19th-century Arab People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the
 The first electronics appeared in the 19th century, with the introduction of the electric relay in 1835, the telegraph and its
The first electronics appeared in the 19th century, with the introduction of the electric relay in 1835, the telegraph and its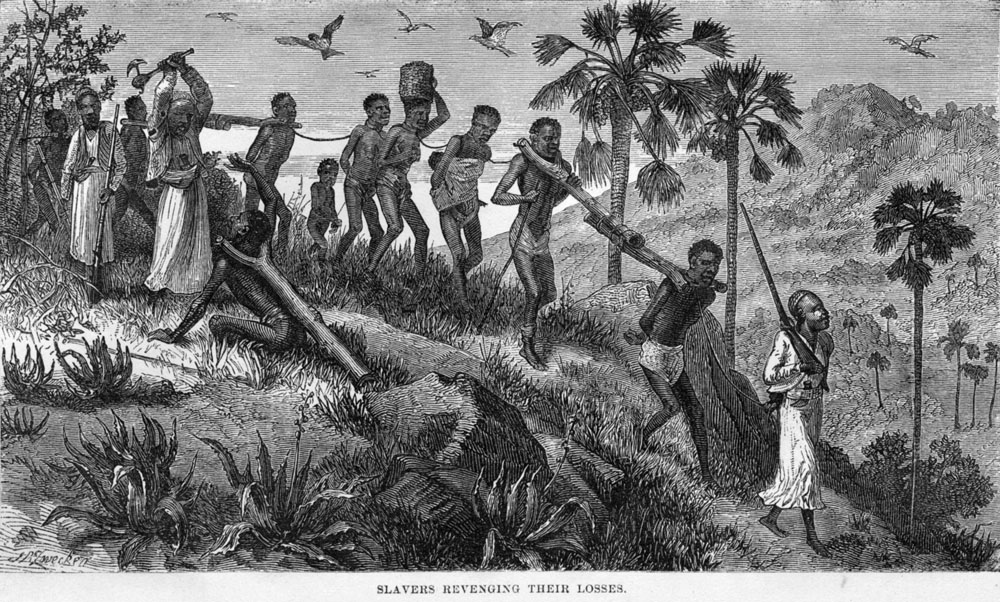  Slavery was greatly reduced around the world. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti, Britain and France stepped up the battle against the
Slavery was greatly reduced around the world. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti, Britain and France stepped up the battle against the  It also marks the fall of the Ottoman rule of the Balkans which led to the creation of Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, and Romania as a result of the
It also marks the fall of the Ottoman rule of the Balkans which led to the creation of Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, and Romania as a result of the
 * Industrial revolution
* European imperialism
* British Regency, Victorian era (UK, British Empire)
*
* Industrial revolution
* European imperialism
* British Regency, Victorian era (UK, British Empire)
*
 The Napoleonic Wars were a series of major conflicts from 1803 to 1815 pitting the
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of major conflicts from 1803 to 1815 pitting the
 Mexico and the majority of the countries in Central America and South America obtained independence from
Mexico and the majority of the countries in Central America and South America obtained independence from
 The Revolutions of 1848 were a series of
The Revolutions of 1848 were a series of
 The
The
 The Taiping Rebellion was the bloodiest conflict of the 19th century, leading to the deaths of around 20-30 million people. Its leader,
The Taiping Rebellion was the bloodiest conflict of the 19th century, leading to the deaths of around 20-30 million people. Its leader,

 * 1803: United States more than doubles in size when it buys out France's territorial claims in North America via the Louisiana Purchase. This begins the U.S.'s westward expansion to the Pacific, referred to as its Manifest Destiny, which involves United States territorial acquisitions, annexing and conquering land from Mexico, Britain, and Native Americans.
* 1817 – 1819: British Empire annexed the Maratha Empire, Maratha Confederacy after the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
* 1823 – 1887: British Empire annexed Burma (now also called Myanmar) after three Anglo-Burmese Wars.
* 1848 – 1849: Sikh Empire is defeated in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. Therefore, the entire Indian subcontinent is under British control.
* 1862: France gained its first foothold in Southeast Asia and in 1863 annexed Cambodia.
* 1867: United States Alaska Purchase, purchased Alaska from Russia.
* 1803: United States more than doubles in size when it buys out France's territorial claims in North America via the Louisiana Purchase. This begins the U.S.'s westward expansion to the Pacific, referred to as its Manifest Destiny, which involves United States territorial acquisitions, annexing and conquering land from Mexico, Britain, and Native Americans.
* 1817 – 1819: British Empire annexed the Maratha Empire, Maratha Confederacy after the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
* 1823 – 1887: British Empire annexed Burma (now also called Myanmar) after three Anglo-Burmese Wars.
* 1848 – 1849: Sikh Empire is defeated in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. Therefore, the entire Indian subcontinent is under British control.
* 1862: France gained its first foothold in Southeast Asia and in 1863 annexed Cambodia.
* 1867: United States Alaska Purchase, purchased Alaska from Russia.
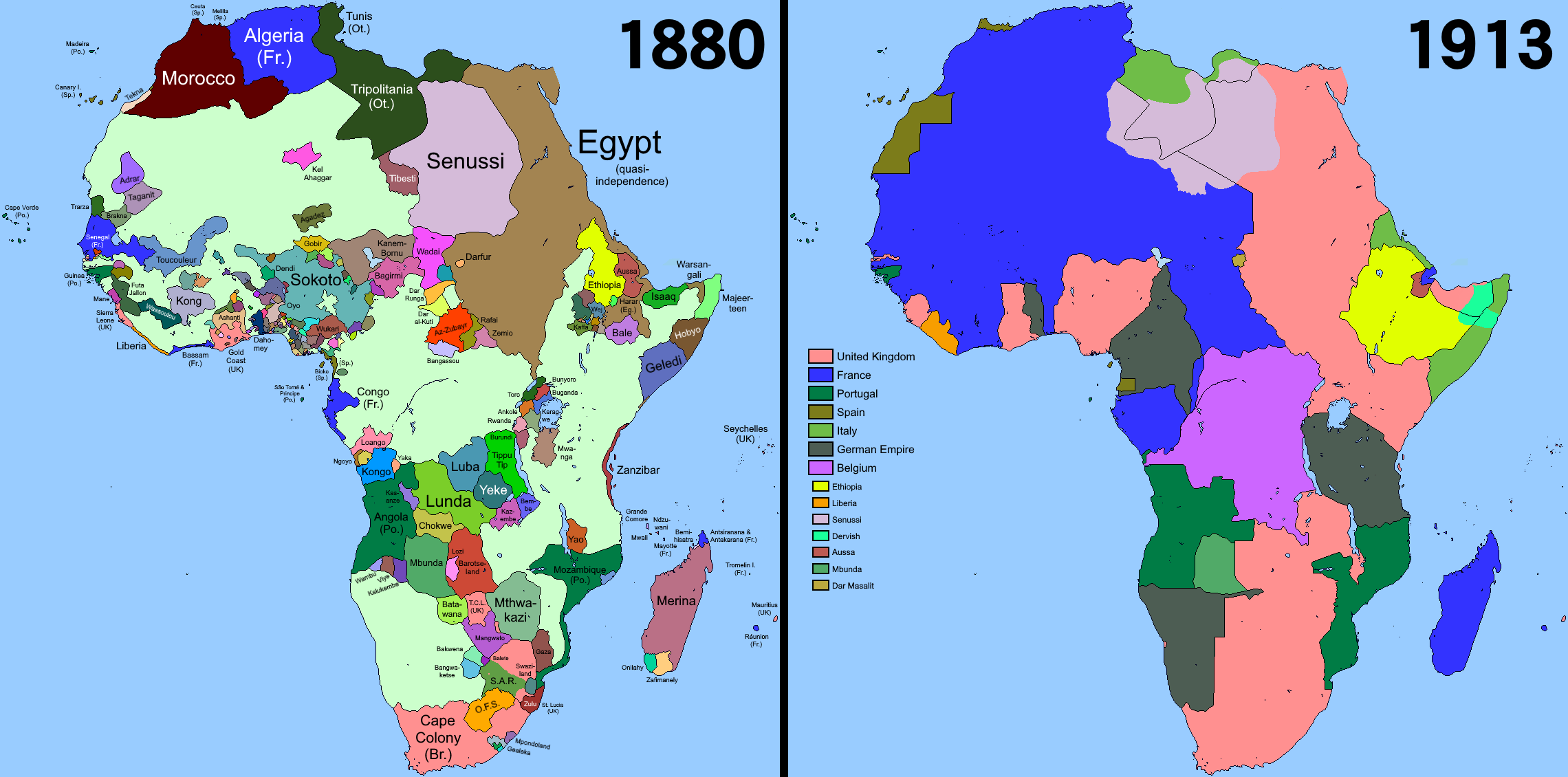 In Africa, European exploration and technology led to the colonization of almost the entire continent by 1898. New medicines such as quinine and more advanced firearms allowed European nations to conquer native populations.
Motivations for the Scramble for Africa included national pride, desire for raw materials, and Christian missionary activity. Britain seized control of Egypt to ensure control of the Suez Canal, but Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia defeated Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa. France, Belgium, Portugal, and Germany also had substantial colonies. The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885 attempted to reach agreement on colonial borders in Africa, but disputes continued, both amongst European powers and in resistance by the native populations.
In 1867, diamonds were discovered in the Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley region of South Africa. In 1886, gold was discovered in South African Republic, Transvaal. This led to colonization in Southern Africa by the British and business interests, led by Cecil Rhodes.
In Africa, European exploration and technology led to the colonization of almost the entire continent by 1898. New medicines such as quinine and more advanced firearms allowed European nations to conquer native populations.
Motivations for the Scramble for Africa included national pride, desire for raw materials, and Christian missionary activity. Britain seized control of Egypt to ensure control of the Suez Canal, but Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia defeated Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa. France, Belgium, Portugal, and Germany also had substantial colonies. The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885 attempted to reach agreement on colonial borders in Africa, but disputes continued, both amongst European powers and in resistance by the native populations.
In 1867, diamonds were discovered in the Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley region of South Africa. In 1886, gold was discovered in South African Republic, Transvaal. This led to colonization in Southern Africa by the British and business interests, led by Cecil Rhodes.
 * 1810: Grito de Dolores begins the Mexican War of Independence.
* 1811: Battle of Tippecanoe: U.S outnumbering Native Americans resulting in defeat and burning of community
* 1812–1815: War of 1812 between the United States and Britain; ends in a draw, except that Native Americans lose power.
* 1813–1837: Afghan–Sikh Wars.
* 1814–1816: Anglo-Nepalese War between Nepal (Gurkha Empire) and British Empire.
* 1817: First Seminole War begins in Florida.
* 1817: Russia commences its Caucasian War, conquest of the Caucasus.
* 1820: Revolutions of 1820 in Southern Europe
* 1821–1830:
* 1810: Grito de Dolores begins the Mexican War of Independence.
* 1811: Battle of Tippecanoe: U.S outnumbering Native Americans resulting in defeat and burning of community
* 1812–1815: War of 1812 between the United States and Britain; ends in a draw, except that Native Americans lose power.
* 1813–1837: Afghan–Sikh Wars.
* 1814–1816: Anglo-Nepalese War between Nepal (Gurkha Empire) and British Empire.
* 1817: First Seminole War begins in Florida.
* 1817: Russia commences its Caucasian War, conquest of the Caucasus.
* 1820: Revolutions of 1820 in Southern Europe
* 1821–1830:  * 1861–1867: Second French intervention in Mexico, French intervention in Mexico and the creation of the Second Mexican Empire, ruled by Maximilian I of Mexico and his consort Carlota of Mexico.
* 1863–1865: January Uprising against the Russian Empire.
* 1864–1870: Paraguayan War ends Paraguayan ambitions for expansion and destroys much of the Paraguayan population.
* 1866: Austro-Prussian War results in the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of the North German Confederation and the Austria-Hungary, Austrian-Hungarian Dual Monarchy.
* 1868-1869: Boshin War results in end of the shogunate and the founding the Japanese Empire.
* 1868–1878: Ten Years' War between Cuba and Kingdom of Spain, Spain.
* 1870–1871: Franco-Prussian War results in the Unification of Germany, unifications of Germany Italian unification, and Italy, the collapse of the Second French Empire and the emergence of a New Imperialism.
* 1870: Napoleon III abdicated after unsuccessful conclusion of Franco-Prussian War. Third Republic proclaimed.
* 1876: The April Uprising in Bulgaria against the Ottoman Empire.
* 1879: Anglo-Zulu War results in British victory and the annexation of the
* 1861–1867: Second French intervention in Mexico, French intervention in Mexico and the creation of the Second Mexican Empire, ruled by Maximilian I of Mexico and his consort Carlota of Mexico.
* 1863–1865: January Uprising against the Russian Empire.
* 1864–1870: Paraguayan War ends Paraguayan ambitions for expansion and destroys much of the Paraguayan population.
* 1866: Austro-Prussian War results in the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of the North German Confederation and the Austria-Hungary, Austrian-Hungarian Dual Monarchy.
* 1868-1869: Boshin War results in end of the shogunate and the founding the Japanese Empire.
* 1868–1878: Ten Years' War between Cuba and Kingdom of Spain, Spain.
* 1870–1871: Franco-Prussian War results in the Unification of Germany, unifications of Germany Italian unification, and Italy, the collapse of the Second French Empire and the emergence of a New Imperialism.
* 1870: Napoleon III abdicated after unsuccessful conclusion of Franco-Prussian War. Third Republic proclaimed.
* 1876: The April Uprising in Bulgaria against the Ottoman Empire.
* 1879: Anglo-Zulu War results in British victory and the annexation of the  * 1882: Anglo-Egyptian War British invasion and subsequent occupation of Khedivate of Egypt, Egypt
* 1883–1898: Mandingo Wars between the French colonial empire and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandinka people, Mandingo people led by Samory Touré.
* 1894–1895: After the First Sino-Japanese War, China cedes Taiwan to Japan and grants Japan a free hand in Korea.
* 1895: Taiwan is ceded to the Empire of Japan as a result of the First Sino-Japanese War.
* 1895–1896: Ethiopia defeats Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa.
* 1895–1898: Cuban War for Independence results in Cuban independence from Spanish Empire, Spain.
* 1896-1898: Philippine Revolution results in a Filipino victory.
* 1898: Spanish–American War results in the independence of Cuba.
* 1899–1901: Boxer Rebellion in China is suppressed by the Eight-Nation Alliance.
* 1899–1902: Thousand Days' War in
* 1882: Anglo-Egyptian War British invasion and subsequent occupation of Khedivate of Egypt, Egypt
* 1883–1898: Mandingo Wars between the French colonial empire and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandinka people, Mandingo people led by Samory Touré.
* 1894–1895: After the First Sino-Japanese War, China cedes Taiwan to Japan and grants Japan a free hand in Korea.
* 1895: Taiwan is ceded to the Empire of Japan as a result of the First Sino-Japanese War.
* 1895–1896: Ethiopia defeats Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa.
* 1895–1898: Cuban War for Independence results in Cuban independence from Spanish Empire, Spain.
* 1896-1898: Philippine Revolution results in a Filipino victory.
* 1898: Spanish–American War results in the independence of Cuba.
* 1899–1901: Boxer Rebellion in China is suppressed by the Eight-Nation Alliance.
* 1899–1902: Thousand Days' War in

 * 1807: Potassium and Sodium are individually isolated by Sir Humphry Davy.
* 1831–1836: Charles Darwin's journey on .
* 1859: Charles Darwin publishes ''On the Origin of Species''.
* 1861: James Clerk Maxwell publishes ''On Physical Lines of Force'', formulating the four Maxwell's equations.
* 1865: Gregor Mendel formulates his laws of inheritance.
* 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev creates the Periodic table.
* 1873: Maxwell's ''A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism'' published.
* 1877: Asaph Hall discovers the moons of Mars
* 1896: Henri Becquerel discovers radioactivity; J. J. Thomson identifies the electron, though not by name.
* 1807: Potassium and Sodium are individually isolated by Sir Humphry Davy.
* 1831–1836: Charles Darwin's journey on .
* 1859: Charles Darwin publishes ''On the Origin of Species''.
* 1861: James Clerk Maxwell publishes ''On Physical Lines of Force'', formulating the four Maxwell's equations.
* 1865: Gregor Mendel formulates his laws of inheritance.
* 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev creates the Periodic table.
* 1873: Maxwell's ''A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism'' published.
* 1877: Asaph Hall discovers the moons of Mars
* 1896: Henri Becquerel discovers radioactivity; J. J. Thomson identifies the electron, though not by name.
 * 1804: Morphine first isolated.
* 1842: Anesthesia used for the first time.
* 1847: Chloroform invented for the first time, given to Queen Victoria at the birth of her eighth child, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany, Prince Leopold in 1853
* 1855: Cocaine is isolated by Friedrich Gaedcke.
* 1885: Louis Pasteur creates the first successful vaccine against rabies for a young boy who had been bitten 14 times by a rabid dog.
* 1889: Aspirin patented.
* 1804: Morphine first isolated.
* 1842: Anesthesia used for the first time.
* 1847: Chloroform invented for the first time, given to Queen Victoria at the birth of her eighth child, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany, Prince Leopold in 1853
* 1855: Cocaine is isolated by Friedrich Gaedcke.
* 1885: Louis Pasteur creates the first successful vaccine against rabies for a young boy who had been bitten 14 times by a rabid dog.
* 1889: Aspirin patented.
 * 1804: First steam locomotive begins operation.
* 1816: Dandy horse, Laufmaschine invented by Karl von Drais.
* 1825: Erie Canal opened connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
* 1825: First isolation of aluminum, aluminium.
* 1825: The Stockton and Darlington Railway, the first public railway in the world, is opened.
* 1826: Samuel Morey patents the internal combustion engine.
* 1829: First electric motor built.
* 1837: Telegraphy patented.
* 1841: The word "dinosaur" is coined by Richard Owen.
* 1844: First publicly funded telegraph line in the world—between Baltimore and Washington—sends demonstration message on 24 May, ushering in the age of the telegraph. This message read "What hath God wrought?" (Bible, Numbers 23:23)
* 1849: The safety pin and the gas mask are invented.
* 1852: The first successful blimp is invented
* 1855: Bessemer process enables steel to be mass-produced.
* 1856: World's first oil refinery in Romania
* 1858: Invention of the phonautograph, the first true device for recorded sound, recording sound.
* 1859: The first ironclad was launched into sea by the French Navy.
* 1860: Benjamin Tyler Henry invents the 16 - shot Henry Rifle
* 1861: Richard Gatling invents the Gatling Gun, first modern machine gun used notably in the battles of Cold Harbor and Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg
* 1862: First meeting in combat of ironclad warships, and , during the American Civil War.
* 1863: First section of the London Underground opens.
* 1866: Successful transatlantic telegraph cable follows an earlier attempt in 1858.
* 1867: Alfred Nobel invents dynamite.
* 1868: Safety bicycle invented.
* 1869: First transcontinental railroad completed in United States on 10 May.
* 1870: Rasmus Malling-Hansen's invention the Hansen Writing Ball becomes the first commercially sold typewriter.
* 1873: Jeans, Blue jeans and barbed wire are invented.
* 1877: Thomas Edison invents the phonograph
* 1878: First commercial telephone exchange in New Haven, Connecticut.
* c. 1875/1880: Introduction of the widespread use of electric lighting. These included early crude systems in France and the UK and the introduction of large scale outdoor Arc lamp, arc lighting systems by 1880.
* 1879: Thomas Edison patents a practical incandescent light bulb.
* 1882: Introduction of large scale Electric power industry, electric power utilities with the Edison Holborn Viaduct power station, Holborn Viaduct (London) and Pearl Street Station, Pearl Street (New York) power stations supplying indoor electric lighting using Edison's incandescent bulb.
* 1884: Sir Hiram Maxim invents the first self-powered Machine gun.
* 1885: Singer Manufacturing Company, Singer begins production of the 'Singer Model 27 and 127, Vibrating Shuttle'. which would become the most popular model of sewing machine.
* 1886: Karl Benz sells the first commercial automobile.
* 1890: The cardboard box is invented.
* 1892: John Froelich develops and constructs the first gasoline/petrol-powered tractor.
* 1894: Karl Elsener (inventor), Karl Elsener invents the Swiss Army knife.
* 1894: First gramophone record.
* 1895: Wilhelm Röntgen identifies x-rays.
* 1804: First steam locomotive begins operation.
* 1816: Dandy horse, Laufmaschine invented by Karl von Drais.
* 1825: Erie Canal opened connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
* 1825: First isolation of aluminum, aluminium.
* 1825: The Stockton and Darlington Railway, the first public railway in the world, is opened.
* 1826: Samuel Morey patents the internal combustion engine.
* 1829: First electric motor built.
* 1837: Telegraphy patented.
* 1841: The word "dinosaur" is coined by Richard Owen.
* 1844: First publicly funded telegraph line in the world—between Baltimore and Washington—sends demonstration message on 24 May, ushering in the age of the telegraph. This message read "What hath God wrought?" (Bible, Numbers 23:23)
* 1849: The safety pin and the gas mask are invented.
* 1852: The first successful blimp is invented
* 1855: Bessemer process enables steel to be mass-produced.
* 1856: World's first oil refinery in Romania
* 1858: Invention of the phonautograph, the first true device for recorded sound, recording sound.
* 1859: The first ironclad was launched into sea by the French Navy.
* 1860: Benjamin Tyler Henry invents the 16 - shot Henry Rifle
* 1861: Richard Gatling invents the Gatling Gun, first modern machine gun used notably in the battles of Cold Harbor and Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg
* 1862: First meeting in combat of ironclad warships, and , during the American Civil War.
* 1863: First section of the London Underground opens.
* 1866: Successful transatlantic telegraph cable follows an earlier attempt in 1858.
* 1867: Alfred Nobel invents dynamite.
* 1868: Safety bicycle invented.
* 1869: First transcontinental railroad completed in United States on 10 May.
* 1870: Rasmus Malling-Hansen's invention the Hansen Writing Ball becomes the first commercially sold typewriter.
* 1873: Jeans, Blue jeans and barbed wire are invented.
* 1877: Thomas Edison invents the phonograph
* 1878: First commercial telephone exchange in New Haven, Connecticut.
* c. 1875/1880: Introduction of the widespread use of electric lighting. These included early crude systems in France and the UK and the introduction of large scale outdoor Arc lamp, arc lighting systems by 1880.
* 1879: Thomas Edison patents a practical incandescent light bulb.
* 1882: Introduction of large scale Electric power industry, electric power utilities with the Edison Holborn Viaduct power station, Holborn Viaduct (London) and Pearl Street Station, Pearl Street (New York) power stations supplying indoor electric lighting using Edison's incandescent bulb.
* 1884: Sir Hiram Maxim invents the first self-powered Machine gun.
* 1885: Singer Manufacturing Company, Singer begins production of the 'Singer Model 27 and 127, Vibrating Shuttle'. which would become the most popular model of sewing machine.
* 1886: Karl Benz sells the first commercial automobile.
* 1890: The cardboard box is invented.
* 1892: John Froelich develops and constructs the first gasoline/petrol-powered tractor.
* 1894: Karl Elsener (inventor), Karl Elsener invents the Swiss Army knife.
* 1894: First gramophone record.
* 1895: Wilhelm Röntgen identifies x-rays.
 * 1808: Beethoven composes Symphony No. 5 (Beethoven), Fifth Symphony
* 1813: Jane Austen publishes ''Pride and Prejudice''
* 1818: Mary Shelley publishes ''Frankenstein''.
* 1819: John Keats writes his John Keats's 1819 odes, six of his best-known odes.
* 1819: Théodore Géricault paints his masterpiece ''The Raft of the Medusa'', and exhibits it in the French Salon of 1819 at the The Louvre, Louvre.
* 1824: Premiere of Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven's ''Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), Ninth Symphony''.
* 1829: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's ''Goethe's Faust, Faust'' premieres.
* 1837: Charles Dickens publishes ''Oliver Twist''.
* 1841: Ralph Waldo Emerson publishes ''Self-Reliance''.
* 1845: Frederick Douglass publishes ''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave''.
* 1847: The Brontë sisters publish ''Jane Eyre'', ''Wuthering Heights'' and ''Agnes Grey''.
* 1848: Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels publish ''The Communist Manifesto''.
* 1849: Josiah Henson publishes The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself.
* 1851: Herman Melville publishes Moby-Dick.
* 1851: Sojourner Truth delivers the speech Ain't I a Woman?.
* 1852: Harriet Beecher Stowe publishes Uncle Tom's Cabin.
* 1855: Walt Whitman publishes the first edition of ''Leaves of Grass''.
* 1855: Frederick Douglass publishes the first edition of ''My Bondage and My Freedom''.
* 1862: Victor Hugo publishes ''Les Misérables''.
* 1863: Jules Verne begins publishing his collection of stories and novels, ''Voyages extraordinaires'', with the novel ''Cinq semaines en ballon''.
* 1865: Lewis Carroll publishes Alice's Adventures in Wonderland.
* 1869: Leo Tolstoy publishes ''War and Peace''.
* 1875: Georges Bizet's opera Carmen premiers in Paris.
* 1876: Richard Wagner's ''Ring Cycle'' is first performed in its entirety.
* 1883: Robert Louis Stevenson's ''Treasure Island'' is published.
* 1884: Mark Twain publishes the ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn''.
* 1886: "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" by Robert Louis Stevenson is published.
* 1887: Sir Arthur Conan Doyle publishes his first Sherlock Holmes story, ''A Study in Scarlet''.
* 1889: Vincent van Gogh paints ''The Starry Night''.
* 1889: Moulin Rouge opens in Paris.
* 1892: Tchaikovsky's ''Nutcracker Suite'' premières in St Petersberg.
* 1894: Rudyard Kipling's ''The Jungle Book'' is published
* 1895: Trial of Oscar Wilde and premiere of his play ''The Importance of Being Earnest''.
* 1897: Bram Stoker writes Dracula.
* 1900: L. Frank Baum publishes The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.
* 1808: Beethoven composes Symphony No. 5 (Beethoven), Fifth Symphony
* 1813: Jane Austen publishes ''Pride and Prejudice''
* 1818: Mary Shelley publishes ''Frankenstein''.
* 1819: John Keats writes his John Keats's 1819 odes, six of his best-known odes.
* 1819: Théodore Géricault paints his masterpiece ''The Raft of the Medusa'', and exhibits it in the French Salon of 1819 at the The Louvre, Louvre.
* 1824: Premiere of Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven's ''Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), Ninth Symphony''.
* 1829: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's ''Goethe's Faust, Faust'' premieres.
* 1837: Charles Dickens publishes ''Oliver Twist''.
* 1841: Ralph Waldo Emerson publishes ''Self-Reliance''.
* 1845: Frederick Douglass publishes ''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave''.
* 1847: The Brontë sisters publish ''Jane Eyre'', ''Wuthering Heights'' and ''Agnes Grey''.
* 1848: Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels publish ''The Communist Manifesto''.
* 1849: Josiah Henson publishes The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself.
* 1851: Herman Melville publishes Moby-Dick.
* 1851: Sojourner Truth delivers the speech Ain't I a Woman?.
* 1852: Harriet Beecher Stowe publishes Uncle Tom's Cabin.
* 1855: Walt Whitman publishes the first edition of ''Leaves of Grass''.
* 1855: Frederick Douglass publishes the first edition of ''My Bondage and My Freedom''.
* 1862: Victor Hugo publishes ''Les Misérables''.
* 1863: Jules Verne begins publishing his collection of stories and novels, ''Voyages extraordinaires'', with the novel ''Cinq semaines en ballon''.
* 1865: Lewis Carroll publishes Alice's Adventures in Wonderland.
* 1869: Leo Tolstoy publishes ''War and Peace''.
* 1875: Georges Bizet's opera Carmen premiers in Paris.
* 1876: Richard Wagner's ''Ring Cycle'' is first performed in its entirety.
* 1883: Robert Louis Stevenson's ''Treasure Island'' is published.
* 1884: Mark Twain publishes the ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn''.
* 1886: "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" by Robert Louis Stevenson is published.
* 1887: Sir Arthur Conan Doyle publishes his first Sherlock Holmes story, ''A Study in Scarlet''.
* 1889: Vincent van Gogh paints ''The Starry Night''.
* 1889: Moulin Rouge opens in Paris.
* 1892: Tchaikovsky's ''Nutcracker Suite'' premières in St Petersberg.
* 1894: Rudyard Kipling's ''The Jungle Book'' is published
* 1895: Trial of Oscar Wilde and premiere of his play ''The Importance of Being Earnest''.
* 1897: Bram Stoker writes Dracula.
* 1900: L. Frank Baum publishes The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.
 The Realism (arts), Realism and Romanticism of the early 19th century gave way to Impressionism and Post-Impressionism in the later half of the century, with Paris being the dominant art capital of the world. In the United States the Hudson River School was prominent. 19th-century painters included:
*Ivan Aivazovsky
*Léon Bakst
*Albert Bierstadt
*William Blake
*Arnold Böcklin
*Rosa Bonheur
*William Burges
*Mary Cassatt
*Camille Claudel
*Paul Cézanne
*Frederic Edwin Church
*Thomas Cole
*Jan Matejko
*John Constable
*Camille Corot
*Gustave Courbet
*Honoré Daumier
*Edgar Degas
*Eugène Delacroix
*Thomas Eakins
*Caspar David Friedrich
*Paul Gauguin
*Théodore Géricault
*Vincent van Gogh
*William Morris
*Francisco Goya
*Andō Hiroshige
*Hokusai
*Winslow Homer
*Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
*Isaac Levitan
*Édouard Manet
*Claude Monet
*Gustave Moreau
*Berthe Morisot
*Edvard Munch
*Mikhail Nesterov
*Camille Pissarro
*Augustus Pugin
*Pierre-Auguste Renoir
*Ilya Repin
*Auguste Rodin
*Albert Pinkham Ryder
*John Singer Sargent
*Valentin Serov
*Georges Seurat
*Ivan Shishkin
*Vasily Surikov
*James Tissot
*Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
*J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Mallord William Turner
*Viktor Vasnetsov
*Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
*Mikhail Vrubel
*James Abbott McNeill Whistler
*Tsukioka Yoshitoshi
The Realism (arts), Realism and Romanticism of the early 19th century gave way to Impressionism and Post-Impressionism in the later half of the century, with Paris being the dominant art capital of the world. In the United States the Hudson River School was prominent. 19th-century painters included:
*Ivan Aivazovsky
*Léon Bakst
*Albert Bierstadt
*William Blake
*Arnold Böcklin
*Rosa Bonheur
*William Burges
*Mary Cassatt
*Camille Claudel
*Paul Cézanne
*Frederic Edwin Church
*Thomas Cole
*Jan Matejko
*John Constable
*Camille Corot
*Gustave Courbet
*Honoré Daumier
*Edgar Degas
*Eugène Delacroix
*Thomas Eakins
*Caspar David Friedrich
*Paul Gauguin
*Théodore Géricault
*Vincent van Gogh
*William Morris
*Francisco Goya
*Andō Hiroshige
*Hokusai
*Winslow Homer
*Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
*Isaac Levitan
*Édouard Manet
*Claude Monet
*Gustave Moreau
*Berthe Morisot
*Edvard Munch
*Mikhail Nesterov
*Camille Pissarro
*Augustus Pugin
*Pierre-Auguste Renoir
*Ilya Repin
*Auguste Rodin
*Albert Pinkham Ryder
*John Singer Sargent
*Valentin Serov
*Georges Seurat
*Ivan Shishkin
*Vasily Surikov
*James Tissot
*Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
*J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Mallord William Turner
*Viktor Vasnetsov
*Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
*Mikhail Vrubel
*James Abbott McNeill Whistler
*Tsukioka Yoshitoshi

 Sonata form matured during the Classical era to become the primary form of instrumental compositions throughout the 19th century. Much of the music from the 19th century was referred to as being in the Romantic music, Romantic style. Many great composers lived through this era such as Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Liszt, Frédéric Chopin, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and Richard Wagner. The list includes:
*Mily Balakirev
*Ludwig van Beethoven
*Hector Berlioz
*Georges Bizet
*Alexander Borodin
*Johannes Brahms
*Anton Bruckner
*Frédéric Chopin
*Claude Debussy
*Antonín Dvořák
*Mikhail Glinka
*Edvard Grieg
*Scott Joplin
*Alexandre Levy
*Franz Liszt
*Gustav Mahler
*Felix Mendelssohn
*Modest Mussorgsky
*Jacques Offenbach
*Niccolò Paganini
*Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
*Gioachino Rossini
*Anton Rubinstein
*Camille Saint-Saëns
*Antonio Salieri
*Franz Schubert
*Robert Schumann
*Alexander Scriabin
*Arthur Sullivan
*Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
*Giuseppe Verdi
*Richard Wagner
Sonata form matured during the Classical era to become the primary form of instrumental compositions throughout the 19th century. Much of the music from the 19th century was referred to as being in the Romantic music, Romantic style. Many great composers lived through this era such as Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Liszt, Frédéric Chopin, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and Richard Wagner. The list includes:
*Mily Balakirev
*Ludwig van Beethoven
*Hector Berlioz
*Georges Bizet
*Alexander Borodin
*Johannes Brahms
*Anton Bruckner
*Frédéric Chopin
*Claude Debussy
*Antonín Dvořák
*Mikhail Glinka
*Edvard Grieg
*Scott Joplin
*Alexandre Levy
*Franz Liszt
*Gustav Mahler
*Felix Mendelssohn
*Modest Mussorgsky
*Jacques Offenbach
*Niccolò Paganini
*Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
*Gioachino Rossini
*Anton Rubinstein
*Camille Saint-Saëns
*Antonio Salieri
*Franz Schubert
*Robert Schumann
*Alexander Scriabin
*Arthur Sullivan
*Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
*Giuseppe Verdi
*Richard Wagner
 * 1810: The Humboldt University of Berlin, University of Berlin was founded. Among its students and faculty are Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Karl Marx, Marx, and Otto von Bismarck, Bismarck. The German university reform proves to be so successful that its model is copied around the world (see History of European universities#European university models in the 19th and 20th centuries, History of European research universities).
* 1814: Elisha Collier invents the Flintlock Revolver.
* 1814 : February 1 Eruption of Mayon Volcano
* 1815: April, Mount Tambora in Sumbawa island erupts, becoming the largest volcanic eruption in recorded history, destroying Tambora culture, and killing at least 71,000 people, including its aftermath. The eruption created global climate anomalies known as "volcanic winter".
* 1816: Year Without a Summer: Unusually cold conditions wreak havoc throughout the Northern Hemisphere, likely influenced by the 1815 explosion of Mount Tambora.
* 1816–1828: Shaka's
* 1810: The Humboldt University of Berlin, University of Berlin was founded. Among its students and faculty are Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Karl Marx, Marx, and Otto von Bismarck, Bismarck. The German university reform proves to be so successful that its model is copied around the world (see History of European universities#European university models in the 19th and 20th centuries, History of European research universities).
* 1814: Elisha Collier invents the Flintlock Revolver.
* 1814 : February 1 Eruption of Mayon Volcano
* 1815: April, Mount Tambora in Sumbawa island erupts, becoming the largest volcanic eruption in recorded history, destroying Tambora culture, and killing at least 71,000 people, including its aftermath. The eruption created global climate anomalies known as "volcanic winter".
* 1816: Year Without a Summer: Unusually cold conditions wreak havoc throughout the Northern Hemisphere, likely influenced by the 1815 explosion of Mount Tambora.
* 1816–1828: Shaka's  * 1829: Sir Robert Peel founds the Metropolitan Police Service, the first modern police force.
* 1829: Sir Robert Peel founds the Metropolitan Police Service, the first modern police force.
 * 1830: Anglo-Russian rivalry over Afghanistan, the Great Game, commences and concludes in 1895.
* 1831: November Uprising ends with crushing defeat for Poland in the Battle of Warsaw (1831), Battle of Warsaw.
* 1832: The British Parliament passes the Great Reform Act.
* 1834–1859: Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus.
* 1835–1836: The Texas Revolution in Mexico resulted in the short-lived Republic of Texas.
* 1836: Samuel Colt popularizes the revolver and sets up a firearms company to manufacture his invention of the Colt Paterson revolver a six bullets firearm shot one by one without reloading manually.
* 1837–1838: Rebellions of 1837 in Canada.
* 1838: By this time, 46,000 Native Americans have been forcibly relocated in the Trail of Tears.
* 1839–1860: After the First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, France, the United Kingdom, the United States and Russia gain many Treaty ports, trade and associated concessions from China resulting in the start of the decline of the Qing dynasty.
* 1839–1919: Anglo-Afghan Wars lead to stalemate and the establishment of the Durand line
* 1842: Treaty of Nanking cedes Hong Kong to the British.
* 1843: The first wagon train sets out from Missouri.
* 1844: Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers establish what is considered the first cooperative in the world.
* 1845–1849: The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of Ireland leads to the Irish diaspora.
* 1848: ''The Communist Manifesto'' published.
* 1848: Seneca Falls Convention is the first women's rights convention in the United States and leads to the History of Women's Suffrage in the United States, battle for women's suffrage.
* 1848–1855: California Gold Rush.
* 1849: Earliest recorded Airstrike, air raid, as Austria employs The Austrian balloons, 200 balloons to deliver ordnance against Venice.
* 1850: The Little Ice Age ends around this time.
* 1850: Franz Hermann Schulze-Delitzsch establishes the first cooperative banking, cooperative financial institution.
* 1830: Anglo-Russian rivalry over Afghanistan, the Great Game, commences and concludes in 1895.
* 1831: November Uprising ends with crushing defeat for Poland in the Battle of Warsaw (1831), Battle of Warsaw.
* 1832: The British Parliament passes the Great Reform Act.
* 1834–1859: Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus.
* 1835–1836: The Texas Revolution in Mexico resulted in the short-lived Republic of Texas.
* 1836: Samuel Colt popularizes the revolver and sets up a firearms company to manufacture his invention of the Colt Paterson revolver a six bullets firearm shot one by one without reloading manually.
* 1837–1838: Rebellions of 1837 in Canada.
* 1838: By this time, 46,000 Native Americans have been forcibly relocated in the Trail of Tears.
* 1839–1860: After the First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, France, the United Kingdom, the United States and Russia gain many Treaty ports, trade and associated concessions from China resulting in the start of the decline of the Qing dynasty.
* 1839–1919: Anglo-Afghan Wars lead to stalemate and the establishment of the Durand line
* 1842: Treaty of Nanking cedes Hong Kong to the British.
* 1843: The first wagon train sets out from Missouri.
* 1844: Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers establish what is considered the first cooperative in the world.
* 1845–1849: The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of Ireland leads to the Irish diaspora.
* 1848: ''The Communist Manifesto'' published.
* 1848: Seneca Falls Convention is the first women's rights convention in the United States and leads to the History of Women's Suffrage in the United States, battle for women's suffrage.
* 1848–1855: California Gold Rush.
* 1849: Earliest recorded Airstrike, air raid, as Austria employs The Austrian balloons, 200 balloons to deliver ordnance against Venice.
* 1850: The Little Ice Age ends around this time.
* 1850: Franz Hermann Schulze-Delitzsch establishes the first cooperative banking, cooperative financial institution.
 * 1860: Giuseppe Garibaldi launches the Expedition of the Thousand.
* 1861: Russia Emancipation reform of 1861 in Russia, abolishes serfdom.
* 1862–1877: Dungan revolt (1862–1877), Muslim Rebellion in north-west China.
* 1863: Formation of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, International Red Cross is followed by the adoption of the First Geneva Convention in 1864.
* 1865–1877: Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction in the United States; Slavery is banned in the United States by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
* 1868: Michael Barrett (Fenian), Michael Barrett is the last person to be publicly hanged in England.
* 1869: The Suez Canal opens linking the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to the Red Sea.
* 1860: Giuseppe Garibaldi launches the Expedition of the Thousand.
* 1861: Russia Emancipation reform of 1861 in Russia, abolishes serfdom.
* 1862–1877: Dungan revolt (1862–1877), Muslim Rebellion in north-west China.
* 1863: Formation of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, International Red Cross is followed by the adoption of the First Geneva Convention in 1864.
* 1865–1877: Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction in the United States; Slavery is banned in the United States by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
* 1868: Michael Barrett (Fenian), Michael Barrett is the last person to be publicly hanged in England.
* 1869: The Suez Canal opens linking the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to the Red Sea.

 * 1870: Official dismantling of the Cultivation System and beginning of a 'Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies), Liberal Policy' of deregulated exploitation of the Netherlands East Indies.Vickers (2005), page xii
* 1870–1890: Long Depression in Western Europe and North America.
* 1871–1872: List of famines, Famine in Iran, Persia is believed to have caused the death of 2 million.
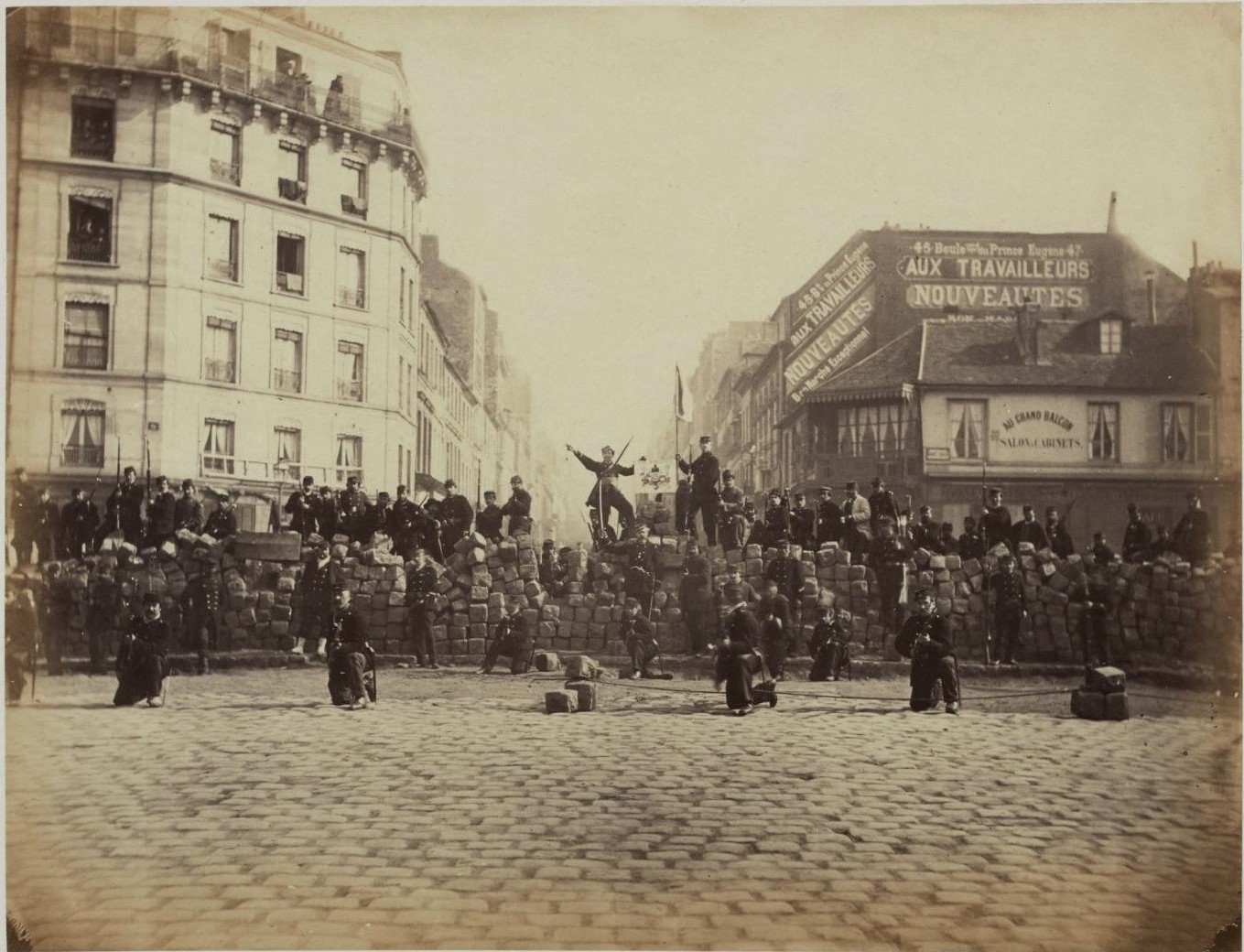
* 1871: The Paris Commune briefly rules the French capital.
* 1872: Yellowstone National Park, the first national park, is created.
* 1874: The ''Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, and Graveurs'', better known as the Impressionists, organize and present their first public group exhibition at the Paris studio of the photographer Nadar (photographer), Nadar.
* 1874: The Home Rule Movement is established in Ireland.
* 1875: ''HMS Challenger'' surveys the deepest point in the Earth's oceans, the Challenger Deep
* 1876: Battle of the Little Bighorn leads to the death of General Custer and victory for the alliance of Lakota people, Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, Cheyenne and Arapaho
* 1876–1914: The massive expansion in population, territory, industry and wealth in the United States is referred to as the Gilded Age.
* 1877: Great Railroad Strike in the United States may have been the world's first nationwide Strike action, labour strike.
* 1881: Wave of Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire, pogroms begins in the Russian Empire.
* 1881–1882: The Jules Ferry laws are passed in French Third Republic, France establishing free, secular education.
* 1883: Krakatoa volcano explosion, one of the largest in modern history.
* 1883: The quagga is rendered extinct.
* 1886: Construction of the Statue of Liberty; Coca-Cola is developed.
* 1888: Founding of the shipping line ''Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij'' (KPM) that supported the unification and development of the colonial economy.
* 1888: The Golden Law abolishes slavery in Brazil.
* 1889: Eiffel Tower is inaugurated in Paris.
* 1870: Official dismantling of the Cultivation System and beginning of a 'Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies), Liberal Policy' of deregulated exploitation of the Netherlands East Indies.Vickers (2005), page xii
* 1870–1890: Long Depression in Western Europe and North America.
* 1871–1872: List of famines, Famine in Iran, Persia is believed to have caused the death of 2 million.
* 1871: The Paris Commune briefly rules the French capital.
* 1872: Yellowstone National Park, the first national park, is created.
* 1874: The ''Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, and Graveurs'', better known as the Impressionists, organize and present their first public group exhibition at the Paris studio of the photographer Nadar (photographer), Nadar.
* 1874: The Home Rule Movement is established in Ireland.
* 1875: ''HMS Challenger'' surveys the deepest point in the Earth's oceans, the Challenger Deep
* 1876: Battle of the Little Bighorn leads to the death of General Custer and victory for the alliance of Lakota people, Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, Cheyenne and Arapaho
* 1876–1914: The massive expansion in population, territory, industry and wealth in the United States is referred to as the Gilded Age.
* 1877: Great Railroad Strike in the United States may have been the world's first nationwide Strike action, labour strike.
* 1881: Wave of Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire, pogroms begins in the Russian Empire.
* 1881–1882: The Jules Ferry laws are passed in French Third Republic, France establishing free, secular education.
* 1883: Krakatoa volcano explosion, one of the largest in modern history.
* 1883: The quagga is rendered extinct.
* 1886: Construction of the Statue of Liberty; Coca-Cola is developed.
* 1888: Founding of the shipping line ''Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij'' (KPM) that supported the unification and development of the colonial economy.
* 1888: The Golden Law abolishes slavery in Brazil.
* 1889: Eiffel Tower is inaugurated in Paris.
 * 1889: A republican military coup establishes the First Brazilian Republic. The Empire of Brazil, parliamentary constitutional monarchy is abolished.
* 1889-1890: 1889–1890 pandemic kills 1 million people.
* 1890: First use of the electric chair as a method of execution.
* 1892: The World's Columbian Exposition was held in Chicago celebrating the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World.
* 1892: Fingerprinting is officially adopted for the first time.
* 1893: New Zealand becomes the first country to enact women's suffrage.
* 1893: The Coremans-de Vriendt law is passed in Belgium, creating legal equality for French language, French and Dutch languages.
* 1894: The Dutch intervention in Lombok and Karangasem resulted in the looting and destruction of Cakranegara Palace in Mataram (city), Mataram.Wahyu Ernawati: "Chapter 8: The Lombok Treasure", in ''Colonial collections Revisited'': Pieter ter Keurs (editor) Vol. 152, CNWS publications. Issue 36 of ''Mededelingen van het Rijksmuseum voor Volkenkunde'', Leiden. CNWS Publications, 2007. . 296 pages. pp. 186–203 J. L. A. Brandes, a Dutch philologist, discovers and secures Nagarakretagama manuscript in Lombok royal library.
* 1896: Philippine Revolution ends declaring Philippines free from Spanish rule.
* 1898: The United States gains control of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines after the Spanish–American War.
* 1898: Empress Dowager Cixi of Qing Dynasty, China engineers a coup d'état, marking the end of the Hundred Days' Reform; the Guangxu Emperor is arrested.
* 1900: Exposition Universelle (1900), Exposition Universelle held in Paris, prominently featuring the growing art trend Art Nouveau.
* 1900–1901: Eight-Nation Alliance, Eight nations invade China at the same time and ransack Forbidden City.
* 1889: A republican military coup establishes the First Brazilian Republic. The Empire of Brazil, parliamentary constitutional monarchy is abolished.
* 1889-1890: 1889–1890 pandemic kills 1 million people.
* 1890: First use of the electric chair as a method of execution.
* 1892: The World's Columbian Exposition was held in Chicago celebrating the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World.
* 1892: Fingerprinting is officially adopted for the first time.
* 1893: New Zealand becomes the first country to enact women's suffrage.
* 1893: The Coremans-de Vriendt law is passed in Belgium, creating legal equality for French language, French and Dutch languages.
* 1894: The Dutch intervention in Lombok and Karangasem resulted in the looting and destruction of Cakranegara Palace in Mataram (city), Mataram.Wahyu Ernawati: "Chapter 8: The Lombok Treasure", in ''Colonial collections Revisited'': Pieter ter Keurs (editor) Vol. 152, CNWS publications. Issue 36 of ''Mededelingen van het Rijksmuseum voor Volkenkunde'', Leiden. CNWS Publications, 2007. . 296 pages. pp. 186–203 J. L. A. Brandes, a Dutch philologist, discovers and secures Nagarakretagama manuscript in Lombok royal library.
* 1896: Philippine Revolution ends declaring Philippines free from Spanish rule.
* 1898: The United States gains control of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines after the Spanish–American War.
* 1898: Empress Dowager Cixi of Qing Dynasty, China engineers a coup d'état, marking the end of the Hundred Days' Reform; the Guangxu Emperor is arrested.
* 1900: Exposition Universelle (1900), Exposition Universelle held in Paris, prominently featuring the growing art trend Art Nouveau.
* 1900–1901: Eight-Nation Alliance, Eight nations invade China at the same time and ransack Forbidden City.
File:Carl Friedrich Gauss 1840 by Jensen.jpg, Carl Friedrich Gauss
File:Charles Robert Darwin by John Collier cropped.jpg, Charles Darwin
File:Victor Hugo by Étienne Carjat 1876 - full.jpg, Victor Hugo c. 1876
File:Kramskoy Mendeleev 01.jpg, Dmitri Mendeleev
File:Louis Pasteur.jpg, Louis Pasteur, 1878
File:Mariecurie.jpg, Marie Curie, c. 1898
File:Nikola Tesla by Sarony c1898.jpg, Nikola Tesla
File:Jose Rizal full.jpg, José Rizal
File:Jane Austen (chopped) 2.jpg, Jane Austen
File:Leo Tolstoy 1897, black and white, 37767u.jpg, Leo Tolstoy c. 1897
File:Edgar Allan Poe 2.jpg, Edgar Allan Poe
File:Félix_Nadar_1820-1910_portraits_Jules_Verne.jpg, Jules Verne
File:Charles Dickens 3.jpg, Charles Dickens
File:Carjat Arthur Rimbaud 1872 n2.jpg, Arthur Rimbaud c. 1872
File:Twain in Tesla's Lab.jpg, Mark Twain, 1894
File:RWEmerson.jpg, Ralph Waldo Emerson
File:Benjamin D. Maxham - Henry David Thoreau - Restored - greyscale - straightened.jpg, Henry David Thoreau, August 1861.
File:Emile Zola 2.jpg, Émile Zola, c. 1900
File:Chekhov 1903 ArM.jpg, Anton Chekhov
File:Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoyevsky 1876.jpg, Fyodor Dostoevsky, 1876
File:John L Sullivan.jpg, John L Sullivan in his prime, c. 1882
File:David Livingstone -1.jpg, David Livingstone 1864, left Great Britain, Britain for Africa in 1840
File:Jesse and Frank James.gif, Jesse James, Jesse and Frank James, 1872
File:William Notman studios - Sitting Bull and Buffalo Bill (1895) edit.jpg, Sitting Bull and Buffalo Bill Cody, Montreal, Quebec, 1885
File:Goyaale.jpg, Geronimo, 1887, prominent leader of the Chiricahua Apache
File:Billy the Kid corrected.jpg, William Bonney aka Henry McCarty aka Billy the Kid, c. late 1870s
File:Wyatt Earp und Bat Masterson 1876.jpg, Deputies Bat Masterson and Wyatt Earp in Dodge City, 1876
File:Mathew Brady 1875 cropped.jpg, Mathew Brady, Self-portrait, c. 1875
File:Alfred Lord Tennyson 1869.jpg, Alfred, Lord Tennyson
File:Thomas Nast - Brady-Handy.jpg, Thomas Nast, c. 1860–1875, photo by Mathew Brady or Levin Handy
File:Hadhrat Mirza Ghulam Ahmad2.jpg, Mirza Ghulam Ahmad
File:Bakunin.png, Mikhail Bakunin
File:Kierkegaard.jpg, Søren Kierkegaard
File:Solomon Northup 001 (cropped).jpg, Solomon Northup
File:Dred Scott photograph (circa 1857).jpg, Dred Scott
File:Madame CJ Walker.gif, Madam C. J. Walker
File:Claude Monet, Impression, soleil levant.jpg, Claude Monet's ''Impression, Sunrise'', 1872, gave the name to Impressionism
File:Paul Cézanne 159.jpg, Paul Cézanne, self-portrait, 1880–1881
File:Scott Joplin.jpg, Scott Joplin
File:NiccoloPaganini.jpeg, Niccolò Paganini, c.1819
File:Eugène Ferdinand Victor Delacroix 043.jpg, Frédéric Chopin, 1838
File:John D. Rockefeller, Sr.jpg, John D. Rockefeller
online free
* Morris, Richard B. and Graham W. Irwin, eds. ''Harper Encyclopedia of the Modern World: A Concise Reference History from 1760 to the Present'' (1970
online frr
* ''New Cambridge Modern History'' (13 vol 1957–79), old but thorough coverage, mostly of Europe; strong on diplomacy **Bury, J. P. T. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History: Vol. 10: the Zenith of European Power, 1830–70'' (1964
online
**Crawley, C. W., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History Volume IX War and Peace In An Age of Upheaval 1793–1830'' (1965)
online
**Darby, H. C. and H. Fullard ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 14: Atlas'' (1972) **Hinsley, F.H., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, vol. 11, Material Progress and World-Wide Problems 1870–1898'' (1979
online
online
* Langer, William. ''The Diplomacy of Imperialism 1890–1902'' (1950); advanced histor
online
* Mowat, R.B. ''A history of European diplomacy, 1815–1914'' (1922
online free
* * Porter, Andrew, ed. ''The Oxford History of the British Empire: Volume III: The Nineteenth Century'' (2001) * Sontag, Raymond. ''European Diplomatic History: 1871–1932'' (1933), basic summary; 425 p
online
* Taylor, A.J.P. ''The Struggle for Mastery in Europe 1848–1918'' (1954) 638 pp; advanced history and analysis of major diplomacy
online free
* Taylor, A.J.P. "International Relations" in F.H. Hinsley, ed., ''The New Cambridge Modern History: XI: Material Progress and World-Wide Problems, 1870–98'' (1962): 542–66
online
*
online
* Cameron, Rondo. ''France and the Economic Development of Europe, 1800–1914: Conquests of Peace and Seeds of War'' (1961), awide-ranging economic and business history. * Evans, Richard J. ''The Pursuit of Power: Europe 1815–1914'' (2016), 934 pp * Gildea, Robert. ''Barricades and Borders: Europe 1800–1914'' (3rd ed. 2003) 544 pp,
online 2nd ed, 1996
* * Mason, David S. ''A Concise History of Modern Europe: Liberty, Equality, Solidarity'' (2011), since 1700 * Merriman, John, and J. M. Winter, eds. ''Europe 1789 to 1914: Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire'' (5 vol. 2006) * Steinberg, Jonathan. ''Bismarck: A Life'' (2011) * Salmi, Hannu. ''19th Century Europe: A Cultural History'' (2008).
excerpt
* Mansfield, Peter, and Nicolas Pelham, ''A History of the Middle East'' (4th ed, 2013). * * Pakenham, Thomas. ''The Scramble for Africa: 1876 to 1912'' (1992)
online
* Lynch, John, ed. ''Latin American revolutions, 1808–1826: old and new world origins'' (University of Oklahoma Press, 1994) * McPherson, James M. ''Battle Cry of Freedom The CIvil War Era'' (1988) Pulitzer Prize for US history * Parry, J.H. ''A Short History of the West Indies'' (1987) * Paxson, Frederic Logan. ''History of the American frontier, 1763–1893'' (1924)
online
Pulitzer Prize * White, Richard. ''The Republic for Which It Stands: The United States during Reconstruction and the Gilded Age, 1865–1896'' (2017)
 The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium
File:2nd millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: in 1492, Christopher Columbus reaches North America, opening the European colonization of the Americas; the American Revolution, one of the late 1700s Enlightenment-inspired Atlantic Rev ...
.
The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
, and the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century
The 20th (twentieth) century began on
January 1, 1901 ( MCMI), and ended on December 31, 2000 ( MM). The 20th century was dominated by significant events that defined the modern era: Spanish flu pandemic, World War I and World War II, nuclear ...
.
The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large Spanish and Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
empires. This paved the way for the growing influence of the British, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Russian, Italian, and Japanese empires along with the United States. The British boasted unchallenged global dominance after 1815.
After the defeat of France in the Napoleonic Wars, the British and Russian empires expanded greatly, becoming two of the world's leading powers. Russia expanded its territory to Central Asia and the Caucasus. The Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
underwent a period of Westernization and reform known as the Tanzimat
The Tanzimat (; ota, تنظيمات, translit=Tanzimāt, lit=Reorganization, ''see'' nizām) was a period of reform in the Ottoman Empire that began with the Gülhane Hatt-ı Şerif in 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 1876. ...
, vastly increasing their control over their core territories in the Middle East. However, it remained in decline and became known as the sick man of Europe
"Sick man of Europe" is a label given to a nation which is located in some part of Europe and experiencing a time of economic difficulty or impoverishment.
Emperor Nicholas I of the Russian Empire is considered to be the first to use the term " ...
, losing territory in the Balkans and North Africa.
The remaining powers in the Indian subcontinent such as the Maratha and Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
empires have suffered a massive decline and their dissatisfaction with the British East India Company's rule led to the Indian Rebellion of 1857, marking its dissolution. India was later ruled directly by the British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
through the establishment of the British Raj.
Britain's overseas possessions grew rapidly in the first half of the century, especially with the expansion of vast territories in Canada, Australia, South Africa, India, and in the last two decades of the century in Africa. By the end of the century, the British controlled a fifth of the world's land and one-quarter of the world's population. During the post-Napoleonic era, it enforced what became known as the Pax Britannica, which had ushered in unprecedented globalization on a massive scale.
Overview
 The first electronics appeared in the 19th century, with the introduction of the electric relay in 1835, the telegraph and its
The first electronics appeared in the 19th century, with the introduction of the electric relay in 1835, the telegraph and its Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
protocol in 1837, the first telephone call in 1876, and the first functional light bulb
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the soc ...
in 1878.
The 19th century was an era of rapidly accelerating scientific discovery and invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an i ...
, with significant developments in the fields of mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, electricity, and metallurgy that laid the groundwork for the technological advances of the 20th century. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain and spread to continental Europe, North America, and Japan. The Victorian era was notorious for the employment of young children in factories and mines, as well as strict social norm
Social norms are shared standards of acceptance, acceptable behavior by groups. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into wikt:rule, rules and laws. Social normat ...
s regarding modesty and gender roles. Japan embarked on a program of rapid modernization following the Meiji Restoration, before defeating China, under the Qing dynasty, in the First Sino-Japanese War. Advances in medicine and the understanding of human anatomy and disease prevention took place in the 19th century, and were partly responsible for rapidly accelerating population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
in the Western world. Europe's population doubled during the 19th century, from approximately 200 million to more than 400 million. The introduction of railroads provided the first major advancement in land transportation for centuries, changing the way people lived and obtained goods, and fuelling major urbanization movements in countries across the globe. Numerous cities worldwide surpassed populations of a million or more during this century. London became the world's largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
and capital of the British Empire. Its population increased from 1 million in 1800 to 6.7 million a century later. The last remaining undiscovered landmasses of Earth, including vast expanses of interior Africa and Asia, were explored during this century, and with the exception of the extreme zones of the Arctic and Antarctic, accurate and detailed maps of the globe were available by the 1890s. Liberalism became the pre-eminent reform movement
A reform movement or reformism is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social or also a political system closer to the community's ideal. A reform movement is distinguished from more radical social movements such as revolutionary mo ...
in Europe.
 Slavery was greatly reduced around the world. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti, Britain and France stepped up the battle against the
Slavery was greatly reduced around the world. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti, Britain and France stepped up the battle against the Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
and succeeded in stopping their enslavement of Europeans. The UK's Slavery Abolition Act charged the British Royal Navy with ending the global slave trade. The first colonial empire in the century to abolish slavery was the British, who did so in 1834. America's Thirteenth Amendment following their Civil War abolished slavery there in 1865, and in Brazil slavery was abolished in 1888 (see abolitionism
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
). Similarly, serfdom was abolished in Russia in 1861.
The 19th century was remarkable in the widespread formation of new settlement
Settlement may refer to:
*Human settlement, a community where people live
*Settlement (structural), the distortion or disruption of parts of a building
*Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
*Settlement (fina ...
foundations which were particularly prevalent across North America and Australia, with a significant proportion of the two continents' largest cities being founded at some point in the century. Chicago in the United States and Melbourne in Australia were non-existent in the earliest decades but grew to become the 2nd largest cities in the United States and British Empire respectively by the end of the century. In the 19th century, approximately 70 million people left Europe, with most migrating to the United States.
The 19th century also saw the rapid creation, development, and codification of many sports, particularly in Britain and the United States. Association football, rugby union, baseball, and many other sports were developed during the 19th century, while the British Empire facilitated the rapid spread of sports such as cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
to many different parts of the world. Also, women's fashion
Fashion is a form of self-expression and autonomy at a particular period and place and in a specific context, of clothing, footwear, lifestyle, accessories, makeup, hairstyle, and body posture. The term implies a look defined by the fashion ind ...
was a very sensitive topic during this time, as women showing their ankles was viewed to be scandalous.
 It also marks the fall of the Ottoman rule of the Balkans which led to the creation of Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, and Romania as a result of the
It also marks the fall of the Ottoman rule of the Balkans which led to the creation of Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, and Romania as a result of the second Russo-Turkish War
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each ...
, which in itself followed the great Crimean War.
Eras
 * Industrial revolution
* European imperialism
* British Regency, Victorian era (UK, British Empire)
*
* Industrial revolution
* European imperialism
* British Regency, Victorian era (UK, British Empire)
*Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* ...
, July Monarchy, French Second Republic, Second French Empire, French Third Republic ( France)
*Belle Époque
The Belle Époque or La Belle Époque (; French for "Beautiful Epoch") is a period of French and European history, usually considered to begin around 1871–1880 and to end with the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era ...
(Europe)
* Edo period, Meiji period (Japan)
* Qing dynasty (China)
* Nguyen dynasty (Vietnam)
*Joseon
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and re ...
dynasty (Korea)
*Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
(South Africa)
*Tanzimat
The Tanzimat (; ota, تنظيمات, translit=Tanzimāt, lit=Reorganization, ''see'' nizām) was a period of reform in the Ottoman Empire that began with the Gülhane Hatt-ı Şerif in 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 1876. ...
