Alpini Battalion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Alpini are the


 In 1872, Captain
In 1872, Captain
 ''
''


 During
During

 Each division consisted of two Alpini regiments with three battalions each, one Alpine Artillery Regiment with three Artillery groups, one Mixed Engineer Battalion, one Logistic Battalion and some support units. The strength of each division was 573 officers and 16,887 NCOs and soldiers for a total strength of 17,460 men. Also each division had almost 5,000 mules and 500 vehicles of various types at its disposal.
Each division consisted of two Alpini regiments with three battalions each, one Alpine Artillery Regiment with three Artillery groups, one Mixed Engineer Battalion, one Logistic Battalion and some support units. The strength of each division was 573 officers and 16,887 NCOs and soldiers for a total strength of 17,460 men. Also each division had almost 5,000 mules and 500 vehicles of various types at its disposal.
The divisions saw combat in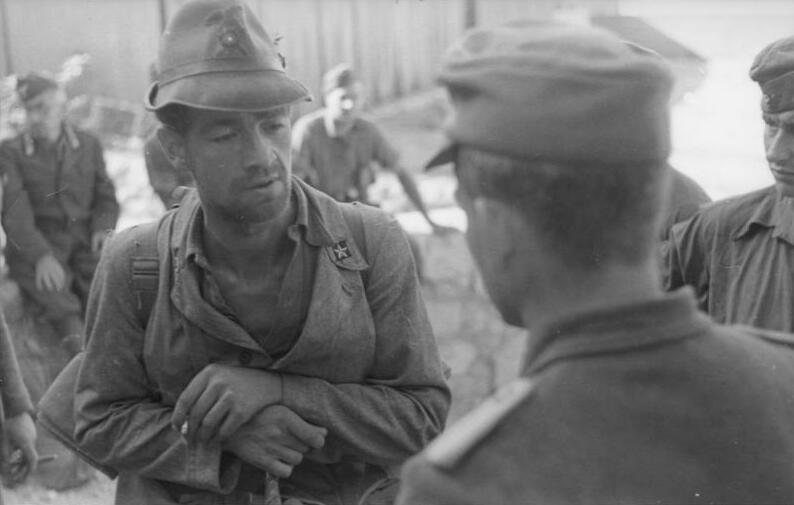 After the
After the

 After World War II the Alpini units were once more tasked with defending Italy's northern borders. On 15 October 1949 the Alpine Brigade ''Julia'' was activated in
After World War II the Alpini units were once more tasked with defending Italy's northern borders. On 15 October 1949 the Alpine Brigade ''Julia'' was activated in 
 Taurinense
**
Taurinense
**  Tridentina
**
Tridentina
** 


 After the end of the
After the end of the  Tridentina Division:
**
Tridentina Division:
**  Command and Tactical Supports Unit "Tridentina"
Command and Tactical Supports Unit "Tridentina"  *
* 
 1st Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit
1st Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit  **
** 
 "Saluzzo" Battalion
**
"Saluzzo" Battalion
** 
 "Susa" Battalion
**
"Susa" Battalion
** 
 "L'Aquila" Battalion and
"L'Aquila" Battalion and  "Vicenza" Battalion
**
"Vicenza" Battalion
**  1st Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)
1st Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)  "Aosta" Mountain Artillery Group
**
"Aosta" Mountain Artillery Group
**  32nd Engineer Regiment
32nd Engineer Regiment  30th Sapper Battalion
**
30th Sapper Battalion
**  Logistic Regiment "Taurinense"
Logistic Regiment "Taurinense"  Logistic Battalion
*
Logistic Battalion
* 
 14th Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit
14th Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit  **
** 
 "Morbegno" Battalion
**
"Morbegno" Battalion
** 
 "Feltre" Battalion
**
"Feltre" Battalion
** 
 "Tolmezzo" Battalion
**
"Tolmezzo" Battalion
**  3rd Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)
3rd Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)  "Conegliano" Mountain Artillery Group
**
"Conegliano" Mountain Artillery Group
**  2nd Alpine Engineer Regiment
2nd Alpine Engineer Regiment  "Iseo" Sapper Battalion
**
"Iseo" Sapper Battalion
**  Logistic Regiment "Julia" with
Logistic Regiment "Julia" with  Logistic Battalion
* as part of other Military Commands:
**
Logistic Battalion
* as part of other Military Commands:
** 
 "Monte Cervino" Battalion
**
"Monte Cervino" Battalion
**  2nd Alpine Signal Regiment
2nd Alpine Signal Regiment  "Gardena" Battalion and
"Gardena" Battalion and  "Pordoi" Battalion
**
"Pordoi" Battalion
**  Alpine Training Center
Alpine Training Center  "Aosta" Battalion, in
"Aosta" Battalion, in 
 "Bassano" Battalion (high altitude training), in
"Bassano" Battalion (high altitude training), in 



I
Dai fidi tetti del villaggio i bravi alpini son partiti,
mostran la forza ed il coraggio della lor salda gioventù. Son dell'Alpe i bei cadetti, nella robusta giovinezza
dai loro baldi e forti petti spira un'indomita fierezza. Chorus (2x)
''Oh valore alpin! Difendi sempre la frontiera!
E là sul confin tien sempre alta la bandiera.'' ''Sentinella all'erta per il suol nostro italiano
dove amor sorride e più benigno irradia il sol.
'' II
Là tra le selve ed i burroni, là tra le nebbie fredde e il gelo,
piantan con forza i lor picconi le vie rendon più brevi. E quando il sole brucia e scalda le cime e le profondità,
il fiero Alpino scruta e guarda, pronto a dare il "Chi va là?" ''Repeat Chorus 2x''
Italian Army- The Alpini
COMALP- Alpine Troops Command
The largest picture collection of 2012 Bolzano
Brief History and picturesSite dedicated to Alpini, in ItalianThe war in the Dolomites: men, mountains and battles (in italian)Alpine Military School, Aosta
Alpini, Italian Army Military units and formations of Italy Military units and formations of the Boxer Rebellion Mountain troops Military units and formations established in 1872 1872 establishments in Italy
Italian Army
"The safeguard of the republic shall be the supreme law"
, colors =
, colors_labels =
, march = ''Parata d'Eroi'' ("Heroes's parade") by Francesco Pellegrino, ''4 Maggio'' (May 4) ...
's specialist mountain infantry
Mountain warfare (also known as alpine warfare) is warfare in mountains or similarly rough terrain. Mountain ranges are of strategic importance since they often act as a natural border, and may also be the origin of a water source (for example, t ...
. Part of the army's infantry corps, the speciality distinguished itself in combat during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Currently the active Alpini units are organized in two operational brigades, which are subordinated to the Alpine Troops Headquarters. The Alpini's name comes from their inceptive association with the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
, the mountain range that Italy shares with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. An individual soldier of the Alpini is called Alpino.
Established in 1872, the Alpini are the oldest active mountain infantry in the world. Their original mission was to protect Italy's border with France and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. In 1888 the Alpini deployed on their first mission abroad, in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, a continent to which they returned on several occasions and during various wars of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
they fought a three-year campaign on the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
against Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
Kaiserjäger
The ''Kaiserjäger'' (officially designated by the Imperial and Royal (''k.u.k.'') military administration as the ''Tiroler Jäger-Regimenter'' or "Tyrolean Rifle Regiments"), were formed in 1895 as four normal infantry regiments within the Commo ...
and the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
Alpenkorps
The Alpenkorps was a provisional mountain formation of Division (military), division size formed by the German Army (German Empire), Imperial German Army during World War I. It was considered by the Allies to be one of the best in the German Army. ...
in what has since become known as the " War in snow and ice". During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Alpini fought alongside the Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
*Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinate ...
forces primarily in the Balkans Campaigns and on the Eastern Front.
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
the Alpini formed five brigades, which during the 1990s were reduced to two.
History
1872 to 1887


 In 1872, Captain
In 1872, Captain Giuseppe Perrucchetti
Giuseppe Domenico Perrucchetti (13 July 1839 – 5 October 1916) was an Italian general and politician, the creator of the Alpini corps.
He was born in Cassano d'Adda, in what is now the province of Milan in Lombardy. He studied architecture at ...
published a study in the May edition of the Military Review (Italian: ''Rivista Militare''). In the study, he proposed to assign the defence of mountain borders of the recently established Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
to soldiers recruited locally. Indeed, thanks to their knowledge of the surroundings and personal attachment to the area, they would be highly capable and better motivated defenders. Perrucchetti drew heavily on the work of Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Agostino Ricci, who in 1868 had organised exercises in the mountains to assess the feasibility of a specialised mountain infantry corps. Five months after Perrucchetti's article, the first 15 Alpini companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared go ...
were formed by Royal decree no. 1056, with their activation effective on October 15, 1872 - the date marked as the official Corps Day. The activation of the mountain companies thus made the Alpini the oldest active Mountain Infantry in the world.
At first the Alpini were organized as a militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
, capable of defending Italy's northern mountainous borders. Austria's surrender in the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
of 1866 resulted in Italy annexing the province of Venetia, the northern borders of which coincided in large part with the Alpine Arch. Prior to gaining the new northern borders, homeland defence was based on the so-called ''Quadrilatero
The ''Quadrilatero'' (, for greater specificity often called the "Quadrilateral fortresses") is the traditional name of a defensive system of the Austrian Empire in the Lombardy-Venetia region of Italy, which connected the fortresses of Peschie ...
'' strategy
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art ...
. That outdated strategy, however, ignored the geopolitics
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
of the new Italian Kingdom. It called for primary defence of the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
region ("''Pianura Padana''") farther to the southwest, but left the Alpine region undefended (as it was considered a territory mainly unsuitable for military operations).
Recruiting Italy's mountain valleys locals and organising them into a special corps was indeed an innovative idea. They possessed superior knowledge of mountain territory and greatest adaptability to Alpine conditions. At the beginning, the mountain regions were divided into seven military districts, each commanded by an Officer and home to at least two Alpini companies, each consisting of 120 personnel. Soldiers were equipped with the Vetterli 1870 rifle. In 1873 nine more companies were added, thus totalling 24. In 1875, the companies doubled in size, having 250 soldiers and 5 officers, which were then organised into 7 Alpini battalions. Each battalion was named after one of the seats of the seven military districts:
: 1° ''Cuneo'', 2° ''Mondovi'', 3° ''Torino (Susa)'', 4° ''Torino (Chivasso)'', 5° ''Como'', 6° ''Treviso'', 7° ''Udine''
In 1877, five Alpini mountain artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
were formed and - in the following year - the Alpini had already grown to 36 mountain infantry companies organised into 10 battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are ...
s. On November 1, 1882, the Alpini organisation doubled in size to 72 companies and a total of 20 Alpini battalions. The latter plus 8 Alpini mountain artillery batteries were now organized into six numbered Alpini regiments and two Alpini mountain artillery brigades with their respective headquarters and support formations. Each battalion was named after the area it was required to defend in case of war:
The numbers used earlier to distinguish the battalions were dropped while - at the same time - the companies were now numbered from 1 to 72. In order to distinguish the battalions, soldiers and non-commissioned officers were issued thread tufts of various colors (the ''Nappina''), which were added to the ''Cappello Alpino
The Cappello Alpino is the most distinctive feature of the Italian Army's Alpini troops uniform. The ''Alpini'' are light Infantry troops, specializing in mountain combat. Initially the Cappello was only issued to the Alpini, but soon the Cappell ...
'': white for the First Bn., red for the Second Bn., and Green for the Third Bn. of each regiment. Special Bn. and Fourth Bn. were issued blue tufts. Soldiers of the Mountain Artillery units were issued a green tuft with a black patch in the middle onto which the number of the battery was written in yellow numbers.
On June 7, 1883, the green flames (Italian: "''fiamme verdi''") collar patch was introduced, thus making the Alpini officially a specialty within the Italian infantry corps. The ''Cappello Alpino
The Cappello Alpino is the most distinctive feature of the Italian Army's Alpini troops uniform. The ''Alpini'' are light Infantry troops, specializing in mountain combat. Initially the Cappello was only issued to the Alpini, but soon the Cappell ...
'', with its black raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
feather, was also introduced at that time. The distinctive headdress quickly led the Alpini to be nicknamed "The Black feathers" (Italian: "''Le Penne Nere''"). Officers hats had the black feather replaced with a white eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
feather. At first, the hat was a black felt
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or wood ...
hat, but as soon as the new green-grey uniform was adopted in 1909 the hat was changed to the distinctive grey felt still in service today.
The Alpini were also distinguished by the green cuffs on the dark blue tunics worn for full dress
Western dress codes are a set of dress codes detailing what clothes are worn for what occasion. Conversely, since most cultures have intuitively applied some level equivalent to the more formal Western dress code traditions, these dress codes a ...
and barrack dress until 1915, and by green piping on their light blue/grey trousers. When grey-green service uniforms were trialled by the Alpini in 1906, before being adopted by the entire army in 1909, the distinctive green collar patches and typical headdress were retained.
The materials, weapons, and equipment of each battalion were stored in the major village of a specific area they were required to defend in case of war. Soldiers of a battalion were only recruited from that area. In 1887, the names of the battalions were changed from those of the defended areas to those of local villages. Therefore, e.g., the ''Edolo'' Bn. soldiers were recruited in the vicinity of that village Edolo
Edolo ( Camunian: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Brescia, Lombardy, northern Italy, located in the upper Camonica valley. Edolo is neighbour to the comuni of Corteno Golgi, Incudine, Lovero, Malonno, Monno, Ponte di Legno, Saviore ...
- where the battalion's arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
, training ground, and officer's housing were also located. Local recruitment generated strong bonds with and self-identification between the locals and the Alpini units, as men assigned to a single company were all recruited from the same village, and the companies from one valley were all part of the same battalion.
In 1887 the Mountain Troops Inspectorate (Italian: ''Ispettorato delle truppe alpine'') was established in Rome, and took administrative command of all Mountain troops. This led to the reorganization of the Alpini Corps: on August 1, 1887, the 7th Alpini Regiment
The 7th Alpini Regiment ( it, 7° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II.
History Formation
The 7th Alpini Reg ...
was formed in Conegliano Veneto
Conegliano (; Venetian: ''Conejan'') is a town and ''comune'' of the Veneto region, Italy, in the province of Treviso, about north by rail from the town of Treviso. The population of the city is of people. The remains of a 10th-century castle ar ...
and assigned two battalions from the 6th regiment. The number of battalions had grown by two, thus reaching 22. On November 1, 1887, the 1st Mountain Artillery Regiment was formed in Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
with nine batteries, each equipped with four 75 mm howitzers. The resulting new layout of the Alpini Corps was as follows:
::: * (renamed ''"Exilles Exilles (Occitan: ''Eissilhas''; nonstandard Occitan: ''Isiya''; Piedmontese: ''Isiles''; Latin: ''Excingomagus'' or ''Scingomagus''; Italianization under Italian Fascism: ''Esille'') is a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Turin in the Itali ...
"'' in 1889) ** (renamed ''"Vestone
Vestone ( Brescian: ) is a ''comune'' in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy, Italy. It is situated on the river Chiese. Neighboring communes are Barghe, Bione, Casto, Lavenone, Mura, Pertica Alta, Pertica Bassa, Preseglie, Provaglio Val Sabbi ...
"'' in 1889)
1888 to 1914
Although established as a defensive mountain warfare force, the ''1° Battaglione Alpini d’Africa'' (1st African Alpini Battalion) was established in 1887. The battalion's four companies were composed of volunteers taken from all other Alpini battalions. As part of the ''Corpo Speciale d'Africa'' (Special African Corps), the battalion deployed toEritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
to take revenge for the lost battle of Dogali
The Battle of Dogali was fought on 26 January 1887 between Italy and Ethiopia in Dogali near Massawa, in present-day Eritrea.
History
The Italians, after their unification in 1861, wanted to establish a colonial empire to cement their great p ...
. The battalion returned on April 27, 1888, to Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, having lost its commanding officer and 13 men due to tropical diseases.
Back in Italy, eight mules were assigned to each Alpini company in the same year. The Vetterli 70 rifle was replaced by the newer Vetterli-Vitali mod. 70/87 rifle. Also, based on a general reorganization of the Italian militia system, 38 Alpini companies and 15 mountain batteries were assigned to active units of the Regio Esercito
The Royal Italian Army ( it, Regio Esercito, , Royal Army) was the land force of the Kingdom of Italy, established with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. During the 19th century Italy started to unify into one country, and in 1861 Manfre ...
(Royal Italian Army). In 1892 the Alpini were the first troops to be issued with the new Mod. 91 rifle, which was replaced in 1897 by the Mod. 91TS version and remained in service until 1945.
When the tensions between Italy and Abyssinia escalated into the First Italo–Abyssinian War the ''1° Battaglione Alpini d’Africa'' was reformed and sent to Eritrea again. It would soon become the first Alpini unit to engage combat. Four batteries of the 1st Mountain Artillery Regiment were also sent to Eritrea to augment the four deployed brigades under command of Oreste Baratieri
Oreste Baratieri (né Oreste Baratter, 13 November 1841 – 7 August 1901) was an Italian general and governor of Italian Eritrea.
Early career
Born in Condino (County of Tyrol, now Trentino), Baratieri began his career as a volunteer for Giusepp ...
. The battalions' first engagement was on March 1, 1896, during the Battle of Adowa
The Battle of Adwa (; ti, ውግእ ዓድዋ; , also spelled ''Adowa'') was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The Ethiopian forces defeated the Italian invading force on Sunday 1 March 1896, near the town of Adwa. The d ...
. The Alpini were outnumbered and heavily defeated by Abyssinian troops. Over 400 out of 530 men died, including the commanding officer, Lt.Col. Davide Menini. After the battle, the first Gold Medal for Military Valor (Italian: ''Medaglia d'oro al valor militare'') was awarded to a member of the Alpini Corps: Capitan Pietro Cella and his Alpini from the 4th company occupied and held the '' Amba Rajo'' (English: Rajo Mountain) until March 2, thus allowing the rest of defeated Italian Army forces to flee. Capitan Cella and all his men died in the effort. In memory of their ultimate sacrifice, he has been awarded the Gold Medal for Military Valor (). After such a defeat, an Alpini expeditionary regiment with 5 battalions was formed and sent to Eritrea on March 7, 1896, but it saw little combat and was repatriated in June of the same year.
During the 1900 Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
, a Mountain Artillery Battery was sent to China as part of the international relief force that lifted the siege of the International Compound in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, and remained on garrison duty in Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popul ...
until the end of 1901. On November 13, 1902, after a short period of experimentation with ski
A ski is a narrow strip of semi-rigid material worn underfoot to glide over snow. Substantially longer than wide and characteristically employed in pairs, skis are attached to ski boots with ski bindings, with either a free, lockable, or partial ...
s the Alpini began to form specially-equipped and trained Skiing Companies (Italian: ''Compagnie Sciatori''). After a heavy earthquake on September 8, 1905, in the Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
region (Southern Italy), the Alpini deployed to the area for three months to assist in the clearance of debris and reconstruction efforts. They experienced a similar situation in 1908, after the devastating Messina earthquake.
A massive expansion of the Alpini begun in 1909. On July 15 the 2nd Mountain Artillery Regiment was formed in Vicenza
Vicenza ( , ; ) is a city in northeastern Italy. It is in the Veneto region at the northern base of the ''Monte Berico'', where it straddles the Bacchiglione River. Vicenza is approximately west of Venice and east of Milan.
Vicenza is a th ...
with four artillery groups and a total of 12 batteries. In 1908, two new battalions - namely the ''Tolmezzo'' and ''Pallanza
Pallanza is a district of the Italian ''comune'' (municipality) of Verbania. It is located in the Province of Verbano-Cusio-Ossola, on the bank of Lake Maggiore.
History
Pallanza was autonomous until 1939 when it was merged with Intra to form ...
'' (later renamed as '' Intra'' in 1909) - had already been formed and assigned to the 7th and 4th regiments, respectively. On October 1, 1909, the “Tolmezzo” and "Gemona" battalions from the 7th Alpini regiment, along with the newly raised Cividale battalion, became the three battalions of new 8th Alpini Regiment
The 8th Alpini Regiment ( it, 8° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. As of 2022 the regiment is assigned to ...
, based in Udine. The first commander of the 8th Alpini regiment was Col. Antonio Cantore
Antonio Cantore (4 August 1860 – 20 July 1915) was an Italian general.
Biography
Born at Sampierdarena, in Genoa, he fought as commander of the 8th Special Alpini Regiment in the Italo-Turkish War taking place in Libya. At his return to Italy ...
, who would become a living legend to the Alpini during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. As the 8th Alpini regiment was formed, the Alpini could now count on 25 battalions organised into 8 regiments, 2 mountain artillery regiments with 24 batteries organised into 8 groups, and 75 reserve companies organised into 22 battalions. Reserve battalions were named after the valleys from where their soldiers, former Alpini, were recruited (also known as the 'Valle' battalions).
In 1910 the last pre-war Alpini battalion was established as the  ''
''Belluno
Belluno (; lld, Belum; vec, Belùn) is a town and province in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Located about north of Venice, Belluno is the capital of the province of Belluno and the most important city in the Eastern Dolomites region ...
'' Bn. in the very same city.
When Italy declared war on Turkey in 1911 in an attempt to conquer Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, the Alpini units were once again deployed on desert combat. From 1911 to 1914, the Saluzzo, Mondovì, Ivrea, Verona, Tolmezzo, Feltre, Susa, Vestone, Fenestrelle, and Edolo battalions, together with the ''Torino-Susa'', ''Mondovì'', and ''Vicenza'' artillery groups, were deployed to Libya on missions of different duration. The first units to be sent to Libya were the Saluzzo (25 October 1911), Mondovì (3 November 1911), Ivrea (3 November 1911) and Verona (16 December 1911) battalions. When the unexpected Turkish resistance caused an embarrassingly slow advance of the Italian forces, reinforcements were sent to Libya. On October 18, 1912 Turkey and Italy signed the Treaty of Lausanne, which ended the war between the two nations. Italy, however, had now to face a full-scale rebellion by the local population, and required more troops than those deployed in combat to suppress it. Therefore, in October 1912 the Tolmezzo, Feltre, Susa, and Vestone battalions were deployed in Zanzur, Libya, and formed the 8th Special Alpini Regiment (Italian: ''8° Reggimento Alpini Speciale'') under the command of Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Antonio Cantore. The last Alpini unit to leave Libya was the ''Feltre'' battalion. It reached Italy in August 1914, while the Bedouin rebellion in Libya continued unabated.
World War I


 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
the 26 peacetime ''Alpini'' battalions were increased by 62 battalions and saw heavy combat all over the alpine arch. During the war years the ''Alpini'' regiments consisted of the following battalions (the pre-war raised battalions are in bold; their reserve battalions, named after valleys (in Italian: ''Val'' or ''Valle''), and the newly raised battalions, named after mountains (in Italian: ''Monte'') drawn from the same recruiting areas as the original battalions follow below the pre-war battalions):
The Alpini battalions fielded 264 companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared go ...
of one captain, four lieutenants and 250 men each. The Alpini regiments were never sent into battle, but remained at their seats to continue training recruits. The Alpini battalions were grouped together in regiment-sized Groups (''Gruppo''), and the groups were attached to brigade-sized Groupings (''Raggruppamento''), which deployed the Alpini battalions as needed.
The war, today known as the " War in snow and ice", as most of the 600 km frontline ran through mountains and glaciers of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
. 12 meters (40 feet) of snow were a usual occurrence during the winter of 1915/16 and thousands of soldiers were lost in avalanches
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.
Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and earth ...
. The remains of these soldiers are still being uncovered today. The Alpini, as well as their Austrian counterparts: Kaiserschützen
The ''k.k. Landesschützen'' (in English, "imperial-royal country 'or'' provincialrifleman") – from 16 January 1917 ''Kaiserschützen'' ("imperial rifleman") – were three regiments of Austro-Hungarian mountain infantry during the '' kais ...
, Standschützen
The ''Standschützen'' (singular: ''Standschütze''
The German noun ''Standschütze'' is a so-called nominal composition, composed of the nouns ''Stand-'' (en = social position, standing, status) and ''-Schütze'' (en = rifle man). In the Imper ...
and Landeschützen occupied every hill and mountain top around the whole year. Huge underground bases were drilled and dug into the mountainsides and into the ice of glaciers such as the Marmolada
Marmolada (Ladin: ''Marmolèda''; German: ''Marmolata'', ) is a mountain in northeastern Italy and the highest mountain of the Dolomites (a section of the Alps). It lies between the borders of Trentino and Veneto. The Marmolada is an ultra-pr ...
. Guns were dragged by hundreds of troops on mountains up to 3,890 m (12,760 feet) high. Roads, cable cars, mountain railroads and walkways were built up, through and along the steepest of cliffs. Many of these walkways and roads are still visible today, and many are maintained as Via Ferrata
A via ferrata (Italian for "iron path", plural ''vie ferrate'' or in English ''via ferratas'') is a protected climbing route found in the Alps and certain other locations. The term "via ferrata" is used in most countries and languages except n ...
for climbing enthusiasts. In addition, along the former frontline it is still possible to see what is left of hundreds of kilometers of barbed wire.
In this kind of warfare, whoever occupied the higher ground first was almost impossible to dislodge, so both sides turned to drilling tunnels under mountain peaks, filling them up with explosives and then detonated the summits, including its defenders, to pieces: i.e. Col di Lana
The Col di Lana is a mountain of the Fanes Group in the Italian Dolomites. The actual peak is called ''Cima Lana'' and situated in the municipality of Livinallongo del Col di Lana (German: ''Buchenstein'') in the Province of Belluno, Veneto r ...
, Monte Pasubio, Lagazuoi
Lagazuoi is a mountain in the Dolomites of northern Italy, lying at an elevation of , about southwest by road from Cortina d'Ampezzo in the Veneto Region. The mountain is part of the "Natural Park of the Ampezzo Dolomites".
It is accessible by c ...
, etc.
Climbing and skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IO ...
became essential skills for the troops of both sides and soon ski battalions and special climbing units were formed. It was during these years that the Alpini, their spirit and their deeds became famous. Most of the Alpini songs
The Alpini are a mountain infantry corps of the Italian Army, that distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. They are also famous in Italy for their songs and choirs.
The first Alpini units were formed in 1872 by recruiti ...
originated during this time and reflect upon the hardships of the "War in Snow and Ice".
At the war's end the Alpini counted 114,948 casualties: 14,175 KIA
Kia Corporation, commonly known as Kia (, ; formerly known as Kyungsung Precision Industry and Kia Motors Corporation), is a South Korean multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Seoul, South Korea. It is South Korea's second lar ...
, 61,620 WIA, 39,153 MIA
Mia, MIA, or M.I.A. may refer to:
Music Artists
* M.I.A. (rapper) (born 1975), English rapper and singer
* M.I.A. (band), 1980s punk rock band from Orange County, California
* MIA., a German rock/pop band formed in 1997
* Mia (singer) (born 1983) ...
(most lost in avalanches or to mine warfare Mine warfare refers to the use of different types of explosive devices:
*Land mine, a weight-triggered explosive device intended to maim or kill people or to disable or destroy vehicles
*Minelaying, deployment of explosive mines at sea
**Naval mine ...
).
World War II
After World War I all battalions with the exception of the pre-war battalions were dissolved. In 1919 the Alpini gained the9th Alpini Regiment
The 9th Alpini Regiment ( it, 9° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. Based in the city of L'Aquila in Abruzzo t ...
. In 1935 the fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
government of Italy reorganized its Armed Forces, creating five Alpine divisions and forming a new Alpini regiment: the 11th Alpini Regiment. A 12th Alpini Regiment was also formed to oversee the battalions of the 9th Alpini Regiment
The 9th Alpini Regiment ( it, 9° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. Based in the city of L'Aquila in Abruzzo t ...
, which were not sent with the regimental command and the 5 Alpine Division Pusteria
5 (five) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typ ...
to fight in the Italian attack on Abyssinia
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historica ...
. After the return of the 7th Regiment, the 12 Alpini regiment was dissolved. In 1941 the 6th Alpine Division Alpi Graie
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number.
In mathematics
Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second small ...
was raised with reserve units of the other five Alpine divisions.
Thus Italy fielded the following six alpine divisions during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
:
* 1st Alpine Division "Taurinense"
* 2nd Alpine Division "Tridentina"
The 2nd Alpine Division "Tridentina" ( it, 2ª Divisione alpina "Tridentina") was a division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II, which specialized in mountain warfare. The Alpini that formed the divisions are a highly decorated and eli ...
* 3rd Alpine Division "Julia"
The 3rd Alpine Division "Julia" ( it, 3ª Divisione alpina "Julia") was a division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II, which specialized in mountain warfare. The Alpini that formed the divisions are a highly decorated, elite mountain c ...
* 4th Alpine Division "Cuneense"
The 4th Alpine Division "Cuneense" ( it, 4ª Divisione alpina "Cuneense") was a division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II, which specialized in mountain warfare. The headquarters of the division was in the city of Cuneo, and the major ...
* 5th Alpine Division "Pusteria"
* 6th Alpine Division "Alpi Graie"

 Each division consisted of two Alpini regiments with three battalions each, one Alpine Artillery Regiment with three Artillery groups, one Mixed Engineer Battalion, one Logistic Battalion and some support units. The strength of each division was 573 officers and 16,887 NCOs and soldiers for a total strength of 17,460 men. Also each division had almost 5,000 mules and 500 vehicles of various types at its disposal.
Each division consisted of two Alpini regiments with three battalions each, one Alpine Artillery Regiment with three Artillery groups, one Mixed Engineer Battalion, one Logistic Battalion and some support units. The strength of each division was 573 officers and 16,887 NCOs and soldiers for a total strength of 17,460 men. Also each division had almost 5,000 mules and 500 vehicles of various types at its disposal.The divisions saw combat in
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. One Alpini battalion was employed in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
. In 1942, Tridentina, Julia and Cuneense division were sent to fight in the Soviet Union. In Russia, instead of being deployed in the Caucasus mountains as expected, the Alpini were tasked with holding a front on the plains of the Don River
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire.
Its ...
. As a result of this disastrous strategic decision, troops armed, trained, and equipped for mountain warfare were pitted in the plains against tanks and mechanized infantry, to counter which they were neither equipped nor trained. Despite this, the Alpini held the front until January 1943, when, due to the collapse of the Axis front, they were encircled by the advancing Soviet Army. The Alpini were able to break the encirclement in Battle of Nikolayevka
The Battle of Nikolayevka was the breakout of Italian forces in January 1943, as a small part of the larger Battle of Stalingrad. The breakout involved the Alpine Army Corps of the Italian 8th Army near the village of Nikolayevka (now Livenka, ...
and fight their way towards the new line of the front established after the Axis retreat. Only about one third of the Tridentina division (4250 survivors of 15,000 troops deployed) and one tenth of the Julia (1,200/15,000) were able to survive this odyssey. The Cuneense division was annihilated.
 After the
After the Armistice of Cassibile
The Armistice of Cassibile was an armistice signed on 3 September 1943 and made public on 8 September between the Kingdom of Italy and the Allies during World War II.
It was signed by Major General Walter Bedell Smith for the Allies and Brig ...
between the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
and Western Allies
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. ...
became public on 8 September 1943, Italy split in half. The king went to the South of Italy and left the Royal Italian Army
The Royal Italian Army ( it, Regio Esercito, , Royal Army) was the land force of the Kingdom of Italy, established with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. During the 19th century Italy started to unify into one country, and in 1861 Manfre ...
without any orders. Subsequently, most divisions of the Army surrendered without a fight to the invading German forces. The only Alpini division to resist the Germans was the 1st Alpine Division "Taurinense", which along with the 19th Infantry Division "Venezia"
The 19th Infantry Division "Venezia" ( it, 19ª Divisione di fanteria "Venezia") was a infantry division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II. The Venezia was classified as a mountain infantry division, which meant that the division's art ...
and remnants of the 155th Infantry Division "Emilia" resisted German attempts to occupy Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. After suffering heavy casualties the divisions troops were given the choice to either surrender or to retreat into the Durmitor
Durmitor ( Montenegrin: Дурмитор, or ) is a massif located in northwestern Montenegro. It is part of the Dinaric Alps. Its highest peak, Bobotov Kuk, reaches a height of .
The massif is limited by the Tara River Canyon on the north, the ...
mountains and continue the fight. The 16,000 men, who had chosen to fight, formed then the Italian Partisan Division ''Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
'', which entered the II Corps of the Yugoslav Partisans
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослобод ...
and fought on the Yugoslav Front
World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was swiftly conquered by Axis forces and partitioned between Germany, Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria and their client regimes. Shortly after Germany attacked the US ...
until it returned to Italy in March 1945.
On June 25, 1944, the 3rd Alpini Regiment
The 3rd Alpini Regiment ( it, 3° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. The regiment is based in Pinerolo and assi ...
was recreated in Southern Italy with the battalions ''Piemonte'' and ''Monte Granero''. Along with the 4th Bersaglieri Regiment it formed the 1st Italian Brigade of the Italian Liberation Corps
The Italian Liberation Corps ( it, Corpo Italiano di Liberazione (CIL)) was an corps of the Italian Co-belligerent Army during the Italian campaign of World War II. After the announcement of the Armistice of Cassibile on 8 September 1943 the Ita ...
, which fought in the war on the Allied side. After the Bersaglieri regiment had suffered heavy casualties the two regiments were merged on 30 September 1944 to form the Special Infantry Regiment, which entered the ''Legnano'' Combat Group. The Combat Group was equipped with British weapons and materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specifi ...
and fought as part of the Polish II Corps
The Polish II Corps ( pl, Drugi Korpus Wojska Polskiego), 1943–1947, was a major tactical and operational unit of the Polish Armed Forces in the West during World War II. It was commanded by Lieutenant General Władysław Anders and fought wit ...
on the extreme left of the British 8th Army
The Eighth Army was an Allied field army formation of the British Army during the Second World War, fighting in the North African and Italian campaigns. Units came from Australia, British India, Canada, Czechoslovakia, Free French Forces ...
near the river Idice
The Idice is a river in the Tuscany and Emilia-Romagna regions of Italy. The source of the river is in the province of Florence near Monghidoro in the Appennino Tosco-Emiliano mountains. The river flows north into the province of Bologna near Mon ...
.
In the north a fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
regime under dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
, known as the Republic of Salò
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
continued the war alongside the Germans. Its Army, the fascist National Republican Army
The National Republican Army (Esercito Nazionale Repubblicano, or ENR) was the army of the Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, or RSI) from 1943 to 1945 that fought on the side of Nazi Germany during World War II.
The ENR ...
, raised the 4th Alpine Division "Monterosa"
The 4th Alpine Division "Monterosa" ( it, 4ª Divisione alpina "Monterosa") was one of four divisions raised by Mussolini's Italian Social Republic. It existed from 1st January 1944 until 28 April 1945.
''Monterosa'' is Italian taken from the nam ...
, which was trained and equipped by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. The division fought along the Gothic Line
The Gothic Line (german: Gotenstellung; it, Linea Gotica) was a German Defense line, defensive line of the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Generalfeldmarschall, Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's la ...
, notably against units of Brazilian Expeditionary Division, U.S. 92nd Infantry Division and 8th Indian Infantry Division
The 8th Mountain Division was raised as the 8th Indian Infantry division of the British Indian Army. It is now part of the Indian Army and specialises in mountain warfare.
The 8th Indian Infantry Division was formed as an infantry division in ...
. At the end of the final allied offensive, the division surrendered after the Battle of Collecchio
The Battle of Collecchio-Fornovo (26–29 April 1945) was a battle of the Second World War between the Brazilian Expeditionary Force (''Força Expedicionária Brasileira'' – FEB), along with Italian partisans and units from the American 1st Ar ...
.
Cold War

 After World War II the Alpini units were once more tasked with defending Italy's northern borders. On 15 October 1949 the Alpine Brigade ''Julia'' was activated in
After World War II the Alpini units were once more tasked with defending Italy's northern borders. On 15 October 1949 the Alpine Brigade ''Julia'' was activated in Udine
Udine ( , ; fur, Udin; la, Utinum) is a city and ''comune'' in north-eastern Italy, in the middle of the Friuli Venezia Giulia region, between the Adriatic Sea and the Alps (''Alpi Carniche''). Its population was 100,514 in 2012, 176,000 with t ...
; on 1 May 1951 the Alpine Brigade ''Tridentina'' was activated in Brixen
Brixen (, ; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ) is a town in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about north of Bolzano.
Geography
First mentioned in 901, Brixen is the third largest city and oldest town in the province, and the artistic and ...
; on 15 April 1952 the Alpine Brigade ''Taurinense'' was activated in Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
; on 1 January 1953 the Alpine Brigade ''Orobica'' was activated in Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
and on 1 July 1953 the Alpine Brigade ''Cadore'' was activated in Belluno
Belluno (; lld, Belum; vec, Belùn) is a town and province in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Located about north of Venice, Belluno is the capital of the province of Belluno and the most important city in the Eastern Dolomites region ...
. Each brigade recruited its soldiers from specific parts of the mountainous areas of Italy thus creating a strong bond with the local populations. But only in 1972 when the ''Taurinense'' joined the IV Army Corps a singular command was finally in place for all the Alpini, Alpine and Mountain units of the Italian Army.
* IV Alpine Army Corps
** 
Julia
Julia is usually a feminine given name. It is a Latinate feminine form of the name Julio and Julius. (For further details on etymology, see the Wiktionary entry "Julius".) The given name ''Julia'' had been in use throughout Late Antiquity (e.g. ...
**  Taurinense
**
Taurinense
**  Tridentina
**
Tridentina
** 
Cadore
Cadore (; lld, Ciadòre; vec, italic=yes, Cadór or, rarely, ''Cadòria''; german: italic=yes, Cadober or ''Kadober''; Sappada German: ''Kadour'';
** 
Orobica
The Orobica or Valgerola is a breed of domestic goat from the Val Gerola in the province of Sondrio, in the Bergamo Alps of northern Italy. It is raised in the Val Gerola and the Valchiavenna in the province of Sondrio, in the Alto Lario ...
After the 1976 reform the IV Alpine Army Corps was responsible to defend the Italian border along the main chain of the alps
The main chain of the Alps, also called the Alpine divide is the central line of mountains that forms the drainage divide of the range. Main chains of mountain ranges are traditionally designated in this way, and generally include the highest p ...
from the Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
-Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
n-Italian border tripoint
A tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints as of 2020. Nearly half are situated in rivers, l ...
in the west to the Italian-Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
n border in the east. In case of war with Yugoslavia the IV Alpine Army Corps would remain static in its position guarding the left flank of the Italian V Corps, which would meet the enemy forces in the plains of Friuli-Venezia Giulia
(man), it, Friulana (woman), it, Giuliano (man), it, Giuliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_t ...
. The only brigade which would have seen combat in such a case would have been the ''Julia''.
In case of a war with the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
the IV Alpine Army Corps had two war plans: one in the case the Soviet Southern Group of Forces
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and Hungarian Army
The Hungarian Ground Forces ( hu, Magyar Szárazföldi Haderő) is the land branch of the Hungarian Defence Forces, and is responsible for ground activities and troops including artillery, tanks, APCs, IFVs and ground support. Hungary's ground f ...
would march through Yugoslavia and the other in case the Warsaw Pact would violate the Austrian neutrality
The Declaration of Neutrality (german: Neutralitätserklärung) was a declaration by the Austrian Parliament declaring the country permanently neutral. It was enacted on 26 October 1955 as a constitutional act of parliament, i.e., as part of th ...
and march through Austria. In case the enemy forces would come through Yugoslavia, the Julia would cover the mountainous left flank of the 5th Corps, which with its four armoured and five mechanized brigades would try to wear down the enemy before it could break out into the North Italian Padan plain
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
. The other Alpini brigades would remain static.
In the more likely case the Soviet and Hungarian divisions would invade Austria and march through Southern Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
and through the valley in Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost States of Austria, Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German language, German. Its regional dialects belong to t ...
the Alpini brigades would have been the first front line units of the Italian Army: the ''Julia
Julia is usually a feminine given name. It is a Latinate feminine form of the name Julio and Julius. (For further details on etymology, see the Wiktionary entry "Julius".) The given name ''Julia'' had been in use throughout Late Antiquity (e.g. ...
'' would have defended the Canal valley, the ''Cadore
Cadore (; lld, Ciadòre; vec, italic=yes, Cadór or, rarely, ''Cadòria''; german: italic=yes, Cadober or ''Kadober''; Sappada German: ''Kadour'';
'' would have defended the Piave valley and the '' Tridentina'' the Puster valley
The Puster Valley ( it, Val Pusteria ; german: Pustertal, ) is one of the largest longitudinal valleys in the Alps that runs in an east-west direction between Lienz in East Tyrol, Austria, and Mühlbach near Brixen in South Tyrol, Italy. The Sou ...
