Algerine Channel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the
History of Algeria
. from the Arabic name ''al-Jazāʾir'' (), "The Islands". This name refers to the four former islands which lay off the city's coast before becoming part of the mainland in 1525. ''Al-Jazāʾir'' is itself a truncated form of the city's older name ''Jazaʾir Banī Mazghanna'' (), "The Islands of the Banu Mazghanna, Sons of Mazghana", used by early medieval geographers such as al-Idrisi and
 Algiers from this time became the chief seat of the
Algiers from this time became the chief seat of the 
 Formally part of the Ottoman Empire but essentially free from Ottoman control, starting in the 16th century Algiers turned to piracy and ransoming. Due to its location on the periphery of both the Ottoman and European economic spheres, and depending for its existence on a Mediterranean that was increasingly controlled by European shipping, backed by European navies, piracy became the primary economic activity. Repeated attempts were made by various nations to subdue the pirates that disturbed shipping in the western Mediterranean and engaged in slave raids as far north as Iceland. By the 17th century, up to 40% of the city's 100,000 inhabitants were enslaved Europeans. The United States fought two wars (the First and Second Barbary Wars) over Algiers' attacks on shipping.
Among the notable people held for ransom was the future Spanish novelist, Miguel de Cervantes, who was held captive in Algiers for almost five years, and wrote two plays set in Algiers of the period. The primary source for knowledge of Algiers of this period, since there are no contemporary local sources, is the ''Topografía e historia general de Argel'' (1612, but written earlier), published by Diego de Haedo, but whose authorship is disputed. This work describes in detail the city, the behavior of its inhabitants, and its military defenses, with the unsuccessful hope of facilitating an attack by Spain so as to end the piracy.
A significant number of renegades lived in Algiers at the time, Christians converted voluntarily to
Formally part of the Ottoman Empire but essentially free from Ottoman control, starting in the 16th century Algiers turned to piracy and ransoming. Due to its location on the periphery of both the Ottoman and European economic spheres, and depending for its existence on a Mediterranean that was increasingly controlled by European shipping, backed by European navies, piracy became the primary economic activity. Repeated attempts were made by various nations to subdue the pirates that disturbed shipping in the western Mediterranean and engaged in slave raids as far north as Iceland. By the 17th century, up to 40% of the city's 100,000 inhabitants were enslaved Europeans. The United States fought two wars (the First and Second Barbary Wars) over Algiers' attacks on shipping.
Among the notable people held for ransom was the future Spanish novelist, Miguel de Cervantes, who was held captive in Algiers for almost five years, and wrote two plays set in Algiers of the period. The primary source for knowledge of Algiers of this period, since there are no contemporary local sources, is the ''Topografía e historia general de Argel'' (1612, but written earlier), published by Diego de Haedo, but whose authorship is disputed. This work describes in detail the city, the behavior of its inhabitants, and its military defenses, with the unsuccessful hope of facilitating an attack by Spain so as to end the piracy.
A significant number of renegades lived in Algiers at the time, Christians converted voluntarily to
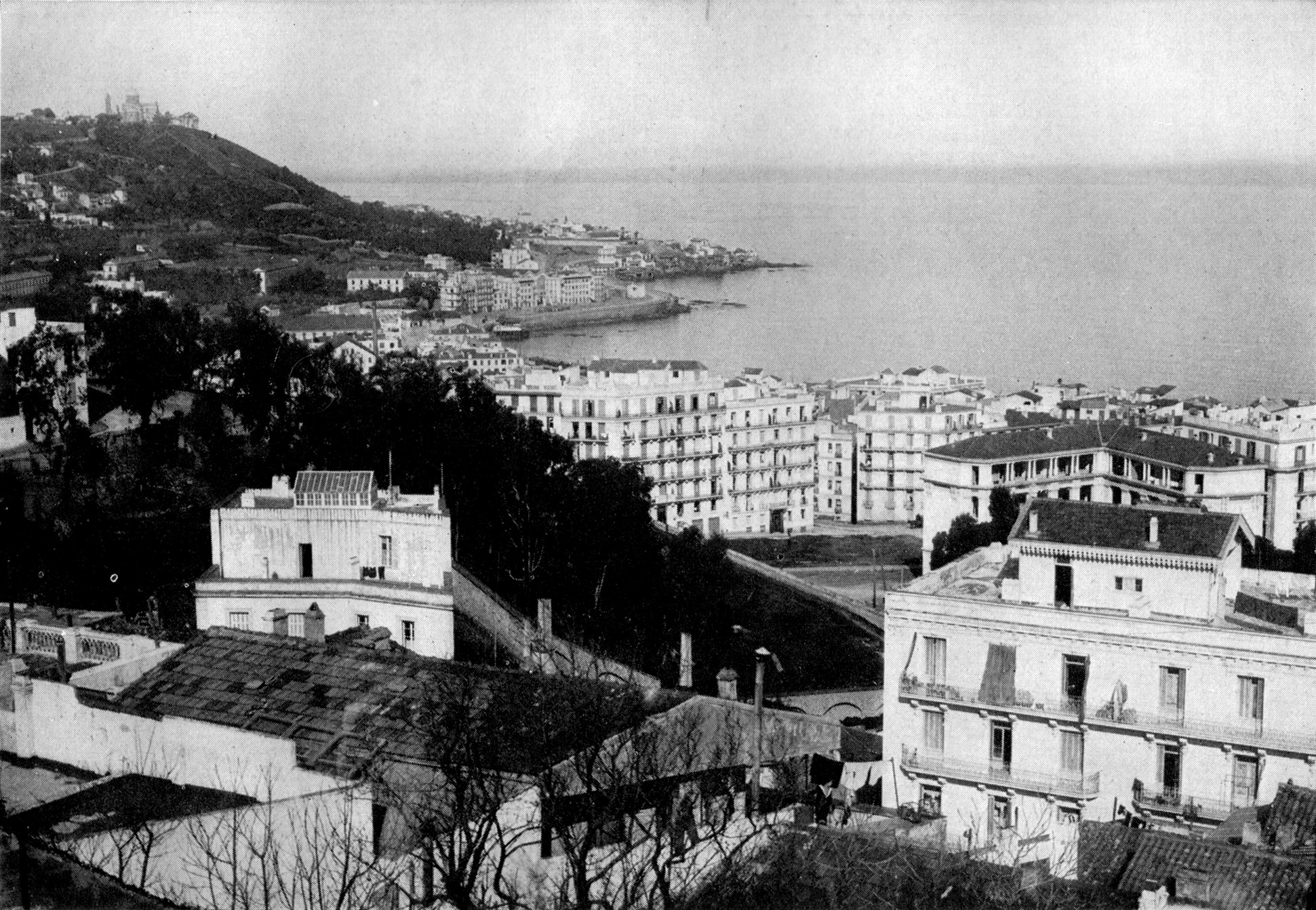 In 1962, after a bloody independence struggle in which hundreds of thousands (estimates range between 350,000 and 1,500,000) died (mostly Algerians but also French and
In 1962, after a bloody independence struggle in which hundreds of thousands (estimates range between 350,000 and 1,500,000) died (mostly Algerians but also French and
 * The Casbah (of ''Al Qasbah'', "the Citadel"), Ier District of Algiers: called ''Al-Djazaïr Al Mahroussa'' ("Well Kept Algiers"), is founded on the ruins of old Icosium. It is a small city which, built on a hill, goes down towards the sea, divided in two: the High city and the Low city. One finds there masonries and mosques of the 17th century; Ketchaoua mosque (built in 1794 by the Dey Baba Hassan) flanked by two minarets, mosque el Djedid (built in 1660, at the time of Turkish regency) with its large finished ovoid cupola points some and its four coupolettes, mosque El Kébir (oldest of the mosques, it was built by Almoravid Youssef Ibn Tachfin and rebuilt later in 1794), mosque Ali Betchnin (Raïs, 1623), Dar Aziza, palate of Jénina. In the Kasbah, there are also labyrinths of lanes and houses that are very picturesque, and if one gets lost there, it is enough to go down again towards the sea to reposition oneself.
