Amazon (river) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by
 During what many
During what many
 In March 1500, Spanish
In March 1500, Spanish
 In 1560, another Spanish
In 1560, another Spanish 
 upIglesia Matriz in Iquitos, Peru
The Cabanagem revolt (1835–1840) was directed against the white ruling class. It is estimated that from 30% to 40% of the population of Grão-Pará, estimated at 100,000 people, died.
The population of the Brazilian portion of the Amazon basin in 1850 was perhaps 300,000, of whom about 175,000 were Europeans and 25,000 were slaves. The Brazilian Amazon's principal commercial city, Pará (now Belém), had from 10,000 to 12,000 inhabitants, including slaves. The town of Manáos, now Manaus, at the mouth of the Rio Negro, had a population between 1,000 and 1,500. All the remaining villages, as far up as Tabatinga, on the Brazilian frontier of Peru, were relatively small.
On 6 September 1850, Emperor
upIglesia Matriz in Iquitos, Peru
The Cabanagem revolt (1835–1840) was directed against the white ruling class. It is estimated that from 30% to 40% of the population of Grão-Pará, estimated at 100,000 people, died.
The population of the Brazilian portion of the Amazon basin in 1850 was perhaps 300,000, of whom about 175,000 were Europeans and 25,000 were slaves. The Brazilian Amazon's principal commercial city, Pará (now Belém), had from 10,000 to 12,000 inhabitants, including slaves. The town of Manáos, now Manaus, at the mouth of the Rio Negro, had a population between 1,000 and 1,500. All the remaining villages, as far up as Tabatinga, on the Brazilian frontier of Peru, were relatively small.
On 6 September 1850, Emperor

 Since colonial times, the Portuguese portion of the Amazon basin has remained a land largely undeveloped by agriculture and occupied by indigenous people who survived the arrival of European diseases.
Four centuries after the European discovery of the Amazon river, the total cultivated area in its basin was probably less than , excluding the limited and crudely cultivated areas among the mountains at its extreme headwaters. This situation changed dramatically during the 20th century.
Wary of foreign exploitation of the nation's resources, Brazilian governments in the 1940s set out to develop the interior, away from the seaboard where foreigners owned large tracts of land. The original architect of this expansion was president Getúlio Vargas, with the demand for rubber from the Allied forces in World War II providing funding for the drive.
In the 1960s, economic exploitation of the Amazon basin was seen as a way to fuel the "economic miracle" occurring at the time. This resulted in the development of "Operation Amazon", an economic development project that brought large-scale agriculture and ranching to Amazonia. This was done through a combination of credit and fiscal incentives.
However, in the 1970s the government took a new approach with the National Integration Program (PIN). A large-scale colonization program saw families from northeastern Brazil relocated to the "land without people" in the Amazon Basin. This was done in conjunction with infrastructure projects mainly the Trans-Amazonian Highway (''Transamazônica'').
The Trans-Amazonian Highway's three pioneering highways were completed within ten years but never fulfilled their promise. Large portions of the Trans-Amazonian and its accessory roads, such as
Since colonial times, the Portuguese portion of the Amazon basin has remained a land largely undeveloped by agriculture and occupied by indigenous people who survived the arrival of European diseases.
Four centuries after the European discovery of the Amazon river, the total cultivated area in its basin was probably less than , excluding the limited and crudely cultivated areas among the mountains at its extreme headwaters. This situation changed dramatically during the 20th century.
Wary of foreign exploitation of the nation's resources, Brazilian governments in the 1940s set out to develop the interior, away from the seaboard where foreigners owned large tracts of land. The original architect of this expansion was president Getúlio Vargas, with the demand for rubber from the Allied forces in World War II providing funding for the drive.
In the 1960s, economic exploitation of the Amazon basin was seen as a way to fuel the "economic miracle" occurring at the time. This resulted in the development of "Operation Amazon", an economic development project that brought large-scale agriculture and ranching to Amazonia. This was done through a combination of credit and fiscal incentives.
However, in the 1970s the government took a new approach with the National Integration Program (PIN). A large-scale colonization program saw families from northeastern Brazil relocated to the "land without people" in the Amazon Basin. This was done in conjunction with infrastructure projects mainly the Trans-Amazonian Highway (''Transamazônica'').
The Trans-Amazonian Highway's three pioneering highways were completed within ten years but never fulfilled their promise. Large portions of the Trans-Amazonian and its accessory roads, such as
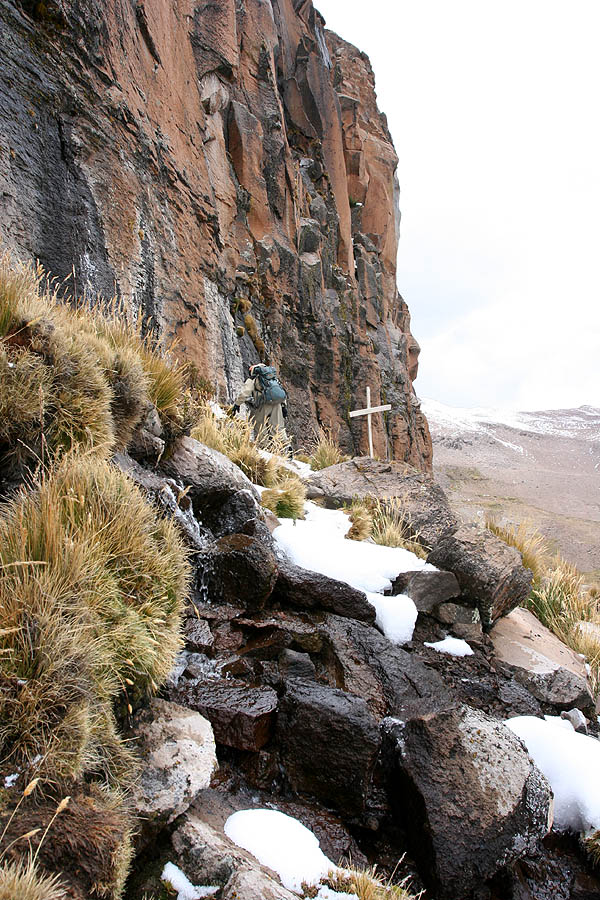
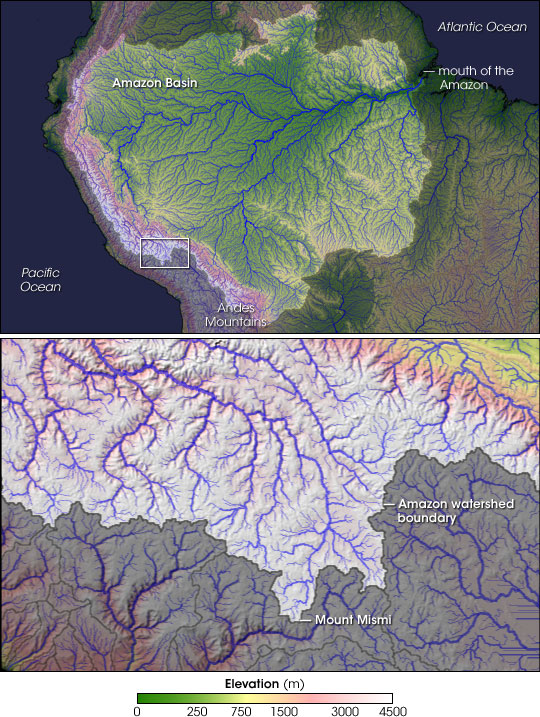
 The most distant source of the Amazon was thought to be in the Apurímac river drainage for nearly a century. Such studies continued to be published even recently, such as in 1996, 2001, 2007, and 2008, where various authors identified the snowcapped Nevado Mismi peak, located roughly west of Lake Titicaca and southeast of Lima, as the most distant source of the river. From that point, Quebrada
The most distant source of the Amazon was thought to be in the Apurímac river drainage for nearly a century. Such studies continued to be published even recently, such as in 1996, 2001, 2007, and 2008, where various authors identified the snowcapped Nevado Mismi peak, located roughly west of Lake Titicaca and southeast of Lima, as the most distant source of the river. From that point, Quebrada
 Although the Ucayali–Marañón confluence is the point at which most geographers place the beginning of the Amazon River proper, in Brazil the river is known at this point as the '' Solimões das Águas''. The river systems and flood plains in Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela, whose waters drain into the ''Solimões'' and its tributaries, are called the "Upper Amazon".
