ГңrГјmqi Metro Map on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ГңrГјmqi ( ; also spelled ГңrГјmchi or without umlauts), formerly known as Dihua (also spelled Tihwa), is the capital of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the far
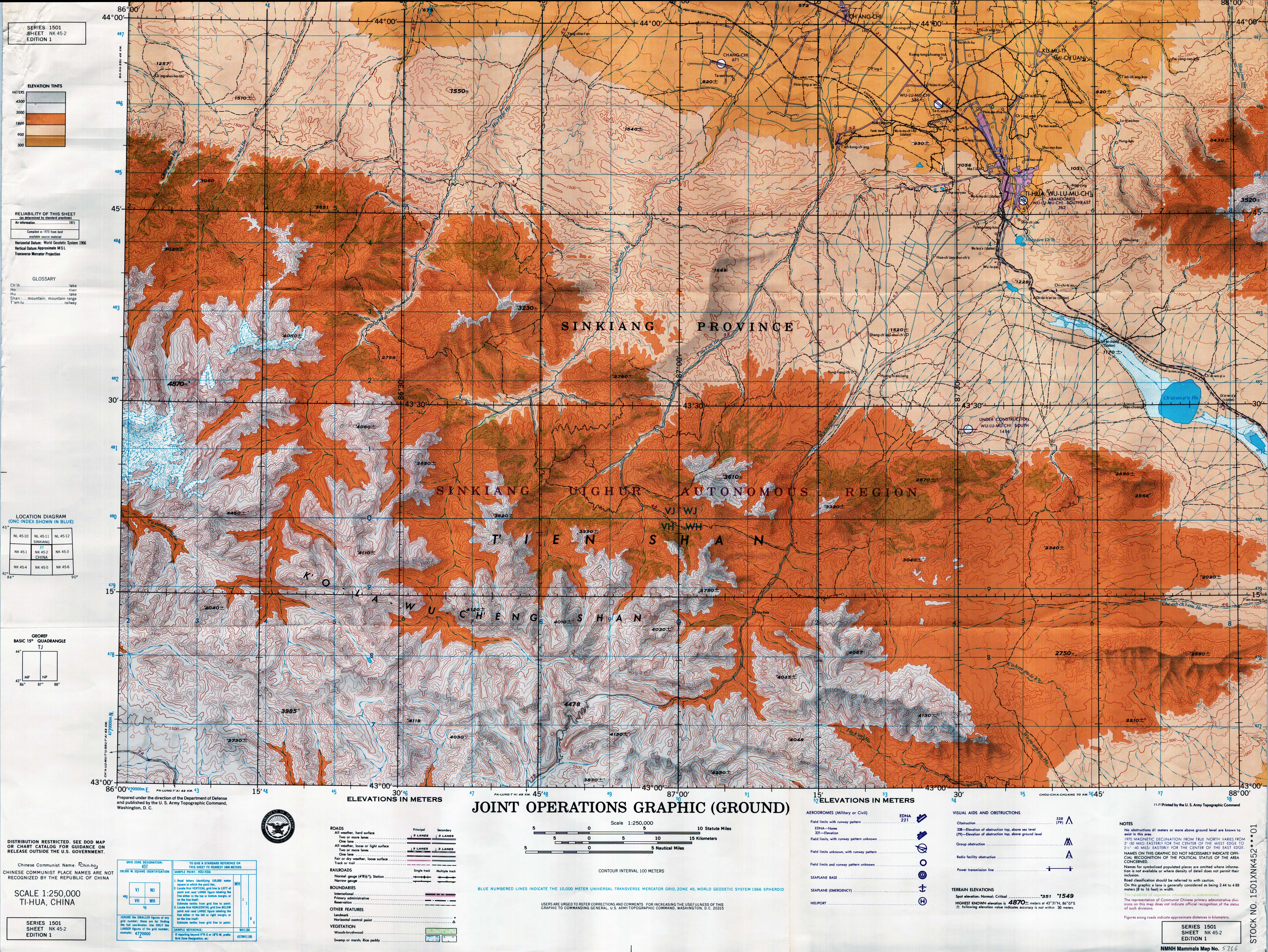
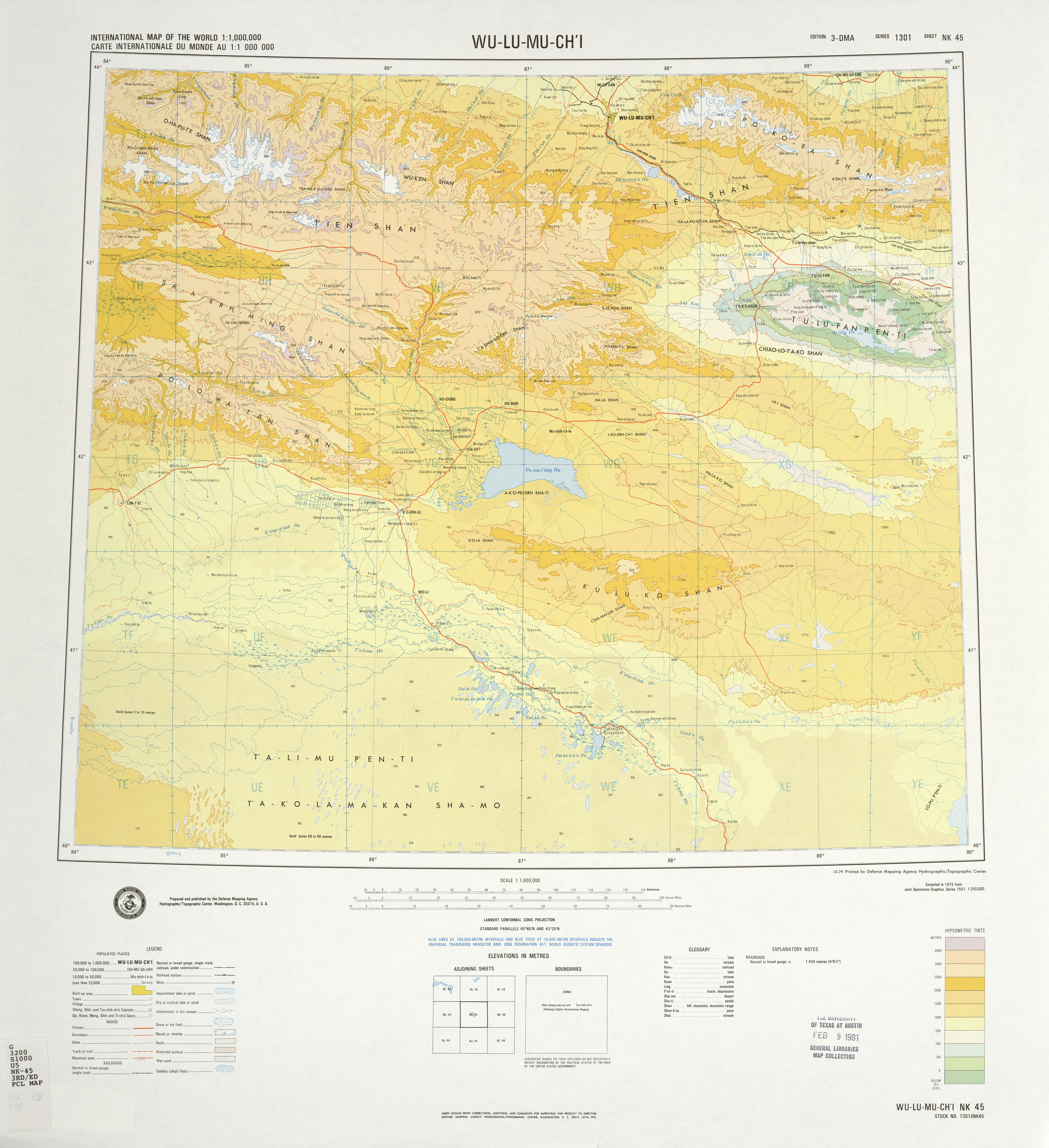 ГңrГјmqi currently comprises 8 county-level subdivisions: 7
ГңrГјmqi currently comprises 8 county-level subdivisions: 7
 ГңrГјmqi is a major industrial center within Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi, together with Karamay and Korla, account for 64.5 percent of the total industrial output of Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi is also the largest consumer center in the region, recording ВҘ41.9 billion retail sales of consumer goods in 2008, an increase of 26 percent from 2007. The GDP per capita reached US$6,222 in 2008. According to statistics, ГңrГјmqi ranked 7th in 2008 by the disposable income for urban residents among cities in Western China. ГңrГјmqi has been a central developmental target for the China Western Development project that the Central Government is pursuing.
The
ГңrГјmqi is a major industrial center within Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi, together with Karamay and Korla, account for 64.5 percent of the total industrial output of Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi is also the largest consumer center in the region, recording ВҘ41.9 billion retail sales of consumer goods in 2008, an increase of 26 percent from 2007. The GDP per capita reached US$6,222 in 2008. According to statistics, ГңrГјmqi ranked 7th in 2008 by the disposable income for urban residents among cities in Western China. ГңrГјmqi has been a central developmental target for the China Western Development project that the Central Government is pursuing.
The  Xinjiang Guanghui Industry Investment Group () is the largest real estate enterprise and most powerful privately owned company in Xinjiang and is currently engaged in energy and automobiles. China CITIC Bank Mansion (), headquarters of Guanghui, located in one of the CBDs in North Xinhua Road, is the tallest building in ГңrГјmqi and Xinjiang; with a height of , it is also the tallest in Northwestern China and Central Asia. Zhongshan Road (Sun Yat-sen Road; zh, links=no, c=дёӯеұұи·Ҝ) has been one of the ten most famous commercial streets in China since 2005. Zhongshan Road has always been the hub of consumer electronics in the city, with the largest computer, mobile phone and consumer electronics market in Xinjiang, including Baihuacun, Cyber Digital Plaza and Fountain Plaza.
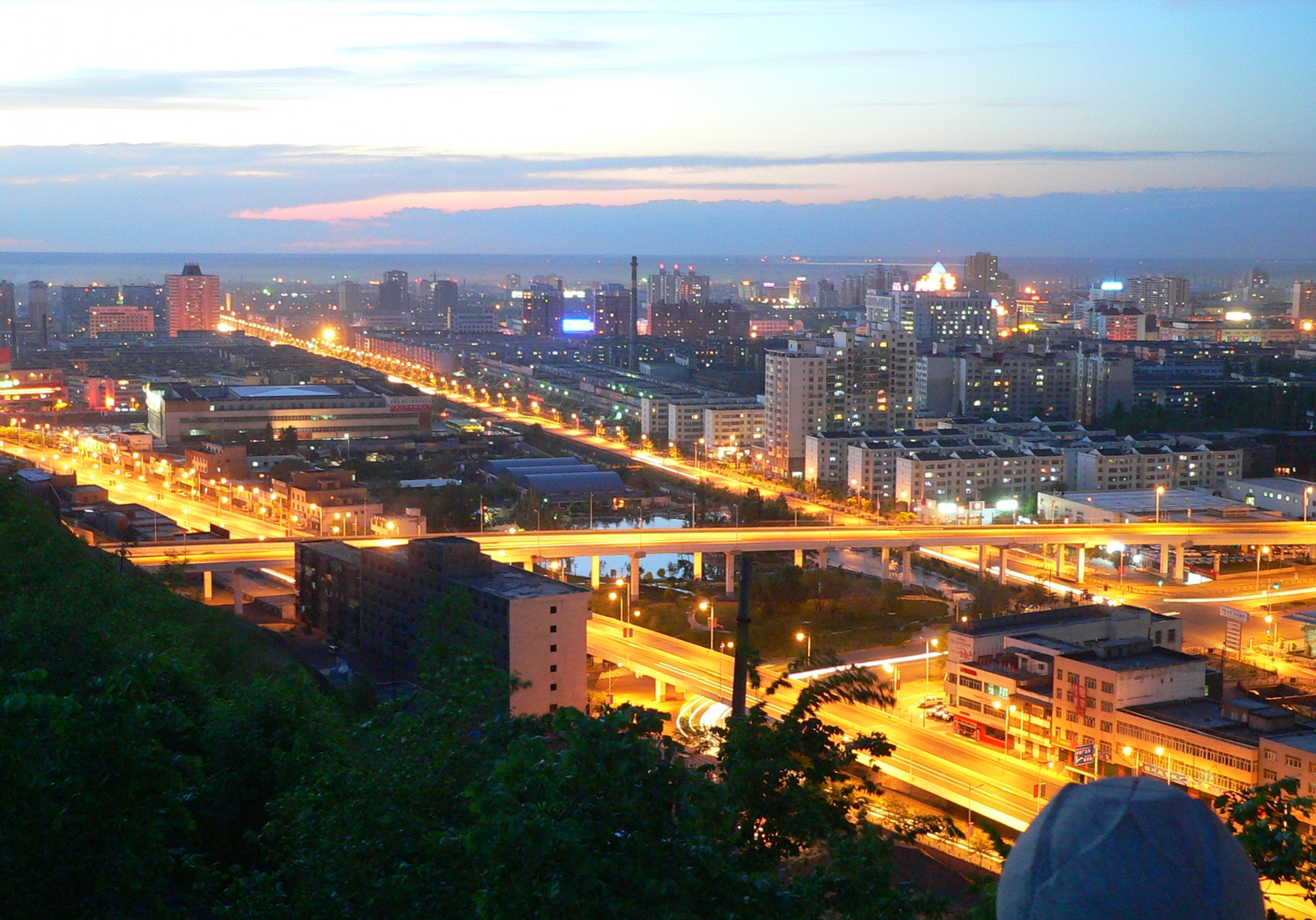
As the economic center in Xinjiang, ГңrГјmqi has expanded its urban area since the 1990s. The CBDs in the city increased rapidly all around the major districts. Despite the old city areas being primarily in the south, the development in the north part began since the late 1980s. The completion of the new office tower for ГңrГјmqi Municipal Government in 2003 at
Xinjiang Guanghui Industry Investment Group () is the largest real estate enterprise and most powerful privately owned company in Xinjiang and is currently engaged in energy and automobiles. China CITIC Bank Mansion (), headquarters of Guanghui, located in one of the CBDs in North Xinhua Road, is the tallest building in ГңrГјmqi and Xinjiang; with a height of , it is also the tallest in Northwestern China and Central Asia. Zhongshan Road (Sun Yat-sen Road; zh, links=no, c=дёӯеұұи·Ҝ) has been one of the ten most famous commercial streets in China since 2005. Zhongshan Road has always been the hub of consumer electronics in the city, with the largest computer, mobile phone and consumer electronics market in Xinjiang, including Baihuacun, Cyber Digital Plaza and Fountain Plaza.