* Bab El Oued: Literally ''the River's Gate'', the popular district which extends from the Casbah beyond "the gate of the river". It is the capital's darling and best liked borough. Famous for its square with "the three clocks" and for its "market Triplet", it is also a district of workshops and manufacturing plants.
*
* The Casbah (of ''Al Qasbah'', "the Citadel"), Ier District of Algiers: called ''Al-Djazaïr Al Mahroussa'' ("Well Kept Algiers"), is founded on the ruins of old Icosium. It is a small city which, built on a hill, goes down towards the sea, divided in two: the High city and the Low city. One finds there masonries and mosques of the 17th century; Ketchaoua mosque (built in 1794 by the Dey Baba Hassan) flanked by two minarets, mosque el Djedid (built in 1660, at the time of Turkish regency) with its large finished ovoid cupola points some and its four coupolettes, mosque El Kébir (oldest of the mosques, it was built by Almoravid Youssef Ibn Tachfin and rebuilt later in 1794), mosque Ali Betchnin (Raïs, 1623), Dar Aziza, palate of Jénina. In the Kasbah, there are also labyrinths of lanes and houses that are very picturesque, and if one gets lost there, it is enough to go down again towards the sea to reposition oneself.
* Bab El Oued: Literally ''the River's Gate'', the popular district which extends from the Casbah beyond "the gate of the river". It is the capital's darling and best liked borough. Famous for its square with "the three clocks" and for its "market Triplet", it is also a district of workshops and manufacturing plants.
* 

 There are many public buildings of interest, including the whole Kasbah quarter, Martyrs Square (''Sahat ech-Chouhada'' ساحة الشهداء), the government offices (formerly the British consulate), the " Grand", " New", and Ketchaoua Mosques, the Roman Catholic cathedral of Notre Dame d'Afrique, the Bardo Museum, the old ''Bibliothèque Nationale d'Alger''—a moorish palace built in 1799–1800 and the new National Library, built in a style reminiscent of the British Library.
The main building in the Kasbah was begun in 1516 on the site of an older building, and served as the palace of the deys until the French conquest. A road has been cut through the centre of the building, the mosque turned into
There are many public buildings of interest, including the whole Kasbah quarter, Martyrs Square (''Sahat ech-Chouhada'' ساحة الشهداء), the government offices (formerly the British consulate), the " Grand", " New", and Ketchaoua Mosques, the Roman Catholic cathedral of Notre Dame d'Afrique, the Bardo Museum, the old ''Bibliothèque Nationale d'Alger''—a moorish palace built in 1799–1800 and the new National Library, built in a style reminiscent of the British Library.
The main building in the Kasbah was begun in 1516 on the site of an older building, and served as the palace of the deys until the French conquest. A road has been cut through the centre of the building, the mosque turned into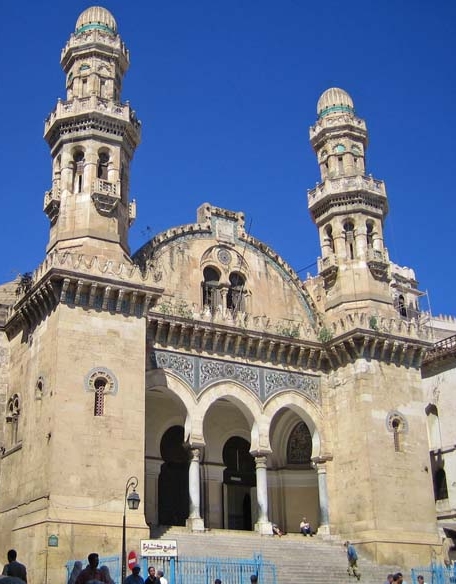  The Ketchaoua Mosque (''Djamaa Ketchaoua'' جامع كتشاوة), at the foot of the Casbah, was before independence in 1962 the cathedral of St Philippe, itself made in 1845 from a mosque dating from 1612. The principal entrance, reached by a flight of 23 steps, is ornamented with a
The Ketchaoua Mosque (''Djamaa Ketchaoua'' جامع كتشاوة), at the foot of the Casbah, was before independence in 1962 the cathedral of St Philippe, itself made in 1845 from a mosque dating from 1612. The principal entrance, reached by a flight of 23 steps, is ornamented with a

 * Notre Dame d'Afrique, accessible by one
* Notre Dame d'Afrique, accessible by one  * The El Jedid mosque at the Place des Martyrs near the port.
* Place of the Emir Abdelkader (formerly
* The El Jedid mosque at the Place des Martyrs near the port.
* Place of the Emir Abdelkader (formerly
 Algiers is an important economic, commercial and financial center, with in particular a stock exchange with a capitalisation of 60 million euros. The city has the highest cost of living of any city in North Africa, as well as the 50th highest worldwide, as of March 2007, having gained one position compared to the previous year.
Mohamed Ben Ali El Abbar, president of the Council of Administration of the Emirate Group EMAAR, presented five "megaprojects" to Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, during a ceremony which took place Saturday, July 15, in the
Algiers is an important economic, commercial and financial center, with in particular a stock exchange with a capitalisation of 60 million euros. The city has the highest cost of living of any city in North Africa, as well as the 50th highest worldwide, as of March 2007, having gained one position compared to the previous year.
Mohamed Ben Ali El Abbar, president of the Council of Administration of the Emirate Group EMAAR, presented five "megaprojects" to Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, during a ceremony which took place Saturday, July 15, in the  The third project will relate to restructuring an area of Algiers, qualified by the originators of the project of "city of wellness". El Abbar indicated to the journalists that the complex would be "agreeable for all those which will want to combine tourism and well-being or tourism and relaxation". The complex will include a university, a research center and a medical centre. It should also include a hospital complex, a care centre, a hotel zone, an urban centre and a thermal spa with villas and apartments. The university will include a medical school and a school for care male nurses which will be able to accommodate 500 students. The university campus will have the possibility of seeing setting up broad ranges of buildings of research laboratories and residences.
Another project relates to technological implantation of a campus in Sidi Abdellah, south-east from Algiers. This site will include shopping centres, residential zones with high standard apartments and a golf course surrounded by villas and hotels. Two other residential zones, including 1.800 apartments and 40 high standard villas, will be built on the surrounding hills.
The fifth project is that of the tourist complex Colonel Abbès, which will be located west from Algiers. This complex will include several retail zones, meeting places, and residential zones composed of apartments and villas with views of the sea.
There is another project under construction, by the name of Algiers Medina. The first step of the project is nearly complete.
A
The third project will relate to restructuring an area of Algiers, qualified by the originators of the project of "city of wellness". El Abbar indicated to the journalists that the complex would be "agreeable for all those which will want to combine tourism and well-being or tourism and relaxation". The complex will include a university, a research center and a medical centre. It should also include a hospital complex, a care centre, a hotel zone, an urban centre and a thermal spa with villas and apartments. The university will include a medical school and a school for care male nurses which will be able to accommodate 500 students. The university campus will have the possibility of seeing setting up broad ranges of buildings of research laboratories and residences.
Another project relates to technological implantation of a campus in Sidi Abdellah, south-east from Algiers. This site will include shopping centres, residential zones with high standard apartments and a golf course surrounded by villas and hotels. Two other residential zones, including 1.800 apartments and 40 high standard villas, will be built on the surrounding hills.
The fifth project is that of the tourist complex Colonel Abbès, which will be located west from Algiers. This complex will include several retail zones, meeting places, and residential zones composed of apartments and villas with views of the sea.
There is another project under construction, by the name of Algiers Medina. The first step of the project is nearly complete.
A
 Some to the west of Algiers are such seaside resorts as Sidi Fredj (ex-Sidi Ferruch), Palm Beach,
Some to the west of Algiers are such seaside resorts as Sidi Fredj (ex-Sidi Ferruch), Palm Beach,
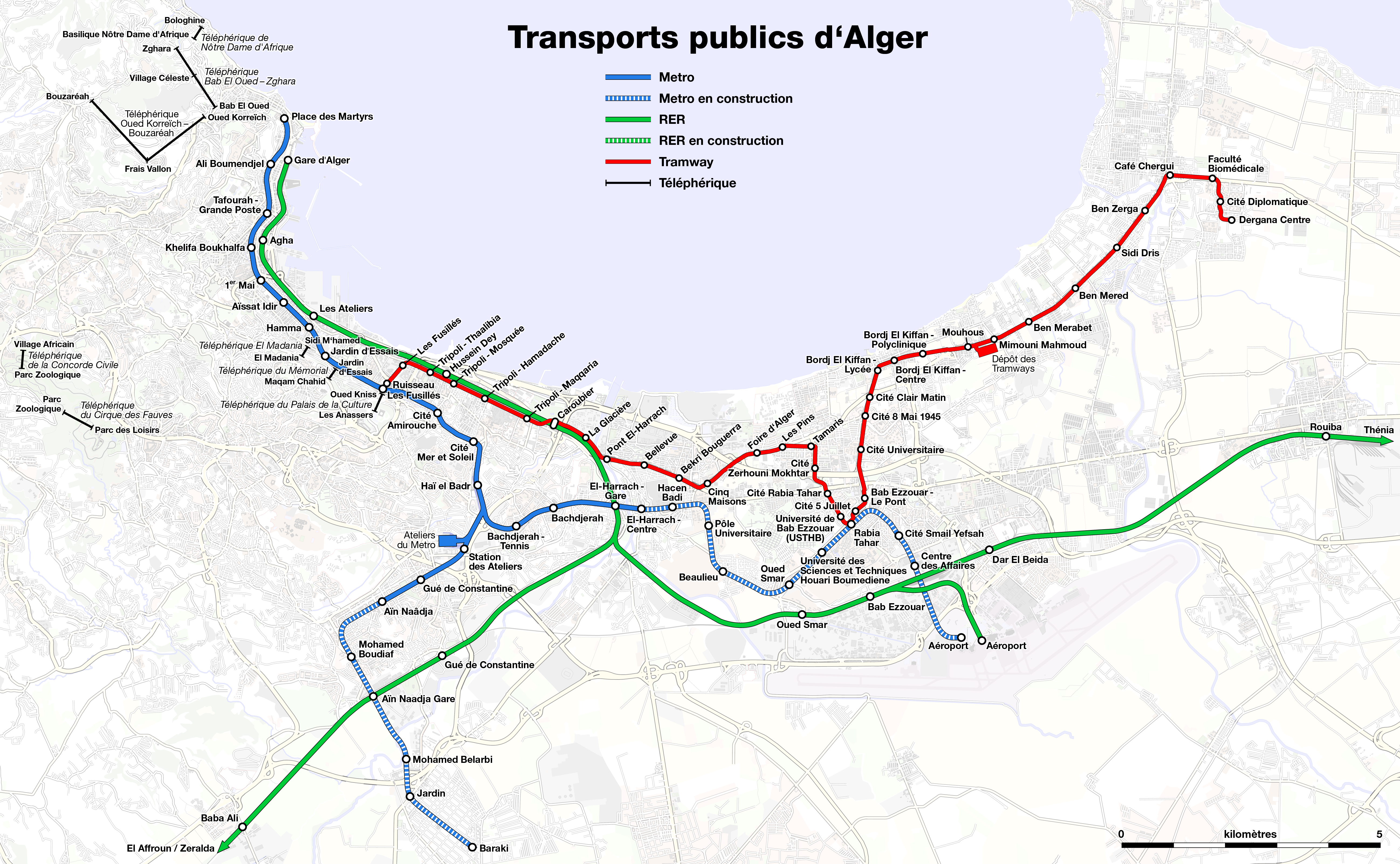
 * ETUSA (urban and suburban bus transportation for Algiers) operates bus service in Algiers and the surrounding suburbs. 54 lines are operating, with service from 5:30 a.m. to 12:45 a.m.
* SNTF (national railroad company) operates commuter-rail lines connecting the capital to the surrounding suburbs.
*
* ETUSA (urban and suburban bus transportation for Algiers) operates bus service in Algiers and the surrounding suburbs. 54 lines are operating, with service from 5:30 a.m. to 12:45 a.m.
* SNTF (national railroad company) operates commuter-rail lines connecting the capital to the surrounding suburbs.
*
 * ''
* ''
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques de l'Algérie (web). and in 2020 was estimated to be around 4,500,000. Algiers is located on the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
and in the north-central portion of Algeria.
Algiers is situated on the west side of a bay of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. The modern part of the city is built on the level ground by the seashore; the old part, the ancient city of the dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Ottoman Algeria, Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Ottoman Tu ...
s, climbs the steep hill behind the modern town and is crowned by the Casbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, قَـصَـبَـة, qaṣaba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territo ...
or citadel (a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
), above the sea. The casbah and the two quays form a triangle.
Names
The city's name is derived viaFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
''Origins of Algiers'' by Louis Leschi
Louis Leschi (2 December 1893 – 7 January 1954) was a 20th-century French historian, epigrapher and archaeologist, a specialist of ancient North Africa.
Biography
The son of academics, Louis Leschi followed himself an exemplary curriculum wh ...
, speech delivered June 16, 1941, published in ''El Djezair Sheets'', July 194History of Algeria
. from the Arabic name ''al-Jazāʾir'' (), "The Islands". This name refers to the four former islands which lay off the city's coast before becoming part of the mainland in 1525. ''Al-Jazāʾir'' is itself a truncated form of the city's older name ''Jazaʾir Banī Mazghanna'' (), "The Islands of the Banu Mazghanna, Sons of Mazghana", used by early medieval geographers such as al-Idrisi and
Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) ( ar, ياقوت الحموي الرومي) was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine Greek ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th-13th centuries). He is known fo ...
.
In antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
knew the town as ''Ikósion'' ( grc, Ἰκόσιον), which was Latinized as Icosium
Icosium ( grc, Ἰκόσιον, Ikósion) was a Berber city that was part of Numidia which became an important Roman colony and an early medieval bishopric (now a Latin titular see) in the casbah area of actual Algiers.
History
Legends
I ...
under Roman rule. The Greeks explained the name as coming from their word for "twenty" (, ''eíkosi''), supposedly because it had been founded by 20 companions of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
when he visited the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. It separates the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range. It stretches around through Moroc ...
during his labors..
Algiers is also known as ''el-Behdja'' (, "The Joyous") or "Algiers the White" (french: Alger la Blanche, links=no) for its whitewashed buildings, seen rising from the sea.
History
Early history
The city's earliest history was as a small port in the Carthage where Phoenicians were trading with other Mediterraneans. After thePunic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
, the Romans eventually took over administration of the town, which they called Icosium
Icosium ( grc, Ἰκόσιον, Ikósion) was a Berber city that was part of Numidia which became an important Roman colony and an early medieval bishopric (now a Latin titular see) in the casbah area of actual Algiers.
History
Legends
I ...
. Its ruins now form part of the modern city's marine quarter, with the Rue de la Marine following a former Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
. Roman cemeteries existed near '' Bab-el-Oued'' and ''Bab Azoun
''Bab Azoun'' ("Gate of Grief") is the name of a city gate of Algiers.
The ''rue Bab Azoun'' which runs parallel to the ''boulevard de la Republique'' and crosses the ''rue Bab El Oued
Bab El Oued is a neighbourhood in Algiers, the capital of A ...
''. The city was given Latin rights by the emperor Vespasian. The bishops of Icosium are mentioned as late as the 5th century, but the ancient town fell into obscurity during the Muslim conquest of North Africa.
The present city was founded in 944 by Bologhine ibn Ziri
Buluggin ibn Ziri, often transliterated Bologhine, in full ʾAbū al Futūḥ Sayf ad Dawlah Bulukīn ibn Zīrī ibn Manād aṣ Ṣanhājī ( ar, أبو الفتوح سيف الدولة بلكين بن زيري بن مناد الصنهاجي; die ...
, the founder of the Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
Zirid dynasty. He had earlier (935) built his own house and a Sanhaja center at Ashir, just south of Algiers. Although his Zirid dynasty was overthrown by Roger II of Sicily
Roger II ( it, Ruggero II; 22 December 1095 – 26 February 1154) was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Rog ...
in 1148, the Zirids had already lost control of Algiers to their cousins the Hammadid
The Hammadid dynasty () was a branch of the Sanhaja Berber dynasty that ruled an area roughly corresponding to north-eastern modern Algeria between 1008 and 1152. The state reached its peak under Nasir ibn Alnas during which it was briefly the ...
s in 1014. The city was wrested from the Hammadids by the Almohads in 1159, and in the 13th century came under the dominion of the Ziyanid sultans of Tlemcen. Nominally part of the sultanate of Tlemcen, Algiers had a large measure of independence under Thaaliba amirs of its own due to Oran
Oran ( ar, وَهران, Wahrān) is a major coastal city located in the north-west of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria after the capital Algiers, due to its population and commercial, industrial, and cultural ...
being the chief seaport of the Ziyanids.
The Peñón of Algiers, an islet in front of Algiers harbour had been occupied by the Spaniards as early as 1302. Thereafter, a considerable amount of trade began to flow between Algiers and Spain. However, Algiers continued to be of comparatively little importance until after the expulsion of the Moors from Spain, many of whom sought asylum in the city. In 1510, following their occupation of Oran and other towns on the coast of Africa, the Spaniards fortified the islet of Peñon and imposed a levy intended to suppress corsair
A corsair is a privateer or pirate, especially:
* Barbary corsair, Ottoman and Berber pirates and privateers operating from North Africa
* French corsairs, privateers operating on behalf of the French crown
Corsair may also refer to:
Arts and ...
activity.
Ottoman rule
In 1516, the amir of Algiers, Selim b. Teumi, invited the corsair brothers Aruj and Hayreddin ''Barbarossa'' to expel the Spaniards. Aruj came to Algiers, ordered the assassination of Selim, and seized the town and ousted the Spanish in theCapture of Algiers (1516)
The Capture of Algiers in 1516 was accomplished by the Ottoman brothers Aruj and Kheireddin Barbarossa against Sālim al-Tūmī, the ruler of the city of Algiers.
Background
In 1510, the Spaniards had established themselves on a small isl ...
. Hayreddin, succeeding Aruj after the latter was killed in battle against the Spaniards in the Fall of Tlemcen (1517), was the founder of the '' pashaluk'', which subsequently became the '' beylik'', of Algeria. Barbarossa lost Algiers in 1524 but regained it with the Capture of Algiers (1529), and then formally invited the Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent to accept sovereignty over the territory and to annex Algiers to the Ottoman Empire.
 Algiers from this time became the chief seat of the
Algiers from this time became the chief seat of the Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
. In October 1541 in the Algiers expedition, the King of Spain and Holy Roman Emperor Charles V sought to capture the city, but a storm destroyed a great number of his ships, and his army of some 30,000, chiefly made up of Spaniards, was defeated by the Algerians under their Pasha, Hassan.

 Formally part of the Ottoman Empire but essentially free from Ottoman control, starting in the 16th century Algiers turned to piracy and ransoming. Due to its location on the periphery of both the Ottoman and European economic spheres, and depending for its existence on a Mediterranean that was increasingly controlled by European shipping, backed by European navies, piracy became the primary economic activity. Repeated attempts were made by various nations to subdue the pirates that disturbed shipping in the western Mediterranean and engaged in slave raids as far north as Iceland. By the 17th century, up to 40% of the city's 100,000 inhabitants were enslaved Europeans. The United States fought two wars (the First and Second Barbary Wars) over Algiers' attacks on shipping.
Among the notable people held for ransom was the future Spanish novelist, Miguel de Cervantes, who was held captive in Algiers for almost five years, and wrote two plays set in Algiers of the period. The primary source for knowledge of Algiers of this period, since there are no contemporary local sources, is the ''Topografía e historia general de Argel'' (1612, but written earlier), published by Diego de Haedo, but whose authorship is disputed. This work describes in detail the city, the behavior of its inhabitants, and its military defenses, with the unsuccessful hope of facilitating an attack by Spain so as to end the piracy.
A significant number of renegades lived in Algiers at the time, Christians converted voluntarily to
Formally part of the Ottoman Empire but essentially free from Ottoman control, starting in the 16th century Algiers turned to piracy and ransoming. Due to its location on the periphery of both the Ottoman and European economic spheres, and depending for its existence on a Mediterranean that was increasingly controlled by European shipping, backed by European navies, piracy became the primary economic activity. Repeated attempts were made by various nations to subdue the pirates that disturbed shipping in the western Mediterranean and engaged in slave raids as far north as Iceland. By the 17th century, up to 40% of the city's 100,000 inhabitants were enslaved Europeans. The United States fought two wars (the First and Second Barbary Wars) over Algiers' attacks on shipping.
Among the notable people held for ransom was the future Spanish novelist, Miguel de Cervantes, who was held captive in Algiers for almost five years, and wrote two plays set in Algiers of the period. The primary source for knowledge of Algiers of this period, since there are no contemporary local sources, is the ''Topografía e historia general de Argel'' (1612, but written earlier), published by Diego de Haedo, but whose authorship is disputed. This work describes in detail the city, the behavior of its inhabitants, and its military defenses, with the unsuccessful hope of facilitating an attack by Spain so as to end the piracy.
A significant number of renegades lived in Algiers at the time, Christians converted voluntarily to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, many fleeing the law or other problems at home. Once converted to Islam, they were safe in Algiers. Many occupied positions of authority, such as Samson Rowlie
Samson Rowlie (died after 1588), was Chief Eunuch and Treasurer of Algiers during Ottoman rule. Born in Norfolk, England, the son of a Bristol merchant, Francis Rowlie, he was captured aboard of the ''Swallow'' and castrated by the Ottomans in 1 ...
, an Englishman who became Treasurer of Algiers.
The city under Ottoman control was enclosed by a wall on all sides, including along the seafront. In this wall, five gates allowed access to the city, with five roads from each gate dividing the city and meeting in front of the Ketchaoua Mosque. In 1556, a citadel was constructed at the highest point in the wall. A major road running north to south divided the city in two: The upper city (al-Gabal, or 'the mountain') which consisted of about fifty small quarters of Andalusian
Andalusia is a region in Spain.
Andalusian may also refer to:
Animals
*Andalusian chicken, a type of chicken
*Andalusian donkey, breed of donkey
*Andalusian hemipode, a buttonquail, one of a small family of birds
*Andalusian horse, a breed of ho ...
, Jewish, Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
and Kabyle communities, and the lower city (al-Wata, or 'the plains') which was the administrative, military and commercial centre of the city, mostly inhabited by Ottoman Turkish dignitaries and other upper-class families.