, First Constitutional Era ( Ottoman Empire)
* Russian Empire
* American Manifest Destiny, The Gilded Age, Wild West
Wars
Napoleonic Wars
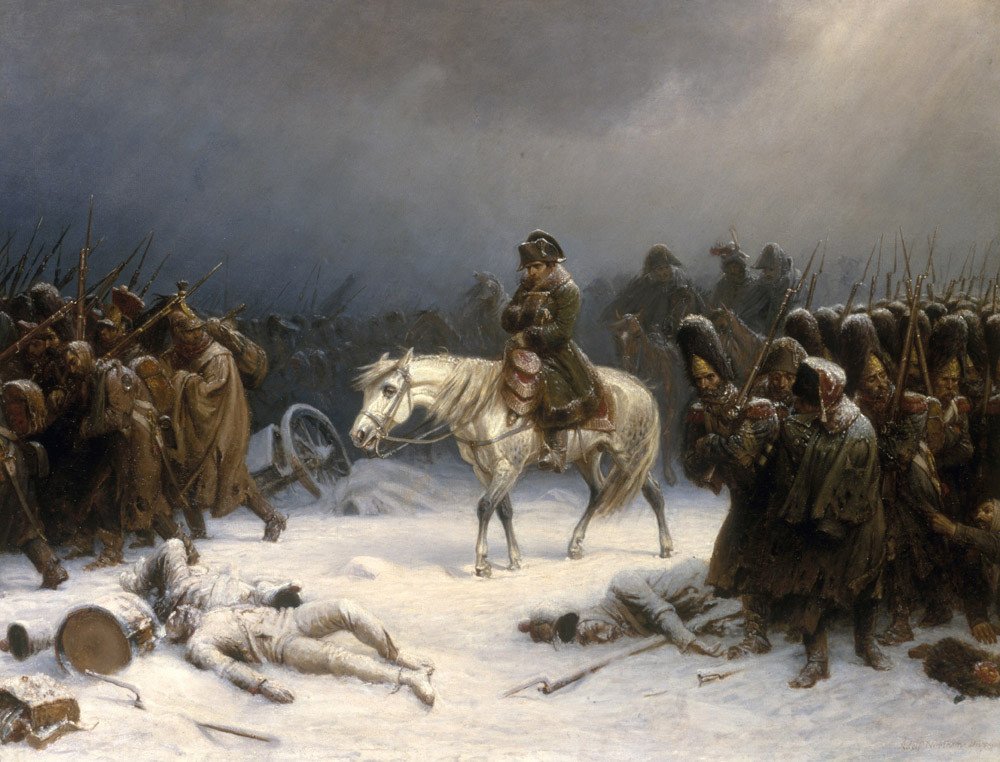
 The Napoleonic Wars were a series of major conflicts from 1803 to 1815 pitting the
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of major conflicts from 1803 to 1815 pitting the French Empire
French Empire (french: Empire Français, link=no) may refer to:
* First French Empire, ruled by Napoleon I from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815 and by Napoleon II in 1815, the French state from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815
* Second French Empire, led by Nap ...
and its allies, led by Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, against a fluctuating array of European powers formed into various coalitions, financed and usually led by the United Kingdom. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and its resultant conflict.
In the aftermath of the French Revolution, Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
gained power in France in 1799. In 1804, he crowned himself Emperor of the French.
In 1805, the French victory over an Austrian-Russian army at the Battle of Austerlitz ended the War of the Third Coalition. As a result of the Treaty of Pressburg, the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved.
Later efforts were less successful. In the Peninsular War, France unsuccessfully attempted to establish Joseph Bonaparte as King of Spain. In 1812, the French invasion of Russia
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental block ...
had massive French casualties, and was a turning point in the Napoleonic Wars.
In 1814, after defeat in the War of the Sixth Coalition, Napoleon abdicated and was exiled to Elba. Later that year, he escaped exile and began the Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration ...
before finally being defeated at the Battle of Waterloo and exiled to Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constitu ...
, an island in the South Atlantic Ocean.
After Napoleon's defeat, the Congress of Vienna was held to determine new national borders. The Concert of Europe attempted to preserve this settlement was established to preserve these borders, with limited impact.
Latin American independence
 Mexico and the majority of the countries in Central America and South America obtained independence from
Mexico and the majority of the countries in Central America and South America obtained independence from colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
overlords during the 19th century. In 1804, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
gained independence from France. In Mexico, the Mexican War of Independence was a decade-long conflict that ended in Mexican independence in 1821.
Due to the Napoleonic Wars, the royal family of Portugal relocated to Brazil from 1808 to 1821, leading to Brazil having a separate monarchy from Portugal.
The Federal Republic of Central America gained independence from Spain in 1821 and from Mexico in 1823. After several rebellions, by 1841 the federation had dissolved into the independent countries of Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
.
In 1830, the post-colonial nation of Gran Colombia dissolved and the nations of Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
(including modern-day Panama), Ecuador, and Venezuela took its place.
Revolutions of 1848
 The Revolutions of 1848 were a series of
The Revolutions of 1848 were a series of political upheaval
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
s throughout Europe in 1848. The revolutions were essentially democratic and liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old monarchical structures and creating independent nation states.
The first revolution began in January in Sicily. Revolutions then spread across Europe after a separate revolution began in France in February. Over 50 countries were affected, but with no coordination or cooperation among their respective revolutionaries.
According to Evans and von Strandmann (2000), some of the major contributing factors were widespread dissatisfaction with political leadership, demands for more participation in government and democracy, demands for freedom of the press, other demands made by the working class, the upsurge of nationalism, and the regrouping of established government forces.
Abolition and the American Civil War
 The
The abolitionism
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
movement achieved success in the 19th century. The Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
was abolished in the United States in 1808, and by the end of the century, almost every government had banned slavery. The Slavery Abolition Act of 1833 banned slavery throughout the British Empire, and the Lei Áurea abolished slavery in Brazil in 1888.
Abolitionism in the United States continued until the end of the American Civil War. Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman were two of many American abolitionists who helped win the fight against slavery. Douglass was an articulate orator and incisive antislavery writer, while Tubman worked with a network of antislavery activists and safe houses known as the Underground Railroad.
The American Civil War took place from 1861 to 1865. Eleven southern states Southern States may refer to:
*The independent states of the Southern hemisphere
United States
* Southern United States, or the American South
* Southern States Cooperative, an American farmer-owned agricultural supply cooperative
* Southern Stat ...
seceded from the United States, largely over concerns related to slavery. In 1863, President Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the Civil War. The Proclamation changed the legal sta ...
. Lincoln issued a preliminary on September 22, 1862 warning that in all states still in rebellion ( Confederacy) on January 1, 1863, he would declare their slaves "then, thenceforward, and forever free." He did so. The Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution, ratified in 1865, officially abolished slavery in the entire country.
Five days after Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nort ...
surrendered at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia
The Appomattox Courthouse is the current courthouse in Appomattox, Virginia built in 1892. It is located in the middle of the state about three miles (5 km) southwest of the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park, once known as ...
, Lincoln was assassinated by actor and Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between ...
sympathiser John Wilkes Booth.
Decline of the Ottoman Empire
In 1830, Greece became the first country to break away from the Ottoman Empire after theGreek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
. In 1831, the Bosnian Uprising
Bosnian may refer to:
*Anything related to the state of Bosnia and Herzegovina or its inhabitants
*Anything related to Bosnia (region) or its inhabitants
* Bosniaks, an ethnic group mainly inhabiting Bosnia and Herzegovina and one of three const ...
against Ottoman rule occurred. In 1817, the Principality of Serbia became suzerain
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is calle ...
from the Ottoman Empire, and in 1867, it passed a constitution that defined its independence from the Ottoman Empire. In 1876, Bulgarians instigated the April Uprising against Ottoman rule. Following the Russo-Turkish War, the Treaty of Berlin recognized the formal independence of the Serbia, Montenegro, and Romania. Bulgaria became autonomous.
China: Taiping Rebellion
 The Taiping Rebellion was the bloodiest conflict of the 19th century, leading to the deaths of around 20-30 million people. Its leader,
The Taiping Rebellion was the bloodiest conflict of the 19th century, leading to the deaths of around 20-30 million people. Its leader, Hong Xiuquan
Hong Xiuquan (1 January 1814 – 1 June 1864), born Hong Huoxiu and with the courtesy name Renkun, was a Chinese revolutionary who was the leader of the Taiping Rebellion against the Qing dynasty. He established the Taiping Heavenly Kingdo ...
, declared himself the younger brother of Jesus Christ and developed a new Chinese religion known as the God Worshipping Society
The God Worshipping Society, in its literal translation Emperor Worshipping Society (), was a religious movement founded and led by Hong Xiuquan which drew on his own unique interpretation of Protestant Christianity and combined it with Chinese ...
. After proclaiming the establishment of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom in 1851, the Taiping army conquered a large part of China, capturing Nanjing in 1853. In 1864, after the death of Hong Xiuquan, Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
forces recaptured Nanjing and ended the rebellion.
Japan: Meiji Restoration
During the Edo period, History of Japan, Japan largely pursued an Sakoku, isolationist foreign policy. In 1853, United States Navy Commodore Matthew C. Perry threatened the Japanese capital Edo with gunships, demanding that they agree to open trade. This led to Bakumatsu, the opening of trade relations between Japan and foreign countries, with the policy of Sakoku formally ended in 1854. By 1872, the Japanese government under Emperor Meiji had Abolition of the han system, eliminated the ''daimyō'' system and established a strong central government. Further reforms included the abolishment of the samurai class, rapid industrialization and modernization of government, closely following European models.Colonialism

 * 1803: United States more than doubles in size when it buys out France's territorial claims in North America via the Louisiana Purchase. This begins the U.S.'s westward expansion to the Pacific, referred to as its Manifest Destiny, which involves United States territorial acquisitions, annexing and conquering land from Mexico, Britain, and Native Americans.
* 1817 – 1819: British Empire annexed the Maratha Empire, Maratha Confederacy after the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
* 1823 – 1887: British Empire annexed Burma (now also called Myanmar) after three Anglo-Burmese Wars.
* 1848 – 1849: Sikh Empire is defeated in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. Therefore, the entire Indian subcontinent is under British control.
* 1862: France gained its first foothold in Southeast Asia and in 1863 annexed Cambodia.
* 1867: United States Alaska Purchase, purchased Alaska from Russia.
* 1803: United States more than doubles in size when it buys out France's territorial claims in North America via the Louisiana Purchase. This begins the U.S.'s westward expansion to the Pacific, referred to as its Manifest Destiny, which involves United States territorial acquisitions, annexing and conquering land from Mexico, Britain, and Native Americans.
* 1817 – 1819: British Empire annexed the Maratha Empire, Maratha Confederacy after the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
* 1823 – 1887: British Empire annexed Burma (now also called Myanmar) after three Anglo-Burmese Wars.
* 1848 – 1849: Sikh Empire is defeated in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. Therefore, the entire Indian subcontinent is under British control.
* 1862: France gained its first foothold in Southeast Asia and in 1863 annexed Cambodia.
* 1867: United States Alaska Purchase, purchased Alaska from Russia.
Africa
 In Africa, European exploration and technology led to the colonization of almost the entire continent by 1898. New medicines such as quinine and more advanced firearms allowed European nations to conquer native populations.
Motivations for the Scramble for Africa included national pride, desire for raw materials, and Christian missionary activity. Britain seized control of Egypt to ensure control of the Suez Canal, but Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia defeated Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa. France, Belgium, Portugal, and Germany also had substantial colonies. The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885 attempted to reach agreement on colonial borders in Africa, but disputes continued, both amongst European powers and in resistance by the native populations.
In 1867, diamonds were discovered in the Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley region of South Africa. In 1886, gold was discovered in South African Republic, Transvaal. This led to colonization in Southern Africa by the British and business interests, led by Cecil Rhodes.
In Africa, European exploration and technology led to the colonization of almost the entire continent by 1898. New medicines such as quinine and more advanced firearms allowed European nations to conquer native populations.
Motivations for the Scramble for Africa included national pride, desire for raw materials, and Christian missionary activity. Britain seized control of Egypt to ensure control of the Suez Canal, but Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia defeated Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa. France, Belgium, Portugal, and Germany also had substantial colonies. The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885 attempted to reach agreement on colonial borders in Africa, but disputes continued, both amongst European powers and in resistance by the native populations.
In 1867, diamonds were discovered in the Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley region of South Africa. In 1886, gold was discovered in South African Republic, Transvaal. This led to colonization in Southern Africa by the British and business interests, led by Cecil Rhodes.
Other wars
* 1801–1815: First Barbary War and the Second Barbary War between the United States and the Barbary States of North Africa. * 1802: Tây Sơn dynasty, Tay Son army recaptured Thừa Thiên Huế province, Phu Xuan, causing Vo Tanh to commit suicide, Gia Long, Nguyen Phuc Anh successfully captured Hanoi, Thang Long, founded the Nguyen Dynasty * 1804–1810: Fulani War, Fulani Jihad in Nigeria. * 1804–1813: Russo-Persian War (1804–1813), Russo-Persian War. * 1806–1812: Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), Russo-Turkish War, Treaty of Bucharest (1812), Treaty of Bucharest. * 1807–1837: Musket Wars among Māori people, Māori in many parts of New Zealand. * 1808–1809: Russia conquers Finland from Sweden in the Finnish War. * 1810: Grito de Dolores begins the Mexican War of Independence.
* 1811: Battle of Tippecanoe: U.S outnumbering Native Americans resulting in defeat and burning of community
* 1812–1815: War of 1812 between the United States and Britain; ends in a draw, except that Native Americans lose power.
* 1813–1837: Afghan–Sikh Wars.
* 1814–1816: Anglo-Nepalese War between Nepal (Gurkha Empire) and British Empire.
* 1817: First Seminole War begins in Florida.
* 1817: Russia commences its Caucasian War, conquest of the Caucasus.
* 1820: Revolutions of 1820 in Southern Europe
* 1821–1830:
* 1810: Grito de Dolores begins the Mexican War of Independence.
* 1811: Battle of Tippecanoe: U.S outnumbering Native Americans resulting in defeat and burning of community
* 1812–1815: War of 1812 between the United States and Britain; ends in a draw, except that Native Americans lose power.
* 1813–1837: Afghan–Sikh Wars.
* 1814–1816: Anglo-Nepalese War between Nepal (Gurkha Empire) and British Empire.
* 1817: First Seminole War begins in Florida.
* 1817: Russia commences its Caucasian War, conquest of the Caucasus.
* 1820: Revolutions of 1820 in Southern Europe
* 1821–1830: Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
against the Ottoman Empire.
* 1825–1830: Java War begins.
* 1826–1828: After the final Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), Russo-Persian War, the Qajar dynasty, Persian Empire took back territory lost to Russia from the previous war.
* 1828–1832: Black War in Tasmania leads to the near extinction of the Tasmanian aborigines
* 1830: July Revolution overthrew old line of Bourbons.
* 1830: November Uprising in Poland against Russia.
* 1830: Belgian Revolution results in Belgium's independence from Netherlands.
* 1830: End of the Java War. The whole area of Yogyakarta and Surakarta Manca nagara Dutch seized. 27 September, Klaten Agreement determines a fixed boundary between Surakarta and Yogyakarta and permanently divide the kingdom of Mataram was signed by Sasradiningrat, Pepatih Dalem Surakarta, and Danurejo, Pepatih Dalem Yogyakarta. Mataram is a de facto and de yure controlled by the Dutch East Indies.
* 1831: France French rule in Algeria, invades and occupies Algeria.
* 1831–1833: Egyptian–Ottoman War (1831–1833), Egyptian–Ottoman War.
* 1832–1875: Regimental rebellions of Brazil
* 1835–1836: Texas Revolution results in Texas's independence from Mexico.
* 1839–1842: First Opium War begins.
* 1846–1848: Mexican–American War leads to Mexico's cession of much of the modern-day Southwestern United States.
* 1848: French Revolution of 1848, February Revolution overthrew Louis Philippe's government. Second Republic proclaimed; Louis Napoleon, nephew of Napoleon I, elected president.
* 1853–1856: Crimean War between France, the United Kingdom, the Ottoman Empire and Russia.
* 1857: Indian Rebellion of 1857, Indian Rebellion against the Company Raj. After this the power of the East India Company is transferred to the British Raj, British Crown.
* 1859: Second Italian War of Independence, Franco-Austrian War is part of the wars of Italian unification.
* 1861–1865: American Civil War between the Union (American Civil War), Union and seceding Confederacy.  * 1861–1867: Second French intervention in Mexico, French intervention in Mexico and the creation of the Second Mexican Empire, ruled by Maximilian I of Mexico and his consort Carlota of Mexico.
* 1863–1865: January Uprising against the Russian Empire.
* 1864–1870: Paraguayan War ends Paraguayan ambitions for expansion and destroys much of the Paraguayan population.
* 1866: Austro-Prussian War results in the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of the North German Confederation and the Austria-Hungary, Austrian-Hungarian Dual Monarchy.
* 1868-1869: Boshin War results in end of the shogunate and the founding the Japanese Empire.
* 1868–1878: Ten Years' War between Cuba and Kingdom of Spain, Spain.
* 1870–1871: Franco-Prussian War results in the Unification of Germany, unifications of Germany Italian unification, and Italy, the collapse of the Second French Empire and the emergence of a New Imperialism.
* 1870: Napoleon III abdicated after unsuccessful conclusion of Franco-Prussian War. Third Republic proclaimed.
* 1876: The April Uprising in Bulgaria against the Ottoman Empire.
* 1879: Anglo-Zulu War results in British victory and the annexation of the
* 1861–1867: Second French intervention in Mexico, French intervention in Mexico and the creation of the Second Mexican Empire, ruled by Maximilian I of Mexico and his consort Carlota of Mexico.
* 1863–1865: January Uprising against the Russian Empire.
* 1864–1870: Paraguayan War ends Paraguayan ambitions for expansion and destroys much of the Paraguayan population.
* 1866: Austro-Prussian War results in the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of the North German Confederation and the Austria-Hungary, Austrian-Hungarian Dual Monarchy.
* 1868-1869: Boshin War results in end of the shogunate and the founding the Japanese Empire.
