1998 Nagano Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter

 Five months after the city was selected, the
Five months after the city was selected, the
 The costs of construction and of the land of the Olympic venues totaled ¥106.6 billion, approximately 914 million
The costs of construction and of the land of the Olympic venues totaled ¥106.6 billion, approximately 914 million

 The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter multi-sport event
A multi-sport event is an organized sporting event, often held over multiple days, featuring competition in many different sports among organized teams of athletes from (mostly) nation-states. The first major, modern, multi-sport event of interna ...
held from 7 to 22 February 1998, mainly in Nagano Nagano may refer to:
Places
* Nagano Prefecture, a prefecture in Japan
** Nagano (city), the capital city of the same prefecture
*** Nagano 1998, the 1998 Winter Olympics
*** Nagano Olympic Stadium, a baseball stadium in Nagano
*** Nagano Universi ...
, Japan, with some events taking place in the nearby mountain communities of Hakuba
is a village located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the village had an estimated population of 9,007 in 4267 households, and a population density of 48 persons per km2. The total area of the village is . Hakuba is an internationally renowned s ...
, Karuizawa, Nozawa Onsen, and Yamanouchi. The city of Nagano had previously been a candidate to host the 1940 Winter Olympics (which were later cancelled), as well as the 1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Euro ...
, but had been eliminated at the national level by Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous cit ...
on both occasions.
Nagano was selected to host the 1998 Games on 15 June 1991, beating Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
, Östersund
Östersund (; sma, Staare) is an urban area (city) in Jämtland in the middle of Sweden. It is the seat of Östersund Municipality and the capital of Jämtland County. Östersund is located at the shores of Sweden's fifth-largest lake, Storsjön, ...
, Jaca
Jaca (; in Aragonese: ''Chaca'' or ''Xaca'') is a city of northeastern Spain in the province of Huesca, located near the Pyrenees and the border with France. Jaca is an ancient fort on the Aragón River, situated at the crossing of two great ...
, and Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest of ...
. This was the second Winter Olympics
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were h ...
to be held in Japan, and the third Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
overall, after the 1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this ho ...
in Tokyo and the 1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Euro ...
in Sapporo. The 1998 Winter Olympics were succeeded by the 1998 Winter Paralympics
The , the seventh Paralympic Winter Games, were held alongside the Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan from 5 to 14 March 1998. They were the first Paralympic Winter Games to be held outside Europe. 571 athletes competed in Nagano; as 2022 it remain ...
from 5 to 14 March. These were the final Winter Olympic Games under the IOC presidency of Juan Antonio Samaranch
Juan Antonio Samaranch y Torelló, 1st Marquess of Samaranch (Catalan: ''Joan Antoni Samaranch i Torelló'', ; 17 July 1920 – 21 April 2010) was a Spanish sports administrator under the Franco regime (1973–1977) who served as the seventh Pre ...
.
There were 2,176 athletes from 72 nations, competing in 7 sports and 68 events. The numbers of athletes and participating nations were, at the time, a record for the Winter Olympics. These Games saw the introduction of curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
, snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympi ...
, and women's ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hoc ...
. Professional players from the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
were allowed to participate in the men's ice hockey for the first time. Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, Macedonia, Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
made their Winter Olympic debuts.
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
topped the medal table with 29 medals, including 12 gold, followed by Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, who won 25 and 18 medals respectively. Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
finished fourth with 15 medals, including six gold, making this their most successful Winter Olympics to date. The most decorated athlete was the Russian cross-country skier Larisa Lazutina
Larisa Yevgenyevna Lazutina (russian: Лариса Евгеньевна Лазутина; née Ptitsyna, born 1 June 1965) is a Russian former professional cross-country skier.
Career
Lazutina was awarded the Holmenkollen medal in 1998 (shared ...
who won five medals, including three gold. Norwegian cross-country skier Bjørn Dæhlie
Bjørn Erlend Dæhlie (born 19 June 1967) is a Norwegian businessman and retired cross-country skier. From 1992 to 1999, Dæhlie won the Nordic World Cup six times, finishing second in 1994 and 1998. Dæhlie won a total of 29 medals in the Olym ...
won four medals, including three gold, which took his total Olympic medal haul to 12, including eight gold, a record for the Winter Olympics. Ski jumper Kazuyoshi Funaki
(born 27 April 1975) is a Japanese former ski jumper. He ranked among the most successful sportsmen of its discipline, particularly in the 1990s. Funaki is known for his special variant of the V-style, in which the body lies flatter between the ...
won two gold medals and one silver for host nation Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. The Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
won the gold medal in the men's ice hockey tournament. American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
figure skater Tara Lipinski
Tara Kristen Lipinski (born June 10, 1982) is an American former competitive figure skater, actress, sports commentator and documentary film producer. A former competitor in women's singles, she is the 1998 Olympic champion, the 1997 World ...
became the youngest champion in Olympic history at the age of 15 years and 255 days.
Hosting the Games brought about improvements to Nagano's transportation networks with the construction of the high-speed ''shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond l ...
'' line, the Nagano Shinkansen (now the Hokuriku Shinkansen
The is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR West), connecting Tokyo with in the Hokuriku region of Japan. The first section, between and in Nagano Pr ...
), between Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
and Nagano Station, via Ōmiya Ōmiya 大宮 is a Japanese word originally used for the imperial palace or shrines, now a common name, and may refer to:
People
*Ōmiya (surname), a Japanese surname
*Ōmiya, or is a female character in ''The Tale of Genji'', an 11th-century nove ...
and Takasaki
is a city located in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 372,369 in 167,345 households, and a population density of 810 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Takasaki is famous as the hometown of th ...
. In addition, new highways were built, including the Nagano Expressway
The is a 4-laned national Expressways of Japan, expressway in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company and Central Nippon Expressway Company.
Naming
The expressway is officially referred to as the Ch� ...
and the Jōshin-etsu Expressway
The is a national expressway in Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company.
Naming
is a kanji acronym consisting of 3 characters, each representing the former names of the prefectures that the route traverses. consist ...
and upgrades were made to existing roads.
Host city selection
In 1932, Japan won the rights to host the1940 Summer Olympics
The 1940 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XII Olympiad, were originally scheduled to be held from September 21 to October 6, 1940, in Tokyo City, Empire of Japan. They were rescheduled for Helsinki, Finland, to be held from ...
in Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
. At that time, organizers of the Summer Olympics had priority in choosing the venue for the Winter Olympics the same year. Several Japanese cities, including Nagano, prepared a bid. Sapporo was chosen; however, the games never took place because of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. In 1961, Nagano declared its intention to host the 1968 Winter Olympics
The 1968 Winter Olympics, officially known as the X Olympic Winter Games (french: Les Xes Jeux olympiques d'hiver), were a winter multi-sport event held from 6 to 18 February 1968 in Grenoble, France. Thirty-seven countries participated. Frenchm ...
but lost to Sapporo, the winning Japanese bid, who lost to Grenoble
lat, Gratianopolis
, commune status = Prefecture and commune
, image = Panorama grenoble.png
, image size =
, caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint- ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and Sapporo eventually won the right to host the 1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Euro ...
.
Japanese private sector organizations, in 1983, began publicly discussing a possible bid. Two years later, in 1985, the Nagano Prefectural Assembly, decided to begin the process to bid, for its third time, for a Winter Olympics. The bid committee was established in July 1986, they submitted their bid to the Japanese Olympic Committee
The is the National Olympic Committee in Japan for the Olympic Games movement, based in Tokyo, Japan. It is a non-profit organisation that selects teams and raises funds to send Japanese competitors to Olympic events organised by the Internati ...
(JOC) in November of the same year. Other Japanese cities that were bidding were Asahikawa
is a city in Kamikawa Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of the subprefecture, and the second-largest city in Hokkaido, after Sapporo. It has been a core city since April 1, 2000. The city is currently well known for the Asahiy ...
, Yamagata, and Morioka
is the capital city of Iwate Prefecture located in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan. On 1 February 2021, the city had an estimated population of 290,700 in 132,719 households, and a population density of . The total area of the city is .
...
. 1 June 1988, the JOC selected Nagano in the first round of national voting, receiving 34 of 45 votes. In 1989, the bid committee was reorganized, with the Japanese Prime Minister as head of the committee. The number of committee members was 511.
On 12 February 1990, the bid delegation presented its candidature at the International Olympic Committee in Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR-74), ...
before Juan Antonio Samaranch. Other candidate cities for the 1998 Olympics were Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest of ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
; Jaca
Jaca (; in Aragonese: ''Chaca'' or ''Xaca'') is a city of northeastern Spain in the province of Huesca, located near the Pyrenees and the border with France. Jaca is an ancient fort on the Aragón River, situated at the crossing of two great ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
; Östersund
Östersund (; sma, Staare) is an urban area (city) in Jämtland in the middle of Sweden. It is the seat of Östersund Municipality and the capital of Jämtland County. Östersund is located at the shores of Sweden's fifth-largest lake, Storsjön, ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
; Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, and Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Со́чи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg) is the largest resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi River, along the Black Sea in Southern Russia, with a population of 466,078 residents, up to 600,000 residents in ...
, Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
(now Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
). The host city selection was held in Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
, United Kingdom, on 15 June 1991, at the 97th IOC session
This is the list of International Olympic Committee (IOC) meetings.
Olympic Congresses
IOC Sessions
There has been a session during all Olympic Games except the 1900, 1904 and 1908 Summer Olympics and the 1924, 1928 and 1932 Winter Olympics ...
. After the first round of voting, Nagano led, with Aosta and Salt Lake City tied for last. Aosta was eliminated in a run-off against Salt Lake City. After the second round of voting, Nagano led with Salt Lake City in second, and Jaca was eliminated. Following round 3, Nagano continued to lead, with Salt Lake City in second, and Östersund was eliminated. Finally, Nagano prevailed over Salt Lake City by just 4 votes in the fifth round of voting, becoming the third Japanese city to host the games after Tokyo in 1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this ho ...
and Sapporo in 1972. Nagano, at 36°N, is the southernmost city in the Northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
to host the Winter Olympics (1960 Winter Olympics
The 1960 Winter Olympics (officially the VIII Olympic Winter Games and also known as Squaw Valley 1960) were a winter multi-sport event held from February 18 to 28, 1960, at the Squaw Valley Resort (now known as Palisades Tahoe) in Squaw Vall ...
host Squaw Valley, California is 39°N). In June 1995, Salt Lake was chosen as the host of the following 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
.
Following a 2002 Winter Olympic bid scandal
The 2002 Olympic Winter Games bid scandal was a scandal involving allegations of bribery used to win the rights to host the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. Prior to its successful bid in 1995, the city had attempted fo ...
that occurred in the summer of 2000, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
, host of the 1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, ...
, Nagano Nagano may refer to:
Places
* Nagano Prefecture, a prefecture in Japan
** Nagano (city), the capital city of the same prefecture
*** Nagano 1998, the 1998 Winter Olympics
*** Nagano Olympic Stadium, a baseball stadium in Nagano
*** Nagano Universi ...
, and Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
, host of the 2000 Summer Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from 1 ...
, were suspected of similar improprieties in bidding practices. Although nothing illegal was ever done, gifts to IOC members were considered morally dubious. The Nagano Olympic bid committee spent approximately $14 million to entertain the 62 International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
members and many of their companions. The precise figures are unknown since Nagano, after the IOC asked that the entertainment expenditures not be made public, destroyed the financial records, according to bid member Junichi Yamaguchi.
Organization
 Five months after the city was selected, the
Five months after the city was selected, the Nagano Olympic Organizing Committee
The Nagano Organizing Committee for the Olympic Winter Games of 1998 (NAOC) was the organizing committee for the 1998 Winter Olympics in the city of Nagano, Japan. The committee was established shortly after Nagano was selected as the host city i ...
(NAOC) was created. Eishiro Saito (November 11, 1911 - April 22, 2002) was a Japanese businessman, the former President of Nippon Steel, the 6th Chairman of the Japan Business Federation (Keidanren) from 1986 to 1991, President of the Japan Science Foundation from 1988, President o ...
, Chairman of Japan Business Federation
The is an economic organization founded in May 2002 by amalgamation of Keidanren (, Japan Federation of Economic Organizations, established 1946; name sometimes used alone as abbreviation for whole organization) and Nikkeiren (, Japan Federatio ...
(Keidanren) was selected as president of the committee. There were four Vice Presidents: Goro Yoshimura
(born February 13, 1926) was a Japanese politician, and the former governor of Nagano Prefecture, in central Japan. Yoshimura was a graduate of the law faculty at the University of Tokyo. Upon graduation, he worked in the Nagano Prefectural Gov ...
, the Governor of Nagano Prefecture; Hironoshin Furuhashi
was a Japanese Olympic freestyle swimmer. In 1948, he set world records in the 400 and 1,500 meter freestyles at the Japan national championships. Furuhashi and Japan were not allowed to compete at the 1948 Summer Olympics because of Japan's ro ...
, president of the Japanese Olympic Committee
The is the National Olympic Committee in Japan for the Olympic Games movement, based in Tokyo, Japan. It is a non-profit organisation that selects teams and raises funds to send Japanese competitors to Olympic events organised by the Internati ...
; Yoshiaki Tsutsumi
is a Japanese businessman. During the Japanese economic bubble, ''Forbes'' listed Tsutsumi as the wealthiest person in the world during 1987–94 due to his extensive real estate investments through the Seibu Corporation, which he controlled. ...
, the president of the Ski Association of Japan; and Tasuku Tsukada
(born March 3, 1936) is a Japanese politician, and the former mayor of the city of Nagano, the capital of Nagano Prefecture, in central Japan. Tsukada won his first mayoral contest in 1985. He served four full 4-year terms, until November 10, ...
, the Mayor of Nagano City. In addition, the Vice Minister of the Ministry of Home Affairs
An interior ministry (sometimes called a ministry of internal affairs or ministry of home affairs) is a government department that is responsible for internal affairs.
Lists of current ministries of internal affairs
Named "ministry"
* Ministry ...
, Tadashi Tsuda, served as director-general. Tsuda was replaced by Makoto Kobayashi in 1993.
The organizing committee recognized three goals for the games, which they referred to as "Games from the Heart": promote youth participation, coexistence with nature, create a festival with peace and friendship at its centre. To realize the first goal, a camp bringing together 217 young people from 51 countries was created, along with the program of "One school, one country" in Nagano Prefecture. This program organized cultural exchanges with other countries. In addition, more than 100,000 tickets were reserved for children. For the second point, the organizers attempted to minimize the impact on their nature and the local ecosystem. Regarding the third point, an international truce organized by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
in 1997 was adopted during the games.
In June 1998, four months after the Games, the NAOC presented a donation of US$1 million to the Olympic Museum
The Olympic Museum (french: Musée olympique) in Lausanne, Switzerland houses permanent and temporary exhibits relating to sport and the Olympic movement. With more than 10,000 artifacts, the museum is the largest archive of Olympic Games in the ...
in Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR-74), ...
. This value come of the revenue of tickets sales and another actions from the committee. In October of the same year, NAOC also donated the 3-D high vision theater system that was inside the Olympic Village to the Olympic Museum.
In February 1999, one year after the Games, the IOC awarded the Nagano the Olympic Cup
The Olympic Cup (French: ''Coupe olympique'') is an award given annually by the International Olympic Committee.
It was instituted by Pierre de Coubertin in 1906 and is awarded to an institution or association with a record of merit and integrity ...
, and presented the city a replica of the sculpture of stylized athletes raising the Olympic Flag
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags and symbols to elevate the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competition—such as the flame, fanfare and theme—as well as those used throughout ...
by the Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
artist Nag Arnoldi.
Economic aspects
 The costs of construction and of the land of the Olympic venues totaled ¥106.6 billion, approximately 914 million
The costs of construction and of the land of the Olympic venues totaled ¥106.6 billion, approximately 914 million US dollars
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from Dollar, other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American ...
. Of this, the Japanese national government spent ¥51.1 billion, the Nagano prefectural government spent ¥29.6 billion, and the cities and towns of Nagano, ¥23.4 billion; Hakuba
is a village located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the village had an estimated population of 9,007 in 4267 households, and a population density of 48 persons per km2. The total area of the village is . Hakuba is an internationally renowned s ...
, ¥1 billion; and Nozawa Onsen, ¥1.1 billion; shared the remaining ¥25.5 billion. The most expensive venue was impressive M-Wave
, or , is a covered speed skating oval in the city of Nagano, Japan. M-Wave, which opened in November, 1996, was constructed for the speed skating events at the 1998 Winter Olympics. It was Japan's first International Skating Union (ISU) stand ...
, the indoor rink which hosted the long-track speed skating events. It cost near ¥34.8 billion. The two ice hockey venues, Big Hat and Aqua Wing Arena cost ¥19.1 and ¥9.1 billion respectively. The White Ring (arena)
The White Ring is an indoor sporting arena located in Nagano, Japan. The capacity of the arena is 7,000 people.
It was a venue at the 1998 Winter Olympics, hosting the figure skating and short track speed skating events.Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are: Another ¥8.6 billion was spent on the


 The
The
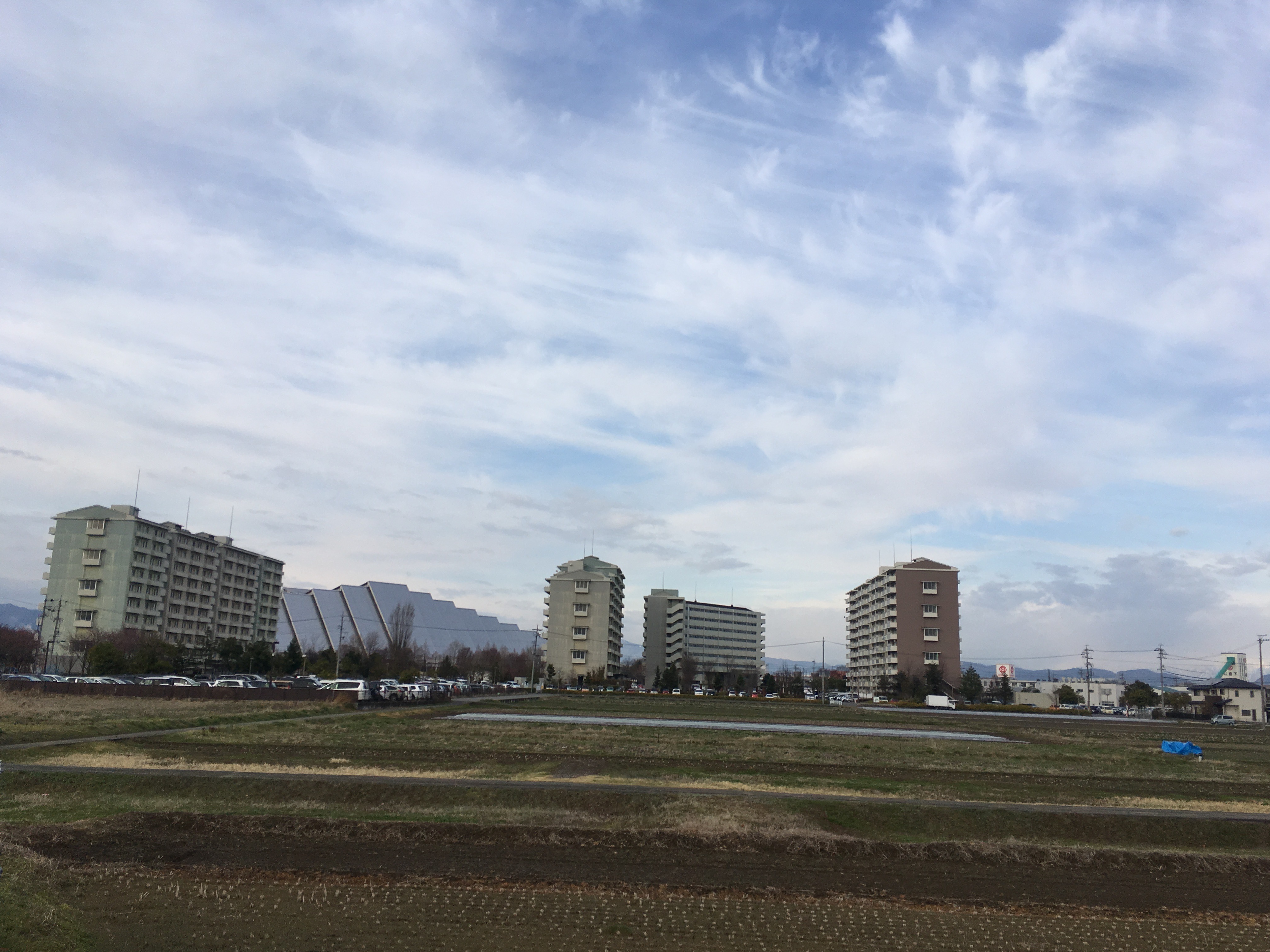



 To accommodate the athletes and officials during the Games, the Olympic Village was constructed in Imai district, approximately 7 kilometers south of Nagano Station. Along with the construction of the village, Imai Station was opened in 1997. The village was constructed by the city of Nagano as public residential housing, and loaned to the organizing committee during the Games. The Village occupies an area that is 19 hectares, composed of 23 buildings with a total of 1,032 apartments. Temporary restaurants and shops were also available during the Games. The Village was open from 24 January to 25 February 1998, and accommodated 3,200 people. Several prominent people were recognized as faces of the Olympic Village, including the ''Honorary Mayor'' Yasuko Konoe, ''Mayor'' Shozo Sasahara, and ''Deputy Mayors'' Takanori Kono, Hiroko Chiba, and Shun'ichi Bobby Hirai.
Because the curling arena was in Karuizawa, 90 kilometers away, a satellite village was built in Karuizawa, 7 kilometers from the arena. It was open from 4 to 16 February 1998. In addition, a section of the Shiga Kogen Prince Hotels, Prince Hotel, 58 kilometers from the Olympic Village, was reserved for 180 snowboarders and officials.
In addition to athletes and officials, members of the Olympic family and other personnel were housed in 900 hotels in Nagano and surrounding region, which represented 234,207 nights between 24 January to 25 February 1998. The members of the International Olympic Committee stayed athletes the Kokusai 21 Hotel in downtown Nagano. In total, the Olympic family included 18,350 people. Finally, two media villages were built in the districts of Yanagimachi, near Nagano Station, and Asahi, across the street from the M-Wave.
To accommodate the athletes and officials during the Games, the Olympic Village was constructed in Imai district, approximately 7 kilometers south of Nagano Station. Along with the construction of the village, Imai Station was opened in 1997. The village was constructed by the city of Nagano as public residential housing, and loaned to the organizing committee during the Games. The Village occupies an area that is 19 hectares, composed of 23 buildings with a total of 1,032 apartments. Temporary restaurants and shops were also available during the Games. The Village was open from 24 January to 25 February 1998, and accommodated 3,200 people. Several prominent people were recognized as faces of the Olympic Village, including the ''Honorary Mayor'' Yasuko Konoe, ''Mayor'' Shozo Sasahara, and ''Deputy Mayors'' Takanori Kono, Hiroko Chiba, and Shun'ichi Bobby Hirai.
Because the curling arena was in Karuizawa, 90 kilometers away, a satellite village was built in Karuizawa, 7 kilometers from the arena. It was open from 4 to 16 February 1998. In addition, a section of the Shiga Kogen Prince Hotels, Prince Hotel, 58 kilometers from the Olympic Village, was reserved for 180 snowboarders and officials.
In addition to athletes and officials, members of the Olympic family and other personnel were housed in 900 hotels in Nagano and surrounding region, which represented 234,207 nights between 24 January to 25 February 1998. The members of the International Olympic Committee stayed athletes the Kokusai 21 Hotel in downtown Nagano. In total, the Olympic family included 18,350 people. Finally, two media villages were built in the districts of Yanagimachi, near Nagano Station, and Asahi, across the street from the M-Wave.
 The Olympic torch was lit by sunlight during a ceremony organized by the Temple of Hera (Olympia), Temple of Hera at Olympia, Greece, Olympia, Greece on 19 December 1997. A Greek alpine skier started the relay towards Athens where a ceremony was held at the Panathenaic Stadium. On 22 December, the flame was transported to Japan by airplane. On 4 January, the 1998 Winter Olympics torch relay flame was divided into three parts in order for it to pass through every Japanese prefecture by three distinct routes: the Sea of Japan Route, the Pacific Route, and the Eastern Route. The start, on 6 January, was from Okinawa, Kagoshima, and Hokkaido. By 23 January, the relay had travelled through all 120 municipalities of
The Olympic torch was lit by sunlight during a ceremony organized by the Temple of Hera (Olympia), Temple of Hera at Olympia, Greece, Olympia, Greece on 19 December 1997. A Greek alpine skier started the relay towards Athens where a ceremony was held at the Panathenaic Stadium. On 22 December, the flame was transported to Japan by airplane. On 4 January, the 1998 Winter Olympics torch relay flame was divided into three parts in order for it to pass through every Japanese prefecture by three distinct routes: the Sea of Japan Route, the Pacific Route, and the Eastern Route. The start, on 6 January, was from Okinawa, Kagoshima, and Hokkaido. By 23 January, the relay had travelled through all 120 municipalities of
 The number in parentheses represents the number of athletes participating in official events.
The number in parentheses represents the number of athletes participating in official events.
