Gaudí's personal appearance—Nordic features, blond hair and blue eyes—changed radically over the course of time. As a young man, he dressed like a
Gaudí's personal appearance—Nordic features, blond hair and blue eyes—changed radically over the course of time. As a young man, he dressed like a dandy
A dandy is a man who places particular importance upon physical appearance, refined language, and leisurely hobbies, pursued with the appearance of nonchalance. A dandy could be a self-made man who strove to imitate an aristocratic lifestyle desp ...
in costly suits, sporting well-groomed hair and beard, indulging gourmet
Gourmet (, ) is a cultural idea associated with the culinary arts of fine food and drink, or haute cuisine, which is characterized by refined, even elaborate preparations and presentations of aesthetically balanced meals of several contrasting, of ...
taste, making frequent visits to the theatre and the opera and visiting his project sites in a horse carriage. The older Gaudí ate frugally, dressed in old, worn-out suits, and neglected his appearance to the extent that sometimes he was taken for a beggar
Begging (also panhandling) is the practice of imploring others to grant a favor, often a gift of money, with little or no expectation of reciprocation. A person doing such is called a beggar or panhandler. Beggars may operate in public place ...
, such as after the accident that caused his death.
Gaudí left hardly any written documents, apart from technical reports of his works required by official authorities, some letters to friends (particularly to Joan Maragall) and a few journal articles. Some quotes collected by his assistants and disciples have been preserved, above all by Josep Francesc Ràfols, Joan Bergós, Cèsar Martinell and Isidre Puig i Boada. The only written document Gaudí left is known as the Manuscrito de Reus (Reus Manuscript) (1873–1878), a kind of student diary in which he collected diverse impressions of architecture and decorating, putting forward his ideas on the subject. Included are an analysis of the Christian church and of his ancestral home, as well as a text about ornamentation and comments on the design of a desk.
Catalan identity
Gaudí was a committed Catalan nationalist and proponent of Catalan culture but was reluctant to become politically active to campaign for its autonomy. Politicians, such asFrancesc Cambó
Francesc Cambó i Batlle (; 2 September 1876 – 30 April 1947) was a conservative Spanish politician from Catalonia, founder and leader of the autonomist party ''Lliga Regionalista''. He was a minister in several Spanish governments. He supported ...
and Enric Prat de la Riba
Enric Prat de la Riba i Sarrà (; 29 November 1870 – 1 August 1917) was a Catalan politician, lawyer and writer. He was a member of the , where one of the earliest definitions of Catalan nationalism was formulated. He became the first Pr ...
, suggested that he run for deputy
Deputy or depute may refer to:
* Steward (office)
* Khalifa, an Arabic title that can signify "deputy"
* Deputy (legislator), a legislator in many countries and regions, including:
** A member of a Chamber of Deputies, for example in Italy, Spai ...
but he refused. Compared to some of his colleagues and contemporaries, his Catalan nationalism was less political and more geared towards art, history, culture, and language.
Gaudí has a deep attachment to his native Catalan language
Catalan (; autonym: , ), known in the Valencian Community and Carche as ''Valencian'' (autonym: ), is a Western Romance language. It is the official language of Andorra, and an official language of three autonomous communities in eastern Spa ...
. When King of Spain
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, Alfo ...
visited the Sagrada Familia Sagrada is a Spanish word meaning "sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. T ...
, Gaudí declined to speak in Spanish and only spoke to him in Catalan. Gaudí also refused to speak Spanish with Prime Minister Antonio Maura
Antonio Maura Montaner (2 May 1853 – 13 December 1925) was Prime Minister of Spain on five separate occasions.
Early life
Maura was born in Palma, on the island of Mallorca, and studied law in Madrid. In 1878, Maura married Constanci ...
, who, being a native of Mallorca and therefore Catalan-speaking, ended up responding to Gaudí in Catalan, thus breaking protocol in front of the King Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, Alfo ...
. Similarly, when philosopher Miguel de Unamuno
Miguel de Unamuno y Jugo (29 September 1864 – 31 December 1936) was a Spanish essayist, novelist, poet, playwright, philosopher, professor of Greek and Classics, and later rector at the University of Salamanca.
His major philosophical essay w ...
visited the Sagrada Família, poet Joan Maragall
Joan Maragall i Gorina (; 10 October 1860 in Barcelona – 20 December 1911) was a Spanish poet, journalist and translator, the foremost member of the ''modernisme'' movement in literature. His manuscripts are preserved in the Joan Maragall ...
had to translate Gaudí's Catalan tour into Spanish. Gaudí also spoke Catalan in public, despite it being declared illegal by the dictatorship of Primo de Rivera Primo de Rivera is a Spanish family prominent in politics of the 19th and 20th centuries:
*Fernando Primo de Rivera (1831–1921), Spanish politician and soldier
*Miguel Primo de Rivera (1870–1930), nephew of Fernando, military officer and dictat ...
, which severely tried to suppress Catalan culture.
 In 1920 he was beaten by police in a riot during the
In 1920 he was beaten by police in a riot during the Floral Games
Floral Games were any of a series of historically related poetry contests with floral prizes. In Occitan, their original language, and Catalan they are known as ''Jocs florals'' (; modern Occitan: ''Jòcs florals'' , or ''floraus'' ). In French the ...
celebrations, a Catalan culture celebration. On 11 September 1924, National Day of Catalonia
)
, type = National day
, longtype = National day
, significance = Commemorates the fall of Barcelona during the War of the Spanish Succession in 1714.
, image = Rafael Casanova 11 Setembre.jpg
, caption = Floral of ...
, he was beaten at a demonstration against the banning of the Catalan language by the dictatorship of Primo de Rivera. Gaudí was arrested by the Civil Guard as he was headed to the church of Sant Just i Sant Pastor to attend a mass in memory of the Catalonian patriots. Gaudí refused to speak Castilian Spanish and kept responding in Catalan, stating that "My profession obliges me to pay my taxes, and I pay them, but not to stop speaking my own language." He was then taken to prison, from which he was freed after paying 50 pesetas bail.
Gaudí incorporated elements of Catalan culture and identity in his works. Gaudí was part of the Catalan Renaissance (''Renaixença'' in Catalan), romantic revivalist and cultural movement that aimed at restoring Catalan language and arts combined with an anti-Castilian political "Catalanism." Park Güell, which was commissioned by Catalan patriot Eusebi Güell
Eusebi Güell i Bacigalupi, 1st Count of Güell (; 15 December 1846 – 8 July 1918) was a Catalan entrepreneur who profited greatly from the industrial revolution in Catalonia in the late 19th century. He married Luisa Isabel Lopez y Bru —a d ...
, was envisioned by Gaudí as a focus of Catalan nationalism and cultural aspirations. Gaudí inserted numerous motifs from Catalan culture in the park, such as a large mosaic with the Catalan flag or the representations of dragons, which were seen as Catalan symbols during the ''Renaixença'' because of their connection to the Catalan patron saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldier ...
. The Park was also host to the ''First Congress of the Catalan Language'' while it was still under construction. Casa Batlló
() is a building in the center of Barcelona. It was designed by Antoni Gaudí, and is considered one of his masterpieces. A remodel of a previously built house, it was redesigned in 1904 by Gaudí and has been refurbished several times after th ...
, which is considered among Gaudí's finest examples of Catalan Modernism, is known as "the House of the Dragon" due to its symbolism related to the legend of Saint George, the patron saint of Catalonia. The Sagrada Familia Sagrada is a Spanish word meaning "sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. T ...
is decorated with many words and writings, such as on the towers and doors, and are mainly in Catalan, such as the Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also called the Our Father or Pater Noster, is a central Christian prayer which Jesus taught as the way to pray. Two versions of this prayer are recorded in the gospels: a longer form within the Sermon on the Mount in the Gosp ...
in Catalan on the main doors. The Palau Güell
The Palau Güell (, en, Güell Palace) is a mansion designed by the architect Antoni Gaudí for the industrial tycoon Eusebi Güell, and was built between 1886 and 1888. It is situated on the Carrer Nou de la Rambla, in the El Raval neighbor ...
's entrance is decorated with the Catalan coat of arms and a helmet with a winged dragon. His project for Barcelona's Muralla de Mar featured shields and names of battles and Catalan admirals. The Torre Bellesguard (1900–1909), former summer palace of King Martin I the Humane, was restored by Gaudí and its spire decorated the Catalan flag and the royal crown. He also designed a project (never terminated) to crown El Cavall Bernat (a mountain peak) with a viewpoint in the shape of a royal crown and a 20 meters (66 ft) high Catalan coat of arms. The Catalan flag was also present in a banner designed for Our Lady of Mercy of Reus
Reus () is the capital of Baix Camp, in the province of Tarragona, in Catalonia, Spain. The area has always been an important producer of wines and spirits, and gained continental importance at the time of the Phylloxera plague. Nowadays it is k ...
and a monument (not completed) to Catalan politician Enric Prat de la Riba
Enric Prat de la Riba i Sarrà (; 29 November 1870 – 1 August 1917) was a Catalan politician, lawyer and writer. He was a member of the , where one of the earliest definitions of Catalan nationalism was formulated. He became the first Pr ...
in Castellterçol
Castellterçol is a town in Catalonia. It is in the province of Barcelona, in the comarca of Moianès; until May 2015 it was in Vallès Oriental
Vallès Oriental () is a comarca (county) in Catalonia, Spain. Its capital is Granollers. Along wit ...
. Even before he became an architect, he was very interested in the history of medieval Catalonia, when it was a big player in Mediterranean politics and history. He joined several Catalan associations, such as Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc
The Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc (, meaning in English "Saint Lluc Artists' Circle") is an arts society which was founded in Barcelona (Catalonia) in 1893 by Joan Llimona, Josep Llimona, Antoni Utrillo, Alexandre de Riquer, the city councillo ...
, ''Lliga Espiritual de la Mare de Déu de Montserrat'', ''Associació Catalanista d'Excursions Científiques''. The latter was a group dedicated to preserve and celebrate the art, landscape, culture, and language of Catalunya.
Death
 On 7 June 1926, Gaudí was taking his daily walk to the Sant Felip Neri church for his habitual prayer and confession. While walking along the
On 7 June 1926, Gaudí was taking his daily walk to the Sant Felip Neri church for his habitual prayer and confession. While walking along the Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes
Gran may refer to:
People
*Grandmother, affectionately known as "gran"
* Gran (name)
Places
* Gran, the historical German name for Esztergom, a city and the primatial metropolitan see of Hungary
* Gran, Norway, a municipality in Innlandet coun ...
between Girona and Bailén streets, he was struck by a passing number 30 tram and lost consciousness. Assumed to be a beggar, the unconscious Gaudí did not receive immediate aid. Eventually some passers-by transported him in a taxi to the Santa Creu Hospital, where he received rudimentary care.
By the time that the chaplain of the Sagrada Família, Mosén Gil Parés, recognised him on the following day, Gaudí's condition had deteriorated too severely to benefit from additional treatment. Gaudí died on 10 June 1926 at the age of 73 and was buried two days later. A large crowd gathered to bid farewell to him in the chapel of Our Lady of Mount Carmel in the crypt of the Sagrada Família. His gravestone bears this inscription:
Antonius Gaudí Cornet. Reusensis. Annos natus LXXIV, vitae exemplaris vir, eximiusque artifex, mirabilis operis hujus, templi auctor, pie obiit Barcinone die X Junii MCMXXVI, hinc cineres tanti hominis, resurrectionem mortuorum expectant. R.I.P.
(Antoni Gaudí Cornet. From Reus. At the age of 74, a man of exemplary life, and an extraordinary craftsman, the author of this marvelous work, the church, died piously in Barcelona on the tenth day of June 1926; henceforward the ashes of so great a man await the resurrection of the dead. May he rest in peace.)
Style
Gaudí and ''Modernisme''
 Gaudí's professional life was distinctive in that he never ceased to investigate mechanical building structures. Early on, Gaudí was inspired by oriental arts (India,
Gaudí's professional life was distinctive in that he never ceased to investigate mechanical building structures. Early on, Gaudí was inspired by oriental arts (India, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Japan) through the study of the historicist
Historicism is an approach to explaining the existence of phenomena, especially social and cultural practices (including ideas and beliefs), by studying their history, that is, by studying the process by which they came about. The term is widely u ...
architectural theoreticians, such as Walter Pater
Walter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 – 30 July 1894) was an English essayist, art critic and literary critic, and fiction writer, regarded as one of the great stylists. His first and most often reprinted book, ''Studies in the History of the Re ...
, John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and politi ...
and William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was a British textile designer, poet, artist, novelist, architectural conservationist, printer, translator and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He ...
. The influence of the Oriental movement can be seen in works like the Capricho, the Güell Palace, the Güell Pavilions and the Casa Vicens
Casa Vicens () is a modernist building situated in the Gràcia neighbourhood of Barcelona. It is the work of architect Antoni Gaudí and is considered to be his first major project. It was built between 1883 and 1885, although Gaudí drew up the ...
. Later on, he adhered to the neo-Gothic movement that was in fashion at the time, following the ideas of the French architect Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc (; 27 January 181417 September 1879) was a French architect and author who restored many prominent medieval landmarks in France, including those which had been damaged or abandoned during the French Revolution. H ...
. This influence is reflected in the Teresian College, the Episcopal Palace in Astorga, the Casa Botines and the Bellesguard house as well as in the crypt and the apse of the Sagrada Família. Eventually, Gaudí embarked on a more personal phase, with the organic style inspired by nature in which he would build his major works.
During his time as a student, Gaudí was able to study a collection of photographs of Egyptian, Indian, Persian, Mayan, Chinese and Japanese art owned by the School of Architecture. The collection also included Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
monuments in Spain, which left a deep mark on him and served as an inspiration in many of his works. He also studied the book ''Plans, elevations, sections and details of the Alhambra'' by Owen Jones
Owen Jones (born 8 August 1984) is a British newspaper columnist, political commentator, journalist, author, and left-wing activist. He writes a column for ''The Guardian'' and contributes to the ''New Statesman'' and '' Tribune.'' He has two ...
, which he borrowed from the School's library. He took various structural and ornamental solutions from Nasrid and Mudéjar
Mudéjar ( , also , , ca, mudèjar , ; from ar, مدجن, mudajjan, subjugated; tamed; domesticated) refers to the group of Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period despite the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for ...
art, which he used with variations and stylistic freedom in his works. Notably, Gaudí observed of Islamic art
Islamic art is a part of Islamic culture and encompasses the visual arts produced since the 7th century CE by people who lived within territories inhabited or ruled by Muslim populations. Referring to characteristic traditions across a wide ra ...
its spatial uncertainty, its concept of structures with limitless space; its feeling of sequence, fragmented with holes and partitions, which create a divide without disrupting the feeling of open space by enclosing it with barriers.
Undoubtedly the style that most influenced him was the Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
, promoted in the latter half of the 19th century by the theoretical works of Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc (; 27 January 181417 September 1879) was a French architect and author who restored many prominent medieval landmarks in France, including those which had been damaged or abandoned during the French Revolution. H ...
. The French architect called for studying the styles of the past and adapting them in a rational manner, taking into account both structure and design. Nonetheless, for Gaudí the Gothic style was "imperfect", because despite the effectiveness of some of its structural solutions it was an art that had yet to be "perfected". In his own words:
 After these initial influences, Gaudí moved towards ''Modernisme'', then in its heyday. ''Modernisme'' in its earlier stages was inspired by historic architecture. Its practitioners saw its return to the past as a response to the industrial forms imposed by the
After these initial influences, Gaudí moved towards ''Modernisme'', then in its heyday. ''Modernisme'' in its earlier stages was inspired by historic architecture. Its practitioners saw its return to the past as a response to the industrial forms imposed by the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
's technological advances. The use of these older styles represented a moral regeneration that allowed the bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
to identify with values they regarded as their cultural roots. The ''Renaixença
The ''Renaixença'' (; also written ''Renaixensa'' before spelling standardisation), or Catalan Renaissance, was a romantic revivalist movement in Catalan language and culture through the mid 19th century, akin to the Galician ''Rexurdimento ...
'' (rebirth), the revival of Catalan culture that began in the second half of the 19th century, brought more Gothic forms into the Catalan "national" style that aimed to combine nationalism and cosmopolitanism while at the same time integrating into the European modernizing movement.
Some essential features of ''Modernisme'' were: an anticlassical language inherited from Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
with a tendency to lyricism and subjectivity; the determined connection of architecture with the applied arts and artistic work that produced an overtly ornamental style; the use of new materials from which emerged a mixed constructional language, rich in contrasts, that sought a plastic effect for the whole; a strong sense of optimism and faith in progress that produced an emphatic art that reflected the atmosphere of prosperity of the time, above all of the esthetic of the bourgeoisie.
Quest for a new architectural language
Gaudí is usually considered the great master of Catalan Modernism, but his works go beyond any one style or classification. They are imaginative works that find their main inspiration in geometry and nature forms. Gaudí studied organic andanarchic
Anarchy is a society without a government. It may also refer to a society or group of people that entirely rejects a set hierarchy. ''Anarchy'' was first used in English in 1539, meaning "an absence of government". Pierre-Joseph Proudhon adopted ...
geometric forms of nature thoroughly, searching for a way to give expression to these forms in architecture. Some of his greatest inspirations came from visits to the mountain of Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, the caves of Mallorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Bal ...
, the saltpetre
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitra ...
caves in Collbató
Collbató () is a municipality in the ''comarca'' of the Baix Llobregat in Catalonia, Spain. It is situated on the southern slopes of Montserrat. The area has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC, as shown by Neolithic remains found in caves a ...
, the crag of Fra Guerau in the Prades Mountains
Prades Mountains, also known as Muntanyes de Prades, is a large calcareous mountain massif straddling the comarcas of Alt Camp, Baix Camp, Conca de Barberà, Garrigues and Priorat, in Catalonia, Spain. They are a Site of Community Importance.
The ...
behind Reus, the Pareis mountain in the north of Mallorca and Sant Miquel del Fai
Sant Miquel del Fai is a cenobitic Benedictine monastery in Bigues i Riells, Catalonia, Spain. The 11th-century building was declared a Bien de Interés Cultural landmark in 1988.
Location
The monastery is located in a well-preserved natural env ...
in Bigues i Riells.
Geometrical forms
 This study of nature translated into his use of ruled geometrical forms such as the
This study of nature translated into his use of ruled geometrical forms such as the hyperbolic paraboloid
In geometry, a paraboloid is a quadric surface that has exactly one axis of symmetry and no center of symmetry. The term "paraboloid" is derived from parabola, which refers to a conic section that has a similar property of symmetry.
Every plane ...
, the hyperboloid
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by defo ...
, the helicoid
The helicoid, also known as helical surface, after the plane and the catenoid, is the third minimal surface to be known.
Description
It was described by Euler in 1774 and by Jean Baptiste Meusnier in 1776. Its name derives from its similarit ...
and the cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
, which reflect the forms Gaudí found in nature. Ruled surfaces are forms generated by a straight line known as the generatrix
In geometry, a generatrix () or describent is a point, curve or surface that, when moved along a given path, generates a new shape. The path directing the motion of the generatrix motion is called a directrix or dirigent.
Examples
A cone can be ...
, as it moves over one or several lines known as directrices. Gaudí found abundant examples of them in nature, for instance in rushes, reeds and bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s; he used to say that there is no better structure than the trunk of a tree or a human skeleton. These forms are at the same time functional and aesthetic, and Gaudí discovered how to adapt the language of nature to the structural forms of architecture. He used to equate the helicoid
The helicoid, also known as helical surface, after the plane and the catenoid, is the third minimal surface to be known.
Description
It was described by Euler in 1774 and by Jean Baptiste Meusnier in 1776. Its name derives from its similarit ...
form to movement and the hyperboloid
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by defo ...
to light. Concerning ruled surfaces, he said:
Another element widely used by Gaudí was the catenary arch
A catenary arch is a type of architectural arch that follows an inverted catenary curve. The catenary curve has been employed in buildings since ancient times. It forms an underlying principle to the overall system of vaults and buttresses in ...
. He had studied geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
thoroughly when he was young, studying numerous articles about engineering, a field that praised the virtues of the catenary curve as a mechanical element, one which at that time, however, was used only in the construction of suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridg ...
s. Gaudí was the first to use this element in common architecture. Catenary arches in works like the Casa Milà
Casa Milà (, ), popularly known as ''La Pedrera'' (, ; "the stone quarry") in reference to its unconventional rough-hewn appearance, is a '' Modernista'' building in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It was the last private residence designed by arc ...
, the Teresian College, the crypt of the Colònia Güell and the Sagrada Família
The Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família, shortened as the Sagrada Família, is an unfinished church in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is the largest unfinished Catholic church in the world. Designed by ...
allowed Gaudí to add an element of great strength to his structures, given that the catenary distributes the weight it regularly carries evenly, being affected only by self-canceling tangential
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More ...
forces.
Gaudí evolved from plane
Plane(s) most often refers to:
* Aero- or airplane, a powered, fixed-wing aircraft
* Plane (geometry), a flat, 2-dimensional surface
Plane or planes may also refer to:
Biology
* Plane (tree) or ''Platanus'', wetland native plant
* ''Planes' ...
to spatial geometry
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position (geometry), position of an element (i.e., Point (m ...
, to ruled geometry. These constructional forms are highly suited to the use of cheap materials such as brick. Gaudí frequently used brick laid with mortar in successive layers, as in the traditional Catalan vault
The Catalan vault ( ca, volta catalana), also called thin-tile vault, Catalan turn, Catalan arch, boveda ceiling (Spanish ''bóveda'' 'vault'), or timbrel vault, is a type of low brickwork arch forming a vaulted ceiling that often supports a floor ...
, using the brick laid flat instead of on its side. This quest for new structural solutions culminated between 1910 and 1920, when he exploited his research and experience in his masterpiece, the Sagrada Família
The Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família, shortened as the Sagrada Família, is an unfinished church in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is the largest unfinished Catholic church in the world. Designed by ...
. Gaudí conceived the interior of the church as if it were a forest, with a set of tree-like columns
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
divided into various branches to support a structure of intertwined hyperboloid vaults. He inclined the columns so they could better resist the perpendicular pressure on their section. He also gave them a double-turn helicoidal shape (right turn and left turn), as in the branches and trunks of trees. This created a structure that is now known as fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illu ...
. Together with a modulation of the space that divides it into small, independent and self-supporting modules, it creates a structure that perfectly supports the mechanical traction forces without need for buttresses
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral (si ...
, as required by the neo-Gothic style. Gaudí thus achieved a rational, structured and perfectly logical solution, creating at the same time a new architectural style that was original, simple, practical and aesthetic.
Surpassing the Gothic
This new constructional technique allowed Gaudí to achieve his greatest architectural goal; to perfect and go beyond Gothic style. The hyperboloid vaults have their center where Gothic vaults had their keystone, and the hyperboloid allows for a hole in this space to let natural light in. In the intersection between vaults, where Gothic vaults have ribs, the hyperboloid allows for holes as well, which Gaudí employed to give the impression of a starry sky. Gaudí complemented this organic vision of architecture with a unique spatial vision that allowed him to conceive his designs in three dimensions, unlike the flat design of traditional architecture. He used to say that he had acquired this spatial sense as a boy by looking at the drawings his father made of the boilers and stills he produced. Because of this spatial conception, Gaudí always preferred to work with casts and scale models or even improvise on-site as a work progressed. Reluctant to draw plans, only on rare occasions did he sketch his works—in fact, only when required by authorities. Another of Gaudí's innovations in the technical realm was the use of a scale model to calculate structures: for the church of the Colònia Güell, he built a 1:10 scale model with a height of in a shed next to the building. There, he set up a model that had strings with small bags full of
Another of Gaudí's innovations in the technical realm was the use of a scale model to calculate structures: for the church of the Colònia Güell, he built a 1:10 scale model with a height of in a shed next to the building. There, he set up a model that had strings with small bags full of birdshot
A shotgun shell, shotshell or simply shell is a type of rimmed, cylindrical (straight-walled) cartridges used specifically in shotguns, and is typically loaded with numerous small, pellet-like spherical sub-projectiles called shot, fired throu ...
hanging from them. On a drawing board that was attached to the ceiling he drew the floor of the church, and he hung the strings (for the catenaries) with the birdshot (for the weight) from the supporting points of the building—columns, intersection of walls. These weights produced a catenary curve in both the arches and vaults. At that point, he took a picture that, when inverted, showed the structure for columns and arches that Gaudí was looking for. Gaudí then painted over these photographs with gouache
Gouache (; ), body color, or opaque watercolor is a water-medium paint consisting of natural pigment, water, a binding agent (usually gum arabic or dextrin), and sometimes additional inert material. Gouache is designed to be opaque. Gouache h ...
or pastel
A pastel () is an art medium in a variety of forms including a stick, a square a pebble or a pan of color; though other forms are possible; they consist of powdered pigment and a binder. The pigments used in pastels are similar to those use ...
. The outline of the church defined, he recorded every single detail of the building: architectural, stylistic and decorative.
Gaudí's position in the history of architecture is that of a creative genius who, inspired by nature, developed a style of his own that attained technical perfection as well as aesthetic value, and bore the mark of his character. Gaudí's structural innovations were to an extent the result of his journey through various styles, from Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
to Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
via Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, his main inspiration. It could be said that these styles culminated in his work, which reinterpreted and perfected them. Gaudí passed through the historicism and eclecticism of his generation without connecting with other architectural movements of the 20th century that, with their rationalist postulates, derived from the Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the Bauhaus (), was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., 200 ...
school, and represented an antithetical evolution to that initiated by Gaudí, given that it later reflected the disdain and the initial lack of comprehension of the work of the ''modernista'' architect.
Among other factors that led to the initial neglect of the Catalan architect's work was that despite having numerous assistants and helpers, Gaudí created no school of his own and never taught, nor did he leave written documents. Some of his subordinates adopted his innovations, above all Francesc Berenguer and Josep Maria Jujol
José María Jujol Gibert (16 September 1879 – 1 May 1949) was a Spanish architect. Jujol's wide field of activity ranged from furniture designs and painting, to architecture. He worked with Antoni Gaudí on many of his most famous works. ...
; others, like Cèsar Martinell, Francesc Folguera and Josep Francesc Ràfols graduated towards Noucentisme
Noucentisme in Catalonia (, ''noucentista'' being its adjective) was a Catalan cultural movement of the early 20th century that originated largely as a reaction against Modernisme, both in art and ideology, and was, simultaneously, a perception o ...
, leaving the master's trail. Despite this, a degree of influence can be discerned in some architects that either formed part of the ''Modernista'' movement or departed from it and who had had no direct contact with him, such as Josep Maria Pericas (Casa Alòs, Ripoll
Ripoll () is the capital of the ''comarca'' of Ripollès, in the province of Girona, Catalonia, Spain. It is located on confluence of the Ter River and its tributary Freser, next to the Pyrenees near the French border. The population was 11,05 ...
), Bernardí Martorell (Olius
Olius is a municipality in the ''comarca'' of the Solsonès in Catalonia, Spain. It is situated on the Cardener river above the reservoir of Sant Ponç. The village is served by the C-149 road between Solsona and Berga. The church of Sant Estev ...
cemetery) and Lluís Muncunill (Masia Freixa
The Masia Freixa is a modernisme building located in Parc de Sant Jordi in Terrassa (Catalonia, Spain).
History
Designed in 1896 to be a textile factory, the actual form of the building was planned in 1907 when Catalan industrialist Josep Frei ...
