Aminolysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
R-X + R'-NH2 -> R-NH-R' + HX
 After the reaction is completed, ammonium acetate is heated under reflux (170 °C) to dehydrate the salt and eliminate excess acetic acid and water producing
After the reaction is completed, ammonium acetate is heated under reflux (170 °C) to dehydrate the salt and eliminate excess acetic acid and water producing 

chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, aminolysis (/am·i·nol·y·sis/) is any chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
in which a molecule is lysed (split into two parts) by reacting with ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
() or an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
(any molecule containing a nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
atom with a lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
, :N). The case where the reaction involves ammonia may be more specifically referred to as ammonolysis
In chemistry, ammonolysis (/am·mo·nol·y·sis/) is the process of splitting ammonia into NH2- + H+. Ammonolysis reactions can be conducted with organic compounds to produce amines (molecules containing a nitrogen atom with a lone pair, :N), o ...
.
Reactions
Alkyl group
An example of an aminolysis reaction is the replacement of ahalogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
in an alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalk ...
group () by an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
() and the elimination of hydrogen halide
In chemistry, hydrogen halides (hydrohalic acids when in the aqueous phase) are diatomic, inorganic compounds that function as Arrhenius acids. The formula is HX where X is one of the halogens: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine. ...
(HX).
:Synthesis of peptides
Another common example is the reaction of a primary amine or secondary amine with acarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
or with a carboxylic acid derivative to form an amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
. This reaction is widely used, especially in the synthesis of peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s. On the simple addition of an amine to a carboxylic acid, a salt of the organic acid and base is obtained. To overcome this, the carboxylic acid first needs to be "activated". This is usually done by converting the acid into a more reactive derivative (i.e. anhydride
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the pa ...
, acid halide
In organic chemistry, an acyl halide (also known as an acid halide) is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with a halide group (, where X is a halogen).
If the acid is a carboxylic acid (), the compound c ...
) or by using a coupling agent
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end mov ...
. In some cases, high temperatures (>200 °C) can overcome salt formation by driving off water, without the need for "activation" of the carboxyl group. The downside to this simple reaction is that the compounds may decompose at these elevated temperatures.
The carboxylic acid derivatives can be ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
s, anhydrides, acid halides or any other activated species.
The choice of activated carboxyl group or coupling agent can be very important in peptide synthesis, as using the wrong one can lead to racemization In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic (optically inactive) form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred too as a racemic mixture (i.e. con ...
.
Synthesis of amides from carboxylic acids
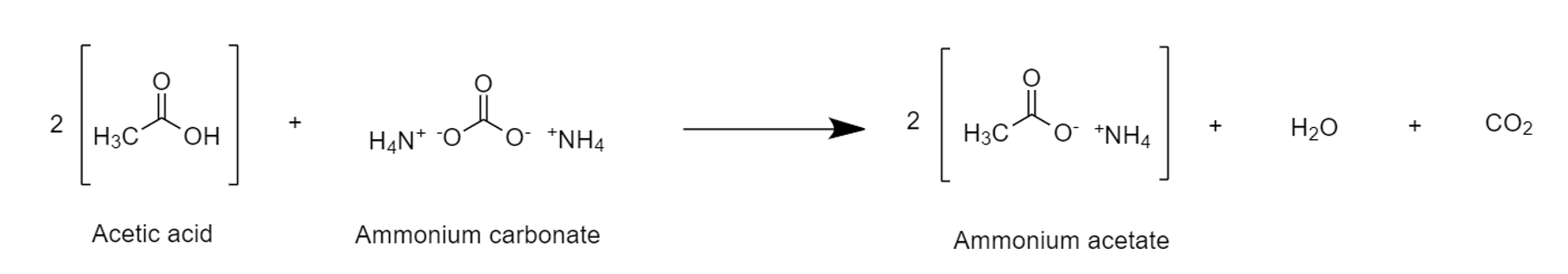
Making an amide is one of the processes which require ammonia as a reactant. There are other processes of preparing an amide such as from acid anhydrides and acyl chloride. Carboxylic acids react withammonium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate is a salt with the chemical formula (NH4)2CO3. Since it readily degrades to gaseous ammonia and carbon dioxide upon heating, it is used as a leavening agent and also as smelling salt. It is also known as baker's ammonia and is ...
, to convert the carboxylic acids to ammonium salts. For example, acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
reacts with ammonium carbonate to produce ammonium acetate
Ammonium acetate, also known as spirit of Mindererus in aqueous solution, is a chemical compound with the formula NH4CH3CO2. It is a white, hygroscopic solid and can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is available commerci ...
.
 After the reaction is completed, ammonium acetate is heated under reflux (170 °C) to dehydrate the salt and eliminate excess acetic acid and water producing
After the reaction is completed, ammonium acetate is heated under reflux (170 °C) to dehydrate the salt and eliminate excess acetic acid and water producing acetamide
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is the simplest amide derived from acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound ''N'',''N''-dimeth ...
:

Usage
PET degradation
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) belongs to the polyester family, it can be used for many purposes such as plastic bottles and filter cloth as it is thermoplastic polymer. PET can be degraded by using aminolysis which works similarly to solvolytic reaction and aminoglycolysis. For aminolysis, PET reacts with DETA (diethylenetriamine) or TETA (triethylenetetramine) which is polyamine. The reaction involves 200 - 210 Celsius. From this reaction, the products are symmetrical primary amides, asymmetrical primary/ secondary diamides, and symmetrical secondary diamides. The remaining waste material products can be used for hardening of epoxy resins. Similarly, in solvolytic reaction, the polyester reacts with water, acid, amine or alcohol, and in aminoglycolysis reaction, the polyester reacts with TEA (triethanolamine). This is PET degradation with polyamines through aminolysis route.
See also
*Solvolysis
In chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (S1/S2) or elimination reaction, elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of S1 reactions, solvolysis of a chirality (chemistry), chiral reactant affor ...
References
{{Reflist Substitution reactions General chemistry