 The 1998 Winter Olympics were held from Saturday, 7 February to Sunday, 22 February. This was 16 days and included three weekends. The number of events increased from 61 at the 1994 Winter Olympics to 68 in 1998. Two sports,
The 1998 Winter Olympics were held from Saturday, 7 February to Sunday, 22 February. This was 16 days and included three weekends. The number of events increased from 61 at the 1994 Winter Olympics to 68 in 1998. Two sports,

 The gold, silver, and bronze medals each measured 80 mm in diameter and 9.7 mm in thickness. The gold medals weighed 256 Gram, g, the silver 250 g, and the bronze 230 g. The medals were made using a traditional Japanese lacquerware technique known as , in which a brass core is imprinted with the design by layering gold powder onto the wet lacquer using a method called maki-e. On the front of the medals are borders of olive leaves, and in the center, a ''maki-e'' morning sun rises over a cloisonné emblem of the Nagano Olympics. On the reverse side, the snowflower emblem of the Games sits above a ''maki-e'' image of the mountains surrounding Nagano glowing in the morning sunrise. The initial lacquering was handcrafted by artisans from the region of Kiso, Nagano (town), Kiso, Nagano, and the medals were completed at the Japan Mint, Mint Bureau of the Ministry of Finance (Japan), Japanese Ministry of Finance.
In addition to the medals awarded to the athletes in each event, more than 19,000 commemorative medals were given to all athletes, officials, International Olympic Committee members, media personnel, volunteers and others. These medals, made by the Mint Bureau in cooperation with NAOC, were made from an alloy of 90% copper and 10% zinc. As the Olympic Charter also determines, diplomas, written in Japanese language, Japanese, French language, French, and English language, English, were given to the top eight finishers in each event, and every participant also received a commemorative diploma.
The gold, silver, and bronze medals each measured 80 mm in diameter and 9.7 mm in thickness. The gold medals weighed 256 Gram, g, the silver 250 g, and the bronze 230 g. The medals were made using a traditional Japanese lacquerware technique known as , in which a brass core is imprinted with the design by layering gold powder onto the wet lacquer using a method called maki-e. On the front of the medals are borders of olive leaves, and in the center, a ''maki-e'' morning sun rises over a cloisonné emblem of the Nagano Olympics. On the reverse side, the snowflower emblem of the Games sits above a ''maki-e'' image of the mountains surrounding Nagano glowing in the morning sunrise. The initial lacquering was handcrafted by artisans from the region of Kiso, Nagano (town), Kiso, Nagano, and the medals were completed at the Japan Mint, Mint Bureau of the Ministry of Finance (Japan), Japanese Ministry of Finance.
In addition to the medals awarded to the athletes in each event, more than 19,000 commemorative medals were given to all athletes, officials, International Olympic Committee members, media personnel, volunteers and others. These medals, made by the Mint Bureau in cooperation with NAOC, were made from an alloy of 90% copper and 10% zinc. As the Olympic Charter also determines, diplomas, written in Japanese language, Japanese, French language, French, and English language, English, were given to the top eight finishers in each event, and every participant also received a commemorative diploma.
 In all, 24 of the 72 participating nations at these Games won at least one medal, as shown in the table below. A total of 15 countries won at least one gold medal and 18 nations won two or more medals. In total, 205 medals were distributed.
In all, 24 of the 72 participating nations at these Games won at least one medal, as shown in the table below. A total of 15 countries won at least one gold medal and 18 nations won two or more medals. In total, 205 medals were distributed.
 The biathlon competitions took place at
The biathlon competitions took place at
 The luge competitions took place in Iizuna, Nagano, at the
The luge competitions took place in Iizuna, Nagano, at the
 From 8–20 February 171 athletes from 25 countries took part in the long-track speed skating events that were held in Nagano City at
From 8–20 February 171 athletes from 25 countries took part in the long-track speed skating events that were held in Nagano City at
 The cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing events took place at Nozawa Onsen Ski Resort, in the town of Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Nozawaonsen, approximately 50 kilometers north of Nagano. In all, 228 athletes, including 126 men and 102 women, from 37 countries took part.
The cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing events took place at Nozawa Onsen Ski Resort, in the town of Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Nozawaonsen, approximately 50 kilometers north of Nagano. In all, 228 athletes, including 126 men and 102 women, from 37 countries took part.
 The ski jumping competitions took place at the
The ski jumping competitions took place at the
 In the decade leading up the games, snowboarding had become popular in both North America and Europe, as well as Japan, and as a result, in August 1994, the Nagano Olympic Organizing Committee, NAOC received a request from the IOC president Samaranch to consider including snowboarding at the 1998 Winter Olympics. To reduce costs, NAOC asked the host community to cover a portion of the costs – the town Yamanouchi agreed – and International Ski Federation, FIS was expected to support financially as well. In November 1995, the NAOC executive board agreed to add snowboarding, and this was approved by the IOC at their December meeting the following month in Karuizawa. This was the first Winter Olympics with snowboarding events. The events took place at Mount Yakebitai and Kanbayashi Snowboard Park in Yamanouchi, Nagano, 30 kilometers northeast of Nagano City, from 8 to 12 February. In all, 125 athletes from 22 countries participated in the men's and women's Halfpipe and Giant slalom. Athletes from
In the decade leading up the games, snowboarding had become popular in both North America and Europe, as well as Japan, and as a result, in August 1994, the Nagano Olympic Organizing Committee, NAOC received a request from the IOC president Samaranch to consider including snowboarding at the 1998 Winter Olympics. To reduce costs, NAOC asked the host community to cover a portion of the costs – the town Yamanouchi agreed – and International Ski Federation, FIS was expected to support financially as well. In November 1995, the NAOC executive board agreed to add snowboarding, and this was approved by the IOC at their December meeting the following month in Karuizawa. This was the first Winter Olympics with snowboarding events. The events took place at Mount Yakebitai and Kanbayashi Snowboard Park in Yamanouchi, Nagano, 30 kilometers northeast of Nagano City, from 8 to 12 February. In all, 125 athletes from 22 countries participated in the men's and women's Halfpipe and Giant slalom. Athletes from
Volume 1
Volume 2Volume 3Appendix
retrieved on 17 January 2010.
1998 Winter Olympics Official website
{{Portal bar, 1990s, Olympics, Japan 1998 Winter Olympics, 1998 in Japanese sport, Winter Olympics Olympic Games in Japan Winter Olympics by year 1998 in multi-sport events Sports competitions in Nagano (city) February 1998 sports events in Asia Winter sports competitions in Japan
Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium
Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium is a ski jumping hill in Hakuba, Japan. It hosted the ski jumping and the ski jumping part of the Nordic combined events at the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonl ...
, ¥7 billion for Snow Harp
Snow Harp is a cross-country skiing venue located in Hakuba, Nagano, Japan. For the 1998 Winter Olympics, the venue hosted the cross-country skiing and the cross-country skiing portion of the Nordic combined
Nordic combined is a winter sport ...
– the cross-country skiing venue, and ¥3 billion for the biathlon venue at Nozawa Onsen Snow Resort
is a skiing venue located in Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Japan.
Nozawa Onsen Village is located at the foot of the ski resort, which spans across three main areas. The resort is a large ski area that opened over seventy years ago.
Covering , the sout ...
.
The organizing committee financed all costs, totaling ¥113.9 billion. It spent ¥99.4 billion for operational expenses, ¥21.6 billion for public relations, ¥20.7 billion for installations, ¥18.4 billion for telecommunications, ¥15.9 billion for running the competitions, and ¥14.4 billion for administration. Television rights were worth ¥35.4 billion, and marketing earned ¥31.3 billion. Ticket sales were worth ¥10.5 billion. The total cost of the Nagano Games is estimated to have been US$15.25 billion (in 2015), of which the largest factor in the cost of the games was the extension of the shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond l ...
to Nagano. This compares, for example, with US$2.5 billion for the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
, US$4.35 billion for the 2006 Winter Olympics
The 2006 Winter Olympics, officially the XX Olympic Winter Games ( it, XX Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Torino 2006, were a winter multi-sport event held from 10 to 26 February 2006 in Turin, Italy. This marked the second t ...
, US$7.56 billion for the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
, and US$51 billion for the 2014 Winter Olympics
, ''Zharkie. Zimnie. Tvoi'')
, nations = 88
, events = 98 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, athletes = 2,873
, opening = 7 February 2014
, closing = 23 February 2014
, opened_by = President Vladimir Putin
, cauldron =
, stadium = Fisht Olympic ...
Transportation


Nagano Nagano may refer to:
Places
* Nagano Prefecture, a prefecture in Japan
** Nagano (city), the capital city of the same prefecture
*** Nagano 1998, the 1998 Winter Olympics
*** Nagano Olympic Stadium, a baseball stadium in Nagano
*** Nagano Universi ...
is situated at the Japanese Alps area and receives large snowfalls every year. These combined to make transportation an important challenge for the organizing committee. In addition, the Olympic Village was a distance of 7 kilometers from the center of the city, and sporting events were spread over five surrounding cities. The complicating matters were that many of the venues had one single road in-out, which limited possibilities and led to traffic jams.
To improve access to Nagano, the government decided to link the prefecture with the high-speed ''shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond l ...
'' train network. Called Nagano Shinkansen, (now the Hokuriku Shinkansen
The is a high-speed Shinkansen railway line jointly operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and West Japan Railway Company (JR West), connecting Tokyo with in the Hokuriku region of Japan. The first section, between and in Nagano Pr ...
), was inaugurated five months before the start of the Games. This reduced by half the travel time between Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
and Nagano, to 79 minutes for 221 kilometers. The length of the track between Takasaki Station
is a junction railway station located in the city of Takasaki, Gunma, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and the private railway operator Jōshin Dentetsu. It is also a freight depot for the Japan Freight Railway Compa ...
and Nagano Station is 125.7 km, which includes 63.4 km of tunnels. The high speed train network carried 655,000 passengers during the Games.
Two highways, the Nagano Expressway
The is a 4-laned national Expressways of Japan, expressway in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company and Central Nippon Expressway Company.
Naming
The expressway is officially referred to as the Ch� ...
and the Jōshin-etsu Expressway
The is a national expressway in Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company.
Naming
is a kanji acronym consisting of 3 characters, each representing the former names of the prefectures that the route traverses. consist ...
, were also built in the Nagano region. In May 1993, the 75.8-kilometer section of the Nagano Expressway was completed, and in October 1997, the 111.4 kilometer section of the Jōshin-etsu Expressway was completed. In addition, another 114.9 kilometers of roads within Nagano Prefecture
is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the ...
were improved.
Transportation systems for the Games ran for 33 days, from the opening of the Athletes Village until 3 days after the Paralympics closing ceremony. Approximately 64% of the athletes arrived between 1 and 6 February, and 74% left Nagano between 22 and 25 February. Transportation operations were directed from a transportation centre situated at the same building of the organizing committee. Two regional transportation hubs were created in Hakuba
is a village located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the village had an estimated population of 9,007 in 4267 households, and a population density of 48 persons per km2. The total area of the village is . Hakuba is an internationally renowned s ...
and Yamanouchi, as well as a traffic center for vehicles in Karuizawa. The media, as well as representatives of different national Olympic committees generally were transported by car, from their arrival airport, that was the Narita International Airport
Narita International Airport ( ja, 成田国際空港, Narita Kokusai Kūkō) , also known as Tokyo-Narita, formerly and originally known as , is one of two international airports serving the Greater Tokyo Area, the other one being Haneda Airport ...
, but some delegations arrived by Kansai International Airport
Kansai International Airport ( ja, 関西国際空港, Kansai Kokusai Kūkō) commonly known as is the primary international airport in the Greater Osaka Area of Japan and the closest international airport to the cities of Osaka, Kyoto, and ...
and Chubu Centrair International Airport
is an international airport on an artificial island in Ise Bay, Tokoname City in Aichi Prefecture, south of Nagoya in central Japan.
Centrair is classified as a first class airport and is the main international gateway for the Chubu (" ...
in Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most pop ...
, to the three Olympic Villages. The members of the IOC traveled by Shinkansen.
To improve transportation for spectators, the number and hours of local trains were extended. During the heaviest traffic days, more cars were put in service and up to 68 parking areas, for 8,000 vehicles were at available for various Olympic delegations, and another 17 parking areas for 23,000 cars for spectators. Approximately 1,200 vehicles had navigation systems which transmitted their locations in real time.
As one of the principal aims of the Games was to respect nature, many vehicles were considered ecological or semi-ecological. In addition, there were more than 100 electric vehicles, hybrid mini-buses and other environmentally-friendly vehicles.
Marketing
 The
The emblem
An emblem is an abstract or representational pictorial image that represents a concept, like a moral truth, or an allegory, or a person, like a king or saint.
Emblems vs. symbols
Although the words ''emblem'' and '' symbol'' are often use ...
of the 1998 Winter Olympics consisted of a stylized snow flower with each petal representing an athlete participating in a winter sport. The figure could also represent a snowflake
A snowflake is a single ice crystal that has achieved a sufficient size, and may have amalgamated with others, which falls through the Earth's atmosphere as snow.Knight, C.; Knight, N. (1973). Snow crystals. Scientific American, vol. 228, no. ...