As the economic center in Xinjiang, ГңrГјmqi has expanded its urban area since the 1990s. The CBDs in the city increased rapidly all around the major districts. Despite the old city areas being primarily in the south, the development in the north part began since the late 1980s. The completion of the new office tower for ГңrГјmqi Municipal Government in 2003 at

 * Grand Bazaar, a
* Grand Bazaar, a


Ethnic variation in network composition in ГңrГјmchi: do state policies matter?
''
northwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsвҖ”north, east, south, and westвҖ”each sep ...
of the People's Republic of China. ГңrГјmqi developed its reputation as a leading cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
and commercial center during the Qing dynasty in the 19th century.
With a census population of 4 million in 2020, ГңrГјmqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an as well as the largest in Central Asia in terms of population. According to the ''Guinness Book of Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
'', ГңrГјmqi is the most remote city from any sea in the world. ГңrГјmqi has seen significant economic development since the 1990s and currently serves as a regional transport node and a cultural, political and commercial center.
ГңrГјmqi is one of the top 500 cities in the world by scientific research output, as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is also home to Xinjiang University, a comprehensive university with the highest academic level in Xinjiang, under the Project 211 and the Double First Class University Plan.
Etymology
The name "ГңrГјmqi" comes from the Mongolic Oirat language and means "beautiful pasture". It was originally the name of a small town founded by the Oirat-speaking Mongol Dzungar people. The Qing dynasty took ГңrГјmqi by force in 1755, during its conquest of the Dzungar Khanate. Qing forces expanded the town into a walled city from 1763 to 1767. Upon completing the expansion, the Qing renamed the city "Dihua" ( zh, c=иҝӘеҢ–, links=no; previously romanized as "Tihwa"), which literally means "to enlighten and civilize". Believing the name "Dihua" to be belittling and ethnically chauvinist, the Chinese Communist Party restored the name "ГңrГјmqi" on 1 February 1954.History
Although ГңrГјmqi is situated near the northern route of theSilk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, the present city is relatively new. The earliest known settlement in the area can be dated to the 7th century CE, but there was no permanent settlement for a long period and it was not known as ГңrГјmqi until the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th century. The current city dates from the rebuilding started in the 18th century.
Early period
During the area's prehistory, the Jushi Kingdom was established by a nomadic people who lived on the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains. The oldest known settlement in the area, a village called Urabo (or Wulabo), was located about from the southern suburbs of present-day ГңrГјmqi. Under the name "Luntai", the city was established near Urabo by theTang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century вҖ“ 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (е”җ) b ...
government during the 22nd year of Emperor Taizong's reign (648 AD), as part of the Protectorate General to Pacify the West that controlled Xinjiang. It was a seat of local government and collected taxes from the caravans along the northern route of the Silk Road.
After the Tang retreated from the Western Regions, the region came under the control of the Uyghurs of the Khaganate and Gaochang / Qocho. There is little information about the ГңrГјmqi area during the time between the Tang and Qing dynasties, and researchers believe that there was no permanent settlements there for most of this period. The Mongols referred to the wider area as Bishbalik, meaning five cities, a reference to the five towns that surrounded the present-day ГңrГјmqi area.
Dzungar period
The Oirat-speakingDzungar
Dzungar may refer to:
*Dzungar people, Oirat tribes in the Dzungar Khanate
*Dzungar Khanate, a historical empire
* Jungar Banner, an administrative division of China
*Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in ...
tribes that formed the Dzungar Khanate were the last major power to control ГңrГјmqi before the Manchus gained control of Xinjiang. During the Ming dynasty, there was a record of a place at Jiujiawan to the west of present ГңrГјmqi, which may have been the Dzungar town that was later destroyed during the Qing conquest. The Mongolians also used the area as herding ground in this period. Steppe peoples had used the location, the pass between the Bogda Shan
The Bogda Shan ( mn, Р‘РҫРіРҙ РЈСғР», Bogd Uul; zh, s=еҚҡж јиҫҫеұұ, t=еҚҡж јйҒ”еұұ, p=BГіgГ©dГЎ shДҒn) range is part of the Eastern Tian Shan mountains and located in Xinjiang, some 60 km east of ГңrГјmqi. The topography of the area graduall ...
to the east and the Tian Shan to the west, connecting the Dzungar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in Northwest China. It is located in Xinjiang, and enclosed by the Tarbagatai Mountains of Kazakhstan in the northwest, the Altai Mountains of Mongolia in the northeast, and the Heaven ...
to the north and the Turpan Depression to the south.
ГңrГјmqi remained a small town of lesser importance than the oasis and Silk Road trade center Turpan to the southeast. Fighting for the control of Dzungaria led to the Khoshuuts (now classified as Mongols) leaving ГңrГјmqi for Qinghai and Tibet in the 1620s and 1630s. The Uyghurs were introduced into the ГңrГјmqi area in the 18th century by the Dzungars who moved them from the west Tarim region to be ''taranchis'' or farmers in ГңrГјmqi.
Qing rule
In the 18th century, the Qing went to war against the Dzungar Khanate. ГңrГјmqi was taken by the Qing in 1755, and the Dzungars of the region were eliminated in theDzungar genocide
The Dzungar genocide () was the mass extermination of the Mongol Dzungar people by the Qing dynasty. The Qianlong Emperor ordered the genocide due to the rebellion in 1755 by Dzungar leader Amursana against Qing rule, after the dynasty first co ...