, Terrassa
Terrassa (, es, Tarrasa) is a city in the east central region of Catalonia, Spain, in the province of Barcelona, ''comarca'' of Vallès Occidental, of which it is the co-capital along with Sabadell.
The name ''Terrassa'' derives from Latin ' ...
). Nonetheless, Gaudí left a deep mark on 20th-century architecture: masters like Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
declared themselves admirers, and the works of other architects like Pier Luigi Nervi
Pier Luigi Nervi (21 June 1891 – 9 January 1979) was an Italian engineer and architect. He studied at the University of Bologna graduating in 1913. Nervi taught as a professor of engineering at Rome University from 1946 to 1961 and is known wor ...
, Friedensreich Hundertwasser
Friedrich Stowasser (15 December 1928 – 19 February 2000), better known by his pseudonym Friedensreich Regentag Dunkelbunt Hundertwasser (), was an Austrian visual artist and architect who also worked in the field of environmental protection ...
, Oscar Niemeyer
Oscar Ribeiro de Almeida Niemeyer Soares Filho (15 December 1907 – 5 December 2012), known as Oscar Niemeyer (), was a Brazilian architect considered to be one of the key figures in the development of modern architecture. Niemeyer was ...
, Félix Candela
Félix Candela Outeriño (; January 27, 1910 – December 7, 1997) was a Spanish and Mexican architect who was born in Madrid and at the age of 26, emigrated to Mexico, acquiring double nationality.
He is known for his significant role ...
, Eduardo Torroja
Eduardo Torroja y Miret, 1st Marques of Torroja (27 August 1899 – 15 June 1961) was a Spanish structural engineer and a pioneer in the design of concrete shell structures.
Education
Torroja was born in Madrid where he studied civil engineering ...
and Santiago Calatrava
Santiago Calatrava Valls (born 28 July 1951) is a Spanish architect, structural engineer, sculptor and painter, particularly known for his bridges supported by single leaning pylons, and his railway stations, stadiums, and museums, whose sculpt ...
were inspired by Gaudí. Frei Otto
Frei Paul Otto (; 31 May 1925 – 9 March 2015) was a German architect and structural engineer noted for his use of lightweight structures, in particular tensile and membrane structures, including the roof of the Olympic Stadium in Munich for ...
used Gaudí's forms in the construction of the Munich Olympic Stadium
Olympiastadion () is a stadium located in Munich, Germany. Situated at the heart of the '' Olympiapark München'' in northern Munich, the stadium was the main venue for the 1972 Summer Olympics.
The original capacity was maximally and officiall ...
. In Japan, the work of Kenji Imai bears evidence of Gaudí's influence, as can be seen in the Memorial for the Twenty-six Martyrs of Japan in Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
(Japanese National Architecture Award in 1962), where the use of Gaudí's famous "trencadís" stands out.
Design and craftsmanship
 During his student days, Gaudí attended craft workshops, such as those taught by Eudald Puntí, Llorenç Matamala and Joan Oñós, where he learned the basic aspects of techniques relating to architecture, including sculpture, carpentry,
During his student days, Gaudí attended craft workshops, such as those taught by Eudald Puntí, Llorenç Matamala and Joan Oñós, where he learned the basic aspects of techniques relating to architecture, including sculpture, carpentry, wrought ironwork
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" ...
, stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
, ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
, plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for Molding (decorative), moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of ...
modelling, etc. He also absorbed new technological developments, integrating into his technique the use of iron and reinforced concrete in construction. Gaudí took a broad view of architecture as a multifunctional design, in which every single detail in an arrangement has to be harmoniously made and well-proportioned. This knowledge allowed him to design architectural projects, including all the elements of his works, from furnishings to illumination to wrought ironwork.
Gaudí was also an innovator in the realm of craftsmanship, conceiving new technical and decorative solutions with his materials, for example his way of designing ceramic mosaics made of waste pieces ("trencadís
''Trencadís'' (), also known as pique assiette, broken tile mosaics, bits and pieces, memoryware, and shardware, is a type of mosaic made from cemented-together tile shards and broken chinaware. Glazed china tends to be preferred, and glass is so ...
") in original and imaginative combinations. For the restoration of Mallorca Cathedral he invented a new technique to produce stained glass, which consisted of juxtaposing three glass panes of primary colours
A set of primary colors or primary colours (see spelling differences) consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a bro ...
, and sometimes a neutral one, varying the thickness of the glass in order to graduate the light's intensity.
 This was how he personally designed many of the Sagrada Família's sculptures. He would thoroughly study the
This was how he personally designed many of the Sagrada Família's sculptures. He would thoroughly study the anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
of the figure, concentrating on gestures. For this purpose, he studied the human skeleton and sometimes used dummies made of wire to test the appropriate posture of the figure he was about to sculpt. In a second step, he photographed his models, using a mirror system that provided multiple perspectives. He then made plaster casts of the figures, both of people and animals (on one occasion he made a donkey stand up so it would not move). He modified the proportions of these casts to obtain the figure's desired appearance, depending on its place in the church (the higher up, the bigger it would be). Eventually, he sculpted the figures in stone.
Urban spaces and landscaping
Gaudí also practiced landscaping, often in urban settings. He aimed to place his works in the most appropriate natural and architectural surroundings by studying the location of his constructions thoroughly and trying to naturally integrate them into those surroundings. For this purpose, he often used the material that was most common in the nearby environment, such as theslate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
of Bellesguard and the grey Bierzo
El Bierzo (; ; gl, O Bierzo) is a ''comarca'' in the province of León, Spain. Its capital is the town of Ponferrada. Other major towns are Bembibre and Villafranca del Bierzo, the historical capital.
The territory of El Bierzo includes m ...
granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
in the Episcopal Palace, Astorga. Many of his projects were gardens, such as the Güell Park and the Can Artigas Gardens, or incorporated gardens, as in the Casa Vicens or the Güell Pavilions. Gaudí's harmonious approach to landscaping is exemplified at the First Mystery of the Glory of the Rosary at Montserrat, where the architectural framework is nature itself—here the Montserrat rock—nature encircles the group of sculptures that adorned the path to the Holy Cave.
Interiors
 Equally, Gaudí stood out as
Equally, Gaudí stood out as interior decorator
Interior design is the art and science of enhancing the interior of a building to achieve a healthier and more aesthetically pleasing environment for the people using the space. An interior designer is someone who plans, researches, coordin ...
, decorating most of his buildings personally, from the furnishings to the smallest details. In each case he knew how to apply stylistic particularities, personalising the decoration according to the owner's taste, the predominant style of the arrangement or its place in the surroundings—whether urban or natural, secular or religious. Many of his works were related to liturgical
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
furnishing. From the design of a desk for his office at the beginning of his career to the furnishings designed for the Sobrellano Palace of Comillas
Comillas is a small township and municipality in the northern reaches of Spain, in the autonomous community of Cantabria. The Marquessate of Comillas, a fiefdom of Spanish nobility, holds ceremonial office in the seat of power at a small castle ...
, he designed all furnishing of the Vicens, Calvet, Batlló and Milà houses, of the Güell Palace and the Bellesguard Tower, and the liturgical furnishing of the Sagrada Família. It is noteworthy that Gaudí studied some ergonomy
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learnin ...
in order to adapt his furnishings to human anatomy. Many of his furnishings are exhibited at Gaudí House Museum.
 Another aspect is the intelligent distribution of space, always with the aim of creating a comfortable, intimate, interior atmosphere. For this purpose, Gaudí would divide the space into sections, adapted to their specific use, by means of low walls, dropped ceilings, sliding doors and wall closets. Apart from taking care of every detail of all structural and ornamental elements, he made sure his constructions had good lighting and ventilation. For this purpose, he studied each project's orientation with respect to the cardinal points, as well as the local climate and its place in its surroundings. At that time, there was an increasing demand for more domestic comfort, with piped water and gas and the use of electric light, all of which Gaudí expertly incorporated. For the Sagrada Família, for example, he carried out thorough studies on
Another aspect is the intelligent distribution of space, always with the aim of creating a comfortable, intimate, interior atmosphere. For this purpose, Gaudí would divide the space into sections, adapted to their specific use, by means of low walls, dropped ceilings, sliding doors and wall closets. Apart from taking care of every detail of all structural and ornamental elements, he made sure his constructions had good lighting and ventilation. For this purpose, he studied each project's orientation with respect to the cardinal points, as well as the local climate and its place in its surroundings. At that time, there was an increasing demand for more domestic comfort, with piped water and gas and the use of electric light, all of which Gaudí expertly incorporated. For the Sagrada Família, for example, he carried out thorough studies on acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
and illumination, in order to optimise them. With regard to light, he stated:
Lighting also served Gaudí for the organisation of space, which required a careful study of the gradient of light intensity to adequately adapt to each specific environment. He achieved this with different elements such as skylights, windows, shutters and blinds; a notable case is the gradation of colour used in the atrium
Atrium may refer to:
Anatomy
* Atrium (heart), an anatomical structure of the heart
* Atrium, the genital structure next to the genital aperture in the reproductive system of gastropods
* Atrium of the ventricular system of the brain
* Pulmona ...
of the Casa Batlló
() is a building in the center of Barcelona. It was designed by Antoni Gaudí, and is considered one of his masterpieces. A remodel of a previously built house, it was redesigned in 1904 by Gaudí and has been refurbished several times after th ...
to achieve uniform distribution of light throughout the interior. He also tended to build south-facing houses to maximise sunlight.
Works
Gaudí's work is normally classed as '' modernista'', and it belongs to this movement because of its eagerness to renovate without breaking with tradition, its quest for modernity, the ornamental sense applied to works, and the multidisciplinary character of its undertakings, where craftsmanship plays a central role. To this, Gaudí adds a dose of the baroque, adopts technical advances and continues to use traditional architectural language. Together with his inspiration from nature and the original touch of his works, this amalgam gives his works their personal and unique character in the history of architecture. Chronologically, it is difficult to establish guidelines that illustrate the evolution of Gaudí's style faithfully. Although he moved on from his initially historicist approach to immerse himself completely in the ''modernista'' movement which arose so vigorously in the last third of the 19th century in Catalonia, before finally attaining his personal, organic style, this process did not consist of clearly defined stages with obvious boundaries: rather, at every stage there are reflections of all the earlier ones, as he gradually assimilated and surpassed them. Among the best descriptions of Gaudí's work was made by his disciple and biographer Joan Bergós, according to plastic and structural criteria. Bergós establishes five periods in Gaudí's productions: preliminary period, mudéjar-morisco (Moorish/mudéjar art), emulated Gothic, naturalist and expressionist, and organic synthesis.Early works
Gaudí's first works both from his student days and the time just after his graduation stand out for the precision of their details, the use of geometry and the prevalence of mechanical considerations in the structural calculations.University years
During his studies, Gaudí designed various projects, among which the following stand out: a cemetery gate (1875), a Spanish pavilion for the Philadelphia World Fair of 1876, a quay-side building (1876), a courtyard for theDiputació de Barcelona
Barcelona (, ) is a province of eastern Spain, in the center of the autonomous community of Catalonia. The province is bordered by the provinces of Tarragona, Lleida, and Girona, and by the Mediterranean Sea. Its area is .Plaça Catalunya in Barcelona (1877) and a university
 A new task of the Güell-López's for
A new task of the Güell-López's for
 In 1895 he designed a funerary chapel for the Güell family at the abbey of Montserrat Abbey, Montserrat, but little is known about this work, which was never built. That year, construction finally began on the Bodegas Güell, the 1882 project for a hunting lodge and some wineries at La Cuadra de Garraf (Sitges), property of Eusebi Güell. Constructed between 1895 and 1897 under the direction of Francesc Berenguer, Gaudí's aide, the wineries have a triangular end façade, a very steep stone roof, a group of chimneys and two bridges that join them to an older building. It has three floors: the bottom one for a garage, an apartment and a chapel with catenary arches, with the altar in the centre. It was completed with a porter's lodge, notable for the iron gate in the shape of a fishing net.
In the township of Sant Gervasi de Cassoles (now a district of Barcelona), the widow of Jaume Figueras commissioned Gaudí to renovate the Torre Bellesguard (1900–1909), former summer palace of King Martin I the Humane. Gaudí designed it in a neo-Gothic style, respecting the former building as much as possible, and tried as always to integrate the architecture into the natural surroundings. This influenced his choice of local slate for the construction. The building's ground-plan measures 15 x 15 meters, with the corners oriented to the four cardinal points. Constructed in stone and brick, it is taller than it is wide, with a spire topped with the four-armed cross, the Catalan flag and the royal crown. The house has a basement, ground floor, first floor and an attic, with a gable roof.
In 1895 he designed a funerary chapel for the Güell family at the abbey of Montserrat Abbey, Montserrat, but little is known about this work, which was never built. That year, construction finally began on the Bodegas Güell, the 1882 project for a hunting lodge and some wineries at La Cuadra de Garraf (Sitges), property of Eusebi Güell. Constructed between 1895 and 1897 under the direction of Francesc Berenguer, Gaudí's aide, the wineries have a triangular end façade, a very steep stone roof, a group of chimneys and two bridges that join them to an older building. It has three floors: the bottom one for a garage, an apartment and a chapel with catenary arches, with the altar in the centre. It was completed with a porter's lodge, notable for the iron gate in the shape of a fishing net.
In the township of Sant Gervasi de Cassoles (now a district of Barcelona), the widow of Jaume Figueras commissioned Gaudí to renovate the Torre Bellesguard (1900–1909), former summer palace of King Martin I the Humane. Gaudí designed it in a neo-Gothic style, respecting the former building as much as possible, and tried as always to integrate the architecture into the natural surroundings. This influenced his choice of local slate for the construction. The building's ground-plan measures 15 x 15 meters, with the corners oriented to the four cardinal points. Constructed in stone and brick, it is taller than it is wide, with a spire topped with the four-armed cross, the Catalan flag and the royal crown. The house has a basement, ground floor, first floor and an attic, with a gable roof.
