Amber Oneal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Amber is
Amber is
Retrieved 6 September 2018.
37.11
. Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the
Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the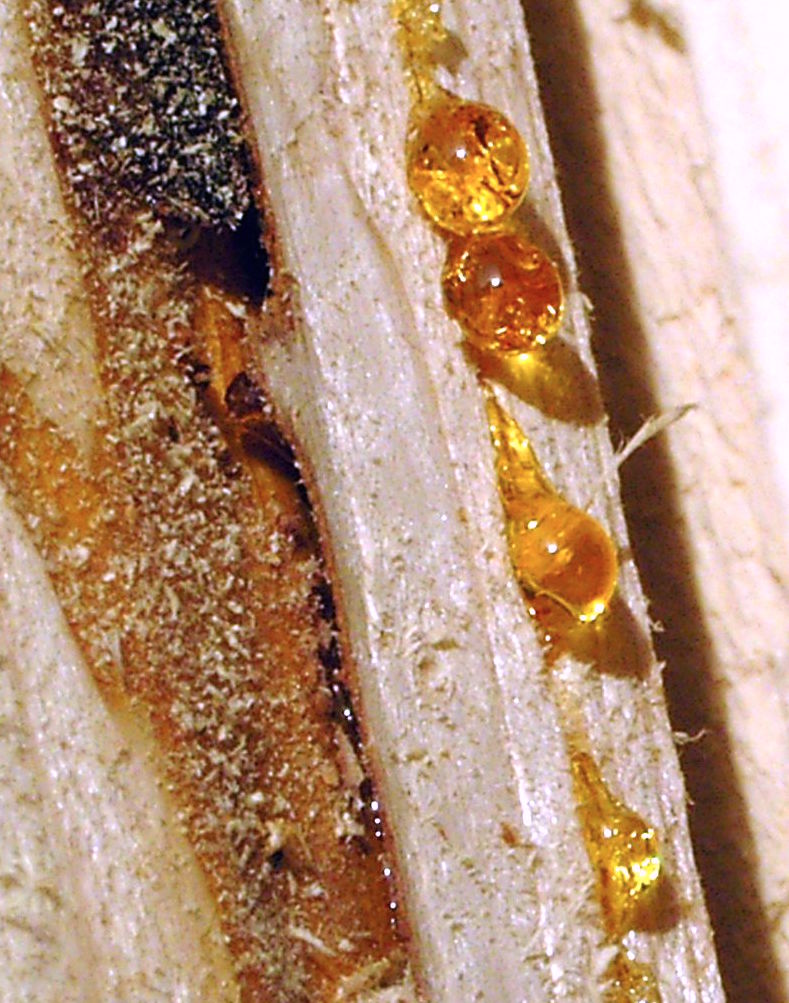  Pliny also cites the opinion of
Pliny also cites the opinion of
 The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber. Impurities are quite often present, especially when the resin dropped onto the ground, so the material may be useless except for varnish-making. Such impure amber is called ''firniss''. Such
The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber. Impurities are quite often present, especially when the resin dropped onto the ground, so the material may be useless except for varnish-making. Such impure amber is called ''firniss''. Such 

 Amber is globally distributed, mainly in rocks of
Amber is globally distributed, mainly in rocks of
 Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even
Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even 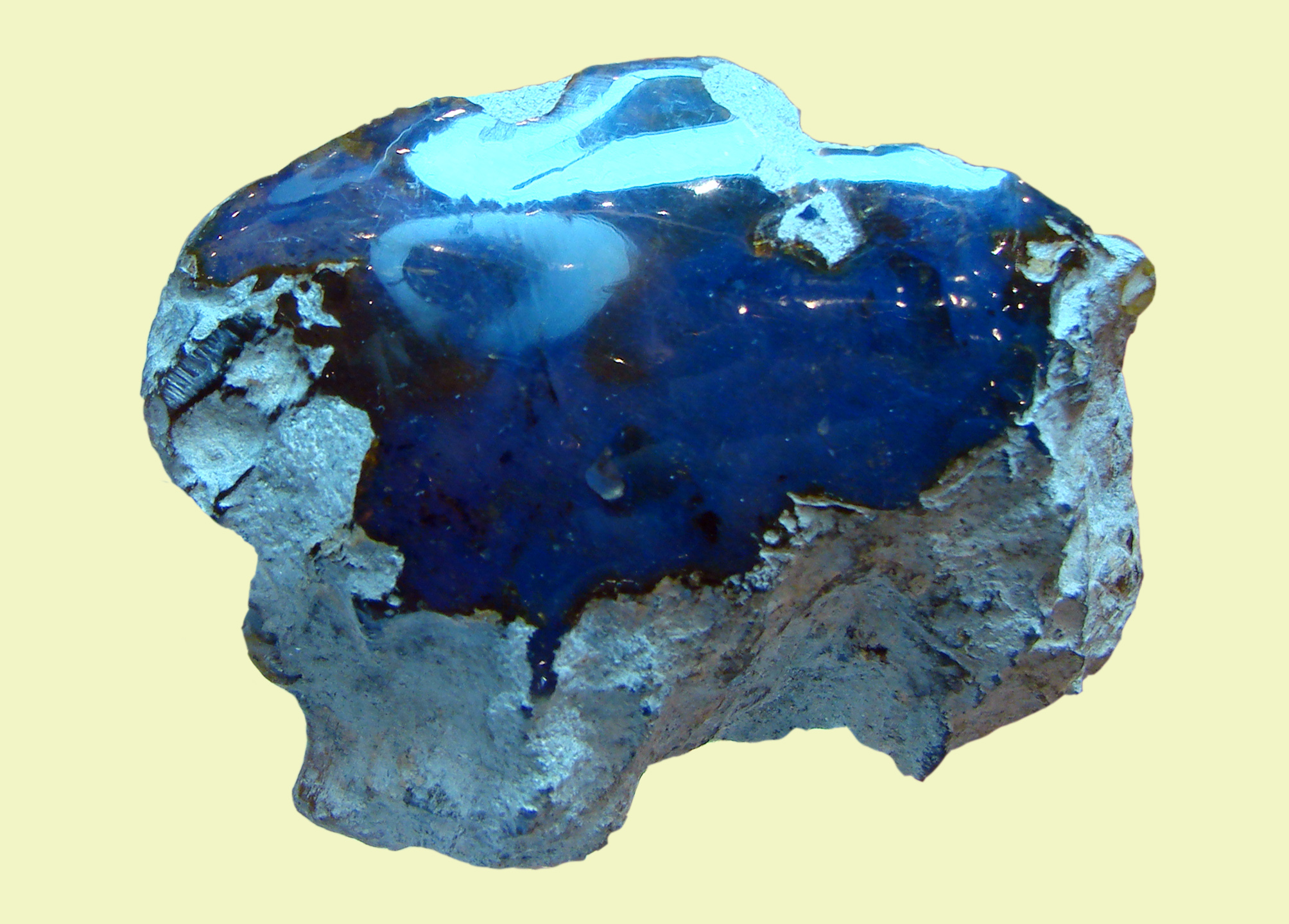 Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
 The oldest amber recovered dates to the
The oldest amber recovered dates to the 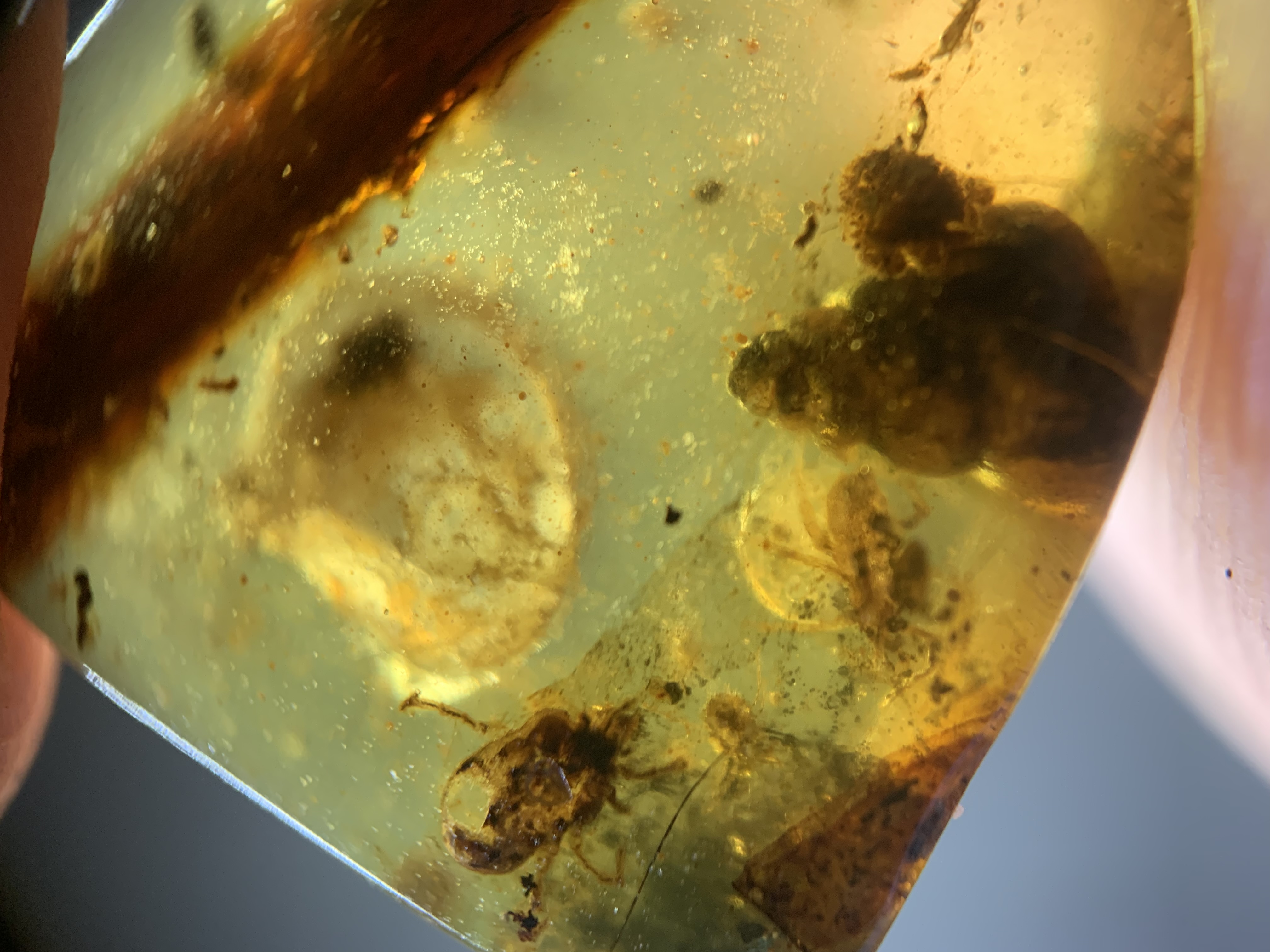
 The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel '' Jurassic Park'' and the 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric
The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel '' Jurassic Park'' and the 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric
 Amber has been used since prehistory (
Amber has been used since prehistory (

 Amber has been used as jewelry since the Stone Age, from 13,000 years ago. Amber ornaments have been found in Mycenaean tombs and elsewhere across Europe. To this day it is used in the manufacture of smoking and glassblowing mouthpieces. Amber's place in culture and tradition lends it a tourism value;
Amber has been used as jewelry since the Stone Age, from 13,000 years ago. Amber ornaments have been found in Mycenaean tombs and elsewhere across Europe. To this day it is used in the manufacture of smoking and glassblowing mouthpieces. Amber's place in culture and tradition lends it a tourism value;
Farlang many full text historical references on Amber
IPS Publications on amber inclusions
International Paleoentomological Society: Scientific Articles on amber and its inclusions
Webmineral on Amber
Physical properties and mineralogical information
Image and locality information on amber
40 million year old extinct bee in Dominican amber {{Authority control Fossil resins Amorphous solids Traditional medicine

 Amber is
Amber is fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ized tree resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia of New Jersey'', Rutgers University Press, . Amber is used in jewelry
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
and has been used as a healing agent in folk medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
.
There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents. Because it originates as a soft, sticky tree resin, amber sometimes contains animal and plant material as inclusions. Amber occurring in coal seams is also called resinite, and the term ''ambrite'' is applied to that found specifically within New Zealand coal seams.
Etymology
The English word ''amber'' derives fromArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
(ultimately from Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
''ambar'') via Middle Latin ''ambar'' and Middle French
Middle French (french: moyen français) is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the 14th to the 16th century. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from ...
''ambre''. The word was adopted in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
in the 14th century as referring to what is now known as ''ambergris
Ambergris ( or , la, ambra grisea, fro, ambre gris), ''ambergrease'', or grey amber is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull grey or blackish colour produced in the digestive system of sperm whales. Freshly produced ambergris has a mari ...