. One writer, Wei Yuan, described the resulting desolation in what became northern Xinjiang as "an empty plain for a thousand '' li'', with no trace of man". A fort was built (either in 1755 or 1758 depending on sources), and the Qing then established garrisons of Manchu and Mongol bannermen and Han Chinese troops at ГңrГјmqi. After 1759, the Qing government established state farms in the under-populated areas around ГңrГјmqi, where there was fertile, well-watered land. Manchu soldiers also constructed a temple with red walls dedicated to Guandi
Guan Yu (; ), courtesy name Yunchang, was a Chinese military general serving under the warlord Liu Bei during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Along with Zhang Fei, he shared a brotherly relationship with Liu Bei and accompanied him on m ...
on Pingding mountain overlooking ГңrГјmqi, which gave ГңrГјmqi the nickname "Red Temple".
The Manchus began to construct a walled city in 1763 to the south of the first fort, and it was completed in 1767. The Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
named the new settlement "Dihua" ( zh, c=иҝӘеҢ–, p=DГӯhuГ , links=no; Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616вҖ“1636) and ...
: ''Wen de dahabure fu''), meaning "to enlighten and civilize". In 1771, another city named Gongning Cheng () was built nearby to the northwest to house Manchu bannermen, and this would become the seat of government. The bannermen settlement to the west was commonly referred to as "Mancheng" ( zh, labels=no, t=ж»ҝеҹҺ , l=Manchu City), while Dihua to the east became a Han Chinese town commonly called "Hancheng" ( zh, labels=no, t=жјўеҹҺ , l=Han City). The ГңrГјmqi of the early period was therefore a twin-city, with Gongning Cheng as the administrative center while Dihua grew into Xinjiang's commercial and financial center.
Han Chinese from all over China moved into Dihua, as did Chinese Hui Muslims from Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
and Shaanxi. The origin of Hui in ГңrГјmqi is often indicated by the names of their mosques. By 1762, more than 500 shops had already been opened by Chinese migrants to the area of modern-day ГңrГјmqi. Those Qing literati who visited Dihua were impressed by its cultural sophistication and similarity to eastern China. The writer Ji Yun
Ji Yun (; 1724вҖ“1805), also known as Ji Xiaolan () or Ji Chunfan () was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and writer. He was an influential scholar of Qing dynasty China and many anecdotes have been recorded about him. Ji Yun left behind a bo ...
compared Dihua to Beijing, in that both had numerous wine shops which offered daily performances of Chinese music and dance.
In 1870, the Battle of ГңrГјmqi took place between the Turkic Muslim forces of Yaqub Beg against the Dungan Muslim forces of Tuo Ming (Daud Khalifa). With the help of Xu Xuegong's Han Chinese militia, Yaqub Beg's forces defeated the Dungans. Gongning Cheng was captured, its Qing administrator killed, and the city burnt to the ground and abandoned. The Qing later regained control of ГңrГјmqi. In 1884, the Guangxu Emperor established Xinjiang as a province, with Dihua as its capital.
Republican era
After the collapse of the Qing dynasty, Xinjiang was ruled from ГңrГјmqi by a succession of warlords: Yang Zengxin (1911вҖ“1928),Jin Shuren
Jin Shuren (; c. 1883–1941) was a Chinese Xinjiang clique warlord who served as Governor of Xinjiang between 1928 and 1933.
Biography
Jin Shuren was born in Yongjing, Hezhou, Gansu. He graduated at the Gansu provincial academy and th ...
(1928вҖ“1933), Sheng Shicai (1933вҖ“1942), and Zhang Zhizhong as governor of Xinjiang in 1942вҖ“1949. Of these, Yang and Sheng were considered capable rulers.
During the Kumul Rebellion
The Kumul Rebellion (, "Hami Uprising") was a rebellion of Hami, Kumulik Uyghurs from 1931 to 1934 who conspired with Hui people, Hui Islam in China, Chinese Muslim Gen. Ma Zhongying to overthrow Jin Shuren, governor of Xinjiang. The Kumul Uygh ...
, the Battle of ГңrГјmqi (1933) and the Battle of ГңrГјmqi (1933вҖ“34) took place between the forces of Ma Zhongying's 36th Division (National Revolutionary Army)
The New 36th Division was a cavalry division in the National Revolutionary Army. It was created in 1932 by the Kuomintang for General Ma Zhongying, who was also its first commander. It was made almost entirely out of Hui Muslim troops, all of ...
and Jin Shuren
Jin Shuren (; c. 1883–1941) was a Chinese Xinjiang clique warlord who served as Governor of Xinjiang between 1928 and 1933.
Biography
Jin Shuren was born in Yongjing, Hezhou, Gansu. He graduated at the Gansu provincial academy and th ...
and Sheng Shicai's provincial forces. At the second battle, Ma was assisted by the Han Chinese General Zhang Peiyuan
Zhang Peiyuan (traditional Chinese: ејөеҹ№е…ғ) ( – 1 June 1934) was a Han chinese general, commander of the Ili garrison. He fought against Uighur and Tungans during the Kumul revolt, but then secretly negotiated with the Tungan general ...
.
People's Republic era
On 1 February 1954, following the founding of the People's Republic of China, the city's name was officially changed back to ГңrГјmqi. The ruling Chinese Communist Party believed that the name "Dihua", which literally means "to enlighten and civilize", was belittling and ethnically chauvinist. In the late 1970s, Deng Xiaoping relaxed China's tight control over Xinjiang, and ГңrГјmqi benefited from the development of the oil and gas industry in Xinjiang. New mosques were built in ГңrГјmqi with financial assistance from the Chinese government. While the Chinese government implemented strict rules on religion in southern Xinjiang, the treatment of the Uyghurs and their religion in ГңrГјmqi were more lax and permissive. In May 1989, unrest in ГңrГјmqi resulted in 150 injuries. In February 1997, bombings in ГңrГјmqi following the Ghulja incident resulted in 20 deaths and scores of injuries.July 2009 riots and subsequent unrest
In the largest eruption of ethnic violence in China in decades, there were riots in July 2009 between ethnic Han Chinese and Uyghurs. The ''New York Times'' reporter covering the riot described the violence as "clashes with riot police and Uyghurs rampaging through the city and killing Han civilians. Then, for at least three days, bands of Han vigilantes roamed Urumqi, attacking and killing Uyghurs." Before the riot broke out, young Uyghurs had marched through the city "to protest a case of judicial discrimination". According to official figures, most of the 197 killed in the riot were Han, a statement which ''New York Times'' reporterEdward Wong
Edward Wong (born November 14, 1972) is an American journalist. He is a diplomatic correspondent for The New York Times.
Early life and education
Wong was born November 14, 1972 in Washington, D.C. He grew up in Alexandria, Virginia.