The Amazon proper runs mostly through Brazil and Peru, and is part of the border between Colombia and Perú. It has a series of major tributaries in
Although the Ucayali–Marañón confluence is the point at which most geographers place the beginning of the Amazon River proper, in Brazil the river is known at this point as the '' Solimões das Águas''. The river systems and flood plains in Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela, whose waters drain into the ''Solimões'' and its tributaries, are called the "Upper Amazon".
The Amazon proper runs mostly through Brazil and Peru, and is part of the border between Colombia and Perú. It has a series of major tributaries in

 The Lower Amazon begins where the darkly colored waters of the Rio Negro meets the sandy-colored
The Lower Amazon begins where the darkly colored waters of the Rio Negro meets the sandy-colored
 Belém is the major city and port at the mouth of the river at the Atlantic Ocean. The definition of where exactly the mouth of the Amazon is located, and how wide it is, is a matter of dispute, because of the area's peculiar geography. The Pará and the Amazon are connected by a series of river channels called ''furos'' near the town of Breves; between them lies Marajó, the world's largest combined river/sea island.
If the Pará river and the Marajó island ocean frontage are included, the Amazon estuary is some wide. In this case, the width of the mouth of the river is usually measured from Cabo Norte, the cape located straight east of Pracuúba in the Brazilian state of
Belém is the major city and port at the mouth of the river at the Atlantic Ocean. The definition of where exactly the mouth of the Amazon is located, and how wide it is, is a matter of dispute, because of the area's peculiar geography. The Pará and the Amazon are connected by a series of river channels called ''furos'' near the town of Breves; between them lies Marajó, the world's largest combined river/sea island.
If the Pará river and the Marajó island ocean frontage are included, the Amazon estuary is some wide. In this case, the width of the mouth of the river is usually measured from Cabo Norte, the cape located straight east of Pracuúba in the Brazilian state of
 While debate as to whether the Amazon or
While debate as to whether the Amazon or
 Not all of the Amazon's tributaries flood at the same time of the year. Many branches begin flooding in November and might continue to rise until June. The rise of the Rio Negro starts in February or March and begins to recede in June. The Madeira River rises and falls two months earlier than most of the rest of the Amazon river.
The depth of the Amazon between Manacapuru and Óbidos has been calculated as between . At Manacapuru, the Amazon's water level is only about above mean sea level. More than half of the water in the Amazon downstream of Manacapuru is below sea level. In its lowermost section, the Amazon's depth averages , in some places as much as .
The main river is navigable for large ocean steamers to
Not all of the Amazon's tributaries flood at the same time of the year. Many branches begin flooding in November and might continue to rise until June. The rise of the Rio Negro starts in February or March and begins to recede in June. The Madeira River rises and falls two months earlier than most of the rest of the Amazon river.
The depth of the Amazon between Manacapuru and Óbidos has been calculated as between . At Manacapuru, the Amazon's water level is only about above mean sea level. More than half of the water in the Amazon downstream of Manacapuru is below sea level. In its lowermost section, the Amazon's depth averages , in some places as much as .
The main river is navigable for large ocean steamers to
 More than one-third of all known species in the world live in the
More than one-third of all known species in the world live in the
 Along with the Orinoco, the Amazon is one of the main habitats of the '' boto'', also known as the Amazon river dolphin (''Inia geoffrensis''). It is the largest species of river dolphin, and it can grow to lengths of up to . The colour of its skin changes with age; young animals are gray, but become pink and then white as they mature. The dolphins use echolocation to navigate and hunt in the river's tricky depths. The ''boto'' is the subject of a legend in Brazil about a dolphin that turns into a man and seduces maidens by the riverside.
The tucuxi (''Sotalia fluviatilis''), also a dolphin species, is found both in the rivers of the Amazon basin and in the coastal waters of South America. The
Along with the Orinoco, the Amazon is one of the main habitats of the '' boto'', also known as the Amazon river dolphin (''Inia geoffrensis''). It is the largest species of river dolphin, and it can grow to lengths of up to . The colour of its skin changes with age; young animals are gray, but become pink and then white as they mature. The dolphins use echolocation to navigate and hunt in the river's tricky depths. The ''boto'' is the subject of a legend in Brazil about a dolphin that turns into a man and seduces maidens by the riverside.
The tucuxi (''Sotalia fluviatilis''), also a dolphin species, is found both in the rivers of the Amazon basin and in the coastal waters of South America. The
 The Anaconda is found in shallow waters in the Amazon basin. One of the world's largest species of snake, the anaconda spends most of its time in the water with just its nostrils above the surface. Species of caimans, that are related to alligators and other crocodilians, also inhabit the Amazon as do varieties of turtles.Cuvier's smooth-fronted caiman (''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'')
The Anaconda is found in shallow waters in the Amazon basin. One of the world's largest species of snake, the anaconda spends most of its time in the water with just its nostrils above the surface. Species of caimans, that are related to alligators and other crocodilians, also inhabit the Amazon as do varieties of turtles.Cuvier's smooth-fronted caiman (''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'')
 The Amazonian fish fauna is the centre of diversity for neotropical fishes, some of which are popular aquarium specimens like the neon tetra and the freshwater angelfish. More than 5,600 species were known , and approximately fifty new species are discovered each year. The arapaima, known in Brazil as the ''pirarucu'', is a South American tropical freshwater fish, one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, with a length of up to . Another Amazonian freshwater fish is the arowana (or ''aruanã'' in Portuguese), such as the silver arowana (''
The Amazonian fish fauna is the centre of diversity for neotropical fishes, some of which are popular aquarium specimens like the neon tetra and the freshwater angelfish. More than 5,600 species were known , and approximately fifty new species are discovered each year. The arapaima, known in Brazil as the ''pirarucu'', is a South American tropical freshwater fish, one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, with a length of up to . Another Amazonian freshwater fish is the arowana (or ''aruanã'' in Portuguese), such as the silver arowana (''
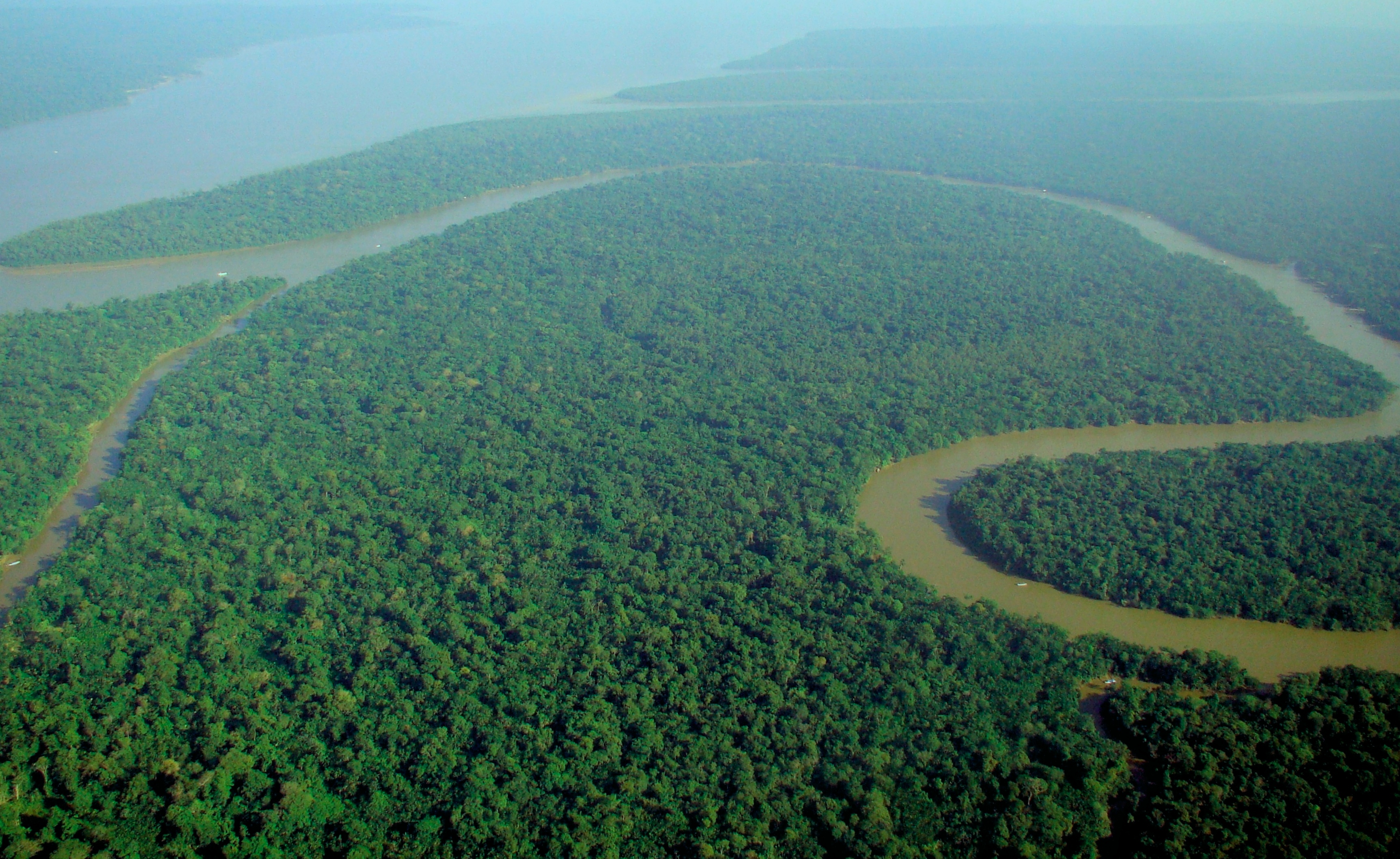
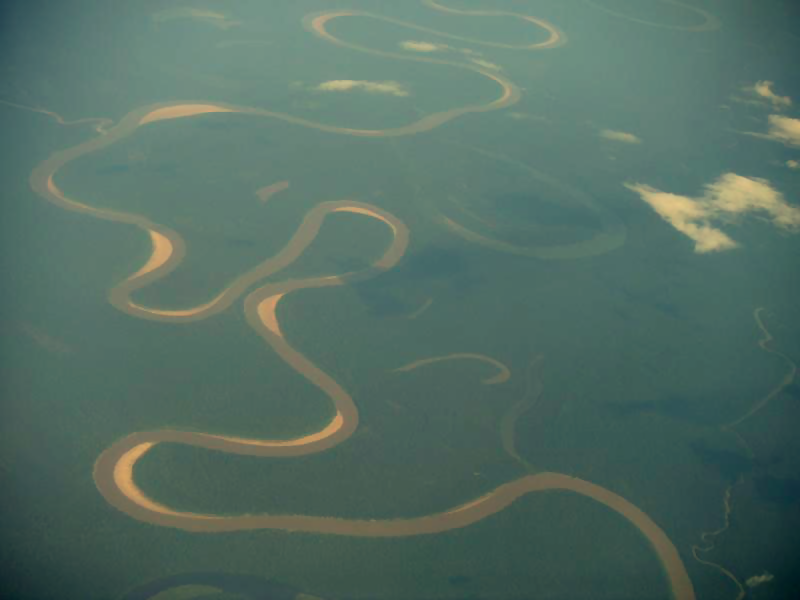
 The Amazon has over 1,100 tributaries, twelve of which are over long. Some of the more notable ones are:
* Branco
* Casiquiare canal
* Caquetá
* Huallaga
* Putumayo (or Içá River)
* Javary (or Yavarí)
* Juruá
*
The Amazon has over 1,100 tributaries, twelve of which are over long. Some of the more notable ones are:
* Branco
* Casiquiare canal
* Caquetá
* Huallaga
* Putumayo (or Içá River)
* Javary (or Yavarí)
* Juruá
*
Information on the Amazon from Extreme Science
A photographic journey up the Amazon River from its mouth to its source
Amazon Alive: Light & Shadow documentary film about the Amazon river
Amazon River Ecosystem
Research on the influence of the Amazon River on the Atlantic Ocean at the University of Southern California
* {{Authority control Amazon basin Amazon rainforest Upper Amazon Rivers of South America International rivers of South America Rivers of Colombia Rivers of Peru Colombia–Peru border Rivers of Amapá Rivers of Amazonas (Brazilian state) Rivers of Loreto Region Rivers of Pará
 The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge
Discharge may refer to
Expel or let go
* Discharge, the act of firing a gun
* Discharge, or termination of employment, the end of an employee's duration with an employer
* Military discharge, the release of a member of the armed forces from serv ...
volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of the Apurímac River on Nevado Mismi had been considered for nearly a century as the Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
's most distant source, until a 2014 study found it to be the headwaters of the Mantaro River on the Cordillera Rumi Cruz in Peru. The Mantaro and Apurímac rivers join, and with other tributaries form the Ucayali River
The Ucayali River ( es, Río Ucayali, ) is the main headstream of the Amazon River. It rises about north of Lake Titicaca, in the Arequipa region of Peru and becomes the Amazon at the confluence of the Marañón close to Nauta city. The city of ...
, which in turn meets the Marañón River upstream of Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
, Peru, forming what countries other than Brazil consider to be the main stem of the Amazon. Brazilians call this section the Solimões River above its confluence with the Rio Negro forming what Brazilians call the Amazon at the Meeting of Waters ( pt, Encontro das Águas) at Manaus
Manaus () is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. It is the seventh-largest city in Brazil, with an estimated 2020 population of 2,219,580 distributed over a land area of about . Located at the east center of the s ...
, the largest city on the river.
The Amazon River has an average discharge of about –—approximately – per year, greater than the next seven largest independent rivers combined. Two of the top ten rivers by discharge are tributaries of the Amazon river. The Amazon represents 20% of the global riverine discharge into oceans. The Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
is the largest drainage basin in the world, with an area of approximately . The portion of the river's drainage basin in Brazil alone is larger than any other river's basin. The Amazon enters Brazil with only one-fifth of the flow it finally discharges into the Atlantic Ocean, yet already has a greater flow at this point than the discharge of any other river.Tom Sterling: ''Der Amazonas''. Time-Life Bücher 1979, 7th German Printing, p. 19.
Etymology
The Amazon was initially known by Europeans as the Marañón, and the Peruvian part of the river is still known by that name today. It later became known as Rio Amazonas in Spanish and Portuguese. The name Rio Amazonas was reportedly given after native warriors attacked a 16th-century expedition by Francisco de Orellana. The warriors were led by women, reminding de Orellana of the Amazon warriors, a tribe of women warriors related to Iranian Scythians and Sarmatians mentioned in Greek mythology. The word Amazon itself may be derived from the Iranian compound *ha-maz-an- "(one) fighting together" orethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
''*ha-mazan-'' "warriors", a word attested indirectly through a derivation, a denominal verb in Hesychius of Alexandria's gloss ("': 'to make war' in Persian"), where it appears together with the Indo-Iranian root ''*kar-'' "make" (from which Sanskrit '' karma'' is also derived).
Other scholars claim that the name is derived from the Tupi Tupi may refer to:
* Tupi people of Brazil
* Tupi or Tupian languages, spoken in South America
** Tupi language, an extinct Tupian language spoken by the Tupi people
* Tupi oil field off the coast of Brazil
* Tupi Paulista, a Brazilian municipalit ...
word ''amassona'', meaning "boat destroyer"/
History
Geological history
Recent geological studies suggest that for millions of years the Amazon River used to flow in the opposite direction - from east to west. Eventually theAndes Mountains
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the List of mountain ranges#Mountain ranges by length, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range i ...
formed, blocking its flow to the Pacific Ocean, and causing it to switch directions to its current mouth in the Atlantic Ocean.
Pre-Columbian era
 During what many
During what many archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
s called the '' formative stage'', Amazonian societies were deeply involved in the emergence of South America's highland agrarian systems. The trade with Andean civilizations in the terrains of the headwaters in the Andes formed an essential contribution to the social and religious development of higher-altitude civilizations like the Muisca and Incas. Early human settlements were typically based on low-lying hills or mounds.
Shell mounds were the earliest evidence of habitation; they represent piles of human refuse (waste) and are mainly dated between 7500 and 4000 years BC. They are associated with ceramic age cultures; no preceramic shell mounds have been documented so far by archaeologists. Artificial earth platforms for entire villages are the second type of mounds. They are best represented by the Marajoara culture. Figurative mound
Figurative may refer to:
* Figurative analogy, a comparison between things that are not alike but do share some common property
* Figurative art, representational artwork
* Literal and figurative language
Literal and figurative language is a dis ...
s are the most recent types of occupation.
There is ample evidence that the areas surrounding the Amazon River were home to complex and large-scale indigenous societies, mainly chiefdoms who developed towns and cities. Archaeologists estimate that by the time the Spanish conquistador De Orellana traveled across the Amazon in 1541, more than 3 million indigenous people lived around the Amazon.Wohl, 2011, pp. 24–25. These pre-Columbian settlements created highly developed civilizations. For instance, pre-Columbian indigenous people on the island of Marajó may have developed social stratification and supported a population of 100,000 people. To achieve this level of development, the indigenous inhabitants of the Amazon rainforest altered the forest's ecology by selective cultivation
Selective may refer to:
* Selective school, a school that admits students on the basis of some sort of selection criteria
** Selective school (New South Wales)
Selective strength: the human body transitions between being weak and strong. This ran ...
and the use of fire. Scientists argue that by burning areas of the forest repeatedly, the indigenous people caused the soil to become richer in nutrients. This created dark soil areas known as '' terra preta de índio'' ("Indian dark earth").Wohl, 2011, p. 25. Because of the terra preta, indigenous communities were able to make land fertile and thus sustainable for the large-scale agriculture needed to support their large populations and complex social structures. Further research has hypothesized that this practice began around 11,000 years ago. Some say that its effects on forest ecology and regional climate explain the otherwise inexplicable band of lower rainfall through the Amazon basin.
Many indigenous tribes engaged in constant warfare. According to James S. Olson
James Stuart Olson is an academic and Pulitzer Prize-nominated author. In 1994, he was appointed Distinguished Professor of History at Sam Houston State University in Huntsville, Texas.
Olson is the author (or co-author) of over thirty books, pr ...
, "The Munduruku expansion (in the 18th century) dislocated and displaced the Kawahíb, breaking the tribe down into much smaller groups ... undurukufirst came to the attention of Europeans in 1770 when they began a series of widespread attacks on Brazilian settlements along the Amazon River."
Arrival of Europeans
 In March 1500, Spanish
In March 1500, Spanish conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
Vicente Yáñez Pinzón was the first documented European to sail up the Amazon River. Pinzón called the stream ''Río Santa María del Mar Dulce'', later shortened to ''Mar Dulce'', literally, ''sweet sea'', because of its freshwater pushing out into the ocean. Another Spanish explorer, Francisco de Orellana, was the first European to travel from the origins of the upstream river basins, situated in the Andes, to the mouth of the river. In this journey, Orellana baptized some of the affluents of the Amazonas like Rio Negro, Napo and Jurua.
The name Amazonas is thought to be taken from the native warriors that attacked this expedition, mostly women, that reminded De Orellana of the mythical female Amazon warriors from the ancient Hellenic culture in Greece (see also Origin of the name).
Exploration
Gonzalo Pizarro set off in 1541 to explore east ofQuito
Quito (; qu, Kitu), formally San Francisco de Quito, is the capital and largest city of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its urban area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley o ...
into the South American interior in search of ''El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king o ...
'', the "city of gold" and La Canela, the "valley of cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfa ...
". He was accompanied by his second-in-command Francisco de Orellana. After , the Coca River joined the Napo River
The Napo River ( es, Río Napo) is a tributary to the Amazon River that rises in Ecuador on the flanks of the east Andean volcanoes of Antisana, Sincholagua and Cotopaxi.
The total length is . The river drains an area of . The mean annual discha ...
(at a point now known as Puerto Francisco de Orellana
Puerto Francisco de Orellana (), also known as El Coca (), is the capital of province of Orellana in eastern Ecuador. The city is located in the Amazon Rainforest at the confluence of the Coca River and the Napo River (the smaller Payamino Riv ...
); the party stopped for a few weeks to build a boat just upriver from this confluence. They continued downriver through an uninhabited area, where they could not find food. Orellana offered and was ordered to follow the Napo River, then known as ''Río de la Canela'' ("Cinnamon River"), and return with food for the party. Based on intelligence received from a captive native chief named Delicola, they expected to find food within a few days downriver by ascending another river to the north.
De Orellana took about 57 men, the boat, and some canoes and left Pizarro's troops on 26 December 1541. However, De Orellana missed the confluence (probably with the Aguarico) where he was searching supplies for his men. By the time he and his men reached another village, many of them were sick from hunger and eating "noxious plants", and near death. Seven men died in that village. His men threatened to mutiny if the expedition turned back to attempt to rejoin Pizarro, the party being over 100 leagues downstream at this point. He accepted to change the purpose of the expedition to discover new lands in the name of the king of Spain, and the men built a larger boat in which to navigate downstream. After a journey of down the Napo River, they reached a further major confluence, at a point near modern Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
, and then followed the upper Amazon, now known as the Solimões, for a further to its confluence with the Rio Negro (near modern Manaus
Manaus () is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. It is the seventh-largest city in Brazil, with an estimated 2020 population of 2,219,580 distributed over a land area of about . Located at the east center of the s ...
), which they reached on 3 June 1542.
Regarding the initial mission of finding cinnamon, Pizarro reported to the king that they had found cinnamon trees, but that they could not be profitably harvested. True cinnamon (''Cinnamomum Verum'') is not native to South America. Other related cinnamon-containing plants (of the family ''Lauraceae'') are fairly common in that part of the Amazon and Pizarro probably saw some of these. The expedition reached the mouth of the Amazon on 24 August 1542, demonstrating the practical navigability of the Great River.
 In 1560, another Spanish
In 1560, another Spanish conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
, Lope de Aguirre, may have made the second descent of the Amazon. Historians are uncertain whether the river he descended was the Amazon or the Orinoco River, which runs more or less parallel to the Amazon further north.
Portuguese explorer Pedro Teixeira was the first European to travel up the entire river. He arrived in Quito in 1637, and returned via the same route.
From 1648 to 1652, Portuguese Brazilian '' bandeirante'' António Raposo Tavares
António Raposo Tavares ''o Velho'' ( Portuguese: ''the old one'') (1598–1658) was a Portuguese colonial bandeirante who explored mainland eastern South America and claimed it for Portugal, extending the territory of the colony beyond the lim ...
led an expedition from São Paulo overland to the mouth of the Amazon, investigating many of its tributaries, including the Rio Negro, and covering a distance of over .
In what is currently in Brazil, Ecuador, Bolivia, Colombia, Peru, and Venezuela, several colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
and religious settlements were established along the banks of primary rivers and tributaries for trade, slaving, and evangelization among the indigenous peoples of the vast rainforest, such as the Urarina. In the late 1600s, Czech Jesuit Father Samuel Fritz, an apostle of the Omagus established some forty mission villages. Fritz proposed that the Marañón River must be the source of the Amazon, noting on his 1707 map that the Marañón "has its source on the southern shore of a lake that is called Lauricocha, near Huánuco." Fritz reasoned that the Marañón is the largest river branch one encounters when journeying upstream, and lies farther to the west than any other tributary of the Amazon. For most of the 18th–19th centuries and into the 20th century, the Marañón was generally considered the source of the Amazon.

Scientific exploration
Early scientific, zoological, and botanical exploration of the Amazon River and basin took place from the 18th century through the first half of the 19th century. * Charles Marie de La Condamine explored the river in 1743. * Alexander von Humboldt, 1799–1804 *Johann Baptist von Spix
Johann Baptist Ritter von Spix (9 February 1781 – 13 March 1826) was a German natural history, biologist. From his expedition to Brazil, he brought to Germany a large variety of specimens of plants, insects, mammals, birds, amphibians and fish. ...
and Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius, 1817–1820
* Georg von Langsdorff, 1826–1828
* Henry Walter Bates and Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
, 1848–1859
* Richard Spruce
Richard Spruce (10 September 1817 – 28 December 1893) was an English botanist specializing in bryology. One of the great Victorian botanical explorers, Spruce spent 15 years exploring the Amazon from the Andes to its mouth, and was one of t ...