, while the ''Orobica
The Orobica or Valgerola is a breed of domestic goat from the Val Gerola in the province of Sondrio, in the Bergamo Alps of northern Italy. It is raised in the Val Gerola and the Valchiavenna in the province of Sondrio, in the Alto Lario ...
'' had a special mission and the '' Taurinense'' would remain in reserve.
Today
Structure

 After the end of the
After the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, all but the Julia and Taurinense Brigades were dissolved, thus leaving the following Alpini units, that still carry the "fiamme verdi" collar insignia:
*  Tridentina Division:
**
Tridentina Division:
**  Command and Tactical Supports Unit "Tridentina"
Command and Tactical Supports Unit "Tridentina"  *
* 
Alpine Brigade "Taurinense"
The Alpine Brigade "Taurinense" is a light Infantry brigade of the Italian Army, specializing in Mountain Combat. Its core units are Alpini, the mountain infantry corps of the Italian Army, that distinguished itself in combat during World War I ...
**  1st Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit
1st Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit  **
** 
2nd Alpini Regiment
The 2nd Alpini Regiment ( it, 2° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. The regiment was disbanded in 1943 due t ...
 "Saluzzo" Battalion
**
"Saluzzo" Battalion
** 
3rd Alpini Regiment
The 3rd Alpini Regiment ( it, 3° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. The regiment is based in Pinerolo and assi ...
 "Susa" Battalion
**
"Susa" Battalion
** 
9th Alpini Regiment
The 9th Alpini Regiment ( it, 9° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. Based in the city of L'Aquila in Abruzzo t ...
 "L'Aquila" Battalion and
"L'Aquila" Battalion and  "Vicenza" Battalion
**
"Vicenza" Battalion
**  "Aosta" Mountain Artillery Group
**
"Aosta" Mountain Artillery Group
**  32nd Engineer Regiment
32nd Engineer Regiment  30th Sapper Battalion
**
30th Sapper Battalion
**  Logistic Regiment "Taurinense"
Logistic Regiment "Taurinense"  Logistic Battalion
*
Logistic Battalion
* 
Alpine Brigade Julia
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
**  14th Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit
14th Alpini Command and Tactical Supports Unit  **
** 
5th Alpini Regiment
The 5th Alpini Regiment ( it, 5° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. The regiment is based in Sterzing and assi ...
 "Morbegno" Battalion
**
"Morbegno" Battalion
** 
7th Alpini Regiment
The 7th Alpini Regiment ( it, 7° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II.
History Formation
The 7th Alpini Reg ...
 "Feltre" Battalion
**
"Feltre" Battalion
** 
8th Alpini Regiment
The 8th Alpini Regiment ( it, 8° Reggimento Alpini) is a regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. As of 2022 the regiment is assigned to ...
 "Tolmezzo" Battalion
**
"Tolmezzo" Battalion
**  3rd Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)
3rd Field Artillery Regiment (Mountain)  "Conegliano" Mountain Artillery Group
**
"Conegliano" Mountain Artillery Group
**  2nd Alpine Engineer Regiment
2nd Alpine Engineer Regiment  "Iseo" Sapper Battalion
**
"Iseo" Sapper Battalion
**  Logistic Regiment "Julia" with
Logistic Regiment "Julia" with  Logistic Battalion
* as part of other Military Commands:
**
Logistic Battalion
* as part of other Military Commands:
** 
4th Alpini Paratroopers Regiment
The 4th Alpini Paratroopers Regiment ( it, 4° Reggimento Alpini Paracadutisti) is a Ranger-type special forces regiment of the Italian Army, specializing in mountain combat. The regiment is one of three regiments of the Army Special Forces Comm ...
 "Monte Cervino" Battalion
**
"Monte Cervino" Battalion
**  2nd Alpine Signal Regiment
2nd Alpine Signal Regiment  "Gardena" Battalion and
"Gardena" Battalion and  "Pordoi" Battalion
**
"Pordoi" Battalion
**  Alpine Training Center
Alpine Training Center  "Aosta" Battalion, in
"Aosta" Battalion, in Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest of ...
*** 
6th Alpini Regiment
The 6th Alpini Regiment ( it, 6° Reggimento Alpini) is a training regiment of the Italian Army's mountain infantry speciality, the Alpini, which distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II. The regiment is based in Bruneck ...
 "Bassano" Battalion (high altitude training), in
"Bassano" Battalion (high altitude training), in Bruneck
Bruneck (; it, Brunico or Ladin: ''Bornech'' or ''Burnech''; la, Branecium or ''Brunopolis'' is the largest town in the Puster Valley in the Italian province of South Tyrol.
Geography
Bruneck rises up in the middle of a wide valley (perhaps a ...
(South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol
, settlement_type = Autonomous province
, image_skyline =
, image_alt ...
)

Geographical distribution



Armament
Currently an Alpino is equipped with aBeretta ARX 160
The Beretta ARX160 is an Italian modular assault rifle manufactured by Beretta. Developed for the Italian Armed Forces as part of the ''Soldato Futuro'' (English: "Future Soldier") program, the ARX160 was launched in 2008 as a commercial weapon ...
assault rifle, usually fitted with an Aimpoint
Aimpoint AB is a Swedish optics company based in Malmö, Sweden that manufactures red dot sights.
Aimpoint is a contractor for the United States military and supplies the Aimpoint CompM2. Aimpoint products are used by various armed forces, a ...
M3 Reddot, a Beretta 92 FS
Fabbrica d'Armi Pietro Beretta (; "Pietro Beretta Weapon Factory") is a Privately held company, privately held Italian firearms manufacturing company operating in several countries. Its firearms are used worldwide for a variety of civilian, law ...
pistol, OD/82SE hand grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
s, a Type III AP/98 (they are now slowly being provided with the newest NC4/09 bulletproof vest, phasing out the AP/98) bullet-proof vest
A bulletproof vest, also known as a ballistic vest or a bullet-resistant vest, is an item of body armor that helps absorb the impact and reduce or stop penetration to the torso from firearm-fired projectiles and fragmentation from explosions. ...
and a 3rd generation night vision device.
The squad automatic weapon is the FN Minimi or, alternatively, the Rheinmetall MG3.
Supporting fire can be provided also by M2 Browning (0.50") machine gun, the Hirtenberger M6C-210 Commando 60 mm, man-portable light mortar or by the Mortier 120mm Rayé Tracté Modèle F1, MO-120-RT-61 120 mm heavy mortar.
Mobility is provided by the use of Iveco LMV, Iveco VTLM Lince 4WD tactical vehicles, Puma (AFV), Puma 6x6 Armored Personal Carriers and Bandvagn 206, Bv 206 / Bv 206S all terrain tracked vehicles.
The anti-tank weapons are the Panzerfaust 3 rocket propelled grenade and the MILAN, MILAN 2 and BGM-71 TOW, TOW II anti-tank guided missiles. The later two will be replaced by the Spike (missile), Spike anti-tank guided missile over the next years.
In 1999 the artillery regiments have been issued with the FH-70 howitzer. This has led to a great increase in firepower compared to the previously used OTO Melara Mod 56 pack howitzer, but also reduced their versatility. Indeed, they are not designated now as "mountain artillery", but as "Field Artillery (Mountain)" regiments.
