AMD Turion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption (''mobile'') processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the '' Pentium M'' and the Intel Core and Intel Core 2 processors.
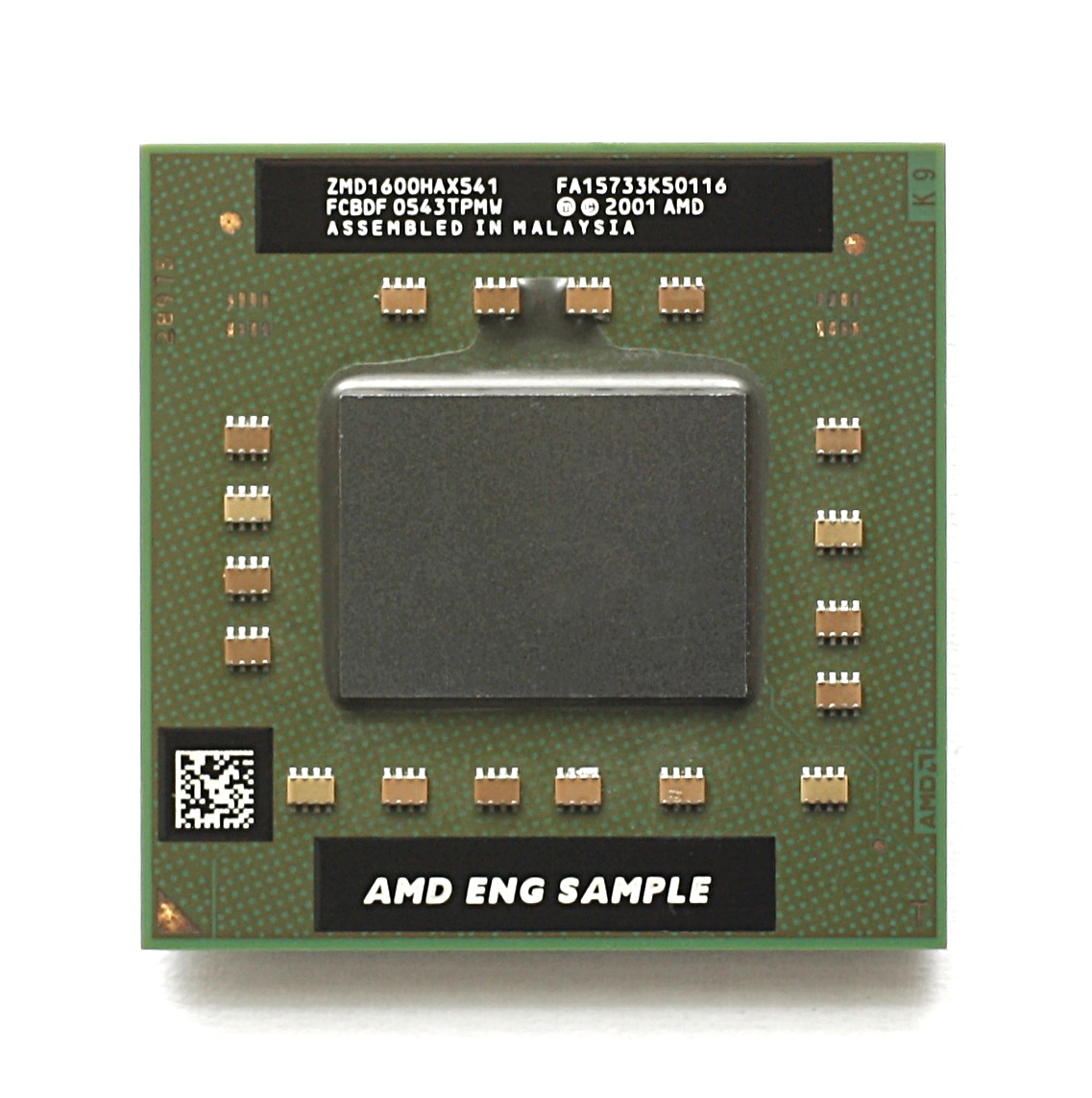 Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and
Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and
/ref> The Turion X2 Ultra processor, unlike earlier Turions, implements three voltage planes: one for the northbridge and one for each core.AnandTech review
/ref> This, along with multiple phase-locked loops (PLL), allows one core to alter its voltage and operating frequency independently of the other core, and independently of the northbridge. Indeed, in a matter of microseconds, the processor can switch to one of 8 frequency levels and one of 5 voltage levels. By adjusting frequency and voltage during use, the processor can adapt to different workloads and help reduce power consumption. It can operate as low as 250 MHz to conserve power during light use. Additionally, the processor features deep sleep state C3, deeper sleep state C4 (AltVID), and HyperTransport 3.0 up to 2.6 GHz, or up to 41.6 GB/s bandwidth per link at 16-bit link width and dynamic scaling of HT link width down to 0-bit ("disconnected") in both directions from and to the chipset for four different usage scenarios.PC Watch image
/ref> It also implements multiple on-die thermal sensors through integrated SMBUS (SB-TSI) interface (replaces and eliminates the thermal monitor circuit chip through SMBUS in its predecessors) with additional MEMHOT signal sent from embedded controller to the processor, and reduces memory temperature. The Turion X2 Ultra processor uses the same socket S1 as its predecessor, Turion 64 X2, but the pinout is different. It is designed to work with the RS780M chipset. Given the above enhancements on the architecture, the cores were minimally modified and are based on the K8 instead of the K10 microarchitecture. AMD Fellow Maurice Steinman has said the cores are almost transistor-for-transistor identical to those found in the 65 nm Turion 64 X2 processors .

