Agência Espacial Brasileira on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Brazilian Space Agency ( pt, Agência Espacial Brasileira; AEB) is the civilian authority in
 The then president
The then president

Brazilian Space Agency. Retrieved on 2009-07-30. It is located in the peninsula of Alcântara, in the state of
GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved on 2009-07-30. This region presents some excellent requirements, such as low
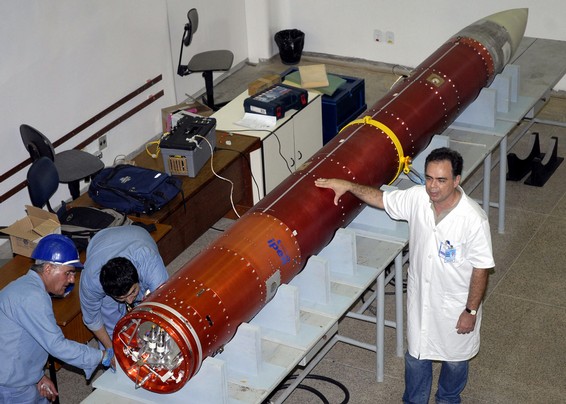


 The Brazilian Space Agency has operated a series of sounding rockets.
* Sonda I
* Sonda II
* Sonda III
* Sonda IV
*
The Brazilian Space Agency has operated a series of sounding rockets.
* Sonda I
* Sonda II
* Sonda III
* Sonda IV
*
 Brazil has forged a cooperative arrangement with Germany to develop a dedicated micro-satellite launch vehicle. As a result, the VLM "Veiculo Lançador de Microsatelites" (Microsatelite Launch Vehicle) based on the S50 rocket engine is being studied, with the objective of orbiting satellites up to 150 kg in circular orbits ranging from 250 to 700 km. The first qualifying and test flight will be on 2022 from the Alcântara Space Center. The second flight is scheduled for the following years as part of the SHEFEX mission, to be conducted also from Alcântara, in partnership with the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Brazil has forged a cooperative arrangement with Germany to develop a dedicated micro-satellite launch vehicle. As a result, the VLM "Veiculo Lançador de Microsatelites" (Microsatelite Launch Vehicle) based on the S50 rocket engine is being studied, with the objective of orbiting satellites up to 150 kg in circular orbits ranging from 250 to 700 km. The first qualifying and test flight will be on 2022 from the Alcântara Space Center. The second flight is scheduled for the following years as part of the SHEFEX mission, to be conducted also from Alcântara, in partnership with the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
The Internet Encyclopedia of Science. Retrieved on 2009-07-29. The vehicle's first stage has four solid fuel motors derived from the Sonda sounding rockets. It is intended to deploy 100 to 380 kg
Brazilian Air Force. Retrieved on 2012-03-06. . After subsequent delays, the project was cancelled in 2016.
 The Brazilian Space Agency was developing a new family of
The Brazilian Space Agency was developing a new family of
SpaceDaily.com. Retrieved on 2009-07-29. The five rockets of the Southern Cross family will be based on Russia's Angara vehicle and liquid-propellant engines. The first stage of the VLS Gama, Delta and Epsilon rockets was to be powered by a unit based on the RD-191 engine. The second stage, which will be the same for all the Southern Cross rockets, will be driven by an engine based on the Molniya rocket. The third stage will be a solid-propellant booster based on an upgraded version of the
 Brazil is also investing in the domain of the hypersonic technology. The 14-X, a
Brazil is also investing in the domain of the hypersonic technology. The 14-X, a
 A number of different engines were developed for usage on the several launch vehicles:
* S-10-1 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 27 kN.
* S-10-2 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 4.20 kN, burn time: 32 s.
* S-20 Avibras solid rocket engine. Used on
A number of different engines were developed for usage on the several launch vehicles:
* S-10-1 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 27 kN.
* S-10-2 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 4.20 kN, burn time: 32 s.
* S-20 Avibras solid rocket engine. Used on
GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved on 2011-01-17. Pontes was the first Brazilian astronaut,
NASA. Retrieved on 2011-01-17. having launched with the
 The Brazilian Space Agency is a bilateral partner of
The Brazilian Space Agency is a bilateral partner of
Official site in Portuguese
AEB on Twitter
{{authority control Space agencies Scientific organisations based in Brazil Government agencies of Brazil 1994 establishments in Brazil Organisations based in Brasília
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
responsible for the country's space program
A space program is an organized effort by a government or a company with a goal related to outer space.
Lists of space programs include:
* List of government space agencies
* List of private spaceflight companies
* List of human spaceflight prog ...
. It operates a spaceport
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport'', and even more so ''cosmodrome'', has traditionally been used for sites capable ...
at Alcântara, and a rocket launch site at Barreira do Inferno. It is the largest and most prominent space agency in Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
.
