Adamantyl on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adamantane is an
 Adamantane was first synthesized by
Adamantane was first synthesized by  Prelog's method was refined in 1956. The decarboxylation yield was increased by the addition of the Heinsdecker pathway (11%) and the Hoffman reaction (24%) that raised the total yield to 6.5%. The process was still too complex, and a more convenient method was found in 1957 by
Prelog's method was refined in 1956. The decarboxylation yield was increased by the addition of the Heinsdecker pathway (11%) and the Hoffman reaction (24%) that raised the total yield to 6.5%. The process was still too complex, and a more convenient method was found in 1957 by
by ultrasound and super acid catalysts
Today, adamantane is an affordable chemical compound with a cost of about $1 a gram. All the above methods yield adamantane as a polycrystalline powder. Using this powder, single crystals can be grown from the melt, solution, or vapor phase (e.g. with the Bridgman–Stockbarger technique). Melt growth results in the worst crystalline quality with a mosaic spread in the X-ray reflection of about 1°. The best crystals are obtained from the liquid phase, but the growth is impracticably slow – several months for a 5–10 mm crystal. Growth from the vapor phase is a reasonable compromise in terms of speed and quality. Adamantane is sublimed in a quartz tube placed in a furnace, which is equipped with several heaters maintaining a certain temperature gradient (about 10 °C/cm for adamantane) along the tube. Crystallization starts at one end of the tube, which is kept near the freezing point of adamantane. Slow cooling of the tube, while maintaining the temperature gradient, gradually shifts the melting zone (rate ~2 mm/hour) producing a single-crystal boule.
All the above methods yield adamantane as a polycrystalline powder. Using this powder, single crystals can be grown from the melt, solution, or vapor phase (e.g. with the Bridgman–Stockbarger technique). Melt growth results in the worst crystalline quality with a mosaic spread in the X-ray reflection of about 1°. The best crystals are obtained from the liquid phase, but the growth is impracticably slow – several months for a 5–10 mm crystal. Growth from the vapor phase is a reasonable compromise in terms of speed and quality. Adamantane is sublimed in a quartz tube placed in a furnace, which is equipped with several heaters maintaining a certain temperature gradient (about 10 °C/cm for adamantane) along the tube. Crystallization starts at one end of the tube, which is kept near the freezing point of adamantane. Slow cooling of the tube, while maintaining the temperature gradient, gradually shifts the melting zone (rate ~2 mm/hour) producing a single-crystal boule.
 As deduced by
As deduced by
SDBS database
The simplicity of these spectra is consistent with high molecular symmetry.
 The adamantane molecule is composed of only carbon and hydrogen and has Td symmetry. Therefore, its 16 hydrogen and 10 carbon atoms can be described by only two sites, which are labeled in the figure as 1 (4 equivalent sites) and 2 (6 equivalent sites).
Structural relatives of adamantane are noradamantane and homoadamantane, which respectively contain one less and one more CH2 link than the adamantane.
The adamantane molecule is composed of only carbon and hydrogen and has Td symmetry. Therefore, its 16 hydrogen and 10 carbon atoms can be described by only two sites, which are labeled in the figure as 1 (4 equivalent sites) and 2 (6 equivalent sites).
Structural relatives of adamantane are noradamantane and homoadamantane, which respectively contain one less and one more CH2 link than the adamantane.

 The
The
 Boiling of adamantane with bromine results in a monosubstituted adamantane, 1-bromadamantane. Multiple substitution with bromine is achieved by adding a
Boiling of adamantane with bromine results in a monosubstituted adamantane, 1-bromadamantane. Multiple substitution with bromine is achieved by adding a



File: Adapalene structure.svg,
File: Adamantane acsv.svg, Adamantane
File: Hexamine.svg,
Conjoining adamantane cages produces higher
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexan ...
rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of car ...
crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
or diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of car ...
). It is a white solid with a camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel ('' Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the k ...
-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid In chemistry, diamondoids are variants of the carbon cage molecule known as adamantane (C10H16), the smallest unit cage structure of the diamond crystal lattice. Diamondoids also known as nanodiamonds or condensed adamantanes may include one or more ...
.
The discovery of adamantane in petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants.
History and synthesis
In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted laboratory synthesis was made in 1924 by German chemistHans Meerwein
Hans Meerwein (May 20, 1879 in Hamburg, Germany – October 24, 1965 in Marburg, Germany) was a German chemist.