Wong rec ...
says is disputed by Uyghurs.
Geography
The largest city in western China, ГңrГјmqi has earned a place in the ''Guinness Book of Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
'' as the most remote city from any sea in the world. It is about from the nearest coastline as ГңrГјmqi is the closest major city to the Eurasian pole of inaccessibility, although Karamay and Altay, both in Xinjiang, are closer. The city has an administrative area of and has an average elevation of .
The location in the southwestern suburbs of ГңrГјmqi (ГңrГјmqi County
ГңrГјmqi County is a county of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Northwest China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of ГңrГјmqi, the capital of Xinjiang. It contains an area of 4,601 kmВІ and according to the 20 ...
) was designated by local geography experts as the "center point of Asia" in 1992, and a monument to this effect was erected there in the 1990s. The site is a local tourist attraction.
Water supply
Although surrounded by deserts (the GurbantГјnggГјt in the north and the Taklamakan in the south), the ГңrГјmqi area is naturally watered by a number of small rivers flowing from the snow-capped Tian Shan mountains: the main range of the Tian Shan in south of the city (ГңrГјmqi County
ГңrГјmqi County is a county of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Northwest China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of ГңrГјmqi, the capital of Xinjiang. It contains an area of 4,601 kmВІ and according to the 20 ...
), and the Bogda Shan
The Bogda Shan ( mn, Р‘РҫРіРҙ РЈСғР», Bogd Uul; zh, s=еҚҡж јиҫҫеұұ, t=еҚҡж јйҒ”еұұ, p=BГіgГ©dГЎ shДҒn) range is part of the Eastern Tian Shan mountains and located in Xinjiang, some 60 km east of ГңrГјmqi. The topography of the area graduall ...
east of the city (Dabancheng District
Dabancheng District ( zh, s=иҫҫеқӮеҹҺеҢә, t=йҒ”еқӮеҹҺеҚҖ, p=DГЎbЗҺnchГ©ng QЕ«) or Dawan Cheng ( ug, ШҜШ§ЫӢШ§ЩҶЪҶЩүЪӯ ШұШ§ЩҠЩҲЩҶЩү, translit=Dawanching Rayoni, ), is one of 7 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of ГңrГјmqi, the capital of ...
). A network consisting of thousands of miles of canals, reservoirs, and tunnels called ''karez'', redistribute the water throughout the extensively irrigated area along the foothills of the mountain range. It is based on an ancient irrigation system built 2,000 years ago.
There are 20,000 glaciers in Xinjiang вҖ“ nearly half of all the glaciers in China. Since the 1950s, Xinjiang's glaciers have retreated by between 21 percent to 27 percent due to global warming. Tianshan Glacier No. 1
The Tian Shan,, , otk, рҗ°ҙрҗ°Ј рҗұ…рҗ°ӯрҗ°јрҗ°ғ, , tr, TanrДұ DaДҹДұ, mn, РўСҚРҪРіСҚСҖ СғСғР», , ug, ШӘЫ•ЪӯШұЩүШӘШ§Шә, , , kk, РўУҷТЈС–СҖСӮР°СғСӢ / РҗлаСӮР°Сғ, , , ky, РўРөТЈРёСҖ-РўРҫРҫ / Рҗла-РўРҫРҫ, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / TangritogвҖҳ ...
(), origin of ГңrГјmqi River, is the largest glacier near a major city in China, but has already split into two smaller glaciers.
As the ГңrГјmqi region's population and economy are growing, the water demand exceeds the natural supply. To alleviate water shortages, the IrtyshвҖ“ГңrГјmqi Canal was constructed in the first decade of the 21st century. The canal's main trunk terminates in the so-called "Reservoir 500" (; ) in the far north-eastern suburbs of the city (on the border of ГңrГјmqi's suburban Midong District and Fukang City). A new industrial area, called Ganquanbao Industrial Park (), or Industrial New City 500 () was being developed in 2009, west of the reservoir, relying on it for water supply. From the reservoir area water is further distributed over a network of canals throughout the lower Midong District.
Climate
In ГңrГјmqi, a continental cold semi-arid climate ( KГ¶ppen climate classification '' BSk'') prevails, with very large differences between summer and winter. It has warm summers, with a July daily average of , and very cold winters, with a January daily average of . The annual average temperature is . The city is semi-arid, with its summers slightly wetter than its winters, yet sunny weather is much more likely in the warmer months, and relative humidity is the lowest during summer. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 30 percent in December to 70 percent in August and September, the city receives 2,523 hours of bright sunshine annually. Its annual precipitation is about . Extremes since 1951 have ranged from on 27 February 1951 to on 1 August 1973.Cityscape
Air quality and pollution
According to the National Environmental Analysis released by Tsinghua University and the Asian Development Bank in January 2013, ГңrГјmqi is among the top ten cities in the world with the most air pollution. According to this report, seven of these cities are in China, includingTaiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province. ...
, Beijing, Lanzhou
Lanzhou (, ; ) is the capital and largest city of Gansu Province in Northwest China. Located on the banks of the Yellow River, it is a key regional transportation hub, connecting areas further west by rail to the eastern half of the country. H ...
, Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwes ...
, Jinan
Jinan (), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Tsinan, is the Capital (political), capital of Shandong province in East China, Eastern China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is the second-largest city i ...
, and Shijiazhuang
Shijiazhuang (; ; Mandarin: ), formerly known as Shimen and romanized as Shihkiachwang, is the capital and most populous city of ChinaвҖҷs North China's Hebei Province. Administratively a prefecture-level city, it is about southwest of Beijin ...
(besides ГңrГјmqi).
Blacksmith Institute mentioned ГңrГјmqi in ''2007 World's Worst Polluted Places'' caused by air pollution along with Linfen and Lanzhou
Lanzhou (, ; ) is the capital and largest city of Gansu Province in Northwest China. Located on the banks of the Yellow River, it is a key regional transportation hub, connecting areas further west by rail to the eastern half of the country. H ...
, all in China. In 2008, ''Toronto Star
The ''Toronto Star'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet daily newspaper. The newspaper is the country's largest daily newspaper by circulation. It is owned by Toronto Star Newspapers Limited, a subsidiary of Torstar Corporation and part ...
'' listed ГңrГјmqi as one of the Top Ten worst places to live in the world due to sulphurous pollution. Heavy haze is extremely common in winter, which frequently affects air traffic. Officials believed that severe winter air pollution in ГңrГјmqi is mainly caused by energy-heavy industries and the outdated coal-firing winter heating system.
According to a report by Department of Environmental Science and Engineering of Fudan University, the average PM2.5 and TSP concentrations in the winter of 2007 were 12 times higher than USA standard for PM2.5 and 3 times the National Ambient Air Quality Standard of China for TSP. The sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
from industrial emissions mixed with the local anthropogenic aerosol with the transported soil dust from outside the city were the main sources of the high concentration of sulfate, one of the main factors causing the heavy air pollution over ГңrГјmqi.