, or a mountain flower, which refers to the importance of the natural environment to the city of Nagano. Similarly, Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
used cherry blossoms
A cherry blossom, also known as Japanese cherry or sakura, is a flower of many trees of genus ''Prunus'' or ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus''. They are common species in East Asia, including China, Korea and especially in Japan. They generall ...
in its logo for its candidature for the 2020 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and also known as , was an international multi-sport event held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some preliminary events that began on 21 July.
Tokyo was selected as the host city during the ...
.
Landor Associates
Landor is a brand consulting firm founded in 1941 by Walter Landor, who pioneered some research, design, and consulting methods that the branding industry still uses.
Headquartered in San Francisco, the company maintains 26 offices in 20 count ...
conceived the official mascots that were used by the communication team for the Games. They consisted of four owlets, Sukki, Nokki, Lekki and Tsukki
Sukki, Nokki, Lekki and Tsukki, also known as the Snowlets, are the mascots of the 1998 Winter Olympics, 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano and are four snowy owls. They represent respectively fire (Sukki), air (Nokki), earth (Lekki) and water (Tsukk ...
, also called ''Snowlets''. The names were chosen from more than 47,000 suggestions. Four represents the number of years between each Olympic Games, and also represent the four elements
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simi ...
, fire, air, earth, and water.
The official poster for the Games was designed by the graphic designer
A graphic designer is a professional within the graphic design and graphic arts industry who assembles together images, typography, or motion graphics to create a piece of design. A graphic designer creates the graphics primarily for published, ...
Masuteru Aoba presented a thrush perched on ski poles with light in the background shining on snow-capped mountain peaks. Here, as with the emblem and the mascots, the importance of the natural environment in these Olympic Games and a desire to create harmony between athletes and the natural surroundings are shown. In addition to the official poster, a separate poster was created for the opening ceremony. Marketing for the games cost the organizing committee 5.9 billion yen.
These Olympic Games were sponsored by 11 worldwide partners, 8 gold partners, and 18 official supports and suppliers. Marketing revenues for sponsoring or for the rights to use the emblems and mascots of the Games totaled 31.3 billion yen.
Mascots
Sukki, Nokki, Lekki and Tsukki, also known as the Snowlets, are the 1998 Winter Olympic mascots and are four snowy owls. They represent respectively fire (Sukki), air (Nokki), earth (Lekki) and water (Tsukki) and together they represent the four major islands of Japan.Sponsors of the 1998 Winter Olympics
The development of Rights Packages were based on International Olympic Committee policy of offering exclusive rights to a limited number of companies, with one company allowed to purchase the rights for any single product or service category, and these were based on previous Games, with adaptations for the local market. Sponsors were permitted to use the emblem and mascots as long as consent was obtained from the International Olympic Committee,Japanese Olympic Committee
The is the National Olympic Committee in Japan for the Olympic Games movement, based in Tokyo, Japan. It is a non-profit organisation that selects teams and raises funds to send Japanese competitors to Olympic events organised by the Internati ...
, and the NAOC. Hospitality packages for sponsors included priority for accommodations, tickets, and transportation services. The Sponsor Hospitality Village, next to the Nagano Olympic Stadium
is a baseball stadium in Nagano, Nagano, Japan. It was used for the opening and closing ceremonies for the 1998 Winter Olympics. The stadium holds 35,000 people.
The stadium is the finishing point for the annual Nagano Olympic Commemorative Ma ...
, welcomed 32,000 guests.
To promote awareness of the sponsors, advertising was done in various media from 1995, and on banners and buses immediately before the games. Dick Pound
Richard William Duncan Pound (born March 22, 1942), better known as Dick Pound, is a Canadian swimming (sport), swimming champion, lawyer, and Spokesperson, spokesman for ethics in sport. He was the first president of the World Anti ...
noted, during the Games, the excellence of the marketing program, citing the "''perfect example of how the private and public sectors can work together''".
The Games had 11 Worldwide Olympic Partners, eight Gold Sponsors and 18 Official Supporters and Suppliers.
Worldwide Olympic Partners:
*The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational beverage corporation founded in 1892, best known as the producer of Coca-Cola. The Coca-Cola Company also manufactures, sells, and markets other non-alcoholic beverage concentrates and syrups, ...
* IBM
*John Hancock Financial
John Hancock Life Insurance Company, U.S.A. is a Boston-based insurance company. Established April 21, 1862, it was named in honor of John Hancock, a prominent American Patriot.
In 2004, John Hancock was acquired by the Canadian multinational li ...
*Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
*McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain, founded in 1940 as a restaurant operated by Richard and Maurice McDonald, in San Bernardino, California, United States. They rechri ...
*Panasonic
formerly between 1935 and 2008 and the first incarnation of between 2008 and 2022, is a major Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka, Kadoma, Osaka P ...
*Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of ...
*Time Inc.
Time Inc. was an American worldwide mass media corporation founded on November 28, 1922, by Henry Luce and Briton Hadden and based in New York City. It owned and published over 100 magazine brands, including its namesake ''Time'', ''Sports Illu ...
*United Parcel Service
United Parcel Service (UPS, stylized as ups) is an American multinational corporation, multinational package delivery, shipping & receiving and supply chain management company founded in 1907. Originally known as the American Messenger Company ...
*Visa Inc.
Visa Inc. (; stylized as ''VISA'') is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered in San Francisco, California. It facilitates electronic funds transfers throughout the world, most commonly through Visa-branded cred ...
*Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (; also known simply as Xerox) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut (ha ...
(Fuji Xerox
was a joint venture partnership between the Japanese photographic firm Fujifilm Holdings and the American document management company Xerox to develop, produce and sell xerographic and document-related products and services in the Asia-Pacifi ...
)
Gold Sponsors:
*Amway
Amway (short for "American Way") is an American multi-level marketing (MLM) company that sells health, beauty, and home care products. The company was founded in 1959 by Jay Van Andel and Richard DeVos and is based in Ada, Michigan. Amway and it ...
* Hachijuni Bank
*KDDI
() is a Japanese telecommunications operator formed on October 1, 2000 through the merger of DDI Corp. (Daini-Denden Inc.), KDD (Kokusai Denshin Denwa) Corp. (itself a former listed state-owned enterprise privatized in 1998), and IDO Corp. It h ...
*Kirin Company
is a Japanese integrated beverages company. It is a subsidiary of Kirin Holdings Company, Limited.
Its major operating units include Kirin Brewery Company, Limited, Mercian Corporation and Kirin Beverages Company, Limited. Kirin is a member o ...
*Mizuno Corporation
() is a Japanese sports equipment and sportswear company, founded in Osaka in 1906 by Rihachi Mizuno. Today, Mizuno is a global corporation which makes a wide variety of sports equipment and sportswear for badminton, baseball, boxing, cyclin ...
*Nippon Telegraph and Telephone
, commonly known as NTT, is a Japanese telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Ranked 55th in Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500, NTT is the fourth largest telecommunications company in the world in terms of revenue, as w ...
*Seiko
, commonly known as Seiko ( , ), is a Japanese maker of watches, clocks, electronic devices, semiconductors, jewelry, and optical products. Founded in 1881 by Kintarō Hattori in Tokyo, Seiko introduced one of the first quartz watches and the ...
*Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
Official Supporters and Suppliers:
*Bridgestone
is a Japanese multinational tire manufacturer founded in 1931 by Shojiro Ishibashi (1889–1976) in the city of Kurume, Fukuoka, Japan. The name Bridgestone comes from a calque translation and transposition of , meaning 'stone bridge' in Japan ...
*Brother Industries
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational electronics and electrical equipment company headquartered in Nagoya, Japan. Its products include Printer (computing), printers, multifunction printers, desktop computers, sewing machin ...
* Corona Corp.
* Hanamaruki Foods
*Hitachi Zosen Corporation
is a major Japanese industrial and engineering corporation. It produces waste treatment plants, industrial plants, precision machinery, industrial machinery, steel mill process equipment, steel structures, construction machinery, tunnel boring ma ...
*Idemitsu Kosan
is a Japanese petroleum company. It owns and operates oil platforms, refineries, produces and sells petroleum, oils and petrochemical products, and also operates gas stations under the brand and (until 2023) in its own ''Idemitsu'' and ''Sh ...
*Japan Agricultural Cooperatives
, also known as or JA Group, refers to the national group of 694 regional co-ops in Japan that supply members with input for production, undertake packaging, transportation, and marketing of agricultural products, and provide financial services. A ...
*Japan Airlines
, also known as JAL (''Jaru'') or , is an international airline and Japan's flag carrier and largest airline as of 2021 and 2022, headquartered in Shinagawa, Tokyo. Its main hubs are Tokyo's Narita International Airport and Haneda Airport, as w ...
* KOKUYO
* MAYEKAWA
* Marudai Foods
*Oji Paper Company
is a Japanese manufacturer of paper products. In 2012 the company was the third largest company in the global forest, paper and packaging industry.
The company's stock is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the stock is constituent of the Ni ...
* Pia Corporation
* Sankosya Corporation
*Snow Brand Milk Products
, formerly is one of the largest dairy companies in Japan.
In 2000, more than 14,000 people got sick from old milk sold by Snow Brand contaminated with the staphylococcus aureus bacteria, the worst case of food poisoning in Japan.
A criminal ...
*Tokio Marine
, is a multinational insurance holding company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is the largest property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. ...
*Tokyo Gas
, founded in 1885, is the primary provider of natural gas to the main cities of Tokyo, Kanagawa, Saitama, Chiba, Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Yamanashi, and Nagano. , Tokyo Gas is the largest natural gas utility in Japan.
Timeline
*October 1, ...
*Yamazaki Baking
is a Japanese food company and the world's largest bread-baking corporation, that makes bread, bakery products and confectionery. It was established by Tojuro Iijima in Japan on 9 March 1948 and started mass production of bread in 1955, and is s ...
Ticket sales
From 7 February 1997, the organizing committee put up for sale 1,286,000 tickets for the various competitions and ceremonies. The number of tickets sold was 1,149,615, which represented 89.4% of available tickets. Including people connected to the Games, the total number of spectators was 1,275,529. This number was slightly higher than in 1994 but slightly lower than the1988 Winter Olympics
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games (french: XVes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Calgary 1988 ( bla, Mohkínsstsisi 1988; sto, Wîchîspa Oyade 1988 or ; cr, Otôskwanihk 1998/; srs, Guts� ...
in Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
. Tickets sales were a success in Japan with a reservation list of 6 million. For the most popular sports, a lottery was used. In total, ticket sales raised 10.5 billion yen for the organizing committee.
The ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
matches represented 295,802 tickets sold, 26% of the total. Tickets sold for alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether for ...
totaled 166,092; for ski jumping
Ski jumping is a winter sport in which competitors aim to achieve the farthest jump after sliding down on their skis from a specially designed curved ramp. Along with jump length, competitor's aerial style and other factors also affect the final ...
, 96,000, and speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors racing, race each other in travelling a certain distance on Ice skate, skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marath ...
, 93,000. For multiple sports, ski jumping, Nordic combined jumps, freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, Mogul Skiing, moguls, Ski Cross, cross, Half-pipe skiing, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Freestyle skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics. It can consist of a ...
, all three skating disciplines, bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Feder ...
, and curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
, as well as the ceremonies, all tickets were sold. By contrast, only 56.6% of the 146,000 available tickets for cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreation ...
were sold.
Cost and cost overrun
''The Oxford Olympics Study'' established the outturn cost of the Nagano 1998 Winter Olympics at US$2.2 billion in 2015-dollars and cost overrun at 56% in real terms. This includes sports-related costs only, that is, (i) ''operational costs'' incurred by the organizing committee for the purpose of staging the Games, e.g., expenditures for technology, transportation, workforce, administration, security, catering, ceremonies, and medical services, and (ii) ''direct capital costs'' incurred by the host city and country or private investors to build, e.g., the competition venues, the Olympic village, international broadcast center, and media and press center, which are required to host the Games. Indirect capital costs are ''not'' included, such as for road, rail, or airport infrastructure, or for hotel upgrades or other business investment incurred in preparation for the Games but not directly related to staging the Games. The cost and cost overrun for Nagano 1998 compares with costs of US$2.5 billion and a cost overrun of 13% for Vancouver 2010, and costs of US$51 billion and a cost overrun of 289% for Sochi 2014, the latter being the most costly Olympics to date. Average cost for Winter Games since 1960 is US$3.1 billion, average cost overrun is 142%.Venues


Sport sites
For the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan, a total of fourteen sports venues, all withinNagano Prefecture
is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the ...
, were used. Construction of these venues, and of the Olympic Stadium which hosted the ceremonies, began in 1990 and lasted until 1997, with construction and land costs totaling 106.6 billion yen. The most expensive venue constructed for the games was the long-track speed skating venue, M-Wave
, or , is a covered speed skating oval in the city of Nagano, Japan. M-Wave, which opened in November, 1996, was constructed for the speed skating events at the 1998 Winter Olympics. It was Japan's first International Skating Union (ISU) stand ...
built 5 kilometers from Nagano Station. Between March 1996 and November 1997, these sites were tested with 16 different world champion events, world cups, and other international competitions to allow the organizers to prepare for the running of the Games.