Several reactions and reagents bear his name, most notably the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction, the Wagner–Meerwein rearran ...
using the reaction of formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section F ...
with diethyl malonate
Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds su ...
in the presence of piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless ...
. Instead of adamantane, Meerwein obtained 1,3,5,7-tetracarbomethoxybicyclo .3.1onane-2,6-dione: this compound, later named Meerwein's ester, was used in the synthesis of adamantane and its derivatives. D. Bottger tried to obtain adamantane using Meerwein's ester as precursor. The product, tricyclo- .3.1.13,7 was not adamantane, but a derivative.
Other researchers attempted to synthesize adamantane using phloroglucinol
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyqu ...
and derivatives of cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexan ...
, but also failed.
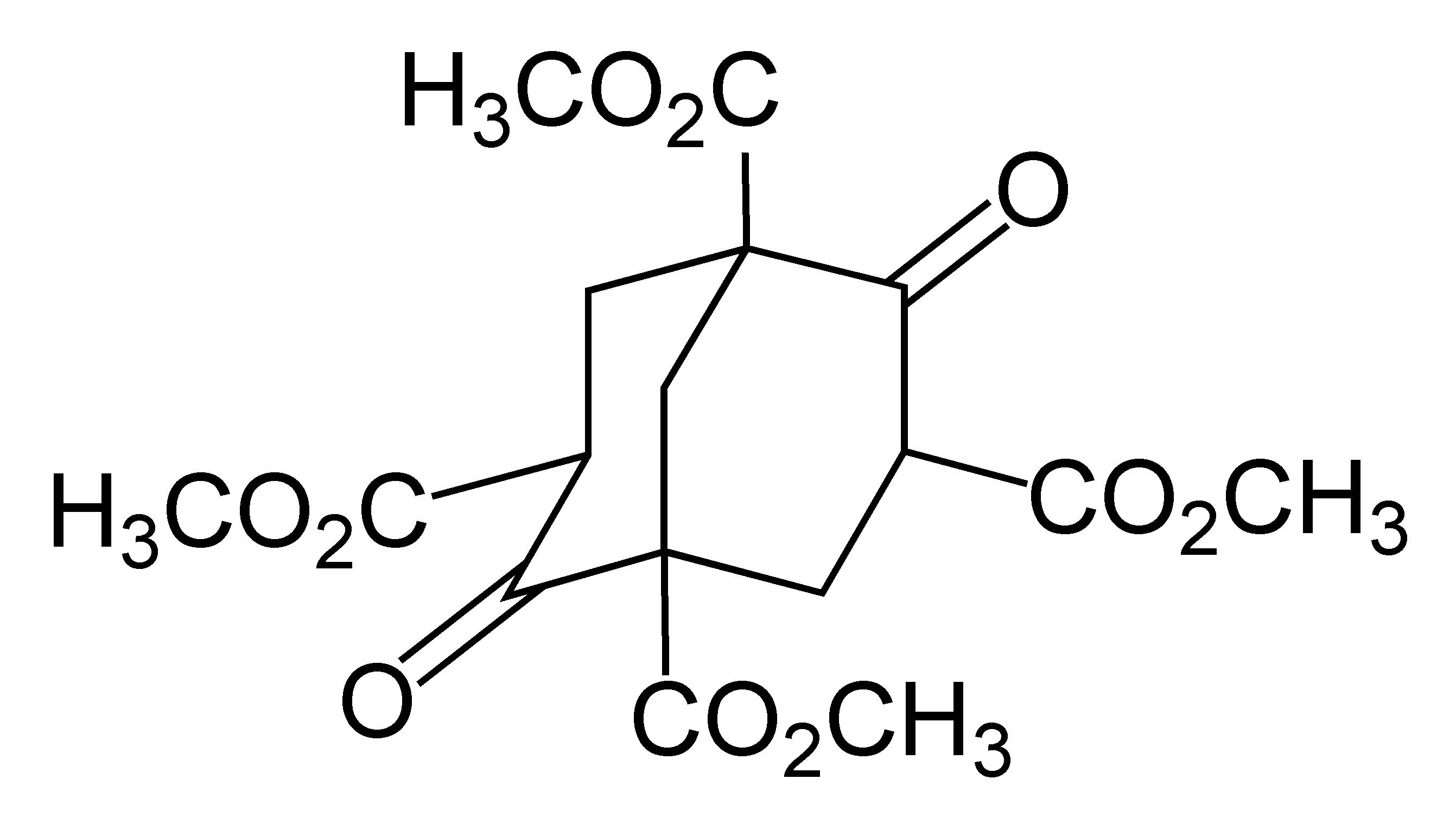
 Adamantane was first synthesized by
Adamantane was first synthesized by Vladimir Prelog
Vladimir Prelog (23 July 1906 – 7 January 1998) was a Croatian-Swiss organic chemist who received the 1975 Nobel Prize in chemistry for his research into the stereochemistry of organic molecules and reactions. Prelog was born and grew up in ...
in 1941 from Meerwein's ester. With a yield of 0.16%, the five-stage process was impractical (simplified in the image below). The method is used to synthesize certain derivatives of adamantane.
 Prelog's method was refined in 1956. The decarboxylation yield was increased by the addition of the Heinsdecker pathway (11%) and the Hoffman reaction (24%) that raised the total yield to 6.5%. The process was still too complex, and a more convenient method was found in 1957 by
Prelog's method was refined in 1956. The decarboxylation yield was increased by the addition of the Heinsdecker pathway (11%) and the Hoffman reaction (24%) that raised the total yield to 6.5%. The process was still too complex, and a more convenient method was found in 1957 by Paul von Ragué Schleyer
Paul von Ragué Schleyer (February 27, 1930 – November 21, 2014) was an American physical organic chemist whose research is cited with great frequency. A 1997 survey indicated that Dr. Schleyer was, at the time, the world's third most cited chem ...
: dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white brittle wax, although lower purity samples can be straw coloured liquids. The pure material smells somewhat of soy wax or camphor ...
was first hydrogenated
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic co ...
in the presence of a catalyst (e.g. platinum dioxide
Adams' catalyst, also known as platinum dioxide, is usually represented as platinum(IV) oxide hydrate, PtO2•H2O. It is a catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis in organic synthesis. This dark brown powder is commercially available. The ...
) and then transformed into adamantane using a Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
(e.g. aluminium chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contam ...
) as another catalyst. This method increased the yield to 30–40% and provided an affordable source of adamantane; it therefore stimulated characterization of adamantane and is still used in laboratory practice. The adamantane synthesis yield was later increased to 60% and 98by ultrasound and super acid catalysts
Today, adamantane is an affordable chemical compound with a cost of about $1 a gram.
 All the above methods yield adamantane as a polycrystalline powder. Using this powder, single crystals can be grown from the melt, solution, or vapor phase (e.g. with the Bridgman–Stockbarger technique). Melt growth results in the worst crystalline quality with a mosaic spread in the X-ray reflection of about 1°. The best crystals are obtained from the liquid phase, but the growth is impracticably slow – several months for a 5–10 mm crystal. Growth from the vapor phase is a reasonable compromise in terms of speed and quality. Adamantane is sublimed in a quartz tube placed in a furnace, which is equipped with several heaters maintaining a certain temperature gradient (about 10 °C/cm for adamantane) along the tube. Crystallization starts at one end of the tube, which is kept near the freezing point of adamantane. Slow cooling of the tube, while maintaining the temperature gradient, gradually shifts the melting zone (rate ~2 mm/hour) producing a single-crystal boule.
All the above methods yield adamantane as a polycrystalline powder. Using this powder, single crystals can be grown from the melt, solution, or vapor phase (e.g. with the Bridgman–Stockbarger technique). Melt growth results in the worst crystalline quality with a mosaic spread in the X-ray reflection of about 1°. The best crystals are obtained from the liquid phase, but the growth is impracticably slow – several months for a 5–10 mm crystal. Growth from the vapor phase is a reasonable compromise in terms of speed and quality. Adamantane is sublimed in a quartz tube placed in a furnace, which is equipped with several heaters maintaining a certain temperature gradient (about 10 °C/cm for adamantane) along the tube. Crystallization starts at one end of the tube, which is kept near the freezing point of adamantane. Slow cooling of the tube, while maintaining the temperature gradient, gradually shifts the melting zone (rate ~2 mm/hour) producing a single-crystal boule.
Natural occurrence
Adamantane was first isolated from petroleum by the Czech chemists S. Landa, V. Machacek, and M. Mzourek. They usedfractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
of petroleum based. Landa ''et al.'' could produce only a few milligrams of adamantane, but noticed its high boiling and melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
s. Because of the (assumed) similarity of its structure to that of diamond, the new compound was named adamantane.
Petroleum remains a source of adamantane; the content varies from between 0.0001% and 0.03% depending on the oil field and is too low for commercial production. Special practical problem for the students of IV year. Department of Petroleum Chemistry and Organic Catalysis MSU.
Petroleum contains more than thirty derivatives of adamantane. Their isolation from a complex mixture of hydrocarbons is possible due to their high melting point and the ability to distill with water vapor and form stable adduct
An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all co ...
s with thiourea
Thiourea () is an organosulfur compound with the formula and the structure . It is structurally similar to urea (), except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom (as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix); however, the properties of urea ...
.
Physical properties
Pure adamantane is a colorless, crystalline solid with a characteristic camphor smell. It is practically insoluble in water, but readily soluble in nonpolarorganic solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
s. Adamantane has an unusually high melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
for a hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
. At 270 °C, its melting point is much higher than other hydrocarbons with the same molecular weight, such as camphene
Camphene is a bicyclic organic compound. It is one of the most pervasive monoterpenes. As for other terpenes, it is insoluble in water, flammable, colorless, and has a pungent smell. It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as tur ...
(45 °C), limonene
Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The -isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring ag ...
(−74 °C), ocimene
Ocimenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons. The ocimenes are monoterpenes found within a variety of plants and fruits. α-Ocimene and the two β-ocimenes differ in the position of the isolated double bond: it is terminal in the alpha isomer. ...
(50 °C), terpinene
The terpinenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons that are classified as monoterpenes. They each have the same molecular formula and carbon framework, but they differ in the position of carbon-carbon double bonds. α-Terpinene has been isolate ...
(60 °C) or twistane (164 °C), or than a linear C10H22 hydrocarbon decane
Decane is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H22. Although 75 structural isomers are possible for decane, the term usually refers to the normal-decane ("''n''-decane"), with the formula CH3(CH2)8CH3. All isomers, however, exhib ...
(−28 °C). However, adamantane slowly sublimes even at room temperature. Adamantane can be distilled with water vapor.
Structure
 As deduced by
As deduced by electron diffraction
Electron diffraction refers to the bending of electron beams around atomic structures. This behaviour, typical for waves, is applicable to electrons due to the wave–particle duality stating that electrons behave as both particles and waves. Si ...
and X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
, the molecule has Td symmetry. The carbon–carbon bond lengths are 1.54 Å, almost identical to that of diamond. The carbon–hydrogen distances are 1.112 Å.
At ambient conditions, adamantane crystallizes in a face-centered cubic structure (space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchan ...
Fm3m, ''a'' = 9.426 ± 0.008 Å, four molecules in the unit cell) containing orientationally disordered adamantane molecules. This structure transforms into an ordered, primitive, tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square ...
phase (''a'' = 6.641 Å, ''c'' = 8.875 Å) with two molecules per cell, either upon cooling to 208 K or pressurizing to above 0.5 GPa.
This phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of ...
is of the first order; it is accompanied by an anomaly in the heat capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K).
Heat capacity i ...
, elastic, and other properties. In particular, whereas adamantane molecules freely rotate in the cubic phase, they are frozen in the tetragonal one; the density increases stepwise from 1.08 to 1.18 g/cm3 and the entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
changes by a significant amount of 1594 J/(mol·K).
Hardness
Elastic constants of adamantane were measured using large (centimeter-sized) single crystals and the ultrasonic echo technique. The principal value of theelasticity tensor
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of ...
, C11, was deduced as 7.52, 8.20, and 6.17 GPa for the <110>, <111>, and <100> crystalline directions. For comparison, the corresponding values for crystalline diamond are 1161, 1174, and 1123 GPa. The arrangement of carbon atoms is the same in adamantane and diamond. However, in the adamantane solid, molecules do not form a covalent lattice as in diamond, but interact through weak Van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and th ...
s. As a result, adamantane crystals are very soft and plastic.
Spectroscopy
Thenuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a ...
(NMR) spectrum of adamantane consists of two poorly resolved signals, which correspond to sites 1 and 2 (see picture below). The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts are respectively 1.873 and 1.756 ppm and are 28.46 and 37.85 ppm.NMR, IR and mass spectra of adamantane can be found in thSDBS database
The simplicity of these spectra is consistent with high molecular symmetry.
Mass spectra
A mass spectrum is a histogram plot of intensity vs. ''mass-to-charge ratio'' (''m/z'') in a chemical sample, usually acquired using an instrument called a ''mass spectrometer''. Not all mass spectra of a given substance are the same; for example ...
of adamantane and its derivatives are rather characteristic. The main peak at ''m''/''z'' = 136 corresponds to the ion. Its fragmentation results in weaker signals as ''m''/''z'' = 93, 80, 79, 67, 41 and 39.
The infrared absorption spectrum of adamantane is relatively simple because of the high symmetry of the molecule. The main absorption bands and their assignment are given in the table:
* Legends correspond to types of oscillations: δ – deformation, ν – stretching, ρ and ω – out of plane deformation vibrations of CH2 groups.
Optical activity
Adamantane derivatives with different substituents at every nodal carbon sites arechiral
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from ...
. Such optical activity was described in adamantane in 1969 with the four different substituents being hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simila ...
and methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
and carboxyl group
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
. The values of specific rotation
In chemistry, specific rotation ( �'') is a property of a chiral chemical compound. It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane-polarized light, per unit distance–concentration product, as the light passes through a sampl ...
are small and are usually within 1°.
Nomenclature
Using the rules of systematic nomenclature, adamantane is called tricyclo .3.1.13,7ecane. However,IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
recommends using the name "adamantane".
Chemical properties
Adamantane cations
The adamantane cation can be produced by treating 1-fluoro-adamantane with SbF5. Its stability is relatively high. Thedication
A dication is any cation, of general formula X2+, formed by the removal of two electrons from a neutral species.
Diatomic dications corresponding to stable neutral species (e.g. formed by removal of two electrons from H2) often decay quickly into ...
of 1,3-didehydroadamantane was obtained in solutions of superacid
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid ...
s. It also has elevated stability due to the phenomenon called "three-dimensional aromaticity" or homoaromaticity
Homoaromaticity, in organic chemistry, refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugated system, conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 orbital hybridisation, hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous ov ...
. This four-center two-electron bond A 4-center 2-electron (4c–2e) bond is a type of chemical bond in which four atoms share two electrons in bonding, with a net bond order of . This type of bonding differs from the usual covalent bond, which involves two atoms sharing two electrons ...
involves one pair of electrons delocalized among the four bridgehead atoms.

Reactions
Most reactions of adamantane occur via the 3-coordinated carbon sites. They are involved in the reaction of adamantane with concentratedsulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
which produces adamantanone.
 The
The carbonyl group
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a ...
of adamantanone allows further reactions via the bridging site. For example, adamantanone is the starting compound for obtaining such derivatives of adamantane as 2-adamantanecarbonitrile and 2-methyl-adamantane.
Bromination
Adamantane readily reacts with various brominating agents, including molecularbromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simila ...
. The composition and the ratio of the reaction products depend on the reaction conditions and especially the presence and type of catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s.
 Boiling of adamantane with bromine results in a monosubstituted adamantane, 1-bromadamantane. Multiple substitution with bromine is achieved by adding a
Boiling of adamantane with bromine results in a monosubstituted adamantane, 1-bromadamantane. Multiple substitution with bromine is achieved by adding a Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
catalyst.
The rate of bromination is accelerated upon addition of Lewis acids and is unchanged by irradiation or addition of free radicals. This indicates that the reaction occurs via an ionic mechanism.
Fluorination
The first fluorinations of adamantane were conducted using 1-hydroxyadamantane and 1-aminoadamantane as initial compounds. Later, fluorination was achieved starting from adamantane itself. In all these cases, reaction proceeded via formation of adamantane cation which then interacted with fluorinated nucleophiles. Fluorination of adamantane with gaseousfluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
has also been reported.
Carboxylation
Carboxylation of adamantane with formic acid gives 1-adamantanecarboxylic acid.
Oxidation
1-Hydroxyadamantane is readily formed by hydrolysis of 1-bromadamantane in aqueous solution ofacetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscib ...
. It can also be produced by ozonation
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
of the adamantane: Oxidation of the alcohol gives adamantanone.
Others
Adamantane interacts withbenzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
in the presence of Lewis acids, resulting in a Friedel–Crafts reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions ...
. Aryl-substituted adamantane derivatives can be easily obtained starting from 1-hydroxyadamantane. In particular, the reaction with anisole
Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H5. It is a colorless liquid with a smell reminiscent of anise seed, and in fact many of its derivatives are found in natural and artificial fragrances. The compound is ...
proceeds under normal conditions and does not require a catalyst.