'' (''ambre gris'' or "grey amber"), a solid waxy substance derived from the sperm whale. In the Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
, the sense of the word was extended to Baltic amber
The Baltic region is home to the largest known deposit of amber, called Baltic amber or succinite. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that these forests created more than ...
(fossil resin) from as early as the late 13th century. At first called white or yellow amber (''ambre jaune''), this meaning was adopted in English by the early 15th century. As the use of ambergris waned, this became the main sense of the word. and
The two substances ("yellow amber" and "grey amber") conceivably became associated or confused because they both were found washed up on beaches. Ambergris is less dense than water and floats, whereas amber is too dense to float, though less dense than stone.
The classical names for amber, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''electrum'' and Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
(''ēlektron''), are connected to a term ἠλέκτωρ (''ēlektōr'') meaning "beaming Sun".
Homeric
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
(Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Odys ...
6.513, 19.398). The feminine being later used as a name of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
.
According to myth, when Phaëton son of Helios (the Sun) was killed, his mourning sisters became poplar trees, and their tears became ''elektron'', amber. The word ''elektron'' gave rise to the words ''electric, electricity'', and their relatives because of amber's ability to bear a charge of static electricity."Electric." ''Online Etymological Dictionary.''Retrieved 6 September 2018.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
says that the German name of amber was '' glæsum'', "for which reason the Romans, when Germanicus commanded the fleet in those parts, gave to one of these islands the name of Glæsaria, which by the barbarians was known as Austeravia". This is confirmed by the recorded Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
word ''glas'' and by the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
word ''glær
In Norse mythology, Glær or Glenr is a horse listed in both '' Grímnismál'' and ''Gylfaginning'' among the steeds ridden by the gods
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of Englis ...
'' for "amber" (compare ''glass''). In Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
, amber was known as ''berne-, barn-, börnstēn'' (with etymological roots related to "burn" and to "stone"). The Low German term became dominant also in High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
by the 18th century, thus modern German ''Bernstein'' besides Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
''barnsteen''. In the Baltic languages, the Lithuanian term for amber is ''gintaras'' and the Latvian ''dzintars''. These words, and the Slavic ''jantar'' and Hungarian ''gyanta'' ('resin'), are thought to originate from Phoenician ''jainitar'' ("sea-resin").
History
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
discussed amber in the 4th century BCE, as did Pytheas (), whose work "On the Ocean" is lost, but was referenced by Pliny, according to whose '' Natural History'' (in what is also the earliest known mention of the name '' Germania''):''Natural History'37.11
.
 Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the
Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
Hi ...
n coast and called Balcia by Xenophon of Lampsacus (author of a fanciful travel book in Greek)—as ''Basilia''—a name generally equated with ''Abalus''. Given the presence of amber, the island could have been Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
, Zealand
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020.
It is the 1 ...
, the shores of Gdańsk Bay
Gdańsk Bay or the Gulf of Gdańsk ( pl, Zatoka Gdańska; csb, Gduńskô Hôwinga; russian: Гданьская бухта, Gdan'skaja bukhta, and german: Danziger Bucht) is a southeastern bay of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the adjacent por ...
, the Sambia Peninsula
Sambia (russian: Самбийский полуостров, lit=Sambian Peninsula, translit=Sambiysky poluostrov) or Samland (russian: Земландский полуостров, lit=Zemlandic Peninsula, translit=Zemlandsky poluostrov) or Kalini ...
or the Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; russian: Куршский залив, lt, Kuršių marios, pl, Zalew Kuroński, german: Kurisches Haff, lv, Kuršu joma) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surfac ...
, which were historically the richest sources of amber in northern Europe. It is assumed that there were well-established trade routes for amber connecting the Baltic with the Mediterranean (known as the "Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
"). Pliny states explicitly that the Germans exported amber to Pannonia, from where the Veneti distributed it onwards.
The ancient Italic peoples of southern Italy used to work amber; the National Archaeological Museum of Siritide (Museo Archeologico Nazionale della Siritide) at Policoro
Policoro ( Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Matera, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. With some 17,000 inhabitants, is bounded by the towns of Rotondella, Scanzano Jonico and Tursi. Situated on the coast, its po ...
in the province of Matera
The province of Matera ( it, Provincia di Matera; Materano: ) is a province in the Basilicata region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Matera. It has an area of and a total population of 201,133; the city Matera has a population of 61,204. Th ...
( Basilicata) displays important surviving examples. Amber used in antiquity, as at Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. ...
and in the prehistory of the Mediterranean, comes from deposits in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
 Pliny also cites the opinion of
Pliny also cites the opinion of Nicias
Nicias (; Νικίας ''Nikias''; c. 470–413 BC) was an Athenian politician and general during the period of the Peloponnesian War. Nicias was a member of the Athenian aristocracy and had inherited a large fortune from his father, which was inve ...
( 470–413 BCE), according to whom amber Besides the fanciful explanations according to which amber is "produced by the Sun", Pliny cites opinions that are well aware of its origin in tree resin, citing the native Latin name of ''succinum'' (''sūcinum'', from ''sucus'' "juice"). In Book 37, section XI of ''Natural History'', Pliny wrote:
He also states that amber is also found in Egypt and India, and he even refers to the electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest ( static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amb ...
properties of amber, by saying that "in Syria the women make the whorls of their spindles of this substance, and give it the name of ''harpax'' rom ἁρπάζω, "to drag"from the circumstance that it attracts leaves towards it, chaff, and the light fringe of tissues".
Amber has a long history of use in China, with the first written record from 200 BCE. Early in the 19th century, the first reports of amber found in North America came from discoveries in New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
along Crosswicks Creek
Crosswicks Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 tributary of the Delaware River in Burlington County, New Jersey.
Description
Crosswicks Creek water ...
near Trenton, at Camden, and near Woodbury Woodbury may refer to:
Geography
Antarctica
*Woodbury Glacier, a glacier on Graham Land, British Antarctic Territory
Australia
* Woodbury, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
England
* Woodbury, Bournemouth, an area in Dorset
*Woodbury, East Devo ...
.
Composition and formation
Amber is heterogeneous in composition, but consists of severalresin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
ous bodies more or less soluble in alcohol, ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be ...
and chloroform, associated with an insoluble bituminous
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
substance. Amber is a macromolecule by free radical polymerization
In polymer chemistry, free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks ( repeat units). Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechani ...
of several precursors in the labdane
Labdane is a natural bicyclic diterpene. It forms the structural core for a wide variety of natural products collectively known as ''labdanes'' or ''labdane diterpenes''. The labdanes were so named because the first members of the class were ori ...
family, e.g. communic acid, cummunol, and biformene. These labdanes are diterpene
Diterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being ...
s (C20H32) and trienes, equipping the organic skeleton with three alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
groups for polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. As amber matures over the years, more polymerization takes place as well as isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomeriz ...
reactions, crosslinking Cross-linking may refer to
*Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers ca ...
and cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
.