* 1868–1878: Ten Years' War between Cuba and Kingdom of Spain, Spain.
* 1870–1871: Franco-Prussian War results in the Unification of Germany, unifications of Germany Italian unification, and Italy, the collapse of the Second French Empire and the emergence of a New Imperialism.
* 1870: Napoleon III abdicated after unsuccessful conclusion of Franco-Prussian War. Third Republic proclaimed.
* 1876: The April Uprising in Bulgaria against the Ottoman Empire.
* 1879: Anglo-Zulu War results in British victory and the annexation of the Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
.
* 1879–1880: Little War (Cuba), Little War against Spanish rule in Cuba leads to rebel defeat.
* 1879–1883: Chile battles with Peru and Bolivia over Andean territory in the War of the Pacific.
* 1880–1881: First Boer War begins.
* 1881–1899: Mahdist War in Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Sudan. * 1882: Anglo-Egyptian War British invasion and subsequent occupation of Khedivate of Egypt, Egypt
* 1883–1898: Mandingo Wars between the French colonial empire and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandinka people, Mandingo people led by Samory Touré.
* 1894–1895: After the First Sino-Japanese War, China cedes Taiwan to Japan and grants Japan a free hand in Korea.
* 1895: Taiwan is ceded to the Empire of Japan as a result of the First Sino-Japanese War.
* 1895–1896: Ethiopia defeats Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa.
* 1895–1898: Cuban War for Independence results in Cuban independence from Spanish Empire, Spain.
* 1896-1898: Philippine Revolution results in a Filipino victory.
* 1898: Spanish–American War results in the independence of Cuba.
* 1899–1901: Boxer Rebellion in China is suppressed by the Eight-Nation Alliance.
* 1899–1902: Thousand Days' War in
* 1882: Anglo-Egyptian War British invasion and subsequent occupation of Khedivate of Egypt, Egypt
* 1883–1898: Mandingo Wars between the French colonial empire and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandinka people, Mandingo people led by Samory Touré.
* 1894–1895: After the First Sino-Japanese War, China cedes Taiwan to Japan and grants Japan a free hand in Korea.
* 1895: Taiwan is ceded to the Empire of Japan as a result of the First Sino-Japanese War.
* 1895–1896: Ethiopia defeats Italy in the First Italo–Ethiopian War at the Battle of Adwa.
* 1895–1898: Cuban War for Independence results in Cuban independence from Spanish Empire, Spain.
* 1896-1898: Philippine Revolution results in a Filipino victory.
* 1898: Spanish–American War results in the independence of Cuba.
* 1899–1901: Boxer Rebellion in China is suppressed by the Eight-Nation Alliance.
* 1899–1902: Thousand Days' War in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
breaks out between the "Liberalism, Liberales" and "Conservatism, Conservadores", culminating with the loss of Panama in 1903.
* 1899–1902: Second Boer War begins.
* 1899–1902: Philippine–American War begins.
Science and technology
The 19th century saw the birth of science as a profession; the term scientist was coined in 1833 by William Whewell, which soon replaced the older term of natural philosopher. Among the most influential ideas of the 19th century were those of Charles Darwin (alongside the independent researches of Alfred Russel Wallace), who in 1859 published the book ''The Origin of Species'', which introduced the idea of evolution by natural selection. Another important landmark in medicine and biology were the successful efforts to prove the germ theory of disease. Following this, Louis Pasteur made the first vaccine against rabies, and also made many discoveries in the field of chemistry, including the Enantiomer, asymmetry of crystals. In chemistry, Dmitri Mendeleev, following the atomic theory of John Dalton, created the first periodic table of Chemical element, elements. In physics, the experiments, theories and discoveries of Michael Faraday, André-Marie Ampère, James Clerk Maxwell, and their contemporaries led to the creation of electromagnetism as a new branch of science. Thermodynamics led to an understanding of heat and the notion of energy was defined. Other highlights include the discoveries unveiling the nature of atomic structure and matter, simultaneously with chemistry – and of new kinds of radiation. In astronomy, the planet Neptune was discovered. In mathematics, the notion of complex numbers finally matured and led to a subsequent analytical theory; they also began the use of hypercomplex numbers. Karl Weierstrass and others carried out the arithmetization of analysis for functions of Function of a real variable, real and complex variables. It also saw rise to Non-Euclidean geometry, new progress in geometry beyond those classical theories of Euclid, after a period of nearly two thousand years. The mathematical science of logic likewise had revolutionary breakthroughs after a similarly long period of stagnation. But the most important step in science at this time were the ideas formulated by the creators of electrical science. Their work changed the face of physics and made possible for new technology to come about including a rapid spread in the use of electric illumination and power in the last two decades of the century and radio wave communication at the end of the 1890s.
 * 1807: Potassium and Sodium are individually isolated by Sir Humphry Davy.
* 1831–1836: Charles Darwin's journey on .
* 1859: Charles Darwin publishes ''On the Origin of Species''.
* 1861: James Clerk Maxwell publishes ''On Physical Lines of Force'', formulating the four Maxwell's equations.
* 1865: Gregor Mendel formulates his laws of inheritance.
* 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev creates the Periodic table.
* 1873: Maxwell's ''A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism'' published.
* 1877: Asaph Hall discovers the moons of Mars
* 1896: Henri Becquerel discovers radioactivity; J. J. Thomson identifies the electron, though not by name.
* 1807: Potassium and Sodium are individually isolated by Sir Humphry Davy.
* 1831–1836: Charles Darwin's journey on .
* 1859: Charles Darwin publishes ''On the Origin of Species''.
* 1861: James Clerk Maxwell publishes ''On Physical Lines of Force'', formulating the four Maxwell's equations.
* 1865: Gregor Mendel formulates his laws of inheritance.
* 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev creates the Periodic table.
* 1873: Maxwell's ''A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism'' published.
* 1877: Asaph Hall discovers the moons of Mars
* 1896: Henri Becquerel discovers radioactivity; J. J. Thomson identifies the electron, though not by name.
Medicine
 * 1804: Morphine first isolated.
* 1842: Anesthesia used for the first time.
* 1847: Chloroform invented for the first time, given to Queen Victoria at the birth of her eighth child, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany, Prince Leopold in 1853
* 1855: Cocaine is isolated by Friedrich Gaedcke.
* 1885: Louis Pasteur creates the first successful vaccine against rabies for a young boy who had been bitten 14 times by a rabid dog.
* 1889: Aspirin patented.
* 1804: Morphine first isolated.
* 1842: Anesthesia used for the first time.
* 1847: Chloroform invented for the first time, given to Queen Victoria at the birth of her eighth child, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany, Prince Leopold in 1853
* 1855: Cocaine is isolated by Friedrich Gaedcke.
* 1885: Louis Pasteur creates the first successful vaccine against rabies for a young boy who had been bitten 14 times by a rabid dog.
* 1889: Aspirin patented.
Inventions
 * 1804: First steam locomotive begins operation.
* 1816: Dandy horse, Laufmaschine invented by Karl von Drais.
* 1825: Erie Canal opened connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
* 1825: First isolation of aluminum, aluminium.
* 1825: The Stockton and Darlington Railway, the first public railway in the world, is opened.
* 1826: Samuel Morey patents the internal combustion engine.
* 1829: First electric motor built.
* 1837: Telegraphy patented.
* 1841: The word "dinosaur" is coined by Richard Owen.
* 1844: First publicly funded telegraph line in the world—between Baltimore and Washington—sends demonstration message on 24 May, ushering in the age of the telegraph. This message read "What hath God wrought?" (Bible, Numbers 23:23)
* 1849: The safety pin and the gas mask are invented.
* 1852: The first successful blimp is invented
* 1855: Bessemer process enables steel to be mass-produced.
* 1856: World's first oil refinery in Romania
* 1858: Invention of the phonautograph, the first true device for recorded sound, recording sound.
* 1859: The first ironclad was launched into sea by the French Navy.
* 1860: Benjamin Tyler Henry invents the 16 - shot Henry Rifle
* 1861: Richard Gatling invents the Gatling Gun, first modern machine gun used notably in the battles of Cold Harbor and Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg
* 1862: First meeting in combat of ironclad warships, and , during the American Civil War.
* 1863: First section of the London Underground opens.
* 1866: Successful transatlantic telegraph cable follows an earlier attempt in 1858.
* 1867: Alfred Nobel invents dynamite.
* 1868: Safety bicycle invented.
* 1869: First transcontinental railroad completed in United States on 10 May.
* 1870: Rasmus Malling-Hansen's invention the Hansen Writing Ball becomes the first commercially sold typewriter.
* 1873: Jeans, Blue jeans and barbed wire are invented.
* 1877: Thomas Edison invents the phonograph
* 1878: First commercial telephone exchange in New Haven, Connecticut.
* c. 1875/1880: Introduction of the widespread use of electric lighting. These included early crude systems in France and the UK and the introduction of large scale outdoor Arc lamp, arc lighting systems by 1880.
* 1879: Thomas Edison patents a practical incandescent light bulb.
* 1882: Introduction of large scale Electric power industry, electric power utilities with the Edison Holborn Viaduct power station, Holborn Viaduct (London) and Pearl Street Station, Pearl Street (New York) power stations supplying indoor electric lighting using Edison's incandescent bulb.
* 1884: Sir Hiram Maxim invents the first self-powered Machine gun.
* 1885: Singer Manufacturing Company, Singer begins production of the 'Singer Model 27 and 127, Vibrating Shuttle'. which would become the most popular model of sewing machine.
* 1886: Karl Benz sells the first commercial automobile.
* 1890: The cardboard box is invented.
* 1892: John Froelich develops and constructs the first gasoline/petrol-powered tractor.
* 1894: Karl Elsener (inventor), Karl Elsener invents the Swiss Army knife.
* 1894: First gramophone record.
* 1895: Wilhelm Röntgen identifies x-rays.
* 1804: First steam locomotive begins operation.
* 1816: Dandy horse, Laufmaschine invented by Karl von Drais.
* 1825: Erie Canal opened connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
* 1825: First isolation of aluminum, aluminium.
* 1825: The Stockton and Darlington Railway, the first public railway in the world, is opened.
* 1826: Samuel Morey patents the internal combustion engine.
* 1829: First electric motor built.
* 1837: Telegraphy patented.
* 1841: The word "dinosaur" is coined by Richard Owen.
* 1844: First publicly funded telegraph line in the world—between Baltimore and Washington—sends demonstration message on 24 May, ushering in the age of the telegraph. This message read "What hath God wrought?" (Bible, Numbers 23:23)
* 1849: The safety pin and the gas mask are invented.
* 1852: The first successful blimp is invented
* 1855: Bessemer process enables steel to be mass-produced.
* 1856: World's first oil refinery in Romania
* 1858: Invention of the phonautograph, the first true device for recorded sound, recording sound.
* 1859: The first ironclad was launched into sea by the French Navy.
* 1860: Benjamin Tyler Henry invents the 16 - shot Henry Rifle
* 1861: Richard Gatling invents the Gatling Gun, first modern machine gun used notably in the battles of Cold Harbor and Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg
* 1862: First meeting in combat of ironclad warships, and , during the American Civil War.
* 1863: First section of the London Underground opens.
* 1866: Successful transatlantic telegraph cable follows an earlier attempt in 1858.
* 1867: Alfred Nobel invents dynamite.
* 1868: Safety bicycle invented.
* 1869: First transcontinental railroad completed in United States on 10 May.
* 1870: Rasmus Malling-Hansen's invention the Hansen Writing Ball becomes the first commercially sold typewriter.
* 1873: Jeans, Blue jeans and barbed wire are invented.
* 1877: Thomas Edison invents the phonograph
* 1878: First commercial telephone exchange in New Haven, Connecticut.
* c. 1875/1880: Introduction of the widespread use of electric lighting. These included early crude systems in France and the UK and the introduction of large scale outdoor Arc lamp, arc lighting systems by 1880.
* 1879: Thomas Edison patents a practical incandescent light bulb.
* 1882: Introduction of large scale Electric power industry, electric power utilities with the Edison Holborn Viaduct power station, Holborn Viaduct (London) and Pearl Street Station, Pearl Street (New York) power stations supplying indoor electric lighting using Edison's incandescent bulb.
* 1884: Sir Hiram Maxim invents the first self-powered Machine gun.
* 1885: Singer Manufacturing Company, Singer begins production of the 'Singer Model 27 and 127, Vibrating Shuttle'. which would become the most popular model of sewing machine.
* 1886: Karl Benz sells the first commercial automobile.
* 1890: The cardboard box is invented.
* 1892: John Froelich develops and constructs the first gasoline/petrol-powered tractor.
* 1894: Karl Elsener (inventor), Karl Elsener invents the Swiss Army knife.
* 1894: First gramophone record.
* 1895: Wilhelm Röntgen identifies x-rays.
Religion
* 1818: The first permanent Reform Judaism congregation, the Hamburg Temple, Neuer Israelitischer Tempel, is founded in Hamburg on October 18. Around the same time, through the development of ''Wissenschaft des Judentums'', the seeds of Conservative Judaism are sown. * 1830: The Church of Christ (Latter Day Saints), Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints is established. * 1844: The Báb announces his revelation on 23 May, founding Bábism. He announced to the world of the coming of "He whom God shall make manifest". He is considered the forerunner of Bahá'u'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith. * 1850s–1890s: In Islam, Salafism grows in popularity. * 1851:Hong Xiuquan
Hong Xiuquan (1 January 1814 – 1 June 1864), born Hong Huoxiu and with the courtesy name Renkun, was a Chinese revolutionary who was the leader of the Taiping Rebellion against the Qing dynasty. He established the Taiping Heavenly Kingdo ...
, the leader of the God Worshipping Society
The God Worshipping Society, in its literal translation Emperor Worshipping Society (), was a religious movement founded and led by Hong Xiuquan which drew on his own unique interpretation of Protestant Christianity and combined it with Chinese ...
, founds the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.
* 1868: In Japan, State Shinto is established amidst the Meiji Restoration.
* 1869–1870: The First Vatican Council is convened, articulating the dogma of papal infallibility and promoting a Neo-scholasticism, revival of scholastic theology.
* 1871–1878: In German Empire, Germany, Otto von Bismarck challenges the Catholic Church in the ''Kulturkampf'' ("Culture War")
* 1875: Helena Blavatsky co-founds the Theosophical Society and becomes the leading articulator of Theosophy.
* 1879: Mary Baker Eddy founds the Church of Christ, Scientist. ''The Watchtower,'' published by the Jehovah's Witnesses, releases its first issue.
* 1881: In the Sudan, Muhammad Ahmad claims to be the Mahdi, founding the Mahdist State and declaring war on the Khedivate of Egypt.
* 1889: Mirza Ghulam Ahmad establishes the Ahmadiyya, Ahmadiyya Muslim Community.
* 1891: Pope Leo XIII issues the papal encyclical ''Rerum novarum'', the first major document informing modern Catholic social teaching.
Culture
 * 1808: Beethoven composes Symphony No. 5 (Beethoven), Fifth Symphony
* 1813: Jane Austen publishes ''Pride and Prejudice''
* 1818: Mary Shelley publishes ''Frankenstein''.
* 1819: John Keats writes his John Keats's 1819 odes, six of his best-known odes.
* 1819: Théodore Géricault paints his masterpiece ''The Raft of the Medusa'', and exhibits it in the French Salon of 1819 at the The Louvre, Louvre.
* 1824: Premiere of Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven's ''Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), Ninth Symphony''.
* 1829: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's ''Goethe's Faust, Faust'' premieres.
* 1837: Charles Dickens publishes ''Oliver Twist''.
* 1841: Ralph Waldo Emerson publishes ''Self-Reliance''.
* 1845: Frederick Douglass publishes ''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave''.
* 1847: The Brontë sisters publish ''Jane Eyre'', ''Wuthering Heights'' and ''Agnes Grey''.
* 1848: Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels publish ''The Communist Manifesto''.
* 1849: Josiah Henson publishes The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself.
* 1851: Herman Melville publishes Moby-Dick.
* 1851: Sojourner Truth delivers the speech Ain't I a Woman?.
* 1852: Harriet Beecher Stowe publishes Uncle Tom's Cabin.
* 1855: Walt Whitman publishes the first edition of ''Leaves of Grass''.
* 1855: Frederick Douglass publishes the first edition of ''My Bondage and My Freedom''.
* 1862: Victor Hugo publishes ''Les Misérables''.
* 1863: Jules Verne begins publishing his collection of stories and novels, ''Voyages extraordinaires'', with the novel ''Cinq semaines en ballon''.
* 1865: Lewis Carroll publishes Alice's Adventures in Wonderland.
* 1869: Leo Tolstoy publishes ''War and Peace''.
* 1875: Georges Bizet's opera Carmen premiers in Paris.
* 1876: Richard Wagner's ''Ring Cycle'' is first performed in its entirety.
* 1883: Robert Louis Stevenson's ''Treasure Island'' is published.
* 1884: Mark Twain publishes the ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn''.
* 1886: "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" by Robert Louis Stevenson is published.
* 1887: Sir Arthur Conan Doyle publishes his first Sherlock Holmes story, ''A Study in Scarlet''.
* 1889: Vincent van Gogh paints ''The Starry Night''.
* 1889: Moulin Rouge opens in Paris.
* 1892: Tchaikovsky's ''Nutcracker Suite'' premières in St Petersberg.
* 1894: Rudyard Kipling's ''The Jungle Book'' is published
* 1895: Trial of Oscar Wilde and premiere of his play ''The Importance of Being Earnest''.
* 1897: Bram Stoker writes Dracula.
* 1900: L. Frank Baum publishes The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.
* 1808: Beethoven composes Symphony No. 5 (Beethoven), Fifth Symphony
* 1813: Jane Austen publishes ''Pride and Prejudice''
* 1818: Mary Shelley publishes ''Frankenstein''.
* 1819: John Keats writes his John Keats's 1819 odes, six of his best-known odes.
* 1819: Théodore Géricault paints his masterpiece ''The Raft of the Medusa'', and exhibits it in the French Salon of 1819 at the The Louvre, Louvre.
* 1824: Premiere of Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven's ''Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), Ninth Symphony''.
* 1829: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's ''Goethe's Faust, Faust'' premieres.
* 1837: Charles Dickens publishes ''Oliver Twist''.
* 1841: Ralph Waldo Emerson publishes ''Self-Reliance''.
* 1845: Frederick Douglass publishes ''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave''.
* 1847: The Brontë sisters publish ''Jane Eyre'', ''Wuthering Heights'' and ''Agnes Grey''.
* 1848: Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels publish ''The Communist Manifesto''.
* 1849: Josiah Henson publishes The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself.
* 1851: Herman Melville publishes Moby-Dick.
* 1851: Sojourner Truth delivers the speech Ain't I a Woman?.
* 1852: Harriet Beecher Stowe publishes Uncle Tom's Cabin.
* 1855: Walt Whitman publishes the first edition of ''Leaves of Grass''.
* 1855: Frederick Douglass publishes the first edition of ''My Bondage and My Freedom''.
* 1862: Victor Hugo publishes ''Les Misérables''.
* 1863: Jules Verne begins publishing his collection of stories and novels, ''Voyages extraordinaires'', with the novel ''Cinq semaines en ballon''.
* 1865: Lewis Carroll publishes Alice's Adventures in Wonderland.
* 1869: Leo Tolstoy publishes ''War and Peace''.
* 1875: Georges Bizet's opera Carmen premiers in Paris.
* 1876: Richard Wagner's ''Ring Cycle'' is first performed in its entirety.
* 1883: Robert Louis Stevenson's ''Treasure Island'' is published.
* 1884: Mark Twain publishes the ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn''.
* 1886: "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" by Robert Louis Stevenson is published.
* 1887: Sir Arthur Conan Doyle publishes his first Sherlock Holmes story, ''A Study in Scarlet''.
* 1889: Vincent van Gogh paints ''The Starry Night''.
* 1889: Moulin Rouge opens in Paris.
* 1892: Tchaikovsky's ''Nutcracker Suite'' premières in St Petersberg.
* 1894: Rudyard Kipling's ''The Jungle Book'' is published
* 1895: Trial of Oscar Wilde and premiere of his play ''The Importance of Being Earnest''.
* 1897: Bram Stoker writes Dracula.
* 1900: L. Frank Baum publishes The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.
Literature
On the literary front the new century opens with romanticism, a movement that spread throughout Europe in reaction to 18th-century rationalism, and it develops more or less along the lines of the Industrial Revolution, with a design to react against the dramatic changes wrought on nature by the steam engine and the railway. William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge are considered the initiators of the new school in England, while in the continent the German ''Sturm und Drang'' spreads its influence as far as Italy and Spain. French arts had been hampered by the Napoleonic Wars but subsequently developed rapidly. Modernism began. The Goncourts and Émile Zola in France and Giovanni Verga in Italy produce some of the finest Naturalism (literature), naturalist novels. Italian naturalist novels are especially important in that they give a social map of the new unified Italy to a people that until then had been scarcely aware of its ethnic and cultural diversity. There was a huge literary output during the 19th century. Some of the most famous writers included the Russians Alexander Pushkin, Nikolai Gogol, Leo Tolstoy, Anton Chekhov and Fyodor Dostoyevsky; the English Charles Dickens, John Keats, Alfred, Lord Tennyson and Jane Austen; the Scottish Sir Walter Scott, Thomas Carlyle and Arthur Conan Doyle (creator of the character Sherlock Holmes); the Irish Oscar Wilde; the Americans Edgar Allan Poe, Ralph Waldo Emerson, and Mark Twain; and the French Victor Hugo, Honoré de Balzac, Jules Verne, Alexandre Dumas and Charles Baudelaire. Some American literary writers, poets and novelists were: Walt Whitman, Mark Twain, Harriet Ann Jacobs, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Herman Melville, Frederick Douglass, Harriet Beecher Stowe, Joel Chandler Harris, and Emily Dickinson to name a few.Photography
*Ottomar Anschütz, chronophotographer *Mathew Brady, documented the American Civil War *Edward S. Curtis, documented the American West notably Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans *Louis Daguerre, inventor of daguerreotype process of photography, chemist *Thomas Eakins, pioneer motion photographer *George Eastman, inventor of Photographic film, roll film *Hércules Florence, pioneer inventor of photography *Auguste and Louis Lumière, pioneer film-makers, inventors *Étienne-Jules Marey, pioneer motion photographer, chronophotographer *Eadweard Muybridge, pioneer motion photographer, chronophotographer *Nadar (photographer), Nadar a.k.a. Gaspard-Félix Tournachon, portrait photographer *Nicéphore Niépce, pioneer inventor of photography *Louis Le Prince, motion picture inventor and pioneer film-maker *Sergey Prokudin-Gorsky, chemist and photographer *William Fox Talbot, inventor of the negative / positive photographic process.Visual artists, painters, sculptors
 The Realism (arts), Realism and Romanticism of the early 19th century gave way to Impressionism and Post-Impressionism in the later half of the century, with Paris being the dominant art capital of the world. In the United States the Hudson River School was prominent. 19th-century painters included:
*Ivan Aivazovsky
*Léon Bakst
*Albert Bierstadt
*William Blake
*Arnold Böcklin
*Rosa Bonheur
*William Burges
*Mary Cassatt
*Camille Claudel
*Paul Cézanne
*Frederic Edwin Church
*Thomas Cole
*Jan Matejko
*John Constable
*Camille Corot
*Gustave Courbet
*Honoré Daumier
*Edgar Degas
*Eugène Delacroix
*Thomas Eakins
*Caspar David Friedrich
*Paul Gauguin
*Théodore Géricault
*Vincent van Gogh
*William Morris
*Francisco Goya
*Andō Hiroshige
*Hokusai
*Winslow Homer
*Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
*Isaac Levitan
*Édouard Manet
*Claude Monet
*Gustave Moreau
*Berthe Morisot
*Edvard Munch
*Mikhail Nesterov
*Camille Pissarro
*Augustus Pugin
*Pierre-Auguste Renoir
*Ilya Repin
*Auguste Rodin
*Albert Pinkham Ryder
*John Singer Sargent
*Valentin Serov
*Georges Seurat
*Ivan Shishkin
*Vasily Surikov
*James Tissot
*Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
*J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Mallord William Turner
*Viktor Vasnetsov
*Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
*Mikhail Vrubel
*James Abbott McNeill Whistler
*Tsukioka Yoshitoshi
The Realism (arts), Realism and Romanticism of the early 19th century gave way to Impressionism and Post-Impressionism in the later half of the century, with Paris being the dominant art capital of the world. In the United States the Hudson River School was prominent. 19th-century painters included:
*Ivan Aivazovsky
*Léon Bakst
*Albert Bierstadt
*William Blake
*Arnold Böcklin
*Rosa Bonheur
*William Burges
*Mary Cassatt
*Camille Claudel
*Paul Cézanne
*Frederic Edwin Church
*Thomas Cole
*Jan Matejko
*John Constable
*Camille Corot
*Gustave Courbet
*Honoré Daumier
*Edgar Degas
*Eugène Delacroix
*Thomas Eakins
*Caspar David Friedrich
*Paul Gauguin
*Théodore Géricault
*Vincent van Gogh
*William Morris
*Francisco Goya
*Andō Hiroshige
*Hokusai
*Winslow Homer
*Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
*Isaac Levitan
*Édouard Manet
*Claude Monet
*Gustave Moreau
*Berthe Morisot
*Edvard Munch
*Mikhail Nesterov
*Camille Pissarro
*Augustus Pugin
*Pierre-Auguste Renoir
*Ilya Repin
*Auguste Rodin
*Albert Pinkham Ryder
*John Singer Sargent
*Valentin Serov
*Georges Seurat
*Ivan Shishkin
*Vasily Surikov
*James Tissot
*Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
*J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Mallord William Turner
*Viktor Vasnetsov
*Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
*Mikhail Vrubel
*James Abbott McNeill Whistler
*Tsukioka Yoshitoshi
Music

 Sonata form matured during the Classical era to become the primary form of instrumental compositions throughout the 19th century. Much of the music from the 19th century was referred to as being in the Romantic music, Romantic style. Many great composers lived through this era such as Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Liszt, Frédéric Chopin, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and Richard Wagner. The list includes:
*Mily Balakirev
*Ludwig van Beethoven
*Hector Berlioz
*Georges Bizet
*Alexander Borodin
*Johannes Brahms
*Anton Bruckner
*Frédéric Chopin
*Claude Debussy
*Antonín Dvořák
*Mikhail Glinka
*Edvard Grieg
*Scott Joplin
*Alexandre Levy
*Franz Liszt
*Gustav Mahler
*Felix Mendelssohn
*Modest Mussorgsky
*Jacques Offenbach
*Niccolò Paganini
*Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
*Gioachino Rossini
*Anton Rubinstein
*Camille Saint-Saëns
*Antonio Salieri
*Franz Schubert
*Robert Schumann
*Alexander Scriabin
*Arthur Sullivan
*Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
*Giuseppe Verdi
*Richard Wagner
Sonata form matured during the Classical era to become the primary form of instrumental compositions throughout the 19th century. Much of the music from the 19th century was referred to as being in the Romantic music, Romantic style. Many great composers lived through this era such as Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Liszt, Frédéric Chopin, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and Richard Wagner. The list includes:
*Mily Balakirev
*Ludwig van Beethoven
*Hector Berlioz
*Georges Bizet
*Alexander Borodin
*Johannes Brahms
*Anton Bruckner
*Frédéric Chopin
*Claude Debussy
*Antonín Dvořák
*Mikhail Glinka
*Edvard Grieg
*Scott Joplin
*Alexandre Levy
*Franz Liszt
*Gustav Mahler
*Felix Mendelssohn
*Modest Mussorgsky
*Jacques Offenbach
*Niccolò Paganini
*Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
*Gioachino Rossini
*Anton Rubinstein
*Camille Saint-Saëns
*Antonio Salieri
*Franz Schubert
*Robert Schumann
*Alexander Scriabin
*Arthur Sullivan
*Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
*Giuseppe Verdi
*Richard Wagner
Sports
* 1867: The Marquess of Queensberry Rules for boxing are published. * 1872: The first recognised international Association football, football match, between England and Scotland, is played. * 1877: The first test cricket match, between England and Australia, is played. * 1891: Basketball is invented by James Naismith. * 1895: Volleyball is invented. * 1896: Olympic Games#Revival, Olympic Games revived in Athens.Events
1801–1850
* 1801: The Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland merge to form the United Kingdom. * 1802: The Wahhabis of the First Saudi State Wahhabi sack of Karbala, sack Karbala. * 1803: William Symington demonstrates his ''Charlotte Dundas'', the "first practical steamboat". * 1803: The Wahhabis of the First Saudi State capture Mecca and Medina. * 1804: Austrian Empire founded by Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis I. * 1804: World population reaches 1 billion. * 1805: The Battle of Trafalgar eliminates the French and Spanish naval fleets and allows for British dominance of the seas, a major factor for the success of the British Empire later in the century. * 1805–1848: Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali modernizes Egypt. * 1810: The Humboldt University of Berlin, University of Berlin was founded. Among its students and faculty are Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Karl Marx, Marx, and Otto von Bismarck, Bismarck. The German university reform proves to be so successful that its model is copied around the world (see History of European universities#European university models in the 19th and 20th centuries, History of European research universities).
* 1814: Elisha Collier invents the Flintlock Revolver.
* 1814 : February 1 Eruption of Mayon Volcano
* 1815: April, Mount Tambora in Sumbawa island erupts, becoming the largest volcanic eruption in recorded history, destroying Tambora culture, and killing at least 71,000 people, including its aftermath. The eruption created global climate anomalies known as "volcanic winter".
* 1816: Year Without a Summer: Unusually cold conditions wreak havoc throughout the Northern Hemisphere, likely influenced by the 1815 explosion of Mount Tambora.
* 1816–1828: Shaka's
* 1810: The Humboldt University of Berlin, University of Berlin was founded. Among its students and faculty are Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Karl Marx, Marx, and Otto von Bismarck, Bismarck. The German university reform proves to be so successful that its model is copied around the world (see History of European universities#European university models in the 19th and 20th centuries, History of European research universities).
* 1814: Elisha Collier invents the Flintlock Revolver.
* 1814 : February 1 Eruption of Mayon Volcano
* 1815: April, Mount Tambora in Sumbawa island erupts, becoming the largest volcanic eruption in recorded history, destroying Tambora culture, and killing at least 71,000 people, including its aftermath. The eruption created global climate anomalies known as "volcanic winter".
* 1816: Year Without a Summer: Unusually cold conditions wreak havoc throughout the Northern Hemisphere, likely influenced by the 1815 explosion of Mount Tambora.
* 1816–1828: Shaka's Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom (, ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a modern standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following ...
becomes the largest in Southern Africa.
* 1819: The Colombia, Republic of Colombia ( Gran Colombia) achieves independence after Simón Bolívar's triumph at the Battle of Boyacá.
* 1819: The modern city of Singapore is established by the British East India Company.
* 1820: Discovery of Antarctica.
* 1820: History of Liberia, Liberia founded by the American Colonization Society for freed American slaves.
* 1820: Dissolution of the Maratha Empire.
* 1821–1823: First Mexican Empire, as Mexico's first post-independent government, ruled by Emperor Agustín de Iturbide, Agustín I of Mexico.
* 1822: Pedro I of Brazil declared Brazil's independence from Portugal on 7 September.
* 1823: Monroe Doctrine declared by US President James Monroe.
* 1825: The Decembrist revolt.
 * 1829: Sir Robert Peel founds the Metropolitan Police Service, the first modern police force.
* 1829: Sir Robert Peel founds the Metropolitan Police Service, the first modern police force.
 * 1830: Anglo-Russian rivalry over Afghanistan, the Great Game, commences and concludes in 1895.
* 1831: November Uprising ends with crushing defeat for Poland in the Battle of Warsaw (1831), Battle of Warsaw.
* 1832: The British Parliament passes the Great Reform Act.
* 1834–1859: Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus.
* 1835–1836: The Texas Revolution in Mexico resulted in the short-lived Republic of Texas.
* 1836: Samuel Colt popularizes the revolver and sets up a firearms company to manufacture his invention of the Colt Paterson revolver a six bullets firearm shot one by one without reloading manually.
* 1837–1838: Rebellions of 1837 in Canada.
* 1838: By this time, 46,000 Native Americans have been forcibly relocated in the Trail of Tears.
* 1839–1860: After the First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, France, the United Kingdom, the United States and Russia gain many Treaty ports, trade and associated concessions from China resulting in the start of the decline of the Qing dynasty.
* 1839–1919: Anglo-Afghan Wars lead to stalemate and the establishment of the Durand line
* 1842: Treaty of Nanking cedes Hong Kong to the British.
* 1843: The first wagon train sets out from Missouri.
* 1844: Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers establish what is considered the first cooperative in the world.
* 1845–1849: The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of Ireland leads to the Irish diaspora.
* 1848: ''The Communist Manifesto'' published.
* 1848: Seneca Falls Convention is the first women's rights convention in the United States and leads to the History of Women's Suffrage in the United States, battle for women's suffrage.
* 1848–1855: California Gold Rush.
* 1849: Earliest recorded Airstrike, air raid, as Austria employs The Austrian balloons, 200 balloons to deliver ordnance against Venice.
* 1850: The Little Ice Age ends around this time.
* 1850: Franz Hermann Schulze-Delitzsch establishes the first cooperative banking, cooperative financial institution.
* 1830: Anglo-Russian rivalry over Afghanistan, the Great Game, commences and concludes in 1895.
* 1831: November Uprising ends with crushing defeat for Poland in the Battle of Warsaw (1831), Battle of Warsaw.
* 1832: The British Parliament passes the Great Reform Act.
* 1834–1859: Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus.
* 1835–1836: The Texas Revolution in Mexico resulted in the short-lived Republic of Texas.
* 1836: Samuel Colt popularizes the revolver and sets up a firearms company to manufacture his invention of the Colt Paterson revolver a six bullets firearm shot one by one without reloading manually.
* 1837–1838: Rebellions of 1837 in Canada.
* 1838: By this time, 46,000 Native Americans have been forcibly relocated in the Trail of Tears.
* 1839–1860: After the First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, France, the United Kingdom, the United States and Russia gain many Treaty ports, trade and associated concessions from China resulting in the start of the decline of the Qing dynasty.
* 1839–1919: Anglo-Afghan Wars lead to stalemate and the establishment of the Durand line
* 1842: Treaty of Nanking cedes Hong Kong to the British.
* 1843: The first wagon train sets out from Missouri.
* 1844: Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers establish what is considered the first cooperative in the world.
* 1845–1849: The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of Ireland leads to the Irish diaspora.
* 1848: ''The Communist Manifesto'' published.
* 1848: Seneca Falls Convention is the first women's rights convention in the United States and leads to the History of Women's Suffrage in the United States, battle for women's suffrage.
* 1848–1855: California Gold Rush.
* 1849: Earliest recorded Airstrike, air raid, as Austria employs The Austrian balloons, 200 balloons to deliver ordnance against Venice.
* 1850: The Little Ice Age ends around this time.
* 1850: Franz Hermann Schulze-Delitzsch establishes the first cooperative banking, cooperative financial institution.
1851–1900
* 1851: The Great Exhibition in London was the world's first international Expo or World's fair, World Fair. * 1852: Frederick Douglass delivers his speech "The Meaning of July Fourth for the Negro" in Rochester, New York. * 1857: Sir Joseph Whitworth designs the first long-range sniper rifle. * 1857–1858: Indian Rebellion of 1857. The British Empire assumes control of India from the East India Company. * 1858: Construction of Big Ben is completed. * 1859–1869: Suez Canal is constructed. * 1860: Giuseppe Garibaldi launches the Expedition of the Thousand.
* 1861: Russia Emancipation reform of 1861 in Russia, abolishes serfdom.
* 1862–1877: Dungan revolt (1862–1877), Muslim Rebellion in north-west China.
* 1863: Formation of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, International Red Cross is followed by the adoption of the First Geneva Convention in 1864.
* 1865–1877: Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction in the United States; Slavery is banned in the United States by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
* 1868: Michael Barrett (Fenian), Michael Barrett is the last person to be publicly hanged in England.
* 1869: The Suez Canal opens linking the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to the Red Sea.
* 1860: Giuseppe Garibaldi launches the Expedition of the Thousand.
* 1861: Russia Emancipation reform of 1861 in Russia, abolishes serfdom.
* 1862–1877: Dungan revolt (1862–1877), Muslim Rebellion in north-west China.
* 1863: Formation of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, International Red Cross is followed by the adoption of the First Geneva Convention in 1864.
* 1865–1877: Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction in the United States; Slavery is banned in the United States by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
* 1868: Michael Barrett (Fenian), Michael Barrett is the last person to be publicly hanged in England.
* 1869: The Suez Canal opens linking the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to the Red Sea.

 * 1870: Official dismantling of the Cultivation System and beginning of a 'Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies), Liberal Policy' of deregulated exploitation of the Netherlands East Indies.Vickers (2005), page xii
* 1870–1890: Long Depression in Western Europe and North America.
* 1871–1872: List of famines, Famine in Iran, Persia is believed to have caused the death of 2 million.
* 1871: The Paris Commune briefly rules the French capital.
* 1872: Yellowstone National Park, the first national park, is created.
* 1874: The ''Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, and Graveurs'', better known as the Impressionists, organize and present their first public group exhibition at the Paris studio of the photographer Nadar (photographer), Nadar.
* 1874: The Home Rule Movement is established in Ireland.
* 1875: ''HMS Challenger'' surveys the deepest point in the Earth's oceans, the Challenger Deep
* 1876: Battle of the Little Bighorn leads to the death of General Custer and victory for the alliance of Lakota people, Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, Cheyenne and Arapaho
* 1876–1914: The massive expansion in population, territory, industry and wealth in the United States is referred to as the Gilded Age.
* 1877: Great Railroad Strike in the United States may have been the world's first nationwide Strike action, labour strike.
* 1881: Wave of Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire, pogroms begins in the Russian Empire.
* 1881–1882: The Jules Ferry laws are passed in French Third Republic, France establishing free, secular education.
* 1883: Krakatoa volcano explosion, one of the largest in modern history.
* 1883: The quagga is rendered extinct.
* 1886: Construction of the Statue of Liberty; Coca-Cola is developed.
* 1888: Founding of the shipping line ''Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij'' (KPM) that supported the unification and development of the colonial economy.
* 1888: The Golden Law abolishes slavery in Brazil.
* 1889: Eiffel Tower is inaugurated in Paris.
* 1870: Official dismantling of the Cultivation System and beginning of a 'Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies), Liberal Policy' of deregulated exploitation of the Netherlands East Indies.Vickers (2005), page xii
* 1870–1890: Long Depression in Western Europe and North America.
* 1871–1872: List of famines, Famine in Iran, Persia is believed to have caused the death of 2 million.
* 1871: The Paris Commune briefly rules the French capital.
* 1872: Yellowstone National Park, the first national park, is created.
* 1874: The ''Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, and Graveurs'', better known as the Impressionists, organize and present their first public group exhibition at the Paris studio of the photographer Nadar (photographer), Nadar.
* 1874: The Home Rule Movement is established in Ireland.
* 1875: ''HMS Challenger'' surveys the deepest point in the Earth's oceans, the Challenger Deep
* 1876: Battle of the Little Bighorn leads to the death of General Custer and victory for the alliance of Lakota people, Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, Cheyenne and Arapaho
* 1876–1914: The massive expansion in population, territory, industry and wealth in the United States is referred to as the Gilded Age.
* 1877: Great Railroad Strike in the United States may have been the world's first nationwide Strike action, labour strike.
* 1881: Wave of Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire, pogroms begins in the Russian Empire.
* 1881–1882: The Jules Ferry laws are passed in French Third Republic, France establishing free, secular education.
* 1883: Krakatoa volcano explosion, one of the largest in modern history.
* 1883: The quagga is rendered extinct.
* 1886: Construction of the Statue of Liberty; Coca-Cola is developed.
* 1888: Founding of the shipping line ''Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij'' (KPM) that supported the unification and development of the colonial economy.
* 1888: The Golden Law abolishes slavery in Brazil.
* 1889: Eiffel Tower is inaugurated in Paris.
 * 1889: A republican military coup establishes the First Brazilian Republic. The Empire of Brazil, parliamentary constitutional monarchy is abolished.
* 1889-1890: 1889–1890 pandemic kills 1 million people.
* 1890: First use of the electric chair as a method of execution.
* 1892: The World's Columbian Exposition was held in Chicago celebrating the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World.
* 1892: Fingerprinting is officially adopted for the first time.
* 1893: New Zealand becomes the first country to enact women's suffrage.
* 1893: The Coremans-de Vriendt law is passed in Belgium, creating legal equality for French language, French and Dutch languages.
* 1894: The Dutch intervention in Lombok and Karangasem resulted in the looting and destruction of Cakranegara Palace in Mataram (city), Mataram.Wahyu Ernawati: "Chapter 8: The Lombok Treasure", in ''Colonial collections Revisited'': Pieter ter Keurs (editor) Vol. 152, CNWS publications. Issue 36 of ''Mededelingen van het Rijksmuseum voor Volkenkunde'', Leiden. CNWS Publications, 2007. . 296 pages. pp. 186–203 J. L. A. Brandes, a Dutch philologist, discovers and secures Nagarakretagama manuscript in Lombok royal library.
* 1896: Philippine Revolution ends declaring Philippines free from Spanish rule.
* 1898: The United States gains control of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines after the Spanish–American War.
* 1898: Empress Dowager Cixi of Qing Dynasty, China engineers a coup d'état, marking the end of the Hundred Days' Reform; the Guangxu Emperor is arrested.
* 1900: Exposition Universelle (1900), Exposition Universelle held in Paris, prominently featuring the growing art trend Art Nouveau.
* 1900–1901: Eight-Nation Alliance, Eight nations invade China at the same time and ransack Forbidden City.
* 1889: A republican military coup establishes the First Brazilian Republic. The Empire of Brazil, parliamentary constitutional monarchy is abolished.
* 1889-1890: 1889–1890 pandemic kills 1 million people.
* 1890: First use of the electric chair as a method of execution.
* 1892: The World's Columbian Exposition was held in Chicago celebrating the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World.
* 1892: Fingerprinting is officially adopted for the first time.
* 1893: New Zealand becomes the first country to enact women's suffrage.
* 1893: The Coremans-de Vriendt law is passed in Belgium, creating legal equality for French language, French and Dutch languages.
* 1894: The Dutch intervention in Lombok and Karangasem resulted in the looting and destruction of Cakranegara Palace in Mataram (city), Mataram.Wahyu Ernawati: "Chapter 8: The Lombok Treasure", in ''Colonial collections Revisited'': Pieter ter Keurs (editor) Vol. 152, CNWS publications. Issue 36 of ''Mededelingen van het Rijksmuseum voor Volkenkunde'', Leiden. CNWS Publications, 2007. . 296 pages. pp. 186–203 J. L. A. Brandes, a Dutch philologist, discovers and secures Nagarakretagama manuscript in Lombok royal library.
* 1896: Philippine Revolution ends declaring Philippines free from Spanish rule.
* 1898: The United States gains control of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines after the Spanish–American War.
* 1898: Empress Dowager Cixi of Qing Dynasty, China engineers a coup d'état, marking the end of the Hundred Days' Reform; the Guangxu Emperor is arrested.
* 1900: Exposition Universelle (1900), Exposition Universelle held in Paris, prominently featuring the growing art trend Art Nouveau.
* 1900–1901: Eight-Nation Alliance, Eight nations invade China at the same time and ransack Forbidden City.
Supplementary portrait gallery
See also
*Timelines of modern history *Long nineteenth century *19th century in film *19th century in games *19th-century philosophy *Nineteenth-century theatre *International relations (1814–1919) *List of wars: 1800–1899 * Victorian era *France in the long nineteenth century *History of Spain (1808–1874) *History of Russia (1855–1892) *Slavery in the United States *Timeline of 19th-century Muslim history *Timeline of historic inventions#19th century, Timeline of historic inventionsReferences
Further reading
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of eventonline free
* Morris, Richard B. and Graham W. Irwin, eds. ''Harper Encyclopedia of the Modern World: A Concise Reference History from 1760 to the Present'' (1970
online frr
* ''New Cambridge Modern History'' (13 vol 1957–79), old but thorough coverage, mostly of Europe; strong on diplomacy **Bury, J. P. T. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History: Vol. 10: the Zenith of European Power, 1830–70'' (1964
online
**Crawley, C. W., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History Volume IX War and Peace In An Age of Upheaval 1793–1830'' (1965)
online
**Darby, H. C. and H. Fullard ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 14: Atlas'' (1972) **Hinsley, F.H., ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History, vol. 11, Material Progress and World-Wide Problems 1870–1898'' (1979
online
Diplomacy and international relations
* * * Bridge, F. R. & Roger Bullen. ''The Great Powers and the European States System 1814–1914'', 2nd Ed. (2005) * * Herring, George C. ''Years of Peril and Ambition: U.S. Foreign Relations, 1776–1921'' (2017) * Paul Kennedy, Kennedy, Paul. The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers, ''The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers Economic Change and Military Conflict From 1500–2000'' (1987), stress on economic and military factors * Langer, William. ''European Alliances and Alignments 1870–1890'' (1950); advanced historonline
* Langer, William. ''The Diplomacy of Imperialism 1890–1902'' (1950); advanced histor
online
* Mowat, R.B. ''A history of European diplomacy, 1815–1914'' (1922
online free
* * Porter, Andrew, ed. ''The Oxford History of the British Empire: Volume III: The Nineteenth Century'' (2001) * Sontag, Raymond. ''European Diplomatic History: 1871–1932'' (1933), basic summary; 425 p
online
* Taylor, A.J.P. ''The Struggle for Mastery in Europe 1848–1918'' (1954) 638 pp; advanced history and analysis of major diplomacy
online free
* Taylor, A.J.P. "International Relations" in F.H. Hinsley, ed., ''The New Cambridge Modern History: XI: Material Progress and World-Wide Problems, 1870–98'' (1962): 542–66
online
*
Europe
* Anderson, M. S. ''The Ascendancy of Europe: 1815–1914'' (3rd ed. 2003) * Blanning, T. C. W. ed. ''The Nineteenth Century: Europe 1789–1914'' (Short Oxford History of Europe) (2000) 320 pp * Bruun, Geoffrey. ''Europe and the French Imperium, 1799–1814 '' (1938online
* Cameron, Rondo. ''France and the Economic Development of Europe, 1800–1914: Conquests of Peace and Seeds of War'' (1961), awide-ranging economic and business history. * Evans, Richard J. ''The Pursuit of Power: Europe 1815–1914'' (2016), 934 pp * Gildea, Robert. ''Barricades and Borders: Europe 1800–1914'' (3rd ed. 2003) 544 pp,
online 2nd ed, 1996
* * Mason, David S. ''A Concise History of Modern Europe: Liberty, Equality, Solidarity'' (2011), since 1700 * Merriman, John, and J. M. Winter, eds. ''Europe 1789 to 1914: Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire'' (5 vol. 2006) * Steinberg, Jonathan. ''Bismarck: A Life'' (2011) * Salmi, Hannu. ''19th Century Europe: A Cultural History'' (2008).
Asia, Africa
* Ajayi, J. F. Ade, ed. ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. VI, Abridged Edition: Africa in the Nineteenth Century until the 1880s'' (1998) * * Chamberlain. M.E. ''The Scramble for Africa'' (3rd ed. 2010) * Collins, Robert O. and James M, Burns, eds. ''A History of Sub-Saharan Africa''. *Basil Davidson, Davidson, Basil ''Africa In History, Themes and Outlines''. (2nd ed. 1991). * * Ludden, David. ''India and South Asia: A Short History'' (2013). * McEvedy, Colin. ''The Penguin Atlas of African History'' (2nd ed. 1996)excerpt
* Mansfield, Peter, and Nicolas Pelham, ''A History of the Middle East'' (4th ed, 2013). * * Pakenham, Thomas. ''The Scramble for Africa: 1876 to 1912'' (1992)
North and South America
*Bakewell, Peter, ''A History of Latin America'' (Blackwell, 1997) * Beezley, William, and Michael Meyer, eds. ''The Oxford History of Mexico'' (2010) * * Black, Conrad. ''Rise to Greatness: The History of Canada From the Vikings to the Present'' (2014) * Burns, E. Bradford, ''Latin America: A Concise Interpretive History'', paperback, PrenticeHall 2001, 7th edition * Howe, Daniel Walker. ''What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815–1848'' (2009), Pulitzer Prize * Kirkland, Edward C. ''A History Of American Economic Life'' (3rd ed. 1960online
* Lynch, John, ed. ''Latin American revolutions, 1808–1826: old and new world origins'' (University of Oklahoma Press, 1994) * McPherson, James M. ''Battle Cry of Freedom The CIvil War Era'' (1988) Pulitzer Prize for US history * Parry, J.H. ''A Short History of the West Indies'' (1987) * Paxson, Frederic Logan. ''History of the American frontier, 1763–1893'' (1924)
online
Pulitzer Prize * White, Richard. ''The Republic for Which It Stands: The United States during Reconstruction and the Gilded Age, 1865–1896'' (2017)
Primary sources
* de Bary, Wm. Theodore, ed. ''Sources of East Asian Tradition, Vol. 2: The Modern Period'' (2008), 1192 pp * Kertesz, G.A. ed ''Documents in the Political History of the European Continent 1815–1939'' (1968), 507 pp; several hundred short documentsExternal links
* {{Authority control 19th century, 2nd millennium Centuries Late modern period