Timing of sunrise
Because of the use of a single time zone for all of China, in ГңrГјmqi which is at a far western location in China, the sun is 2 hours and 10 minutes behind China Standard Time (CST = UTC+8). During early January the sun does not rise until 09:45 and it sets between 18:45 and 19:10 local time. In September and March the sun rises around 08:00, and sets around 19:45. However, in June the sun rises at about 06:25 and does not set until 21:45.Administrative divisions

 ГңrГјmqi currently comprises 8 county-level subdivisions: 7
ГңrГјmqi currently comprises 8 county-level subdivisions: 7 districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
and 1 county.
Demographics
ГңrГјmqi has been a multi-ethnic city from the time of the Qing conquest; in the early years, the Manchus lived in Gongning Cheng, Han Chinese in Dihua and various other ethnic groups such as the Hui, Uyghurs and others in the suburban districts. Muslims settled to the south of the walled-city of Dihua, and although the walls have since been demolished, the Muslims are still concentrated there. A census in 1787 showed that there were 114,348 Hui and Han in the prefectures of Zhenxi (which included BarkГ¶l and Hami) and ГңrГјmqi. In ГңrГјmqi city itself, there were 39,000 people in the 1880s and by the early 20th century, 50,000 people. ГңrГјmqi in 1908 was said to have been inhabited by Uyghurs (then called Turkis), Chinese, Manchus and a few Mongols, with the Uyghurs estimated to comprise a quarter of the population. In the People's Republic era, an active program to resettle Han population in Xinjiang was initiated. In 1960, there were 76,496 Uyghurs and 477,321 Han Chinese in ГңrГјmqi. According to the 2000 census, ГңrГјmqi had 2,081,834 inhabitants, with a population density of 174.53 inhabitants/km2 (452.3 inhabitants/sq. mi.). In the 2010 census, the population was recorded as 3,112,559. Part of the increase was due to boundary changes, for example, Miquan was merged into Midong District and became part of ГңrГјmqi in 2007. In 2021, ГңrГјmqi was estimated to have a population of 4.544 million people.Economy
 ГңrГјmqi is a major industrial center within Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi, together with Karamay and Korla, account for 64.5 percent of the total industrial output of Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi is also the largest consumer center in the region, recording ВҘ41.9 billion retail sales of consumer goods in 2008, an increase of 26 percent from 2007. The GDP per capita reached US$6,222 in 2008. According to statistics, ГңrГјmqi ranked 7th in 2008 by the disposable income for urban residents among cities in Western China. ГңrГјmqi has been a central developmental target for the China Western Development project that the Central Government is pursuing.
The
ГңrГјmqi is a major industrial center within Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi, together with Karamay and Korla, account for 64.5 percent of the total industrial output of Xinjiang. ГңrГјmqi is also the largest consumer center in the region, recording ВҘ41.9 billion retail sales of consumer goods in 2008, an increase of 26 percent from 2007. The GDP per capita reached US$6,222 in 2008. According to statistics, ГңrГјmqi ranked 7th in 2008 by the disposable income for urban residents among cities in Western China. ГңrГјmqi has been a central developmental target for the China Western Development project that the Central Government is pursuing.
The ГңrГјmqi Foreign Economic Relations and Trade Fair Urumqi Foreign Economic Relations and Trade Fair (), commonly abbreviated as Urumqi Fair (), is an annual trade fair held in Urumqi of Xinjiang, China, since it was started on September 2, 1992. Its purpose is to promote trading and market explorat ...
( zh, c=д№ҢжҙҪдјҡ) has been held annually since 1991 and has been upgraded into the first China-Eurasia Expo in 2011. Its purpose is to promote domestic and foreign markets. The 17th Fair has attracted participants from the Ministry of Commerce A Ministry of Trade and Industry, Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry or variations is a ministry that is concerned with a nation's trade, industry and commerce.
Notable examples are:
List
*Algeria: Ministry of Industry and M ...
and the China Council for Promotion of International Trade
The China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (; CCPIT) is a trade body founded in 1952. It also goes by the name of the China Chamber of International Commerce (, CCOIC). CCPIT is under the Ministry of Commerce.
The CCPIT develops bu ...
.
Nanhu Square Nanhu () may refer to the following in mainland China or Taiwan:
*Nanhu Mountain (еҚ—ж№–еӨ§еұұ), 3,740 m-high mountain in Taiwan
*Nanhu District (еҚ—ж№–еҢә), in Jiaxing, Zhejiang, China
;Lakes (еҚ—ж№–)
* South Lake (Nanning), Guangxi
* South Lake ( ...
() in Nanhu Road marked a shift of the city center to the north. Lacking a subway, the city commenced the construction of viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide v ...
s for Outer Ring Road () since 2003, which considerably facilitates transport. Youhao Road () and surrounding neighborhood, is the commercial center for business, shopping and amusement. Youhao Group (), the namesake local enterprise, owns a major market share of retails. Maison Mode Urumqi (), open since 2008, became one of the few notable department stores for luxury merchandise in the city. The ГңrГјmqi Economic and Technological Development Zone (UETD) located in the northern Toutunhe District
The Toutunhe District ( zh, s=еӨҙеұҜжІіеҢә, t=й ӯеұҜжІіеҚҖ, p=TГіutГәnhГ© QЕ«; ug, ШӘЫҮШҜЫҮЪӯШ®Ш§ШЁШ§ ШұШ§ЩҠЩҲЩҶЩү, translit=Tudungxaba Rayoni, Tudunghaba Rayoni, ) is one of 7 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wulumuqi, the capit ...
, has been a leading base for steel, machinery manufacturing, biochemistry and other industrial innovations.
Tourism

 * Grand Bazaar, a
* Grand Bazaar, a bazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small Market stall, stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, suc ...
on South Jiefang Road ().
* Hong Shan (Red Mountain) is the symbol of ГңrГјmqi, located in Hongshan Park.
* People's Park, south of Hongshan Park.
* People's Square
* Nanhu Square ()
* Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Museum (), which was completely rebuilt in the early 2000s.
* Heavenly Lake Scenic Area, a popular park with some of China's most famous alpine scenery, over two hours outside ГңrГјmqi.
* Shuimogou Hot Springs () is located northeast of ГңrГјmqi.
* Xinjiang Silk Road Museum () is located next to the Grand Bazaar at No. 160 Shengli Road. It is located on the fourth and fifth floors of a large European-style building which houses a shopping complex as well. Most of the exhibits have English names as well and some of the guides speak some English.
* ГңrГјmqi City Museum () is located at South Nanhu Road 123 ().