Most amber has a hardness between 2.0 and 2.5 on the Mohs scale
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by th ...
, a refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
of 1.5–1.6, a specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest ...
between 1.06 and 1.10, and a melting point of 250–300 °C. Heated above , amber decomposes, yielding an oil of amber, and leaves a black residue which is known as "amber colophony", or "amber pitch"; when dissolved in oil of turpentine
Turpentine (which is also called spirit of turpentine, oil of turpentine, terebenthene, terebinthine and (colloquially) turps) is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin harvested from living trees, mainly pines. Mainly used as a spec ...
or in linseed oil this forms "amber varnish" or "amber lac".
Molecular polymerization, resulting from high pressures and temperatures produced by overlying sediment, transforms the resin first into copal
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes re ...
. Sustained heat and pressure drives off terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes ...
s and results in the formation of amber. For this to happen, the resin must be resistant to decay. Many trees produce resin, but in the majority of cases this deposit is broken down by physical and biological processes. Exposure to sunlight, rain, microorganisms, and extreme temperatures tends to disintegrate the resin. For the resin to survive long enough to become amber, it must be resistant to such forces or be produced under conditions that exclude them. Fossil resins from Europe fall into two categories, the Baltic ambers and another that resembles the '' Agathis'' group. Fossil resins from the Americas and Africa are closely related to the modern genus ''Hymenaea
''Hymenaea'' is a genus of plants in the legume family Fabaceae. Of the fourteen living species in the genus, all but one are native to the tropics of the Americas, with one additional species (''Hymenaea verrucosa'') on the east coast of Afr ...
'', while Baltic ambers are thought to be fossil resins from plants of the family Sciadopityaceae
''Sciadopitys verticillata'', the or Japanese umbrella-pine, is a unique conifer endemic to Japan. It is the sole member of the family Sciadopityaceae and genus ''Sciadopitys'', a living fossil with no close relatives. The oldest fossils of ' ...
that once lived in north Europe. The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber. Impurities are quite often present, especially when the resin dropped onto the ground, so the material may be useless except for varnish-making. Such impure amber is called ''firniss''. Such
The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber. Impurities are quite often present, especially when the resin dropped onto the ground, so the material may be useless except for varnish-making. Such impure amber is called ''firniss''. Such inclusion
Inclusion or Include may refer to:
Sociology
* Social inclusion, aims to create an environment that supports equal opportunity for individuals and groups that form a society.
** Inclusion (disability rights), promotion of people with disabiliti ...
of other substances can cause the amber to have an unexpected color. Pyrites
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue ...
may give a bluish color. ''Bony amber'' owes its cloudy opacity to numerous tiny bubbles inside the resin. However, so-called ''black amber'' is really a kind of jet. In darkly clouded and even opaque amber, inclusions can be imaged using high-energy, high-contrast, high-resolution X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s.
Extraction and processing
Distribution and mining

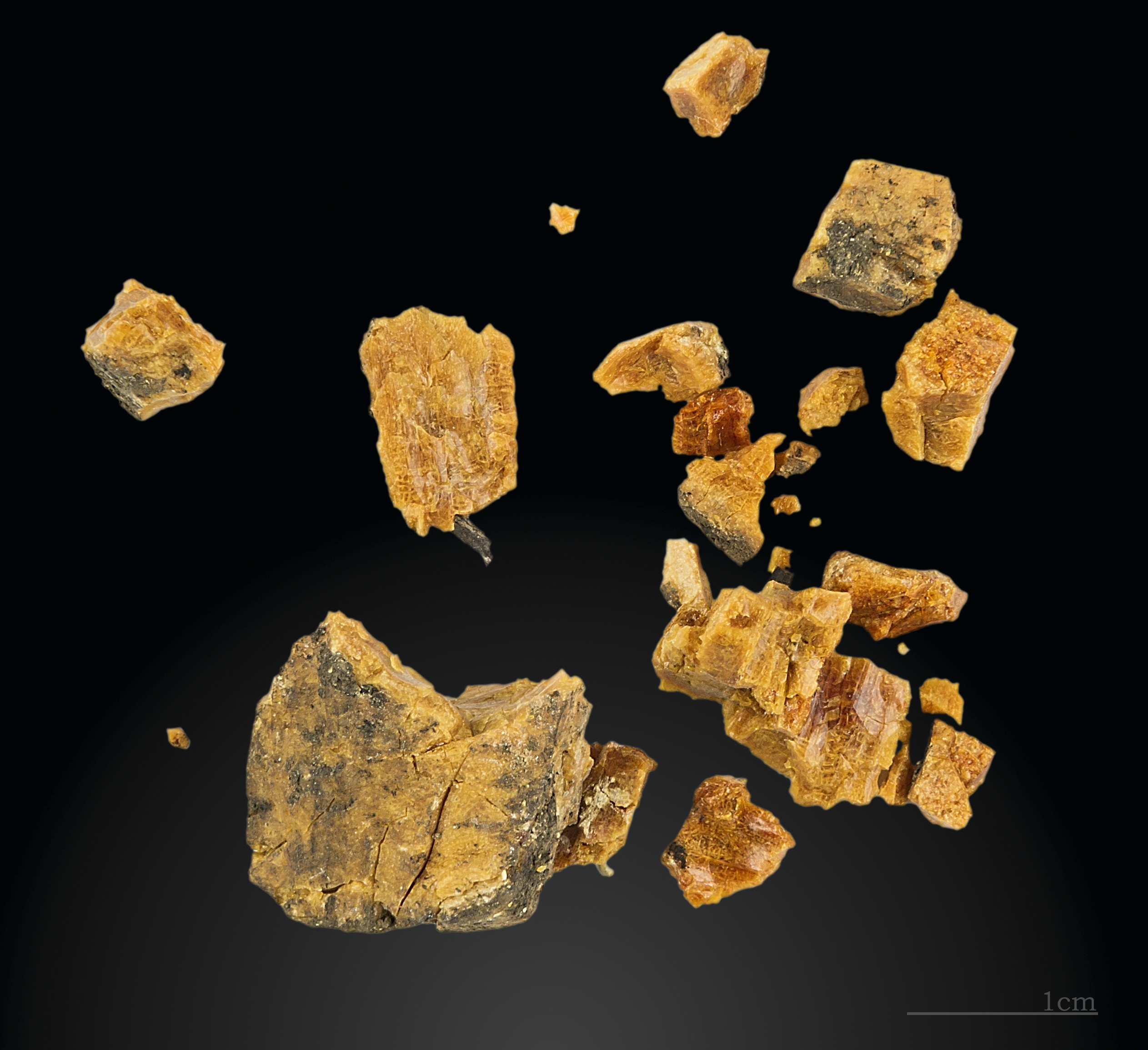
 Amber is globally distributed, mainly in rocks of
Amber is globally distributed, mainly in rocks of Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
age or younger. Historically, the coast west of Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was name ...
in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
was the world's leading source of amber. The first mentions of amber deposits there date back to the 12th century. About 90% of the world's extractable amber is still located in that area, which became the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and admin ...
of Russia in 1946.