 * Stepping E5
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 or 1024 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE,
* Stepping E5
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 or 1024 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE,
 * Dual AMD64 core
* Stepping F2
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB ( data + instructions) per core
* L2 cache: 256 KiB (''Taylor'') or 512 KiB (''Trinidad'') per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz
* MMX, Extended
* Dual AMD64 core
* Stepping F2
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB ( data + instructions) per core
* L2 cache: 256 KiB (''Taylor'') or 512 KiB (''Trinidad'') per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz
* MMX, Extended
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31, 33, 35 watt max * First release: May 17, 2006 * Clock rate: 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200 MHz ** 31W TDP: *** TL-50: 1600 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) *** TL-52: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) ** 33W TDP: *** TL-56: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) ** 35W TDP: *** TL-60: 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) *** TL-64: 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
AMD official website
Reuters news report on the announcement of the chips
PCworld Turion based notebooks review
Acer Aspire 5020 Series Review from www.notebookreview.com
Detailed review at www.anandtech.com
The Register : AMD, IBM "stress" silicon for 65nm process, by Tony Smith
Article from ExtremeTech: AMD Adds Second Core To Turion Notebook Chip
* http://support.amd.com/us/psearch/Pages/psearch.aspx?type=2.2%3b2.3&product=2.2.8&contentType=Tech+Doc+Embedded&ostype=&keywords=&items=20 {{DEFAULTSORT:Turion Advanced Micro Devices x86 microprocessors
Features
Turion 64
Earliest Turion 64 processors are plugged into AMD's Socket 754. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KiB of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die DDR-400 memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport bus. Battery saving features, like '' PowerNow!'', are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1 and have a double-channel DDR2 controller.Turion 64 X2
 Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and
Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and Core 2
Intel Core 2 is the processor family encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single- die, whereas the quad-cor ...
CPUs. The Turion 64 X2 was launched on May 17, 2006, after several delays. These processors use Socket S1 and feature DDR2 memory. They also include AMD Virtualization Technology and more power-saving features.
The earlier 90 nm devices were codenamed Taylor and Trinidad, while the newer 65 nm cores have codename Tyler.
Turion X2 Ultra
Turion X2 Ultra (codenamed ''Griffin'') is the first processor family from AMD solely for the mobile platform, based on theAthlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. T ...
(K8 Revision G) architecture with some specific architectural enhancements similar to current Phenom processors aimed at lower power consumption and longer battery life. The Turion Ultra processor was released as part of the "''Puma
Puma or PUMA may refer to:
Animals
* ''Puma'' (genus), a genus in the family Felidae
** Puma (species) or cougar, a large cat
Businesses and organisations
* Puma (brand), a multinational shoe and sportswear company
* Puma Energy, a mid- and d ...
''" mobile platform in June 2008.
The Turion X2 Ultra is a dual-core processor fabricated on 65 nm
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch ...
technology using 300 mm SOI wafers. It supports DDR2-800
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR ...
SO-DIMMs and features a DRAM prefetcher to improve performance and a mobile-enhanced northbridge (memory controller, HyperTransport controller, and crossbar switch). Each processor core comes with 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
L2 cache for a total of 2 MiB L2 cache for the entire processor. This is double the L2 cache found on the Turion 64 X2 processor. Clock rates range from 2.0 GHz to 2.4 GHz, and thermal design power (TDP) range from 32 watts to 35 watts.AMD mobile CPU roadmap at Engadget/ref> The Turion X2 Ultra processor, unlike earlier Turions, implements three voltage planes: one for the northbridge and one for each core.AnandTech review
/ref> This, along with multiple phase-locked loops (PLL), allows one core to alter its voltage and operating frequency independently of the other core, and independently of the northbridge. Indeed, in a matter of microseconds, the processor can switch to one of 8 frequency levels and one of 5 voltage levels. By adjusting frequency and voltage during use, the processor can adapt to different workloads and help reduce power consumption. It can operate as low as 250 MHz to conserve power during light use. Additionally, the processor features deep sleep state C3, deeper sleep state C4 (AltVID), and HyperTransport 3.0 up to 2.6 GHz, or up to 41.6 GB/s bandwidth per link at 16-bit link width and dynamic scaling of HT link width down to 0-bit ("disconnected") in both directions from and to the chipset for four different usage scenarios.