Nitration of adamantane is a difficult reaction characterized by moderate yields. A nitrogen-substituted drug amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to wid ...
can be prepared by reacting adamantane with bromine or nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
to give the bromide or nitroester at the 1-position. Reaction of either compound with acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not clas ...
affords the acetamide, which is hydrolyzed to give 1-adamantylamine:

Uses
Adamantane itself enjoys few applications since it is merely an unfunctionalizedhydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
. It is used in some dry etching
Dry etching refers to the removal of material, typically a masked pattern of semiconductor material, by exposing the material to a bombardment of ions (usually a plasma of reactive gases such as fluorocarbons, oxygen, chlorine, boron trichloride; ...
masks and polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
formulations.
In solid-state NMR
Solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy is a technique for characterizing atomic level structure in solid materials e.g. powders, single crystals and amorphous samples and tissues using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The anisotropic pa ...
spectroscopy, adamantane is a common standard for chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of ...
referencing.
In dye laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 na ...
s, adamantane may be used to extend the life of the gain medium; it cannot be photoionized under atmosphere because its absorption bands lie in the vacuum-ultraviolet region of the spectrum. Photoionization energies have been determined for adamantane as well as for several bigger diamondoids In chemistry, diamondoids are variants of the carbon cage molecule known as adamantane (C10H16), the smallest unit cage structure of the diamond crystal lattice. Diamondoids also known as nanodiamonds or condensed adamantanes may include one or mor ...
.
In medicine
All medical applications known so far involve not pure adamantane, but its derivatives. The first adamantane derivative used as a drug wasamantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to wid ...
– first (1967) as an antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
against various strains of influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
and then to treat Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
. Other drugs among adamantane derivatives include adapalene
Adapalene is a third-generation topical retinoid primarily used in the treatment of mild-moderate acne, and is also used off-label to treat keratosis pilaris as well as other skin conditions. Studies have found adapalene is as effective as othe ...
, adapromine, bromantane
Bromantane, sold under the brand name Ladasten, is an atypical psychostimulant and anxiolytic drug of the adamantane family related to amantadine and memantine which is used in Russia in the treatment of neurasthenia. Although the effects of t ...
, carmantadine, chlodantane, dopamantine, memantine
Memantine is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include headache, constipation, sleepiness, and dizziness. Severe side effects may include blood clots ...
, rimantadine
Rimantadine ( INN, sold under the trade name 'Flumadine'') is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can s ...
, saxagliptin
Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic ( anti-diabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-My ...
, tromantadine
Tromantadine is an antiviral medicine used to treat herpes simplex virus. It is available in a topical gel under trade names Viru-Merz and Viru-Merz Serol. Its performance is similar to aciclovir.
Like rimantadine, amantadine, and adapromine, ...
, and vildagliptin
Vildagliptin, sold under the brand name Galvus and others, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent (anti-diabetic drug) of the DPP-4 inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. Vildagliptin inhibits the inactivation of Glucag ...
. Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s of adamantane have been patented as antiviral agents against HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
.
Influenza virus strains have developed drug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
to amantadine and rimantadine, which are not effective against prevalent strains as of 2016.
Adapalene
Adapalene is a third-generation topical retinoid primarily used in the treatment of mild-moderate acne, and is also used off-label to treat keratosis pilaris as well as other skin conditions. Studies have found adapalene is as effective as othe ...
File: Adapromine.svg, Adapromine
File: Amantadine.svg , Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to wid ...
File: Bromantane structure.svg, Bromantane
Bromantane, sold under the brand name Ladasten, is an atypical psychostimulant and anxiolytic drug of the adamantane family related to amantadine and memantine which is used in Russia in the treatment of neurasthenia. Although the effects of t ...
File: Memantine structure.svg, Memantine
Memantine is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include headache, constipation, sleepiness, and dizziness. Severe side effects may include blood clots ...
File: Rimantadine.svg, Rimantadine
Rimantadine ( INN, sold under the trade name 'Flumadine'') is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can s ...
File: Saxagliptin.svg, Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic ( anti-diabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-My ...
File: Tromantadine.svg, Tromantadine
Tromantadine is an antiviral medicine used to treat herpes simplex virus. It is available in a topical gel under trade names Viru-Merz and Viru-Merz Serol. Its performance is similar to aciclovir.
Like rimantadine, amantadine, and adapromine, ...
File: Vildagliptin.svg, Vildagliptin
Vildagliptin, sold under the brand name Galvus and others, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent (anti-diabetic drug) of the DPP-4 inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. Vildagliptin inhibits the inactivation of Glucag ...
In designer drugs
Adamantane was recently identified as a key structural subunit in several syntheticcannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
designer drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Des ...
s, namely AB-001
AB-001 (1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole) is a designer drug that was found as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends in Ireland in 2010 and Hungary and Germany in 2011. It is unclear who AB-001 was originally developed by, but it is ...
and SDB-001
APICA (2NE1, SDB-001, ''N''-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1''H''-indole-3-carboxamide) is an indole based drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors.
It had never previously been reported in the scientific or patent literature, a ...
.
Spacecraft propellant
Adamantane is an attractive candidate for propellant inHall-effect thruster
In spacecraft propulsion, a Hall-effect thruster (HET) is a type of ion thruster in which the propellant is accelerated by an electric field. Hall-effect thrusters (based on the discovery by Edwin Hall) are sometimes referred to as Hall thruster ...
s because it ionizes easily, can be stored in solid form rather than a heavy pressure tank, and is relatively nontoxic.
Potential technological applications
Some alkyl derivatives of adamantane have been used as a working fluid in hydraulic systems. Adamantane-based polymers might find application for coatings oftouchscreen
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often ...
s, and there are prospects for using adamantane and its homologues in nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal o ...
. For example, the soft cage-like structure of adamantane solid allow incorporation of guest molecules, which can be released inside the human body upon breaking the matrix.
Adamantane could be used as molecular building blocks for self-assembly of molecular crystals.
Adamantane analogues
Many molecules and ions adopt adamantane-like cage structures. Those includephosphorus trioxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexaoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, a ...
P4O6, arsenic trioxide
Arsenic trioxide, sold under the brand name Trisenox among others, is an inorganic compound and medication. As an industrial chemical, whose major uses include in the manufacture of wood preservatives, pesticides, and glass. As a medication, i ...
As4O6, phosphorus pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4 O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydra ...
P4O10 = (PO)4O6, phosphorus pentasulfide
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula (monomer) or (dimer). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon d ...
P4S10 = (PS)4S6, and hexamethylenetetramine
Hexamethylenetetramine, also known as methenamine, hexamine, or urotropin, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)6N4. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like s ...
C6N4H12 = N4(CH2)6. Particularly notorious is tetramethylenedisulfotetramine
Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound used as a rodenticide (rat poison). It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. It is a sulfamid ...
, often shortened to "tetramine", a rodenticide
Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despi ...
banned in most countries for extreme toxicity to humans. The silicon analogue of adamantane, sila-adamantane, was synthesized in 2005.
Arsenicin A is a naturally occurring organoarsenic
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fu ...
analogue isolated from the New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
n marine sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through ...
'' Echinochalina bargibanti'' and is the first known polyarsenic organic compound.
Hexamethylenetetramine
Hexamethylenetetramine, also known as methenamine, hexamine, or urotropin, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)6N4. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like s ...
File: Phosphorus-pentoxide-2D-dimensions.png, Phosphorus pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4 O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydra ...
File: Phosphorus-pentasulfide-2D-dimensions.png, Phosphorus pentasulfide
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula (monomer) or (dimer). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon d ...
File: Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine.png, Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine
Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound used as a rodenticide (rat poison). It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. It is a sulfamid ...
File: Tetrodotoxin.svg, Tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovered ...
File: Arsenicin A.png, Arsenicin A
diamondoids In chemistry, diamondoids are variants of the carbon cage molecule known as adamantane (C10H16), the smallest unit cage structure of the diamond crystal lattice. Diamondoids also known as nanodiamonds or condensed adamantanes may include one or mor ...
, such as diamantane
Diamantane (also called congressane) is an organic compound that is a member of the diamondoids. These are cage hydrocarbons with structures similar to a subunit of the diamond lattice. It is a colorless solid that has been a topic of research si ...
(C14H20 – two fused adamantane cages), triamantane (C18H24), tetramantane (C22H28), pentamantane (C26H32), hexamantane (C26H30), etc. Their synthesis is similar to that of adamantane and like adamantane, they can also be extracted from petroleum, though at even much smaller yields.
See also
* twistane * UrotropinReferences
{{Authority control