Pieces of amber torn from the seafloor are cast up by the waves and collected by hand, dredging, or diving. Elsewhere, amber is mined, both in open works and underground galleries. Then nodules of ''blue earth'' have to be removed and an opaque crust must be cleaned off, which can be done in revolving barrels containing sand and water. Erosion removes this crust from sea-worn amber. Dominican amber
Dominican amber is amber from the Dominican Republic derived from resin of the extinct tree '' Hymenaea protera''.
Dominican amber differentiates itself from Baltic amber by being nearly always transparent, and it has a higher number of fossil inc ...
is mined through bell pitting, which is dangerous because of the risk of tunnel collapse.
An important source of amber is Kachin State in northern Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, which has been a major source of amber in China for at least 1,800 years. Contemporary mining of this deposit has attracted attention for unsafe working conditions and its role in funding internal conflict in the country. Amber from the Rivne Oblast
Rivne Oblast ( uk, Рі́вненська о́бласть, translit=Rivnenska oblast), also referred to as Rivnenshchyna ( uk, Рі́вненщина) is an oblast (province) of Ukraine. Its administrative center is Rivne. The surface area of th ...
of Ukraine, referred to as Rovno amber
Rivne amber, occasionally called Ukrainian amber, is amber found in the Rivne Oblast and surrounding regions of Ukraine and Belarus. The amber is dated between Late Eocene and Early Miocene, and suggested to be contemporaneous to Baltic amber. ...
, is mined illegally by organised crime groups, who deforest the surrounding areas and pump water into the sediments to extract the amber, causing severe environmental deterioration.
Treatment
The Vienna amber factories, which use pale amber to manufacture pipes and other smoking tools, turn it on a lathe and polish it with whitening and water or withrotten stone
Rotten stone, sometimes spelled as rottenstone, also known as tripoli, is fine powdered porous rock used as a polishing abrasive for metalsmithing and in woodworking. It is usually weathered limestone mixed with diatomaceous, amorphous, or crys ...
and oil. The final luster is given by polishing with flannel.
When gradually heated in an oil bath, amber "becomes soft and flexible. Two pieces of amber may be united by smearing the surfaces with linseed oil, heating them, and then pressing them together while hot. Cloudy amber may be clarified in an oil bath, as the oil fills the numerous pores that cause the turbidity. Small fragments, formerly thrown away or used only for varnish are now used on a large scale in the formation of "ambroid" or "pressed amber". The pieces are carefully heated with exclusion of air and then compressed into a uniform mass by intense hydraulic pressure, the softened amber being forced through holes in a metal plate. The product is extensively used for the production of cheap jewelry and articles for smoking. This pressed amber yields brilliant interference colors in polarized light."
Amber has often been imitated by other resins like copal
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes re ...
and kauri gum
Kauri gum is resin from kauri trees (''Agathis australis''), which historically had several important industrial uses. It can also be used to make crafts such as jewellery. Kauri forests once covered much of the North Island of New Zealand, bef ...
, as well as by celluloid
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common contemporary ...
and even glass. Baltic amber is sometimes colored artificially but also called "true amber".
Appearance
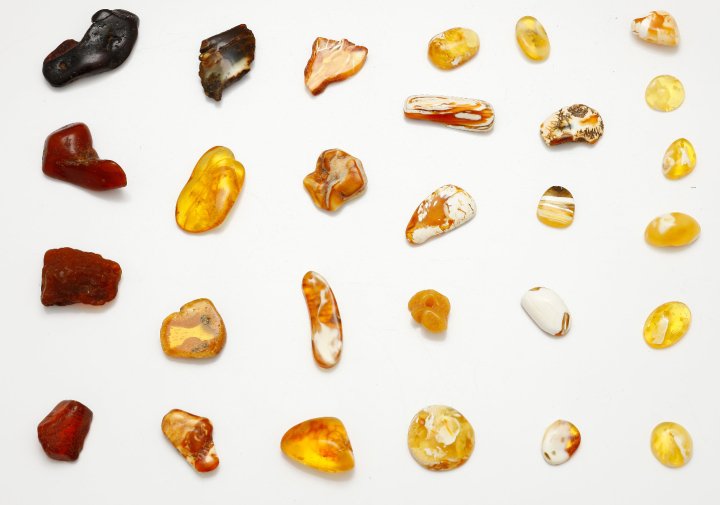
 Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even
Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even blue amber
Blue amber is a rare variety of amber resin that exhibits a blue coloration. Blue amber has been most commonly found in the Dominican Republic—especially in the amber mines around the city of Santiago and, less commonly, in the eastern half of ...
, which is rare and highly sought after.
Yellow amber is a hard fossil resin from evergreen trees, and despite the name it can be translucent, yellow, orange, or brown colored. Known to the Iranians by the Pahlavi compound word kah-ruba (from kah "straw" plus rubay "attract, snatch", referring to its electrical properties), which entered Arabic as kahraba' or kahraba (which later became the Arabic word for electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
, كهرباء ''kahrabā''), it too was called amber in Europe (Old French and Middle English ambre). Found along the southern shore of the Baltic Sea, yellow amber reached the Middle East and western Europe via trade. Its coastal acquisition may have been one reason yellow amber came to be designated by the same term as ambergris. Moreover, like ambergris, the resin could be burned as an incense. The resin's most popular use was, however, for ornamentation—easily cut and polished, it could be transformed into beautiful jewelry. Much of the most highly prized amber is transparent, in contrast to the very common cloudy amber and opaque amber. Opaque amber contains numerous minute bubbles. This kind of amber is known as "bony amber".
 Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light source. In long-wave UV light it has a very strong reflection, almost white. Only about is found per year, which makes it valuable and expensive.