Five sites, all constructed for the Games, are located in the city of Nagano. Nagano Olympic Stadium, Minami Nagano Sports Park, built to serve as a baseball park, was constructed in the south section of the city, near Shinonoi Station, and approximately 9 kilometers from Nagano Station. The stadium, which held the opening and closing ceremonies, resembles a cherry blossom, a symbol of Japan. The stadium can accommodate 50,000 with temporary stands added, but usually accommodates 35,000 spectators. Big Hat, named for its shape, was the principal site of ice hockey at the 1998 Winter Olympics, ice hockey. Big Hat, located approximately 2 kilometers from Nagano Station, has a capacity of 10,104 spectators. Aqua Wing Arena was the second ice hockey arena at the Games. Shaped like a wing, it had a capacity of 6000 during the Olympics. After the Games, it was modified into an interior swimming pool. Aqua Wing is approximately 5 kilometers from Nagano Station. Its closest stations are Kita-Nagano Station and Asahi Station (Nagano), Asahi Station. M-Wave, used for speed skating at the 1998 Winter Olympics, speed skating, is the first indoor, long-track speed skating venue in Japan. It was built to accommodate 10,000 spectators. The venue, which gets its name from its M-shape, representing the surrounding mountains, is approximately 5 kilometers from Nagano Station. Finally, White Ring (arena), White Ring, with a maximum capacity of 7,351 spectators, was built for figure skating at the 1998 Winter Olympics, figure skating and short track speed skating at the 1998 Winter Olympics, short track speed skating. White Ring, which is used as a public gymnasium, is approximately 6 kilometers from Nagano Station.
Hakuba, Nagano, Hakuba village is situated 50 kilometers west of the city of Nagano. Hakuba hosted three Olympics sites. Alpine skiing at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Alpine skiing's Downhill, Super G and Combined were situated at Happo'one Resort. Three courses between altitudes of 840 meters and 1,765 meters were used, one for the men's, women's and Combined for both men's and women's. The site has a capacity of 20,000 spectators. Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium
Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium is a ski jumping hill in Hakuba, Japan. It hosted the ski jumping and the ski jumping part of the Nordic combined events at the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonl ...
was the first ski jump built in Japan with parallel 90 and 120 K-point hills. The ski jumping stadium can accommodate 45,000 spectators. Snow Harp
Snow Harp is a cross-country skiing venue located in Hakuba, Nagano, Japan. For the 1998 Winter Olympics, the venue hosted the cross-country skiing and the cross-country skiing portion of the Nordic combined
Nordic combined is a winter sport ...
Kamishiro was built for cross-country skiing at the 1998 Winter Olympics, cross country skiing and Nordic combined. It includes three tracks of 4.8, 4.8, and 7.8 kilometers, 6 meters wide. The stadium is another 1.2 kilometers. In total, Snow Harp has 19 kilometers of tracks. Up to 20,000 spectators can be accommodated.
Nozawa Onsen Ski Resort, in the town of Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Nozawaonsen, was site of biathlon at the 1998 Winter Olympics, biathlon. Nozawa is approximately 50 kilometers north of Nagano. At Nozawa Onsen, the stadium was built around six existing tracks. Two tracks, of 4 kilometers and 7 kilometers, were used for the Games. The stadium can accommodate 20,000 spectators.
Two sites in the town of Yamanouchi, approximately 30 kilometers northeast of Nagano, were used. Giant Slalom was held at Mount Yakebitai at Shiga Highlands, Shiga Kogen Resort, at an altitude between 1,530 and 1,969 meters. The site can accommodate 20,000 spectators. Also in Shiga Kogen, at Mount Higashidate, giant slalom events in Alpine skiing and snowboarding were held. Kanbayashi Snowboard Park was the site of the snowboarding at the 1998 Winter Olympics, half pipe events. The track is 120 meters long and 15 meters wide, with walls of 3.5 meters. 10,000 spectators can be accommodated at Kanbayashi.
The town of Iizuna, Nagano, Iizuna, approximately 12 kilometers northwest of Nagano, was the site of freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, Mogul Skiing, moguls, Ski Cross, cross, Half-pipe skiing, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Freestyle skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics. It can consist of a ...
and Spiral (bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton), bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton at Iizuna Kogen Ski Area. 8,000 spectators can watch the free style skiing on a course that 250 meters long and 12,000 can watch the jumps. The Spiral, which held the sledding events, was the first artificially refrigerated track in Asia. It is 1700 meters long, with a difference in height of 114 meters and 15 turns. At the Spiral, approximately 40,000 saplings, mainly beech and oak, were planted two per square meter, as part of the environmental stewardship committed during the Winter Games. The site can accommodate 10,000 spectators.
Finally, the town of Karuizawa, approximately 80 southwest of Nagano, hosted the curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
events at Kazakoshi Park Arena. The venue was built as a multi-purpose venue. Its ice surface is 60 meters by 30. Its maximum capacity is 1,924 spectators. The town of Karuizawa also hosted the Equestrian at the 1964 Summer Olympics, equestrian events at the 1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this ho ...
, thus becoming the first place in the world to host both the Summer Olympics and Winter Olympics.
Accommodation
 To accommodate the athletes and officials during the Games, the Olympic Village was constructed in Imai district, approximately 7 kilometers south of Nagano Station. Along with the construction of the village, Imai Station was opened in 1997. The village was constructed by the city of Nagano as public residential housing, and loaned to the organizing committee during the Games. The Village occupies an area that is 19 hectares, composed of 23 buildings with a total of 1,032 apartments. Temporary restaurants and shops were also available during the Games. The Village was open from 24 January to 25 February 1998, and accommodated 3,200 people. Several prominent people were recognized as faces of the Olympic Village, including the ''Honorary Mayor'' Yasuko Konoe, ''Mayor'' Shozo Sasahara, and ''Deputy Mayors'' Takanori Kono, Hiroko Chiba, and Shun'ichi Bobby Hirai.
Because the curling arena was in Karuizawa, 90 kilometers away, a satellite village was built in Karuizawa, 7 kilometers from the arena. It was open from 4 to 16 February 1998. In addition, a section of the Shiga Kogen Prince Hotels, Prince Hotel, 58 kilometers from the Olympic Village, was reserved for 180 snowboarders and officials.
In addition to athletes and officials, members of the Olympic family and other personnel were housed in 900 hotels in Nagano and surrounding region, which represented 234,207 nights between 24 January to 25 February 1998. The members of the International Olympic Committee stayed athletes the Kokusai 21 Hotel in downtown Nagano. In total, the Olympic family included 18,350 people. Finally, two media villages were built in the districts of Yanagimachi, near Nagano Station, and Asahi, across the street from the M-Wave.
To accommodate the athletes and officials during the Games, the Olympic Village was constructed in Imai district, approximately 7 kilometers south of Nagano Station. Along with the construction of the village, Imai Station was opened in 1997. The village was constructed by the city of Nagano as public residential housing, and loaned to the organizing committee during the Games. The Village occupies an area that is 19 hectares, composed of 23 buildings with a total of 1,032 apartments. Temporary restaurants and shops were also available during the Games. The Village was open from 24 January to 25 February 1998, and accommodated 3,200 people. Several prominent people were recognized as faces of the Olympic Village, including the ''Honorary Mayor'' Yasuko Konoe, ''Mayor'' Shozo Sasahara, and ''Deputy Mayors'' Takanori Kono, Hiroko Chiba, and Shun'ichi Bobby Hirai.
Because the curling arena was in Karuizawa, 90 kilometers away, a satellite village was built in Karuizawa, 7 kilometers from the arena. It was open from 4 to 16 February 1998. In addition, a section of the Shiga Kogen Prince Hotels, Prince Hotel, 58 kilometers from the Olympic Village, was reserved for 180 snowboarders and officials.
In addition to athletes and officials, members of the Olympic family and other personnel were housed in 900 hotels in Nagano and surrounding region, which represented 234,207 nights between 24 January to 25 February 1998. The members of the International Olympic Committee stayed athletes the Kokusai 21 Hotel in downtown Nagano. In total, the Olympic family included 18,350 people. Finally, two media villages were built in the districts of Yanagimachi, near Nagano Station, and Asahi, across the street from the M-Wave.
The Games
The Olympic torch relay
Nagano Prefecture
is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the ...
, and finally arrived in Nagano City on 5 February. The following day, after traveling through each district of the city, the relay arrived at the central square where three former athletes passed the flames to three members of the organizing committee. These three committee members then lit a torch held by Juan Antonio Samaranch
Juan Antonio Samaranch y Torelló, 1st Marquess of Samaranch (Catalan: ''Joan Antoni Samaranch i Torelló'', ; 17 July 1920 – 21 April 2010) was a Spanish sports administrator under the Franco regime (1973–1977) who served as the seventh Pre ...
. On 7 February, the flame travelled another 10 kilometers, and the figure skater Midori Ito lit the cauldron at Nagano Olympic Stadium
is a baseball stadium in Nagano, Nagano, Japan. It was used for the opening and closing ceremonies for the 1998 Winter Olympics. The stadium holds 35,000 people.
The stadium is the finishing point for the annual Nagano Olympic Commemorative Ma ...
during the opening ceremonies.
The Olympic Flame Relay in Japan was sponsored by Coca-Cola, lasted 33 days and travelled 1,162 kilometers. A group of 5.5 million people took part in relay activities. Over the distance of the relay, which was run or skied, the flame was always followed by a group of six people: the runner who carried the flame, some who accompanied the carrier, and four people in supporting roles, for a total of 6,901 people. In addition, each relay was followed by two groups of 11 vehicles and more than 20 people.
The shape of the torch represented a traditional Japanese torch called ''taimatsu''. It was built with aluminum, was 55 centimeters long, and weighed 1.3 kilograms. The exterior of the torch was painted silver, to represent winter. Runners were blue and white uniforms symbolizing the color of the games and of snow. The runners' uniforms included logos for the Nagano Olympics and the Olympic Games, a logo of the relay, and of Coca-Cola.
Participating National Olympic Committees
72 nations participated in the 1998 Winter Olympic Games for a total of 2,176 athletes, of which 787 were female and 1,389 were male. With the addition of five countries and another 439 athletes since the 1994 Winter Olympic Games at Lillehammer, Norway, these were the largest Winter Olympics ever at the time. The nations ofAzerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, Macedonia, Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
participated in their first Winter Olympic Games. Iran returned to the Winter games after a 22-year absence, and North Korea at the 1998 Winter Olympics, North Korea, India at the 1998 Winter Olympics, India, Ireland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Ireland, and Yugoslavia at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Yugoslavia returned after 6 years. Five countries, Fiji, Mexico, San Marino, American Samoa, and Senegal, which were at the 1994 Games, did not participate in 1998.
The United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, United States had the largest athlete delegation with 186, followed by host Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
with 156, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
with 144, and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
with 125. Despite the large number of participating delegations, 40 of the 72 delegations had less than 10 athletes, with 12 nations having one sole athlete. 15 nations had between 11 and 50 athletes, 11 nations had between 51 and 100 athletes, and six nations had more than 101 athletes. Nations that participated in the ice hockey tournaments generally had the largest athlete delegations. With the exception of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Switzerland, all 12 national delegations with 60 or more athletes participated in either or both of the female or male ice hockey tournaments.
 The number in parentheses represents the number of athletes participating in official events.
The number in parentheses represents the number of athletes participating in official events.
Calendar
 The 1998 Winter Olympics were held from Saturday, 7 February to Sunday, 22 February. This was 16 days and included three weekends. The number of events increased from 61 at the 1994 Winter Olympics to 68 in 1998. Two sports,
The 1998 Winter Olympics were held from Saturday, 7 February to Sunday, 22 February. This was 16 days and included three weekends. The number of events increased from 61 at the 1994 Winter Olympics to 68 in 1998. Two sports, curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
and snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympi ...
were added to the program, as was women's ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hoc ...
. This increased the number of sports to seven, and the number of disciplines to 14. The sporting program started and ended with ice hockey. The first matches started at 4:00 pm on 7 February featuring Kazakhstan men's national ice hockey team, Kazakhstan defeating Italy men's national ice hockey team, Italy 5–3, and Slovakia men's national ice hockey team, Slovakia tying Austria men's national ice hockey team, Austria 2–2. The final match was played on Sunday 22 February from 1:45 pm, and the Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech Republic defeated Russia men's national ice hockey team, Russia 1–0.
Due to averse weather conditions, multiple events were delayed, including six alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether for ...
races, snowboarding, and Biathlon at the 1998 Winter Olympics, biathlon. Of these, the men's downhills was delayed five days.
:''All dates are in Japan Standard Time (UTC+9)''
Ceremonies

Opening ceremony
The opening ceremony took place atNagano Olympic Stadium
is a baseball stadium in Nagano, Nagano, Japan. It was used for the opening and closing ceremonies for the 1998 Winter Olympics. The stadium holds 35,000 people.