The Brazilian Space Agency is the institutional successor of Brazil's space program, which had been managed by the Brazilian military
The Brazilian Armed Forces ( pt, Forças Armadas Brasileiras, ) are the unified military forces of the Federative Republic of Brazil. Consisting of three service branches, it comprises the Brazilian Army (including the Brazilian Army Aviati ...
until its transfer to civilian control on 10 February 1994. It suffered a major setback in 2003, when a rocket explosion killed 21 technicians. Brazil successfully launched its first rocket into space, the VSB-30
VSB-30 - "''Veículo de Sondagem Booster – 30''" (Booster Sounding Vehicle) or "''Foguete Suborbital VSB-30''" is the designation of a Brazilian sounding rocket, which replaced the Skylark rocket at ''Esrange''.
The VSB-30 is based on the VS- ...
, on 23 October 2004 from the Alcântara Launch Center
Alcantara, Alcântara ( Portuguese), Alcántara ( Spanish), Alcàntara, Alcàntera, El-Qantarah and (El) Kantara are all transliterations of the Arabic word ''al qantara'' (القنطرة), meaning "the bridge".
Alcantara may refer to:
People
* ...
; several other successful launches have followed. Brazil was briefly a partner in the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
, and in 2006, AEB astronaut Marcos Pontes
Marcos Cesar Pontes (born 11 March 1963) is a Brazilian Air Force pilot, engineer, AEB astronaut, politician and author. He became the first South American and the first Lusophone to go into space when he docked onto the International Space Sta ...
became the first Brazilian and the first native Portuguese-speaker to go into space, when he arrived at the ISS for a week. During his trip, Pontes carried out eight experiments selected by the Brazilian Space Agency, including testing flight dynamics of saw blades in zero gravity environments. In June 2021, the AEB signed the Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords are a series of non-binding multilateral agreements between the United States government and other world governments participating in the Artemis Program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2025, with the u ...
to the joint exploration of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
from 2024 as part of the Artemis program
The Artemis program is a robotic and human Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) along with three partner agencies: European Space Agency (ESA), Japan Aerospace Exploration ...
.
History
 The then president
The then president Jânio Quadros
Jânio da Silva Quadros (; January 25, 1917 – February 16, 1992) was a Brazilian lawyer and Politics of Brazil, politician who served as the 22nd president of Brazil from January 31 to August 25, 1961, when he resigned from office. He als ...
in 1960 established a commission that elaborated a national program for the space exploration. As a result of this work, in August 1961, the Organization Group of the National Commission of Space Activities (Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
: ''Grupo de Organização da Comissão Nacional de Atividades Espaciais'') was formed, operating in São José dos Campos
São José dos Campos (, meaning Saint Joseph of the Fields) is a major city and the seat of the municipality of the same name in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. One of the leading industrial and research centers with emphasis in aerospace scien ...
, in the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the Ga ...
. Its researchers participated in international projects in the areas of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, geodesy, geomagnetism and meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
.
The GOCNAE was replaced in April 1971 by the Institute for Space Research, currently called the National Institute for Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research ( pt, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific research an ...
(INPE). Since the creation of the then Technical Center of Aeronautics (CTA), the current Department of Aerospace Science and Technology (DCTA) of the Brazilian Air Force, in 1946, the country has been following the international progress in the aerospace sector.
With the creation of the Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA), a fully qualified institution was formed to train highly qualified human resources in areas of state-of-the-art technology. The DCTA, through the ITA and the Institute of Aeronautics and Space (IAE), play a key role in the consolidation of the Brazilian space program
The Brazilian space program is the rocketry and space exploration programs conducted by Brazil from 1961 until the creation of the Brazilian Space Agency in 1994. It had significant capabilities in launch vehicles, launch sites, and satellite ...
.
In the early 1970s, the Brazilian Space Activities Commission (COBAE) was created - a body linked to the then General Staff of the Armed Forces (EMFA) - to coordinate and monitor the implementation of the space program. This coordinating role, in February 1994, was transferred to the Brazilian Space Agency. The creation of the AEB represents a change in government orientation by establishing a central coordinating body for the space program
A space program is an organized effort by a government or a company with a goal related to outer space.
Lists of space programs include:
* List of government space agencies
* List of private spaceflight companies
* List of human spaceflight prog ...
, reporting directly to the Presidency of the Republic.
In 2011 Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
's defense minister, Arturo Puricelli, made a proposal to the Brazilian minister, Celso Amorim
Celso Luiz Nunes Amorim (born 3 June 1942) is a Brazilian diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 20 July 1993 to 31 December 1994 under President Itamar Franco and again from 1 January 2003 to 31 December 2010 under President Lu ...
, for the creation of a unified South American space agency by the year 2025, according to the European Space Agency. In 2015, however, the Brazilian Space Agency and the Ministry of Defense rejected the Argentine proposal "because it understood that it would be an organ that would yield a lot of bureaucracy and few results like the 'confederation' proposed by the United States and never came to anything" and also because, according to the agency's adviser, "A regional space agency would reverberate in the Brazilian pocket that, due to its territorial size, would end up getting most of the invoice to pay".
Launch sites

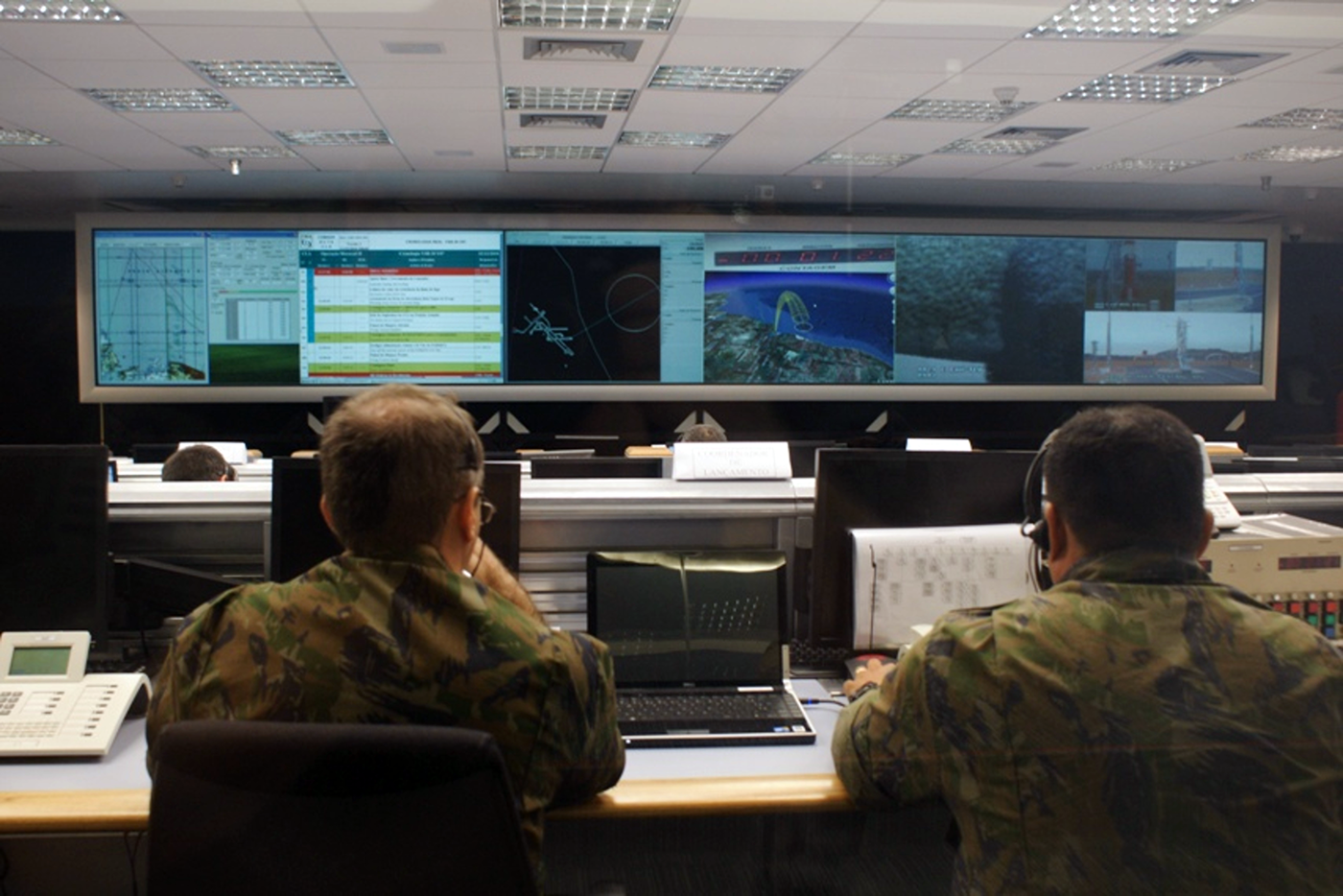
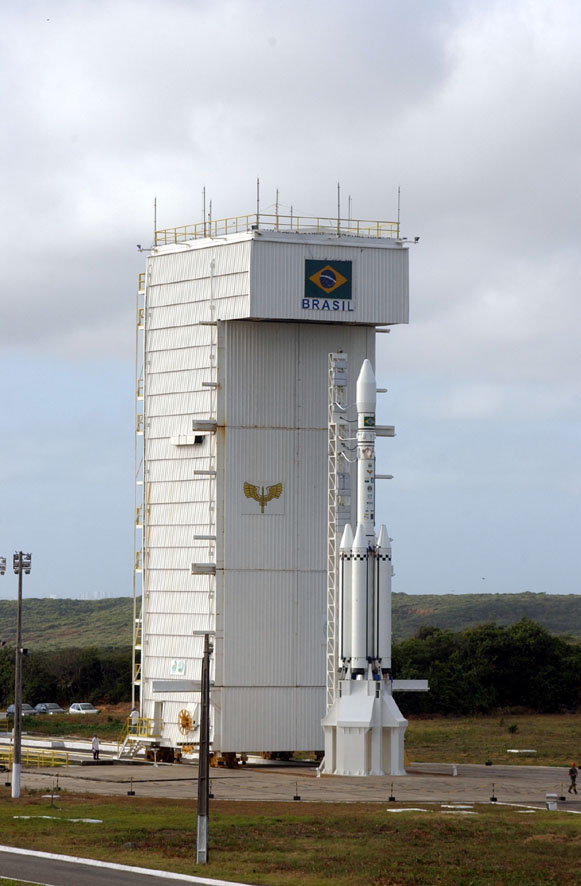
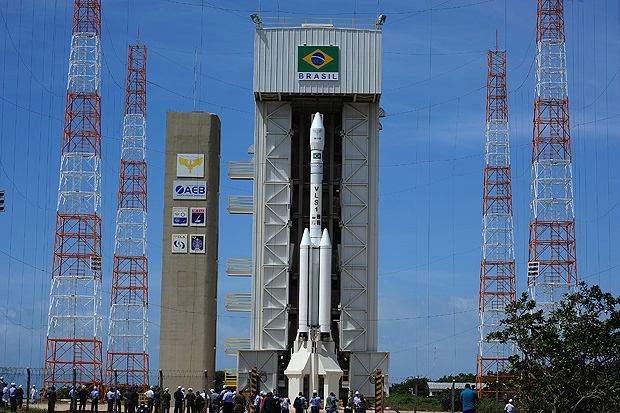
Alcântara Space Center
The Alcântara Launch Center ( pt, Centro de Lançamento de Alcântara; CLA) is the main launch site and operational center of the Brazilian Space Agency.Centros de Lançamentos: CLABrazilian Space Agency. Retrieved on 2009-07-30. It is located in the peninsula of Alcântara, in the state of
Maranhão
Maranhão () is a state in Brazil. Located in the country's Northeast Region, it has a population of about 7 million and an area of . Clockwise from north, it borders on the Atlantic Ocean for 2,243 km and the states of Piauí, Tocantins and ...
.Alcantara Launch Center (2°20'S; 44°24'W)GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved on 2009-07-30. This region presents some excellent requirements, such as low
population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
, excellent security conditions and easiness of aerial and maritime access. The most important factor is its closeness to the Equator - Alcântara is the closest launching base to the Equator. This gives the launch site a significant advantage in launching geosynchronous satellite
A geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns to the same position in the sky after each sidereal day, and over the course of a day tra ...
s.
Barreira do Inferno Launch Center
The Barreira do Inferno Launch Center ( pt, Centro de Lançamento da Barreira do Inferno; CLBI) is a rocket launch base of the Brazilian Space Agency. It is located in the city ofParnamirim
Parnamirim is a city in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, next to the state capital city of Natal and part of its metropolitan area.
Natal Air Force Base - ALA10, one of the most important bases of the Brazilian Air Force, is located in ...
, in the state of Rio Grande do Norte
Rio Grande do Norte (, , ) is one of the states of Brazil. It is located in the northeastern region of the country, forming the northeasternmost tip of the South American continent. The name literally translates as "Great Northern River", re ...
. It is primarily used to launch sounding rockets and to support the Alcântara Launch Center.
Launch vehicles
Sounding rockets


 The Brazilian Space Agency has operated a series of sounding rockets.
* Sonda I
* Sonda II
* Sonda III
* Sonda IV
*
The Brazilian Space Agency has operated a series of sounding rockets.
* Sonda I
* Sonda II
* Sonda III
* Sonda IV
* VSB-30
VSB-30 - "''Veículo de Sondagem Booster – 30''" (Booster Sounding Vehicle) or "''Foguete Suborbital VSB-30''" is the designation of a Brazilian sounding rocket, which replaced the Skylark rocket at ''Esrange''.
The VSB-30 is based on the VS- ...
* VS-30
The VS-30 is a Brazilian sounding rocket, derived from the Sonda 3 sounding rocket's first stage.
* VS-40
The VS-40 (''Foguete Suborbital VS-40'') is a Brazilian sounding rocket using solid fuel, stabilized aerodynamically, distributed between the first stage S40TM (4,200 kg) engine and the second stage S44M (810 kg) engine.
This configura ...
* VS-50
VS-50 (suborbital rocket VS-50) is a joint development of sounding rocket from the Institute of Aeronautics and Space (IAE) and German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Characteristics
It is a suborbital vehicle that uses solid fuel, having two stages: ...