 Among Gaudí's largest and most striking works is the
Among Gaudí's largest and most striking works is the  The same year he built a workshop, the Taller Badia, for Josep and Lluís Badia Miarnau,
blacksmiths who worked for Gaudí on several of his works, such as the Batlló and Milà houses, the Park Güell and the Sagrada Família. Located at 278 Carrer Nàpols, it was a simple stone building. Around that time he also designed hexagonal Cement tile, hydraulic floor tiles for the Casa Batlló, they were eventually used instead for the Casa Milà; they were a green colour and were decorated with seaweed, shells and starfish. These tiles were subsequently chosen to pave Barcelona's Passeig de Gràcia.
Also in 1904 he built the Chalet de Catllaràs, in La Pobla de Lillet, for the Asland cement factory, owned by Eusebi Güell. It has a simple structure though very original, in the shape of a pointed arch, with two semi-circular flights of stairs leading to the top two floors. This building fell into ruin when the cement works closed, and when it was eventually restored its appearance was radically altered, the ingenious original staircase being replaced with a simpler metal one. In the same area he created the Can Artigas Gardens between 1905 and 1907, in an area called Font de la Magnesia, commissioned by the textile merchant Joan Artigas i Alart; men who had worked the Park Güell were also involved on this project, similar to the famous park in Barcelona.
The same year he built a workshop, the Taller Badia, for Josep and Lluís Badia Miarnau,
blacksmiths who worked for Gaudí on several of his works, such as the Batlló and Milà houses, the Park Güell and the Sagrada Família. Located at 278 Carrer Nàpols, it was a simple stone building. Around that time he also designed hexagonal Cement tile, hydraulic floor tiles for the Casa Batlló, they were eventually used instead for the Casa Milà; they were a green colour and were decorated with seaweed, shells and starfish. These tiles were subsequently chosen to pave Barcelona's Passeig de Gràcia.
Also in 1904 he built the Chalet de Catllaràs, in La Pobla de Lillet, for the Asland cement factory, owned by Eusebi Güell. It has a simple structure though very original, in the shape of a pointed arch, with two semi-circular flights of stairs leading to the top two floors. This building fell into ruin when the cement works closed, and when it was eventually restored its appearance was radically altered, the ingenious original staircase being replaced with a simpler metal one. In the same area he created the Can Artigas Gardens between 1905 and 1907, in an area called Font de la Magnesia, commissioned by the textile merchant Joan Artigas i Alart; men who had worked the Park Güell were also involved on this project, similar to the famous park in Barcelona.
 In 1906 he designed a bridge over the Torrent de Pomeret, between Sarrià and Sant Gervasi. This river flowed directly between two of Gaudí's works, Bellesguard and the Chalet Graner, and so he was asked to bridge the divide. Gaudí designed an interesting structure composed of juxtaposed triangles that would support the bridge's framework, following the style of the viaducts that he made for the Park Güell. It would have been built with cement, and would have had a length of and a height of ; the balustrade would have been covered with glazed tiles, with an inscription dedicated to Santa Eulàlia. The project was not approved by the Town Council of Sarrià.
The same year Gaudí apparently took part in the construction of the Torre Damià Mateu, in Llinars del Vallès in collaboration with his disciple Francesc Berenguer, though the project's authorship is not clear or to what extent they each contributed to it. The style of the building evokes Gaudí's early work, such as the Casa Vicens or the Güell Pavilions; it had an entrance gate in the shape of a fishing net, currently installed in the Park Güell. The building was demolished in 1939. Also in 1906 he designed a new banner, this time for the Guild of metalworkers and blacksmiths for the Corpus Christi procession of 1910, in Barcelona Cathedral. It was dark green in colour, with Barcelona's coat of arms in the upper left corner, and an image of Saint Eligius, patron of the guild, with typical tools of the trade. The banner was burned in July 1936.
In 1906 he designed a bridge over the Torrent de Pomeret, between Sarrià and Sant Gervasi. This river flowed directly between two of Gaudí's works, Bellesguard and the Chalet Graner, and so he was asked to bridge the divide. Gaudí designed an interesting structure composed of juxtaposed triangles that would support the bridge's framework, following the style of the viaducts that he made for the Park Güell. It would have been built with cement, and would have had a length of and a height of ; the balustrade would have been covered with glazed tiles, with an inscription dedicated to Santa Eulàlia. The project was not approved by the Town Council of Sarrià.
The same year Gaudí apparently took part in the construction of the Torre Damià Mateu, in Llinars del Vallès in collaboration with his disciple Francesc Berenguer, though the project's authorship is not clear or to what extent they each contributed to it. The style of the building evokes Gaudí's early work, such as the Casa Vicens or the Güell Pavilions; it had an entrance gate in the shape of a fishing net, currently installed in the Park Güell. The building was demolished in 1939. Also in 1906 he designed a new banner, this time for the Guild of metalworkers and blacksmiths for the Corpus Christi procession of 1910, in Barcelona Cathedral. It was dark green in colour, with Barcelona's coat of arms in the upper left corner, and an image of Saint Eligius, patron of the guild, with typical tools of the trade. The banner was burned in July 1936.
 Another of Gaudí's major projects and among his most admired works is the
Another of Gaudí's major projects and among his most admired works is the
 The final project for his great patron Eusebi Güell was the church for the Colònia Güell, an industrial village in Santa Coloma de Cervelló (1890–1918). The project began in 1890, and the factory, service buildings and housing for the workers were constructed. What would have been the colony's church was designed by Gaudí in 1898, though the first stone was not laid until 4 October 1908. Unfortunately only the crypt (known today as Crypt of the Colònia Güell) was built, as Güell's sons abandoned the project after his death in 1918. Gaudí designed an oval church with five aisles, one central aisle and two at either side. He conceived it as fully integrated into nature. A porch of hyperbolic paraboloid vaults precedes the crypt, the first time that Gaudí used this structure and notably the first use of paraboloid vaults in the history of architecture. In the crypt the large hyperboloid stained glass windows stand out, with the shapes of flower petals and butterfly wings. Inside, circular brick pillars alternate with slanted basalt columns from Castellfollit de la Roca.
The final project for his great patron Eusebi Güell was the church for the Colònia Güell, an industrial village in Santa Coloma de Cervelló (1890–1918). The project began in 1890, and the factory, service buildings and housing for the workers were constructed. What would have been the colony's church was designed by Gaudí in 1898, though the first stone was not laid until 4 October 1908. Unfortunately only the crypt (known today as Crypt of the Colònia Güell) was built, as Güell's sons abandoned the project after his death in 1918. Gaudí designed an oval church with five aisles, one central aisle and two at either side. He conceived it as fully integrated into nature. A porch of hyperbolic paraboloid vaults precedes the crypt, the first time that Gaudí used this structure and notably the first use of paraboloid vaults in the history of architecture. In the crypt the large hyperboloid stained glass windows stand out, with the shapes of flower petals and butterfly wings. Inside, circular brick pillars alternate with slanted basalt columns from Castellfollit de la Roca.
 During the last years of his career, dedicated almost exclusively to the
During the last years of his career, dedicated almost exclusively to the
 From 1915 Gaudí devoted himself almost exclusively to his Masterpiece, magnum opus, the Sagrada Família, a synthesis of his architectural evolution. After completion of the crypt and the apse, still in Gothic style, the rest of the church is conceived in an organic style, imitating natural shapes with their abundance of
From 1915 Gaudí devoted himself almost exclusively to his Masterpiece, magnum opus, the Sagrada Família, a synthesis of his architectural evolution. After completion of the crypt and the apse, still in Gothic style, the rest of the church is conceived in an organic style, imitating natural shapes with their abundance of
Gaudí's life and works
Sagrada Família information and discussion of lesser-known Gaudí works
Sagrada Família image gallery
Casa Batlló information and image gallery
Analysis of fractals and other mathematical elements in Gaudí's architectural style
Pàgina del Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc
A virtual walk through the Guard House at Park Guell
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gaudi, Antoni 1852 births 1926 deaths 19th-century Spanish architects 20th-century Spanish architects Architects of Roman Catholic churches Burials at Sagrada Família Architects from Catalonia Modernisme architects Mosaicists Organic architecture Pedestrian road incident deaths People from Reus Railway accident deaths in Spain Spanish ecclesiastical architects Spanish Roman Catholics Spanish Servants of God Antoni Gaudí,
assembly hall
An assembly hall is a hall to hold public meetings or meetings of an organization such as a school, church, or deliberative assembly. An example of the last case is the Assembly Hall (Washington, Mississippi) where the general assembly of the st ...
(1877).
Gaudí started his professional career while still at university. To pay for his studies, he worked as a draughtsman for some of the most outstanding Barcelona architects of the time, such as Joan Martorell, Josep Fontserè, Francisco de Paula del Villar y Lozano, Leandre Serrallach and Emili Sala Cortés. Gaudí had a long-standing relationship with Josep Fontserè, since his family was also from Riudoms and they had known each other for some time. Despite not having an architecture degree, Fontserè received the commission from the city council for the Parc de la Ciutadella
The (; "Citadel Park") is a park on the northeastern edge of Ciutat Vella, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. For decades following its creation in the mid-19th century, this park was the city's only green space. The grounds include the city zoo (on ...
development, carried out between 1873 and 1882. For this project, Gaudí was in charge of the design of the Park's entrance gate, the bandstand's balustrade and the water project for the monumental fountain, where he designed an artificial cave that showed his liking for nature and the organic touch he would give his architecture.
Gaudí worked for Francisco de Paula del Villar
Francisco de Paula del Villar y Lozano (1828, in Murcia – 1901, in Barcelona) was a Spanish architect.
Biography
Villar studied architecture in Madrid at the Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando, and qualified in 1852. The following year he ...
on the apse of the Montserrat monastery, designing the niche for the image of the Black Virgin of Montserrat in 1876. He would later substitute Villar in the works of the Sagrada Família. With Leandre Serrallach, he worked on a tram line project to Villa Arcadia in Montjuïc. Eventually, he collaborated with Joan Martorell on the Jesuit church on Carrer Casp and the Salesian convent in Passeig de Sant Joan, as well as the Villaricos church (Almería). He also carried out a project for Martorell for the competition for a new façade for Barcelona cathedral
The Cathedral of the Holy Cross and Saint Eulalia ( ca, Catedral de la Santa Creu i Santa Eulàlia), also known as Barcelona Cathedral, is the Gothic cathedral and seat of the Archbishop of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. The cathedral was constru ...
, which was never accepted. His relationship with Martorell, whom he always considered one of his main and most influential masters, brought him unexpected luck; he later recommended Gaudí for the Sagrada Família.
Early post-graduation projects
After his graduation as an architect in 1878, Gaudí's first work was a set of lampposts for thePlaça Reial
Plaça Reial (In Spanish ''Plaza Real'', meaning "Royal Plaza") is a square in the Barri Gòtic of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is close to La Rambla, and is a popular tourist attraction, especially at night. The plaza hosts many restauran ...
, the project for the Girossi newsstands and the Mataró cooperative, which was his first important work. He received the request from the city council of Barcelona in February 1878, when he had graduated but not yet received his degree, which was sent from Madrid on 15 March of the same year. For this commission he designed two types of lampposts: one with six arms, of which two were installed in the Plaça Reial, and another with three, of which two were installed in the Pla del Palau, opposite the Civil Government. The lampposts were inaugurated during the Mercè festivities in 1879. Made of cast iron with a marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the ...
base, they have a decoration in which the caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
of Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
is prominent, symbol of commerce and emblem of Barcelona.
The Girossi newsstands project, which was never carried out, was a commission from the tradesman Enrique Girossi de Sanctis. It would have consisted of 20 newsstands
A newsagent's shop or simply newsagent's or paper shop (British English), newsagency (Australian English) or newsstand (American and Canadian English) is a business that sells newspapers, magazines, cigarettes, snacks and often items of local ...
, spread throughout Barcelona. Each would have included a public lavatory, a flower stand and glass panels for advertisements as well as a clock, a calendar, a barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis ...
and a thermometer
A thermometer is a device that temperature measurement, measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a merc ...
. Gaudí conceived a structure with iron pillars and marble and glass slabs, crowned by a large iron and glass roof, with a gas illumination system.
The Cooperativa Obrera Mataronense (Mataró Workers' Cooperative) was Gaudí's first big project, on which he worked from 1878 to 1882, for Salvador Pagès i Anglada. The project, for the cooperative's head office in Mataró, comprised a factory, a worker's housing estate, a social centre and a services building, though only the factory and the services building were completed. In the factory roof Gaudí used the catenary arch for the first time, with a bolt assembly system devised by Philibert de l'Orme. He also used ceramic tile decoration for the first time in the services building. Gaudí laid out the site taking account of solar orientation, another signature of his works, and included landscaped areas. He even designed the Cooperative's banner, with the figure of a bee, symbol of industriousness.
In May 1878 Gaudí designed a display cabinet for the Esteban Comella glove factory, which was exhibited in the Spanish pavilion at the Paris World Exhibition that year. It was this work that attracted the attention of the entrepreneur Eusebi Güell
Eusebi Güell i Bacigalupi, 1st Count of Güell (; 15 December 1846 – 8 July 1918) was a Catalan entrepreneur who profited greatly from the industrial revolution in Catalonia in the late 19th century. He married Luisa Isabel Lopez y Bru —a d ...
, visiting the French capital; he was so impressed that he wanted to meet Gaudí on his return, beginning a long friendship and professional collaboration. Güell became Gaudí's main patron and sponsor of many of his large projects.
First Güell projects
Güell's first task for Gaudí, that same year, was the design of the furniture for the pantheon chapel of the Palacio de Sobrellano in Comillas, which was then being constructed by Joan Martorell, Gaudí's teacher, at the request of the Marquis of Comillas, Güell's father in law. Gaudí designed a chair, a bench and a prayer stool: the chair was upholstered with velvet, finished with two eagles and the Marquis's coat of arms; the bench stands out with the motif of a dragon, designed by Llorenç Matamala; the prayer stool is decorated with plants. Also in 1878 he drew up the plans for a theatre in the former town of Sant Gervasi de Cassoles (now a district of Barcelona); Gaudí did not take part in the construction of the theatre, which no longer exists. The following year he designed the furniture and counter for the Gibert Pharmacy, withmarquetry
Marquetry (also spelled as marqueterie; from the French ''marqueter'', to variegate) is the art and craft of applying pieces of veneer to a structure to form decorative patterns, designs or pictures. The technique may be applied to case furn ...
of Arab influence. The same year he made five drawings for a procession in honour of the poet Francesc Vicent Garcia i Torres in Vallfogona de Riucorb
Vallfogona de Riucorb () is a municipality and village in the ''comarca'' of the Conca de Barberà in central Catalonia, Spain. It is situated in the Comalats range in the north of the ''comarca'', with the Cap de Cans rising to 759 m. Vallfo ...
, where this celebrated 17th-century writer and friend of Lope de Vega
Félix Lope de Vega y Carpio ( , ; 25 November 156227 August 1635) was a Spanish playwright, poet, and novelist. He was one of the key figures in the Spanish Golden Age of Baroque literature. His reputation in the world of Spanish literature ...
was the parish priest. Gaudí's project was centred on the poet and on several aspects of agricultural work, such as reaping and harvesting grapes and olives; however, as a result of organisational problems Gaudí's ideas were not carried out.
Between 1879 and 1881 he drew up a proposal for the decoration of the church of Sant Pacià, belonging to the Colegio de Jesús-María in Sant Andreu del Palomar: he created the altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
in a Gothic style, the monstrance with Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
influence, the mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
s and the lighting, as well as the school's furniture. The church caught fire during the Tragic Week of 1909, and now only the mosaics remain, of "opus tesselatum", probably the work of the Italian mosaicist Luigi Pellerin. He was given the task of decorating the church of the Colegio de Jesús-María in Tarragona (1880–1882): he created the altar in white Italian marble, and its front part, or antependium
An ''antependium'' (from Latin ''ante-'' and ''pendēre'' "to hang before"; pl: ''antependia''), also known as a ''parament'' or ''hanging'', or, when speaking specifically of the hanging for the altar, an altar frontal (Latin: ''pallium altaris ...
, with four columns bearing medallions of polychrome alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that includes ...
, with figures of angels; the ostensory
A monstrance, also known as an ostensorium (or an ostensory), is a vessel used in Roman Catholic, Old Catholic, High Church Lutheran and Anglican churches for the display on an altar of some object of piety, such as the consecrated Eucharistic ...
with gilt wood, the work of Eudald Puntí, decorated with rosaries, angels, tetramorph
A tetramorph is a symbolic arrangement of four differing elements, or the combination of four disparate elements in one unit. The term is derived from the Greek ''tetra'', meaning four, and ''morph'', shape.
In Christian art, the tetramorph is t ...
symbols and the dove of the Holy Ghost; and the choir stalls, which were destroyed in 1936.
In 1880 he designed an electric lighting project for Barcelona's Muralla de Mar, or seawall
A seawall (or sea wall) is a form of coastal defense constructed where the sea, and associated coastal processes, impact directly upon the landforms of the coast. The purpose of a seawall is to protect areas of human habitation, conservation ...
, which was not carried out. It consisted of eight large iron streetlamps, profusely decorated with plant motifs, frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor ...
s, shields and names of battles and Catalan admirals. The same year he participated in the competition for the construction of the San Sebastián social centre (now town hall), won by Luis Aladrén Mendivi and Adolfo Morales de los Ríos; Gaudí submitted a project that synthesised several of his earlier studies, such as the fountain for the Plaça Catalunya and the courtyard of the Provincial Council.
Collaboration with Martorell
 A new task of the Güell-López's for
A new task of the Güell-López's for Comillas
Comillas is a small township and municipality in the northern reaches of Spain, in the autonomous community of Cantabria. The Marquessate of Comillas, a fiefdom of Spanish nobility, holds ceremonial office in the seat of power at a small castle ...
was the gazebo
A gazebo is a pavilion structure, sometimes octagonal or turret-shaped, often built in a park, garden or spacious public area. Some are used on occasions as bandstands.
Etymology
The etymology given by Oxford Dictionaries (website), Oxford D ...
for Alfonso XII
Alfonso XII (Alfonso Francisco de Asís Fernando Pío Juan María de la Concepción Gregorio Pelayo; 28 November 185725 November 1885), also known as El Pacificador or the Peacemaker, was King of Spain from 29 December 1874 to his death in 188 ...
's visit to the Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east ...
n town in 1881. Gaudí designed a small pavilion in the shape of a Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
turban
A turban (from Persian دولبند, ''dulband''; via Middle French ''turbant'') is a type of headwear based on cloth winding. Featuring many variations, it is worn as customary headwear by people of various cultures. Communities with promine ...
, covered in mosaics and decorated with an abundance of small bells which jingled constantly. It was subsequently moved into the Güell Pavilions.
In 1882 he designed a Benedictine monastery and a church dedicated to the Holy Spirit in Villaricos (Cuevas de Vera
Cuevas or Cueva (Spanish for "''cave(s)''") may refer to:
Places
* Cueva de Ágreda, a municipality located in the province of Soria, Castile and León, Spain
* Cuevas Bajas, a town and municipality in the province of Málaga, part of the autonom ...
, Almería
Almería (, , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, located in Andalusia. It is the capital of the province of the same name. It lies on southeastern Iberia on the Mediterranean Sea. Caliph Abd al-Rahman III founded the city in 955. The city gr ...
) for his former teacher, Joan Martorell. It was of neo-Gothic design, similar to the Convent of the Salesians that Gaudí also planned with Martorell. Ultimately it was not carried out, and the project plans were destroyed in the looting of the Sagrada Família in 1936. The same year he was tasked with constructing a hunting lodge and wine cellar
A wine cellar is a storage room for wine in bottles or barrels, or more rarely in carboys, amphorae, or plastic containers. In an ''active'' wine cellar, important factors such as temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate control system. ...
s at a country residence known as La Cuadra, in Garraf (Sitges), property of baron Eusebi Güell. Ultimately the wine cellars, but not the lodge, were built some years later. With Martorell he also collaborated on three other projects: the church of the Jesuit School in Carrer Caspe; the Convent of the Salesians in Passeig de Sant Joan, a neo-Gothic project with an altar in the centre of the crossing; and the façade project for Barcelona cathedral, for the competition convened by the cathedral chapter in 1882, ultimately won by Josep Oriol Mestres and August Font i Carreras.
Gaudí's collaboration with Martorell was a determining factor in Gaudí's recommendation for the Sagrada Família. The church was the idea of Josep Maria Bocabella, founder of the Devotees of Saint Joseph Association, which acquired a complete block of Barcelona's Eixample
The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and what were once surrounding small towns (Sants, Gràcia, Sant Andreu, etc.), constructed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its population was 262,000 at t ...
district. The project was originally entrusted to Francisco de Paula del Villar y Lozano, who planned the construction of a neo-Gothic church, on which work began in 1882. However, the following year Villar resigned due to disagreements with the construction board, and the task went to Gaudí, who completely redesigned the project, apart from the part of the crypt that had already been built. Gaudí devoted the rest of his life to the construction of the church, which was to be the synthesis of all of his architectural discoveries.
Orientalist period
During these years Gaudí completed a series of works with a distinctly oriental flavour, inspired by the art of the Middle and Far East (India, Persia, Japan), as well as Islamic-Hispanic art, mainly Mudejar and Nazari. Gaudí used ceramic tile decoration abundantly, as well as Moorish arches, columns of exposed brick and pinnacles in the shape of pavilions or domes. Between 1883 and 1888 he constructed theCasa Vicens
Casa Vicens () is a modernist building situated in the Gràcia neighbourhood of Barcelona. It is the work of architect Antoni Gaudí and is considered to be his first major project. It was built between 1883 and 1885, although Gaudí drew up the ...
, commissioned by stockbroker Manuel Vicens i Montaner. It was constructed with four floors, with façades on three sides and an extensive garden, including a monumental brick fountain. The house was surrounded by a wall with iron gates, decorated with palmetto leaves, work of Llorenç Matamala. The walls of the house are of stone alternated with lines of tile, which imitate yellow flowers typical of this area; the house is topped with chimneys and turrets. In the interior the polychrome wooden roof beams stand out, adorned with floral themes of papier maché
Papier may refer to :
*paper in French, Dutch, Afrikaans, Polish or German, word that can be found in the following expressions:
**Papier-mâché, a construction material made of pieces of paper stuck together using a wet paste
**Papier collé, a p ...
; the walls are decorated with vegetable motifs, as well as paintings by Josep Torrescasana; finally, the floor consists of Roman-style mosaics of "opus tesselatum". Among the most original rooms is the smoking room, notable the ceiling, decorated with Moorish honeycomb-work, reminiscent of the Generalife
The Generalife (; ar, جَنَّة الْعَرِيف, translit=Jannat al-‘Arīf) was a summer palace and country estate of the Nasrid rulers of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus. It is located directly east of and uphill from the Alham ...
in the Alhambra
The Alhambra (, ; ar, الْحَمْرَاء, Al-Ḥamrāʾ, , ) is a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Andalusia, Spain. It is one of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture and one of the best-preserved palaces of the ...
in Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
.
In the same year, 1883, Gaudí designed the Santísimo Sacramento chapel for the parish church of San Félix de Alella, as well as some topographical plans for the Can Rosell de la Llena country residence in Gelida. He also received a commission to build a small annex to the Palacio de Sobrellano, for the Baron of Comillas, in the Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east ...
n town of the same name. Known as El Capricho, it was commissioned by Máximo Díaz de Quijano and constructed between 1883 and 1885. Cristòfor Cascante i Colom, Gaudí's fellow student, directed the construction. In an oriental style, it has an elongated shape, on three levels and a cylindrical tower in the shape of a Persian minaret, faced completely in ceramics. The entrance is set behind four columns supporting depressed arches, with capitals decorated with birds and leaves, similar to those that can be seen at the Casa Vicens. Notable are the main lounge, with its large sash window
A sash window or hung sash window is made of one or more movable panels, or "sashes". The individual sashes are traditionally paned window (architecture), paned windows, but can now contain an individual sheet (or sheets, in the case of double gla ...
, and the smoking room with a ceiling consisting of a false Arab-style stucco vault.
Gaudí carried out a second commission from Eusebi Güell between 1884 and 1887, the Güell Pavilions in Pedralbes, now on the outskirts of Barcelona. Güell had a country residence in Les Corts de Sarrià, consisting of two adjacent properties known as Can Feliu and Can Cuyàs de la Riera. The architect Joan Martorell had built a Caribbean-style mansion, which was demolished in 1919 to make way for the Royal Palace of Pedralbes. Gaudí undertook to refurbish the house and construct a wall and porter's lodge. He completed the stone wall with several entrances, the main entrance with an iron gate in the shape of a dragon, with symbology
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conce ...
allusive to the myths of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
and the Garden of the Hesperides
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides (; , ) are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides () from their reputed father, the Titan (mytho ...
. The buildings consist of a stable, covered longeing
Longeing (US English, classical spelling) or lungeing (UK English, informal US) is a technique for training and exercising horses. It is also a critical component of the sport of equestrian vaulting.
The horse is asked to work at the end of a ...
ring and porter's lodge: the stable has a rectangular base and catenary arches; the longeing ring has a square base with a hyperboloid dome; the porter's lodge consists of three small buildings, the central one being polygonal with a hyperbolic dome, and the other two smaller and cubic. All three are topped by ventilators in the shape of chimneys faced with ceramics. The walls are of exposed brick in various shades of reds and yellows; in certain sections prefabricated cement blocks are also used. The Pavilions are now the headquarters of the Real Cátedra Gaudí, of the Polytechnic University of Catalonia.
In 1885 Gaudí accepted a commission from Josep Maria Bocabella, promoter of the Sagrada Família, for an altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
in the oratory of the Bocabella family, who had obtained permission from the Pope to have an altar in their home. The altar is made of varnished mahogany
Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus ''Swietenia'', indigenous to the AmericasBridgewater, Samuel (2012). ''A Natural History of Belize: Inside the Maya Forest''. Austin: Unive ...
, with a slab of white marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed ...
in the centre for relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
. It is decorated with plants and religious motifs, such as the Greek letters alpha and omega, symbol of the beginning and end, gospel phrases and images of Saint Francis of Paola
Francis of Paola, O.M., (or: Francesco di Paola or Francis the Fire Handler; 27 March 1416 – 2 April 1507) was an Italian mendicant friar and the founder of the Roman Catholic Order of Minims. Unlike the majority of founders of men's religiou ...
, Saint Teresa of Avila
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Ortho ...
and the Holy Family
The Holy Family consists of the Child Jesus, the Virgin Mary and Saint Joseph. The subject became popular in art from the 1490s on, but veneration of the Holy Family was formally begun in the 17th century by Saint François de Laval, the first ...
and closed with a curtain of crimson embroidery. It was made by the cabinet maker Frederic Labòria, who also collaborated with Gaudí on the Sagrada Família.
Shortly after, Gaudí received an important new commission from Güell: the construction of his family house, in the Carrer Nou de la Rambla in Barcelona. The Palau Güell
The Palau Güell (, en, Güell Palace) is a mansion designed by the architect Antoni Gaudí for the industrial tycoon Eusebi Güell, and was built between 1886 and 1888. It is situated on the Carrer Nou de la Rambla, in the El Raval neighbor ...
