|
Trichomycteridae
Trichomycteridae is a family of catfishes commonly known as pencil catfishes or parasitic catfishes. This family includes the candiru fish (''Vandellia cirrhosa''), feared by some people for its alleged habit of entering into the urethra of humans. They are one of the few parasitic chordates. Another species is the life monsefuano (''Trichomycterus punctulatus'') which was important to the Moche culture and still an important part of Peruvian cuisine.FondazioneslowfoodLife monsefuano.Retrieved 28 April 2017. This family is prohibited from being imported into various parts of the United States. Taxonomy The Trichomycteridae comprise about 42 genera and 286 species described. It is the second-most diverse family of the superfamily Loricarioidea. Numerous species still remain undescribed. The monophyly of Trichomycteridae is well-supported. The family is divided into eight subfamilies. The only subfamily that is not monophyletic is the largest one, Trichomycterinae. A large cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ituglanis
''Ituglanis'' is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family Trichomycteridae native to South America. Their greatest diversity seems to occur in the Amazon River basin.Datovo, A. & Landim, M.I. (2005)''Ituglanis macunaima'', a new catfish from the rio Araguaia basin, Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae).''Neotropical Ichthyology, 3 (4): 455–464.'' Most species inhabit leaf litter, with several species living in caves. This genus was first erected for nine species previously classified in ''Trichomycterus''.Sarmento-Soares, L.M., Martins-Pinheiro, R.F., Aranda, A.T. & Chamon, C.C. (2006)''Ituglanis cahyensis'', a new catfish from Bahia, Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae).''Neotropical Ichthyology, 4 (3): 309-318.'' ''Ituglanis'' is believed to be a monophyletic group. There may be two monophyletic groups within this genus. ''Ituglanis'' is currently considered a member of the subfamily Trichomycterinae though its position as a member of any of the current subfamilies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoglanidinae
The Sarcoglanidinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera: ''Ammoglanis'', '' Malacoglanis'', '' Microcambeva'', '' Sarcoglanis'', '' Stauroglanis'', and ''Stenolicmus''. Taxonomy The subfamily Sarcoglanidinae was first established in 1966 for ''Sarcoglanis simplex'' and ''Malacoglanis gelatinosus''. A third species of the subfamily, ''Stauroglanis gouldingi'', was described about 25 years later. Descriptions of additional species have followed, though most genera remain monotypic. The relationships of the genus ''Ammoglanis'' with other sarcoglanidines are not well-established; however, this genus is currently included within Sarcoglanidinae. This subfamily has been proposed to have a sister group relationship to Glanapteryginae. Like the members of this subfamily, many glanapterygines are sand-dwelling fish. Distribution and habitat All genera except ''Microcambeva'' are endemic to the Amazon River; ''Microca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copionodontinae
The Copionodontinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes two genera, '' Copionodon'' and ''Glaphyropoma''. Classification Copionodontines are remarkably primitive in body form, and lack many of the synapomorphies previously used to diagnose the family Trichomycteridae. Little doubt exists that the Copionodontinae form a monophyletic group, diagnosed by several unambiguous synapomorphies, including a unique dentition composed of spatulate teeth not seen anywhere else in the Trichomycteridae. A few characters also support the genera ''Copionodon'' and ''Glaphyropoma'' as monophyletic subunits. Distribution and ecology Copionodontines occur exclusively in the Chapada Diamantina; though the plateau is drained by four river basins, so far, these fish are exclusively found in drainages associated with the Paraguaçu River The Paraguaçu River () is a river in Bahia state of eastern Brazil. It runs from the Chapada Diamantina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores (species that eat dead material on the bottom), and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, ''Vandellia cirrhosa''. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus '' Corydoras'', are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomycterinae
The Trichomycterinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera, '' Bullockia'', '' Hatcheria'', '' Rhizosomichthys'', and '' Eremophilus'', all monotypic, '' Silvinichthys'' with two species, and '' Trichomycterus'', with over 100 species. The former five genera are diagnosed by putatively apomorphic characters, whereas ''Trichomycterus'' is defined by the lack of those specializations and is likely not monophyletic. This subfamily has historically served as much of a wastebasket for trichomycterids that lack the specializations of the other subfamilies. Species of Trichomycterinae dwell in headwaters and small, cold clear water streams running over stony beds. Due to the patchy distribution of their habitats, trichomycterines generally have restricted geographic distributions, thus display a high level of endemism Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glanapteryginae
The Glanapteryginae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes four genera, '' Glanapteryx'', '' Listrura'', ''Pygidianops'', and ''Typhlobelus''. Phylogeny Monophyly of the subfamily is supported by five synapomorphies involving reductions in the fins, caudal skeleton, and laterosensory system. It has been proposed that the sister group to this subfamily is the Sarcoglanidinae. ''Listrura'' is the sister group to the remainder of the subfamily. ''Glanapteryx'' is sister to a clade formed by the sister taxa ''Pygidianops'' and ''Typhlobelus''. Distribution ''Glanapteryx'', ''Pygidianops'', and ''Typhlobelus'' are distributed in the Orinoco and Amazon River basins. ''Listrura'' species are from Brazil, outside of the Amazon River basin. However, the distribution of glanapterygines may be greater than previously thought. Description Most of the subfamily is constituted by 'miniaturized' species. Though miniaturized fish usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegophilinae
The Stegophilinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes 12 genera: '' Acanthopoma'', '' Apomatoceros'', '' Haemomaster'', '' Henonemus'', '' Homodiaetus'', '' Megalocentor'', ''Ochmacanthus'', '' Parastegophilus'', '' Pareiodon'', '' Pseudostegophilus'', '' Schultzichthys'', and '' Stegophilus''. A monophyletic group within the Stegophilinae is supported by two characteristics of the lateral line, including ''Acanthopoma'', ''Henonemus'', ''Megalocentor'', ''Pareiodon'', ''Parastegophilus'', and ''Pseudostegophilus''. ''Acanthopoma'' and ''Henonemus'' have a sister group relationship. The Stegophilinae are widely distributed in the main South American river basins, including the Amazon, Orinoco, São Francisco, Paraná-Paraguay, and those of southern Brazil. Eight of the genera are distributed in Venezuela. Stegophilines are sometimes considered candirú, so are considered parasites or semiparasites, because of their pecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichogeninae
''Trichogenes'' is a genus of pencil catfishes. It is currently the only genus within the subfamily ''Trichogeninae''. A third species was described in 2020 from archival material of unknown origin. The wild distribution of the new species, ''T. beagle,'' is unknown. Distribution ''Trichogenes'' species are endemic to Brazil. Species There are currently three recognized species in this genus: * '' Trichogenes beagle'' * '' Trichogenes claviger'' de Pinna, Helmer, Britski & Nunes, 2010 * ''Trichogenes longipinnis ''Trichogenes longipinnis'' (the long-finned cambeva), is a species of catfish (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. ''T. longipinnis'' is endemic to coastal streams in the Atlantic forest between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo Sta ...'' Britski & Ortega, 1983 References Trichomycteridae Fish of Brazil Freshwater fish genera Catfish genera Taxa named by Heraldo Antonio Britski Taxa named by Hernán Ortega {{Trichomycteridae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
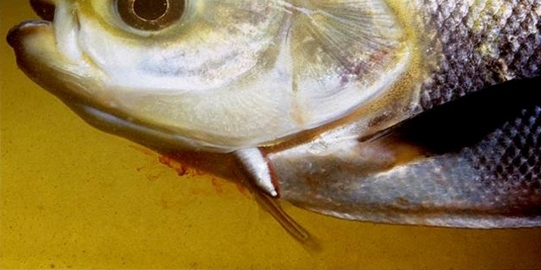
Candiru (fish)
Candiru (''Vandellia cirrhosa''), also known as cañero, toothpick fish, or vampire fish, is a species of parasitic freshwater catfish in the family Trichomycteridae native to the Amazon Basin where it is found in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The definition of ''candiru'' differs between authors. The word has been used to refer to only ''Vandellia cirrhosa'', the entire genus '' Vandellia'', the subfamily Vandelliinae, or even the two subfamilies Vandelliinae and Stegophilinae. Although some candiru species have been known to grow to a size of in length, others are considerably smaller. These smaller species are known for an alleged tendency to invade and parasitise the human urethra; however, despite ethnological reports dating back to the late 19th century, the first documented case of the removal of a candiru from a human urethra did not occur until 1997, and even that incident has remained a matter of controversy. Description Candirus ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glanapteryx
''Glanapteryx'' is a genus of catfishes native to South America. Taxonomy ''Glanapteryx'' is a monophyletic genus. ''Glanapteryx'' has been proposed as the sister group to a clade composed of '' Pygidianops'' and '' Typhlobelus'', with ''Listrura'' the sister group to those three. Species There are currently two recognized species in this genus: * '' Glanapteryx anguilla'' Myers, 1927 * '' Glanapteryx niobium'' de Pinna, 1998 Distribution and habitat ''G. anguilla'' originates from the Negro and Orinoco River basins of Brazil and Venezuela, growing to a length of about 6.1 centimetres (2.4 in) TL. ''G. niobium'' reaches about 5.5 cm (2.2 in). These species lack an anal fin Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se .... ''Glanapteryx anguilla'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loricarioidea
Loricarioidea is a superfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes). It contains the six families Trichomycteridae, Nematogenyiidae, Callichthyidae, Scoloplacidae, Astroblepidae, and Loricariidae. Some schemes also include Amphiliidae. This superfamily, including Amphiliidae, includes about 156 genera and 1,187 species. Taxonomy Loricarioidea is traditionally considered a part of Siluroidei, a clade of all catfishes excluding Diplomystidae. In Nelson, 2006, this grouping is sister to the superfamily Sisoroidea. However, in a recent molecular analysis, it was determined that the suborder Loricarioidei (not including Amphiliidae) is sister to a group including Diplomystidae and Siluroidei. Amphiliidae, in this analysis, was found to be much more closely related to Mochokidae or Malapteruridae. Loricarioidea is currently diagnosed by the derived presence of a reduced gas bladder, encapsulated in expansions of the parapophysis of the first vertebrae, and of odontodes, small derma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaphyropoma
''Glaphyropoma'' is a genus of small pencil catfishes native to Bahia in Brazil. Species There are currently two recognized species in this genus: * '' Glaphyropoma rodriguesi'' de Pinna, 1992 * '' Glaphyropoma spinosum'' Bichuette, de Pinna & Trajano, 2008 The single synapomorphy proposed for ''Glaphyropoma'' is the marked narrowing of the first hypobranchial, giving the hypobranchial a slender shape. ''G. rodriguesi'' grows to about 5.1 centimetres (2.0 in) in standard length and originates from the Mucujê River, a tributary of Paraguaçu River in Brazil. ''G. spinosum'' is known to grow as large as 5.8 cm (2.3 in) in standard length. It is known from subterranean waters in the Diamantina Plateau of the Bahia State in central northeastern Brazil. This is the first-known troglomorphic species in the subfamily Copionodontinae. These fish live in quartzitic caves formed by erosion Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |