Albino Manca on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the terms mean that written reports of albinistic animals can be difficult to verify. Albinism can reduce the survivability of an animal; for example, it has been suggested that albino alligators have an average survival span of only 24 hours due to the lack of protection from UV radiation and their lack of camouflage to avoid predators. It is a common misconception that all albino animals have characteristic pink or red eyes (resulting from the lack of pigment in the
 Definitions of albinism vary and are inconsistent. While they are clear and precise for humans and other mammals, this is because the majority of mammals have only one pigment, melanin. Many animals have pigments other than melanin, and some also have structural colours. Some definitions of albinism, whilst taking most taxa into account, ignore others. So, "a person or animal with very pale skin, white hair or fur, and pink eyes caused by a medical condition that they were born with" and "a person or animal with white skin and hair and pink eyes" do not include feathers, scales or cuticles of birds, fish and invertebrates, nor do they include plants. Some definitions are too broad to be of much use, e.g. "an animal or plant with a marked deficiency in pigmentation".
Other definitions of albinism encompass most of the major animal taxa, but ignore the several other pigments that non-mammalian animals have and also structural colouration. For example, "Absence of the pigment melanin in the eyes, skin, hair, scales, or feathers." refers only to the pigment melanin.
Because of the various uses of different terms applied to colouration, some authors have indicated that the colour of the eyes is the defining characteristic of albinism, e.g. "This leads to a good diagnostic feature with which to distinguish leucistic and albino individuals – the colour of the eye." However, there are multiple forms of albinism – currently seven types recognised for humans – most of which do not result in red or pink pupils.
The term "partial albino" is sometimes used in the literature, however, it has been stated that "A common misnomer is 'partial albino' – this is not possible since albinism affects the whole plumage of a bird, not just part" and the definition of albinism precludes the possibility of "partial albinism" in which a mostly white bird shows some form of melanin pigmentation. "It is simply impossible, just like being 'partially pregnant' ". Conditions that are commonly termed "partial albino" include neural crest disorders such as
Definitions of albinism vary and are inconsistent. While they are clear and precise for humans and other mammals, this is because the majority of mammals have only one pigment, melanin. Many animals have pigments other than melanin, and some also have structural colours. Some definitions of albinism, whilst taking most taxa into account, ignore others. So, "a person or animal with very pale skin, white hair or fur, and pink eyes caused by a medical condition that they were born with" and "a person or animal with white skin and hair and pink eyes" do not include feathers, scales or cuticles of birds, fish and invertebrates, nor do they include plants. Some definitions are too broad to be of much use, e.g. "an animal or plant with a marked deficiency in pigmentation".
Other definitions of albinism encompass most of the major animal taxa, but ignore the several other pigments that non-mammalian animals have and also structural colouration. For example, "Absence of the pigment melanin in the eyes, skin, hair, scales, or feathers." refers only to the pigment melanin.
Because of the various uses of different terms applied to colouration, some authors have indicated that the colour of the eyes is the defining characteristic of albinism, e.g. "This leads to a good diagnostic feature with which to distinguish leucistic and albino individuals – the colour of the eye." However, there are multiple forms of albinism – currently seven types recognised for humans – most of which do not result in red or pink pupils.
The term "partial albino" is sometimes used in the literature, however, it has been stated that "A common misnomer is 'partial albino' – this is not possible since albinism affects the whole plumage of a bird, not just part" and the definition of albinism precludes the possibility of "partial albinism" in which a mostly white bird shows some form of melanin pigmentation. "It is simply impossible, just like being 'partially pregnant' ". Conditions that are commonly termed "partial albino" include neural crest disorders such as
 Melanin is an organic pigment that produces most of the colour seen in mammals. Depending on how it is created, melanin comes in two colour ranges, eumelanin (producing dark browns and blacks) and
Melanin is an organic pigment that produces most of the colour seen in mammals. Depending on how it is created, melanin comes in two colour ranges, eumelanin (producing dark browns and blacks) and
 In all albino mammals studied, the centre of the retina is under-developed and there is a deficit of rod cells; the central ganglion cell density is approximately 25% below normal (except for the gray squirrel). In nearly all mammals, the overwhelming majority of photoreceptors are rods rather than cones. Albinism specifically affects the rod cells, but the number and distribution of the cones is unaffected. In contrast, the retinas of birds are cone rich meaning that the vision of albino birds is affected less than albino mammals.
In all albino mammals studied, the centre of the retina is under-developed and there is a deficit of rod cells; the central ganglion cell density is approximately 25% below normal (except for the gray squirrel). In nearly all mammals, the overwhelming majority of photoreceptors are rods rather than cones. Albinism specifically affects the rod cells, but the number and distribution of the cones is unaffected. In contrast, the retinas of birds are cone rich meaning that the vision of albino birds is affected less than albino mammals.
 It has been claimed that "Squirrels are the only known albino mammal to survive successfully in the wild". The retina of the squirrel (''
It has been claimed that "Squirrels are the only known albino mammal to survive successfully in the wild". The retina of the squirrel (''
 The costs of albinism for marine mammals may include reduced heat absorption in colder waters, poor camouflage from predators, increased sensitivity to sunlight, and impaired visual communication. Despite the costs, some individuals do reach adult age and breeding status.
Albino dolphins were first sighted in the Gulf of Mexico in 1962. Since 1994, three further individuals have been seen. These tend to be pink in colour due to blood vessels showing through the blubber and unpigmented skin.
A report published in 2008 stated that in marine mammals, "anomalously white" individuals have been reported for 21 cetacean species and 7
The costs of albinism for marine mammals may include reduced heat absorption in colder waters, poor camouflage from predators, increased sensitivity to sunlight, and impaired visual communication. Despite the costs, some individuals do reach adult age and breeding status.
Albino dolphins were first sighted in the Gulf of Mexico in 1962. Since 1994, three further individuals have been seen. These tend to be pink in colour due to blood vessels showing through the blubber and unpigmented skin.
A report published in 2008 stated that in marine mammals, "anomalously white" individuals have been reported for 21 cetacean species and 7

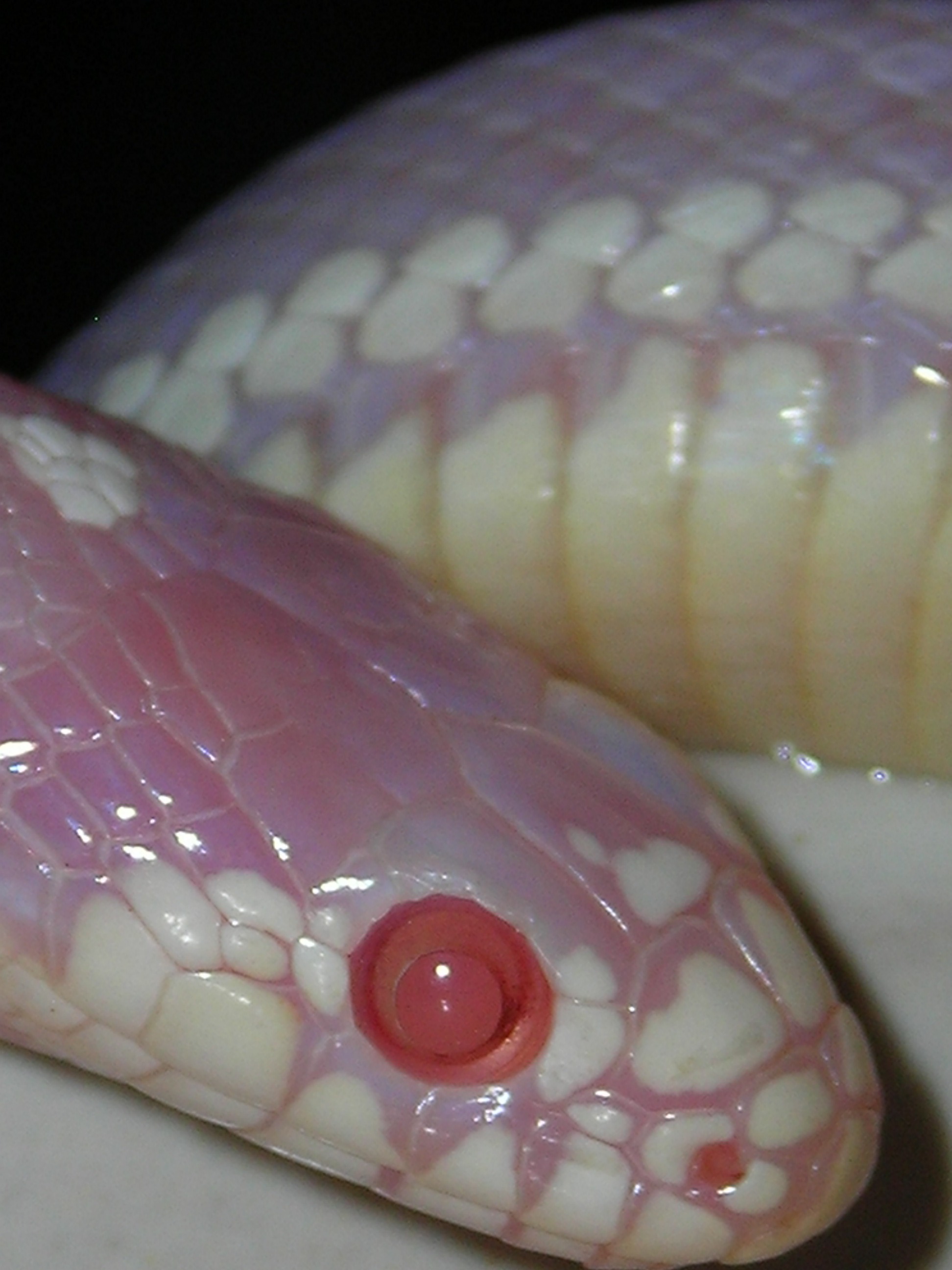 Many reptiles labeled as albino are, in fact, not completely lacking in all colour pigments. They are actually Amelanism, amelanistic, not albino. Reptiles often possess at least two pigments. Among the most common are xanthin (yellow) and erythrin (red). An amelanistic reptile therefore, may still have pale yellow, orange, or red pigmentation.
