Antiproton Collector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Antiproton Collector (AC) was part of the antiparticle factory at CERN designed to decelerate and store
Retrieved 3 August 2018 The update comprised improvement work on the antiproton source, the construction of the Antiproton Collector (AC), as well as reconstructions of the injection and ejection systems of the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) and its stochastic cooling system. The estimated budget of the upgrade program was 40.2 million CHF. The changes were implemented during 1986 and 1987, with the AC getting constructed tightly around the existing AA ring."E. Jones: ''Progress on ACOL''" (1985)
Retrieved 3 August 2018 The Antiproton Accumulator Complex (AAC) served its last particles to the Proton-Antiproton Collider SpS in 1991. After the (SpS) was shut down, AAC continued to produce antiprotons for LEAR. Operation stopped in 1997, when the AA was dismantled and the AC was converted into the"B. Autin et al.: ''The antiproton decelerator (AD), a simplified antiproton source (feasibility study)''" (1995)
Retrieved 3 August 2018
 The main scope of the Antiproton Collector (AC) was to increase the antiproton luminosity in CERN's accelerator complex. Upgrading to the AC increased the number of available antiprotons tenfold to around antiprotons per second. The reason for this was the much larger acceptance of the AC compared to the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) alone. Additionally, several methods to compress the antiproton beams' phase space volume were applied, e.g. stochastic cooling."B. Autin: ''The CERN Antiproton Collector''" (1985)
The main scope of the Antiproton Collector (AC) was to increase the antiproton luminosity in CERN's accelerator complex. Upgrading to the AC increased the number of available antiprotons tenfold to around antiprotons per second. The reason for this was the much larger acceptance of the AC compared to the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) alone. Additionally, several methods to compress the antiproton beams' phase space volume were applied, e.g. stochastic cooling."B. Autin: ''The CERN Antiproton Collector''" (1985)
Retrieved 3 August 2018 The antiprotons were produced by accelerating protons onto a target. The resulting antiprotons emitted by the target material had a large
The History of Antimatter
*Record fo
Antiproton Collector
experiment on INSPIRE-HEP {{CERN Particle experiments CERN accelerators Particle physics facilities CERN facilities CERN
antimatter
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding particles in "ordinary" matter. Antimatter occurs in natural processes like cosmic ray collisions and some types of radioac ...
, to study the properties of antimatter and to create atoms of antihydrogen. It was built in 1986 around the existing Antiproton Accumulator
The Antiproton Accumulator (AA) was an infrastructure connected to the Proton–Antiproton Collider (SpS) – a modification of the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) – at CERN. The AA was built in 1979 and 1980, for the production and accumulati ...
(AA) to improve the antiproton production by a factor of 10. Together, the Antiproton Collector and the Antiproton Accumulator formed the so-called Antiproton Accumulator Complex (AAC).
Low energy antiproton research continues at CERN using the Antiproton Decelerator
The Antiproton Decelerator (AD) is a storage ring at the CERN laboratory near Geneva. It was built from the Antiproton Collector (AC) to be a successor to the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) and started operation in the year 2000. Antiproto ...
. It was built as a successor to LEAR and started operation in 2000.
History
After theAntiproton Accumulator
The Antiproton Accumulator (AA) was an infrastructure connected to the Proton–Antiproton Collider (SpS) – a modification of the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) – at CERN. The AA was built in 1979 and 1980, for the production and accumulati ...
(AA) had been operational since 1980, the update program ACOL (Antiproton COLlector) was proposed in 1983."CERN Scientific Committee: ''Design Study of an Antiproton Collector for the Antiproton Accumulator (ACOL)''" (1983) Retrieved 3 August 2018 The update comprised improvement work on the antiproton source, the construction of the Antiproton Collector (AC), as well as reconstructions of the injection and ejection systems of the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) and its stochastic cooling system. The estimated budget of the upgrade program was 40.2 million CHF. The changes were implemented during 1986 and 1987, with the AC getting constructed tightly around the existing AA ring."E. Jones: ''Progress on ACOL''" (1985)
Retrieved 3 August 2018 The Antiproton Accumulator Complex (AAC) served its last particles to the Proton-Antiproton Collider SpS in 1991. After the (SpS) was shut down, AAC continued to produce antiprotons for LEAR. Operation stopped in 1997, when the AA was dismantled and the AC was converted into the
Antiproton Decelerator
The Antiproton Decelerator (AD) is a storage ring at the CERN laboratory near Geneva. It was built from the Antiproton Collector (AC) to be a successor to the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) and started operation in the year 2000. Antiproto ...