The stadium is the finishing point for the annual Nagano Olympic Commemorative Ma ...
, Nagano, Japan, on 7 February 1998. Japanese figure skater, Midori Ito, the first female skater to land seven triple jumps in a free skating competition, and the silver medalist at the 1992 Winter Olympics, lit the cauldron during the ceremony.
Seiji Ozawa, a Japanese Conducting, conductor, directed an orchestra from five continents, performing the fourth movement of Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), Beethoven's Symphony No. 9 (Ode to Joy).
In all, 2,302 athletes from 72 countries and regions participated in the Games, including 814 female athletes and 1488 male athletes. Both the number of participating delegations and the number of athletes participating in the competition were, at the time, the most ever hosted at the Winter Olympics.
Medal ceremonies
The medal ceremonies for indoor events (skating, ice hockey, and curling) were held at the venues immediately after the finals, with the exception of the bronze medal presentations for the ice hockey at the 1998 Winter Olympics, ice hockey events, which took place directly after the bronze medal matches. The Olympic Charter determines the outdoor events (skiing, biathlon, bobsleigh and luge), there was a simple ceremony in which bouquets of flowers were presented, and the medal ceremonies are held on Medals Plaza that was localizated at the Nagano City Central Square, approximately midway between Nagano Station and Zenkō-ji. A short fanfare of music was played, the athletes has positioned, and the medals, in the order of gold, silver, and bronze, were awarded. Finally, the national flags of the athletes were raised, and the national anthem of the winning athlete(s) was played. In all, 167,200 people attended the medal ceremonies, which were held at 7:00 p.m. each night. National and international artists presented every evening at the place before the medal presentations.Closing ceremony
The closing ceremonies, like those of the opening, took place in theNagano Olympic Stadium
is a baseball stadium in Nagano, Nagano, Japan. It was used for the opening and closing ceremonies for the 1998 Winter Olympics. The stadium holds 35,000 people.
The stadium is the finishing point for the annual Nagano Olympic Commemorative Ma ...
, with 60,000 spectators, including Akihito, the Emperor of Japan at the time, and his wife Empress Michiko. After the athletes entered, hundreds of drums were beat and a traditional hose and lion dance was presented. At the Antwerp Ceremony, Tasuku Tsukada
(born March 3, 1936) is a Japanese politician, and the former mayor of the city of Nagano, the capital of Nagano Prefecture, in central Japan. Tsukada won his first mayoral contest in 1985. He served four full 4-year terms, until November 10, ...
, then mayor of Nagano Nagano may refer to:
Places
* Nagano Prefecture, a prefecture in Japan
** Nagano (city), the capital city of the same prefecture
*** Nagano 1998, the 1998 Winter Olympics
*** Nagano Olympic Stadium, a baseball stadium in Nagano
*** Nagano Universi ...
presented the Olympic Flag
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags and symbols to elevate the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competition—such as the flame, fanfare and theme—as well as those used throughout ...
to Deedee Corradini, then mayor of Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
, the host of the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
, after this moment Juan Antonio Samaranch
Juan Antonio Samaranch y Torelló, 1st Marquess of Samaranch (Catalan: ''Joan Antoni Samaranch i Torelló'', ; 17 July 1920 – 21 April 2010) was a Spanish sports administrator under the Franco regime (1973–1977) who served as the seventh Pre ...
declared the games closed. This was followed by a performance from the Japanese singer Anri and the Olympic Cauldron was extinguished. The ceremony ended with the words "" ("Goodbye, Thank you") and a major fireworks performance accompanied by the song: "Ile Aiye" or "Let's Make a Circle and Dance" performed by Japanese pop group Agharta.
Medal table
 In all, 24 of the 72 participating nations at these Games won at least one medal, as shown in the table below. A total of 15 countries won at least one gold medal and 18 nations won two or more medals. In total, 205 medals were distributed.
In all, 24 of the 72 participating nations at these Games won at least one medal, as shown in the table below. A total of 15 countries won at least one gold medal and 18 nations won two or more medals. In total, 205 medals were distributed. Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
finished on top of the table with 29 medals, including 12 gold, nine silver, and eight bronze. Germany, which finished in third place in the medal standings at the 1994 Winter Olympics, won most of its medals in Alpine skiing, speed skating, and luge, in which it won all three gold medals. German female athletes won 22 of the country's 29 medals. Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
finished in second, as in 1994, with 25 medals, including nine won in cross-country skiing and five in biathlon. Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, which finished atop the medals standing in 1994, finished in third in 1998, with 9 gold medals, including the five gold at the stake on the women's cross-country skiing. Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
moved from a discret seventh in 1994 to fourth in 1998 with 6 gold medals, and the United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, United States remained in fifth place. Netherlands at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Netherlands finished in 6th place, 12 places higher than in 1994 and their domination at the speed skating started with 5 gold medals. Host Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
beat its previous record of medals at a Winter Games, with 10 medals, including respectable 5 gold medals. Australia at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Australia became the second country from the Southern Hemisphere to win a medal, a bronze in alpine skiing. Also, Denmark at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Denmark each won your first ever medal, the silver at women's curling. In addition, Bulgaria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Bulgaria and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
each won their first gold medals at a Winter Olympics in women's biathlon and men's ice hockey respectively. Finally, Kazakhstan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Kazakhstan won its first medal from a female athlete.
Podium sweeps
Sports
The 1998 Winter Olympics featured 68 medal events over 14 disciplines in seven sports. This was an increase from 61 events in 12 disciplines across six sports from the 1994 Winter Olympics. Curling at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Curling was the additional sport,snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympi ...
was an additional discipling in skiing, and women's ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hoc ...
was added to the ice hockey program.
Biathlon
 The biathlon competitions took place at
The biathlon competitions took place at Nozawa Onsen Snow Resort
is a skiing venue located in Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Japan.
Nozawa Onsen Village is located at the foot of the ski resort, which spans across three main areas. The resort is a large ski area that opened over seventy years ago.
Covering , the sout ...
, north of Nagano City. The six events were the sprint, individual, and relay, for both men and women. In all, 183 athletes took part, including 96 men and 87 women from 32 countries. Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
each won five medals, with Uschi Disl from the latter country winning one gold, one silver, and one bronze.
The first event was the women's 15 km individual race that took place in falling snow on 9 February. The surprise gold medalist was Ekaterina Dafovska from Bulgaria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Bulgaria, who had been ranked 51st at the previous Biathlon World Cup. Her gold medal was the first-ever Bulgarian gold medal at a Winter Olympics. Her time was 54:52.0, with only one target missed. Olena Petrova from Ukraine at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Ukraine won the silver, 17.8 seconds behind, and Uschi Disl won the bronze, 25.9 seconds behind Dafovska.
The first men's event, the 20 km individual race, took place on 11 February. The Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian Halvard Hanevold missed his second-last target, but finished first in a time of 56:16.4. The Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italian Pieralberto Carrara, who missed no targets, target, won the silver, 5.05 seconds behind. The Belarus at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Belarusian Alexei Aidarov was 30.1 seconds behind the Norwegian, and won the bronze.
Bobsleigh
The bobsleigh competitions took place at Spiral (bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton), the Spiral, in Iizuna, Nagano, Iizuna, just north of Nagano City. The Spiral course measured 1700 m in length, with fifteen curves, descended 113 m from start to finish, and included two short uphill sections. The two events were the two-man and four-man, for men only. Female competitors would begin competing in the Bobsleigh at the 2002 Winter Olympics – Two-woman, two woman events at the subsequent Winter Olympics, the2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
in Salt Lake City.
In all, 156 athletes took part from 28 countries. The bobsleigh events resulted in two ties, for the two-man gold and for the four-man bronze. This was the first time in Olympic bobsleigh history that there were ties for the medal positions. Christoph Langen and Markus Zimmermann won bronze in the two-man competition and were part of the winning four-man team. In all, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
win one gold and one bronze; Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italy and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
also won one gold each when the two-man team. Six team in all won medals. The first time since the 1968 Winter Olympics
The 1968 Winter Olympics, officially known as the X Olympic Winter Games (french: Les Xes Jeux olympiques d'hiver), were a winter multi-sport event held from 6 to 18 February 1968 in Grenoble, France. Thirty-seven countries participated. Frenchm ...
did more than four countries win bobsleigh medals. In addition, Germany and Switzerland were the only two countries to place two sleds in the top ten of either event.
The 1996 and 1997 IBSF World Championships (bobsleigh and skeleton), Bobsleigh World Champions were teams from Germany and Italy respectively. However, Günther Huber and Antonio Tartaglia from Italy tied with the two-man team from Canada, Pierre Lueders: and Dave MacEachern for the gold medal, each with combined times of 3:37.24. No silver medal was awarded. The German team of Christoph Langen and Markus Zimmermann were 0.65 seconds behind, and were awarded the bronze.
In the four-man event, bad weather restricted the competition to three runs only. The German team of Christoph Langen, Markus Zimmermann, Marco Jakobs and Olaf Hampel completed the three runs in 2:39.41 for the gold medal. The Swiss team of Marcel Rohner (bobsleigh), Marcel Rohner, Markus Nüssli, Markus Wasser, and Beat Seitz finished second with a time of 2:40.01. Two teams, were awarded bronze medals after completing the three runs in 2:40.06. These were the team from Great Britain, made up of Sean Olsson, Dean Ward, Courtney Rumbolt, and Paul Attwood; and the team from France, composed of Bruno Mingeon, Emmanuel Hostache, Éric Le Chanony, and Max Robert.
Curling
Curling was included in the program for the Nagano Olympics in 1993 following discussions that had begun in 1992. At the time, it was considered that curling was making its official Olympic debut following its appearance as a demonstration sport at the 1932 Winter Olympics, 1932, 1988 Winter Olympics, 1988, and 1992 Winter Olympics, 1992. At the Games in Nagano, both the men's and the women's curling tournament took place at Kazakoshi Park Arena in Karuizawa, Nagano, 30 minutes by shinkansen, bullet train (''shinkansen'') south of Nagano City. Eight teams played a total of seven games in the round robin in both tournaments, with the four best teams going to the semifinals.Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
won gold in the women's competition and silver in the men's; Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Switzerland won the gold in the men's tournament.
In the men's tournament, the Mike Harris (curler), Mike Harris team from Canada easily completed the round-robin tournament winning six of its seven games, only losing to the Eigil Ramsfjell team from Norway. In the semi-finals, the Canadian team defeated Tim Somerville, Tim Somerville's team from the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
by a score of 7–1; and in the other semi-final, the team from Switzerland led by Patrick Hürlimann defeated Norway 8–7. In the gold medal game, Switzerland shocked Canada by winning 9–3. In the bronze medal game, Eigil Ramsfjell's team from Norway defeated Tim Somerville's USA team by a score of 9–4.
In the women's tournament, the Sandra Schmirler team from Canada and the Elisabet Gustafson team from Sweden easily completed the round-robin tournament, with both teams winning six of their seven games. Canada only lost to the Dordi Nordby team from Norway, and Sweden's only loss was to Canada. In the semi-finals, the Canadian team defeated the team led by Kirsty Hay representing Team GB, team Great Britain by a score of 6–5; and in the other semi-final, the team from Denmark led by Helena Blach Lavrsen defeated Sweden 7–5. In the gold medal game, Canada defeated Denmark by a score of 7–5. In the bronze medal game, Elisabet Gustafso's team from Sweden defeated Kirsty Hay's GB team by a score of 10–6.
Ice hockey
The ice hockey matches took place at two purpose-built arenas in Nagano City, Big Hat and Aqua Wing Arena. The ice hockey events were significant for two reasons: the first Olympic ice hockey tournament for women and the participation of players from the NHL. The Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech Republic defeated Russia men's national ice hockey team, Russia in the gold medal game for the men's final, and United States women's national ice hockey team, Americans defeated Canada women's national ice hockey team, Canadians in the gold medal game for the women's final. The men's competition began on 7 February with eight teams playing in two groups of four, Group A and B, with each team playing three games. The winners of these two groups, Kazakhstan men's national ice hockey team, Kazakhstan and Belarus men's national ice hockey team, Belarus, advanced to join Groups C and D, composed of the six highest ranked men's national ice hockey teams in the world. Russia men's national ice hockey team, Russia, Czech Republic men's national ice hockey team, Czech Republic, and Finland men's national ice hockey team, Finland were joined by Kazakhstan in Group C; Canada men's national ice hockey team, Canada, Sweden men's national ice hockey team, Sweden, and United States men's national ice hockey team, USA were joined by Belarus in Group D. On 22 February, with 10,010 spectators in attendance at Big Hat, the Czech Republic defeated Russia in the gold medal game for the men's final, 1–0, with the lone goal of the match scored with 12 minutes remaining. Finland defeated Canada for the bronze medal by a score of 3–2. The first IIHF Women's World Championship, women's ice hockey world championship, a biennial tournament, took place in 1990 IIHF Women's World Championship, 1990. Discussions to include women's ice hockey at the 1998 games began in 1992, and it was decided to include them in the program in 1993. The tournament included six teams playing in a one-group round-robin tournament. The top two team advanced to the gold medal game, and the teams ranked third and fourth played in the bronze medal match. The favorites were the Canada women's national ice hockey team, Canadians, who had won the three previous world championships, with the United States women's national ice hockey team, Americans finishing second each time. In the round-robin tournament, the Americans finished first, with the Canadians second. In the last round-robin game, the Americans handily defeated the Canadians, 7–4, with the two teams scoring nine goals in the third period. In the gold medal match, with 8,626 fans in attendance at Big Hat, the Americans defeated the Canadians 3–1. Team Finland women's national ice hockey team, Finland defeated Team China women's national ice hockey team, China 4–1 for the bronze medal.Luge
 The luge competitions took place in Iizuna, Nagano, at the
The luge competitions took place in Iizuna, Nagano, at the Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
making their Olympic debut in luge events. There were three events, men's single, women's single, and doubles. Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
won all three gold medals, one silver, and one bronze. The United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, United States won one silver and one bronze. Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italy and Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austria rounded out the medal table.
The first event with 24 lugers was the men's singles. Each athlete completed four runs over two days, 8 and 9 February. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German athlete, Georg Hackl, who had won gold at the 1992 Winter Olympics and 1994 Winter Olympics, had entered the competition winless in the 1997–1998 season. Hackl raced in a newly designed luge and aerodynamic shoes. Several team protested but these protests were rejected. Hackl dominated all four races, and finished with a time of 3:18.436, half a second ahead of the Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italian Armin Zöggeler. Zöggeler finished .154 seconds ahead of Jens Müller (luger), Jens Müller of Germany, who had won gold at the 1988 Winter Olympics
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games (french: XVes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Calgary 1988 ( bla, Mohkínsstsisi 1988; sto, Wîchîspa Oyade 1988 or ; cr, Otôskwanihk 1998/; srs, Guts� ...
when he competed for East Germany.
On 10 and 11 February, the women's singles event took place, with each athlete completing four runs. In all, 29 athletes took part. The race for gold was very tight between two Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German athletes, Silke Kraushaar and Barbara Niedernhuber, with Kraushaar winning by .002 seconds, with a total time of 3:23.779 – the smallest margin of victory ever at the Olympics. Angelika Neuner of Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austria won the bronze, 0.474 seconds behind the gold medalist.
The two-race doubles competition, which in theory were open to females, consisted of 17 male pairs. The event took place 13 February. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Germans Stefan Krauße and Jan Behrendt, who had competed together for 14 years, won the gold medal with a time of 1:41.105. Two American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
teams won silver and bronze, with Chris Thorpe and Gordy Sheer finishing .022 seconds behind the gold medalists and Brian Martin (luger), Brian Martin and Mark Grimmette a further .09 seconds behind. The win by Krauße and Behrendt was their
four medal at the Olympics since they won silver at the 1988 Winter Olympics
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games (french: XVes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Calgary 1988 ( bla, Mohkínsstsisi 1988; sto, Wîchîspa Oyade 1988 or ; cr, Otôskwanihk 1998/; srs, Guts� ...
when they competed for East Germany. This was the first time since the introduction of luge at the 1964 Winter Olympics that athletes other than those from Austria, Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
won medals.
Skating
Figure skating
The figure skating events took place at theWhite Ring (arena)
The White Ring is an indoor sporting arena located in Nagano, Japan. The capacity of the arena is 7,000 people.
It was a venue at the 1998 Winter Olympics, hosting the figure skating and short track speed skating events.Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
won five medals, including three gold and two silver. The United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, USA won one gold and one silver. France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, France won two bronze medals. Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
won one silver, with China at the 1998 Winter Olympics, China and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
each winning one bronze. American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
figure skater Tara Lipinski
Tara Kristen Lipinski (born June 10, 1982) is an American former competitive figure skater, actress, sports commentator and documentary film producer. A former competitor in women's singles, she is the 1998 Olympic champion, the 1997 World ...
became the youngest competitor in Winter Olympics history to earn a gold medal in an individual event.
Short track speed skating
Six short track speed skating events took place at theWhite Ring (arena)
The White Ring is an indoor sporting arena located in Nagano, Japan. The capacity of the arena is 7,000 people.
It was a venue at the 1998 Winter Olympics, hosting the figure skating and short track speed skating events.Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
won four medals, including two gold. Host Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
won one gold and one silver; and China at the 1998 Winter Olympics, China won five silver and one bronze medal.
The 14th ranked Japan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Japanese skater Takafumi Nishitani beat the Olympic record in the 500m semi-finals. In the final, he led from the start and won the gold medal with a time of 42.862 seconds. The Canada at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Canadian Marc Gagnon, who was in second place, fell with two laps remaining. The China at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Chinese skater An Yulong won the silver with a time of 43.022, 0.5 seconds of the Japanese skater Hitoshi Uematsu. In the 1000 meters, world record holder Marc Gagnon was disqualified for obstruction in the quarter-finals. The Chinese skater Li Jiajun, who led for most of the final, was passed by the South Korea at the 1998 Winter Olympics, South Korean skater, Kim Dong-sung, in the final corner. Kim won with a time of 1:32.375, 0.053 seconds ahead of the silver medalist. The Canadian Éric Bédard won the bronze, .223 seconds further behind. In the 5000m relays, world-title holders from Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italy led at the beginning of the relay but were passed by the Canadians, and fell. With about one-quarter of the race left, a Chinese skater fell, bringing down with him a South Korean skater, allowing the Canadians to easily win the gold, with a time of 7:06.075. The South Koreans were .701 seconds behind, with the Chinese finishing with the bronze a further 4 seconds back. The Japanese team won the B-Final with a time that was five seconds faster than the gold medalists.
In the women's 500m final, the Canada at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Canadian Isabelle Charest collided with the China at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Chinese Wang Chunlu, and both fell. Charest was disqualified and Wang, angry, never finished the race. The Canadian Annie Perreault won the gold with a time of 46.568 seconds, 0.059 seconds ahead of Yang Yang (S) of China. Because these were the only two to finish the race, the bronze medal went to the winner of the B-Final, the South Korea at the 1998 Winter Olympics, South Korean Chun Lee-kyung. In the 1000m race, the Chinese skater Yang Yang (A) led the race but was passed by the 500m bronze medalist, Chun, in the last straight away to the finish line. Chun won the race with a time of 1:42.776 seconds. Yang Yang (A) was disqualified for using her elbow to try to block Chun. Yang Yang (S) won the silver, 0.567 seconds behind the gold medalist from South Korea. Won Hye-kyung, also of South Korea, won the bronze a further 0.18 seconds behind. In the 3000m relay, the Chinese team led for most of the race but the South Korean skater Kim Yun-mi (speed skater), Kim Yun-mi passed Yang Yang (A) in the last changeover. Both teams beat the World Record, with the South Koreans finishing with a time of 4:16.260, and the Chinese were 0.123 seconds behind. The Canadian team won bronze with a time of 4:21.205.
Speed skating
 From 8–20 February 171 athletes from 25 countries took part in the long-track speed skating events that were held in Nagano City at
From 8–20 February 171 athletes from 25 countries took part in the long-track speed skating events that were held in Nagano City at M-Wave
, or , is a covered speed skating oval in the city of Nagano, Japan. M-Wave, which opened in November, 1996, was constructed for the speed skating events at the 1998 Winter Olympics. It was Japan's first International Skating Union (ISU) stand ...
, Japan's first indoor, long-track speed skating venue. In all, eight countries won medals. The Netherlands at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Netherlands won 11 medals, including five gold and four silver. Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, host Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and the United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, USA also won multiple medals. Twelve Olympic records and five World records were established at the Games on the ice at M-Wave. Gianni Romme and Marianne Timmer, both of the Netherlands, each won two gold medals. The Nagano Olympics were the first where athletes wore clap skates.
On the men's side, the world record holder in the men's 500m was the Japan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Japanese skater Hiroyasu Shimizu. Shimizu was the smallest skater at the Games, 1.62m tall. The 500m was run over two races for the first time at these Games. Shimizu was fastest in both races becoming only the second ever Japanese to win a singles title at the Olympic Games. Finishing in second and third were the Canada at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Canadian skaters, Jeremy Wotherspoon and Kevin Overland, who are 1.91m and 1.84 m tall, respectively. Shimizu's combined time was 1:11.35, 0.49 seconds ahead of Wotherspoon, and another 0.02 seconds ahead of Overland. The 1500m was won by Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian Ådne Søndrål with a world record time of 1:47.87. Søndrål was 0.26 and 0.65 seconds ahead of two Netherlands at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Dutch skaters, Ids Postma, and Rintje Ritsma. In the 1000m, Postma won gold, with a time of 1:10.64, followed by another Dutch skater Jan Bos, who was 0.07 seconds behind, and Shimizu who won the bronze with a time of 1:11.00. In the 5000m, the Dutch skater Gianni Romme won gold, with a world record time of 6:22.20, followed by Ritsma, who was 6.04 seconds behind, and Bart Veldkamp, representing Belgium at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Belgium who won the bronze with a time of 6:28.31. Finally, in the 10,000m, three Dutch skaters won medals. Romme won gold with a world record time, 15 seconds ahead of the world record, of 13:15.33, Bob de Jong won silver, and Ritsma won bronze.
On the women's side, the 500 m title was won by the Canadian Catriona Le May Doan, the favorite, who beat or equalled the world record four times before the Games. Her teammate, Susan Auch, finished second. Both were coached by Susan's brother, Derrick Auch. Tomomi Okazaki, of host Japan, won the bronze medal. In the 1500m, Netherlands at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Dutch skater Marianne Timmer won gold with a world record time of 1:57.58. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German skater Gunda Niemann-Stirnemann, Gunda Niemann was second, 1.08 seconds behind, and the American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
skater Chris Witty won bronze with a time of 1:58.97. In the 1000m, Timmer won gold again, with a time of 1:16.51. Witty won silver, 0.26 seconds behind, and Le May Doan won bronze with a time of 1:17.37. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German skater Franziska Schenk, one of the favorites, fell during the second lap. In the 3000m, German skaters won all three medals. Niemann won gold with a time of 4:07.29; Claudia Pechstein won silver, 1.18 seconds back; and Anni Friesinger-Postma, Anni Friesinger won bronze with a time of 4:09.44. Finally, in the 5000m, Pechstein won gold with a world record time of 6:59.61; Niemann was 0.04 seconds back for silver, and the Kazakhstan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Kazakh skater Lyudmila Prokasheva won bronze, with a time of 7:11.14. Prokasheva's medal was the first medal by a female Kazakh athlete at any Winter Olympics.
Skiing
Alpine skiing
The Alpine skiing at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Alpine skiing events took place at Hakuba Happoone Winter Resort in Hakuba, Nagano, Hakuba village, 50 kilometers west of Nagano City, and at Mount Higashidate in the Shiga Highlands in Yamanouchi, Nagano, 30 kilometers northeast of Nagano City. In all, 249 athletes, 141 males and 108 females, from 49 countries, took part in the 10 Alpine skiing events, men's and women's downhill, Super-G, Giant Slalom, Slalom, and Combined. Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austria won 11 medals, including three gold.Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
also won three gold, and six medals in total. Seven other countries also won medals, including Australia at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Australia, whose Zali Steggall won that countries first ever individual Winter Olympics medal. The most successful athletes at these Games were Katja Seizinger from Germany, who won two gold medals and one bronze; and Hermann Maier, from Austria, who won two gold medals.
Cross-country skiing
 The cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing events took place at Nozawa Onsen Ski Resort, in the town of Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Nozawaonsen, approximately 50 kilometers north of Nagano. In all, 228 athletes, including 126 men and 102 women, from 37 countries took part.
The cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing events took place at Nozawa Onsen Ski Resort, in the town of Nozawaonsen, Nagano, Nozawaonsen, approximately 50 kilometers north of Nagano. In all, 228 athletes, including 126 men and 102 women, from 37 countries took part. Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
won eight medals, including five gold medals, and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
won nine medals, including four gold medals. Six other countries also won medals, including Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finland with one gold and two bronze, and Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italy with two silver and two bronze. Larisa Lazutina
Larisa Yevgenyevna Lazutina (russian: Лариса Евгеньевна Лазутина; née Ptitsyna, born 1 June 1965) is a Russian former professional cross-country skier.
Career
Lazutina was awarded the Holmenkollen medal in 1998 (shared ...
from Russia won five medals, including three gold; and Bjørn Dæhlie
Bjørn Erlend Dæhlie (born 19 June 1967) is a Norwegian businessman and retired cross-country skier. From 1992 to 1999, Dæhlie won the Nordic World Cup six times, finishing second in 1994 and 1998. Dæhlie won a total of 29 medals in the Olym ...
from Norway won four medals, including three gold.
Freestyle skiing
The freestyle skiing competition was held at the Iizuna Kogen Ski Area, 12 kilometers north of Nagano, from 8 to 18 February. It was the third consecutive Games that freestyle skiing events took place. The four events, men's and women's moguls and aerials, involved 110 athletes from 25 countries . The United States at the 1998 Winter Olympics, United States won three gold medals. HostJapan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
won one gold medal. Athletes from Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finland won a silver and a bronze medal. Six other countries took home either one silver or one bronze medal.
In men's moguls, the American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
Jonny Moseley was first after the qualifications. Two cousins from Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finland, Janne Lahtela and Sami Mustonen, who had never medalled at the FIS Freestyle Ski World Cup, were ranked second and third behind Moseley. Moseley easily won the final with a score of 26.93. Lahtela was .93 points behind, and Mustonen was another .24 points behind. The Canada at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Canadian, Jean-Luc Brassard, gold medalist from the 1994 Winter Olympics, finished in fourth. In men's aerials, the American Eric Bergoust, who had fallen during training, overtook the other competitors with a score of 255.64 points. The France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Frenchmen, Sébastien Foucras, and the Belarus at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Belarusian, Dmitri Dashinski, were second and third. The Canadian, Nicolas Fontaine, 1996–97 FIS Freestyle Skiing World Cup, world champion in 1997, only managed 10th place after falling on his second jump.
The Japan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Japanese moguls skier, Tae Satoya, 11th after qualifications, surprised everyone by winning the gold medal with a score of 25.06. She was the first female Japanese Olympic champion. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German, Tatjana Mittermayer scored 24.62 points and won the silver medal. The Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian, Kari Traa, won the bronze with a score of 24.09 points. In women's aerials, American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
Nikki Stone won the gold medal with a score of 193.00 points. The ex-gymnast, Xu Nannan from China at the 1998 Winter Olympics, China won silver with a score of 186.97, and Colette Brand from Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Switzerland won bronze with a score of 171.83.
Nordic combined skiing
The Nordic combined events were held at theHakuba Ski Jumping Stadium
Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium is a ski jumping hill in Hakuba, Japan. It hosted the ski jumping and the ski jumping part of the Nordic combined events at the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonl ...
and the Snow Harp
Snow Harp is a cross-country skiing venue located in Hakuba, Nagano, Japan. For the 1998 Winter Olympics, the venue hosted the cross-country skiing and the cross-country skiing portion of the Nordic combined
Nordic combined is a winter sport ...
, both in Hakuba, Nagano, Hakuba village, 50 kilometers west of Nagano City. In all, 53 athletes from 14 countries, took part in the two events, individual and team. Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
won both gold medals. Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finland won both silver medals. France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, France and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
each won one of the bronze medals.
The first event was the individual competition that took place on 13 and 14 February. In all, there were 48 athletes. The silver medalist from the 1994 Winter Olympics, the Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian Bjarte Engen Vik, was the 1997–98 FIS Nordic Combined World Cup leader. At the Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium, Vik led after the first two jumps. He was followed by the Russia at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Russian Valeri Stoliarov. The following day, the skiers left, in order of the placement following the ski jump, along te 15 kilometer cross-country race at the Snow Harp. The race was skied in the rain. Vik led throughout and finished with a 27.5 second lead over second place. With three kilometers to the finish line, the Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finnish athlete, 18-year-old Samppa Lajunen, who was sixth after the jumps, caught up with Stoliarov. The skied together until the stadium, and 60 meters from the finish line, Lajunen passed the Russian and picked up the silver medal 0.7 seconds ahead of Stoliarov who won the bronze. The fastest athlete on the course was the Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Swiss skier, Marco Zarucchi, who was 43rd after the jumps, finished in 25th place.
Eleven nations took part in the team event on 19 and 20 February. At previous Olympics, the team event involved three athletes per team, with the completing a 3x10 kilometer relay. At Nagano, the team was enlarged to four athletes who completed a 4x5 kilometer relay. After the jumps, the team from Finland led by four seconds ahead of the Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austrians, eight seconds ahead of the Norwegians, nine ahead of the Czech Republic at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Czechs, and 29 seconds ahead of the Japan at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Japanese. The relay took place in rain. The Norwegians quickly took the lead and never looked back. The last Norwegian skier had the time to grab his country's flag with 500 meters from the finish line, and they won gold with more than one minute lead over the team from Finland. The France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, French team, sixth after the jumps, won the bronze medal ahead of the Austrians. The Japanese, gold medalists at the 1992 Winter Olympics and 1994 Winter Olympics finished in fifth.
Ski jumping
 The ski jumping competitions took place at the
The ski jumping competitions took place at the Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium
Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium is a ski jumping hill in Hakuba, Japan. It hosted the ski jumping and the ski jumping part of the Nordic combined events at the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonl ...
in Hakuba, Nagano, Hakuba village, 50 kilometers west of Nagano City. In all, 68 athletes from 19 countries participated. For the first time, the top 30 jumpers qualified for the second round. Host Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
won the most medals, including two gold in the large hill and large hill team. Finland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Finland, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, and Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austria rounded out the medal table. Kazuyoshi Funaki
(born 27 April 1975) is a Japanese former ski jumper. He ranked among the most successful sportsmen of its discipline, particularly in the 1990s. Funaki is known for his special variant of the V-style, in which the body lies flatter between the ...
from Yoichi, Hokkaido in Japan won two gold and one silver for the host country.
The normal hill jumps took place on 11 February in front of 45,000 spectators. The Japanese, who had dominated the 1997–98 FIS Ski Jumping World Cup season, were the favorites. With a jump of 91.5 meters, Masahiko Harada led after the first round ahead of the Finnish jumper, Jani Soininen
Kazuyoshi Funaki
(born 27 April 1975) is a Japanese former ski jumper. He ranked among the most successful sportsmen of its discipline, particularly in the 1990s. Funaki is known for his special variant of the V-style, in which the body lies flatter between the ...
, who was fourth after the first round, took the lead with a jump of 90.5 meters in the second round. After a delay caused by strong wind, Soininen took the lead with only Harada still to jump. A sidewind blew when Harada jumped, and only managed 84.5 meters to finish in fifth place overall. Soininen won gold with 234.5 points, Funaki was second with 233.5, and the Austrian Andreas Widhölzl finished third with 232.5 points.
On 15 February, the large hill jump competition took place. 60,000 spectators gathered at Hakuba Ski Jumping Stadium. Normal hill bronze medalist Widhölzl led after the first round, ahead of the Japanese jumper Takanobu Okabe, Jani Soininen et Funaki. In the second round, Funaki jumped 132.5 m, and, for the first time at the Olympics, received perfect points for his style. He jumped into first place and won the gold medal with 272.3 points overall. It was the first Japanese gold medal in ski jumping since the 1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Euro ...
in Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous cit ...
. Harada jumped next. Unfortunately, the measurement system was installed between 95 and 135 meters and his jump was beyond that. He was measured manually to be 136 meters. He also had good points but only managed to win the bronze medal with 258.3. meters. Soininen won the silver with a combined score of 260.8 points.
At the 1994 Winter Olympics, the Japanese team were the favorites but Harada jumped poorly, costing the Japanese the gold medal. Again, in 1998, the Japanese were the favorites. The team event took place on 17 February. The start was slowed by 30 minutes because of heavy falling snow. The first two Japanese jumpers, Okabe at Hiroya Saitō, jumped Japan into first place. Harada completely missed his jump, jumping only 79.5 meters, and despite Funaki having a good jump, Japan drop from first to fourth after the first round behind Austria, Germany, and Norway. Okabe jumped 137 meters, which was an Olympic record. Saitō followed this with a good jump. Harada was next, and like Okabe, jumped 137 meters. The last jumper was Funaki who jumped 125 meters, and the Japanese team became Olympic champions with 933.0 points. The Germans won silver with 897.4 points, and the Austrians finished with 881.5 points for the bronze.
Snowboarding
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
won two medals, including one gold. Athletes from Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Switzerland, France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, France, and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
also won gold medals.
In the men's giant slalom, the Canada at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Canadian Jasey-Jay Anderson won the first race with a half-second lead ahead of Rebagliati. During the second race, the event was temporary delayed because of snow and fog. Ross Rebagliati finished with a combined time of 2:03.96, 0.02 seconds ahead of the Italy at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Italian Thomas Prugger, and another 0.10 seconds ahead of the Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Swiss Ueli Kestenholz. Controversy occurred when three days after the men's Giant Slalom, the International Olympic Committee determined that gold medalist Rebagliati from Canada, was disqualified after testing positive for marijuana. It was the first time in Olympic history that an athlete was disqualified for marijuana. The Canadian Olympic Committee lodged a protest and the case quickly went to the Court of Arbitration for Sport where it was ruled that because marijuana was not classified as a "banned" substance, the medal should be returned to the Canadian athlete. In the halfpipe, the gold medal went to the Switzerland at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Swiss Gian Simmen, who had the highest score, 85.2, despite a heavy rain. The Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian Daniel Franck won the silver with a score of 82.4, and the American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
Ross Powers won the bronze with a score of 82.1.
The women's giant slalom was delayed one day because of a snowstorm. The big favorite, the France at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Frenchwoman Karine Ruby won the first race with almost two seconds ahead of her compatriot Isabelle Blanc. Ruby won the second race, with Blanc missing the last gate and falling. Ruby's combined time was 2:17.34. The Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German Heidi Renoth won the silver with a time of 2:19.17, and the Austria at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Austrian Brigitte Köck won the bronze with a time of 2:19.42. In the halfpipe, the Norway at the 1998 Winter Olympics, Norwegian Stine Brun Kjeldaas won the qualification round. However, in the finals, the Germany at the 1998 Winter Olympics, German Nicola Thost, a former gymnast, finished second in both legs, scored 74.6 points, which was enough for the gold medal. Stine Brun Kjeldaas finished fourth in the first leg and first in second, winning the silver with 74.2 points. The American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
Shannon Dunn-Downing won the first leg, but finished seventh in the second leg, leaving her with the bronze with a score of 72.8.
Mascots
The mascots of the 1998 Winter Olympics are four owls named Sukki, Nokki, Lekki and Tsukki, also known as the Snowlets.Media
The Nagano Olympics were covered by more than 10,000 members of the media, including 8,329 accredited journalists, of which 2,586 were from newspaper media and 5,743 television and radio journalists. The Organizing Committee established Main Press Center (MPC, over two buildings, and 17 annexes throughout the different sites. The MPC, which is today the ''Wakasato Civic Cultural Hall'', was built beside Big Hat, the main ice hockey at the 1998 Winter Olympics, ice hockey venue. The MPC had a surface area of 42,728 m2, with one principal room for 600 journalists of 1430m2 and another of 5100m2 that was rented by various press agencies. The largest press offices at the Games were Kyodo News, Associated Press, Agence France-Presse, Reuters, and Deutsche Presse-Agentur. The MPC also included a press conference room for 600 people. The host broadcaster for the Games, the Olympic Radio and Televisions Organization (ORTO'98) was established as a separate organization within NAOC, the organizing committee. ORTO'98 was created between NHK, the Japanese national broadcaster, the National Association of Broadcasters (NAB), and NAOC. A total of 1647 staff worked 386 cameras at the various venues and events, with coverage increasing by 55% over the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer. The Games were broadcast in 160 countries, 40 more than in Lillehammer, and it was estimated that 10.7 billion viewers watched the Games over the 16-day period. Broadcasting rights totaled 513 million US dollars, which was a record for the Winter Olympics, and all contracts with 16 broadcasting rights' holders were record sums. This money was split 60–40 between NAOC and the International Olympic Committee. The United States, American broadcasting network, CBS, paid 375 million US dollars, to distribute the Games in the United States. This would be the last Olympic Games so far to not air on NBC in the US, as they acquired the exclusive rights to both the summer and winter games beginning in 2000 Summer Olympics, 2000.Broadcasting rights
*Asia – Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union, ABU, Asia Television, ATV *Australia – Seven Network, Fox Sports (Australian TV network), Fox Sports *Canada – Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, CBC *Europe – European Broadcasting Union, EBU *Jamaica – CVM Television, CVM TV *Japan – NOJC *Malaysia – Astro (television), Astro *New Zealand – TVNZ *North Africa – African Union of Broadcasting, URTNA *South Africa – South African Broadcasting Corporation, SABC *South Korea – Korean Broadcasting System, KBS *South America – Organización de Telecomunicaciones de Iberoamérica, OTI *Sub-Saharan Africa – SuperSport (South African TV channel), Supersport *United Kingdom – BBC *United States – CBSSee also
* 1998 Winter Olympics flu epidemicReferences
Notes Citations * *External links
* * Downloadable PDFVolume 1
Volume 2
retrieved on 17 January 2010.
1998 Winter Olympics Official website
{{Portal bar, 1990s, Olympics, Japan 1998 Winter Olympics, 1998 in Japanese sport, Winter Olympics Olympic Games in Japan Winter Olympics by year 1998 in multi-sport events Sports competitions in Nagano (city) February 1998 sports events in Asia Winter sports competitions in Japan