The California Academy of Science, in the Steinhart Aquarium, as of 2015, has on display an albino American alligator named "Claude (alligator), Claude". The alligator is partially blind because of lack of pigment in its eyes. The albino alligator hatched from the egg in 1995 in Florida, and was brought to the academy in 2008. This alligator would not have survived in the wild because its whiteness would have made it too easy a prey object. The only known albino alligators are in captivity. While extremely rare, white-coloured crocodiles and alligators do exist in other places. However, most of these animals are Leucism, leucistic given that they have a general loss of pigmentation with some colour tinges remaining on their bodies although looking at first like other albino creatures, thus creating the misconception that the reptiles are albino themselves when they are not. Four such alligators are kept at the Gatorland theme park in the U.S. state of Florida. In Australia, a crocodile believed to be "part-albino" and nicknamed by people in the area as "Michael Jackson", attacked and killed a man.
In snakes, partial absence of pigment is more common than absolute albinism. For snakes that are usually patterned in colours, they appear as a faint blue, peach or yellowish. In these cases, there has been a genetic mutation in the melanin and pigment delivery. The appearance comes from the inability for full colours to be present, such as black, red, brown and others. The eyes of an albino snake are typically red or pink. Albino snakes can remain in the sunlight for several hours with minimal harm. Corn snakes and snakes of larger types, such as a Boa (genus), boa or diamondback snakes, are the most commonly affected by albinism often appearing to be a pinkish or yellowish colour.
Albino tortoises and turtles are uncommon; Sulcata tortoises are the most likely type of turtle to express albinism. The shells have an almost yellow colouration and they have pink eyes. For turtles, a pure white colour is nearly impossible, even with albinism. Albino turtles can have a longer lifespan than many other albino animals; their hard shells help to prevent predation and other environmental challenges. Vision and sensory organs are slightly affected.
In 2012, an albino Dactyloidae, anole was reported and photographed. In 2007, it was reported that an albino stumpy-tail lizard (possibly a shingleback lizard), approximately long and roughly 1 year old, had been found in Victoria, Australia.
There are three known "albino" strains of leopard gecko, however, breeders state that albinos are generally recognized by their lack of black pigment and having red eyes is not a requirement to be considered an albino. These three strains are called "tremper albinos", "rainwater albinos" and "bell albinos".
Many reptiles labeled as albino are, in fact, not completely lacking in all colour pigments. They are actually Amelanism, amelanistic, not albino. Reptiles often possess at least two pigments. Among the most common are xanthin (yellow) and erythrin (red). An amelanistic reptile therefore, may still have pale yellow, orange, or red pigmentation.
The California Academy of Science, in the Steinhart Aquarium, as of 2015, has on display an albino American alligator named "Claude (alligator), Claude". The alligator is partially blind because of lack of pigment in its eyes. The albino alligator hatched from the egg in 1995 in Florida, and was brought to the academy in 2008. This alligator would not have survived in the wild because its whiteness would have made it too easy a prey object. The only known albino alligators are in captivity. While extremely rare, white-coloured crocodiles and alligators do exist in other places. However, most of these animals are Leucism, leucistic given that they have a general loss of pigmentation with some colour tinges remaining on their bodies although looking at first like other albino creatures, thus creating the misconception that the reptiles are albino themselves when they are not. Four such alligators are kept at the Gatorland theme park in the U.S. state of Florida. In Australia, a crocodile believed to be "part-albino" and nicknamed by people in the area as "Michael Jackson", attacked and killed a man.
In snakes, partial absence of pigment is more common than absolute albinism. For snakes that are usually patterned in colours, they appear as a faint blue, peach or yellowish. In these cases, there has been a genetic mutation in the melanin and pigment delivery. The appearance comes from the inability for full colours to be present, such as black, red, brown and others. The eyes of an albino snake are typically red or pink. Albino snakes can remain in the sunlight for several hours with minimal harm. Corn snakes and snakes of larger types, such as a Boa (genus), boa or diamondback snakes, are the most commonly affected by albinism often appearing to be a pinkish or yellowish colour.
Albino tortoises and turtles are uncommon; Sulcata tortoises are the most likely type of turtle to express albinism. The shells have an almost yellow colouration and they have pink eyes. For turtles, a pure white colour is nearly impossible, even with albinism. Albino turtles can have a longer lifespan than many other albino animals; their hard shells help to prevent predation and other environmental challenges. Vision and sensory organs are slightly affected.
In 2012, an albino Dactyloidae, anole was reported and photographed. In 2007, it was reported that an albino stumpy-tail lizard (possibly a shingleback lizard), approximately long and roughly 1 year old, had been found in Victoria, Australia.
There are three known "albino" strains of leopard gecko, however, breeders state that albinos are generally recognized by their lack of black pigment and having red eyes is not a requirement to be considered an albino. These three strains are called "tremper albinos", "rainwater albinos" and "bell albinos".
 The incidence of albinism in frogs, salamanders, and newts is relatively higher than other taxa. It has been estimated that one in four hundred of these animals is albino. When albino tadpoles hatch, they are almost transparent. This may help camouflage them initially, however, after two weeks, when their hindlegs begin to emerge, they become milky white. A survey in 2001 found hundreds of tiny albino plains leopard frogs, but when the researcher returned a few months later, not a single albino adult could be found.
In European Salamandra, Salamandridae, albinism has been recorded in the fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra''), gold-striped salamander (''Chioglossa lusitanica''), Italian crested newt (''Triturus carnifex''), marbled newt (''Triturus marmoratus''), Iberian ribbed newt (''Pleurodeles waltl''), alpine newt (''Ichthyosaura alpestris'') and two sub-species of the smooth newt (''Lissotriton vulgaris vulgaris'' and ''Lissotriton vulgaris meridionalis'').
The incidence of albinism in frogs, salamanders, and newts is relatively higher than other taxa. It has been estimated that one in four hundred of these animals is albino. When albino tadpoles hatch, they are almost transparent. This may help camouflage them initially, however, after two weeks, when their hindlegs begin to emerge, they become milky white. A survey in 2001 found hundreds of tiny albino plains leopard frogs, but when the researcher returned a few months later, not a single albino adult could be found.
In European Salamandra, Salamandridae, albinism has been recorded in the fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra''), gold-striped salamander (''Chioglossa lusitanica''), Italian crested newt (''Triturus carnifex''), marbled newt (''Triturus marmoratus''), Iberian ribbed newt (''Pleurodeles waltl''), alpine newt (''Ichthyosaura alpestris'') and two sub-species of the smooth newt (''Lissotriton vulgaris vulgaris'' and ''Lissotriton vulgaris meridionalis'').
File:BMNSM.JPG, An exhibit showing albino and normal specimens of nine local species of marine molluscs, both gastropods and bivalves (The Bailey-Matthews National Shell Museum in Sanibel, Florida).
File:Pseudofusulus varians.png, Normal (left) and albinistic (right) forms of the land snail ''Pseudofusulus varians'', note that in the albino both the body and the shell are lacking the normal pigmentation.
File:Biomphalaria glabrata.jpg, Albino freshwater snail ''Biomphalaria glabrata'' showing the red oxygen-transport pigment haemoglobin. Without its normal pigment, the shell of this species is translucent.
"The Parblue Puzzle: Part 4—Common Parblue Varieties: The Cockatiel [''Nymphicus hollandicus'']"
in ''The Genetics of Colour in the Budgerigar and Other Parrots'' * Axanthism is a condition common in reptiles and amphibians, in which xanthophore#Xanthophores and erythrophores, xanthophore metabolism is affected rather than Chemical synthesis, synthesis of melanin, resulting in reduction or absence of red and yellow pteridine pigments.
* Leucism differs from albinism in that the melanin is, at least, partially absent but the eyes retain their usual colour. Some leucistic animals are white or pale because of
* Axanthism is a condition common in reptiles and amphibians, in which xanthophore#Xanthophores and erythrophores, xanthophore metabolism is affected rather than Chemical synthesis, synthesis of melanin, resulting in reduction or absence of red and yellow pteridine pigments.
* Leucism differs from albinism in that the melanin is, at least, partially absent but the eyes retain their usual colour. Some leucistic animals are white or pale because of
by Dr. Julie Feinstein of the American Museum of Natural History (NY), in ''Birder's World Magazine'' online archive; sourced December 2006, actual authoring/publication date unspecified.

 In plants, albinism is characterised by partial or complete loss of chlorophyll pigments and incomplete differentiation of chloroplast membranes. Albinism in plants interferes with
In plants, albinism is characterised by partial or complete loss of chlorophyll pigments and incomplete differentiation of chloroplast membranes. Albinism in plants interferes with
iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
allowing the blood vessels of the retina to be visible), however this is not the case for some forms of albinism. Familiar albino animals include in-bred strains of laboratory animals
Animals used by laboratories for testing purposes are largely supplied by dealers who specialize in selling them to universities, medical and veterinary schools, and companies that provide contract animal-testing services. It is comparatively rare ...
(rats, mice and rabbits), but populations of naturally occurring albino animals exist in the wild, e.g. Mexican cave tetra. Albinism is a well-recognized phenomenon in molluscs, both in the shell and in the soft parts. It has been claimed by some, e.g. that albinism can occur for a number of reasons aside from inheritance, including genetic mutations, diet, living conditions, age, disease, or injury. However, this is contrary to definitions where the condition is inherited.
Oculocutaneous albinism
Oculocutaneous albinism is a form of albinism involving the eyes ('' oculo-''), the skin (''-cutaneous''), and the hair.
Overall, an estimated 1 in 20,000 people worldwide are born with oculocutaneous albinism. OCA is caused by mutations in seve ...
(OCA) is a clearly defined set of seven types of genetic mutations which reduce or completely prevent the synthesis of eumelanin or pheomelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the a ...
, resulting in reduced pigmentation. Type I oculocutaneous albinism (OCA1a) is the form most commonly recognised as 'albino' as this results in a complete absence of melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
in the skin, hair/fur/feathers, and pink pupils, however this has led many to assume that all albinos are pure white with pink pupils, which is not the case.
In plants, albinism is characterised by partial or complete loss of chlorophyll pigments and incomplete differentiation of chloroplast membranes. Albinism in plants interferes with photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
, which can reduce survivability. Some plant variations may have white flowers or other parts. However, these plants are not totally devoid of chlorophyll. Terms associated with this phenomenon are "hypochromia" and "albiflora".
Biological colouration
Biological pigments
Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments. Many biol ...
are substances produced by living organisms that have a colour resulting from selective colour absorption. What is perceived as a plant or animal's "colour" is the wavelengths of light that are not absorbed by the pigment, but instead are reflected. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments
Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), color absorption. Biological pigments include plant ...
.
Animal colouration
Animals can appear coloured due to two mechanisms, pigments and structural colours. Animals may have both biological pigments and structural colours, for example, some butterflies with white wings.Pigments
Many animal body-parts, such asskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
, eyes, feathers
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
, fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
, hair, scales and cuticles, contain pigments in specialized cells called chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...
s. These cells are found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
, reptiles, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s and cephalopods. Mammals and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for colouration. The term chromatophore can also refer to coloured, membrane-associated vesicles found in some forms of photosynthetic bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in poikilothermic
A poikilotherm () is an animal whose internal temperature varies considerably. Poikilotherms have to survive and adapt to environmental stress. One of the most important stressors is temperature change, which can lead to alterations in membrane ...
animals and are generated in the neural crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, per ...
during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light:
* xanthophores (yellow): contain yellow pigments in the forms of carotenoids
* erythrophores (red): contain reddish pigments such as carotenoids and pteridine
Pteridine is an aromatic chemical compound composed of fused pyrimidine and pyrazine rings. A pteridine is also a group of heterocyclic compounds containing a wide variety of substitutions on this structure. Pterins and flavins are classes of s ...
* melanophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in cont ...
s (black/brown): contain black and brown pigments such as the melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
s
* cyanophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...
s (blue): limited taxonomic range but found in some fish and amphibians
Structural colours
Animals can also appear coloured due to structural colour, the result ofcoherent scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including ...
perceived as iridescence. The structures themselves are colourless. Light typically passes through multiple layers and is reflected more than once. The multiple reflections compound one another and intensify the colours. Structural colour differs according to the observer's position whereas pigments appear the same regardless of the angle-of-view. Animals that show iridescence include mother of pearl
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother of pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer; it is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent.
Nacre is f ...
seashells, fish, and peacocks. These are just a few examples of animals with this quality, but it is most pronounced in the butterfly family.
* iridophores (reflective/iridescent): sometimes called "guanophores", reflect light using plates of crystalline chemochromes made from guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
* leucophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contras ...
s (reflective white): found in some fish, utilize crystalline purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines ...
s (often guanine) to produce a reflective, shiny, white colour.
Plant colouration
The primary function of pigments in plants isphotosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
, which uses the green pigment chlorophyll along with several red and yellow pigments including porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical com ...
s, carotenoids, anthocyanins and betalain
Betalains are a class of red and yellow tyrosine-derived pigments found in plants of the order Caryophyllales, where they replace anthocyanin pigments. Betalains also occur in some higher order fungi. They are most often noticeable in the petals ...
s.
Definition
 Definitions of albinism vary and are inconsistent. While they are clear and precise for humans and other mammals, this is because the majority of mammals have only one pigment, melanin. Many animals have pigments other than melanin, and some also have structural colours. Some definitions of albinism, whilst taking most taxa into account, ignore others. So, "a person or animal with very pale skin, white hair or fur, and pink eyes caused by a medical condition that they were born with" and "a person or animal with white skin and hair and pink eyes" do not include feathers, scales or cuticles of birds, fish and invertebrates, nor do they include plants. Some definitions are too broad to be of much use, e.g. "an animal or plant with a marked deficiency in pigmentation".
Other definitions of albinism encompass most of the major animal taxa, but ignore the several other pigments that non-mammalian animals have and also structural colouration. For example, "Absence of the pigment melanin in the eyes, skin, hair, scales, or feathers." refers only to the pigment melanin.
Because of the various uses of different terms applied to colouration, some authors have indicated that the colour of the eyes is the defining characteristic of albinism, e.g. "This leads to a good diagnostic feature with which to distinguish leucistic and albino individuals – the colour of the eye." However, there are multiple forms of albinism – currently seven types recognised for humans – most of which do not result in red or pink pupils.
The term "partial albino" is sometimes used in the literature, however, it has been stated that "A common misnomer is 'partial albino' – this is not possible since albinism affects the whole plumage of a bird, not just part" and the definition of albinism precludes the possibility of "partial albinism" in which a mostly white bird shows some form of melanin pigmentation. "It is simply impossible, just like being 'partially pregnant' ". Conditions that are commonly termed "partial albino" include neural crest disorders such as
Definitions of albinism vary and are inconsistent. While they are clear and precise for humans and other mammals, this is because the majority of mammals have only one pigment, melanin. Many animals have pigments other than melanin, and some also have structural colours. Some definitions of albinism, whilst taking most taxa into account, ignore others. So, "a person or animal with very pale skin, white hair or fur, and pink eyes caused by a medical condition that they were born with" and "a person or animal with white skin and hair and pink eyes" do not include feathers, scales or cuticles of birds, fish and invertebrates, nor do they include plants. Some definitions are too broad to be of much use, e.g. "an animal or plant with a marked deficiency in pigmentation".
Other definitions of albinism encompass most of the major animal taxa, but ignore the several other pigments that non-mammalian animals have and also structural colouration. For example, "Absence of the pigment melanin in the eyes, skin, hair, scales, or feathers." refers only to the pigment melanin.
Because of the various uses of different terms applied to colouration, some authors have indicated that the colour of the eyes is the defining characteristic of albinism, e.g. "This leads to a good diagnostic feature with which to distinguish leucistic and albino individuals – the colour of the eye." However, there are multiple forms of albinism – currently seven types recognised for humans – most of which do not result in red or pink pupils.
The term "partial albino" is sometimes used in the literature, however, it has been stated that "A common misnomer is 'partial albino' – this is not possible since albinism affects the whole plumage of a bird, not just part" and the definition of albinism precludes the possibility of "partial albinism" in which a mostly white bird shows some form of melanin pigmentation. "It is simply impossible, just like being 'partially pregnant' ". Conditions that are commonly termed "partial albino" include neural crest disorders such as piebaldism
Piebaldism refers to the absence of mature melanin-forming cells (melanocytes) in certain areas of the skin and hair. It is a rare autosomal dominant disorder of melanocyte development.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews ...
, Waardenburg syndrome
Waardenburg syndrome is a group of rare genetic conditions characterised by at least some degree of congenital hearing loss and pigmentation deficiencies, which can include bright blue eyes (or one blue eye and one brown eye), a white foreloc ...
, or other depigmentation conditions such as vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes the skin to lose its color. Specific causes are unknown but studies suggest a link to immune system changes.
Signs and symptoms
The only sign of vitiligo is the presence of pale patchy areas of depigmen ...
. These conditions result from fundamentally different causes to the seven types of oculocutaneous albinism
Oculocutaneous albinism is a form of albinism involving the eyes ('' oculo-''), the skin (''-cutaneous''), and the hair.
Overall, an estimated 1 in 20,000 people worldwide are born with oculocutaneous albinism. OCA is caused by mutations in seve ...
that have been identified in humans (and confirmed in some other animals) and the use of the term "partial albino" is therefore misleading.