* ГңrГјmqi Tatar Mosque () is located on Jiefang Road. Permission must be obtained prior to visiting the mosque.
* The monument at the Geographical Center of Asian Continent
The location of the geographical centre of Asia (russian: РҰРөРҪСӮСҖ РҗР·РёРё; tyv, РҗР·РёСҸРҪСӢТЈ РўУ©РІТҜ; ) depends on the definition of the borders of Asia, mainly whether remote islands are included to define the extreme points of Asia, and ...
, in Yongfeng Township, ГңrГјmqi County
ГңrГјmqi County is a county of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Northwest China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of ГңrГјmqi, the capital of Xinjiang. It contains an area of 4,601 kmВІ and according to the 20 ...
* ГңrГјmqi Silk Road Ski Resort () is located in ГңrГјmqi County.
*Immaculate Conception Cathedral, ГңrГјmqi
The Immaculate Conception Cathedral () also called ГңrГјmqi Cathedral is a religious building located in the city of ГңrГјmqi (''Urumchi''), capital of the Xinjiang Autonomous Region, in the northwest part of China.
The temple follows the Roman o ...
: Diocesan Cathedral of the Diocese of Xinjiang (зғҸйӯҜжңЁйҪҠеӨ©дё»ж•ҷе Ӯ)
Education and science
ГңrГјmqi has many educational campuses including Xinjiang University,Xinjiang Normal University
Xinjiang Normal University (XJNU) ( ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ЩҫЩүШҜШ§ЪҜЩҲЪҜЫҗЩғШ§ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘЩү; zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеёҲиҢғеӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng ShД«fГ n DГ xuГ©) is a public university in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Rep ...
, Xinjiang Agricultural University
Xinjiang Agricultural University (XAU) ( zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеҶңдёҡеӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng NГіngyГЁ DГ xuГ©; ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ЩҠЫҗШІШ§ШҰЫҗЪҜЩүЩ„ЩүЩғ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘЩү) is a higher education institution in ГңrГјmqi, the capital of the Xinjiang Uy ...
, Xinjiang Medical University
Xinjiang Medical University (XMU) ( zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеҢ»з§‘еӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng YД«kД“ DГ xuГ©; ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ШӘЩүШЁШЁЩүЩҠ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘ, Shinjang Tibbiy Universiteti, 6=РЁРёРҪТ—Р°ТЈ РўРёРұРұРёР№ РЈРҪРёРІРөСҖСҒРёСӮРөСӮРё), formerly th ...
and many others.
Universities
* Xinjiang University () *Xinjiang Normal University
Xinjiang Normal University (XJNU) ( ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ЩҫЩүШҜШ§ЪҜЩҲЪҜЫҗЩғШ§ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘЩү; zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеёҲиҢғеӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng ShД«fГ n DГ xuГ©) is a public university in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Rep ...
()
* Xinjiang Agricultural University
Xinjiang Agricultural University (XAU) ( zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеҶңдёҡеӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng NГіngyГЁ DГ xuГ©; ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ЩҠЫҗШІШ§ШҰЫҗЪҜЩүЩ„ЩүЩғ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘЩү) is a higher education institution in ГңrГјmqi, the capital of the Xinjiang Uy ...
()
* Xinjiang Arts Institute
Xinjiang Arts Institute () is an arts college in Xinjiang. It is ranked at 521st in China, having a score of 15.00.http://rank2008.netbig.com/cn/rnk_1_0_0.htm
50th anniversary
On September 26, 2008, Xinjiang Arts Institute held a conference ...
()
* Xinjiang University of Finance and Economics
Xinjiang University of Finance and Economics () is a university in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang, China. Founded in 1950, it is the key institution for the study of economics. There is a total enrollment of more than 20,000 students. There are 1302 staf ...
()
* ГңrГјmqi Vocational University
ГңrГјmqi ( ; also spelled ГңrГјmchi or without Umlaut (diacritic), umlauts), formerly known as Dihua (also spelled Tihwa), is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the far Northwest China, northwest of the Peopl ...
()
* Xinjiang Vocational and Technical Institute
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=XД«njiДҒng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
()
* Xinjiang Medical University
Xinjiang Medical University (XMU) ( zh, s=ж–°з–ҶеҢ»з§‘еӨ§еӯҰ, p=XД«njiДҒng YД«kД“ DГ xuГ©; ug, ШҙЩүЩҶШ¬Ш§Ъӯ ШӘЩүШЁШЁЩүЩҠ ШҰЫҮЩҶЩүЫӢЫҗШұШіЩүШӘЫҗШӘ, Shinjang Tibbiy Universiteti, 6=РЁРёРҪТ—Р°ТЈ РўРёРұРұРёР№ РЈРҪРёРІРөСҖСҒРёСӮРөСӮРё), formerly th ...
()
High schools
* ГңrГјmqi No.1 High School *Bingtuan No.2 Middle School
The Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (), also known as XPCC or Bingtuan ("The Corps"), is a state-owned economic and paramilitary organization in China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR).
In its history, the XPCC has built ...
* Bayi Senior High School of ГңrГјmqi Bayi may refer to these articles:
Chinese
*BДҒyД« (е…«дёҖ, lit. ''eight-one'', which means "August 1"), refers to the anniversary of the Nanchang Uprising, which is considered as the founding of the People's Liberation Army, and thus a common name ...
* No.70 Senior High School of ГңrГјmqi
* No.8 Senior High School of ГңrГјmqi
* No.6 Senior High School of ГңrГјmqi
''No. 6'' is a Japanese novel series written by Atsuko Asano (writer), Atsuko Asano and published by Kodansha in nine volumes between October 2003 and June 2011. A manga adaptation drawn by Hinoki Kino was serialized in Kodansha's ''Aria (mag ...
Research institutes
*Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO; ) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences was known as ГңrГјmqi Astronomical Observatory before it was renamed in January 2011.
The current research at XAO spans many fields of astronomy. It consists of radio ...
* The Xingjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry.CAS
* Xingjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=XД«njiДҒng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
Transportation


Air
ГңrГјmqi is served by the ГңrГјmqi Diwopu International Airport. It is a hub for China Southern Airlines. ГңrГјmqi Diwopu International Airport is the largest airport in Xinjiang, and the only airport in China to serve flights from Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan.Rail
ГңrГјmqi is Xinjiang's main rail hub with two primary railway stations, the olderГңrГјmqi South railway station
ГңrГјmqi ( ; also spelled ГңrГјmchi or without umlauts), formerly known as Dihua (also spelled Tihwa), is the capital of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the far northwest of the People's Republic of China. ГңrГјmqi developed its ...
