ANGPTL4 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Angiopoietin-like 4 is a
 This gene is induced under hypoxic (low oxygen) condition in various cell types and is the target of
This gene is induced under hypoxic (low oxygen) condition in various cell types and is the target of
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that in human is encoded by the ''ANGPTL4'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. This gene was previously referred to as ANGPTL2, HFARP, PGAR, or FIAF but has been renamed ANGPTL4.
This gene is induced under hypoxic (low oxygen) condition in various cell types and is the target of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes. PPARs play essential roles in the regu ...
s. The encoded protein is a serum hormone directly involved in regulating lipid metabolism.
ANGPTL4 plays an important role in numerous cancers and is implicated in the metastatic process by modulating vascular permeability, cancer cell motility and invasiveness.
Name
The former name, FIAF, stands for Fasting-Induced Adipose Factor.Structure
This gene is a member of the angiopoietin-like gene family and encodes aglycosylated
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
, secreted protein with a coiled-coil N-terminal domain
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
and a fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood cl ...
-like C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
domain.
Expression
In mice, highest mRNA expression levels of ANGPTL4 are found in white and brown adipose tissue, followed by liver, kidney, muscle and intestine. Human ANGPTL4 is most highly expressed in liver as ahepatokine Hepatokines (Greek ''heapto-'', liver; and ''-kinos'', movement) are proteins produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) that are secreted into the circulation and function as hormones across the organism. Research is mostly focused on hepatokines that ...
.
Function
 This gene is induced under hypoxic (low oxygen) condition in various cell types and is the target of
This gene is induced under hypoxic (low oxygen) condition in various cell types and is the target of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes. PPARs play essential roles in the regu ...
s. The encoded protein is a serum hormone directly involved in regulating lipid metabolism. The native full length ANGPTL4 can form higher order structures via intermolecular disulfide bonds. The N-terminal region of ANGPTL4 (nANGPTL4) is responsible for its assembly. The full length ANGPTL4 undergoes proteolytic cleavage at the linker region, releasing nANGPTL4 and the monomeric C-terminal portion of ANGPTL4 (cANGPTL4). The nANGPTL4 and cANGPTL4 have different biological functions. Monoclonal antibodies targeting the nANGPTL4 and cANGPTL4 have been developed to distinguish their functions.
Clinical significance
ANGPTL4 plays an important role in numerous cancers and is implicated in the metastatic process by modulating vascular permeability, cancer cell motility and invasiveness. ANGPTL4 contributes to tumor growth and protects cells fromanoikis Anoikis is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in anchorage-dependent cells when they detach from the surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM). Usually cells stay close to the tissue to which they belong since the communication between proxima ...
, a form of programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell (biology), cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers ...
induced when contact-dependent cells detach from the surrounding tissue matrix. ANGPTL4 secreted from tumors can bind to integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
s, activating downstream signaling and leading to the production of superoxide
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of t ...
to promote tumorigenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
. ANGPTL4 disrupts endothelial cell junction
Cell junctions (or intercellular bridges) are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also main ...
s by directly interacting with integrin, VE-cadherin
Cadherin 5, type 2 or VE-cadherin (vascular endothelial cadherin) also known as CD144 ( Cluster of Differentiation 144), is a type of cadherin. It is encoded by the human gene ''CDH5''.
Function
VE-cadherin is a classical cadherin from the cad ...
and claudin-5 in a sequential manner to facilitate metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
. ANGPTL4, specifically the C-terminal fragment (cANGPTL4), is a key player that coordinates an increase in cellular energy flux crucial for epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via an ANGPTL4:YWHAG (14-3-3γ) signaling axis. The ANGPTL4:YWHAG signaling axis confers metabolic flexibility and enhances EMT competency through interaction with specific phosphorylation signals on target proteins. A direct consequence is that ANGPTL4 secures ample cellular energy to fuel multiple ABC transporters
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC tran ...
to confer EMT-mediated chemoresistance.
ANGPTL4 functions as a matricellular protein A matricellular protein is a dynamically expressed non-structural protein that is present in the extracellular matrix (ECM). Rather than serving as stable structural elements in the ECM, these proteins are rapidly turned over and have regulatory rol ...
to facilitate skin wound healing. ANGPTL4-deficient mice exhibit delayed wound reepithelialization with impaired keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells.
Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
migration, angiogenesis and altered inflammatory response. ANGPTL4 induces nitric oxide production through an integrin/JAK/STAT3-mediated upregulation of iNOS expression in wound epithelia, and enhances angiogenesis to accelerate wound healing in diabetic mice. ANGPTL4 induces a β-catenin-mediated upregulation of ID3 in fibroblasts to reduce scar collagen expression. ANGPTL4 is capable of reversing the fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation induced aligned electrospun fibrous substrates. Cyclic stretching of human tendon fibroblasts stimulated the expression and release of ANGPTL4 protein via TGF-β and HIF-1α signalling, and the released ANGPTL4 was pro-angiogenic. ANGPTL4 is also a potent angiogenic factor whose expression is up-regulated in hypoxic retinal Müller cells in vitro and the ischemic retina in vivo. The expression of ANGPTL4 was increased in the aqueous and vitreous of proliferative diabetic retinopathy patients and localized to areas of retinal neovascularization.
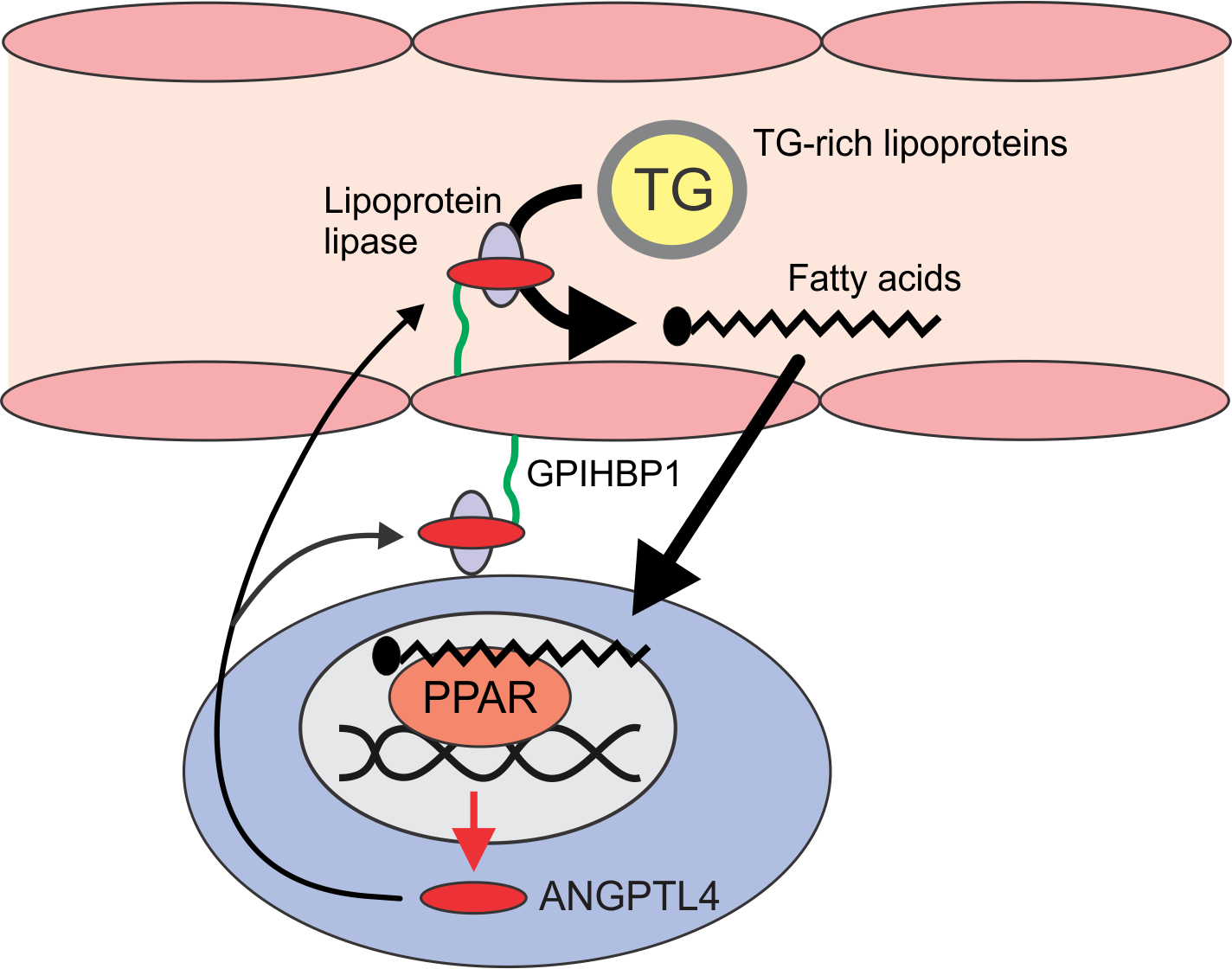
ANGPTL4 has been established as a potent inhibitor of serum triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''wikt:tri-#Prefix, tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other ...
(TG) clearance, causing elevation of serum TG levels via inhibition of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-solubl ...
(LPL). Biochemical studies indicate that ANGPTL4 disables LPL partly by dissociating the catalytically active LPL dimer into inactive LPL monomers. However, evidence also suggests that ANGPTL4 functions as a conventional, non-competitive inhibitor that binds to LPL to prevent the hydrolysis of substrate as part of reversible mechanism. As a consequence, ANGPTL4 knockout mice have reduced serum triglyceride levels, whereas the opposite is true for mice over-expressing ANGPTL4. ANGPTL4 suppresses foam cell formation to reduce atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no s ...