(projected, will use the new S-50 rocket engine)
VLM
 Brazil has forged a cooperative arrangement with Germany to develop a dedicated micro-satellite launch vehicle. As a result, the VLM "Veiculo Lançador de Microsatelites" (Microsatelite Launch Vehicle) based on the S50 rocket engine is being studied, with the objective of orbiting satellites up to 150 kg in circular orbits ranging from 250 to 700 km. The first qualifying and test flight will be on 2022 from the Alcântara Space Center. The second flight is scheduled for the following years as part of the SHEFEX mission, to be conducted also from Alcântara, in partnership with the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Brazil has forged a cooperative arrangement with Germany to develop a dedicated micro-satellite launch vehicle. As a result, the VLM "Veiculo Lançador de Microsatelites" (Microsatelite Launch Vehicle) based on the S50 rocket engine is being studied, with the objective of orbiting satellites up to 150 kg in circular orbits ranging from 250 to 700 km. The first qualifying and test flight will be on 2022 from the Alcântara Space Center. The second flight is scheduled for the following years as part of the SHEFEX mission, to be conducted also from Alcântara, in partnership with the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
VLS
The VLS - Satellite Launch Vehicle ( pt, Veículo Lançador de Satélites) was the Brazilian Space Agency's main satellite launch vehicle. It is a four-stage rocket composed of a core and four strap-on motors.VLS (Brazilian rocket)The Internet Encyclopedia of Science. Retrieved on 2009-07-29. The vehicle's first stage has four solid fuel motors derived from the Sonda sounding rockets. It is intended to deploy 100 to 380 kg
satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioi ...
s into 200 to 1200 km orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
, or to deploy 75 to 275 kg payloads into 200 to 1000 km polar orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of about ...
. The first 3 prototypes for the vehicle failed to launch, with the 3rd exploding on the launch pad in 2003 resulting in the deaths of 21 AEB personnel.
The VLS-1 V4 prototype was expected a launch in 2013.''Saiba como está o projeto Veículo Lançador de Satélite (VLS)''Brazilian Air Force. Retrieved on 2012-03-06. . After subsequent delays, the project was cancelled in 2016.
Southern Cross program
 The Brazilian Space Agency was developing a new family of
The Brazilian Space Agency was developing a new family of launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and ...
s in cooperation with the Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос) ...
.Russia Begins Elbowing Ukraine Out From Brazil's Space ProgramSpaceDaily.com. Retrieved on 2009-07-29. The five rockets of the Southern Cross family will be based on Russia's Angara vehicle and liquid-propellant engines. The first stage of the VLS Gama, Delta and Epsilon rockets was to be powered by a unit based on the RD-191 engine. The second stage, which will be the same for all the Southern Cross rockets, will be driven by an engine based on the Molniya rocket. The third stage will be a solid-propellant booster based on an upgraded version of the
VLS-1
The ''VLS-1'' () was the Brazilian Space Agency's main satellite launch vehicle. The launch vehicle was to be capable of launching satellites into orbit. The launch site was located at the Alcântara Launch Center due to its proximity to the e ...
. The program was named "Southern Cross" in reference to the Crux
Crux () is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name ''Crux'' is Latin for ...
constellation, present on the flag of Brazil
The national flag of Brazil ( pt, bandeira do Brasil), is a blue disc depicting a starry sky (which includes the Southern Cross) spanned by a curved band inscribed with the national motto "''Ordem e Progresso''" ("Order and Progress"), within a ...
and composed of five stars.Programa de Veículos Lançadoeres de Satélites Cruzeiro do SulBrazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology
The Brazilian Department of Science and Aerospace Technology ( pt, Departamento de Ciência e Tecnologia Aeroespacial; DCTA) is the national military research center for aviation and space flight. It is subordinated to the Brazilian Air Force (FAB ...
. Retrieved on 2009-07-29. Hence the names of the future launch vehicles:
*VLS Alfa (light-weight rocket)
The first rocket to be developed. As a direct modification of the VLS-1 of the original project, replacing the fourth and fifth stages by a single liquid fuel engine. It can place payloads in the range 200–400 kg in orbits up to 750 km.
*VLS Beta (light-weight rocket)
Consisting of three stages without auxiliary thrusters. The first stage is a solid fuel propellant 40 tons, the second will have 30 tons of thrust engine and the latter will be 7.5 tons of thrust, with the same mixture "Kerolox". It can place payloads up to 800 kg in orbits up to 800 km.
*VLS Gama (light-weight rocket)
The VLS Gama launcher is part of the light-weight class, but using the near-equatorial position of the Alcântara Launch Center
Alcantara, Alcântara ( Portuguese), Alcántara ( Spanish), Alcàntara, Alcàntera, El-Qantarah and (El) Kantara are all transliterations of the Arabic word ''al qantara'' (القنطرة), meaning "the bridge".
Alcantara may refer to:
People
* ...
, it can place almost 1 ton of payload into orbit up to 800 km.
*VLS Delta (medium-weight rocket)
The VLS Delta launcher is a medium-weight rocket and differs from the Gamma by having four solid-propellant boosters attached to the first stage. Its payload deliverable to a geostationary orbit is 2 tons.
*VLS Epsilon (heavy-weight rocket)
The VLS Epsilon launcher is a heavy-weight rocket with three identical units attached to the first stage. It can place a 4 tons spacecraft in geostationary orbit, if it is launched from Alcântara.
The Brazilian government
The politics of Brazil take place in a framework of a federal presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. The political and administrative o ...
was planning to allocate $1 billion dollars
Dollar is the name of more than 20 currencies. They include the Australian dollar, Brunei dollar, Canadian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Jamaican dollar, Liberian dollar, Namibian dollar, New Taiwan dollar, New Zealand dollar, Singapore dollar, U ...
for the project over six years. It has already set aside $650 million for the construction of five launch pads able to handle up to 12 launches per year. The program was scheduled to be completed by 2022. However, it was cancelled by Brazilian President Dilma Rouseff. Instead, Brazil will focus on a series of smaller launch vehicles that appear to rely more on home-grown technology.
14-X
 Brazil is also investing in the domain of the hypersonic technology. The 14-X, a
Brazil is also investing in the domain of the hypersonic technology. The 14-X, a hypersonic glide vehicle
Hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) is a type of warhead for ballistic missile that can maneuver and glide at hypersonic speed. It is used on ballistic missiles to significantly change their trajectories. Conventional ballistic missiles follow a predi ...
(HGV) under development with the Brazilian Air Force, was conceived in 2007 and launched on 14 February 2022, by a VSB-30 rocket, reaching to 100,000 feet of altitude and a maximum speed of Mach 10.
Engines
 A number of different engines were developed for usage on the several launch vehicles:
* S-10-1 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 27 kN.
* S-10-2 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 4.20 kN, burn time: 32 s.
* S-20 Avibras solid rocket engine. Used on
A number of different engines were developed for usage on the several launch vehicles:
* S-10-1 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 27 kN.
* S-10-2 solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 1. Thrust: 4.20 kN, burn time: 32 s.
* S-20 Avibras solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 2
Sonda is a family of Brazilian-built sounding rockets which serves as an R&D path to the VLS ( pt, Veículo Lançador de Satélites) orbital rocket. Launches started in 1965 and continue to this day. Launch sites include Wallops Island, Andoya ...
and Sonda 3
Sonda is a family of Brazilian-built sounding rockets which serves as an R&D path to the VLS ( pt, Veículo Lançador de Satélites) orbital rocket. Launches started in 1965 and continue to this day. Launch sites include Wallops Island, Andoya, ...
. Thrust:36 kN
* S-23 Avibrassolid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 3M1. Thrust:18 kN
* S-30 IAE solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 3, Sonda 3M1, Sonda 4, VS-30
The VS-30 is a Brazilian sounding rocket, derived from the Sonda 3 sounding rocket's first stage.
, VS-30/Orion and VSB-30
VSB-30 - "''Veículo de Sondagem Booster – 30''" (Booster Sounding Vehicle) or "''Foguete Suborbital VSB-30''" is the designation of a Brazilian sounding rocket, which replaced the Skylark rocket at ''Esrange''.
The VSB-30 is based on the VS- ...
. Thrust: 20.490 kN
* S-31 IAE solid rocket engine. Used on VSB-30. Thrust: 240 kN
* S-40TM IAE solid rocket engine. Used on VLS-R1, VS-40
The VS-40 (''Foguete Suborbital VS-40'') is a Brazilian sounding rocket using solid fuel, stabilized aerodynamically, distributed between the first stage S40TM (4,200 kg) engine and the second stage S44M (810 kg) engine.
This configura ...
, VLS-1
The ''VLS-1'' () was the Brazilian Space Agency's main satellite launch vehicle. The launch vehicle was to be capable of launching satellites into orbit. The launch site was located at the Alcântara Launch Center due to its proximity to the e ...
and VLM-1. Thrust: 208.4 kN, isp=272s.
* S-43 IAE solid rocket engine. Used on Sonda 4, VLS-R1 and VLS-1. Thrust: 303 kN, isp=265s
* S-43TM IAE solid rocket engine. Used on VLS-R1, VLS-1 and VLM. Thrust: 321.7 kN, isp=276s
* S-44 IAE solid rocket engine. Used on VLS-R1, VS-40, VLS-1 and VLM-1. Thrust:33.24 kN, isp=282s
* L5 (Estágio Líquido Propulsivo (EPL)) liquid fuel rocket engine. Tested on VS-30
The VS-30 is a Brazilian sounding rocket, derived from the Sonda 3 sounding rocket's first stage.
and projected for use on VLS-Alfa.http://www.aeb.gov.br/download/revista/RevistaAEB_n13.pdf
* L15 liquid fuel rocket engine. Projected for use on VS-15
The VS-15 is a Brazilian sounding rocket.
It consists of a single, liquid fuel
Liquid fuels are combustible or energy-generating molecules that can be harnessed to create mechanical energy, usually producing kinetic energy; they also must tak ...
. Thrust: 15 kN
* L75 liquid fuel rocket engine, similar to the Russian RD-0109. Projected for use on VLS-Alfa, VLS-Beta, VLS-Omega, VLS-Gama and VLS-Epsilon. Thrust: 75 kN
* S-50 IAE solid rocket engine. Projected for use on VLM-1 and VS-50
VS-50 (suborbital rocket VS-50) is a joint development of sounding rocket from the Institute of Aeronautics and Space (IAE) and German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Characteristics
It is a suborbital vehicle that uses solid fuel, having two stages: ...
.