(1886–1888) continues the tradition of large Catalan urban mansions such as those in Carrer Montcada. Gaudí designed a monumental entrance with a magnificent parabolic arch
A parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola.Article about parabolic arch by The Free DictionaryParabolic arch , Article about parabolic arch by The Free Dictionary accessdate: March 2, 2017 In structures, their curve represents an effi ...
above iron gates, decorated with the Catalan coat of arms and a helmet with a winged dragon, the work of Joan Oñós. A notable feature is the triple-height entrance hall; it is the core of the building, surrounded by the main rooms of the palace, and it is remarkable for its double dome, parabolic within and conical on the outside, a solution typical of Byzantine art. For the gallery on the street façade Gaudí used an original system of catenary arches and columns with hyperbolic capitals, a style he used only here. He designed the interior of the palace with a sumptuous Mudejar-style decoration, where the wood and iron coffered ceilings stand out. The chimneys on the roof are a remarkable feature, faced in vividly coloured ceramic tiles, as is the tall spire in the form of a lantern tower
In architecture, the lantern tower is a tall construction above the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church, with openings through which light from outside can shine down to the crossing (so it also called a crossing lante ...
, which is the external termination of the dome within, and is also faced with ceramic tiles and topped with an iron weather vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , m ...
.
On the occasion of the World Expo held in Barcelona in 1888, Gaudí constructed the pavilion for the Compañía Trasatlántica, property of the Marquis of Comillas, in the Maritime Section of the event. He created it in a Granadinian Nazari style, with horseshoe arches and stucco decoration; the building survived until the Passeig Marítim was opened up in 1960. In the wake of the event he received a commission from Barcelona Council to restore the Saló de Cent and the grand stairs in Barcelona City Hall, as well as a chair for the queen Maria Cristina; only the chair was made, and Mayor Francesc Rius i Taulet presented it to the Queen.
Neo-Gothic period
During this period Gaudí was inspired above all by mediaevalGothic art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern and ...
, but wanted to improve on its structural solutions. Neo-gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
was one of the most successful historicist styles at that time, above all as a result of the theoretical studies of Viollet-le-Duc. Gaudí studied examples in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Roussillon in depth, as well as Leonese and Castillian buildings during his stays in León and Burgos, and became convinced that it was an imperfect style, leaving major structural issues only partly resolved. In his works he eliminated the need of buttresses through the use of ruled surface
In geometry, a surface is ruled (also called a scroll) if through every point of there is a straight line that lies on . Examples include the plane, the lateral surface of a cylinder or cone, a conical surface with elliptical directrix, the ...
s, and abolished crenellations and excessive openwork.
The first example was the Teresian College (''Col·legi de les Teresianes'') (1888–1889), in Barcelona's Carrer Ganduxer, commissioned by San Enrique de Ossó. Gaudí fulfilled the wish of the order that the building should be austere, in keeping with their vows of poverty. He designed a simple building, using bricks for the exterior and some brick elements for the interior. Wrought ironwork, one of Gaudí's favourite materials, appeared on the façades. The building is crowned by a row of merlon
A merlon is the solid upright section of a battlement (a crenellated parapet) in medieval architecture or fortifications.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 202. Merlons are sometimes ...
s which suggest a castle, a possible reference to Saint Teresa's ''Interior Castle''. The corners have brick pinnacles topped by helicoidal columns and culminate in a four-armed cross, typical of Gaudí's works, and with ceramic shields bearing various symbols of the order. The interior includes a corridor which is famous for the series of catenary arches that it contains. These elegant arches are decorative and support the ceiling and the floor above. For Gaudí, the catenary arch was an ideal constructional element, capable of supporting great loads with slender masonry.
Gaudí received his next commission from a clergyman who had been a boyhood friend in his native Reus. When he was appointed bishop of Astorga, Joan Baptista Grau i Vallespinós asked Gaudí to design a new episcopal palace for the city, as the previous building had caught fire. Constructed between 1889 and 1915, in a neo-Gothic style with four cylindrical towers, it was surrounded by a moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
. The stone with which it was built (grey granite from the El Bierzo area) is in harmony with its surroundings, particularly with the cathedral in its immediate vicinity, as well as with the natural landscape, which in late 19th-century Astorga was more visible than today. The porch has three large flared arches, built of ashlar and separated by sloping buttresses. The structure is supported by columns with decorated capitals and by ribbed vaults on pointed arches, and topped with Mudejar-style merlons. Gaudí resigned from the project in 1893, at the death of Bishop Grau, due to disagreements with the Chapter (religion), Chapter, and it was finished in 1915 by Ricardo García Guereta. It currently houses a museum about the Way of Saint James, which passes through Astorga.
Another of Gaudí's projects outside of Catalonia was the Casa Botines, Casa de los Botines, in León (1891–1894), commissioned by Simón Fernández Fernández and Mariano Andrés Luna, textile merchants from León, who were recommended Gaudí by Eusebi Güell, with whom they did business. Gaudí's project was an impressive neo-Gothic style building, which bears his unmistakable ''modernista'' imprint. The building was used to accommodate offices and textile shops on the lower floors, as well as apartments on the upper floors. It was constructed with walls of solid limestone. The building is flanked by four cylindrical turrets surmounted by slate spires, and surrounded by an Area (architecture), area with an iron grille. The Gothic façade style, with its cusped arches, has a clock and a sculpture of Saint George and the Dragon, the work of Llorenç Matamala. As of 2010 it was the headquarters of the Caja España.
In 1892 Gaudí was commissioned by Claudio López Bru, second Marquis of Comillas, with the Franciscana Catholic Missions for the city of Tangier, in Morocco (at the time a Spanish colony). The project included a church, hospital and school, and Gaudí conceived a quadrilobulate ground-plan floor structure, with catenary arches, parabolic towers, and hyperboloid windows. Gaudí deeply regretted the project's eventual demise, always keeping his design with him. In spite of this, the project influenced the works of the Sagrada Família, in particular the design of the towers, with their paraboloid shape like those of the Missions.
 In 1895 he designed a funerary chapel for the Güell family at the abbey of Montserrat Abbey, Montserrat, but little is known about this work, which was never built. That year, construction finally began on the Bodegas Güell, the 1882 project for a hunting lodge and some wineries at La Cuadra de Garraf (Sitges), property of Eusebi Güell. Constructed between 1895 and 1897 under the direction of Francesc Berenguer, Gaudí's aide, the wineries have a triangular end façade, a very steep stone roof, a group of chimneys and two bridges that join them to an older building. It has three floors: the bottom one for a garage, an apartment and a chapel with catenary arches, with the altar in the centre. It was completed with a porter's lodge, notable for the iron gate in the shape of a fishing net.
In the township of Sant Gervasi de Cassoles (now a district of Barcelona), the widow of Jaume Figueras commissioned Gaudí to renovate the Torre Bellesguard (1900–1909), former summer palace of King Martin I the Humane. Gaudí designed it in a neo-Gothic style, respecting the former building as much as possible, and tried as always to integrate the architecture into the natural surroundings. This influenced his choice of local slate for the construction. The building's ground-plan measures 15 x 15 meters, with the corners oriented to the four cardinal points. Constructed in stone and brick, it is taller than it is wide, with a spire topped with the four-armed cross, the Catalan flag and the royal crown. The house has a basement, ground floor, first floor and an attic, with a gable roof.
In 1895 he designed a funerary chapel for the Güell family at the abbey of Montserrat Abbey, Montserrat, but little is known about this work, which was never built. That year, construction finally began on the Bodegas Güell, the 1882 project for a hunting lodge and some wineries at La Cuadra de Garraf (Sitges), property of Eusebi Güell. Constructed between 1895 and 1897 under the direction of Francesc Berenguer, Gaudí's aide, the wineries have a triangular end façade, a very steep stone roof, a group of chimneys and two bridges that join them to an older building. It has three floors: the bottom one for a garage, an apartment and a chapel with catenary arches, with the altar in the centre. It was completed with a porter's lodge, notable for the iron gate in the shape of a fishing net.
In the township of Sant Gervasi de Cassoles (now a district of Barcelona), the widow of Jaume Figueras commissioned Gaudí to renovate the Torre Bellesguard (1900–1909), former summer palace of King Martin I the Humane. Gaudí designed it in a neo-Gothic style, respecting the former building as much as possible, and tried as always to integrate the architecture into the natural surroundings. This influenced his choice of local slate for the construction. The building's ground-plan measures 15 x 15 meters, with the corners oriented to the four cardinal points. Constructed in stone and brick, it is taller than it is wide, with a spire topped with the four-armed cross, the Catalan flag and the royal crown. The house has a basement, ground floor, first floor and an attic, with a gable roof.
Naturalist period
During this period Gaudí perfected his personal style, inspired by the organic shapes of nature, putting into practise a whole series of new structural solutions originating from his deep analysis of Ruled surface, ruled geometry. To this he added a great creative freedom and an imaginative ornamental style. His works acquired a great structural richness, with shapes and volumes devoid of rational rigidity or any classic premise.1898–1900
Commissioned by the company Hijos de Pedro Mártir Calvet, Gaudí built theCasa Calvet
Casa Calvet () is a building, designed by Antoni Gaudí for a textile manufacturer which served as both a commercial property (in the basement and on the ground floor) and a residence. It is located at Carrer de Casp 48, Eixample district of Ba ...
(1898–1899), in Barcelona's Carrer Casp. The façade is built of Montjuïc stone, adorned with wrought iron balconies and topped with two pediments with wrought iron crosses. Another notable feature of the façade is the gallery on the main floor, decorated with plant and mythological motifs. For this project, Gaudí used a Baroque style, visible in the use of Solomonic columns, decoration with floral themes and the design of the terraced roof. In 1900, he won the award for the best building of the year from Barcelona City Council.
A virtually unknown work by Gaudí is the Casa Clapés (1899–1900), at 125 Carrer Escorial, commissioned by the painter Aleix Clapés, who collaborated on occasion with Gaudí, such as in decorating the Palau Güell
The Palau Güell (, en, Güell Palace) is a mansion designed by the architect Antoni Gaudí for the industrial tycoon Eusebi Güell, and was built between 1886 and 1888. It is situated on the Carrer Nou de la Rambla, in the El Raval neighbor ...
and the Casa Milà
Casa Milà (, ), popularly known as ''La Pedrera'' (, ; "the stone quarry") in reference to its unconventional rough-hewn appearance, is a '' Modernista'' building in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It was the last private residence designed by arc ...
. It has a ground floor and three apartments, with stuccoed walls and cast-iron balconies. Due to its lack of decoration or original structural solutions its authorship was unknown until 1976, when the architect's signed plans by Gaudí were discovered. In 1900, he renovated the house of Dr. Pere Santaló, at 32 Carrer Nou de la Rambla, a work of equally low importance. Santaló was a friend of Gaudí's, whom he accompanied during his stay in Puigcerdà in 1911. It was he who recommended him to do manual work for his rheumatism.
Also in 1900, he designed two banners: for the Orfeó Feliuà (of Sant Feliu de Codines), made of brass, leather, cork and silk, with ornamental motifs based on the martyrdom of San Félix (a millstone), music (a staff and clef) and the inscription "Orfeó Feliuà"; and Our Lady of Mercy of Reus, for the pilgrimage of the Reus residents of Barcelona, with an image of Isabel Besora, the shepherdess to whom the Virgin appeared in 1592, work of Aleix Clapés and, on the back, a rose and the Catalan flag. In the same year, for the shrine of Our Lady of Mercy in Reus, Gaudí outlined a project for the renovation of the church's main façade, which ultimately was not undertaken, as the board considered it too expensive. Gaudí took this rejection quite badly, leaving some bitterness towards Reus, possibly the source of his subsequent claim that Riudoms was his place of birth. Between 1900 and 1902 Gaudí worked on the Casa Miralles, commissioned by the industrialist Hermenegild Miralles i Anglès; Gaudí designed only the wall near the gateway, of undulating masonry, with an iron gate topped with the four-armed cross. Subsequently, the house for Señor Miralles was designed by Domènec Sugrañes, associate architect of Gaudí.
Gaudí's main new project at the beginning of the 20th century was the Park Güell
Parc Güell ( ca, Parc Güell ; es, Parque Güell) is a privatized park system composed of gardens and architectural elements located on Carmel Hill, in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. Carmel Hill belongs to the mountain range of Collserola – t ...
(1900–1914), commissioned by Eusebi Güell. It was intended to be a residential estate in the style of an English garden city movement, garden city. The project was unsuccessful: of the 60 plots into which the site was divided only one was sold. Despite this, the park entrances and service areas were built, displaying Gaudí's genius and putting into practice many of his innovative structural solutions. The Park Güell is situated in Barcelona's Càrmel district, a rugged area, with steep slopes that Gaudí negotiated with a system of viaducts integrated into the terrain. The main entrance to the park has a building on each side, intended as a porter's lodge and an office, and the site is surrounded by a stone and glazed-ceramic wall. These entrance buildings are an example of Gaudí at the height of his powers, with Catalan vaults that form a parabolic hyperboloid. After passing through the gate, steps lead to higher levels, decorated with sculpted fountains, notably the dragon fountain, which has become a symbol of the park and one of Gaudí's most recognised emblems. These steps lead to the Hypostyle Hall, which was to have been the residents' market, constructed with large Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
columns. Above this chamber is a large plaza in the form of a Greek theatre, with the famous undulating bench covered in broken ceramics ("trencadís
''Trencadís'' (), also known as pique assiette, broken tile mosaics, bits and pieces, memoryware, and shardware, is a type of mosaic made from cemented-together tile shards and broken chinaware. Glazed china tends to be preferred, and glass is so ...
"), the work of Josep Maria Jujol
José María Jujol Gibert (16 September 1879 – 1 May 1949) was a Spanish architect. Jujol's wide field of activity ranged from furniture designs and painting, to architecture. He worked with Antoni Gaudí on many of his most famous works. ...
. The park's show home, the work of Francesc Berenguer, was Gaudí's residence from 1906 to 1926, and currently houses the Gaudi House Museum, Casa-Museu Gaudí.
During this period Gaudí contributed to a group project, the Rosary of Montserrat (1900–1916). Located on the way to the Holy Cave of Montserrat, it was a series of groups of sculptures that evoked the mysteries of the Virgin, who tells the rosary. This project involved the best architects and sculptors of the era, and is a curious example of Catalan Modernism. Gaudí designed the First Mystery of Glory, which represents the Holy Sepulcher. The series include a statue of Christ Risen, the work of Josep Llimona, and the Three Marys sculpted by Dionís Renart. Another monumental project designed by Gaudí for Montserrat was never carried out: it would have included crowning the summit of El Cavall Bernat (one of the mountain peaks) with a viewpoint in the shape of a royal crown, incorporating a high Catalan coat of arms into the wall.
1901–1903
In 1901 Gaudí decorated the house of Isabel Güell López, Marchioness of Castelldosrius, and daughter of Eusebi Güell. Situated at 19 Carrer Junta de Comerç, the house had been built in 1885 and renovated between 1901 and 1904; it was destroyed by a bomb during the Spanish Civil War, Civil War. The following year Gaudí took part in the decoration of the Bar Torino, property of Flaminio Mezzalana, located at 18 Passeig de Gràcia; Gaudí designed the ornamentation of el Salón Árabe of that establishment, made with varnished Arabian-style cardboard tiles (which no longer exist). A project of great interest to Gaudí was the restoration of the Cathedral of Santa Maria in Palma de Mallorca (1903–1914), commissioned by the city's bishop, Pere Campins i Barceló. Gaudí planned a series of works including removing the baroque altarpiece, revealing the bishop's throne, moving the choir-stalls from the centre of the nave and placing them in the presbytery, clearing the way through chapel of the Holy Trinity, placing new pulpits, fitting the cathedral with electrical lighting, uncovering the Gothic windows of the Royal Chapel and filling them with stained glass, placing a large canopy above the main altar and completing the decoration with paintings. This was coordinated by Joan Rubió i Bellver, Gaudí's assistant. Josep Maria Jujol and the painters Joaquín Torres García, Iu Pascual and Jaume Llongueras were also involved. Gaudí abandoned the project in 1914 due to disagreements with the Cathedral chapter.1904
 Among Gaudí's largest and most striking works is the
Among Gaudí's largest and most striking works is the Casa Batlló
() is a building in the center of Barcelona. It was designed by Antoni Gaudí, and is considered one of his masterpieces. A remodel of a previously built house, it was redesigned in 1904 by Gaudí and has been refurbished several times after th ...
(1904–1906). Commissioned by Josep Batlló i Casanovas to renovate an existing building erected in 1875 by Emili Sala Cortés, Gaudí focused on the façade, the main floor, the patio and the roof, and built a fifth floor for the staff. For this project he was assisted by his aides Domènec Sugrañes, Joan Rubió and Josep Canaleta. The façade is of Montjuïc sandstone cut to create warped ruled surface
In geometry, a surface is ruled (also called a scroll) if through every point of there is a straight line that lies on . Examples include the plane, the lateral surface of a cylinder or cone, a conical surface with elliptical directrix, the ...
s; the columns are bone-shaped with vegetable decoration. Gaudí kept the rectangular shape of the old building's balconies—with iron railings in the shape of masks—giving the rest of the façade an ascending undulating form. He also faced the façade with ceramic fragments of various colours ("trencadís"), which Gaudí obtained from the waste material of the Pelegrí glass works. The interior courtyard is roofed by a skylight supported by an iron structure in the shape of a double T, which rests on a series of catenary aches. The helicoidal chimneys are a notable feature of the roof, topped with conical caps, covered in clear glass in the centre and ceramics at the top, and surmounted by clear glass balls filled with sand of different colours. The façade culminates in catenary vaults covered with two layers of brick and faced with glazed ceramic tiles in the form of scales (in shades of yellow, green and blue), which resemble a dragon's back; on the left side is a cylindrical turret with anagrams of Jesus, Mary and Joseph, and with Gaudí's four-armed cross.
In 1904, commissioned by the painter Lluís Graner, he designed the decoration of the Sala Mercè, in the Rambla dels Estudis, one of the first cinemas in Barcelona; the theatre imitated a cave, inspired by the Coves del Drac (Dragon's Caves) in Mallorca. Also for Graner he designed a detached house in the Bonanova district of Barcelona, of which only the foundations and the main gate were built, with three openings: for people, vehicles and birds; the building would have had a structure similar to the Casa Batlló or the porter's lodge of the Park Güell.
 The same year he built a workshop, the Taller Badia, for Josep and Lluís Badia Miarnau,
blacksmiths who worked for Gaudí on several of his works, such as the Batlló and Milà houses, the Park Güell and the Sagrada Família. Located at 278 Carrer Nàpols, it was a simple stone building. Around that time he also designed hexagonal Cement tile, hydraulic floor tiles for the Casa Batlló, they were eventually used instead for the Casa Milà; they were a green colour and were decorated with seaweed, shells and starfish. These tiles were subsequently chosen to pave Barcelona's Passeig de Gràcia.
Also in 1904 he built the Chalet de Catllaràs, in La Pobla de Lillet, for the Asland cement factory, owned by Eusebi Güell. It has a simple structure though very original, in the shape of a pointed arch, with two semi-circular flights of stairs leading to the top two floors. This building fell into ruin when the cement works closed, and when it was eventually restored its appearance was radically altered, the ingenious original staircase being replaced with a simpler metal one. In the same area he created the Can Artigas Gardens between 1905 and 1907, in an area called Font de la Magnesia, commissioned by the textile merchant Joan Artigas i Alart; men who had worked the Park Güell were also involved on this project, similar to the famous park in Barcelona.
The same year he built a workshop, the Taller Badia, for Josep and Lluís Badia Miarnau,
blacksmiths who worked for Gaudí on several of his works, such as the Batlló and Milà houses, the Park Güell and the Sagrada Família. Located at 278 Carrer Nàpols, it was a simple stone building. Around that time he also designed hexagonal Cement tile, hydraulic floor tiles for the Casa Batlló, they were eventually used instead for the Casa Milà; they were a green colour and were decorated with seaweed, shells and starfish. These tiles were subsequently chosen to pave Barcelona's Passeig de Gràcia.
Also in 1904 he built the Chalet de Catllaràs, in La Pobla de Lillet, for the Asland cement factory, owned by Eusebi Güell. It has a simple structure though very original, in the shape of a pointed arch, with two semi-circular flights of stairs leading to the top two floors. This building fell into ruin when the cement works closed, and when it was eventually restored its appearance was radically altered, the ingenious original staircase being replaced with a simpler metal one. In the same area he created the Can Artigas Gardens between 1905 and 1907, in an area called Font de la Magnesia, commissioned by the textile merchant Joan Artigas i Alart; men who had worked the Park Güell were also involved on this project, similar to the famous park in Barcelona.
1906
 In 1906 he designed a bridge over the Torrent de Pomeret, between Sarrià and Sant Gervasi. This river flowed directly between two of Gaudí's works, Bellesguard and the Chalet Graner, and so he was asked to bridge the divide. Gaudí designed an interesting structure composed of juxtaposed triangles that would support the bridge's framework, following the style of the viaducts that he made for the Park Güell. It would have been built with cement, and would have had a length of and a height of ; the balustrade would have been covered with glazed tiles, with an inscription dedicated to Santa Eulàlia. The project was not approved by the Town Council of Sarrià.
The same year Gaudí apparently took part in the construction of the Torre Damià Mateu, in Llinars del Vallès in collaboration with his disciple Francesc Berenguer, though the project's authorship is not clear or to what extent they each contributed to it. The style of the building evokes Gaudí's early work, such as the Casa Vicens or the Güell Pavilions; it had an entrance gate in the shape of a fishing net, currently installed in the Park Güell. The building was demolished in 1939. Also in 1906 he designed a new banner, this time for the Guild of metalworkers and blacksmiths for the Corpus Christi procession of 1910, in Barcelona Cathedral. It was dark green in colour, with Barcelona's coat of arms in the upper left corner, and an image of Saint Eligius, patron of the guild, with typical tools of the trade. The banner was burned in July 1936.
In 1906 he designed a bridge over the Torrent de Pomeret, between Sarrià and Sant Gervasi. This river flowed directly between two of Gaudí's works, Bellesguard and the Chalet Graner, and so he was asked to bridge the divide. Gaudí designed an interesting structure composed of juxtaposed triangles that would support the bridge's framework, following the style of the viaducts that he made for the Park Güell. It would have been built with cement, and would have had a length of and a height of ; the balustrade would have been covered with glazed tiles, with an inscription dedicated to Santa Eulàlia. The project was not approved by the Town Council of Sarrià.
The same year Gaudí apparently took part in the construction of the Torre Damià Mateu, in Llinars del Vallès in collaboration with his disciple Francesc Berenguer, though the project's authorship is not clear or to what extent they each contributed to it. The style of the building evokes Gaudí's early work, such as the Casa Vicens or the Güell Pavilions; it had an entrance gate in the shape of a fishing net, currently installed in the Park Güell. The building was demolished in 1939. Also in 1906 he designed a new banner, this time for the Guild of metalworkers and blacksmiths for the Corpus Christi procession of 1910, in Barcelona Cathedral. It was dark green in colour, with Barcelona's coat of arms in the upper left corner, and an image of Saint Eligius, patron of the guild, with typical tools of the trade. The banner was burned in July 1936.
 Another of Gaudí's major projects and among his most admired works is the
Another of Gaudí's major projects and among his most admired works is the Casa Milà
Casa Milà (, ), popularly known as ''La Pedrera'' (, ; "the stone quarry") in reference to its unconventional rough-hewn appearance, is a '' Modernista'' building in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It was the last private residence designed by arc ...
, better known as La Pedrera (1906–1910), commissioned by Pere Milà i Camps. Gaudí designed the house around two large, curved courtyards, with a structure of stone, brick and cast-iron columns and steel beams. The façade is built of limestone from Vilafranca del Penedès, apart from the upper level, which is covered in white tiles, evoking a snowy mountain. It has a total of five floors, plus a loft made entirely of catenary arches, as well as two large interior courtyards, one circular and one oval. Notable features are the staircases to the roof, topped with the four-armed cross, and the chimneys, covered in ceramics and with shapes that suggest mediaeval helmets. The interior decoration was carried out by Josep Maria Jujol and the painters Iu Pascual, Xavier Nogués and Aleix Clapés. The façade was to have been completed with a stone, metal and glass sculpture with Our lady of the Rosary accompanied by the archangels Michael and Gabriel, 4m in height. A sketch was made by the sculptor Carles Mani, but due to the events of the Tragic Week in 1909 the project was abandoned.
1907–1908
In 1907, to mark the seventh centenary of the birth of James I of Aragon, King James I, Gaudí designed a monument in his memory. It would have been situated in the Plaça del Rei, and would have also meant the renovation of the adjacent buildings: new roof for the cathedral, as well as the completion of its towers and cupola; placement of three vases above the buttresses of the Chapel of Santa Àgada, dedicated to the Litany of the Blessed Virgin Mary, as well as the figure of an angel on top of the chapel's tower; finally, the opening of a large square next to the walls (now the Plaça Ramon Berenguer el Grand). The project was not executed because the city council disliked it. In 1908 Gaudí devised a project for a skyscraper hotel in New York City, the Hotel Attraction, commissioned by two American entrepreneurs whose names are unknown. It would have been high (taller than the Empire State Building), with a taller parabolic central section, topped with a star, and flanked by four volumes containing museums, art galleries and concert halls, with shapes similar to the Casa Milà. Inside it would have had five large rooms, one dedicated to every continent. The final project for his great patron Eusebi Güell was the church for the Colònia Güell, an industrial village in Santa Coloma de Cervelló (1890–1918). The project began in 1890, and the factory, service buildings and housing for the workers were constructed. What would have been the colony's church was designed by Gaudí in 1898, though the first stone was not laid until 4 October 1908. Unfortunately only the crypt (known today as Crypt of the Colònia Güell) was built, as Güell's sons abandoned the project after his death in 1918. Gaudí designed an oval church with five aisles, one central aisle and two at either side. He conceived it as fully integrated into nature. A porch of hyperbolic paraboloid vaults precedes the crypt, the first time that Gaudí used this structure and notably the first use of paraboloid vaults in the history of architecture. In the crypt the large hyperboloid stained glass windows stand out, with the shapes of flower petals and butterfly wings. Inside, circular brick pillars alternate with slanted basalt columns from Castellfollit de la Roca.
The final project for his great patron Eusebi Güell was the church for the Colònia Güell, an industrial village in Santa Coloma de Cervelló (1890–1918). The project began in 1890, and the factory, service buildings and housing for the workers were constructed. What would have been the colony's church was designed by Gaudí in 1898, though the first stone was not laid until 4 October 1908. Unfortunately only the crypt (known today as Crypt of the Colònia Güell) was built, as Güell's sons abandoned the project after his death in 1918. Gaudí designed an oval church with five aisles, one central aisle and two at either side. He conceived it as fully integrated into nature. A porch of hyperbolic paraboloid vaults precedes the crypt, the first time that Gaudí used this structure and notably the first use of paraboloid vaults in the history of architecture. In the crypt the large hyperboloid stained glass windows stand out, with the shapes of flower petals and butterfly wings. Inside, circular brick pillars alternate with slanted basalt columns from Castellfollit de la Roca.
Final period
 During the last years of his career, dedicated almost exclusively to the
During the last years of his career, dedicated almost exclusively to the Sagrada Família
The Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família, shortened as the Sagrada Família, is an unfinished church in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is the largest unfinished Catholic church in the world. Designed by ...
, Gaudí reached the culmination of this naturalistic style, creating a synthesis of all of the solutions and styles he had tried until then. Gaudí achieved perfect harmony between structural and ornamental elements, between plastic and aesthetic, between function and form, between container and content, achieving the integration of all arts in one structured, logical work.