(formerly the Urumqi railway station) and ГңrГјmqi railway station opened in July 2016. The Lanzhou-Xinjiang High Speed Railway stops at both stations, running from ГңrГјmqi to Lanzhou railway station
Lanzhou railway station () is a railway station located in Chengguan District, Lanzhou, Gansu Province along Huochezhan East Road (). The station was established in October 1952, and is operated by China Railway Lanzhou Group. It handles both ...
, and has been in operation since the end of 2014.
The city is served by several conventional rail lines. ГңrГјmqi is the western terminus of the LanzhouвҖ“Xinjiang (Lanxin) and ГңrГјmqiвҖ“Dzungaria (Wuzhun) Railway, and the eastern terminus of the Northern Xinjiang (Beijiang) and the Second ГңrГјmqiвҖ“Jinghe railway. The Beijiang and the Lanxin Lines form part of the Trans-Eurasian Continental Railway, which runs from Rotterdam through the Alataw Pass on the Kazakhstan border to ГңrГјmqi and on to Lanzhou and Lianyungang.
Road
* China National Highway 216 * China National Highway 312 *China National Highway 314
China National Highway 314 (G314) (sometimes referred to as Gansu Provincial Highway 314) runs southwest from Urumqi, Xinjiang towards the Khunjerab Pass, which is on the northern border of the GilgitвҖ“Baltistan territory in Pakistan-administer ...
Many roads to the north and west typically shut down by early October, remaining closed until the end of winter.
Bus rapid transit
TheГңrГјmqi BRT
ГңrГјmqi Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) is a bus rapid transit system in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang, China. It began trial operations in August, 2011 and official operation in September.
Lines
* BRT1: in length, 21 stations,
* BRT2: in length, 17 stations,
* ...
bus service was launched in August 2011 after an investment of 930 million yuan in an effort to improve urban traffic. There are currently 9 routes operated, BRT1, BRT2, BRT3, BRT4, BRT5, BRT 6, its branch BRT 61, BRT 7, and its branch BRT 71.
Metro
TheГңrГјmqi Metro
The ГңrГјmqi Metro or ГңrГјmqi Subway is a rapid transit system in operation in ГңrГјmqi, capital of the Xinjiang Autonomous Region in China.
The ГңrГјmqi Metro has submitted plans for two lines, Line 1 and Line 2, with an estimated cost of 31.24 ...
opened on 25 October 2018, when the northern section of Line 1 was opened to the public. The southern section of Line 1 opened on 28 June 2019. Line 1 runs between ГңrГјmqi Diwopu International Airport and Santunbei in downtown ГңrГјmqi, with a total length of and 21 stations. It is fully underground.
The planned system consists of 7 lines being in length. The first two lines, Line 1 and Line 2 will be constructed with an estimated cost of 31.24 billion yuan.
Media
TheXinjiang Networking Transmission Limited
Xinjiang Networking Transmission Limited ({{zh, s=ж–°з–Ҷе№ҝз”өдј иҫ“зҪ‘з»ңжңүйҷҗиҙЈд»»е…¬еҸё), also known as Xinjiang Broadcast Network, consists of media broadcasting to ГңrГјmqi and the Xinjiang province area. It operates the Urumqi People's ...
operates the ГңrГјmqi People's Broadcasting Station and the Xinjiang People Broadcasting Station
Xinjiang People's Broadcasting Station (XJBS) consists of radio broadcasting to the Xinjiang province area. It is operated by the Xinjiang Networking Transmission Limited in Mandarin, Uyghur, Kazakh, Kyrgyz and Mongolian languages.
List of pro ...
, broadcasting in the Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
, Uyghur, Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
, Mongolian, Russian and the Kyrgyz Kyrgyz, Kirghiz or Kyrgyzstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kyrgyzstan
*Kyrgyz people
*Kyrgyz national games
*Kyrgyz language
*Kyrgyz culture
*Kyrgyz cuisine
*Yenisei Kirghiz
*The FuyГј GГҜrgГҜs language in Northeastern China
...
languages.
The Xinjiang Television Station (XJTV), located in ГңrГјmqi, is the major TV broadcasting station in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. The local television station for ГңrГјmqi city is ГңrГјmqi Television Station
Urumqi Television Station (UTV) () is a state-owned television station in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang, China. It was established in April, 1985 as a cable network and started broadcasting on September 28 in the same year. Its logo is shaped in red afte ...
(UTV).
Sport
*Xinjiang Flying Tigers
The Xinjiang Guanghui Flying Tigers () is a professional basketball team based in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang, China. The team play its home games at the Hongshan Arena, which has a capacity for 3,800 spectators. The club joined the Chinese Basketball ...
is a basketball team that is part of the Chinese Basketball Association, based in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang. Its corporate sponsor is Xinjiang Guanghui Group.
* Xinjiang Tianshan Leopard F.C.
Xinjiang Tianshan Leopard F.C. () is a professional Chinese football club that participates in the China League One division under licence from the Chinese Football Association (CFA). The team is based in ГңrГјmqi, Xinjiang and their home stadi ...
is a local football team in the China League One.
China started a bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
development programme by organizing educational days in ГңrГјmqi in June 2009.
In 2015, an indoor speed skating arena was opened.
Twin towns and sister cities
ГңrГјmqi is twinned with:Almaty
Almaty (; kk, РҗлмаСӮСӢ; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Рҗлма-РҗСӮР°), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
is a state-level city of Kazakhstan
Notable people
* Dilraba Dilmurat * Gulnazar * Rushan Abbas *Hassan Anvar
Anwar Hassan (born August 25, 1974) is a Uyghur refugee who was wrongly imprisoned for more than seven years in the United States Guantanamo Bay detention camps.http://ccrjustice.org/newsroom/press-releases/17-innocent-uighurs-detained-guant%C3 ...
* Elnigar Iltebir
Elnigar Iltebir ( ug, ШҰЫ•Щ„ЩҶЩүЪҜШ§Шұ ШҰЩүЩ„ШӘЫ•ШЁЩүШұ; born 1984) is a United States-based Uyghur politician and activist. The Trump administration appointed her as Director for China in the United States National Security Council in August 20 ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* Lattimore, Owen . 1973. "Return to China's Northern Frontier." ''The Geographical Journal'' 139(2):233вҖ“42. *Zang, Xiaowei. 2013.Ethnic variation in network composition in ГңrГјmchi: do state policies matter?
''
Ethnic and Racial Studies
''Ethnic and Racial Studies'' is a peer-reviewed social science academic journal that publishes scholarly articles and book reviews on anthropology, cultural studies, ethnicity and race, and sociology. The editors-in-chief are Martin Bulmer ( U ...
'' 36(1):179вҖ“98. .
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Urumqi Populated places along the Silk Road Cities in Central Asia Populated places in Xinjiang Provincial capitals in China Prefecture-level divisions of Xinjiang Populated places established in the 18th century