One definition states that "albinism, (from the Latin albus, meaning "white"), hereditary condition characterized by the absence of pigment in the eyes, skin, hair, scales, or feathers", however, this does not encompass invertebrates, nor does it include plants. Furthermore, it could be interpreted that "...absence of pigment..." does not include an absence of structural colours.
The lack of clarity about the term is furthered when the name of an animal includes the term "albino" although the animals (clearly) do not have the condition. For example, the albino gaur has this name because it is ash-grey whereas other gaur are almost black.
A clear definition appears to be – "Congenital absence of any pigmentation or colouration in a person, animal, or plant, resulting in white hair and pink eyes in mammals." Whilst this does not state specifically that non-mammalian albino animals (or plants) are white, this can be inferred from "...absence of any pigmentation or colouration..." Due to the varied use and interpretation of the term "albino", written reports of albinistic organisms can often not be verified.
Mechanism and frequency
 Melanin is an organic pigment that produces most of the colour seen in mammals. Depending on how it is created, melanin comes in two colour ranges, eumelanin (producing dark browns and blacks) and
Melanin is an organic pigment that produces most of the colour seen in mammals. Depending on how it is created, melanin comes in two colour ranges, eumelanin (producing dark browns and blacks) and pheomelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the a ...
(producing light reddish tans and blondes). The dark and light melanins have their influence either alone or in conjunction, making either plain or multi-coloured coats. Sometimes, in a condition called agouti
The agouti (, ) or common agouti is any of several rodent species of the genus ''Dasyprocta''. They are native to Middle America, northern and central South America, and the southern Lesser Antilles. Some species have also been introduced else ...
, they make multi-coloured individual hairs. The production of melanin occurs in melanocytes in a complex process involving the enzyme tyrosinase
Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxy ...
. Mammals have a gene that codes for the presence of tyrosinase in cells – called the TYR gene. If this gene is altered or damaged, melanin cannot be reliably produced and the mammal becomes an albino. Besides the TYR gene, several other genes can cause albinism. This is because other hormones and proteins are involved in melanin production, the presence of which is genetically determined. In mice, a total of 100 genes are known to affect albinism.
All the genetic traits for albinism are recessive traits. This means that their influence is hidden when paired with stronger traits. For the recessive albino trait to be expressed in a mammal, the offspring must inherit a recessive gene from both parents.
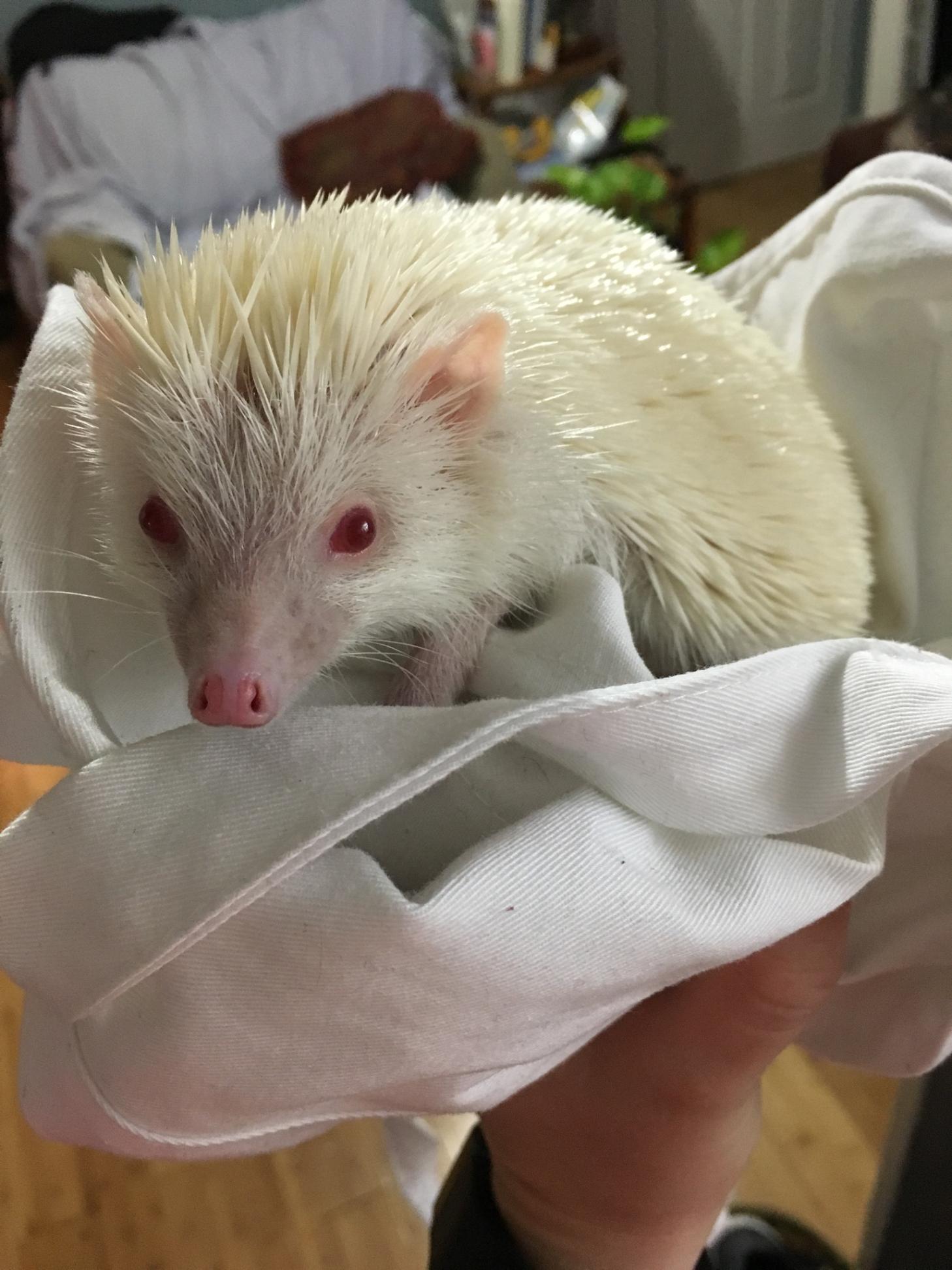
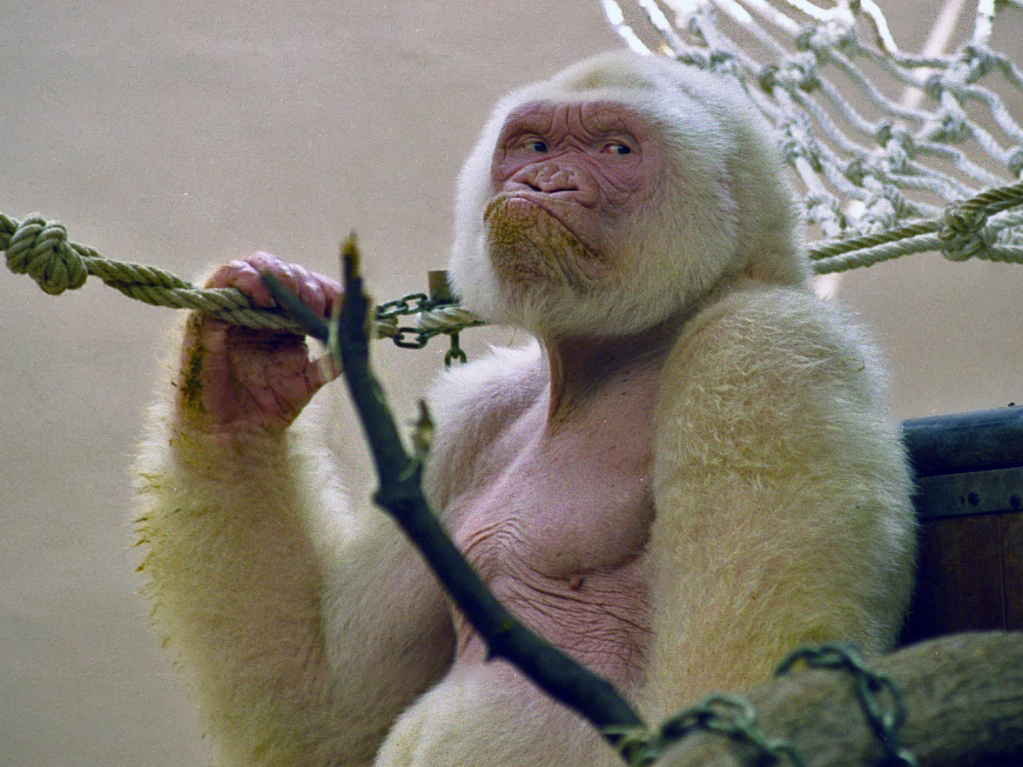
Albinism occurs throughout the animal kingdom. The condition is most commonly seen in birds, reptiles and amphibians, but more rarely seen in mammals and other taxa. It is often difficult to explain occasional occurrences, especially when only one documented incidence has occurred, such as only one albino gorilla and one albino koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the w ...
. In mammals, albinism occurs once in every 10,000 births, but in birds, the rate is once in every 1,764 births.
Some species, such as white peacocks, swans and geese, are not believed to be true albinos, as they do not have red eyes, rather, their colouration is suggested to be the expression of a white fur or feather gene, not a lack of melanin.