The first example of his final stage can be seen in a simple but very ingenious building, the Sagrada Família schools, a small school for the workers' children. Built in 1909, it has a rectangular ground plan of , and contained three classrooms, a vestibule and a chapel. It was built of exposed brick, in three overlapping layers, following the traditional Catalan method. The walls and roof have an undulating shape, giving the structure a sense of lightness but also strength. The Sagrada Família schools have set an example of constructive genius and have served as a source of inspiration for many architects, such is their simplicity, strength, originality, functionality and geometric excellence.
In May 1910 Gaudí paid a short visit to Vic, where he was tasked to design the lampposts for the city's Plaça Major, in commemoration of the first centenary of the birth of Jaume Balmes
Jaime Luciano Balmes y Urpiá ( ca, Jaume Llucià Antoni Balmes i Urpià; August 28, 1810July 9, 1848) was a Spanish philosopher, theologian, Catholic apologist, sociologist and political writer. Familiar with the doctrine of Saint Thomas Aqui ...
. They were obelisk-shaped lamps, with basalt rock bases from Castellfollit de la Roca and wrought iron arms, topped with the four-armed cross; they were decorated with vegetable themes and included the birth and death dates of Balmes. They were demolished in 1924 due to poor maintenance.
The same year, on the occasion of Eusebi Güell's obtaining the title of count, Gaudí designed a coat of arms for his patron. He devised a shield with the lower part in a catenary shape typical of Gaudí. He divided it into two parts: the lantern of Palau Güell features a dove and a gear-wheel on the right in allusion to the Colònia Güell in Santa Coloma de Cervelló (''coloma'' is Catalan for dove), with the phrase ''ahir pastor'' (yesterday Shepherd). On the left is an owl perched on a half-moon—symbol of prudence and wisdom—with the words ''avuy senyor'' (today Lord). The shield is surmounted by a helmet with the count's coronet and the dove symbol of the Holy Spirit.
In 1912 he built two pulpits for the church of Santa Maria in Blanes: the pulpit on the Gospel side had a hexagonal base, decorated with the dove of the Holy Spirit and the names in Latin of the four evangelists and the seven Gifts of the Holy Spirit; the pulpit of the Epistle side had the names of the apostles who wrote epistles (Saint Peter, Saint Paul, Saint John the Evangelist, Saint Judas Thadeus and Saint James the Great), with the three theological virtues and the flames of Pentecost. These pulpits were burned in July 1936.
La Sagrada Família
 From 1915 Gaudí devoted himself almost exclusively to his Masterpiece, magnum opus, the Sagrada Família, a synthesis of his architectural evolution. After completion of the crypt and the apse, still in Gothic style, the rest of the church is conceived in an organic style, imitating natural shapes with their abundance of
From 1915 Gaudí devoted himself almost exclusively to his Masterpiece, magnum opus, the Sagrada Família, a synthesis of his architectural evolution. After completion of the crypt and the apse, still in Gothic style, the rest of the church is conceived in an organic style, imitating natural shapes with their abundance of ruled surface
In geometry, a surface is ruled (also called a scroll) if through every point of there is a straight line that lies on . Examples include the plane, the lateral surface of a cylinder or cone, a conical surface with elliptical directrix, the ...
s. He intended the interior to resemble a forest, with inclined columns like branching trees, helicoidal in form, creating a simple but sturdy structure. Gaudí applied all of his previous experimental findings in this project, from works such as the Park Güell and the crypt of the Colònia Güell, creating a church that is at once structurally perfect, harmonious and aesthetically satisfying.
The Sagrada Família has a cruciform plan, with a five-aisled nave, a transept of three aisles, and an apse with seven chapels. It has three façades dedicated to the birth, passion and glory of Jesus, and when completed it will have eighteen towers: four at each side making a total of twelve for the apostles, four on the transept invoking the evangelists and one on the apse dedicated to the Virgin, plus the central tower in honour of Jesus, which will reach in height. The church will have two sacristy, sacristies adjacent to the apse, and three large chapels: one for the Assumption in the apse, and the Baptism and Penitence chapels at the west end; also, it will be surrounded by a cloister designed for processions and to isolate the building from the exterior. Gaudí used highly symbolic content in the Sagrada Família, both in architecture and sculpture, dedicating each part of the church to a religious theme.
During Gaudí's life only the crypt, apse and part of the Nativity façade were completed. Upon his death his assistant Domènec Sugrañes took over the construction; thereafter it was directed by various architects. Jordi Bonet i Armengol assumed responsibility in 1987 and continued as of 2011. Artists such as Llorenç and Joan Matamala, Carles Mani, Jaume Busquets, Joaquim Ros i Bofarull, Etsuro Sotoo and Josep Maria Subirachs (creator of the Passion façade) have worked on the sculptural decoration. Completion is not expected until at least 2026.
Minor, late projects
During the last years of his life, apart from his devotion to the Sagrada Família, Gaudí participated only in minor projects, which were not completed: in 1916, on the death of his friend bishop Josep Torras i Bages, he designed a monument in his honour, which he wanted to place in front of the Passion façade of the Sagrada Família. He made a sketch of the project, which ultimately was not carried out, and made a plaster bust of the bishop, the work of Joan Matamala under the instruction of Gaudí. It was put in the Sagrada Família, where it would have formed part of the church, but it was destroyed in 1936. Another commemorative monument project, also not carried out, was dedicated to Enric Prat de la Riba, which would have been situated in Castellterçol, birthplace of this Catalan politician. The project dates from 1918, and would have consisted of a tall tower with two porticos and a spire topped with an iron structure flying the Catalan flag. The sketch of the project was done by Lluís Bonet i Garí, Gaudí's assistant. In 1922 Gaudí was commissioned, by the Franciscan Padre Angélico Aranda, to construct a church dedicated to the Assumption in the Chilean city of Rancagua. Gaudí apologised and said that he was occupied exclusively with the Sagrada Família, but sent some sketches of the Assumption chapel which he had designed for the apse of the Sagrada Família, which more or less coincided with what Padre Aranda had asked for. Unfortunately this project was not carried out, though there are currently plans by the Chilean architect Christian Matzner to take up the project. The President of Chile, Michelle Bachelet, has announced that building will begin in 2015, with an expected completion in 2017 and at a cost of US dollar, $7 million. Once completed it will become the first of Gaudí's works to be constructed in the Americas. The same year Gaudí was consulted about the construction of a monumental train station for Barcelona (the future Estació de França). Gaudí suggested an iron structure in the form of a large suspended awning, a solution quite ahead of its time; perhaps for this reason, it put the head engineers off, and they declined Gaudí's offer. The last known projects by the architect are the chapel for the Colónia Calvet in Torelló, of 1923, and a pulpit for Valencia (the exact location is unknown), of 1924. From then on, Gaudí worked exclusively on the Sagrada Família until his death.Collaborators
The enormous task which Gaudí faced, not in terms of the number of works, but in terms of their complexity, required the collaboration of a large number of assistants, artists, architects and craftsmen. Gaudí always led the way, but allowed expression of the individual abilities of all of his collaborators. A test of his expertise both in his field and in interpersonal communication was demonstrated in bringing together a large number of diverse professionals and creating an integrated team. Among his collaborators were: * Architects: Francesc Berenguer, Josep Maria Jujol, Cristòfor Cascante i Colom, Josep Francesc Ràfols, Cèsar Martinell, Joan Bergós, Francesc Folguera, Josep Canaleta, Joan Rubió, Domènec Sugrañes, Francesc Quintana, Isidre Puig i Boada, Lluís Bonet i Garí. * Sculptors: Carles Mani, Joan Flotats, Llorenç Matamala, Joan Matamala, Josep Llimona. * Painters: Ricard Opisso, Aleix Clapés, Iu Pascual, Xavier Nogués, Jaume Llongueras, Joaquín Torres García. * Builders and foremen: Agustí Massip, Josep Bayó i Font, Claudi Alsina i Bonafont, Josep Pardo i Casanova and his nephew Julià Bardier i Pardo. * Craftsmen: Eudald Puntí (carpenter and forger), Joan Oñós (forger), Lluís y Josep Badia i Miarnau (forger), Joan Bertran (plasterer), Joan Munné (cabinet maker), Frederic Labòria (cabinet maker), Antoni Rigalt i Blanch (glazier), Josep Pelegrí (glazier), Mario Maragliano (mosaic artist), Jaume Pujol i Bausis and his son Pau Pujol i Vilà (ceramicists).Death and legacy
Gaudí was run down by a tram, and died on 10 June 1926. He is buried in the Sagrada Familia. After his death, Gaudí's works suffered a period of neglect and were largely unpopular among international critics, who regarded them as baroque and excessively imaginative. In his homeland he was equally disdained by ''Noucentisme
Noucentisme in Catalonia (, ''noucentista'' being its adjective) was a Catalan cultural movement of the early 20th century that originated largely as a reaction against Modernisme, both in art and ideology, and was, simultaneously, a perception o ...
'', the new movement which took the place of ''Modernisme''. In 1936, during the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
, Gaudí's workshop in the Sagrada Família was ransacked, and a great number of his documents, plans and scale models were destroyed.
Gaudí's reputation was beginning to recover by the 1950s, when his work was championed not only by Salvador Dalí but also by architect Josep Lluís Sert. In 1952, the centenary year of the architect's birth, the Asociación de Amigos de Gaudí (Friends of Gaudí Association) was founded with the aim of disseminating and conserving his legacy. Four years later, a retrospective was organised at the Palau Reial Major, Saló del Tinell in Barcelona, and the Gaudí Chair at the Polytechnic University of Catalonia was created with the purpose of deepening the study of Gaudí's works and participating in their conservation. These events were followed in 1957 by Gaudí's first international exhibition, held at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. In 1976, on the 50th anniversary of his death, the Spanish Ministry of Foreign Affairs organised an exhibition about Gaudí and his works that toured the globe.
Between 1950 and 1960, research and writings by international critics like George R. Collins, Nikolaus Pevsner and Roberto Pane spread a renewed awareness of Gaudí's work, while in his homeland it was admired and promoted by Alexandre Cirici, Juan Eduardo Cirlot and Oriol Bohigas. Gaudí's work has since gained widespread international appreciation, such as in Japan where notable studies have been published by Hiroya Tanka Architect, Dr. Hiroya Tanaka (Gaudi Prize winner), Kenji Imai and Tokutoshi Torii. International recognition of Gaudí's contributions to the field of architecture and design culminated in the 1984 listing of Gaudí's key works as UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Gaudí's style have subsequently influenced contemporary architects such as Santiago Calatrava
Santiago Calatrava Valls (born 28 July 1951) is a Spanish architect, structural engineer, sculptor and painter, particularly known for his bridges supported by single leaning pylons, and his railway stations, stadiums, and museums, whose sculpt ...
and Norman Foster.
Gaudí was the subject of the 1984 documentary ''Antonio Gaudi (film), Antonio Gaudi''.
Due to Gaudí's profoundly religious and ascetic lifestyle, the archbishop of Barcelona, Ricard Maria Carles proposed Gaudí's beatification
Beatification (from Latin ''beatus'', "blessed" and ''facere'', "to make”) is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their nam ...
in 1998. In 1999, American composer Christopher Rouse (composer), Christopher Rouse wrote the guitar concerto ''Concert de Gaudí'', which was inspired by Gaudí's work; it went on to win the 44th Annual Grammy Awards, 2002 Grammy Award for Grammy Award for Best Classical Contemporary Composition, Best Classical Contemporary Composition. On the occasion of the 150th anniversary of Gaudí's birth, a number of official ceremonies, concerts, shows and conferences were held, and several books were published. On 24 September of the same year, the musical ''Gaudí'' had its premiere in the Palau dels Esports de Barcelona. The authors of the piece were Jordi Galceran, Esteve Miralles and Albert Guinovart. In 2008 the Gaudí Awards were launched in his honour, organised by the Catalan Film Academy to award the best Catalan films of the year. An Iberia Airbus A340-642, EC-INO is named after Gaudí.
Japanese manga artist Takehiko Inoue wrote and illustrated a travel memoir on the life and architecture of Gaudí, titled ''Pepita: Takehiko Inoue Meets Gaudí'' and published in 2013.
Each year, since 2013, on June 10, the day when Gaudí died, the World Art Nouveau Day is celebrated.
World Heritage
List of Gaudí buildings#World Heritage Sites, Several of Gaudí's works have been granted World Heritage status by UNESCO: in 1984 the Park Güell, the Palau Güell and the Casa Milà; and in 2005 the Nativity façade, the crypt and the apse of the Sagrada Família, the Casa Vicens and the Casa Batlló in Barcelona, together with the crypt of the Colònia Güell in Santa Coloma de Cervelló. The declaration of Gaudí's works as World Heritage aims to recognise his outstanding universal value. According to the citation:Canonization cause
A sainthood guild interested in canonization for Gaudí began their efforts in earnest in 1992. By 2003, the cause was officially opened by the bishops of Catalonia, occasioning for Gaudí the title "Servant of God".See also
* List of Gaudí buildings * Gaudí House Museum * Altarpiece of AlellaNotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Pere Hereu, ''Els anys d'aprenentatge de Gaudí'' * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Gaudí's life and works
Sagrada Família information and discussion of lesser-known Gaudí works
Sagrada Família image gallery
Casa Batlló information and image gallery
Analysis of fractals and other mathematical elements in Gaudí's architectural style
Pàgina del Cercle Artístic de Sant Lluc
A virtual walk through the Guard House at Park Guell
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gaudi, Antoni 1852 births 1926 deaths 19th-century Spanish architects 20th-century Spanish architects Architects of Roman Catholic churches Burials at Sagrada Família Architects from Catalonia Modernisme architects Mosaicists Organic architecture Pedestrian road incident deaths People from Reus Railway accident deaths in Spain Spanish ecclesiastical architects Spanish Roman Catholics Spanish Servants of God Antoni Gaudí,