/ref> It also implements multiple on-die thermal sensors through integrated SMBUS (SB-TSI) interface (replaces and eliminates the thermal monitor circuit chip through SMBUS in its predecessors) with additional MEMHOT signal sent from embedded controller to the processor, and reduces memory temperature. The Turion X2 Ultra processor uses the same socket S1 as its predecessor, Turion 64 X2, but the pinout is different. It is designed to work with the RS780M chipset. Given the above enhancements on the architecture, the cores were minimally modified and are based on the K8 instead of the K10 microarchitecture. AMD Fellow Maurice Steinman has said the cores are almost transistor-for-transistor identical to those found in the 65 nm Turion 64 X2 processors .
Turion II Ultra
Turion II Ultra (codenamed ''Caspian'') is the mobile version of the K10.5 architecture produced using 45 nm fabrication process, also known by its desktop variant ''Regor''. It is a dual core processor, and features clock speeds of 2.5 GHz, 2 MB total L2 cache (1 MB per core), HyperTransport at 3.6 GT/s, and a 128 bit FPU. It maintains a TDP of 35W from its predecessor Turion X2 Ultra (codenamed ''Griffin'').Turion II
Turion II is identical to Turion II Ultra, except that the Turion II features only 1 MB of L2 cache (512 KB per core), and lower clock speeds ranging from 2.2 GHz to 2.6 GHz.Features table
CPU features tableModel naming methodology
The model naming scheme does not make it obvious how to compare one Turion with another, or even anAthlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. T ...
. The model name is two letters, a dash, and a two digit number (for example, ML-34). The two letters together designate a processor class, while the number represents a performance rating (PR). The first letter is M for mono (single) core processors and T for twin (dual) core Turion 64 X2 processors. The later in the alphabet that the second letter appears, the more the model has been designed for mobility (frugal power consumption). Take for instance, an MT-30 and an ML-34. Since the T in the MT-30 is later in the alphabet than the L in ML-34, the MT-30 consumes less power than the ML-34. But since 34 is greater than 30, the ML-34 is faster than the MT-30.
The release of the Turion II Ultra and Turion II lineups have simplified name methodology; all newly released Turions have the letter "M" followed by a number designating relative performance. The higher the number, the higher the clock speed. For example, the Turion II M500 has a clock speed of 2.2 GHz while the Turion II M520 has a clock speed of 2.3 GHz.
Cores
Lancaster (90 nm SOI)

 * Stepping E5
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 or 1024 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE,
* Stepping E5
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 or 1024 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX Bit
* Socket 754, HyperTransport (800 MHz, HT800)
* VCore:
**0.8 V - 1.2 V for ML chips
**0.8 V - 1.35 V for MT chips
* Power consumption ( TDP): 25/35 watt max
* First release: August 25, 2005
* Clock rate: 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200, 2400 MHz
** 25W TDP:
*** MT-28: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-30: 1600 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-32: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-34: 1800 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-37: 2000 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-40: 2200 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
** 35W TDP:
*** ML-28: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-30: 1600 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-32: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-34: 1800 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-37: 2000 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-40: 2200 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-42: 2400 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-44: 2400 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
Richmond (90 nm SOI)
The models support the same features available in Lancaster, plusAMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-as ...
.
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX Bit, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-as ...
* Socket S1, HyperTransport (800 MHz, HT800)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31 watt max
* First release: September 1, 2006
* Clock rate: 2000, 2200 MHz
** 31W TDP:
*** MK-36: 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MK-38: 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
Taylor & Trinidad (90 nm SOI)
 * Dual AMD64 core
* Stepping F2
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB ( data + instructions) per core
* L2 cache: 256 KiB (''Taylor'') or 512 KiB (''Trinidad'') per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz
* MMX, Extended
* Dual AMD64 core
* Stepping F2
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB ( data + instructions) per core
* L2 cache: 256 KiB (''Taylor'') or 512 KiB (''Trinidad'') per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX bit
* Socket S1, HyperTransport (800 MHz, 1600 MT/s, 10.7 GB/s CPU-RAM + 6.4 GB/s CPU-I/O transfer rat* Power consumption ( TDP): 31, 33, 35 watt max * First release: May 17, 2006 * Clock rate: 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200 MHz ** 31W TDP: *** TL-50: 1600 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) *** TL-52: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) ** 33W TDP: *** TL-56: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) ** 35W TDP: *** TL-60: 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core) *** TL-64: 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
Tyler (65 nm SOI)
* Dual AMD64 core * Steppings G1, G2 * L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions) per core * L2 cache: 256 KiB per core (All Athlon & Turion TL-50) or 512 KiB per core (All Others), full speed * Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz (10.6 GB/s full-duplex CPU/RAM bandwidth) * 100 MHz granularity (Dynamic P-state Transitions) * MMX, Extended3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX Bit, AMD-V#AMD virtualization (AMD-V), AMD-V
* Socket S1, HyperTransport (800 MHz / 1600 MT/s)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31, 35 watt max.
* First release: 2007
* Clock rate: 1700, 1800, 1900, 2000, 2100, 2200, 2300, 2400 MHz
** 31W TDP:
*** TK-53 1700 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TK-55 1800 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TL-56 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TK-57 1900 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TL-58 1900 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-60 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
** 35W TDP:
*** TL-62 2100 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-64 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-66 2300 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-68 2400 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
Lion (65 nm SOI)
* Dual AMD64 core * B1 Stepping * L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB ( data + instructions) per core ** L2 cache: 512 KiB per core, full speed, or ** L2 cache: 1MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-800 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX bit, AMD-V#AMD virtualization (AMD-V), AMD-V
* Socket S1 (S1g2)
* HyperTransport (1800 MHz, 3600 MT/s, 12.8 GB/s CPU-RAM + 14.4 GB/s CPU-I/O transfer rate)
* HyperTransport (2200 MHz, 4400 MT/s on ZM-85 y ZM-87 only)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 32, 35 watt max
* First release: June 4, 2008
** Clock rate: 2000, 2100, 2200 MHz (RM-7x, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
)
** Clock rate: 2100, 2200, 2300, 2400, 2500 MHz (ZM-8x, L2 cache: 2 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
)
** 31W TDP:
*** RM-70: 2000 MHz
** 32W TDP:
*** ZM-80: 2100 MHz
** 35W TDP:
*** RM-72: 2100 MHz
*** RM-74: 2200 MHz
*** ZM-82: 2200 MHz
*** ZM-84: 2300 MHz
*** ZM-85: 2300 MHz
*** ZM-86: 2400 MHz
*** ZM-87: 2400 MHz
*** ZM-88: 2500 MHz
Caspian (45 nm SOI)
* Dual Stars core ** L2 cache: 512 KiB per core, full speed (For Turion II, Athlon II and Sempron II), or ** L2 cache: 1MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
per core, full speed (For Turion II Ultra)
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-800 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, SSE4a
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more ...
, AMD64, PowerNow!, NX bit, AMD-V#AMD virtualization (AMD-V), AMD-V
* Socket S1g3
* HyperTransport (1800 MHz, 3600 MT/s on M6xx/M5xx models, 1600 MHz, 3200 MT/s for M3xx models)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 35 watt max
** Clock rate: 2000 (M1xx, L2 cache 512 KiB)
** Clock rate: 2000, 2100, 2200 MHz (M3xx, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
)
** Clock rate: 2200, 2300, 2400 MHz (M5xx, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
)
** Clock rate: 2400, 2500, 2600, 2700 MHz (M6xx, L2 cache: 2 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
)
** 25W TDP:
*** M100: 2000 MHz - Sempron II Single-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M120: 2100 MHz - Sempron II Single-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
** 35W TDP:
*** M300: 2000 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M320: 2100 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M340: 2200 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M500: 2200 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M520: 2300 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M540: 2400 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M600: 2400 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M620: 2500 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M640: 2600 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M660: 2700 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
Champlain
* Based on the AMD K10 microarchitecture * All models support: '' MMX, SSE,SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, SSE4a
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more ...
, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, Cool'n'Quiet'', ''AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-as ...
''
* Memory support: DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed ...
, DDR3L SDRAM
See also
* AMD mobile platform *List of AMD Turion microprocessors
Turion 64 is the name of a family of CPUs designed by AMD for the mobile computing market.
Features overview
CPU features table
Single-core mobile processors
Turion 64
"Lancaster" (90 nm)
* All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enha ...
* List of AMD Mobile Sempron microprocessors
References
External links
AMD official website
Reuters news report on the announcement of the chips
PCworld Turion based notebooks review
Acer Aspire 5020 Series Review from www.notebookreview.com
Detailed review at www.anandtech.com
The Register : AMD, IBM "stress" silicon for 65nm process, by Tony Smith
Article from ExtremeTech: AMD Adds Second Core To Turion Notebook Chip
* http://support.amd.com/us/psearch/Pages/psearch.aspx?type=2.2%3b2.3&product=2.2.8&contentType=Tech+Doc+Embedded&ostype=&keywords=&items=20 {{DEFAULTSORT:Turion Advanced Micro Devices x86 microprocessors