Consequences
Melanin has several functions in most mammals and other animals; these are disrupted by albinism.Abnormal eye development and appearance
Melanin functions in the normal development of various parts of the eye, including the iris, retina, eye muscles, and optic nerve. The absence of melanin results in abnormal development of eyes and leads to problems with focusing, and depth perception. The eyes of albino animals appear red because the colour of the red blood cells in theretina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
can be seen through the iris, which has no pigment to obscure this. Some albino animals may have pale-blue eyes due to other colour generating processes. Albino vertebrates exposed to intense light typically lose photoreceptors due to apoptosis.
 In all albino mammals studied, the centre of the retina is under-developed and there is a deficit of rod cells; the central ganglion cell density is approximately 25% below normal (except for the gray squirrel). In nearly all mammals, the overwhelming majority of photoreceptors are rods rather than cones. Albinism specifically affects the rod cells, but the number and distribution of the cones is unaffected. In contrast, the retinas of birds are cone rich meaning that the vision of albino birds is affected less than albino mammals.
In all albino mammals studied, the centre of the retina is under-developed and there is a deficit of rod cells; the central ganglion cell density is approximately 25% below normal (except for the gray squirrel). In nearly all mammals, the overwhelming majority of photoreceptors are rods rather than cones. Albinism specifically affects the rod cells, but the number and distribution of the cones is unaffected. In contrast, the retinas of birds are cone rich meaning that the vision of albino birds is affected less than albino mammals.
Reduced protection from sunlight in albino creatures
Melanin protects the skin fromultra-violet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
radiation in sunlight. Melanosome
A melanosome is an organelle found in animal cells and is the site for synthesis, storage and transport of melanin, the most common light-absorbing pigment found in the animal kingdom. Melanosomes are responsible for color and photoprotection i ...
s block harmful electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
from the sun while allowing beneficial frequencies to enter the body. This means some animals may die from UV radiation due to a lack of protection. Albino humans must use an excessive amount of sunscreen, even if the sun is hidden behind the clouds.
Survival disadvantages
Many animals with albinism lack their protectivecamouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
and are therefore less able to conceal themselves from their predators or prey: The survival rate of animals with albinism in the wild can be low,Ilo Hiler, Albinos. ''Young Naturalist''. The Louise Lindsey Merrick Texas Environment Series, No. 6, pp. 28–31. Texas A&M University Press, College Station (1983) however, it has been stated that in studies where animals had many places to hide, predators captured albino and normally coloured animals at the same rate. Furthermore, albino animals may be excluded from families or other groups, or rejected as mates.
The novelty of albino animals has occasionally led to their protection by groups such as the Albino Squirrel Preservation Society. They have also been protected in studies on their ecology, sociology and behaviour.
Reduced viability
Studies onmedaka
The Japanese rice fish (''Oryzias latipes''), also known as the medaka, is a member of genus ''Oryzias'' ( ricefish), the only genus in the subfamily Oryziinae. This small (up to about ) native of East Asia is a denizen of rice paddies, marshes, ...
fish in the laboratory, i.e. with no predators, sufficient food supply, controlled temperatures, etc., found that albinos had considerably reduced viability; from 800 albino embryos, only 29 survived to full adulthood. Early studies on fish led some researchers to describe albinism as a "semi-lethal mutation".
Hearing disorders
Pigmentation disorders such as albinism are occasionally associated with hearing impairments in mice, rats, guinea pigs and cats.In mammals
Artificially selected
Intentionally bred albinistic strains of some animal species are commonly used as model organisms in biomedical research and also as pets. Examples include theBALB/c
BALB/c is an albino, laboratory-bred strain of the house mouse from which a number of common substrains are derived. Now over 200 generations from New York in 1920, BALB/c mice are distributed globally, and are among the most widely used inbred ...
mouse and Wistar and Sprague Dawley rat
A laboratory rat or lab rat is a brown rat of the subspecies '' Rattus norvegicus domestica'' which is bred and kept for scientific research. While less commonly used for research than mice (see laboratory mouse), rats have served as an importa ...
strains, laboratory rabbits and ferrets. Albino axolotl
The axolotl (; from nci, āxōlōtl ), ''Ambystoma mexicanum'', is a paedomorphic salamander closely related to the tiger salamander. Axolotls are unusual among amphibians in that they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis. I ...
(an amphibian) are also used widely in the laboratory as their transparent skin allows observation of the underlying tissues during limb regeneration. Some researchers have argued that albino animals are not always the best choice for scientific studies due to the consequences of albinism (e.g. hearing and visual impairments).
Many individual albino mammals are in captivity and were caught while young. It is doubtful whether these individuals would have survived to become adults without the protection and care they receive in captivity.
Naturally occurring
 It has been claimed that "Squirrels are the only known albino mammal to survive successfully in the wild". The retina of the squirrel (''
It has been claimed that "Squirrels are the only known albino mammal to survive successfully in the wild". The retina of the squirrel (''Sciurus carolinensis
The eastern gray squirrel (''Sciurus carolinensis''), also known, particularly outside of North America, as simply the grey squirrel, is a tree squirrel in the genus ''Sciurus''. It is native to eastern North America, where it is the most prodi ...
'') is unusual for mammals as it is rich in cones. Central cell densities are less than 5% lower in albino squirrels than in pigmented individuals. This relatively minor disruption to vision is thought to assist in the survivability of albino squirrels in the wild. This is supported by observations that the behaviour of albinos in the wild, e.g. leaping from branch to branch, is similar to pigmented squirrels.
A 2012 survey of the literature reported that in India, there were several records of albino mammals including the tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ...
, lesser mouse-tailed bat, chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
, common palm civet, northern palm squirrel
The northern palm squirrel (''Funambulus pennantii'') also called the five-striped palm squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. Some authorities recognize two subspecies, ''F. p. pennantii'' and ''F. p. argentescens''. It is a ...
, five-striped palm squirrel and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
.
Albino macaques have been reported in several occasions including a toque macaque
The toque macaque (; ''Macaca sinica'') is a reddish-brown-coloured Old World monkey endemic to Sri Lanka, where it is known as the ''rilewa'' or ''rilawa'' ( Sinhala: රිළවා), (hence "rillow" in the ''Oxford English Dictionary''). Its n ...
(''M. sinica''), rhesus macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally ...
(''M. mulatta''), and bonnet macaque
The bonnet macaque (''Macaca radiata''), also known as zati,Chambers English Dictionary is a species of macaque endemic to southern India. Its distribution is limited by the Indian Ocean on three sides and the Godavari and Tapti Rivers, along wit ...
(''M. radiata'').
Albinism was observed in jungle cats (''Felis chaus'') and jackals
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
(''Canis aureus'') along the coastline of the southern Western Ghats (Kerala and Kanyakumari coast, India). Albinism was observed in jungle cats from the Amaravila area of Trivandrum district in the Kerala State. Albinism in jackals was observed from the Polooni area in Malappuram district and Chaliyam area of Calicut district (Kerala). As albinism is observed in those areas where the density of these mammals is comparatively low, it is concluded that continuous inbreeding could be the reason for expression of albinism.
A study on albinistic prairie vole
The prairie vole (''Microtus ochrogaster'') is a small vole found in central North America. The vole has long, coarse grayish-brown fur on the upper portion of the body and yellowish fur on the lower portion of the body. It has short ears and a ...
s (''Microtus ochrogaster'') found that albinism in this species conferred an advantage for the males compared to the wild-type; albino males had higher mount frequencies than wild-type males. In addition, the albinos had greater differential fertilizing capacity.
Albinism can also occur in marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s and monotremes as well such as echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
s, kangaroo
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern ...
s, koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the w ...
s, possums
Possum may refer to:
Animals
* Phalangeriformes, or possums, any of a number of arboreal marsupial species native to Australia, New Guinea, and Sulawesi
** Common brushtail possum (''Trichosurus vulpecula''), a common possum in Australian urban a ...
, wallabies
A wallaby () is a small or middle-sized macropod native to Australia and New Guinea, with introduced populations in New Zealand, Hawaii, the United Kingdom and other countries. They belong to the same taxonomic family as kangaroos and so ...
and wombat
Wombats are short-legged, muscular quadrupedal marsupials that are native to Australia. They are about in length with small, stubby tails and weigh between . All three of the extant species are members of the family Vombatidae. They are ada ...
s as well.
Marine mammals
 The costs of albinism for marine mammals may include reduced heat absorption in colder waters, poor camouflage from predators, increased sensitivity to sunlight, and impaired visual communication. Despite the costs, some individuals do reach adult age and breeding status.
Albino dolphins were first sighted in the Gulf of Mexico in 1962. Since 1994, three further individuals have been seen. These tend to be pink in colour due to blood vessels showing through the blubber and unpigmented skin.
A report published in 2008 stated that in marine mammals, "anomalously white" individuals have been reported for 21 cetacean species and 7
The costs of albinism for marine mammals may include reduced heat absorption in colder waters, poor camouflage from predators, increased sensitivity to sunlight, and impaired visual communication. Despite the costs, some individuals do reach adult age and breeding status.
Albino dolphins were first sighted in the Gulf of Mexico in 1962. Since 1994, three further individuals have been seen. These tend to be pink in colour due to blood vessels showing through the blubber and unpigmented skin.
A report published in 2008 stated that in marine mammals, "anomalously white" individuals have been reported for 21 cetacean species and 7 pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammal, marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant family (biology ...
species but there were no known reports of anomalously white sea otters
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smalle ...
(''Enhydra lutris'') or sirenia
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise two distinct ...
ns.
Whales and dolphins also may appear white if extensively scarred, or covered with a fungus, such as ''Lacazia loboi
''Lacazia'' is a genus of fungi containing the single species ''Lacazia loboi'', which is responsible for Lobo's disease. It is a member of the order Onygenales.
Description and natural habitats
''Lacazia loboi'' is a yeast-like fungus that c ...
''.
Famous albino mammals
Famous albino mammals include Migaloo, ahumpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hu ...
living off the coast of Australia; Pinky, a bottlenose dolphin living in and around in Calcasieu Lake
Calcasieu Lake is a brackish lake located in southwest Louisiana, United States, located mostly within Cameron Parish, Louisiana, Cameron Parish. The Lake, also known as Big Lake to the local population, is paralleled on its west shore by Louisi ...
, Louisiana; Carolina Snowball, a popular albino bottlenose dolphin displayed at the Miami Seaquarium in the early 1960s; Snowflake
A snowflake is a single ice crystal that has achieved a sufficient size, and may have amalgamated with others, which falls through the Earth's atmosphere as snow.Knight, C.; Knight, N. (1973). Snow crystals. Scientific American, vol. 228, no. ...
, a Barcelona Zoo gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
, and Mahpiya Ska, ( Sioux for White Cloud), a buffalo in Jamestown, North Dakota
Jamestown is a city in Stutsman County, North Dakota, United States. It is the county seat of Stutsman County. The population was 15,849 at the 2020 census, making it the ninth largest city in North Dakota. Jamestown was founded in 1883 and is ...
, and inspiration for Herman Melville
Herman Melville ( born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); ''Typee'' (1846), a rom ...
's novel ''Moby-Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is the sailor Ishmael's narrative of the obsessive quest of Ahab, captain of the whaling ship ''Pequod'', for revenge against Moby Dick, the giant whi ...
'', a sperm whale known as Mocha Dick
Mocha Dick (; died 1838) was a male sperm whale that lived in the Pacific Ocean in the early 19th century, usually encountered in the waters near Mocha Island, off the central coast of Chile. American explorer and author Jeremiah N. Reynolds p ...
.
In birds
The most important pigments that determine plumage colouration in birds are melanines and carotenoids. The latter are ingested in food and transformed into colour pigments by enzymes. Aberrations in this pigmentation are mostly caused by food deficiencies and usually do not have a genetic basis. Well-known examples areflamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbea ...
s, which owe their distinct pink colour to the presence of red carotenoids in their natural food. When these carotenoids are in short supply, these birds appear white after the next moult
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
. Mutations causing changes in carotenoid-based colour pigments are rare; melanine mutations occur much more frequently. Two types of melanin, eumelanin and phaeomelanin, are present in birds. In the skin and eyes, only eumelanin is present. In some bird species, the colour is completely caused by eumelanin, however, both types of melanin are found in most species. In birds, albinism has been defined as "a total lack of both melanins in feathers, eyes and skin as a result of an inherited absence of tyrosinase", however, this ignores the effects of other pigments and structural colours.
An albino bird has a white beak, white plumage, non-coloured skin, white talons
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
and pink or red eyes.
Albinism is only seen in about 1 of every 1,800 birds. The two most common species of albino birds are the common house martin
The common house martin (''Delichon urbicum''), sometimes called the northern house martin or, particularly in Europe, just house martin, is a migratory passerine bird of the swallow family which breeds in Europe, north Africa and across the ...
and the American robin. Famous albino birds include "Snowdrop
''Galanthus'' (from Ancient Greek , (, "milk") + (, "flower")), or snowdrop, is a small genus of approximately 20 species of bulbous perennial herbaceous plants in the family Amaryllidaceae. The plants have two linear leaves and a single sm ...
", a Bristol Zoo
Bristol Zoo was a zoo in the city of Bristol in South West England. The zoo's stated mission was to "maintain and defend” biodiversity through breeding endangered species, conserving threatened species and habitats and promoting a wider unders ...
penguin.
In one study, albinism in birds has been categorised according to the extent of pigment absence. –
# Total albinism – a simultaneous complete absence of melanin from the eyes, skin, and feathers. This is the rarest form. Only 7% of 1,847 cases of avian albinism examined was this type.
# Incomplete albinism – when melanin is not simultaneously absent from the eyes, skin and feathers.
# Imperfect albinism – when melanin is reduced in the eyes, skin and feathers.
# Partial albinism – when albinism is localized to certain areas of the body.
However, it has been argued that the definition of albinism precludes the possibility of "partial albinism" in which a mostly white bird shows some form of melanin pigmentation. "It is simply impossible, just like being 'partially pregnant'.
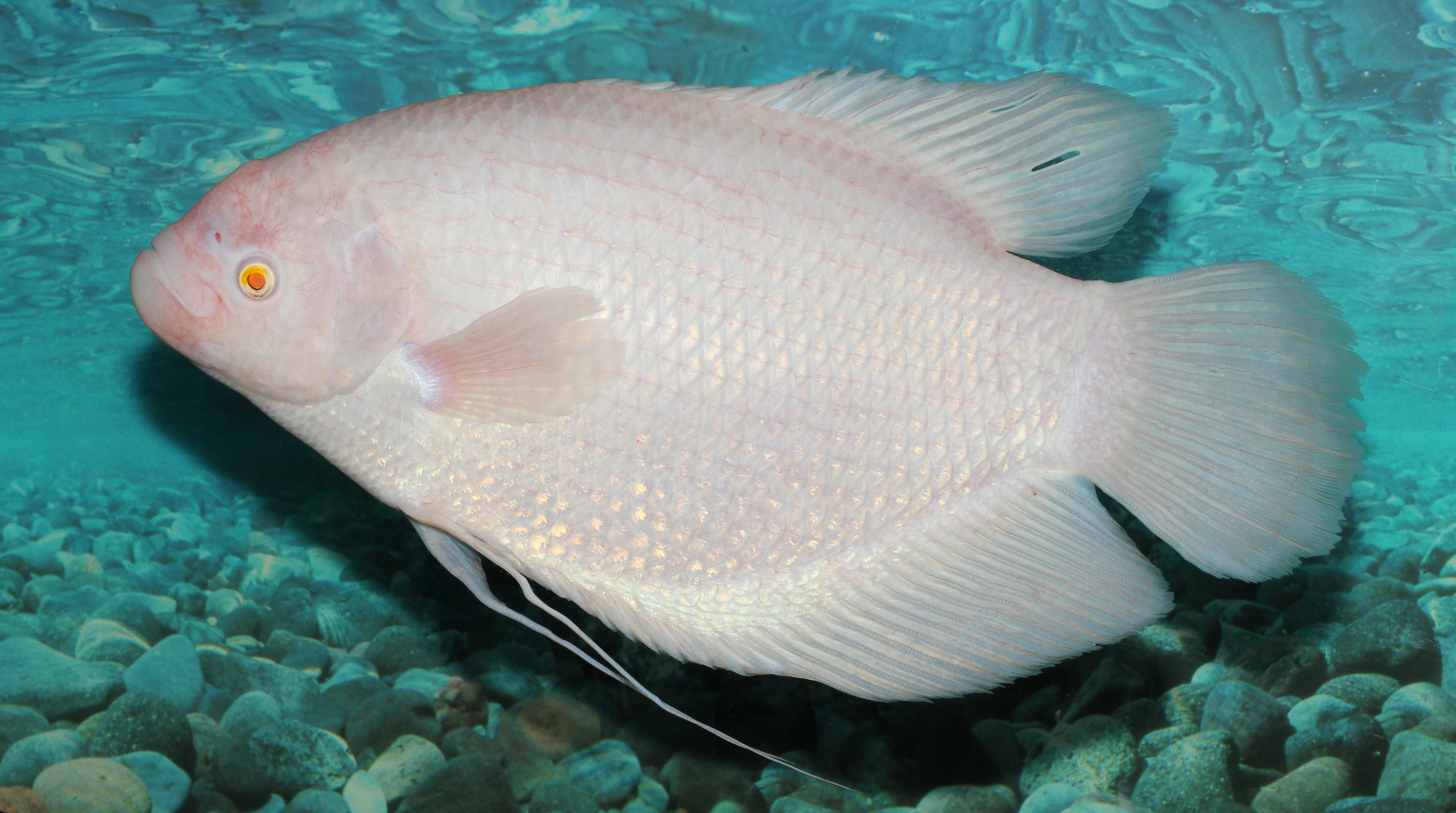
In fish
As with other animals, it has been stated that for fish to be properly described as "albino", they must have a white body and pink or red eyes.Artificially selected

Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often ca ...
have three types of chromatophores—iridophores, melanophores, and xanthophores—which produce silver, black, and yellow pigmentation respectively. Zebrafish that lack iridophores are known as ''roy mutants'', those that lack melanophores as ''albino mutants'', and those which lack both melanophores and iridophores are ''ruby mutants''. The gross eye morphology, feeding and swimming behaviours between wild-type and albino zebrafish were indistinguishable, except under dim or bright light or low contrast.