, 1849–1864
Post-colonial exploitation and settlement
 upIglesia Matriz in Iquitos, Peru
The Cabanagem revolt (1835–1840) was directed against the white ruling class. It is estimated that from 30% to 40% of the population of Grão-Pará, estimated at 100,000 people, died.
The population of the Brazilian portion of the Amazon basin in 1850 was perhaps 300,000, of whom about 175,000 were Europeans and 25,000 were slaves. The Brazilian Amazon's principal commercial city, Pará (now Belém), had from 10,000 to 12,000 inhabitants, including slaves. The town of Manáos, now Manaus, at the mouth of the Rio Negro, had a population between 1,000 and 1,500. All the remaining villages, as far up as Tabatinga, on the Brazilian frontier of Peru, were relatively small.
On 6 September 1850, Emperor
upIglesia Matriz in Iquitos, Peru
The Cabanagem revolt (1835–1840) was directed against the white ruling class. It is estimated that from 30% to 40% of the population of Grão-Pará, estimated at 100,000 people, died.
The population of the Brazilian portion of the Amazon basin in 1850 was perhaps 300,000, of whom about 175,000 were Europeans and 25,000 were slaves. The Brazilian Amazon's principal commercial city, Pará (now Belém), had from 10,000 to 12,000 inhabitants, including slaves. The town of Manáos, now Manaus, at the mouth of the Rio Negro, had a population between 1,000 and 1,500. All the remaining villages, as far up as Tabatinga, on the Brazilian frontier of Peru, were relatively small.
On 6 September 1850, Emperor Pedro II of Brazil
Don (honorific), Dom PedroII (2 December 1825 – 5 December 1891), nicknamed "the Magnanimity, Magnanimous" ( pt, O Magnânimo), was the List of monarchs of Brazil, second and last monarch of the Empire of Brazil, reigning for over 58 years. ...
sanctioned a law authorizing steam navigation on the Amazon and gave the Viscount of Mauá ( Irineu Evangelista de Sousa) the task of putting it into effect. He organised the "Companhia de Navegação e Comércio do Amazonas" in Rio de Janeiro in 1852; in the following year it commenced operations with four small steamers, the ''Monarca'' ('Monarch'), the ''Cametá'', the ''Marajó'' and the ''Rio Negro''.
At first, navigation was principally confined to the main river; and even in 1857 a modification of the government contract only obliged the company to a monthly service between Pará and Manaus, with steamers of 200 tons cargo capacity, a second line to make six round voyages a year between Manaus and Tabatinga, and a third, two trips a month between Pará and Cametá. This was the first step in opening up the vast interior.
The success of the venture called attention to the opportunities for economic exploitation of the Amazon, and a second company soon opened commerce on the Madeira, Purús, and Negro; a third established a line between Pará and Manaus, and a fourth found it profitable to navigate some of the smaller streams. In that same period, the Amazonas Company was increasing its fleet. Meanwhile, private individuals were building and running small steam craft of their own on the main river as well as on many of its tributaries.
On 31 July 1867, the government of Brazil, constantly pressed by the maritime powers and by the countries encircling the upper Amazon basin, especially Peru, decreed the opening of the Amazon to all countries, but they limited this to certain defined points: Tabatinga – on the Amazon; Cametá – on the Tocantins; Santarém – on the Tapajós; Borba – on the Madeira, and Manaus – on the Rio Negro. The Brazilian decree took effect on 7 September 1867.
Thanks in part to the mercantile
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchan ...
development associated with steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
navigation coupled with the internationally driven demand for natural rubber, the Peruvian city of Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
became a thriving, cosmopolitan center of commerce. Foreign companies settled in Iquitos, from where they controlled the extraction of rubber. In 1851 Iquitos had a population of 200, and by 1900 its population reached 20,000. In the 1860s, approximately 3,000 tons of rubber were being exported annually, and by 1911 annual exports had grown to 44,000 tons, representing 9.3% of Peru's exports. During the rubber boom it is estimated that diseases brought by immigrants, such as typhus and malaria, killed 40,000 native Amazonians.
The first direct foreign trade with Manaus commenced around 1874. Local trade along the river was carried on by the English successors to the Amazonas Company—the Amazon Steam Navigation Company—as well as numerous small steamboats, belonging to companies and firms engaged in the rubber trade, navigating the Negro, Madeira, Purús, and many other tributaries, such as the Marañón, to ports as distant as Nauta, Peru.
By the turn of the 20th century, the exports of the Amazon basin were India-rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
, cacao beans, Brazil nuts and a few other products of minor importance, such as pelts
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket ...
and exotic forest produce ( resins, barks, woven hammocks, prized bird feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
s, live animals) and extracted goods, such as lumber and gold.
20th-century development

BR-319
BR-319 is an federal highway that links Manaus, Amazonas to Porto Velho, Rondônia.
The highway runs through a pristine part of the Amazon rainforest.
It was opened by the military government in 1973 but soon deteriorated, and by 1988 was impassi ...
(Manaus- Porto Velho), are derelict and impassable in the rainy season. Small towns and villages are scattered across the forest, and because its vegetation is so dense, some remote areas are still unexplored.
Many settlements grew along the road from Brasília to Belém with the highway and National Integration Program, however, the program failed as the settlers were unequipped to live in the delicate rainforest ecosystem. This, although the government believed it could sustain millions, instead could sustain very few.
With a population of 1.9 million people in 2014, Manaus is the largest city on the Amazon. Manaus alone makes up approximately 50% of the population of the largest Brazilian state of Amazonas. The racial makeup of the city is 64% pardo (mulatto and mestizo) and 32% white.
Although the Amazon river remains undammed, around 412 dams are in operation in the Amazon's tributary rivers. From these 412 dams, 151 are constructed over six of the main tributary rivers that drain into the Amazon. Since only 4% of the Amazon's hydropower potential has been developed in countries like Brazil, more damming projects are underway and hundreds more are planned. After witnessing the negative effects of environmental degradation, sedimentation, navigation and flood control caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River, scientists are worried that constructing more dams in the Amazon will harm its biodiversity in the same way by "blocking fish-spawning runs, reducing the flows of vital oil nutrients and clearing forests". Damming the Amazon River could potentially bring about the "end of free flowing rivers" and contribute to an " ecosystem collapse" that will cause major social and environmental problems.
Course
Origins


Carhuasanta Carhuasanta is a small river located in the Arequipa Region of Peru. It is known as the headwaters of the Amazon River. The brook is fed by the winter snows of Nevado Mismi, (5,597 m), some 6,400 kilometers from the Atlantic Ocean. Of all ...
emerges from Nevado Mismi, joins Quebrada Apacheta and soon forms Río Lloqueta which becomes Río Hornillos and eventually joins the Río Apurímac
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
.
A 2014 study by Americans James Contos and Nicolas Tripcevich in '' Area'', a peer-reviewed journal of the Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
, however, identifies the most distant source of the Amazon as actually being in the Río Mantaro drainage. A variety of methods were used to compare the lengths of the Mantaro river vs. the Apurímac river from their most distant source points to their confluence, showing the longer length of the Mantaro. Then distances from Lago Junín to several potential source points in the uppermost Mantaro river were measured, which enabled them to determine that the Cordillera Rumi Cruz was the most distant source of water in the Mantaro basin (and therefore in the entire Amazon basin). The most accurate measurement method was direct GPS measurement obtained by kayak descent of each of the rivers from their source points to their confluence (performed by Contos). Obtaining these measurements was difficult given the class IV–V nature of each of these rivers, especially in their lower "Abyss" sections. Ultimately, they determined that the most distant point in the Mantaro drainage is nearly 80 km farther upstream compared to Mt. Mismi in the Apurímac drainage, and thus the maximal length of the Amazon river is about 80 km longer than previously thought. Contos continued downstream to the ocean and finished the first complete descent of the Amazon river from its newly identified source (finishing November 2012), a journey repeated by two groups after the news spread.
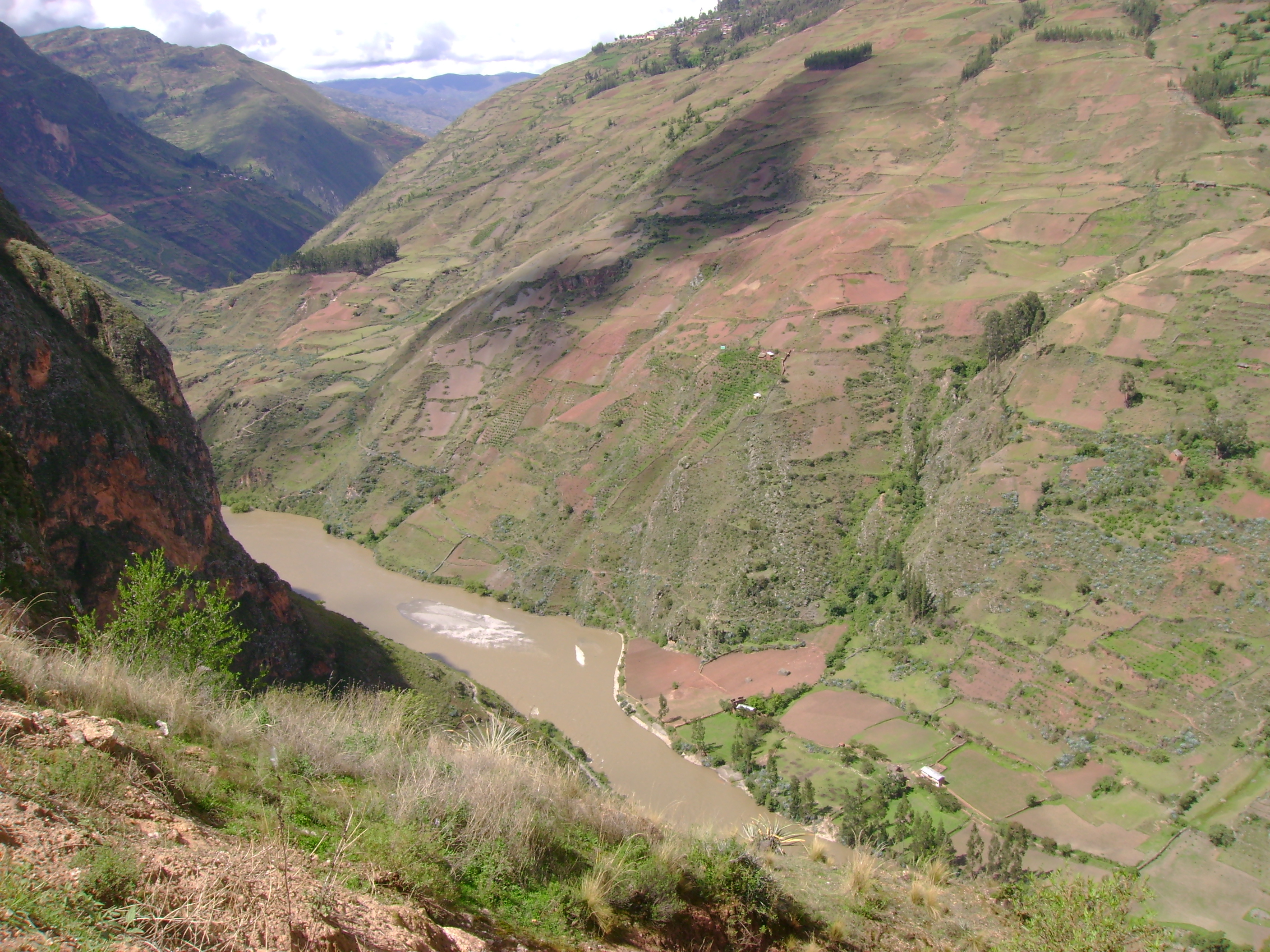
After about , the Apurímac then joins Río Mantaro to form the Ene, which joins the Perene to form the Tambo, which joins the Urubamba River to form the Ucayali. After the confluence of Apurímac and Ucayali, the river leaves Andean terrain and is surrounded by floodplain. From this point to the confluence of the Ucayali and the Marañón, some , the forested banks are just above the water and are inundated long before the river attains its maximum flood stage. The low river banks are interrupted by only a few hills, and the river enters the enormous Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
.
The Upper Amazon or Solimões
 Although the Ucayali–Marañón confluence is the point at which most geographers place the beginning of the Amazon River proper, in Brazil the river is known at this point as the '' Solimões das Águas''. The river systems and flood plains in Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela, whose waters drain into the ''Solimões'' and its tributaries, are called the "Upper Amazon".
The Amazon proper runs mostly through Brazil and Peru, and is part of the border between Colombia and Perú. It has a series of major tributaries in
Although the Ucayali–Marañón confluence is the point at which most geographers place the beginning of the Amazon River proper, in Brazil the river is known at this point as the '' Solimões das Águas''. The river systems and flood plains in Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela, whose waters drain into the ''Solimões'' and its tributaries, are called the "Upper Amazon".
The Amazon proper runs mostly through Brazil and Peru, and is part of the border between Colombia and Perú. It has a series of major tributaries in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, Ecuador and Peru, some of which flow into the Marañón and Ucayali, and others directly into the Amazon proper. These include rivers Putumayo, Caquetá, Vaupés, Guainía, Morona, Pastaza, Nucuray, Urituyacu, Chambira, Tigre, Nanay, Napo, and Huallaga.
At some points, the river divides into anabranch
An anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, th ...
es, or multiple channels, often very long, with inland and lateral channels, all connected by a complicated system of natural canals, cutting the low, flat ''igapó'' lands, which are never more than above low river, into many islands.
From the town of Canaria at the great bend of the Amazon to the Negro, vast areas of land are submerged at high water, above which only the upper part of the trees of the sombre forests appear. Near the mouth of the Rio Negro to Serpa, nearly opposite the river Madeira, the banks of the Amazon are low, until approaching Manaus, they rise to become rolling hills.
The Lower Amazon

Rio Solimões
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
(the upper Amazon), and for over these waters run side by side without mixing. At Óbidos, a bluff above the river is backed by low hills. The lower Amazon seems to have once been a gulf of the Atlantic Ocean, the waters of which washed the cliffs near Óbidos.
Only about 10% of the Amazon's water enters downstream of Óbidos, very little of which is from the northern slope of the valley. The drainage area of the Amazon basin above Óbidos city is about , and, below, only about (around 20%), exclusive of the of the Tocantins basin. The Tocantins River enters the southern portion of the Amazon delta.
In the lower reaches of the river, the north bank consists of a series of steep, table-topped hills extending for about from opposite the mouth of the Xingu as far as Monte Alegre. These hills are cut down to a kind of terrace which lies between them and the river.
On the south bank, above the Xingu, a line of low bluffs bordering the floodplain extends nearly to Santarém in a series of gentle curves before they bend to the southwest, and, abutting upon the lower Tapajós, merge into the bluffs which form the terrace margin of the Tapajós river valley.
Mouth
 Belém is the major city and port at the mouth of the river at the Atlantic Ocean. The definition of where exactly the mouth of the Amazon is located, and how wide it is, is a matter of dispute, because of the area's peculiar geography. The Pará and the Amazon are connected by a series of river channels called ''furos'' near the town of Breves; between them lies Marajó, the world's largest combined river/sea island.
If the Pará river and the Marajó island ocean frontage are included, the Amazon estuary is some wide. In this case, the width of the mouth of the river is usually measured from Cabo Norte, the cape located straight east of Pracuúba in the Brazilian state of
Belém is the major city and port at the mouth of the river at the Atlantic Ocean. The definition of where exactly the mouth of the Amazon is located, and how wide it is, is a matter of dispute, because of the area's peculiar geography. The Pará and the Amazon are connected by a series of river channels called ''furos'' near the town of Breves; between them lies Marajó, the world's largest combined river/sea island.
If the Pará river and the Marajó island ocean frontage are included, the Amazon estuary is some wide. In this case, the width of the mouth of the river is usually measured from Cabo Norte, the cape located straight east of Pracuúba in the Brazilian state of Amapá
Amapá () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is in the northern region of Brazil. It is the second least populous state and the eighteenth largest by area. Located in the far northern part of the country, Amapá is bordered clockwise by Fr ...
, to Ponta da Tijoca near the town of Curuçá
Curuçá is a municipality in the state of Pará in the Northern region of Brazil.
Curuçá was founded in 1775, but only became a city in 1895.
Some of the municipality was split off into separate municipalities in 1939, 1955 and 1991.
The Cur ...
, in the state of Pará.
A more conservative measurement excluding the Pará river estuary, from the mouth of the Araguari River to Ponta do Navio on the northern coast of Marajó, would still give the mouth of the Amazon a width of over . If only the river's main channel is considered, between the islands of Curuá (state of Amapá) and Jurupari (state of Pará), the width falls to about .
The plume generated by the river's discharge covers up to 1.3 million km2 and is responsible for muddy bottoms influencing a wide area of the tropical north Atlantic in terms of salinity, pH, light penetration, and sedimentation.
Lack of bridges
There are no bridges across the entire width of the river. This is not because the river would be too wide to bridge; for most of its length, engineers could build a bridge across the river easily. For most of its course, the river flows through the Amazon Rainforest, where there are very few roads and cities. Most of the time, the crossing can be done by aferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
. The Manaus Iranduba Bridge linking the cities of Manaus and Iranduba spans the Rio Negro, the second-largest tributary of the Amazon, just before their confluence.
Dispute regarding length
 While debate as to whether the Amazon or
While debate as to whether the Amazon or the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
is the world's longest river has gone on for many years, the historic consensus of geographic authorities has been to regard the Amazon as the second longest river in the world, with the Nile being the longest. However, the Amazon has been reported as being anywhere between and long. It is often said to be "at least" long. The Nile is reported to be anywhere from . Often it is said to be "about" long. There are several factors that can affect these measurements, such as the position of the geographical source and the mouth, the scale of measurement, and the length measuring techniques (for details see also List of rivers by length).
In July 2008, the Brazilian Institute for Space Research (INPE) published a news article on their webpage, claiming that the Amazon River was longer than the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
. The Amazon's length was calculated as , taking the Apacheta Creek as its source. Using the same techniques, the length of the Nile was calculated as , which is longer than previous estimates but still shorter than the Amazon. The results were reached by measuring the Amazon downstream to the beginning of the tidal estuary of ''Canal do Sul'' and then, after a sharp turn back, following tidal canals surrounding the isle of Marajó and finally including the marine waters of the ''Río Pará'' bay in its entire length. According to an earlier article on the webpage of the National Geographic, the Amazon's length was calculated as by a Brazilian scientist. In June 2007, Guido Gelli
Guido is a given name Latinisation of names, Latinised from the Old High German name Wido. It originated in Medieval Italy. Guido later became a male first name in Austria, Germany, the Low Countries, Scandinavia, Spain, Portugal, Latin America an ...
, director of science at the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ( pt, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information ...
(IBGE), told London's Telegraph Newspaper that it could be considered that the Amazon was the longest river in the world. However, according to the above sources, none of the two results was published, and questions were raised about the researchers' methodology. In 2009, a peer-reviewed
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ...
article, was published, concluding that the Nile is longer than the Amazon by stating a length of for the Nile and for the Amazon, measured by using a combination of satellite image analysis and field investigations to the source regions.
According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, the final length of the Amazon remains open to interpretation and continued debate.
Watershed
The Amazon basin, the largest in the world, covers about 40% of South America, an area of approximately . It drains from west to east, fromIquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
in Peru, across Brazil to the Atlantic. It gathers its waters from 5 degrees north latitude to 20 degrees south latitude. Its most remote sources are found on the inter- Andean plateau, just a short distance from the Pacific Ocean.
The Amazon River and its tributaries are characterised by extensive forested areas that become flooded every rainy season. Every year, the river rises more than , flooding the surrounding forests, known as '' várzea'' ("flooded forests"). The Amazon's flooded forests are the most extensive example of this habitat type in the world. In an average dry season, of land are water-covered, while in the wet season, the flooded area of the Amazon basin rises to .
The quantity of water released by the Amazon to the Atlantic Ocean is enormous: up to in the rainy season, with an average of from 1973 to 1990. The Amazon is responsible for about 20% of the Earth's fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
entering the ocean. The river pushes a vast plume of fresh water into the ocean. The plume is about long and between wide. The fresh water, being lighter, flows on top of the seawater, diluting the salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
and altering the colour of the ocean surface over an area up to in extent. For centuries ships have reported fresh water near the Amazon's mouth yet well out of sight of land in what otherwise seemed to be the open ocean.
The Atlantic has sufficient wave and tidal energy to carry most of the Amazon's sediments out to sea, thus the Amazon does not form a true delta. The great deltas of the world are all in relatively protected bodies of water, while the Amazon empties directly into the turbulent Atlantic.
There is a natural water union between the Amazon and the Orinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the wor ...
basins, the so-called Casiquiare canal. The Casiquiare is a river distributary
A distributary, or a distributary channel, is a stream that branches off and flows away from a main stream channel. Distributaries are a common feature of river deltas. The phenomenon is known as river bifurcation. The opposite of a distributar ...
of the upper Orinoco, which flows southward into the Rio Negro, which in turn flows into the Amazon. The Casiquiare is the largest river on earth that links two major river systems, a so-called bifurcation.
Flooding
 Not all of the Amazon's tributaries flood at the same time of the year. Many branches begin flooding in November and might continue to rise until June. The rise of the Rio Negro starts in February or March and begins to recede in June. The Madeira River rises and falls two months earlier than most of the rest of the Amazon river.
The depth of the Amazon between Manacapuru and Óbidos has been calculated as between . At Manacapuru, the Amazon's water level is only about above mean sea level. More than half of the water in the Amazon downstream of Manacapuru is below sea level. In its lowermost section, the Amazon's depth averages , in some places as much as .
The main river is navigable for large ocean steamers to
Not all of the Amazon's tributaries flood at the same time of the year. Many branches begin flooding in November and might continue to rise until June. The rise of the Rio Negro starts in February or March and begins to recede in June. The Madeira River rises and falls two months earlier than most of the rest of the Amazon river.
The depth of the Amazon between Manacapuru and Óbidos has been calculated as between . At Manacapuru, the Amazon's water level is only about above mean sea level. More than half of the water in the Amazon downstream of Manacapuru is below sea level. In its lowermost section, the Amazon's depth averages , in some places as much as .
The main river is navigable for large ocean steamers to Manaus
Manaus () is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. It is the seventh-largest city in Brazil, with an estimated 2020 population of 2,219,580 distributed over a land area of about . Located at the east center of the s ...
, upriver from the mouth. Smaller ocean vessels below 9000 tons and with less than draft can reach as far as Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
, Peru, from the sea. Smaller riverboats can reach higher, as far as Achual Point. Beyond that, small boats frequently ascend to the Pongo de Manseriche, just above Achual Point in Peru.
Annual flooding occurs in late northern latitude winter at high tide when the incoming waters of the Atlantic are funnelled into the Amazon delta. The resulting undular tidal bore is called the '' pororoca'', with a leading wave that can be up to high and travel up to inland.
Geology
The Amazon River originated as a transcontinental river in the Miocene epoch between 11.8 million and 11.3 million years ago and took its present shape approximately 2.4 million years ago in the Early Pleistocene. The proto-Amazon during the Cretaceous flowed west, as part of a proto-Amazon-Congo river system, from the interior of present-day Africa when the continents were connected, forming westernGondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
. 80 million years ago, the two continents split. Fifteen million years ago, the main tectonic uplift phase of the Andean chain started. This tectonic movement is caused by the subduction of the Nazca Plate
The Nazca Plate or Nasca Plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Na ...
underneath the South American Plate
The South American Plate is a major tectonic plate which includes the continent of South America as well as a sizable region of the Atlantic Ocean seabed extending eastward to the African Plate, with which it forms the southern part of the Mid-A ...
. The rise of the Andes and the linkage of the Brazilian and Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
bedrock shields, blocked the river and caused the Amazon Basin to become a vast inland sea. Gradually, this inland sea became a massive swampy, freshwater lake and the marine inhabitants adapted to life in freshwater.
Eleven to ten million years ago, waters worked through the sandstone from the west and the Amazon began to flow eastward, leading to the emergence of the Amazon rainforest. During glacial periods, sea levels dropped and the great Amazon lake rapidly drained and became a river, which would eventually become the disputed world's longest, draining the most extensive area of rainforest on the planet.
Paralleling the Amazon River is a large aquifer, dubbed the Hamza River The Hamza River (Portuguese: ''Rio Hamza'') is an unofficial name for what seems to be a slowly flowing aquifer in Brazil and Peru, approximately long at a depth of nearly . Its discovery was announced in 2011 at a meeting of the Geophysical Societ ...
, the discovery of which was made public in August 2011.
Protected areas
Flora and fauna
Flora
Fauna
 More than one-third of all known species in the world live in the
More than one-third of all known species in the world live in the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
. It is the richest tropical forest in the world in terms of biodiversity. In addition to thousands of species of fish, the river supports crabs, algae, and turtles.
Mammals
Amazonian manatee
The Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis'') is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a whit ...
(''Trichechus inunguis''), also known as "seacow", is found in the northern Amazon River basin and its tributaries. It is a mammal and a herbivore. Its population is limited to freshwater habitats, and, unlike other manatees, it does not venture into saltwater. It is classified as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
The Amazon and its tributaries are the main habitat of the giant otter (''Pteronura brasiliensis''). Sometimes known as the "river wolf," it is one of South America's top carnivores. Because of habitat destruction and hunting, its population has dramatically decreased. It is now listed on Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), which effectively bans international trade.
Reptiles
 The Anaconda is found in shallow waters in the Amazon basin. One of the world's largest species of snake, the anaconda spends most of its time in the water with just its nostrils above the surface. Species of caimans, that are related to alligators and other crocodilians, also inhabit the Amazon as do varieties of turtles.Cuvier's smooth-fronted caiman (''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'')
The Anaconda is found in shallow waters in the Amazon basin. One of the world's largest species of snake, the anaconda spends most of its time in the water with just its nostrils above the surface. Species of caimans, that are related to alligators and other crocodilians, also inhabit the Amazon as do varieties of turtles.Cuvier's smooth-fronted caiman (''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'')Birds
The types of birds that pass by or live in the amazon river are toucans, harpy eagles, and much more variations of birds.Fish

 The Amazonian fish fauna is the centre of diversity for neotropical fishes, some of which are popular aquarium specimens like the neon tetra and the freshwater angelfish. More than 5,600 species were known , and approximately fifty new species are discovered each year. The arapaima, known in Brazil as the ''pirarucu'', is a South American tropical freshwater fish, one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, with a length of up to . Another Amazonian freshwater fish is the arowana (or ''aruanã'' in Portuguese), such as the silver arowana (''
The Amazonian fish fauna is the centre of diversity for neotropical fishes, some of which are popular aquarium specimens like the neon tetra and the freshwater angelfish. More than 5,600 species were known , and approximately fifty new species are discovered each year. The arapaima, known in Brazil as the ''pirarucu'', is a South American tropical freshwater fish, one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, with a length of up to . Another Amazonian freshwater fish is the arowana (or ''aruanã'' in Portuguese), such as the silver arowana (''Osteoglossum bicirrhosum
The silver arowana (''Osteoglossum bicirrhosum'') is a South American freshwater bony fish of the family Osteoglossidae. Silver arowanas are sometimes kept in aquariums, but they are predatory and require a very large tank.
The generic name ''Os ...
''), which is a predator and very similar to the arapaima, but only reaches a length of . Also present in large numbers is the notorious piranha, an omnivorous fish that congregates in large schools and may attack livestock. There are approximately 30 to 60 species of piranha. The candirú
Candiru (''Vandellia cirrhosa''), also known as cañero, toothpick fish, or vampire fish, is a species of parasitic freshwater catfish in the family Trichomycteridae native to the Amazon Basin where it is found in the countries of Bolivia, Bra ...
, native to the Amazon River, is a species of parasitic fresh water catfish in the family Trichomycteridae, just one of more than 1200 species of catfish in the Amazon basin. Other catfish 'walk' overland on their ventral fins, while the kumakuma
''Brachyplatystoma filamentosum'', the piraíba or kumakuma, is a species of large catfish of the family Pimelodidae and genus Brachyplatystoma that is native to Amazon and Orinoco River basins and fluvials in Guianas and northeastern Brazil.
D ...
(''Brachyplatystoma filamentosum''), aka ''piraiba'' or "goliath catfish", can reach in length and in weight.
The electric eel (''Electrophorus electricus'') and more than 100 species of electric fishes (Gymnotiformes
The Gymnotiformes are an order of teleost bony fishes commonly known as Neotropical knifefish or South American knifefish. They have long bodies and swim using undulations of their elongated anal fin. Found almost exclusively in fresh water (the ...
) inhabit the Amazon basin. River stingrays ( Potamotrygonidae) are also known. The bull shark (''Carcharhinus leucas'') has been reported up the Amazon River at Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the ninth-most populous city of Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world th ...
in Peru.
Butterflies
Microbiota
Freshwater microbes are generally not very well known, even less so for a pristine ecosystem like the Amazon. Recently, metagenomics has provided answers to what kind of microbes inhabit the river. The most important microbes in the Amazon River are Actinomycetota, Alphaproteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria,Gammaproteobacteria
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria). It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genera-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically imp ...
and Thermoproteota.
Major tributaries

 The Amazon has over 1,100 tributaries, twelve of which are over long. Some of the more notable ones are:
* Branco
* Casiquiare canal
* Caquetá
* Huallaga
* Putumayo (or Içá River)
* Javary (or Yavarí)
* Juruá
*
The Amazon has over 1,100 tributaries, twelve of which are over long. Some of the more notable ones are:
* Branco
* Casiquiare canal
* Caquetá
* Huallaga
* Putumayo (or Içá River)
* Javary (or Yavarí)
* Juruá
* Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
* Marañón
* Morona
* Nanay
* Napo
* Negro
* Pastaza
* Purús
* Tambo
* Tapajós
* Tigre
* Tocantins
* Trombetas
* Ucayali
* Xingu
* Yapura
List of major tributaries
The main river and tributaries are (sorted in order from the confluence of Ucayali and Marañón rivers to the mouth):List by length
# () – Amazon, South America # –Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
, Bolivia/Brazil
# – Purús, Peru/Brazil
# – Japurá or Caquetá, Colombia/Brazil
# – Tocantins, Brazil
# – Araguaia, Brazil (tributary of Tocantins)
# – Juruá, Peru/Brazil
# – Rio Negro, Brazil/Venezuela/Colombia
# – Tapajós, Brazil
# – Xingu, Brazil
# – Ucayali River
The Ucayali River ( es, Río Ucayali, ) is the main headstream of the Amazon River. It rises about north of Lake Titicaca, in the Arequipa region of Peru and becomes the Amazon at the confluence of the Marañón close to Nauta city. The city of ...
, Peru
# – Guaporé, Brazil/Bolivia (tributary of Madeira)
# – Içá (Putumayo), Ecuador/Colombia/Peru
# – Marañón, Peru
# – Teles Pires, Brazil (tributary of Tapajós)
# – Iriri, Brazil (tributary of Xingu)
# – Juruena
Juruena is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.
The city is served by Juruena Airport.
See also
*List of municipalities in Mato Grosso
*Sepotuba River
The Sepotuba River is a river in the state of M ...
, Brazil (tributary of Tapajós)
# – Madre de Dios, Peru/Bolivia (tributary of Madeira)
# – Huallaga, Peru (tributary of Marañón)
List by inflow to the Amazon
See also
*Amazon natural region
Amazonía region in southern Colombia comprises the Departments of Colombia, departments of Amazonas Department, Amazonas, Caquetá Department, Caquetá, Guainía Department, Guainía, Guaviare Department, Guaviare, Putumayo Department, Putumay ...
* Peruvian Amazonia
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Information on the Amazon from Extreme Science
A photographic journey up the Amazon River from its mouth to its source
Amazon Alive: Light & Shadow documentary film about the Amazon river
Amazon River Ecosystem
Research on the influence of the Amazon River on the Atlantic Ocean at the University of Southern California
* {{Authority control Amazon basin Amazon rainforest Upper Amazon Rivers of South America International rivers of South America Rivers of Colombia Rivers of Peru Colombia–Peru border Rivers of Amapá Rivers of Amazonas (Brazilian state) Rivers of Loreto Region Rivers of Pará