Currently the Alpini are being provided with a small number of ARX-160 rifles to field-test the designated standard rifle of the Italian Army in harsh and cold environments.
Ranks of the Alpini
The Alpini share the ranks of the Italian Army but have an additional rank insignia on theirCappello Alpino
The Cappello Alpino is the most distinctive feature of the Italian Army's Alpini troops uniform. The ''Alpini'' are light Infantry troops, specializing in mountain combat. Initially the Cappello was only issued to the Alpini, but soon the Cappell ...
uniform. All enlisted personnel and junior non-commissioned officers wear no insignia, only officers and senior NCOs wear them and special rank insignia are used by them in the form of chevrons increasing by rank until the rank of Colonel and by silver collar ribbons by general officers.
'' Enlisted and Junior NCOs – No Insignia''
* ''Alpino''
* ''Caporale'' – Private E1 (Corporal)
* ''Caporal Maggiore'' – Private First Class (Corporal Major)
* ''Primo caporal maggiore'' – Lance Corporal (Corporal Maj. 1st Class)
* ''Caporale maggiore scelto'' – Corporal (Senior Corporal Major)
* ''Caporal Maggiore capo '' – Master Corporal (Chief Corporal Major)
* ''Caporal Maggiore capo scelto'' – Lance Sergeant (Senior Chief Corporal Major)
* ''Sergente'' – Sergeant
* ''Sergente maggiore'' – Staff Sergeant (Sergeant major)
* ''Sergente maggiore capo'' – Sergeant First Class
* ''Sergente maggiore capo scelto'' - Sergeant First Class
''Senior NCOs''
* ''Maresciallo'' – Master Sergeant (Marshal): ''1 small plain green chevron''
* ''Maresciallo ordinario'' – First Sergeant (Ordinary marshal): ''1 small plain green chevron''
* ''Maresciallo capo'' – Sergeant Major (Chief Marshal): ''1 small plain green chevron''
* ''Primo Maresciallo'' – Command Sergeant Major (First Marshal): ''1 green chevron with red border''
* ''Luogotenente'' – 1st Command Sergeant Major/Warrant officer (Sublieutenant) : ''1 small green chevron with red border and a gold star''
* ''Primo luogotenente'' – Chief warrant officer(Sublieutenant 1st class): ''1 small green chevron with red border and a gold star''
''Junior and Field Officers''
* ''Sottotenente'' – Sublieutenant/Second lieutenant : ''Plain gold small chevron''
* ''Tenente'' – Lieutenant : ''Two gold small chevrons with blue border''
* ''Capitano'' – Captain (OF-2), Captain : ''Three gold chevrons with two blue borders''
* ''Maggiore'' – Major: ''Three gold chevrons with one blue border''
* ''Tenente Colonello'' – Lieutenant colonel : ''Four gold chevrons with two blue borders''
* ''Colonello'' – Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
: ''Six gold chevrons with three blue borders''
''General Officers''
* ''Generale di Brigata'' – Brigadier General (Brigade General) : ''One bright gold star on the silver collar marking''
* ''Generale di Divisione'' – Major general, Major General (Divisional General): ''Two gold stars on the silver collar marking''
* ''Generale di Corpo d'Armata'' – Lieutenant general, Lieutenant General (Corps General): ''Three gold stars on the silver collar marking''
National Alpini Association
The ANA (Associazione Nazionale Alpini or National Alpini Association) is a registered society representing the "Veci" ( ie "the old ones" in English; singular: "vecio" ) or former members of the Alpini corps. As the "Veci" see themselves as merely "on leave" rather than veterans, the ANA is colloquially known to be the 10th Alpini Regiment. Since 1920 every year ANA organizes a national reunion the "Veci". Hundreds of thousands of Alpini congregate with family and friends to an Italian city for a weekend in the late spring to celebrate and have a good time while remembering old times.Hymn of the Alpini Corps
The Alpini Hymn ''L'Inno degli Alpini'' or ''Trentatrè - valore Alpino'' is the official hymn of the Alpini Corps, adapted from an old French mountain song by D'Estel and Travel. As the official anthem of the corps it forms part of the various songs and marches played by the Corps' military bands on parades and concerts, in the latter, the second to the last song to be played before the Italian National Anthem.I
Dai fidi tetti del villaggio i bravi alpini son partiti,
mostran la forza ed il coraggio della lor salda gioventù. Son dell'Alpe i bei cadetti, nella robusta giovinezza
dai loro baldi e forti petti spira un'indomita fierezza. Chorus (2x)
''Oh valore alpin! Difendi sempre la frontiera!
E là sul confin tien sempre alta la bandiera.'' ''Sentinella all'erta per il suol nostro italiano
dove amor sorride e più benigno irradia il sol.
'' II
Là tra le selve ed i burroni, là tra le nebbie fredde e il gelo,
piantan con forza i lor picconi le vie rendon più brevi. E quando il sole brucia e scalda le cime e le profondità,
il fiero Alpino scruta e guarda, pronto a dare il "Chi va là?" ''Repeat Chorus 2x''
Alpini in Media
* The 1943 film ''Men of the Mountain'', an Italian propaganda production starring Amedeo Nazzari and Mariella Lotti * ''Centomila gavette di ghiaccio'' ('One hundred thousand mess tins of ice'), a best seller book by Giulio Bedeschi, former medical officer in the ''Gruppo Conegliano'' of 3rd Mountain Artillery Regiment (Italy), 3rd Mountain Artillery Regiment (3 Alpine Division Julia, Julia Division) in Italian Army in Russia, World War II. The book is about the epic ''Ritirata di Russia'' ('Retreat from Russia') that involved Alpini and other Axis units during the 1942/1943 winter. * ''Mino (miniseries), Mino'', an Italian TV series about the ''Aosta'' battalion inWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
* ''Il sergente nella neve'' ('The sergeant in the snow'), a book by Mario Rigoni Stern about the ''Vestone'' battalion (2 Alpine Division Tridentina, Tridentina Division) in Italian Army in Russia, World War II.
* ''Mai tardi'' ('Never late'), a book by Nuto Revelli about the ''Tirano'' battalion (2 Alpine Division Tridentina, Tridentina Division) in Italian Army in Russia, World War II.
* The mission called "Avanti Savoia!", in the video game Battlefield 1, has the Alpini as protagonists
See also
* List of mountain warfare forces * Argentina: Cazadores de Montaña (Argentine Army) * France: Chasseurs Alpins * Germany: Gebirgsjäger * Poland: Podhale rifles * Romania: Vânători de munteReferences
Sources
Italian Army- The Alpini
COMALP- Alpine Troops Command
The largest picture collection of 2012 Bolzano
External links
{{Commons category, AlpiniBrief History and pictures
Alpini, Italian Army Military units and formations of Italy Military units and formations of the Boxer Rebellion Mountain troops Military units and formations established in 1872 1872 establishments in Italy