In August 1816, the city was bombarded by a British squadron under Lord Exmouth (a descendant of Thomas Pellew, taken in an Algerian slave raid in 1715), assisted by Dutch men-of-war, destroying the corsair fleet harboured in Algiers.
French rule
The history of Algiers from 1830 to 1962 is bound to the larger history ofAlgeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and its relationship to France. On July 4, 1830, under the pretext of an affront to the French consul—whom the dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Ottoman Algeria, Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Ottoman Tu ...
had hit with a fly-whisk when the consul said the French government was not prepared to pay its large outstanding debts to two Algerian merchants—a French army under General de Bourmont
Louis-Auguste-Victor, Count de Ghaisnes de Bourmont (2 September 1773 – 27 October 1846) was a French general, diplomat and statesman who was named Marshal of France in 1830. A lifelong royalist, he emigrated from France soon after the outbreak ...
attacked the city in the 1830 invasion of Algiers. The city capitulated the following day. Algiers became the capital of French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the ...
.
Many Europeans settled in Algiers, and by the early 20th century they formed a majority of the city's population. During the 1930s, the architect Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
drew up plans for a complete redesign of the colonial city. Le Corbusier was highly critical of the urban style of Algiers, describing the European district as "nothing but crumbling walls and devastated nature, the whole a sullied blot". He also criticised the difference in living standards he perceived between the European and African residents of the city, describing a situation in which "the 'civilised' live like rats in holes" whereas "the 'barbarians' live in solitude, in well-being". However, these plans were ultimately ignored by the French administration.
During World War II, Algiers was the first city to be seized from the Axis by the Allies in Operation Terminal
Operation Terminal was an Allied operation during World War II. Part of Operation Torch (the Allied invasion of French North Africa, 8 November 1942) it involved a direct landing of infantry into the Vichy French port of Algiers with the intention ...
, a part of Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of secu ...
.
 In 1962, after a bloody independence struggle in which hundreds of thousands (estimates range between 350,000 and 1,500,000) died (mostly Algerians but also French and
In 1962, after a bloody independence struggle in which hundreds of thousands (estimates range between 350,000 and 1,500,000) died (mostly Algerians but also French and Pieds-Noirs
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the vast majority of whom departed for mainland France as soon as Alger ...
) during fighting between the French Army and the Algerian Front de Libération Nationale, Algeria gained its independence, with Algiers as its capital. Since then, despite losing its entire '' pied-noir'' population, the city has expanded massively. It now has about five million inhabitants, or 10 percent of Algeria's population—and its suburbs now cover most of the surrounding Mitidja plain.
Algerian War
Algiers also played a pivotal role in theAlgerian War
The Algerian War, also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence,( ar, الثورة الجزائرية '; '' ber, Tagrawla Tadzayrit''; french: Guerre d'Algérie or ') and sometimes in Algeria as the War of 1 November ...
(1954–1962), particularly during the Battle of Algiers when the 10th Parachute Division of the French Army, starting on January 7, 1957, and on the orders of the French Minister of Justice François Mitterrand
François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he ...
(who authorized any means "to eliminate the insurrectionists"), led attacks against the Algerian fighters for independence. Algiers remains marked by this battle, which was characterized by merciless fighting between FLN forces which carried out a guerrilla campaign against the French military and police and pro-French Algerian soldiers, and the French Army which responded with a bloody repression, torture and blanket terrorism against the native population. The demonstrations of May 13 during the crisis of 1958 provoked the fall of the Fourth Republic in France, as well as the return of General de Gaulle to power.
Independence
Algeria achieved independence on July 5, 1962. Run by the FLN that had secured independence, Algiers became a member of Non-Aligned Movement during theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. In October 1988, one year before the fall of the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
, Algiers was the site of demonstrations demanding the end of the single-party system and the creation of a ''real'' democracy baptized the "Spring of Algier". The demonstrators were repressed by the authorities (more than 300 dead), but the movement constituted a turning point in the political history of modern Algeria. In 1989, a new constitution was adopted that put an end to the one-party rule and saw the creation of more than fifty political parties, as well as official freedom of the press.
Crisis of the 1990s
The city became the theatre of many political demonstrations of all descriptions until 1993. In 1991, a political entity dominated by religious conservatives called the Islamic Salvation Front engaged in a political test of wills with the authorities. In the 1992 elections for the Algerian National Assembly, the Islamists garnered a large amount of support in the first round. Fearing an eventual win by the Islamists, the army canceled the election process, setting off a civil war between the State and armed religious conservatives which would last for a decade. On December 11, 2007, two car bombs exploded in Algiers. One bomb targeted two United Nations office buildings and the other targeted a government building housing the Supreme Court. The death toll was at least 62, with over two hundred injured in the attacks. However, only 26 remained hospitalized the following day. , it is speculated that the attack was carried out by the Al Qaida cell within the city. Indigenous terrorist groups have been actively operating in Algeria since around 2002.Geography
Districts of Algiers
 * The Casbah (of ''Al Qasbah'', "the Citadel"), Ier District of Algiers: called ''Al-Djazaïr Al Mahroussa'' ("Well Kept Algiers"), is founded on the ruins of old Icosium. It is a small city which, built on a hill, goes down towards the sea, divided in two: the High city and the Low city. One finds there masonries and mosques of the 17th century; Ketchaoua mosque (built in 1794 by the Dey Baba Hassan) flanked by two minarets, mosque el Djedid (built in 1660, at the time of Turkish regency) with its large finished ovoid cupola points some and its four coupolettes, mosque El Kébir (oldest of the mosques, it was built by Almoravid Youssef Ibn Tachfin and rebuilt later in 1794), mosque Ali Betchnin (Raïs, 1623), Dar Aziza, palate of Jénina. In the Kasbah, there are also labyrinths of lanes and houses that are very picturesque, and if one gets lost there, it is enough to go down again towards the sea to reposition oneself.
* Bab El Oued: Literally ''the River's Gate'', the popular district which extends from the Casbah beyond "the gate of the river". It is the capital's darling and best liked borough. Famous for its square with "the three clocks" and for its "market Triplet", it is also a district of workshops and manufacturing plants.
*
* The Casbah (of ''Al Qasbah'', "the Citadel"), Ier District of Algiers: called ''Al-Djazaïr Al Mahroussa'' ("Well Kept Algiers"), is founded on the ruins of old Icosium. It is a small city which, built on a hill, goes down towards the sea, divided in two: the High city and the Low city. One finds there masonries and mosques of the 17th century; Ketchaoua mosque (built in 1794 by the Dey Baba Hassan) flanked by two minarets, mosque el Djedid (built in 1660, at the time of Turkish regency) with its large finished ovoid cupola points some and its four coupolettes, mosque El Kébir (oldest of the mosques, it was built by Almoravid Youssef Ibn Tachfin and rebuilt later in 1794), mosque Ali Betchnin (Raïs, 1623), Dar Aziza, palate of Jénina. In the Kasbah, there are also labyrinths of lanes and houses that are very picturesque, and if one gets lost there, it is enough to go down again towards the sea to reposition oneself.
* Bab El Oued: Literally ''the River's Gate'', the popular district which extends from the Casbah beyond "the gate of the river". It is the capital's darling and best liked borough. Famous for its square with "the three clocks" and for its "market Triplet", it is also a district of workshops and manufacturing plants.
* Edge of sea
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by ...
: from 1840, the architects Pierre-August Guiauchain and Charles Frédéric Chassériau designed new buildings apart from the Casbah, town hall, law courts, buildings, theatre, palace of the Governor, and casino, to form an elegant walk bordered by arcades which is today the boulevard Che Guevara (formerly the Boulevard of the Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
).
* Kouba (will daira
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
of Hussein-dey
Hussein Dey is a district in Algiers Province, Algeria. It was named after the Ottoman provincial ruler of the Regency of Algiers.
He had installed his country house near the beaches of the suburb of Algiers. On the shores of Hussein Dey had fa ...
): Kouba is an old village which was absorbed by the expansion of the town of Algiers. Kouba quickly developed under the French colonial era then continued growing due to formidable demographic expansion that Algiers saw after the independence of Algeria in 1962. It is today a district of Algiers which is largely made up of houses, villas, and buildings not exceeding five stories.
* El Harrach, a suburb of Algiers, is located about to the east of the city.
* The communes of Hydra
Hydra generally refers to:
* Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent in Greek mythology
* ''Hydra'' (genus), a genus of simple freshwater animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria
Hydra or The Hydra may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Hydra (constel ...
, Ben Aknoun
Ben Aknoun ( ar, بن عكنون) is a commune of Algiers Province and a suburb of the city of Algiers in northern Algeria. As of the 2008 census, the commune's population was 18,838.
The Ministry of Finance has its head office in the ''Immeub ...
, El-Biar and Bouzareah form what the inhabitants of Algiers call the "Heights of Algiers". These communes shelter the majority of the foreign embassies of Algiers, of many ministries and university centres, which makes it one of the administrative and policy centres of the country.
* The Didouche Mourad street is located in the 3rd district Of Algiers. It extends from the Grande Post office to the Heights of Algiers. It crosses in particular the place Audin, the Faculty of Algiers, The Crowned Heart and the Freedom Park (formerly Galland). It is bordered by smart stores and restaurants along most of its length. It is regarded as the heart of the capital.

Climate
Algiers has a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Csa''). Its proximity to theMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
aids in moderating the city's temperatures. As a result, Algiers usually does not see the extreme temperatures that are experienced in the adjacent interior. Algiers on average receives roughly of rain per year, the bulk of which is seen between October and April. The precipitation is higher than in most of coastal Mediterranean Spain, and similar to most of coastal Mediterranean France, as opposed to the interior North African semi-arid or arid climate.
Snow is very rare; in 2012, the city received of snowfall, its first snowfall in eight years.
Government
The city (and province) of Algiers is composed of 13 administrative districts, sub-divided into 57 ''communes'' listed below with their populations at the 1998 and 2008 Censuses:Local architecture

 There are many public buildings of interest, including the whole Kasbah quarter, Martyrs Square (''Sahat ech-Chouhada'' ساحة الشهداء), the government offices (formerly the British consulate), the " Grand", " New", and Ketchaoua Mosques, the Roman Catholic cathedral of Notre Dame d'Afrique, the Bardo Museum, the old ''Bibliothèque Nationale d'Alger''—a moorish palace built in 1799–1800 and the new National Library, built in a style reminiscent of the British Library.
The main building in the Kasbah was begun in 1516 on the site of an older building, and served as the palace of the deys until the French conquest. A road has been cut through the centre of the building, the mosque turned into
There are many public buildings of interest, including the whole Kasbah quarter, Martyrs Square (''Sahat ech-Chouhada'' ساحة الشهداء), the government offices (formerly the British consulate), the " Grand", " New", and Ketchaoua Mosques, the Roman Catholic cathedral of Notre Dame d'Afrique, the Bardo Museum, the old ''Bibliothèque Nationale d'Alger''—a moorish palace built in 1799–1800 and the new National Library, built in a style reminiscent of the British Library.
The main building in the Kasbah was begun in 1516 on the site of an older building, and served as the palace of the deys until the French conquest. A road has been cut through the centre of the building, the mosque turned into barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
, and the hall of audience allowed to fall into ruin. There still remain a minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ...
and some marble arches and columns. Traces exist of the vaults in which were stored the treasures of the dey.
Djamaa el Kebir (''Jamaa-el-Kebir'' الجامع الكبير) is the oldest mosque in Algiers. It was first built by Yusuf ibn Tashfin, but reconstructed many times. The pulpit (''minbar
A minbar (; sometimes romanized as ''mimber'') is a pulpit in a mosque where the imam (leader of prayers) stands to deliver sermons (, ''khutbah''). It is also used in other similar contexts, such as in a Hussainiya where the speaker sits and le ...
'' منبر) bears an inscription showing that the building existed in 1097. The minaret was built by the sultan of Tlemcen, in 1324. The interior of the mosque is square and is divided into aisles by columns joined by Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
arches.
The New Mosque (''Jamaa-el-Jedid'' الجامع الجديد), dating from the 17th century, is in the form of a Greek cross, surmounted by a large white cupola, with four small cupolas at the corners. The minaret is high. The interior resembles that of the Grand Mosque.
The church of the Holy Trinity (built in 1870) stands at the southern end of the ''rue d'Isly'' near the site of the demolished Fort Bab Azoun باب عزون. The interior is richly decorated with various coloured marbles. Many of these marbles contain memorial inscriptions relating to the British residents (voluntary and involuntary) of Algiers from the time of John Tipton, the first English consul, in 1580 (NB Some sources give 1585). One tablet records that in 1631 two Algerine pirate crews landed in Ireland, sacked Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was d ...
, and enslaved its inhabitants.
 The Ketchaoua Mosque (''Djamaa Ketchaoua'' جامع كتشاوة), at the foot of the Casbah, was before independence in 1962 the cathedral of St Philippe, itself made in 1845 from a mosque dating from 1612. The principal entrance, reached by a flight of 23 steps, is ornamented with a
The Ketchaoua Mosque (''Djamaa Ketchaoua'' جامع كتشاوة), at the foot of the Casbah, was before independence in 1962 the cathedral of St Philippe, itself made in 1845 from a mosque dating from 1612. The principal entrance, reached by a flight of 23 steps, is ornamented with a portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
supported by four black-veined marble columns. The roof of the nave is of Moorish
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or se ...
plaster work. It rests on a series of arcades supported by white marble columns. Several of these columns belonged to the original mosque. In one of the chapels was a tomb containing the bones of Geronimo
Geronimo ( apm, Goyaałé, , ; June 16, 1829 – February 17, 1909) was a prominent leader and medicine man from the Bedonkohe band of the Ndendahe Apache people. From 1850 to 1886, Geronimo joined with members of three other Central Apache ba ...
. The building seems a curious blend of Moorish and Byzantine styles.
Algiers possesses a college with schools of law, medicine, science and letters. The college buildings are large and handsome. The Bardo Museum holds some of the ancient sculptures and mosaics discovered in Algeria, together with medals and Algerian money.
The port of Algiers is sheltered from all winds. There are two harbours, both artificial—the old or northern harbour and the southern or Agha harbour. The northern harbour covers an area of . An opening in the south jetty affords an entrance into Agha harbour, constructed in Agha Bay. Agha harbour has also an independent entrance on its southern side. The inner harbour was begun in 1518 by Khair-ad-Din Barbarossa
Hayreddin Barbarossa ( ar, خير الدين بربروس, Khayr al-Din Barbarus, original name: Khiḍr; tr, Barbaros Hayrettin Paşa), also known as Hızır Hayrettin Pasha, and simply Hızır Reis (c. 1466/1478 – 4 July 1546), was an O ...
(see History, below), who, to accommodated his pirate vessels, caused the island on which was Fort Penon to be connected with the mainland by a mole. The lighthouse which occupies the site of Fort Penon was built in 1544.
Algiers was a walled city from the time of the deys until the close of the 19th century. The French, after their occupation of the city (1830), built a rampart, parapet and ditch, with two terminal forts, Bab Azoun
''Bab Azoun'' ("Gate of Grief") is the name of a city gate of Algiers.
The ''rue Bab Azoun'' which runs parallel to the ''boulevard de la Republique'' and crosses the ''rue Bab El Oued
Bab El Oued is a neighbourhood in Algiers, the capital of A ...
باب عزون to the south and Bab-el-Oued اد to the north. The forts and part of the ramparts were demolished at the beginning of the 20th century, when a line of forts occupying the heights of Bouzareah بوزريعة (at an elevation of above the sea) took their place.
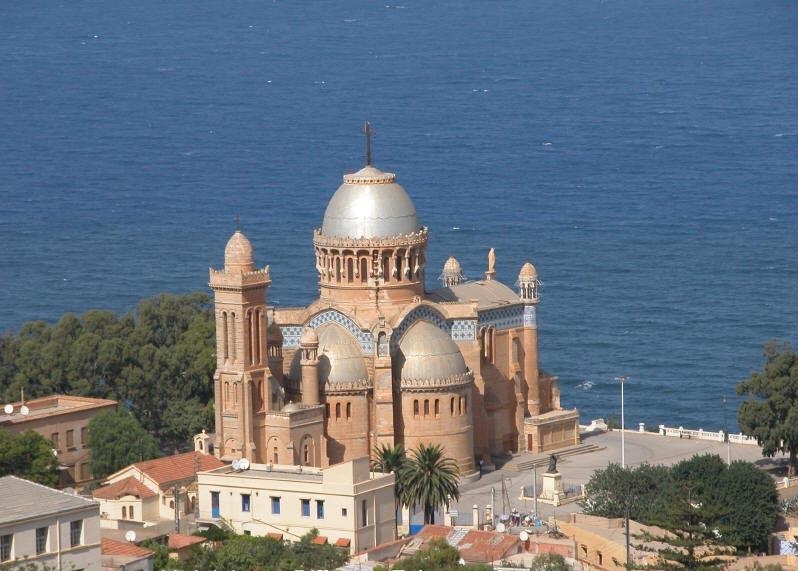
Notre Dame d'Afrique, a church built (1858–1872) in a mixture of the Roman and Byzantine styles, is conspicuously situated overlooking the sea, on the shoulder of the Bouzareah hills,
to the north of the city. Above the altar is a statue of the Virgin depicted as a black woman. The church also contains a solid silver statue of the archangel Michael, belonging to the confraternity of Neapolitan
Neapolitan means of or pertaining to Naples, a city in Italy; or to:
Geography and history
* Province of Naples, a province in the Campania region of southern Italy that includes the city
* Duchy of Naples, in existence during the Early and Hig ...
fishermen.
Villa Abd-el-Tif, former residence of the dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Ottoman Algeria, Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Ottoman Tu ...
, was used during the French period, to accommodate French artists, chiefly painters, and winners of the Abd-el-Tif prize, among whom Maurice Boitel, for a while of two years. Nowadays, Algerian artists are back in the villa's studios.
Monuments
 * Notre Dame d'Afrique, accessible by one
* Notre Dame d'Afrique, accessible by one cable car Cable car most commonly refers to the following cable transportation systems:
* Aerial lift, such as aerial tramways and gondola lifts, in which the vehicle is suspended in the air from a cable
** Aerial tramway
** Chairlift
** Gondola lift
*** Bi ...
, is one of the city's most outstanding monuments: located in the district of Z' will ghara, the basilica was built around 1858.
* Monument des Martyrs
The Maqam Echahid ( ar, مقام الشهيد, , en, Martyrs' Memorial) is a concrete monument commemorating the Algerian War. The monument was opened in 1982, on the 20th anniversary of Algeria's independence. It is fashioned in the shape of ...
(''Marquand E' chahid''): an iconic concrete monument commemorating the Algerian war for independence
The Algerian War, also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence,( ar, الثورة الجزائرية '; '' ber, Tagrawla Tadzayrit''; french: Guerre d'Algérie or ') and sometimes in Algeria as the War of 1 November ...
. The monument was opened in 1982 on the 20th anniversary of Algeria's independence. It is fashioned in the shape of three standing palm leaves which shelter the "Eternal Flame" beneath. At the edge of each palm leaf stands a statue of a soldier, each representing a stage of Algeria's struggle.
 * The El Jedid mosque at the Place des Martyrs near the port.
* Place of the Emir Abdelkader (formerly
* The El Jedid mosque at the Place des Martyrs near the port.
* Place of the Emir Abdelkader (formerly Bugeaud
Thomas Robert Bugeaud, marquis de la Piconnerie, duc d'Isly (15 October 178410 June 1849) was a Marshal of France and Governor-General of Algeria.
Early life
He was born at Limoges, a member of a noble family of Périgord (Occitania), the you ...
): in memory of the famous emir Abd El-Kader, resistant during French conquest of Algeria
The French invasion of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Deylik of Algiers, and the French consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France inva ...
.
* Grand Post Office (1910, by Voinot and Tondoire): construction of the neo-Moorish type which is in full centre town of Algiers.
* The Jardin d'essai (''Garden of Test''; ''El-Hamma''): situated in the east of Algiers, it extends over and contains exotic plants and gardens. It was created in 1832 by A. Hardy.
* Villa Abd-el-Hair, with the top of the Garden of test, one of the old residences of the dey, where until 1962, were placed the artists prizes winner of Price Abd-el-Hair
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the ...
, and in particular Maurice Boitel and Andre Hamburg.
* Citadel.
* Riadh El-Feth (shopping centre and art gallery).
* Ketchaoua Mosque (This mosque became the Saint-Philippe cathedral during colonization before becoming again a mosque).
* National Library, is in the district of El HAMMA and was built in the 1990s.
* Djamaa el Kebir at the Rue de la Marine
''Ruta graveolens'', commonly known as rue, common rue or herb-of-grace, is a species of ''Ruta'' grown as an ornamental plant and herb. It is native to the Balkan Peninsula. It is grown throughout the world in gardens, especially for its bluis ...
. It is the oldest mosque of Algiers and was built during the reign of the Almoravid sultan Yusuf ibn Tashfin.
* Le Bastion 23 – Palais des Rais, built in 1576 by Dey Ramdhan Pacha and located in the lower Casbah in the Bab El Oued neighborhood.
Demographics
Algiers has a population of about 3,335,418 (2012 estimate). The ethnic distribution is 53% from an Arabic-speaking background, 44% from a Berber-speaking background and 3% foreign-born. * 1940 – 300,000 people lived in Algiers. * 1960 – 900,000 people lived in Algiers. * 1963 – 600,000 people lived in Algiers.Economy
 Algiers is an important economic, commercial and financial center, with in particular a stock exchange with a capitalisation of 60 million euros. The city has the highest cost of living of any city in North Africa, as well as the 50th highest worldwide, as of March 2007, having gained one position compared to the previous year.
Mohamed Ben Ali El Abbar, president of the Council of Administration of the Emirate Group EMAAR, presented five "megaprojects" to Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, during a ceremony which took place Saturday, July 15, in the
Algiers is an important economic, commercial and financial center, with in particular a stock exchange with a capitalisation of 60 million euros. The city has the highest cost of living of any city in North Africa, as well as the 50th highest worldwide, as of March 2007, having gained one position compared to the previous year.
Mohamed Ben Ali El Abbar, president of the Council of Administration of the Emirate Group EMAAR, presented five "megaprojects" to Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika, during a ceremony which took place Saturday, July 15, in the People's Palace
People's Palace may refer to:
*People's Palace, Adelaide, a former Salvation Army hostel in Australia
*People's Palace, Brisbane, a former temperance hotel in Australia
*People's Palace, Djibouti City, a monument in Djibouti City, Djibouti
* Peopl ...
of Algiers. These projects will transform the city of Algiers and its surroundings by equipping them with a retail area and restoration and leisure facilities.
The first project will concentrate on the reorganization and the development of the infrastructures of the railway station "Aga" located in the downtown area. The ultramodern station intended to accommodate more than 80.000 passengers per day, will become a centre of circulation in the heart of the grid system, surrounded by commercial offices and buildings and hotels intended for travellers in transit. A shopping centre and three high-rise office buildings rising with the top of the commercial zone will accompany the project.
The second project will not relate to the bay of Algiers and aims to revitalize the sea front. The development of the sea front will include marinas, channels, luxury hotels, offices, apartments of great standing, luxury stores and leisure amenities. A crescent-shaped peninsula will be set up on the open sea. The project of the bay of Algiers will also comprise six small islands, of which four of round form, connected to each other by bridges and marinas and will include tourist and residential complexes.
Hewlett Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
office for French-speaking countries in Africa is in Algiers.
Tourist installations
 Some to the west of Algiers are such seaside resorts as Sidi Fredj (ex-Sidi Ferruch), Palm Beach,
Some to the west of Algiers are such seaside resorts as Sidi Fredj (ex-Sidi Ferruch), Palm Beach, Douaouda
Douaouda is a town and commune in Tipaza Province in northern Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, ...
, Zéralda, and the ''Club of the Pines'' (residence of State); there are tourist complexes, Algerian and other restaurants, souvenir shops, supervised beaches, and other amenities. The city is also equipped with important hotel complexes such as the hotel Hilton, El-Aurassi or El Djazair. Algiers also has the first water park in the country. The tourism of Algiers is growing but is not as developed as that of the larger cities in Morocco or Tunisia.
Education
The presence of a large diplomatic community in Algiers prompted the creation of multiple international educational institutions. These schools include : *American International School of Algiers
The American International School of Algiers (in ar, المدرسة الدولية الأمريكية بالجزائر; in ber, script=Latn, Aɣerbaz Agreɣlan Amarikani n Dzayer), abbreviated as AISA, is a private, coeducational, internatio ...
;
* El Kalimat School
El Kalimat School is an English-language international school in Bouzaréah, Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population a ...
(English-language school);
* Lycée International Alexandre-Dumas d'Alger (French school);
* Roma Italian School of Algiers
Scuola Italiana Roma di Algeri (french: École italienne Rome d'Alger) is a private Italian international school in Algiers, Algeria.Home page
Scu ...
;
* Russian Embassy School in Algiers.
There was formerly the École japonaise d'Alger (アルジェ日本人学校 ''Aruje Nihonjin Gakkō''), a school for Japanese children.
Scu ...
Public transport

 * ETUSA (urban and suburban bus transportation for Algiers) operates bus service in Algiers and the surrounding suburbs. 54 lines are operating, with service from 5:30 a.m. to 12:45 a.m.
* SNTF (national railroad company) operates commuter-rail lines connecting the capital to the surrounding suburbs.
*
* ETUSA (urban and suburban bus transportation for Algiers) operates bus service in Algiers and the surrounding suburbs. 54 lines are operating, with service from 5:30 a.m. to 12:45 a.m.
* SNTF (national railroad company) operates commuter-rail lines connecting the capital to the surrounding suburbs.
* Algiers Metro
The Algiers Metro ( ar, مترو الجزائر العاصمة, french: Métro d'Alger) is a rapid transit system that serves Algiers, the capital of Algeria. Originally designed in the 1970s, it opened in 2011 after decades of delays due to ...
, opened November 1, 2011.
* Algiers tramway, opened on May 8, 2011.
* Houari Boumediene Airport is located from the city. The airport serves domestics, many European cities, West Africa, the Middle East, Asia and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. On July 5, 2006, a new international air terminal was opened for service. The terminal is managed by Aéroports de Paris.
4 urban beltways:
* El Madania – Belouizdad
* Notre Dame d'Afrique – Bologhine
* Memorial des Martyres/Riad el Feth – Jardin d'essais
* Palais de la culture – Oued Kniss
Sports
Algiers is the sporting centre ofAlgeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. The city has a number of professional clubs in the variety of sports, which have won national and international titles. Among the sports facilities within the city, there is an enormous sporting complex – Complex of OCO – Mohamed Boudiaf. This includes the Stade 5 Juillet 1962
The 5 July 1962 Stadium () (the name refers to 5 July 1962, the day Algeria declared independence), is a football and athletics stadium located in Algiers, Algeria. The stadium was inaugurated in 1972 with a capacity of 95,000. It served as the ...
(capacity ), a venue for athletics, an Olympic swimming pool
A swimming pool, swimming bath, wading pool, paddling pool, or simply pool, is a structure designed to hold water to enable Human swimming, swimming or other leisure activities. Pools can be built into the ground (in-ground pools) or built ...
, a multisports room (the Cupola), an 18-hole golf course, and several tennis courts.
The following major sporting events have been held in Algiers (not-exhaustive list):
Football clubs
Major association football club based in Algiers include:International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Algiers istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Montreal, Canada
* Moscow, Russia
* Sofia, Bulgaria
In addition, many of the wards and cities within Algiers maintain sister-city relationships with other foreign cities.
Cooperation agreements
Algiers has cooperation agreements with: *Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, Portugal
* Paris, France
Films about Algiers
 * ''
* ''Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
'', 1938, starring Charles Boyer and Hedy Lamarr, and directed by John Cromwell;
* '' The Battle of Algiers'', 1966, directed by Gillo Pontecorvo;
* ''Tahya ya Didou, Alger Insolite'', 1970, Mohammed Zinet;
* ''Bab El-Oued City
''Bab El-Oued City'' is a 1994 Algerian drama film directed by Merzak Allouache. It was screened in the Un Certain Regard section at the 1994 Cannes Film Festival, where it won the FIPRESCI Award.
Plot
Boualem is a baker's boy who works early m ...
'', 1994, directed by Merzak Allouache;
* ''Viva Laldjérie'', 2003, directed by Nadir Moknèche, with Biyouna and Lubna Azabal
Lubna Azabal (born 15 August 1973) is a Belgian actress of Moroccan–Spanish descent.
Career
Azabal was born on 15 August 1973 in Brussels to a Moroccan father and a Spanish mother.Samy Naceri, Julie Gayet, Faudel;
* ''Once upon a time in the Oued'', 2005, directed by Djamel Bensalah;
* ''Beur, White, Red'', 2005, directed by Mahmoud Zemmouri.
* ''
Delice Paloma
Delice is a town and district of Kırıkkale Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. At the 2000 Turkish census
The 2000 Turkish census was held in 2000 and recorded the population and demographic details of every settlement in Turk ...
'', 2007, directed by Nadir Moknèche, with Biyouna and Nadia Kaci.
* '' Abbott and Costello in the Foreign Legion'', 1950, starring Bud Abbott and Lou Costello.
* '' Carry on Spying'' 1964, directed by Gerald Thomas with Kenneth Williams, Charles Hawtrey, Barbara Windsor & Renee Houston
Notable people
*Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
* Botanical Garden Hamma
The Test Garden of Hamma ( ar, حديقة التجارب الحامة) (french: Jardin d'Essai du Hamma) is a botanical garden ( of gardens and of arboretum) located in the Mohamed Belouizdad (formerly Hamma-Anassers) district of Algiers. It was ...
* List of Ottoman governors of Algiers
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * Carroll, David. ''Albert Camus the Algerian'' (Columbia University Press, 2007). * Emerson, Charles. ''1913: In Search of the World Before the Great War'' (2013) compares Algiers to 20 major world cities; pp 267–79. * . * . * . {{Authority control 944 establishments Barbary Wars Capitals in Africa Former Spanish colonies Mediterranean port cities and towns in Algeria Populated coastal places in Algeria World Heritage Sites in Algeria Coastal cities in Algeria Populated places in Algiers Province Province seats of Algeria Populated places established in the 10th century 10th-century establishments in Africa