Sometimes amber retains the form of drops and stalactites, just as it exuded from the ducts and receptacles of the injured trees. It is thought that, in addition to exuding onto the surface of the tree, amber resin also originally flowed into hollow cavities or cracks within trees, thereby leading to the development of large lumps of amber of irregular form.
Classification
Amber can be classified into several forms. Most fundamentally, there are two types of plant resin with the potential for fossilization.Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes" ...
s, produced by conifers and angiosperms
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants ...
, consist of ring structures formed of isoprene (C5H8) units. Phenolic resins
Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) or phenolic resins (also infrequently called phenoplasts) are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commerc ...
are today only produced by angiosperms, and tend to serve functional uses. The extinct medullosans produced a third type of resin, which is often found as amber within their veins. The composition of resins is highly variable; each species produces a unique blend of chemicals which can be identified by the use of pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ...
– gas chromatography– mass spectrometry. The overall chemical and structural composition is used to divide ambers into five classes. There is also a separate classification of amber gemstones, according to the way of production.
Class I
This class is by far the most abundant. It comprises labdatriene carboxylic acids such as communic or ozic acids. It is further split into three sub-classes. Classes Ia and Ib utilize regular labdanoid diterpenes (e.g. communic acid, communol, biformenes), while Ic uses ''enantio'' labdanoids (ozic acid, ozol, ''enantio'' biformenes). Class Ia includes ''Succinite'' (= 'normal' Baltic amber) and ''Glessite''. They have a communic acid base, and they also include much succinic acid.Baltic amber
The Baltic region is home to the largest known deposit of amber, called Baltic amber or succinite. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that these forests created more than ...
yields on dry distillation succinic acid, the proportion varying from about 3% to 8%, and being greatest in the pale opaque or ''bony'' varieties. The aromatic and irritating fumes emitted by burning amber are mainly from this acid. Baltic amber is distinguished by its yield of succinic acid
Succinic acid () is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula (CH2)2(CO2H)2. The name derives from Latin ''succinum'', meaning amber. In living organisms, succinic acid takes the form of an anion, succinate, which has multiple biological ro ...
, hence the name ''succinite''. Succinite has a hardness between 2 and 3, which is greater than many other fossil resins. Its specific gravity varies from 1.05 to 1.10. It can be distinguished from other ambers via infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or function ...
through a specific carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containi ...
absorption peak. Infrared spectroscopy can detect the relative age of an amber sample. Succinic acid may not be an original component of amber but rather a degradation product of abietic acid
Abietic acid (also known as ''abietinic acid'' or ''sylvic acid'') is an organic compound that occurs widely in trees. It is the primary component of resin acid, is the primary irritant in pine wood and resin, isolated from rosin (via isomerizat ...
.
Class Ib ambers are based on communic acid; however, they lack succinic acid.
Class Ic is mainly based on ''enantio''-labdatrienonic acids, such as ozic and zanzibaric acids. Its most familiar representative is Dominican amber,. which is mostly transparent and often contains a higher number of fossil inclusions. This has enabled the detailed reconstruction of the ecosystem of a long-vanished tropical forest. Resin from the extinct species '' Hymenaea protera'' is the source of Dominican amber and probably of most amber found in the tropics. It is not "succinite" but "retinite Retinite is resin, particularly from beds of brown coal which are near amber in appearance, but contain little or no succinic acid
Succinic acid () is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula (CH2)2(CO2H)2. The name derives from Latin ''su ...
".
Class II
These ambers are formed from resins with a sesquiterpenoid base, such ascadinene
Cadinenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons that occur in a wide variety of essential oil-producing plants. The name is derived from that of the Cade juniper (''Juniperus oxycedrus'' L.), the wood of which yields an oil from which cadinene is ...
.
Class III
These ambers are polystyrenes.Class IV
Class IV is something of acatch-all
A catch-all or catchall is a general term, or metaphoric dumping group, for a variety of similar words or meanings.
Catch-all may also refer to:
* Catch-all party, or big tent party
* Catch-all email filter
*Catch-all taxon
Wastebasket taxon (a ...
: its ambers are not polymerized, but mainly consist of cedrene
Cedrene is a sesquiterpene found in the essential oil of cedar
Cedar may refer to:
Trees and plants
*''Cedrus'', common English name cedar, an Old-World genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae
*Cedar (plant), a list of trees a ...
-based sesquiterpenoids.
Class V
Class V resins are considered to be produced by a pine or pine relative. They comprise a mixture of diterpinoid resins and ''n''-alkyl compounds. Their main variety is '' Highgate copalite''.Geological record
late Carboniferous
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
period (). Its chemical composition makes it difficult to match the amber to its producers – it is most similar to the resins produced by flowering plants; however, there are no flowering plant fossils known from before the Cretaceous, and they were not common until the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
. Amber becomes abundant long after the Carboniferous, in the Early Cretaceous, , when it is found in association with insects. The oldest amber with arthropod inclusions comes from the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. ...
(late Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Triassic series (stratigraphy), Series (or earliest age (geology), age of the Late Triassic Epoch (reference date), Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227 m ...
230 Ma) of Italy, where four microscopic (0.2–0.1 mm) mites, '' Triasacarus,'' '' Ampezzoa, Minyacarus'' and '' Cheirolepidoptus,'' and a poorly preserved nematocera
The Nematocera (the name means "thread-horns") are a suborder of elongated flies with thin, segmented antennae and mostly aquatic larvae. This group is paraphyletic and contains all flies but species from suborder Brachycera (the name means "sh ...
n fly were found in millimetre-sized droplets of amber. The oldest amber with significant numbers of arthropod inclusions comes from Lebanon. This amber, referred to as Lebanese amber
Lebanese amber is fossilized resin found in Lebanon and southwest Syria. It dates back approximately 130-125 million years to the Barremian of the Early Cretaceous. It formed on what was then the northern coast of Gondwana, believed to be a tropi ...
, is roughly 125–135 million years old, is considered of high scientific value, providing evidence of some of the oldest sampled ecosystems.Poinar, P.O., Jr., and R.K. Milki (2001) ''Lebanese Amber: The Oldest Insect Ecosystem in Fossilized Resin.'' Oregon State University Press, Corvallis. .
In Lebanon, more than 450 outcrops of Lower Cretaceous amber were discovered by Dany Azar, a Lebanese paleontologist and entomologist. Among these outcrops, 20 have yielded biological inclusions comprising the oldest representatives of several recent families of terrestrial arthropods. Even older Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
amber has been found recently in Lebanon as well. Many remarkable insects and spiders were recently discovered in the amber of Jordan including the oldest zoraptera
The insect order Zoraptera, commonly known as angel insects, contains small and soft bodied insects with two forms: winged with wings sheddable as in termites, dark and with eyes (compound) and ocelli (simple); or wingless, pale and without eyes ...
ns, clerid beetles, umenocoleid roaches, and achiliid planthoppers.

Burmese amber
Burmese amber, also known as Burmite or Kachin amber, is amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar. The amber is dated to around 100 million years ago, during the latest Albian to earliest Cenomanian ages of the mid-Cretaceous period. The ...
from the Hukawng Valley
The Hukawng Valley ( my, ဟူးကောင်းချိုင့်ဝှမ်း; also spelt Hukaung Valley) is an isolated valley in Myanmar, roughly in area. It is located in Tanaing Township in the Myitkyina District of Kachin State ...
in northern Myanmar is the only commercially exploited Cretaceous amber. Uranium–lead dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routi ...
of zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of t ...
crystals associated with the deposit have given an estimated depositional age of approximately 99 million years ago. Over 1,300 species have been described from the amber, with over 300 in 2019 alone.
Baltic amber is found as irregular nodules in marine glauconitic
Glauconite is an iron potassium phyllosilicate (mica group) mineral of characteristic green color which is very friable and has very low weathering resistance.
It crystallizes with a monoclinic geometry. Its name is derived from the Greek () me ...
sand, known as ''blue earth'', occurring in Upper Eocene strata of Sambia
Sambia (russian: Самбийский полуостров, lit=Sambian Peninsula, translit=Sambiysky poluostrov) or Samland (russian: Земландский полуостров, lit=Zemlandic Peninsula, translit=Zemlandsky poluostrov) or Kalini ...
in Prussia. It appears to have been partly derived from older Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
deposits and it occurs also as a derivative phase in later formations, such as glacial drift. Relics of an abundant flora occur as inclusions trapped within the amber while the resin was yet fresh, suggesting relations with the flora of eastern Asia and the southern part of North America. Heinrich Göppert
Johann Heinrich Robert Göppert (25 July 1800 – 18 May 1884) was a German botanist and paleontologist.
Career
He was born in Sprottau, Lower Silesia, and died at Breslau. In 1831 he became a professor of botany, as well as curator of the bo ...
named the common amber-yielding pine of the Baltic forests ''Pinites succiniter'', but as the wood does not seem to differ from that of the existing genus it has been also called ''Pinus succinifera''. It is improbable that the production of amber was limited to a single species; and indeed a large number of conifers belonging to different genera are represented in the amber-flora.
Paleontological significance
Amber is a unique preservational mode, preserving otherwise unfossilizable parts of organisms; as such it is helpful in the reconstruction of ecosystems as well as organisms; the chemical composition of the resin, however, is of limited utility in reconstructing the phylogenetic affinity of the resin producer.Amber sometimes contains animals or plant matter that became caught in the resin as it was secreted.Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s, spider
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species ...
s and even their webs, annelids, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s, bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and amoebae
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopo ...
, marine microfossils, wood, flowers and fruit, hair, feathers and other small organisms have been recovered in Cretaceous ambers (deposited c. ).
 The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel '' Jurassic Park'' and the 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric
The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel '' Jurassic Park'' and the 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric mosquitoes
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small Diptera, flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning "gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish ...
trapped in amber, from which they genetically clone living dinosaurs. Scientifically this is as yet impossible, since no amber with fossilized mosquitoes has ever yielded preserved blood. Amber is, however, conducive to preserving DNA, since it dehydrates and thus stabilizes organisms trapped inside. One projection in 1999 estimated that DNA trapped in amber could last up to 100 million years, far beyond most estimates of around 1 million years in the most ideal conditions, although a later 2013 study was unable to extract DNA from insects trapped in much more recent Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
copal
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes re ...
. In 1938, 12-year-old David Attenborough (brother of Richard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'stro ...
who played John Hammond in ''Jurassic Park'') was given a piece of amber containing prehistoric creatures from his adoptive sister; it would be the focus of his 2004 BBC documentary ''The Amber Time Machine
''The Amber Time Machine'' is a BBC documentary written and presented by David Attenborough. It's the 12th episode of the 22nd series of the British wildlife documentary television series ''Natural World''. It was first transmitted in 2004 and la ...
.''
Use
 Amber has been used since prehistory (
Amber has been used since prehistory (Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites have been found in modern-day France, Spain and Portugal.
Details
...
) in the manufacture of jewelry and ornaments, and also in folk medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
.
Jewelry

 Amber has been used as jewelry since the Stone Age, from 13,000 years ago. Amber ornaments have been found in Mycenaean tombs and elsewhere across Europe. To this day it is used in the manufacture of smoking and glassblowing mouthpieces. Amber's place in culture and tradition lends it a tourism value;
Amber has been used as jewelry since the Stone Age, from 13,000 years ago. Amber ornaments have been found in Mycenaean tombs and elsewhere across Europe. To this day it is used in the manufacture of smoking and glassblowing mouthpieces. Amber's place in culture and tradition lends it a tourism value; Palanga Amber Museum
The Palanga Amber Museum ( lt, Palangos gintaro muziejus), near the Baltic Sea in Palanga, Lithuania, is a branch of the Lithuanian Art Museum. It is housed in the restored 19th-century Tiškevičiai Palace and is surrounded by the Palanga Botan ...
is dedicated to the fossilized resin.
Historical medicinal uses
Amber has long been used in folk medicine for its purported healing properties. Amber and extracts were used from the time ofHippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
in ancient Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
for a wide variety of treatments through the Middle Ages and up until the early twentieth century. Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of acti ...
uses amber to "tranquilize the mind".
Amber necklaces are a traditional European remedy for colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content out. ...
or teething pain with purported analgesic properties of succinic acid, although there is no evidence that this is an effective remedy or delivery method. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
have warned strongly against their use, as they present both a choking and a strangulation hazard.
Scent of amber and amber perfumery
In ancient China, it was customary to burn amber during large festivities. If amber is heated under the right conditions, oil of amber is produced, and in past times this was combined carefully withnitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
to create "artificial musk" – a resin with a peculiar musk
Musk ( Persian: مشک, ''Mushk'') is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial sub ...
y odor.. Although when burned, amber does give off a characteristic "pinewood" fragrance, modern products, such as perfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Th ...
, do not normally use actual amber because fossilized amber produces very little scent. In perfumery, scents referred to as "amber" are often created and patented to emulate the opulent golden warmth of the fossil.
The scent of amber was originally derived from emulating the scent of ambergris and/or the plant resin labdanum
Labdanum, also called ladanum, ladan, or ladanon, is a sticky brown resin obtained from the shrubs ''Cistus ladanifer'' (western Mediterranean) and '' Cistus creticus'' (eastern Mediterranean), species of rockrose. It was historically used in he ...
, but since sperm whales are endangered, the scent of amber is now largely derived from labdanum. The term "amber" is loosely used to describe a scent that is warm, musky, rich and honey-like, and also somewhat earthy. Benzoin is usually part of the recipe. Vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the p ...
and cloves are sometimes used to enhance the aroma. "Amber" perfumes may be created using combinations of labdanum, benzoin resin, copal (a type of tree resin used in incense manufacture), vanilla, Dammara resin and/or synthetic materials.
Imitation substances
Young resins used as imitations: * Kauri resin from ''Agathis australis
''Agathis australis'', commonly known by its Māori name kauri (), is a coniferous tree in the family '' Araucariaceae'', found north of 38°S in the northern regions of New Zealand's North Island.
It is the largest (by volume) but not t ...
'' trees in New Zealand.
* The copal
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes re ...
s ( subfossil resins). The African and American ( Colombia) copals from '' Leguminosae'' trees family (genus ''Hymenaea
''Hymenaea'' is a genus of plants in the legume family Fabaceae. Of the fourteen living species in the genus, all but one are native to the tropics of the Americas, with one additional species (''Hymenaea verrucosa'') on the east coast of Afr ...
''). Amber of the Dominican or Mexican type ( Class I of fossil resins). Copals from Manilia (Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
) and from New Zealand from trees of the genus '' Agathis'' (family Araucariaceae
Araucariaceae – also known as araucarians – is an extremely ancient family of coniferous trees. The family achieved its maximum diversity during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods and the early Cenozoic, when it was distributed almost worldw ...
)
* Other fossil resins: burmite
Burmese amber, also known as Burmite or Kachin amber, is amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar. The amber is dated to around 100 million years ago, during the latest Albian to earliest Cenomanian ages of the mid-Cretaceous period. The ...
in Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, rumenite in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, and simetite in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
* Other natural resins — cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
or chitin, etc.
Plastics used as imitations:
* Stained glass (inorganic material) and other ceramic materials
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
* Celluloid
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common contemporary ...
* Cellulose nitrate
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid an ...
(first obtained in 1833) — a product of treatment of cellulose with nitration mixture.
* Acetylcellulose (not in the use at present)
* Galalith
Galalith (Erinoid in the United Kingdom) is a synthetic plastic material manufactured by the interaction of casein and formaldehyde. The commercial name is derived from the Ancient Greek words (, "milk") and (, "stone"). It is odourless, insol ...
or "artificial horn" (condensation product of casein and formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
), other trade names: Alladinite, Erinoid, Lactoid.
* Casein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins ( αS1, aS2, β, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in hum ...
— a conjugated protein forming from the casein precursor – caseinogen.
* Resolane (phenolic resins or phenoplasts, not in the use at present)
* Bakelite resine (resol, phenolic resins), product from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
are known under the misleading name "African amber".
* Carbamide
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
resins — melamine
Melamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H6N6. This white solid is a trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. Like cyanamide, it contains 67% nitrogen by mass, and its derivatives have fire retardant properties due t ...
, formaldehyde and urea-formaldehyde resins.
* Epoxy novolac
Novolaks (sometimes: novolacs) are low molecular weight polymers derived from phenols and formaldehyde. They are related to Bakelite, which is more highly crosslinked. The term comes from Swedish "lack" for lacquer and Latin "novo" for new, sinc ...
(phenolic resins), unofficial name "antique amber", not in the use at present
* Polyesters
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
(Polish amber imitation) with styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
. For example, unsaturated polyester resins (polymals) are produced by Chemical Industrial Works " Organika" in Sarzyna
Sarzyna () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Nowa Sarzyna, within Leżajsk County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It lies approximately north-east of Nowa Sarzyna, north-west of Leżajsk, and north-east of ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
; estomal are produced by Laminopol firm. Polybern or sticked amber is artificial resins the curled chips are obtained, whereas in the case of amber – small scraps. "African amber" (polyester, synacryl is then probably other name of the same resine) are produced by Reichhold firm; Styresol trade mark or alkid resin (used in Russia, Reichhold, Inc. patent, 1948.
* Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including b ...
* Epoxy resins
* Polystyrene and polystyrene-like polymers (vinyl polymer
In polymer chemistry, vinyl polymers are a group of polymers derived from substituted vinyl () monomers. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain . In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Examples
Vinyl polymers ...
s).
* The resins of acrylic type (vinyl polymer
In polymer chemistry, vinyl polymers are a group of polymers derived from substituted vinyl () monomers. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain . In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Examples
Vinyl polymers ...
s), especially polymethyl methacrylate PMMA (trade mark Plexiglass, metaplex).
See also
*Ammolite
Ammolite is an opal-like organic gemstone found primarily along the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains of North America. It is made of the fossilized shells of ammonites, which in turn are composed primarily of aragonite, the same mineral co ...
* List of types of amber {{short description, None
This is a list of types of amber.
True ambers
*Baltic amber - the most common amber variety, found along the shores of a large part of the Baltic Sea, Eocene age amber.
*Bitterfeld amber, amber from Bitterfeld, Germany, ...
* Petrified wood
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of '' fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial vegetation. ' ...
* Pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
* Poly(methyl methacrylate)
* Precious coral
Precious coral, or red coral, is the common name given to a genus of marine corals, ''Corallium''. The distinguishing characteristic of precious corals is their durable and intensely colored red or pink-orange skeleton, which is used for m ...
References
*Bibliography
* * *External links
Farlang many full text historical references on Amber
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
, George Frederick Kunz
George Frederick Kunz (September 29, 1856 – June 29, 1932) was an American mineralogist and mineral collector.
Biography
Kunz was born in Manhattan, New York City, USA, and began an interest in minerals at a very young age. By his teens, ...
, and special on Baltic amber
The Baltic region is home to the largest known deposit of amber, called Baltic amber or succinite. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that these forests created more than ...
.
IPS Publications on amber inclusions
International Paleoentomological Society: Scientific Articles on amber and its inclusions
Webmineral on Amber
Physical properties and mineralogical information
Image and locality information on amber
40 million year old extinct bee in Dominican amber {{Authority control Fossil resins Amorphous solids Traditional medicine