|
Superacid
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid is a medium in which the chemical potential of the proton is higher than in pure sulfuric acid. Commercially available superacids include trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (), also known as triflic acid, and fluorosulfuric acid (), both of which are about a thousand times stronger (i.e. have more negative ''H''0 values) than sulfuric acid. Most strong superacids are prepared by the combination of a strong Lewis acid and a strong Brønsted acid. A strong superacid of this kind is fluoroantimonic acid. Another group of superacids, the carborane acid group, contains some of the strongest known acids. Finally, when treated with anhydrous acid, Zeolite, zeolites (microporous aluminosilicate minerals) will contain superacidic sites within their por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Acid
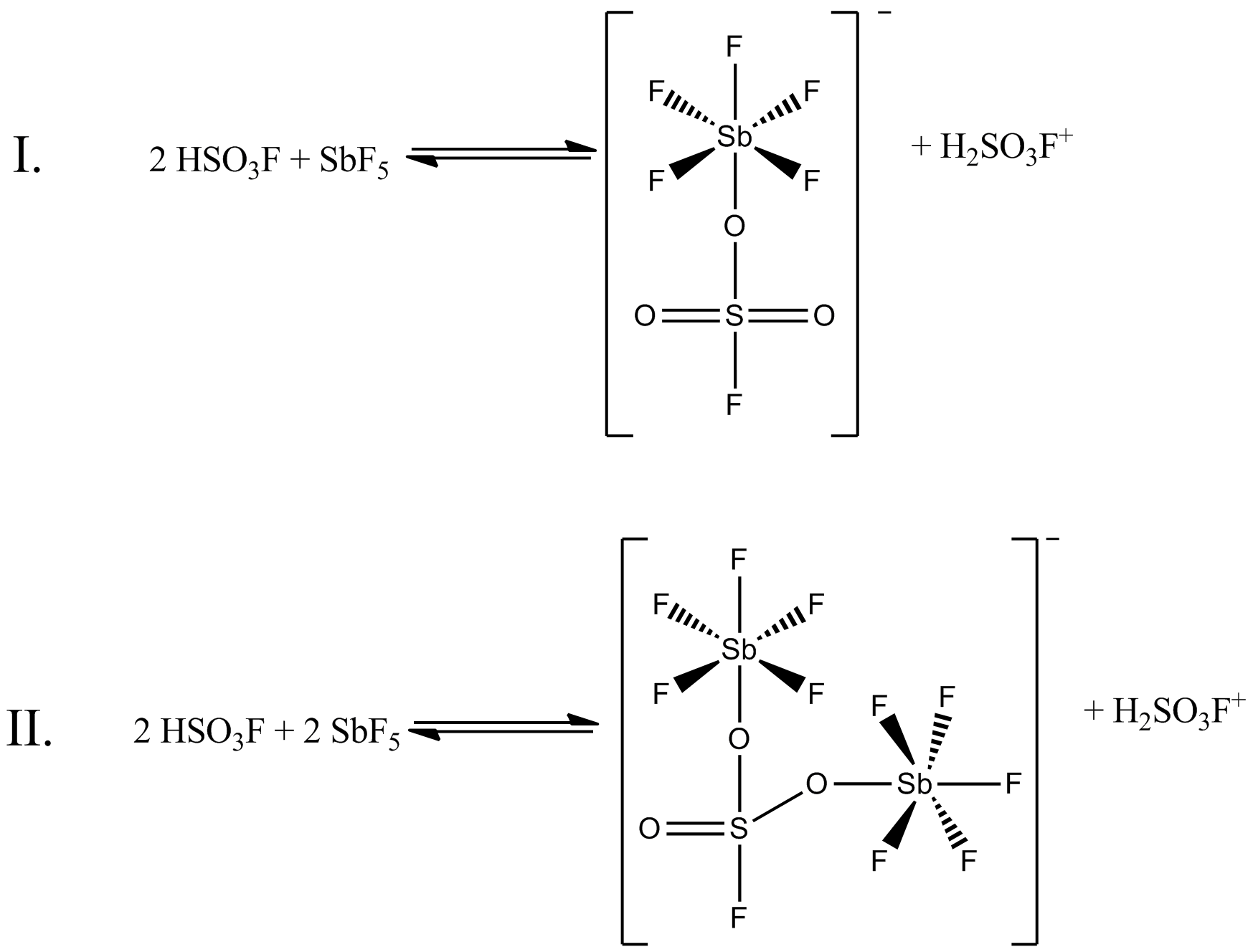
Magic acid (FSO3H·SbF5) is a superacid consisting of a mixture, most commonly in a 1:1 molar ratio, of fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5). This conjugate Brønsted– Lewis superacid system was developed in the 1960s by the George Olah lab at Case Western Reserve University, and has been used to stabilize carbocations and hypercoordinated carbonium ions in liquid media. Magic acid and other superacids are also used to catalyze isomerization of saturated hydrocarbons, and have been shown to protonate even weak bases, including methane, xenon, halogens, and molecular hydrogen. History The term "superacid" was first used in 1927 when James Bryant Conant found that perchloric acid could protonate ketones and aldehydes to form salts in nonaqueous solution. The term itself was coined by R. J. Gillespie later, after Conant combined sulfuric acid with fluorosulfuric acid, and found the solution to be several million times more acidic than sulfuric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carborane Acid
Carborane acids (X, Y, Z = H, Alk, F, Cl, Br, CF3) are a class of superacids, some of which are estimated to be at least one million times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid in terms of their Hammett acidity function values (''H''0 ≤ –18) and possess computed p''K''a values well below –20, establishing them as some of the strongest known Brønsted acids. The best-studied example is the highly chlorinated derivative . The acidity of was found to vastly exceed that of triflic acid, , and bistriflimide, , compounds previously regarded as the strongest isolable acids. Their high acidities stem from the extensive delocalization of their conjugate bases, carboranate anions (CXB11Y5Z6−), which are usually further stabilized by electronegative groups like Cl, F, and CF3. Due to the lack of oxidizing properties and the exceptionally low nucleophilicity and high stability of their conjugate bases, they are the only superacids known to protonate C60 fullerene without deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroantimonic Acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions (the simplest being and ). This substance is a superacid that can be over a billion times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid in terms of its protonating ability measured by Hammett function. It even protonates some hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations ( carbonium ions). Fluoroantimonic acid is corrosive. For example, it cannot be contained directly in glass carboys, as it attacks glass, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon). Chemical composition Fluoroantimonic acid is formed by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride: :SbF5 + 2 HF + H2F+ The speciation (i.e., the inventory of components) of "fluoroantimonic acid" is complex. Spectroscopic measurements show that fluoroantimonic acid consists of a mixture of HF-solvated protons, – (such as ). Thus, the formula "" is a convenient but oversimplifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountered (e.g., ethylene dication ). Until the early 1970s, all carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. This nomenclature was proposed by G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called ' non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Pentafluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. It is notable for its Lewis acidity and its ability to react with almost all known compounds. Preparation Antimony pentafluoride is prepared by the reaction of antimony pentachloride with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride:Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans J. Breunig, Hans Uwe Wolf "Antimony and Antimony Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. :SbCl5 + 5 HF → SbF5 + 5 HCl It can also be prepared from antimony trifluoride and fluorine. Structure and chemical reactions In the gas phase, SbF5 adopts a trigonal bipyramidal structure of D3h point group symmetry (see picture). The material adopts a more complicated structure in the liquid and solid states. The liquid contains polymers wherein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammett Acidity Function