development. The reduction in LPL activity in adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
during fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
is likely caused by increased local production of ANGPTL4. In other tissues such as heart, production of ANGPTL4 is stimulated by fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s and may serve to protect cells against excess fat uptake. ANGPTL4 is more highly induced in nonexercising muscle than in exercising human muscle during acute exercise. ANGPTL4 in nonexercising muscle presumably leads to reduced local uptake of plasma triglyceride-derived fatty acids and their sparing for use by exercising muscle. The induction of ANGPTL4 in exercising muscle likely is counteracted via AMP-activated protein kinase
5' AMP-activated protein kinase or AMPK or 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase is an enzyme (EC 2.7.11.31) that plays a role in cellular energy homeostasis, largely to activate glucose and fatty acid uptake and oxidation when cell ...
(AMPK)-mediated down-regulation, promoting the use of plasma triglycerides as fuel for active muscles.
High-throughput RNA sequencing of lung tissue samples from the 1918 and 2009 influenza pandemic
An influenza pandemic is an epidemic of an influenza virus that spreads across a large region (either multiple continents or worldwide) and infects a large proportion of the population. There have been six major influenza epidemics in the last ...
revealed that ANGPTL4 was one of the most significantly upregulated gene. Murine influenza infection of the lungs stimulated the expression of ANGPTL4 via a STAT3-mediated mechanism. ANGPTL4 enhanced pulmonary tissue leakiness and exacerbated inflammation-induced lung damage. Influenza-infected ANGPTL4-knockout mice displayed diminished lung damage and recovered faster from the infection compared to wild-type mice. The treatment of infected mice with neutralizing anti-ANGPTL4 antibodies significantly accelerated pulmonary recovery and improved lung tissue integrity. It was also shown that antibody treatment against ANGPTL4 reduces pulmonary edema and injury in secondary pneumococcal pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
.
References
External links
* *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * {{refend