In mammals, albinism is occasionally associated with hearing impairments. However, when tested, there was no differences in responses between wild-type and albinistic European wels catfish (''Silurus glanis
The wels catfish ( or ; ''Silurus glanis''), also called sheatfish or just wels, is a large species of catfish native to wide areas of central, southern, and eastern Europe, in the basins of the Baltic, Black and Caspian Seas. It has been introd ...
'') and South American bronze catfish ('' Corydoras aeneus''). Similarly, Mexican blind cave fish (''Astyanax mexicanus
The Mexican tetra (''Astyanax mexicanus''), also known as the blind cave fish, blind cave characin, and blind cave tetra, is a freshwater fish of the family Characidae of the order Characiformes. The type species of its genus, it is native to ...
'') do not differ in hearing sensitivity from the normally pigmented and eyed surface-dwelling populations. Fish lack melanin in the inner ear, meaning that hearing in fishes is less likely to be affected by albinism than in mammals.
Naturally occurring
There are several reports of total albinism in both freshwater and marine fish, however, frequently captured albino fish are only reported in aquarium magazines and local newspapers. The incidence of albinism can be artificially increased in fish by exposing the eggs to heavy metals (e.g. arsenic, cadmium, copper, mercury, selenium, zinc). In the wild, albinism is reasonably common in theteleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tele ...
s, especially the Pleuronectiformes
A flatfish is a member of the ray-finned demersal fish order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating ...
(flatfish), however, it is rarely reported in the Elasmobranchii, elasmobranchs. Albinism has been reported in hagfish, lampreys, sharks, rays and numerous teleost fishes, e.g. catfishes, grunts or cyprinids.
In Actinopterygii
Albino and normally pigmented channel catfish (''Ictalurus punctatus'') differ in their characteristics. Normal individuals of this species are superior to albinos in body weight and total length. Albinos crossed with other albinos require 11 days longer to spawn and produce smaller egg masses. These masses contain eggs of lighter weight with poorer hatchability than crosses of normal fish. The albino fish have lower survival rates than normal fish but dress-out percentages are nearly equal. Some wild cave fish have populations that are albinistic. The Mexican cave tetra is a species that has evolved specialized characteristics in a series of independent caves. One of these is albinism linked to the OCA2, Oca2 gene, a known pigmentation gene, This trait has evolved independently in at least two caves.In Chondrichthyes
In the class Chondrichthyes, several species of naturally occurring albino rays and sharks have been recorded. Furthermore, an albino individual spotted ratfish (''Hydrolagus colliei'') from the order Chimaeriformes has been reported. Albinistic individuals of the following shark species have been reported: * Basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') – 2 cases * Broadnose sevengill shark (''Notorynchus cepedianus'') * Great white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias'') * Grey smooth-hound (''Mustelus californicus'') – 2 cases * Japanese topeshark (''Hemitriakis japanica'') * Japanese wobbegong (''Orectolobus japonicus'') * Java shark (''Carcharhinus amboinensis'') * Leopard shark (''Triakis semifasciata'') * Narrownose smooth-hound (''Mustelus schmitti'') * Pigeye shark (''Carcharhinus amboinensis'') * Porbeagle (''Lamna nasus'') * Scalloped hammerhead shark (''Sphyrna lewini'') * Spiny dogfish (''Squalus acanthias'') * Tawny nurse shark (''Nebrius ferigineus'') * Tiger shark (''Galeocerdo cuvier'') – embryo * Whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') * Whitespotted bamboo shark (''Chiloscyllium plagiosum'') * Zebra shark (''Stegostoma fasciatum'') A study published in 2006 reported albinistic individuals of the following ray species: * Bat ray (''Myliobatis californica'') * Common skate (''Raja batis'') * Common stingray (''Dasyatis pastinaca'') * Common torpedo (''Torpedo torpedo'') * Cownose ray (''Rhinoptera bonasus'') * Giant electric ray (''Narcine entemedor'') * Giant oceanic manta ray (''Manta birostris'') * Ocellate spot skate (''Okamejei kenojei'') * Southern stingray (''Dasyatis americana'') * Thornback ray (''Raja clavata'') * Cuckoo ray (''Raja naevus'')In Hyperoartia
There are several reports of albino lampreys and it has been estimated that this occurs at a frequency of one in 100,000 normal individuals.In Sarcopterygii
Albinism in the African lungfish has been reported on at least two occasions.In reptiles
 Many reptiles labeled as albino are, in fact, not completely lacking in all colour pigments. They are actually Amelanism, amelanistic, not albino. Reptiles often possess at least two pigments. Among the most common are xanthin (yellow) and erythrin (red). An amelanistic reptile therefore, may still have pale yellow, orange, or red pigmentation.
The California Academy of Science, in the Steinhart Aquarium, as of 2015, has on display an albino American alligator named "Claude (alligator), Claude". The alligator is partially blind because of lack of pigment in its eyes. The albino alligator hatched from the egg in 1995 in Florida, and was brought to the academy in 2008. This alligator would not have survived in the wild because its whiteness would have made it too easy a prey object. The only known albino alligators are in captivity. While extremely rare, white-coloured crocodiles and alligators do exist in other places. However, most of these animals are Leucism, leucistic given that they have a general loss of pigmentation with some colour tinges remaining on their bodies although looking at first like other albino creatures, thus creating the misconception that the reptiles are albino themselves when they are not. Four such alligators are kept at the Gatorland theme park in the U.S. state of Florida. In Australia, a crocodile believed to be "part-albino" and nicknamed by people in the area as "Michael Jackson", attacked and killed a man.
In snakes, partial absence of pigment is more common than absolute albinism. For snakes that are usually patterned in colours, they appear as a faint blue, peach or yellowish. In these cases, there has been a genetic mutation in the melanin and pigment delivery. The appearance comes from the inability for full colours to be present, such as black, red, brown and others. The eyes of an albino snake are typically red or pink. Albino snakes can remain in the sunlight for several hours with minimal harm. Corn snakes and snakes of larger types, such as a Boa (genus), boa or diamondback snakes, are the most commonly affected by albinism often appearing to be a pinkish or yellowish colour.
Albino tortoises and turtles are uncommon; Sulcata tortoises are the most likely type of turtle to express albinism. The shells have an almost yellow colouration and they have pink eyes. For turtles, a pure white colour is nearly impossible, even with albinism. Albino turtles can have a longer lifespan than many other albino animals; their hard shells help to prevent predation and other environmental challenges. Vision and sensory organs are slightly affected.
In 2012, an albino Dactyloidae, anole was reported and photographed. In 2007, it was reported that an albino stumpy-tail lizard (possibly a shingleback lizard), approximately long and roughly 1 year old, had been found in Victoria, Australia.
There are three known "albino" strains of leopard gecko, however, breeders state that albinos are generally recognized by their lack of black pigment and having red eyes is not a requirement to be considered an albino. These three strains are called "tremper albinos", "rainwater albinos" and "bell albinos".
Many reptiles labeled as albino are, in fact, not completely lacking in all colour pigments. They are actually Amelanism, amelanistic, not albino. Reptiles often possess at least two pigments. Among the most common are xanthin (yellow) and erythrin (red). An amelanistic reptile therefore, may still have pale yellow, orange, or red pigmentation.
The California Academy of Science, in the Steinhart Aquarium, as of 2015, has on display an albino American alligator named "Claude (alligator), Claude". The alligator is partially blind because of lack of pigment in its eyes. The albino alligator hatched from the egg in 1995 in Florida, and was brought to the academy in 2008. This alligator would not have survived in the wild because its whiteness would have made it too easy a prey object. The only known albino alligators are in captivity. While extremely rare, white-coloured crocodiles and alligators do exist in other places. However, most of these animals are Leucism, leucistic given that they have a general loss of pigmentation with some colour tinges remaining on their bodies although looking at first like other albino creatures, thus creating the misconception that the reptiles are albino themselves when they are not. Four such alligators are kept at the Gatorland theme park in the U.S. state of Florida. In Australia, a crocodile believed to be "part-albino" and nicknamed by people in the area as "Michael Jackson", attacked and killed a man.
In snakes, partial absence of pigment is more common than absolute albinism. For snakes that are usually patterned in colours, they appear as a faint blue, peach or yellowish. In these cases, there has been a genetic mutation in the melanin and pigment delivery. The appearance comes from the inability for full colours to be present, such as black, red, brown and others. The eyes of an albino snake are typically red or pink. Albino snakes can remain in the sunlight for several hours with minimal harm. Corn snakes and snakes of larger types, such as a Boa (genus), boa or diamondback snakes, are the most commonly affected by albinism often appearing to be a pinkish or yellowish colour.
Albino tortoises and turtles are uncommon; Sulcata tortoises are the most likely type of turtle to express albinism. The shells have an almost yellow colouration and they have pink eyes. For turtles, a pure white colour is nearly impossible, even with albinism. Albino turtles can have a longer lifespan than many other albino animals; their hard shells help to prevent predation and other environmental challenges. Vision and sensory organs are slightly affected.
In 2012, an albino Dactyloidae, anole was reported and photographed. In 2007, it was reported that an albino stumpy-tail lizard (possibly a shingleback lizard), approximately long and roughly 1 year old, had been found in Victoria, Australia.
There are three known "albino" strains of leopard gecko, however, breeders state that albinos are generally recognized by their lack of black pigment and having red eyes is not a requirement to be considered an albino. These three strains are called "tremper albinos", "rainwater albinos" and "bell albinos".
In amphibians
As with reptiles, many amphibians labeled as albino are, in fact, not completely lacking in all colour pigments. They are actually amelanistic, not albino. Amphibians have six types of chromatophore in their skin, i.e. melanophores, xanthophores, erythrophores, leucophores, cyanophores and iridophores. An amelanistic amphibian therefore, may still have various pigmentation. The incidence of albinism in frogs, salamanders, and newts is relatively higher than other taxa. It has been estimated that one in four hundred of these animals is albino. When albino tadpoles hatch, they are almost transparent. This may help camouflage them initially, however, after two weeks, when their hindlegs begin to emerge, they become milky white. A survey in 2001 found hundreds of tiny albino plains leopard frogs, but when the researcher returned a few months later, not a single albino adult could be found.
In European Salamandra, Salamandridae, albinism has been recorded in the fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra''), gold-striped salamander (''Chioglossa lusitanica''), Italian crested newt (''Triturus carnifex''), marbled newt (''Triturus marmoratus''), Iberian ribbed newt (''Pleurodeles waltl''), alpine newt (''Ichthyosaura alpestris'') and two sub-species of the smooth newt (''Lissotriton vulgaris vulgaris'' and ''Lissotriton vulgaris meridionalis'').
The incidence of albinism in frogs, salamanders, and newts is relatively higher than other taxa. It has been estimated that one in four hundred of these animals is albino. When albino tadpoles hatch, they are almost transparent. This may help camouflage them initially, however, after two weeks, when their hindlegs begin to emerge, they become milky white. A survey in 2001 found hundreds of tiny albino plains leopard frogs, but when the researcher returned a few months later, not a single albino adult could be found.
In European Salamandra, Salamandridae, albinism has been recorded in the fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra''), gold-striped salamander (''Chioglossa lusitanica''), Italian crested newt (''Triturus carnifex''), marbled newt (''Triturus marmoratus''), Iberian ribbed newt (''Pleurodeles waltl''), alpine newt (''Ichthyosaura alpestris'') and two sub-species of the smooth newt (''Lissotriton vulgaris vulgaris'' and ''Lissotriton vulgaris meridionalis'').
Genetics
Genetic studies of albinism in amphibians have focused on mutations in thetyrosinase
Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxy ...
gene. The albino phenotype of the Northern leopard frog, leopard frog (''Rana pipiens'') has been attributed to a failure in Regulation of gene expression, post-translational control in a single Dominance (genetics), recessive tyrosinase gene which still has some tyrosinase and L-DOPA, DOPA oxidase activity. This is in contrast with Albinism#In mammals, mammals, some of which have mutations that show no tyrosinase or DOPA oxidase activity in albinos. The albino phenotype of the Pelophylax nigromaculatus, pond frog (''Pelophylax nigromaculatus'') has been attributed to one of three mutations that created a dysfunctional tyrosinase. Two of those mutations involve an insertion of a thymine (T), a frameshift mutation, resulting in a truncated Gene isoform, isoform of the TYR protein that is defective. The other mutation involves the deletion of a Genetic code#Codons, codon, three nucleotides that code for a lysine (Lys). In the Japanese wrinkled frog, wrinkled frog (''Glandirana rugosa'') and in the Fejervarya kawamurai, rice frog (''Fejervarya kawamurai''), a substitution from a guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
(G) to an adenine (A) creates a missense mutation, in which a glycine (Gly) changes to an aspartic acid (Asp) and an arginine (Arg), respectively. These changes in the Peptide, polypeptide chain causes a dysfunctional tyrosinase.
In invertebrates
Albinism in molluscs has been recognized to be a hereditary phenomenon at least since 1900. Albinism in molluscs can exist to a variable degree. Sometimes an individual snail has a normally pigmented body, but the shell is completely without the normal pigmentation because of a defect in the cells of the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. Shells of certain mollusc species can be translucent when they lack the normal pigmentation.In insects
The neurohormone [His7]-corazonin induces darkening of the cuticle of ''Locusta migratoria''. The Okinawa strain of this species is deficient in [His7]-corazonin and is albino. One of the typical features of ''Locusta migratoria'' is that they are gregarious locusts. However, the albino strain shows more solitarious behaviour. The ''yellow'' mutation in Drosophila, fruit flies is a mutation causing a congenital lack of normal pigment; it is a similar phenomenon to albinism in other organisms.In echinoderms
The Japanese sea cucumber (''Apostichopus japonicus'') is an echinoderm that is caught in the wild or cultivated for food. Normal Japanese sea cucumbers start to develop pigmentation when they are about 1 cm long. The upperside becomes a dull, yellowish -brown to maroon and the underside a light brown. The body walls of adult, albino Japanese sea cucumbers contain only 0.24% melanin compared to 3.12% in normal adults. The difference in melanin content becomes visually apparent at 60 days of age. The epidermis is thinner in the albinos and contains fewer melanocytes. Albino individuals are similar to normal individuals in growth rate, digestion rate and fertility. Astaxanthin is the main carotenoid in marine crustaceans (and fish). It has been shown that adding astaxanthin to the feed can improve the skin and muscle colour of marine organisms and thereby increase their commercial and ornamental value.In arachnids
"Depigmented" arthropods have been found, usually in cave populations. "Albino" individuals of normally red citrus red mites (''Panonychus citri'') occasionally appear in laboratory colonies, however, these still contain green and yellow pigments. This albinism does not affect mortality.Related pigment disorders
In some animals, albinism-like conditions may affect other pigments or pigment-production mechanisms: * "Whiteface," a condition that affects some parrot species, is caused by a lack of psittacins.Hesford, Clive (January 1998)"The Parblue Puzzle: Part 4—Common Parblue Varieties: The Cockatiel [''Nymphicus hollandicus'']"
in ''The Genetics of Colour in the Budgerigar and Other Parrots''
 * Axanthism is a condition common in reptiles and amphibians, in which xanthophore#Xanthophores and erythrophores, xanthophore metabolism is affected rather than Chemical synthesis, synthesis of melanin, resulting in reduction or absence of red and yellow pteridine pigments.
* Leucism differs from albinism in that the melanin is, at least, partially absent but the eyes retain their usual colour. Some leucistic animals are white or pale because of
* Axanthism is a condition common in reptiles and amphibians, in which xanthophore#Xanthophores and erythrophores, xanthophore metabolism is affected rather than Chemical synthesis, synthesis of melanin, resulting in reduction or absence of red and yellow pteridine pigments.
* Leucism differs from albinism in that the melanin is, at least, partially absent but the eyes retain their usual colour. Some leucistic animals are white or pale because of chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...
(pigment cell) defects, and do not lack melanin.
* Melanism is the direct opposite of albinism. An unusually high level of melanin pigmentation (and sometimes absence of other types of pigment in species that have more than one) results in an appearance darker than non-melanistic specimens from the same gene pool."Feather Colors: What We See"by Dr. Julie Feinstein of the American Museum of Natural History (NY), in ''Birder's World Magazine'' online archive; sourced December 2006, actual authoring/publication date unspecified.
In plants

 In plants, albinism is characterised by partial or complete loss of chlorophyll pigments and incomplete differentiation of chloroplast membranes. Albinism in plants interferes with
In plants, albinism is characterised by partial or complete loss of chlorophyll pigments and incomplete differentiation of chloroplast membranes. Albinism in plants interferes with photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
, which can reduce survivability. Some plant variations may have white flowers or other parts. However, these plants are not totally devoid of chlorophyll. Terms associated with this phenomenon are "hypochromia" and "albiflora".
Plants that are pale simply from being in the dark are termed etiolation, etiolated.
Albino redwoods are rare examples of an albino tree with white needles; despite its lack of chlorophyll it may grow to substantial size as a parasite, usually on the base of the (normal) redwood tree from which it first grew. Only about sixty examples of albino redwoods are known. Additionally, an even smaller number of "chimeric" redwood trees have both normal and white needles.
Albinism has frequently occurred in progeny of Black Tartarian, Bing and Hedelfingen varieties of sweet cherry.
Some herbicides (e.g. glyphosate and triazines) can cause partial chlorosis in plants, even several seasons or years after applicating.
In human culture
The Albino Squirrel Preservation Society was founded at the University of Texas at Austin in 2001. Members of the society at the University of North Texas petitioned for an election to name their albino squirrel as the university's secondary mascot. The University of Louisville in Kentucky also has a documented population of albino squirrels. Albino animals are often kept as pets, for example, African clawed frog, guinea pigs and peacocks.See also
* Albinism in humans * Solid white (chicken plumage)#Albinism and partial albinism, Albinism in chickens * Tree squirrel#Albino and white squirrels, Albino and white squirrels * Dyschromia * Erythrism, unusually red pigmentation * Isabelline (colour)#In animals, Isabellinism * Leukoderma * Mongolian spot * Xanthochromism, unusually yellow pigmentation and lack of yellow pigment * LeucismReferences
{{Authority control Albinism, Animal coat colors