(AD).Retrieved 3 August 2018
Operation
 The main scope of the Antiproton Collector (AC) was to increase the antiproton luminosity in CERN's accelerator complex. Upgrading to the AC increased the number of available antiprotons tenfold to around antiprotons per second. The reason for this was the much larger acceptance of the AC compared to the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) alone. Additionally, several methods to compress the antiproton beams' phase space volume were applied, e.g. stochastic cooling."B. Autin: ''The CERN Antiproton Collector''" (1985)
The main scope of the Antiproton Collector (AC) was to increase the antiproton luminosity in CERN's accelerator complex. Upgrading to the AC increased the number of available antiprotons tenfold to around antiprotons per second. The reason for this was the much larger acceptance of the AC compared to the Antiproton Accumulator (AA) alone. Additionally, several methods to compress the antiproton beams' phase space volume were applied, e.g. stochastic cooling."B. Autin: ''The CERN Antiproton Collector''" (1985)Retrieved 3 August 2018 The antiprotons were produced by accelerating protons onto a target. The resulting antiprotons emitted by the target material had a large
divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of t ...
, which called for special devices to focus them. Instead of quadrupole magnet
Quadrupole magnets, abbreviated as Q-magnets, consist of groups of four magnets laid out so that in the planar multipole expansion of the field, the dipole terms cancel and where the lowest significant terms in the field equations are quadrupole. ...
s, which are conventionally used to focus particle beams, rods of solid lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
with an applied high gradient magnetic field were implemented.
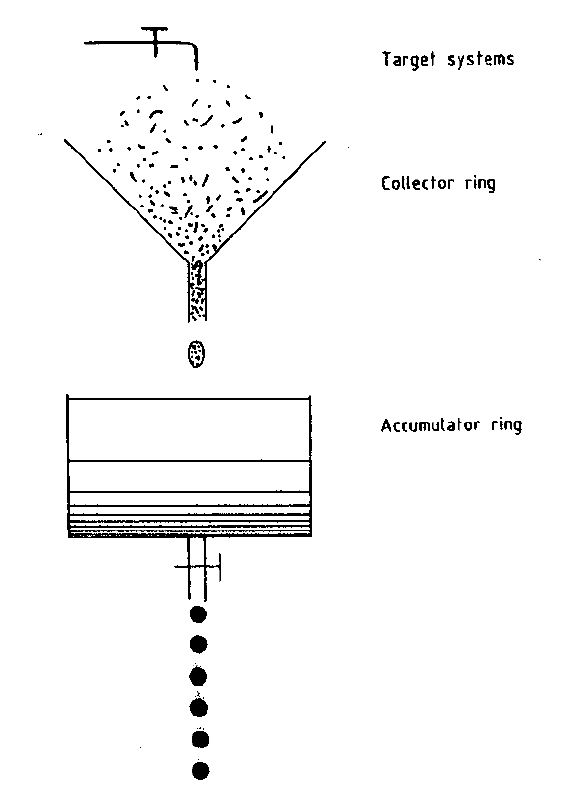
The functionality of the Antiproton Accumulator Complex can be well understood through the analogon of a hydraulic system, which is depicted in the included picture. The tap represents the target systems that produce antiprotons. These are collected in the collector ring with a large acceptance (the funnel). The accumulator ring can be compared to a reservoir, where the antiprotons are accumulated and eventually released as even, well defined bunches.
See also
*Antiproton Accumulator
The Antiproton Accumulator (AA) was an infrastructure connected to the Proton–Antiproton Collider (SpS) – a modification of the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) – at CERN. The AA was built in 1979 and 1980, for the production and accumulati ...
* Stochastic cooling
* Super Proton–Antiproton Synchrotron
References
External links
The History of Antimatter
*Record fo
Antiproton Collector
experiment on INSPIRE-HEP {{CERN Particle experiments CERN accelerators Particle physics facilities CERN facilities CERN