* L1500 liquid fuel rocket engine. Used on VLS-Beta, VLS-Omega, VLS-Gama and VLS-Epsilon. Thrust: 1500 kN
Satellites
The Brazilian Space Agency has several activesatellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioi ...
s in orbit including imagery intelligence, military communications, reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmisher ...
and earth observation
Earth observation (EO) is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet Earth. It can be performed via remote-sensing technologies (Earth observation satellites) or through direct-contact sensors ...
satellites. Several others are currently in development.
Human spaceflight
Marcos Pontes
Marcos Cesar Pontes (born 11 March 1963) is a Brazilian Air Force pilot, engineer, AEB astronaut, politician and author. He became the first South American and the first Lusophone to go into space when he docked onto the International Space Sta ...
, a lieutenant colonel in the Brazilian Air Force, is an astronaut of the Brazilian Space Agency.AEB: Human SpaceflightGlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved on 2011-01-17. Pontes was the first Brazilian astronaut,
NASA. Retrieved on 2011-01-17. having launched with the
Expedition 13
Expedition 13 was the 13th expedition to the International Space Station (ISS), and launched at 02:30 UTC on 30 March 2006. The expedition used the Soyuz TMA-8 spacecraft, which stayed at the station for the duration of the expedition for emerge ...
crew from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
on March 29, 2006, aboard a Soyuz-TMA spacecraft. Pontes docked with the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
(ISS) on March 31, 2006, where he lived and worked for 9 days. Pontes returned to Earth with the Expedition 12
Expedition 12 (2005) was the 12th expedition to the International Space Station, launched from Kazakhstan using the Russian Soyuz TMA-7 spacecraft. The crew landed back in Kazakhstan on 8 April 2006 with the addition of the first Brazilian astron ...
crew, landing in Kazakhstan on April 8, 2006. In January 2019, Pontes was nominated by the Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro as Minister of Science, Technology, Innovation and Communication, a position he held until 2022.
Brazilian aerospace command
The Aerospace Operations Command ( pt, Comando de Operações Aeroespaciais - COMAE) is a Brazilian air and space command created in 2017 which is part of the Brazilian Air Force. The command is responsible for planning, coordinating, executing and controlling the country's air and space operations. TheBrazilian Navy
)
, colors= Blue and white
, colors_label= Colors
, march= "Cisne Branco" ( en, "White Swan") (same name as training ship ''Cisne Branco''
, mascot=
, equipment= 1 multipurpose aircraft carrier7 submarines6 frigates2 corvettes4 amphibious war ...
and Brazilian Army also are part of the organization.
Space operations center
The Space Operations Center (Portuguese: ''Centro de Operações Espaciais'', acronym COPE) is a facility established in 2020 subordinated to the Aerospace Operations Command, with the objective of operating and supervising the Brazilian satellites.Bingo radio telescope
The Bingo radio telescope called ''Baryon Acoustic Oscillations from Integrated Neutral Gas Observations'', is a project coordinated by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation, Brazilian Space Agency, National Institute for Space Research (INPE) and international partners from Europe and China. The telescope will consist of two giant dishes, with 40 meters of diameter each, which will receive radiation from the space and project their spectrum in a series of metal detectors, called ''horns''. Bingo will perform its detections in the radio band in the range of 960 to 1260 MHZ. 80% of the Bingo parts came from the Brazilian industry.International cooperation

China/CBERS
The China–Brazil Earth Resources Satellite program ( CBERS) is a technological cooperation program between Brazil and China which develops and operates Earth observation satellites. Brazil and China negotiated the CBERS project during two years (1986–1988), renewed in 1994 and again in 2004.International Space Station
 The Brazilian Space Agency is a bilateral partner of
The Brazilian Space Agency is a bilateral partner of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
in the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
.NASA Signs International Space Station Agreement With BrazilNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
. Retrieved on 2011-01-17. The agreement for the design, development, operation and use of Brazilian developed flight equipment and payloads for the Space Station was signed in 1997. It includes the development of six items, among which are a Window Observational Research Facility
The Window Observational Research Facility (WORF) is an experiment rack facility manufactured by the Brazilian Space Agency, which remotely operated payloads and crew members can perform Earth and space science research, including hand held pho ...
and a Technology Experiment Facility. In return, NASA will provide Brazil with access to its ISS facilities on-orbit, as well as a flight opportunity for one Brazilian astronaut during the course of the ISS program.
However, due to cost issues, the subcontractor Embraer was unable to provide the promised ExPrESS pallet, and Brazil left the programme in 2007. However, as a compromise, NASA have funded small Brazilian-made components for the Express Logistics Carrier-2 for the ISS, which were installed in 2009.
Ukraine/Ciclone 4
On October 21, 2003, the Brazilian Space Agency and theState Space Agency of Ukraine
The State Space Agency of Ukraine (SSAU; uk, Державне космічне агентство України, ''Derzhavne kosmichne ahentstvo Ukrayiny'', ДКАУ, ''DKAU'') is the Ukrainian government agency responsible for space policy an ...
established a cooperation agreement creating a joint venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and economic risk, risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four rea ...
space enterprise called Alcântara Cyclone Space. The new company will focus on launching satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioi ...
s from the Alcântara Launch Center
Alcantara, Alcântara ( Portuguese), Alcántara ( Spanish), Alcàntara, Alcàntera, El-Qantarah and (El) Kantara are all transliterations of the Arabic word ''al qantara'' (القنطرة), meaning "the bridge".