The Hammett acidity function (''H''0) is a measure of acidity that is used for very concentrated solutions of strong acids, including superacids. It was proposed by the physical organic chemist Louis Plack Hammett and is the best-known acidity function used to extend the measure of Brønsted–Lowry acidity beyond the dilute aqueous solutions for which the pH scale is useful. In highly concentrated solutions, simple approximations such as the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation are no longer valid due to the variations of the activity coefficients. The Hammett acidity function is used in fields such as physical organic chemistry for the study of acid-catalyzed reactions, because some of these reactions use acids in very high concentrations, or even neat (pure).Gerrylynn K. Roberts, Colin Archibald Russell. ''Chemical History: Reviews of the Recent Literature''. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2005. . Definition The Hammett acidity function, ''H''0, can replace the pH in concentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Hydrogen fluoride boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid had been known in the glass industry before then. French chemist Edmond Frémy (1814–1894) is credited with disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid
Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents. Synthesis Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is produced industrially by electrochemical fluorination (ECF) of methanesulfonic acid: : CH3SO3H + 4 HF ->CF3SO2F + H2O + 3 H2 The resulting CF3SO2F is hydrolyzed, and the resulting triflate salt is reprotonated. Alternatively, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid arises by oxidation of trifluoromethylsulfenyl chloride: :CF3SCl + 2 Cl2 + 3 H2O -> CF3SO3H + 5 HCl Triflic acid is purified by distillation from triflic anhydride. Historical Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid was first synthesized in 1954 by Robert Haszeldine and Kidd by the following reaction: : Reactions As an acid In the laboratory, trif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorosulfuric Acid
Fluorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurofluoridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available. It is a tetrahedral molecule and is closely related to sulfuric acid, H2SO4, substituting a fluorine atom for one of the hydroxyl groups. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples are often yellow.Erhardt Tabel, Eberhard Zirngiebl, Joachim Maas "Fluorosulfuric Acid" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Chemical properties Fluorosulfuric acid is a free-flowing colorless liquid. It is soluble in polar organic solvents (e.g. nitrobenzene, acetic acid, and ethyl acetate), but poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents such as alkanes. Reflecting its strong acidity, it dissolves almost all organic compounds that are even weak proton acceptors. HSO3F hydrolyzes slowly to hydrogen fluoride (HF) and sulfuric acid. The related triflic acid () retains the high acidity of HSO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bryant Conant
James Bryant Conant (March 26, 1893 – February 11, 1978) was an American chemist, a transformative President of Harvard University, and the first U.S. Ambassador to West Germany. Conant obtained a Ph.D. in Chemistry from Harvard in 1916. During World War I he served in the U.S. Army, working on the development of poison gases, especially Lewisite. He became an assistant professor of chemistry at Harvard in 1919 and the Sheldon Emery Professor of Organic Chemistry in 1929. He researched the physical structures of natural products, particularly chlorophyll, and he was one of the first to explore the sometimes complex relationship between chemical equilibrium and the reaction rate of chemical processes. He studied the biochemistry of oxyhemoglobin providing insight into the disease methemoglobinemia, helped to explain the structure of chlorophyll, and contributed important insights that underlie modern theories of acid-base chemistry. In 1933, Conant became the Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |