4th century BCE on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 4th century BC started the first day of

* 389 BC: Early in the
*
* 361 BC: Duke Xiao became ruler of
*
* 344 BC: Duke Hui of Wei is the first to claim the royal title of king (Chinese: 王) for himself, proclaiming themselves fully independent kingdoms.
* 344 BC: The rulers of Qi and Wei mutually recognized each other as "kings":
*
*
400 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 400 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Esquilinus, Capitolinus, Vulso, Medullinus, Saccus and Vulscus (or, less frequently, year 354 ''Ab urbe c ...
and ended the last day of 301 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 301 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Dictatorship of Corvus (or, less frequently, year 453 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 301 BC for this year has been used since ...
. It is considered part of the Classical era
An era is a span of time defined for the purposes of chronology or historiography, as in the regnal eras in the history of a given monarchy, a calendar era used for a given calendar, or the geological eras defined for the history of Earth.
Comp ...
, epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
, or historical period.
This century marked the height of Classical Greek civilization in all of its aspects. By the year 400 BC Greek philosophy, art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
had spread far and wide, with the numerous independent Greek colonies
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that i ...
that had sprung up throughout the lands of the eastern Mediterranean.
Arguably the most important series of political events in this period were the conquests of Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, bringing about the collapse of the once formidable Persian Empire and spreading Greek culture far into the east. Alexander dreamt of an east/west union, but when his short life ended in 323 BC, his vast empire was plunged into civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
as his generals each carved out their own separate kingdoms. Thus began the Hellenistic age
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
, a period characterized by a more absolute approach to rule, with Greek kings taking on royal trappings and setting up hereditary successions. While a degree of democracy still existed in some of the remaining independent Greek cities, many scholars see this age as marking the end of classical Greece.
In India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, the Maurya Empire was founded in 322 BC by Chandragupta Maurya who rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, taking advantage of the disruptions of local powers in the wake of the withdrawal westward by the armies of Alexander.
China in the 4th century BC entered an era of constant warfare known as the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
. The period saw the rapid rise of large states (such as Chu) over smaller ones thanks to technological advancement. Though the period has usually been characterized by historians as being excessively violent compared to the Spring and Autumn period, it was also punctuated by several cultural and social growths through the expansion of several different sects of Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a ...
and Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, and the formulation of Legalist thought.
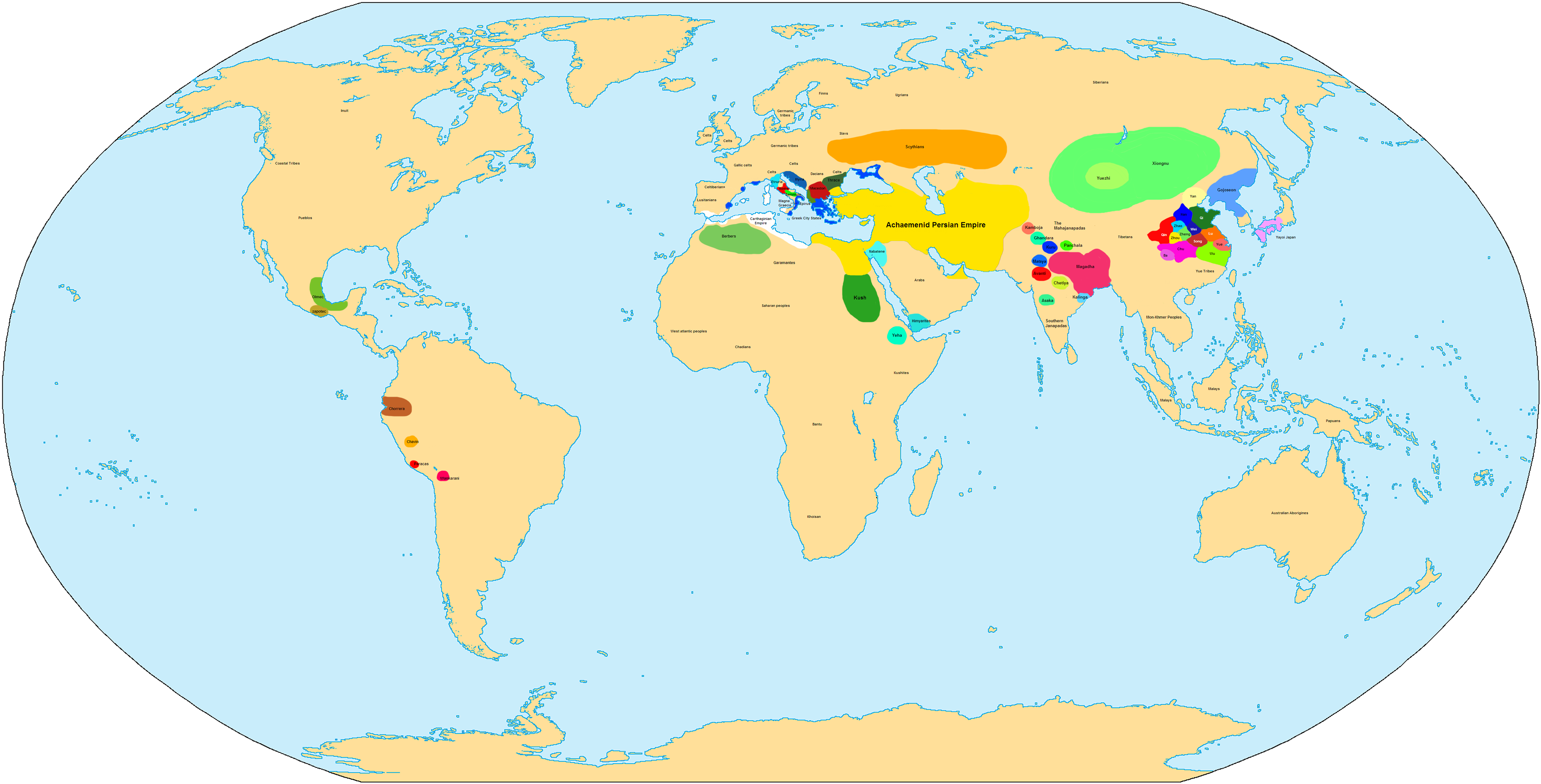
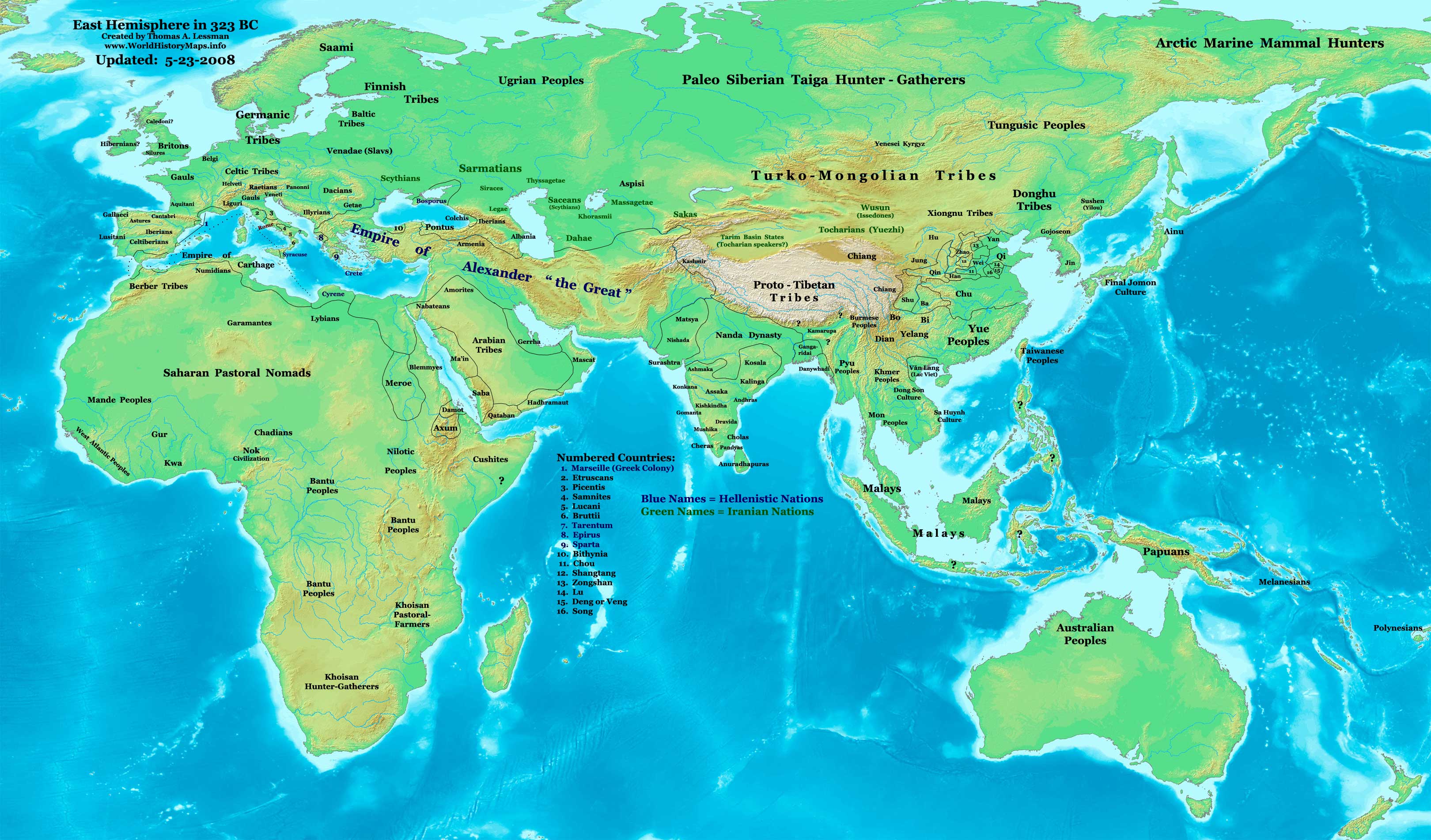
The world in the 4th century BC


Events
390s BC
This article concerns the period 399 BC – 390 BC.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:390s Bc
...
* 399 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 399 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Augurinus, Longus, Priscus, Cicurinus, Rufus and Philo (or, less frequently, year 355 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomin ...
: The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
philosopher Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
is sentenced to death by Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
authorities, condemned for impiety
Impiety is a perceived lack of proper respect for something considered sacred. Impiety is often closely associated with sacrilege, though it is not necessarily a physical action. Impiety cannot be associated with a cult, as it implies a larger b ...
and the corruption of youth. He refuses to flee into exile and dies by drinking hemlock.
* 396 BC: Marcus Furius Camillus
Marcus Furius Camillus (; c. 446 – 365 BC) was a Roman soldier and statesman of the patrician class. According to Livy and Plutarch, Camillus triumphed four times, was five times dictator, and was honoured with the title of ''Second Founder ...
is made dictator
A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a small clique. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in tim ...
by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. Camillus finally destroys the Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
city of Veii
Veii (also Veius; it, Veio) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the ...
in southern Etruria.
* 395 BC: The " Corinthian War" begins, with Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Thebes, Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government refor ...
and Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
...
(with the backing of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
) against Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
.
* 392 BC: A peace conference between the Greek city-states is held in Sparta. Andocides, Athenian orator and politician, goes with three colleagues to negotiate peace with Sparta. The conference is unsuccessful and Athens rejects the terms and exiles the ambassadors.
* 391 BC: Dionysius I, tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to re ...
of Syracuse, begins an attempt to extend his rule to the Greek cities of southern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. He unsuccessfully besieges Rhegium
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label= Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated pop ...
.
* 390 BC: The Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Hakor
Hakor or Hagar, also known by the hellenized forms Achoris or Hakoris, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 29th Dynasty. His reign marks the apex of this feeble and short-lived dynasty, having ruled for 13 years – more than half of its enti ...
(Akoris), concludes a tripartite alliance with Evagoras, king of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
, and Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
.
Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
, Chu is one of the strongest states in China. The state rose to a new level of power when King Dao of Chu
King Dao of Chu (, died 381 BC) was the king of the state of Chu from 401 BC to 381 BC during the early Warring States period of ancient China. He was born Xiong Yi () and King Dao was his posthumous title.
King Dao succeeded his father King S ...
() names the famous reformer Wu Qi
Wu Qi (, 440–381 BC) was a Chinese military leader, Legalist philosopher, and politician in the Warring States period.
Biography
Born in the State of Wey (), he was skilled in leading armies and military strategy. He had served in the state ...
as his chancellor.
* 389 BC: Wu Qi
Wu Qi (, 440–381 BC) was a Chinese military leader, Legalist philosopher, and politician in the Warring States period.
Biography
Born in the State of Wey (), he was skilled in leading armies and military strategy. He had served in the state ...
, the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
of the State of Chu, enacts his first series of political, municipal, and martial reforms. Wu Qi gains the ire and distrust of Chu officials and aristocratic elite who are against his crusades to sweep up corruption in the state and limit their power.
* 388 BC: Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, having left Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
on Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
' death to visit Megara and possibly Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, travels to Syracuse at the invitation of Dionysius I's brother-in-law Dion.
* 387 BC: Under the threat of Spartan intervention, Thebes disbands its league, and Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
...
and Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government refor ...
end their shared government. Corinth, deprived of its strong ally, is incorporated back into Sparta's Peloponnesian League. After eight years of fighting, the Corinthian War is at an end.
* 387 BC: Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
founds the Platonic Academy
The Academy (Ancient Greek: Ἀκαδημία) was founded by Plato in c. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years (367–347 BC) before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic p ...
in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, where he teaches Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
until 347 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 347 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Venno and Torquatus (or, less frequently, year 407 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 347 BC for this year ...
.
* 387 BC: Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
begins to rebuild after being invaded by the Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
under Brennus
Brennus or Brennos is the name of two Gaulish chieftains, famous in ancient history:
* Brennus, chieftain of the Senones, a Gallic tribe originating from the modern areas of France known as Seine-et-Marne, Loiret, and Yonne; in 387 BC, in t ...
.
* 386 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 386 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Camillus, Cornelius, Fidenas, Cincinnatus, Pulvillus and Poplicola (or, less frequently, year 368 '' Ab urbe condita'') ...
: Freed from Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
n attacks by the King's Peace
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled ...
of the previous year, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
turns to quieting Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. Owing to the skill of King Evagoras of Cyprus and of Egypt's Greek mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any ...
general Chabrias
Chabrias ( el, Χαβρίας; bef. 420–357 BC) was an Athenian general active in the first half of the 4th century BC. During his career he was involved in several battles, both on land and sea. The orator Demosthenes described him as one o ...
, these wars drag on for the rest of the decade.
* 386 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 386 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Camillus, Cornelius, Fidenas, Cincinnatus, Pulvillus and Poplicola (or, less frequently, year 368 '' Ab urbe condita'') ...
: The Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
city of Handan is founded by the State of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained significant strength from the mil ...
.
* 385 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 385 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Capitolinus, Cornelius, Capitolinus, Papirius, Capitolinus and Fidenas (or, less frequently, year 369 '' Ab urbe condita ...
: Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
forms his Academy
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosop ...
, teaching mathematics, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
and other science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
s as well as philosophy. It is dedicated to the Attic hero Academus. Philanthropists bear all costs; students pay no fees.
* 384 BC: Lysias
Lysias (; el, Λυσίας; c. 445 – c. 380 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace i ...
, the Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
orator, on the occasion of the Olympiad
An olympiad ( el, Ὀλυμπιάς, ''Olympiás'') is a period of four years, particularly those associated with the ancient and modern Olympic Games.
Although the ancient Olympics were established during Greece's Archaic Era, it was not unti ...
, rebuke
In English law and the canon law of the Church of England, a rebuke is a censure on a member of the clergy. (Google Books) It is the least severe censure available against clergy of the Church of England, less severe than a monition. A rebuke can ...
s the Greeks for allowing themselves to be dominated by the Syracusan tyrant Dionysius I and by the barbarian Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
.
* 384 BC: The Greeks found the colony of Pharos at the site of today's Stari Grad on the island of Hvar
Hvar (; Chakavian: ''Hvor'' or ''For'', el, Φάρος, Pharos, la, Pharia, it, Lesina) is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, located off the Dalmatian coast, lying between the islands of Brač, Vis and Korčula. Approximately long,
wi ...
, defeating Iadasinoi warriors brought in for its defense.
* 383 BC: The 19 year lunar cycle
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
is introduced into the Babylonian calendar.
* 383 BC: The second Buddhist council is convened by king Kalasoka and held at Vaisali.
* 381 BC: Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
increases its hold on central Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
by reestablishing the city of Plataea, which Sparta formerly destroyed in 427 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 427 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ahala and Mugillanus (or, less frequently, year 327 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 427 BC for this year has b ...
.
* 381 BC: Wu Qi
Wu Qi (, 440–381 BC) was a Chinese military leader, Legalist philosopher, and politician in the Warring States period.
Biography
Born in the State of Wey (), he was skilled in leading armies and military strategy. He had served in the state ...
is assassinated at the funeral of King Diao of Chu, although his assassins are executed shortly after by the newly enthroned King Su of Chu.
* 380 BC
38 may refer to:
*38 (number), the natural number following 37 and preceding 39
*one of the years 38 BC, AD 38, 1938, 2038
*.38, a caliber of firearms and cartridges
**.38 Special, a revolver cartridge
*'' Thirty-Eight: The Hurricane That Transfo ...
: Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
forces the Athenians to withdraw their general Chabrias
Chabrias ( el, Χαβρίας; bef. 420–357 BC) was an Athenian general active in the first half of the 4th century BC. During his career he was involved in several battles, both on land and sea. The orator Demosthenes described him as one o ...
from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. Chabrias has been successfully supporting the Egyptian Pharaohs in maintaining their independence from the Persian Empire.
* 380 BC
38 may refer to:
*38 (number), the natural number following 37 and preceding 39
*one of the years 38 BC, AD 38, 1938, 2038
*.38, a caliber of firearms and cartridges
**.38 Special, a revolver cartridge
*'' Thirty-Eight: The Hurricane That Transfo ...
: Cleombrotus I
Cleombrotus I ( el, Κλεόμβροτος ; died 6 July 371 BC) was a Spartan king of the Agiad line, reigning from 380 BC until 371 BC. Little is known of Cleombrotus' early life. Son of Pausanias, he became king of Sparta after the death of h ...
succeeds his brother Agesipolis I
Agesipolis I ( grc-gre, Ἀγησίπολις; died 380 BC) was the twenty-first of the kings of the Agiad dynasty in ancient Sparta.
Agesipolis succeeded his father Pausanias, while still a minor, in 394 BC, and reigned fourteen years. Upon the ...
as king of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
.
376 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 376 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Mugillanus, Lanatus, Cornelius and Praetextatus (or, less frequently, year 378 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 3 ...
: The states of Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
, Wei and Zhao deposed Duke Jing of Jin and divided the last remaining Jin territory between themselves, which marked the final end of the Jin state.Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
.
356 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 356 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ambustus and Laenas (or, less frequently, year 398 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 356 BC for this year has bee ...
: Shang Yang
Shang Yang (; c. 390 – 338 BC), also known as Wei Yang () and originally surnamed Gongsun, was a Chinese jurist, philosopher, and politician.Antonio S. Cua (ed.), 2003, p. 362, ''Encyclopedia of Chinese Philosophy'"The fifth important legali ...
implemented his first set of reforms in Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
.
King Wei of Qi
King Wei of Qi (), whose personal name was Tian Yinqi (田因齊), was the king of the northern Chinese state of Qi during the Warring States period, when Qi was one of the most powerful states in China. He reigned from 356 to 320 BC. or accordin ...
and King Hui of Wei
King Hui of Wei (; 400–319 BC), originally called Marquis Hui of Wei, and after 344, King Hui of Liang () was the third ruler of the state of Wei during the Warring States period, ruling from approximately 369–319 BC. He was a grandson of Marq ...
, in effect declaring their independence from the Zhou court.
* 343 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 343 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Corvus and Arvina (or, less frequently, year 411 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 343 BC for this year has been us ...
: State of Qi wins the Battle of Maling
The Battle of Maling () took place in Maling, currently Dazhangjia Town (), Shen County (), Henan Province, in 342 BC during the Warring States period (476–221 BC). The combatants were the State of Qi, who fought on behalf of the State of Ha ...
over Wei that takes place in Maling, currently Dazhangjia Town, Shen County
Shen County (), or Shenxian, is a county of western Shandong province, People's Republic of China, bordering Henan to the south and southwest and Hebei to the west. It is the southernmost county-level division of the prefecture-level city of Liaoc ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
Province, during the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
. After the death of Pang Juan, Prince Shen was captured by Qi. The power of the state of Wei decreased considerably after this battle.
338 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 338 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camillus and Maenius (or, less frequently, year 416 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 338 BC for this year has b ...
: King Huiwen King Huiwen may refer to:
*King Huiwen of Qin (reigned 338–311 BC)
*King Huiwen of Zhao
King Huiwen of Zhao () (born 310 BCE - died 266 BCE, reigned 298 BCE – 266 BCE) reigned in the State of Zhao during the Warring States period of Chinese hi ...
becomes ruler of Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
.
* 331 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 331 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Marcellus (or, less frequently, year 423 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 331 BC for this year has b ...
: Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
Wins the Battle of Gaugamela, effectively ending Persian hegemony. He would spend much of the 330s conquering the remnants of the Achaemenid Empire.
* 331 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 331 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Marcellus (or, less frequently, year 423 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 331 BC for this year has b ...
: Chu rises to its peak in 334 BC, when it conquers Yue to its east on the Pacific coast.
323 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 323 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Longus and Cerretanus (or, less frequently, year 431 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 323 BC for this year has b ...
: In Babylon, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
dies, ten days after being taken ill after a prolonged banquet and drinking bout.
* 323 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 323 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Longus and Cerretanus (or, less frequently, year 431 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 323 BC for this year has b ...
: The Partition of Babylon sets out the division of the territories conquered by Alexander the Great between his generals. The partition is a result of a compromise, essentially brokered by Eumenes
Eumenes (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης; c. 362316 BC) was a Greek general and satrap. He participated in the Wars of Alexander the Great, serving as both Alexander's personal secretary and as a battlefield commander. He later was a participant in t ...
, following a conflict of opinion between the party of Meleager
In Greek mythology, Meleager (, grc-gre, Μελέαγρος, Meléagros) was a hero venerated in his ''temenos'' at Calydon in Aetolia. He was already famed as the host of the Calydonian boar hunt in the epic tradition that was reworked by Ho ...
, who wishes to give full power to Philip III, and the party of Perdiccas
Perdiccas ( el, Περδίκκας, ''Perdikkas''; 355 BC – 321/320 BC) was a general of Alexander the Great. He took part in the Macedonian campaign against the Achaemenid Empire, and, following Alexander's death in 323 BC, rose to beco ...
, who wishes to wait for the birth of the heir of Alexander and his wife, Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
to give him the throne under the control of a regent.
310s BC
This article concerns the period 319 BC – 310 BC.
References
{{Short pages monitor
















Politics
*Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, king of Macedon
* Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Macedonian diadoch
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wa ...
* Antipater, Macedonian statesman
*Appius Claudius Caecus
Appius Claudius Caecus ( 312–279 BC) was a statesman and writer from the Roman Republic. The first Roman public figure whose life can be traced with some historical certainty, Caecus was responsible for the building of Rome's first road (t ...
, Roman statesman
*Atropates
Atropates ( peo, *Ātr̥pātaʰ and Middle Persian ; grc, Ἀτροπάτης ; c. 370 BC - after 321 BC) was a Persian nobleman who served Darius III, then Alexander the Great, and eventually founded an independent kingdom and dynasty that wa ...
, Persian nobleman that founded an independent kingdom
* Bessus, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
n satrap of Bactria
*Cassander
Cassander ( el, Κάσσανδρος ; c. 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and ''de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
A son of Antipater and a conte ...
, King of Macedon
* Chandragupta Maurya, Founder of the "Mauryan Dynasty
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
"
*Craterus
Craterus or Krateros ( el, Κρατερός; c. 370 BC – 321 BC) was a Macedonian general under Alexander the Great and one of the Diadochi. Throughout his life he was a loyal royalist and supporter of Alexander the Great.Anson, Edward M. (20 ...
, Macedonian diadoch
* Darius III, king of the Achaemenid Empire
* Demetrius Poliocretes, King of Macedon
*Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual pr ...
, Athenian statesman and orator
*Dhana Nanda
Dhana Nanda (died c. 321 BCE), according to the Buddhist text '' Mahabodhivamsa'', was the last ruler of the Nanda dynasty of ancient India. He was the youngest son of Mahapadma Nanda.
Chandragupta Maurya raised an army that eventually conquere ...
, last emperor of the Nanda dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
*Duke Xiao of Qin
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranke ...
, ruler of Qin Qin may refer to:
Dynasties and states
* Qin (state) (秦), a major state during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China
* Qin dynasty (秦), founded by the Qin state in 221 BC and ended in 206 BC
* Daqin (大秦), ancient Chinese name for the Roman Emp ...
*Epaminondas
Epaminondas (; grc-gre, Ἐπαμεινώνδας; 419/411–362 BC) was a Greek general of Thebes and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent posit ...
, Theban statesman
*King Wuling of Zhao
King Wuling of Zhao () (died 295 BCE, reigned 325 BCE – 299 BCE) reigned in the State of Zhao during the Warring States period of Chinese history. His reign was famous for one important event: the reforms consisting of "Wearing the Hu (styled) A ...
, ruler of Zhao
* Lysimachus, Macedonian diadoch and king of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
*Mahapadma Nanda
Mahapadma Nanda (IAST: ''Mahāpadmānanda''; c. mid 4th century BCE), according to the Puranas, was the first Emperor of the Nanda Empire of ancient India. The Puranas describe him as a son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra ...
, founding emperor of the Nanda dynasty
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
*Manius Curius Dentatus
Manius Curius Dentatus (died 270 BC) was a Roman general and statesman noted for ending the Samnite War and for his military exploits during the Pyrrhic War. According to Pliny, he was born with teeth, thus earning the surname Dentatus, "toothed ...
, Roman statesman
* Nakhthorheb, last native Pharaoh of Egypt
*Pelopidas
Pelopidas (; grc-gre, Πελοπίδας; died 364 BC) was an important Theban statesman and general in Greece, instrumental in establishing the mid-fourth century Theban hegemony.
Biography
Athlete and warrior
Pelopidas was a member of a ...
, Theban statesman
*Perdiccas
Perdiccas ( el, Περδίκκας, ''Perdikkas''; 355 BC – 321/320 BC) was a general of Alexander the Great. He took part in the Macedonian campaign against the Achaemenid Empire, and, following Alexander's death in 323 BC, rose to beco ...
, Macedonian diadoch
*Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, King of Macedon
*Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedo ...
, Macedonian diadoch and king of Egypt
*Porus
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only ment ...
, King of the Pauravas
The Pauravas were an ancient dynasty on the Indus (present-day India and Pakistan) to which King Porus may have belonged.
Porus and the Pauravas
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, du ...
, in the Indian Subcontinent
*Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
, Macedonian diadoh and founder of the Seleucid Empire
*Shang Yang
Shang Yang (; c. 390 – 338 BC), also known as Wei Yang () and originally surnamed Gongsun, was a Chinese jurist, philosopher, and politician.Antonio S. Cua (ed.), 2003, p. 362, ''Encyclopedia of Chinese Philosophy'"The fifth important legali ...
, Chinese statesman
*Su Qin
Su Qin (380–284 BCE) was a Chinese political consultant and philosopher who was an influential political strategist during the Warring States period. He was born in Chengxuan Village, Luoyang in present-day Henan Province. According to legend S ...
, Chinese politician and strategist
Military leaders
* Hephaestion, Macedonian general *Pang Juan
Pang Juan (died 342 BC) was an ancient Chinese military general of the Wei state during the Warring States period.
Life
Early life
Pang Juan was a fellow student of Sun Bin and both of them studied military strategy together under the tutela ...
, Chinese general
*Parmenion
Parmenion (also Parmenio; grc-gre, Παρμενίων; c. 400 – 330 BC), son of Philotas, was a Macedonian general in the service of Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great. A nobleman, Parmenion rose to become Philip's chief milita ...
, Macedonian general
*Tian Ji
Tian Ji (), courtesy name Qi (齐), was a military general of the Qi state during the early Warring States period (4th century BC) of Chinese history. Tian Ji met Sun Bin and recommended him to King Wei of Qi as a military strategist. Tian Ji co ...
, Chinese general
* Zhang Yi, Chinese strategist
Visual arts
* Apelles, Greek painter *Cephisodotus the Elder
Cephisodotus or Kephisodotos ( gr, Κηφισόδοτος, flourished about 400 – c. 360 BC) was a Greek sculptor, perhaps the father or an uncle of Praxiteles, one of whose sculptor sons was Cephisodotus the Younger.
The one noted work ...
, Greek sculptor
*Leochares
Leochares () was a Greek sculptor from Athens, who lived in the 4th century BC.
Works
Leochares worked at the construction of the Mausoleum of Mausolos at Halicarnassus, one of the "Seven Wonders of the Ancient World". The '' Diana of Versaill ...
, Greek sculptor
* Lysippos, Greek sculptor
*Praxiteles
Praxiteles (; el, Πραξιτέλης) of Athens, the son of Cephisodotus the Elder, was the most renowned of the Attica sculptors of the 4th century BC. He was the first to sculpt the nude female form in a life-size statue. While no indubita ...
, Greek sculptor
*Scopas
Scopas ( grc-gre, Σκόπας; born in Paros, fl. 4th century BCE) was an ancient Greek sculptor and architect, most famous for his statue of Meleager, the copper statue of Aphrodite, and the head of goddess Hygieia, daughter of Asclepius.
Ea ...
, Greek sculptor and architect
Literature
*Demetrius of Phalerum
Demetrius of Phalerum (also Demetrius of Phaleron or Demetrius Phalereus; grc-gre, Δημήτριος ὁ Φαληρεύς; c. 350 – c. 280 BC) was an Athenian orator originally from Phalerum, an ancient port of Athens. A student of Theophrast ...
, Greek rhetorician
* Isocrates, Greek rhetorician and writer
* Menander, Greek playwright
*Onesicritus
Onesicritus ( el, Ὀνησίκριτος; c. 360 BC – c. 290 BC), a Greek historical writer and Cynic philosopher, who accompanied Alexander the Great on his campaigns in Asia. He claimed to have been the commander of Alexander's fleet but w ...
, Greek historical writer
*Qu Yuan
Qu Yuan ( – 278 BCE) was a Chinese poet and politician in the State of Chu during the Warring States period. He is known for his patriotism and contributions to classical poetry and verses, especially through the poems of the '' ...
, Chinese poet
*Simonides of Ceos
Simonides of Ceos (; grc-gre, Σιμωνίδης ὁ Κεῖος; c. 556–468 BC) was a Greek lyric poet, born in Ioulis on Ceos. The scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria included him in the canonical list of the nine lyric poets estee ...
, Greek lyric poet
*Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, Greek historian and writer
Science and philosophy
*Anaximenes of Lampsacus Anaximenes of Lampsacus (; grc, Ἀναξιμένης ὁ Λαμψακηνός; 320 BC) was a Greek rhetorician and historian. He was one of the teachers of Alexander the Great and accompanied him on his campaigns.
Family
His father was named Aris ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
rhetorician
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
and historian.
*Antisthenes
Antisthenes (; el, Ἀντισθένης; 446 366 BCE) was a Greek philosopher and a pupil of Socrates. Antisthenes first learned rhetoric under Gorgias before becoming an ardent disciple of Socrates. He adopted and developed the ethical side ...
, Greek philosopher
* Archytas, Greek philosopher
* Aristippus, Greek philosopher
*Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
, Greek philosopher
*Callisthenes
Callisthenes of Olynthus (; grc-gre, Καλλισθένης; 360327 BCE) was a well-connected Greek historian in Macedon, who accompanied Alexander the Great during his Asiatic expedition. The philosopher Aristotle was Callisthenes's great ...
, Greek historian
*Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭil ...
, Indian economist and political advisor
*Crates of Thebes
Crates ( grc-gre, Κράτης ὁ Θηβαῖος; c. 365 – c. 285 BC) of Thebes was a Greek Cynic philosopher, the principal pupil of Diogenes of Sinope and the husband of Hipparchia of Maroneia who lived in the same manner as him. Cr ...
, Greek philosopher
*Diogenes of Sinope
Diogenes ( ; grc, Διογένης, Diogénēs ), also known as Diogenes the Cynic (, ) or Diogenes of Sinope, was a Greek philosopher and one of the founders of Cynicism (philosophy). He was born in Sinope, an Ionian colony on the Black Sea ...
, Greek philosopher
* Epicurus, Greek philosopher
* Mencius, Chinese philosopher
* Panini, Indian philosopher and writer
*Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, Greek philosopher
* Pyrrho, Greek philosopher
*Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no te ...
, Greek Philosopher
*Speusippus
Speusippus (; grc-gre, Σπεύσιππος; c. 408 – 339/8 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher. Speusippus was Plato's nephew by his sister Potone. After Plato's death, c. 348 BC, Speusippus inherited the Academy, near age 60, and remaine ...
, Greek philosopher
*Sun Bin
Sun Bin (died 316 BC) was a Chinese general, military strategist, and writer who lived during the Warring States period of Chinese history. A supposed descendant of Sun Tzu, Sun was tutored in military strategy by the hermit Guiguzi. He w ...
, Chinese author and military strategist
*Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
, Greek philosopher
*Wu Qi
Wu Qi (, 440–381 BC) was a Chinese military leader, Legalist philosopher, and politician in the Warring States period.
Biography
Born in the State of Wey (), he was skilled in leading armies and military strategy. He had served in the state ...
, Chinese military strategist and philosopher
*Xenocrates
Xenocrates (; el, Ξενοκράτης; c. 396/5314/3 BC) of Chalcedon was a Greek philosopher, mathematician, and leader ( scholarch) of the Platonic Academy from 339/8 to 314/3 BC. His teachings followed those of Plato, which he attempted t ...
, Greek philosopher
*Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, Greek philosopher, writer and historian
*Zeno of Citium
Zeno of Citium (; grc-x-koine, Ζήνων ὁ Κιτιεύς, ; c. 334 – c. 262 BC) was a Hellenistic philosopher from Citium (, ), Cyprus. Zeno was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy, which he taught in Athens from about 300 B ...
, Greek philosopher
*Zhuangzi Zhuangzi may refer to:
* ''Zhuangzi'' (book) (莊子), an ancient Chinese collection of anecdotes and fables, one of the foundational texts of Daoism
**Zhuang Zhou
Zhuang Zhou (), commonly known as Zhuangzi (; ; literally "Master Zhuang"; als ...
, Chinese philosopher
Health professionals
*Agnodice
Agnodice or Agnodike ( grc, Ἀγνοδίκη ''Agnodikē'', c. 4th century BCE) is a legendary figure credited as the first female midwife or physician in ancient Athens. Her story is told by the Roman author Gaius Julius Hyginus in his ''Fabu ...
, female Athenian physician and midwife
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
* OldestBrahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' ...
dates from this period. Brāhmī is the ancestor of Brahmic scripts
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient Ind ...
, used in much of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
.
* Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
build their first aqueduct.
* Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
use the handheld trigger crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fire ...
for the first time.
* The first crossbow, the gastraphetes
The gastraphetes ( grc, γαστραφέτης, , belly-releaser), also called belly bow or belly shooter, was a hand-held crossbow used by the Ancient Greeks. It was described in the 1st century AD by the Greek author Heron of Alexandria in his ...
, is invented at Syracuse. (pre-421 BC)
* Burnt brick 'or fired bricks' were first used in Mediterranean civilizations.
* Donkey-powered mills or 'Pompeiian Mills' were first used in Greece and Italy.
* In Greece, Aristotle proposes the division of the known sciences.
* Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
with lion's-head terminals, from Susa (modern Shush, Iran
Shush ( fa, شوش; also Romanized as Shūsh, Shoosh, and by name of the ancient nearby city: Sūsa) is a city and capital of Shush County, Khuzestan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 53,897, in 10,689 families. Shush is l ...
) was made. It is now in Musée du Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
, Paris.
* Daric
The Persian daric was a gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos, represented the bimetallic monetary standard of the Achaemenid Persian Empire.Michael Alram"DARIC" ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', December 15, 1994, last updated N ...
, a coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
first minted under Darius I of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
is made. It is now kept in Heberden Coin Room, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
.
* Second half of the 4th century BC – Tomb II, so called Tomb of Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
, Vergina
Vergina ( el, Βεργίνα, ''Vergína'' ) is a small town in northern Greece, part of Veria municipality in Imathia, Central Macedonia. Vergina was established in 1922 in the aftermath of the population exchanges after the Treaty of Laus ...
, Macedonia is made.
* Starting in the year 309 BC, the later Chinese historian Sima Qian (145 BC–90 BC) wrote that the Qin-employed engineer Bi Ling of the newly conquered State of Shu in Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
had the shoulder of a mountain cut through, making the 'Separated Hill' that abated the Mo River, and excavated two canals in the plain of Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese pro ...
. The significance of this was phenomenal, as it allowed the new Guardian irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
system to populate an area of some 40 by 50 miles (60 × 80 km) with over five million people, still in use today (Needham, ''Science and Civilization in China'', Volume 4, Part 3, 288).
* The Chinese astronomer Gan De
Gan De (; fl. 4th century BC), also known as the Lord Gan (Gan Gong), was an ancient Chinese astronomer and astrologer born in the State of Qi. Along with Shi Shen, he is believed to be the first in history known by name to compile a star catal ...
divides the celestial sphere into 365¼ degrees, and the tropical year into 365¼ days at a time when most astronomers used the Babylon division of the celestial sphere as 360 degrees (Deng, Yinke. 005
''005'' is a 1981 arcade game by Sega. They advertised it as the first of their RasterScan Convert-a-Game series, designed so that it could be changed into another game in minutes "at a substantial savings". It is one of the first examples of a ...
(2005). ''Chinese Ancient Inventions''. ).
* First formal system
A formal system is an abstract structure used for inferring theorems from axioms according to a set of rules. These rules, which are used for carrying out the inference of theorems from axioms, are the logical calculus of the formal system.
A form ...
by Pāṇini
, era = ;;6th–5th century BCE
, region = Indian philosophy
, main_interests = Grammar, linguistics
, notable_works = ' ( Classical Sanskrit)
, influenced=
, notable_ideas=Descriptive linguistics
(Devanaga ...
in Mahajanapada
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and ''janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urba ...
, ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
and written in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
.
Sovereign states
See: List of political entities in the 4th century BC.References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:4th century Bc -6 -96