Alcantara may refer to:
People
* ...
using the Tsyklon-4
The Tsyklon-4, also known as Tsiklon-4 and Cyclone-4, was a Ukrainian carrier rocket which was being developed for commercial satellite launches. Derived from the Tsyklon-3, it had a new third stage, a larger payload fairing, and a modernised fl ...
rocket. The company will invest $160 million dollars
Dollar is the name of more than 20 currencies. They include the Australian dollar, Brunei dollar, Canadian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Jamaican dollar, Liberian dollar, Namibian dollar, New Taiwan dollar, New Zealand dollar, Singapore dollar, U ...
in infrastructure for the new launch pad
A launch pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term ''launch pad'' can be used to describe just the central launch platform ( mobile launcher platform), or the entir ...
that will be constructed at the Alcântara Launch Center.
In March 2009, the Brazilian Government increased its financial capital
Financial capital (also simply known as capital or equity in finance, accounting and economics) is any economic resource measured in terms of money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or to provi ...
by US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
50 million.
The first launch was planned for 2014 from the Alcantara Launch Center.
Japan
On November 8, 2010,National Institute for Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research ( pt, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific research an ...
(INPE) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) signed a Letter of Intent regarding the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation in Developing Countries (REDD+) program. Examples of the cooperation include the monitoring of illegal logging
Illegal logging is the harvest, transportation, purchase or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, including using corruption, corrupt means to gain access to forests; extraction without permission, o ...
in the Amazon rainforest utilizing data from JAXA's ALOS
Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS), also called Daichi (a Japanese word meaning "land"), is a 3810 kg Japanese satellite launched in 2006. After five years of service, the satellite lost power and ceased communication with Earth, but ...
satellite. Both Brazil and Japan are members of the Global Precipitation Measurement
Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is a joint mission between JAXA and NASA as well as other international space agencies to make frequent (every 2–3 hours) observations of Earth's precipitation. It is part of NASA's Earth Systematic Mission ...
project.
Artemis program
On 21 October 2020, Brazil was invited by the United States to joinNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Artemis Space Program. On 15 June 2021, the country officially joined the program by signing the Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords are a series of non-binding multilateral agreements between the United States government and other world governments participating in the Artemis Program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2025, with the u ...
with the U.S. and international partners, for the joint exploration of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
from 2024 and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
and beyond in 2030s. The roles of Brazil include the development of a national lunar robot for the use in the future missions.
BRICS satellite constellation
On 18 August 2021, AEB signed cooperation agreements with space agencies ofBRICS
BRICS is an acronym for five leading emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The first four were initially grouped as "BRIC" (or "the BRICs") in 2001 by Goldman Sachs economist Jim O'Neill, who coined the ter ...
(Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa), to the joint-development of a remote sensing satellite constellation, aiming to help with common challenges for the mankind such as the climate change, major disasters and environmental protection. Ground stations located in Cuiabá in Brazil, Moscow Region in Russia, Shadnagar–Hyderabad in India, Sanya in China and Hartebeesthoek in South Africa will receive data from the satellite constellation.
See also
* Aerospace Operations Command Brazilian space command * Alcântara Space Center (CEA) *National Institute for Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research ( pt, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific research an ...
(INPE)
*Aerospace Technology and Science Department
The Brazilian Department of Science and Aerospace Technology ( pt, Departamento de Ciência e Tecnologia Aeroespacial; DCTA) is the national military research center for aviation and space flight. It is subordinated to the Brazilian Air Force (FAB ...
(DCTA)
* Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA)
*Embraer S.A.
Embraer S.A. () is a Brazilian multinational aerospace manufacturer that produces commercial, military, executive and agricultural aircraft, and provides aeronautical services. It was founded in 1969 in São José dos Campos, São Paulo, where i ...
(Brazilian aerospace and defense conglomerate)
*Avibras
Avibrás Indústria Aeroespacial, based in Jacareí, São José dos Campos, Brazil, is a diversified Brazilian company which designs, develops and manufactures defense products and services. Its range of products encompasses artillery and aircr ...
(Brazilian aerospace and defense company)
*List of government space agencies
This is a list of government agencies engaged in activities related to outer space and space exploration.
As of 2022, 77 different government space agencies are in existence, 16 of which have launch capabilities. Six government space agencie ...
*List of Brazilian satellites This list covers all satellites developed totally or partially in Brazil. Brazil does not currently have orbital launch capability and has historically had to rely on other countries.
List Scientific and remote sensing
;Key:
Telecommunication
Br ...
References
External links
Official site in Portuguese
AEB on Twitter
{{authority control Space agencies Scientific organisations based in Brazil Government agencies of Brazil 1994 establishments in Brazil Organisations based in Brasília